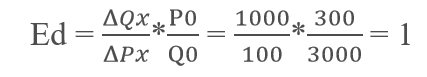Q.1.
In the case of a straight-line (linear) demand curve meeting the two axes, the price-elasticity of demand at the mid-point of the line would be _________.
-
0%
0
-
0%
1
-
0%
1.5
-
0%
2
Q.2.
A right shift in the demand curve for Bread would be predicted from _______.
-
0%
a decrease in the number of breakfast eaters.
-
0%
a change in tastes
-
0%
a fall in the price of Bread
-
0%
a rise in the price of Corn Flakes.
Q.3.
According to graphic or point method of elasticity of demand, the price elasticity of demand at a point on a straight line is equal to _________ of the demand curve.
-
0%
upper segment of the demand curve divided by lower segment
-
0%
lower segment of the demand curve plus upper segment of the demand curve
-
0%
lower segment of the demand curve divided by upper segment
-
0%
lower segment of the demand curve multiplied by upper segment of the demand curve
Q.4.
Demand for a good will tend to be more inelastic if it exhibits which of the following characteristics?
-
0%
The good has many substitutes.
-
0%
The good is a luxury (as opposed to a necessity).
-
0%
Small part of consumer's income is spent on the good.
-
0%
None of the above.
Q.5.
Usually the demand for commodities for which the consumption can be postponed has __________ demand as the prices rise and is expected to fall again.
-
0%
elastic
-
0%
inelastic
-
0%
unitary
-
0%
all of the above
Q.6.
The demand for very costly and very cheap goods is ________.
-
0%
elastic
-
0%
inelastic
-
0%
unitary
-
0%
all of the above
Q.7.
Which of the following assumptions is applicable under the Marshallian approach of consumer behaviour?
-
0%
Law of diminishing utility (DMU) holds true.
-
0%
Marginal utility of money keeps changing.
-
0%
Utility is ordinally measurable.
-
0%
All of the above.
Q.8.
Which of the following has inelastic demand?
-
0%
Very costly goods
-
0%
Very cheap goods
-
0%
Both (A) and (B)
-
0%
Neither (A) nor (B)
Q.9.
A commodity which has several uses will have an __________ demand such as milk, wood, etc.
-
0%
unitary
-
0%
elastic
-
0%
inelastic
-
0%
all of the above
Q.10.
A commodity having only one use will have ___________ demand.
-
0%
inelastic
-
0%
unitary
-
0%
elastic
-
0%
all of the above
Q.11.
Which of the following approach can be used for determining consumer behaviour?
-
0%
Indifference Curve Approach
-
0%
Marshallian Approach
-
0%
Both (A) and (B)
-
0%
Neither (A) or (B)
Q.12.
The demand for necessities is ____________.
-
0%
elastic
-
0%
inelastic
-
0%
unitary
-
0%
all of the above
Q.13.
According to the ____________ when prices decreases, demand rises, and when price increases, demand falls.
-
0%
law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
-
0%
law of supply
-
0%
law of demand
-
0%
elasticity of demand
Q.14.
If individuals are habituated of some commodities the demand for such commodities will be usually ________.
-
0%
elastic
-
0%
inelastic
-
0%
unitary
-
0%
all of the above
Q.15.
Elasticity of demand for a good is not dependent upon the proportion of a consumers budget spent on it.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.16.
Indifference curves can intersect each other.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.17.
Higher level of indifference curve shows lower level of satisfaction.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.18.
Indifference curves intersect Y-Axis.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.19.
_______ is a curve which represents all those combinations of goods which give same level of satisfaction to the consumer.
-
0%
Demand curve
-
0%
Indifference curve
-
0%
Supply curve
-
0%
Production possibility curve
Q.20.
An indifference curve is a curve which represent all those combinations of goods which give _______ level of satisfaction to the consumer.
-
0%
different
-
0%
unequal
-
0%
increased
-
0%
same
Q.21.
Indifference curves do not touch X-Axis.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.22.
Indifference curves are always ________.
-
0%
convex to the origin
-
0%
concave to the origin
-
0%
parallel to the X-Axis
-
0%
parallel to the Y-Axis
Q.23.
On which of the following assumption the indifference curve approach is based?
-
0%
Consumer can rank different combinations of two goods in order of preference i.e. 1st, 2nd, 3rd
-
0%
Consumer behaviour is consistent
-
0%
Consumer is rational
-
0%
All of above
Q.24.
An indifference curve ________.
-
0%
slopes downward from right to left
-
0%
slopes upward from right to left
-
0%
slopes upward from left to right
-
0%
slopes downward from left to right
Q.25.
The concept of indifference curve was introduced by ________.
-
0%
Hicks & Allen
-
0%
Hicks & Marshall
-
0%
Allen & Marshall
-
0%
Marshall & Smith
Q.26.
By consumer surplus economists mean _________
-
0%
the area inside the budget line
-
0%
the difference between the maximum amount a person is willing to pay for a good and its market price
-
0%
the area between the average revenue and marginal revenue curves
-
0%
none of the above
Q.27.
When a consumer moves upward along an indifference curve, his total utility _________.
-
0%
first increases and then decreases
-
0%
first decreases and then increases
-
0%
remains constant
-
0%
increases
Q.28.
Suppose a consumers income increases from Rs. 30,000 to Rs. 36,As a result, the consumer increase her purchases of compact disc (CDs) from 25 CDs to 30 CDs. What is the consumers income elasticity of demand for CDs?
-
0%
2.0
-
0%
1.5
-
0%
1.0
-
0%
0.5
Q.29.
The consumer is in equilibrium at a point where the budget line _________.
-
0%
is above the indifference curve
-
0%
is below the indifference curve
-
0%
is tangent to the indifference curve
-
0%
cuts the indifference curve
Q.30.
