Q.1.
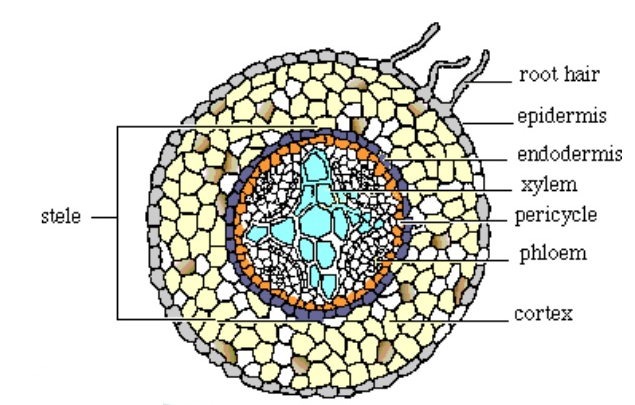
The innermost layer of cortex is
-
0%
Epidermis
-
20%
Hypodermis
-
80%
Endodermis
-
0%
Pericycle
Q.2.
Match the column:
| List I | List II |
| A) Tracheids | I) Cells possess highly thickened walls with oblilateral central human |
| B) Vessels | II) Elongated tube like cells with thick lignified walls and tapering ends |
| C) Xylem parenchyma | III) Individual members are interconnected through perorations in their common walls |
| D) Xylem fibers | IV) Cells are living with thin cellulosic cell walls |
-
75%
A-II B-III C-IV D-I
-
0%
A-II B-IV C-I D-III
-
0%
A-III B-II C-IV D-I
-
25%
A-II B-III C-I D-IV
Q.3.
The polyarch (xylem) condition is found in
-
33%
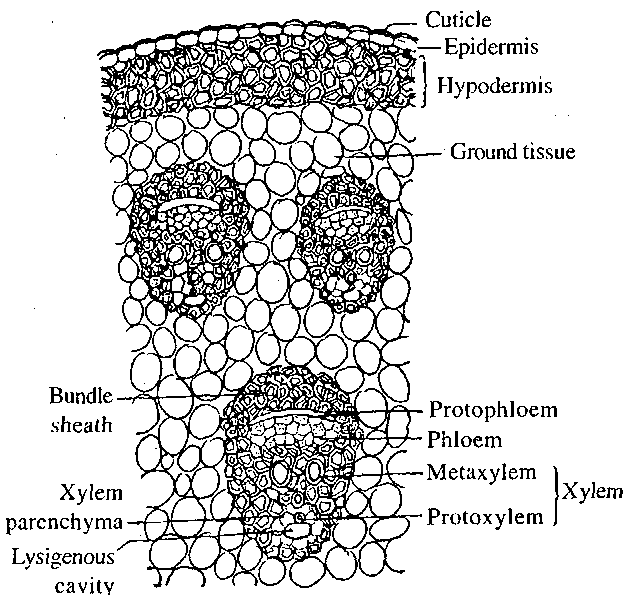
Monocot leaf
-
33%
Dicot root
-
33%
Monocot root
-
0%
Dicot leat
Q.4.
The root hair are produced from
-
0%
Rhizodermis
-
33%
Trichomes
-
33%
Accessory cells
-
33%
Trichoplasts
Q.5.
Which of the following tissues provide maximum mechanical support to plant organs?
-
67%
Sclerenchyma
-
33%
Collenchyma
-
0%
Parenchyma
-
0%
Aerenchyma
Q.6.
Find out the wrong statement about angiosperm roots.
-
33%
Cuticle is absent in young stages
-
0%
The apex is protected by root cap
-
67%
Vascular bundles are collateral
-
0%
Xylem is centripetal in growth in the young roots
Q.7.
The vascular bundles are skull shaped in
-
0%
Dicot root
-
67%
Monocot root
-
0%
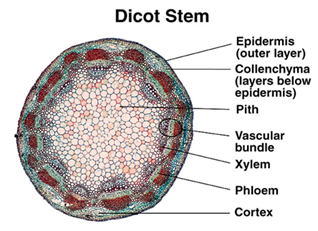
Dicot stem
-
33%
Monocot stem
Q.8.
Cotton clothes are basically cells of
-
33%
Cambium
-
0%
Collenchyma
-
67%
Scelernchyma
-
0%
Scleride
Q.9.
The function of a vessel is
-
0%
Conduction of food
-
100%
Conduction of water and minerals
-
0%
Conduction of hormones
-
0%
All of the.above
Q.10.
Which of the following characteristics defines the collateral vascular bundle?
