Q.1.
With the increase in the consumption of units of a given commodity the marginal utility ________.
-
0%
diminishes
-
0%
increases
-
0%
remain constant
-
0%
is zero
Q.2.
Demand for a good is termed inelastic through the expenditure approach when if (Choose the correct alternative):
-
0%
Price of the good falls; expenditure on it rises
-
0%
Price of the good falls; expenditure on it falls
-
0%
Price of the good falls; expenditure on it remains unchanged
-
0%
Price of the good rises, expenditure on it falls
Q.3.
Warm clothes in winter have _______ utility.
-
0%
time
-
0%
place
-
0%
form
-
0%
service
Q.4.
As consumption increases, the marginal utility also increases.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.5.
The law of equi-marginal utility is introduced by _______.
-
0%
Alfred Marshall
-
0%
Adam Smith
-
0%
K.E. Boulding
-
0%
none of the above
Q.6.
The second can of Pepsi gives lesser satisfaction to a thirsty boy, its is a clear case of __________.
-
0%
law of diminishing marginal utility
-
0%
law of demand
-
0%
law of diminishing returns
-
0%
law of supply
Q.7.
When total utility declines, marginal utility is ________.
-
0%
negative
-
0%
zero
-
0%
increasing
-
0%
decreasing
Q.8.
Diminishing marginal utility is a universal phenomenon.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.9.
Marginal utility increases with increase in consumption
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.10.
The marginal utility curve slopes ______ from left to right.
-
0%
forward
-
0%
downward
-
0%
upward
-
0%
backward
Q.11.
When the price of a commodity rises the demand will fall.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.12.
The relationship between price and demand is positive.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.13.
Pen and Ink are ________.
-
0%
substitute goods
-
0%
complementary goods
-
0%
unrelated goods
-
0%
normal goods
Q.14.
The rise in price is followed by rise in demand.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.15.
Quantity demanded varies directly with price.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.16.
There are no exception to the law of demand.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.17.
Mere desire is not demand.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.18.
A consumer may demand more at the same price if his income increases.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.19.
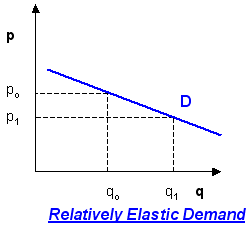
A relatively elastic demand curve has a steeper slope.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.20.
Demand for specialized labour is _____.
-
0%
elastic
-
0%
inelastic
-
0%
perfectly elastic
-
0%
perfectly inelastic
Q.21.
The demand for salt is ______.
-
0%
elastic
-
0%
inelastic
-
0%
infinite elastic
-
0%
unitary elastic
Q.22.
Demand for luxuries is elastic.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.23.
The geometric method is a more exact method of measuring elasticity of demand.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.24.
Demand for pins is ______ .
-
0%
elastic
-
0%
inelastic
-
0%
perfectly elastic
-
0%
perfectly inelastic
Q.25.
Demand for composite commodities is elastic.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.26.
Slope of budget line is equal to ________.
-
0%
marginal rate of substitution between the factor inputs
-
0%
ratio of price of factor input
-
0%
demand of each factor input
-
0%
supply of each factor input
Q.27.
Which of the following is not a type of elasticity in economics?
-
0%
Income elasticity
-
0%
Price elasticity
-
0%
Utility elasticity
-
0%
Cross elasticity
Q.28.
To measure price elasticity of demand, % change in demand is ________.
-
0%
divided by change in price
-
0%
divided by % change in price
-
0%
reduced by change in price
-
0%
reduced by % change in price
Q.29.
To measure price elasticity of demand, change in demand is related to ______.
-
0%
change in supply
-
0%
change in price in relative terms
-
0%
change in price in absolute term
-
0%
change in consumer tastes
Q.30.
If a product has no substitutes its demand ________.
-
0%
will be highly elastic
-
0%
will be inelastic
-
0%
will be unity elastic
-
0%
none of the above
Q.31.
Elasticity is measured in ______.
-
0%
rupee term
-
0%
absolute terms
-
0%
relative terms
-
0%
quantitative terms
Q.32.
The measurement of sensitivity of quantity demand to change in price is called ________.
-
0%
price elasticity
-
0%
income elasticity
-
0%
expansion in demand
-
0%
none of the above
Q.33.
When the price of complementary products increases, the demand of the other products will __________.
-
0%
falls
-
0%
increases
-
0%
remains same
-
0%
increases by 25%
Q.34.