The buying behaviours of consumers, which requires the least effort is?
-
0%
Low involvement in buying
-
0%
New buying situation
-
0%
Routine buying
-
0%
Impulsive buying
Q.31.
If the price of the commodity is reduced from Rs. 300 to Rs. 200 and the quantity demanded increases from 3,000 to 4,000. What is the price elasticity of demand?
-
0%
-1.0
-
0%
1.25
-
0%
-2.0
-
0%
0.8
Q.32.
Which one is not an assumption of the theory of demand based on analysis of indifference curves?
-
0%
Given scale of preferences as between different combinations of two goods.
-
0%
Diminishing marginal rate of substitution.
-
0%
Constant marginal utility of money
-
0%
Consumer would always prefer more of a particular good to less of the other good, other things remaining the same.
Q.33.
Suppose the price of commodity rises from Rs. 120 to Rs. 200. It is observed that the rise in price causes quantity demanded to fall from 300 toWhat is the price elasticity of demand for commodity?
-
0%
-1.2
-
0%
-0.5
-
0%
0.8
-
0%
1.0
Q.34.
Which of the following statements is correct?
-
0%
An indifference curve is downward-sloping to the right
-
0%
Convexity of a curve implies that the slope of the curve diminishes as one moves from left to right
-
0%
The elasticity of substitution between two goods to a consumer is zero.
-
0%
The total effect of a change in the price of a good on its quantity demanded is called the price effect.
Q.35.
________ represent the various combinations of two goods which can be purchased with a given money income and assumed prices of goods.
-
0%
Budget line
-
0%
Market line
-
0%
Price line
-
0%
Both A & C
Q.36.
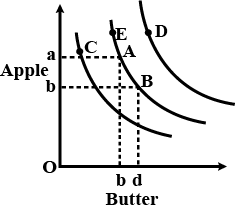
The graph indicates that the consumer __________.

-
0%
at A is different between 0a of apples and 0b of butter
-
0%
at A is consuming either 0a of apples or 0b of butter
-
0%
is indifferent between 0a of apples plus 0b of butter on the one hand and 0b of apples plus 0d of butter
-
0%
is correctly described by all of the above.
Q.37.
Where the budget line is tangent to an IC, ________.
-
0%
equals amounts of goods give equal satisfaction
-
0%
the ratio of price of the goods equals the MRS
-
0%
the prices of the goods are equal
-
0%
none of the above
Q.38.
Calculate cross elasticity of demand when demand for X increases from 10 units to 15 units and price of Y increases from Rs.3 to Rs.6 per unit.
-
0%
0.5
-
0%
1.0
-
0%
1.5
-
0%
2.0
Q.39.
To measure price elasticity over large changes in price we use ______.
-
0%
point elasticity method
-
0%
are elasticity method
-
0%
income elasticity method
-
0%
none of the above
Q.40.
IC theory assumes that ________.
-
0%
buyers can measures satisfaction
-
0%
buyers can identify preferred combinations of goods
-
0%
all buyers have same preference patterns
-
0%
none of the above
Q.41.
Consumer-X buys 100 units of a commodity at Rs. 8 per unit. When its price falls by 50%, the demand rises to 200 units. Find out the price elasticity of demand for this product.
-
0%
4
-
0%
-2
-
0%
2
-
0%
-1.5
Q.42.
As one moves upward towards left along an Indifference curve the MRS of commodity 'X' for commodity 'Y' ___________.
-
0%
increases
-
0%
decreases
-
0%
constant
-
0%
fluctuates
Q.43.
The doctrine of consumer's surplus is based on _______.
-
0%
elasticity of demand
-
0%
indifference curve analysis
-
0%
law of substitution
-
0%
the law of diminishing marginal utility
Q.44.
A demand curve is perfectly inelastic if ______.
-
0%
a rise in price causes a full in quantity demanded
-
0%
a fall in price causes a rise in seller's total receipts
-
0%
the commodity in question is highly perishable
-
0%
a change in price does not change quantity demanded.
Q.45.
How many indifference curves can touch the price line?
-
0%
Two
-
0%
One
-
0%
As many as possible
-
0%
None of the above
Q.46.
A consumer spends Rs. 80 on a commodity when its price is Rs. 1 per unit and spends Rs. 96 when the price rises to Rs. 2 per unit. Calculate the price elasticity coefficient of demand for the commodity.
-
0%
0.2
-
0%
-0.4
-
0%
1.4
-
0%
1.2
Q.47.
"Utility is a subjective concept therefore it could only be ranked" defines the position of _______.
-
0%
cardinal utility theorists
-
0%
ordinal utility theorists
-
0%
behavioral theorists
-
0%
all id the above
Q.48.
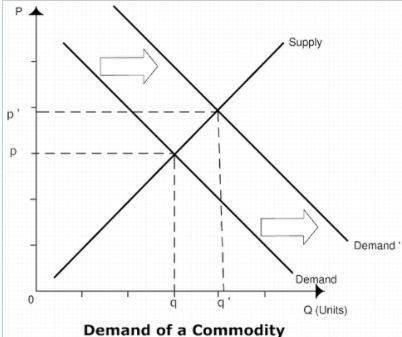
In the figure above at the equilibrium point E, which of the following takes place?


-
0%
Demand is more than supply
-
0%
Supply is more than demand
-
0%
Demand and supply are equal
-
0%
None of the above
Q.49.
An increase in demand for a commodity causes __________.
-
0%
an increase in equilibrium price
-
0%
an increase in equilibrium quantity
-
0%
both (a )& (b)
-
0%
none of the above
Q.50.
Demand for electricity is _______.
-
0%
inelastic
-
0%
elastic
-
0%
less elastic
-
0%
none of these