-
67%
Phloem and xylem lie on the same radius
-
33%
Phloem located toward the periphery of the stem
-
0%
Xylem toward the centre
-
0%
All of the above
Q.11.
Which of the following help in the secondary growth?
-
0%
Lateral meristem
-
0%
Vascular cambium
-
0%
Cork Cambium
-
100%
All of the above
Q.12.
Plant having column of vascular tissues bearing fruits and having a tap root system is?
-
100%
Monocot
-
0%
Dicot
-
0%
Gymnosperm or dicot
-
0%
Gymnosperm or monocot
Q.13.
Astela comprises
-
0%
Xylem, phloem and pith
-
0%
Endodemis, xylernand phloem
-
100%
Vascular tissue, pericycle and pith
-
0%
Vascular tissue, endodermis and pith
Q.14.
Identify the plant parts whose transverse sections show a clear and prominent pith.
-
0%
Dicot root and monocot root
-
0%
Dicot stem and dicot root
-
100%
Dicot stem and monocot stem
-
0%
Dicot stem and monocot root
Q.15.
The loosely arranged non-chlorophyllous parenchyma cells present in lenticels are known as
-
0%
Complementary cells
-
100%
Passage cells
-
0%
Water stomata
-
0%
Albuminous cells
Q.16.
Determination of age of tree by counting growth rings falls under
-
100%
Dendrology
-
0%
Dendrochronology
-
0%
Chronology
-
0%
Chorology
Q.17.
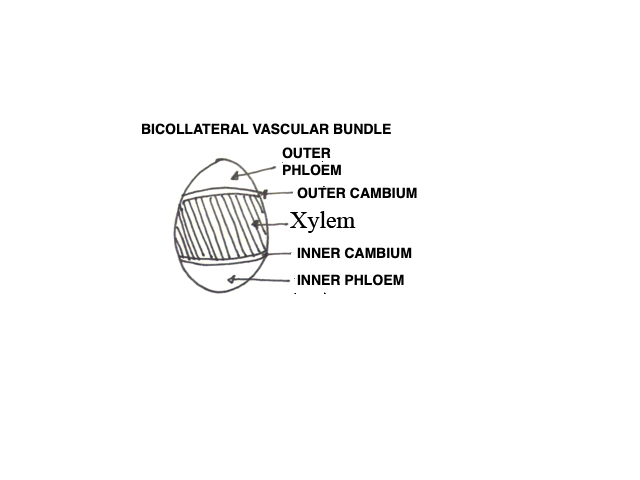
The vascular bundles which have two cambium and two phloem present on both sides of xylem is known as
-
0%
Collateral
-
100%
Bicollateral
-
0%
Concentric
-
0%
none of the above
Q.18.
In Carissa, the thorns are modifications of
-
0%
Axillary buds
-
0%
Apical buds
-
100%
Intercalary buds
-
0%
Extra-axillary buds
Q.19.
Exodermis occurs in
-
100%
Monocot root
-
0%
Dicot root
-
0%
Leaf
-
0%
Stem
Q.20.
Axillary and terminal buds develop by activity of _______.
-
0%
Lateral meristem
-
100%
Intercalary meristem
-
0%
Apical meristem
-
0%
Parenchyma
Q.21.
The term meristem was coined by
-
0%
Hanstein
-
100%
Nageli
-
0%
Schmidt
-
0%
Esau
Q.22.
As compound to other parts of root apical meristem, DNA content of quiescent centre is
-
0%
Low
-
0%
High
-
100%
Same
-
0%
Very high
Q.23.
Periblem forms
-
0%
Endodermis
-
0%
Cortex
-
100%
Both A and B
-
0%
Epidermis
Q.24.
Meristematic tissue occurs in ________.
-
0%
Stems
-
0%
Roots
-
0%
All growing tips
-
100%
Both A and B
Q.25.
Primary plant growth is accomplished by _______.
-
0%
Cambia
-
0%
Intercalary meristem
-
100%
Apical meristem
-
0%
Mass meristem
Q.26.
Shoot apical meristem occurs over the tip of ________
-
0%
Root
-
0%
Radicle
-
100%
Plumule
-
0%
Mesocotyl
Q.27.
Quiescent centre in the middle of root apical meristem was discovered by.
-
0%
Eames
-
0%
Schmidt
-
0%
Clowes
-
100%
Hanstein
Q.28.
Cortex is formed from
-
0%
Cambium
-
100%
Procambium
-
0%
Ground meristem
-
0%
Protoderm
Q.29.
Pericycle that gives rise to lateral roots is made of _______.