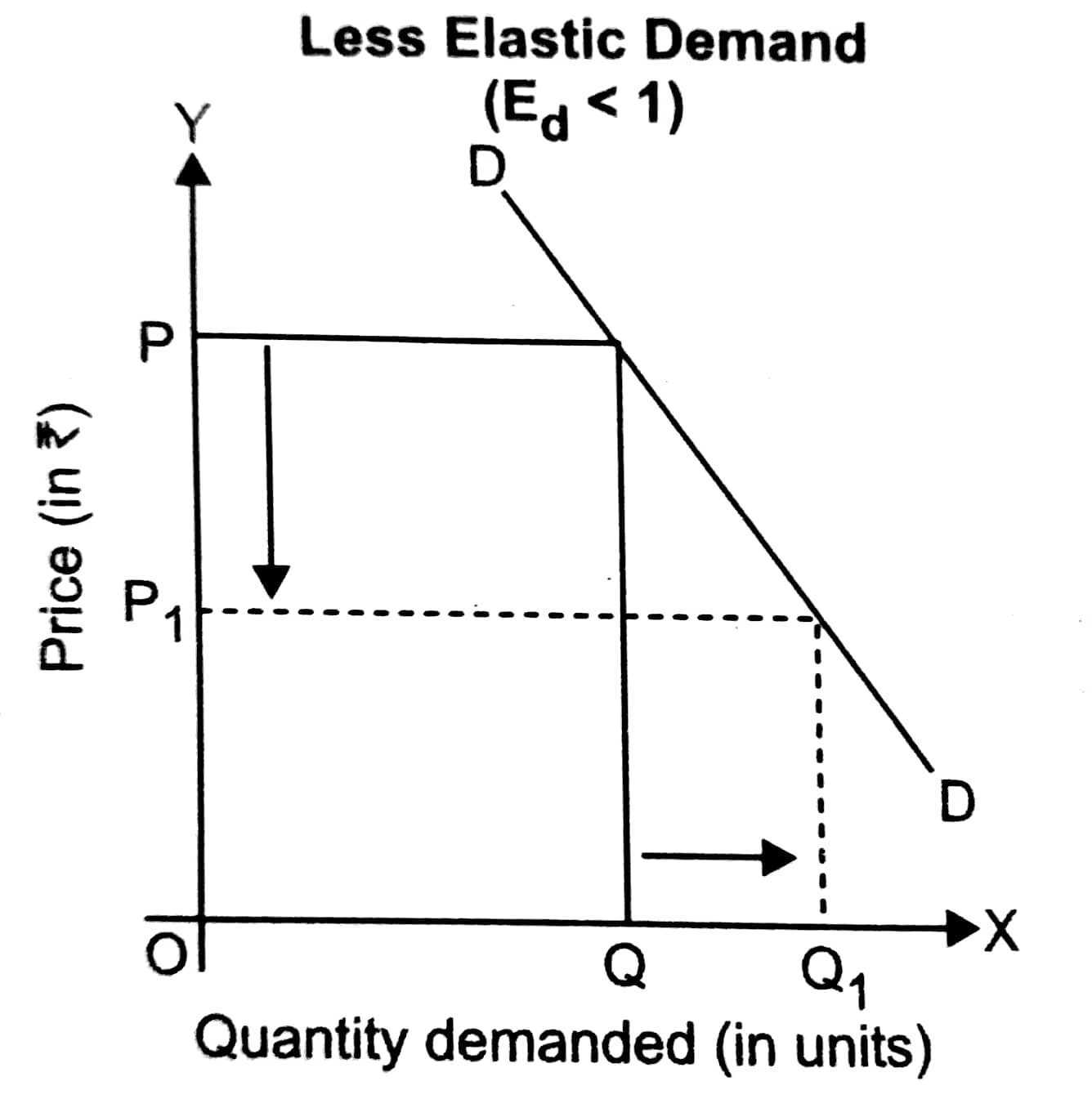
If price of X falls leading to fall in total outlay on X, the demand of X is ______.
-
0%
elastic
-
0%
inelastic
-
0%
unitary elastic
-
0%
less than unit elastic
Q.35.
Elasticity is the ratio of _______ dependent variable to the relative change in independent variable.
-
0%
relative change in a dependent variable
-
0%
absolute change in one variable
-
0%
absolute change in any variable
-
0%
relative change in one fixed variable
Q.36.
In long run, the demand has a tendency to show ________.
-
0%
high elasticity
-
0%
stability
-
0%
zero elasticity
-
0%
fluctuation
Q.37.
In the short run, the demand tends to be _________.
-
0%
highly elastic
-
0%
less elastic
-
0%
volatile
-
0%
zero elastic
Q.38.
If the price elasticity of a product is greater than 1, we can say that ________.
-
0%
the products demand is sensitive to price variation
-
0%
product demand is insensitive to price variation
-
0%
demand and price move in same directions
-
0%
none of the above
Q.39.
The elasticity of a demand curve with a constant slope ________.
-
0%
decrease at lower price
-
0%
decrease at higher price
-
0%
increase at lower price
-
0%
remains constant
Q.40.
Luxury goods have _______ degree of elasticity.
-
0%
high
-
0%
low
-
0%
moderate
-
0%
completely inelastic
Q.41.
Goods which are perfect substitute of each other will have elasticity of substitution _________.
-
0%
unity
-
0%
less than 1
-
0%
more than 1
-
0%
infinite
Q.42.
Goods which are perfect substitute of each other will have rate of substitution __________.
-
0%
unity
-
0%
less than 1
-
0%
more than 1
-
0%
zero
Q.43.
Demand of salt is inelastic because _________.
-
0%
of low price
-
0%
no substitute
-
0%
absence of it makes food tasteless
-
0%
all of the above
Q.44.
The elasticity of a demand curve with a constant slope __________.
-
0%
increase at higher price
-
0%
decrease at higher price
-
0%
increase at lower price
-
0%
remains constant
Q.45.
If the disposal income of a household increases by 10% and the demand for X commodity increased by 25%. The goods can be considered ________.
-
0%
essential goods
-
0%
luxury goods
-
0%
inferior goods
-
0%
normal goods
Q.46.
Complementary goods are those which are _______.
-
0%
consumed simultaneously
-
0%
close competitors
-
0%
both (A) and (B)
-
0%
unrelated
Q.47.
Law of demand explain the relationship between _________.
-
0%
price and quantity demanded
-
0%
price and quantity supplied
-
0%
price and cost of production
-
0%
market demand and market price
Q.48.
Law of demand operates under _______.
-
0%
ceteris paribus condition
-
0%
normal operating condition
-
0%
full employment condition
-
0%
non-inflationary condition
Q.49.
Substitute goods are those which are consumed ______.
-
0%
simultaneously
-
0%
alternatively
-
0%
in fixed proportion
-
0%
rarely
Q.50.
An Engel curve is ________.
-
0%
a type of demand curve which is angular
-
0%
a type of demand curve named after Prof Engel
-
0%
upward sloping demand curve
-
0%
flat demand curve