-
0%
Meristematic cells
-
100%
Parenchyma cells
-
0%
Collenchyma cells
-
0%
Lateral meristem
Q.30.
The formation of annual rings in dicot stem mainly depends upon difference in.
-
0%
Formation of unequal quantities of xylem and phloem
-
100%
Activity of vascular cambium due to seasonal variations
-
0%
Activity of cork cambium due to seasonal variations
-
0%
Formation of unequal quantities of sapwood and heart wood
Q.31.
A distinction of corpus and tunica does not occur in.
-
0%
Oat
-
0%
Sugarcane
-
0%
Apple
-
100%
Castor
Q.32.
Multiseriate vascular rays are present opposite the protoxylem in old
-
0%
Dicot stems
-
100%
Dicot roots
-
0%
Monocot stems
-
0%
Monocot roots
Q.33.
Passage cells are present in
-
0%
Cortex
-
100%
Pericycle
-
0%
Pith
-
0%
Endodermis
Q.34.
Dicot root differs from monocot root in
-
0%
Fewer number of radial vascular bundles with small pith
-
0%
Large number of radial vascular bundles with large pith
-
0%
Fewer number of radial vascular bundles with large pith
-
100%
Large number of radial vascular bundles with small pith
Q.35.
A vascular bundle having both xylem and phloem on same radii is called
-
0%
Concentric
-
0%
Spiral
-
50%
Radial
-
50%
Conjoint
Q.36.
Interfascicular cambium is situated.
-
100%
Between xylem and phloem
-
0%
Between vascular bundles
-
0%
Outside the vascular bundles
-
0%
Inner side of the vascular bundles
Q.37.
Pith and cortex of the stem are parts of
-
0%
Dermal tissue system
-
100%
Vascular tissue system
-
0%
Ground tissue system
-
0%
Epidermal tissue system
Q.38.
The outer cellular complex present on the outside of those stems and roots which have undergone secondary growth is?
-
0%
Periderm
-
100%
Epiblema
-
0%
Phelloderm
-
0%
Phellogen
Q.39.
Oldest part of phloem in a dicot stem is situated just.
-
0%
Outside vascular cambium
-
100%
Inner to primary cortex
-
0%
Inner to vascular cambium
-
0%
Between periderm and primary cortex
Q.40.
Endodermis acts as biological check post and prevents wall to wall flow of materials because it has.
-
100%
Casparian strips
-
0%
Barrel-shaped cells
-
0%
Passage cells
-
0%
Specialised thickenings
Q.41.
Medullary rays are extra prominent in
-
0%
Monocot stem
-
0%
Dicot stem
-
50%
Young dicot root
-
50%
Old dicot root
Q.42.
In an old stem, the oldest secondary xylem is found just
-
50%
Inner to vascular cambium
-
0%
Outside primary xylem
-
50%
Outside vascular cambium
-
0%
Inner to phellogen
Q.43.
The cells which lie between xylem and phloem in dicot root are
-
0%
Pith rays
-
50%
Conjuctive tissue
-
50%
Interfascicular cambium
-
0%
Intrafascicular cambium
Q.44.
Casparian strip is
-
0%
Lens-like thickenings of endodermal cells
-
0%
Strip of thickening found on the outer side of endodermis
-
50%
Ligno-suberin band running in endodermal cell walls
-
50%
Layer of cells between endodermis and cortex
Q.45.
Dicot root having more than six vascular bundles is
-
50%
Pea
-
0%
Sunflower
-
50%
Ficus
-
0%
Ranunculus
Q.46.
The bark of tree commonly comprises
-
0%
All the tissues outside the vascular cambium
-
50%
All the tissues outside teh cork cambium
-
0%
Only the cork
-
50%
The cork and secondary cortex
Q.47.
Ground tissue having differentiated concentric layers is found in
-
0%
Dicot leaf
-
0%
Monocot leaf
-
50%
Dicot stem
-
50%
Monocot stem
Q.48.
Cucurbita stem is an exceptional dicot stem because it has.
-
0%
Bicollateral bundles
-
0%
Bicollateral bundles and several layered thick pericycle
-
50%
Bicollateral bundles and hollow centre
-
50%
Bicollateral bundles arranged in two alternate rings
Q.49.
Phloem parenchyma is absent in
-
0%
Dicot root
-
0%
Dicot leaf
-
100%
Monocot stem
-
0%
Dicot stem
Q.50.
Secondary growth occurs due to activity of.
-
0%
Cork cambium
-
50%
Vascular cambium
-
0%
Intercalary meristem
-
50%
Both A and B