Q.1.
Continuous spectrum is not due to
-
0%
Hydrogen flame
-
0%
Electric bulb
-
0%
Kerosene oil lamp flame
-
0%
Candle flame
Q.2.
Which of the following subshells is represented by the quantum numbers n=4 and l=1?
-
0%
4s
-
0%
4f
-
0%
4d
-
0%
4p
Q.3.
Match the following :
| Type I | Type II |
| a) Continuous emission spectrum | e) Tungsten filament of bulb |
| b) Line emission spectrum | f) CO2 gas |
| c) Band emission spectrum | g) Sodium vapour lamp |
| d) Line absorption spectrum | h) chromosphere of sun |
-
0%
a-e; b-f; c-g; d-h
-
0%
a-f; b-e; c-h; d-e
-
0%
a-e; b-g; c-f; d-h
-
0%
a-h; b-g; c-f; d-e
Q.4.
A cathode ray tube has a potential difference of V between the cathode and anode. The speed of the cathode rays is given by
-
0%
v∝V
-
0%
v∝V−1
-
0%
v∝√V
-
0%
v∝V2
Q.5.
Which of the following relates to photons both as wave motion and as a stream of particles?
-
0%
Interference
-
0%
E=mc2
-
0%
Diffraction
-
0%
E =hν
Q.6.
When the particle and its anti-particle unite, the result is
-
0%
A heavier particle
-
0%
Two or more smaller particles
-
0%
Photons
-
0%
Partly matter and partly photons
Q.7.
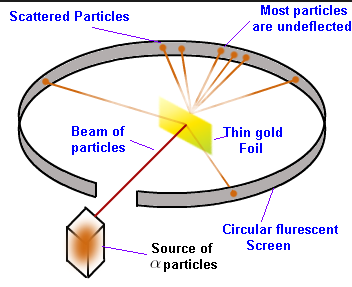
In Rutherford's α-rays scattering experiment, gold foils are used because of ___________.
-
0%
high malleability
-
0%
ductility
-
0%
high melting point
-
0%
high ionisation energy
Q.8.
Which of the following point is not shown by the Rutherford alpha scattering experiment?
-
0%
α - particle can come within a distance of the order of 10−14m of the nucleus
-
0%
The radius of the nucleus is less than 10−14m
-
0%
Sattering follows coulombs law
-
0%
The positively charged parts of an atom move with extremely high velocities
Q.9.
Cathode rays are made to pass between the poles of a magnet as shown in figure. The effect of magnetic field is
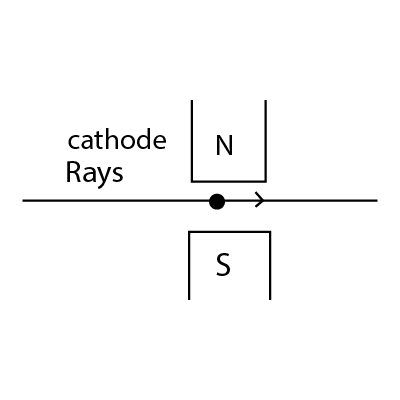

-
0%
To deflect them towards the south pole
-
0%
To deflect them perpendicular to the plane of the paper and towards the observer
-
0%
To deflect them towards the north pole
-
0%
To increase the velocity of the rays
Q.10.
The angular momentum of the α−particles which are scattered through large angles by the heavier nuclei, is conserved because
-
0%
of the nature of repulsive forces
-
0%
the kinetic energy is conserved
-
0%
the potential energy is conserved
-
0%
there is no external torque
Q.11.
The force experienced by the cathode rays when they pass through a uniform electric field of intensity ˉE is:
-
0%
in the direction of the electric field
-
0%
in the direction opposite to that of the electric field
-
0%
at right angles to the electric field
-
0%
zero, because cathode rays do not have any charge
Q.12.
In Rutherford's alpha-ray scattering experiment, a screen is used to detect the alpha particles which is coated by:
-
0%
carbon black
-
0%
platinum black
-
0%
zinc sulphide
-
0%
poly tetrafluoro ethylene
Q.13.
An electron makes transition from n=3,n=1 state in a hydrogen atom. The different possible number of photons that can be emitted is :
-
0%
1
-
0%
2
-
0%
3
-
0%
6
Q.14.
In the lowest energy level of hydrogen atom, electron has an angular momentum equal to:
-
0%
πh
-
0%
hπ
-
0%
h2π
-
0%
2πh
Q.15.
The ionization energy of a hydrogen-like ion A is greater than that of another hydrogen-like ion B. Let u and E represent the speed of the electron and energy of the atom respectively in the ground state. Then,
-
0%
rA>rB
-
0%
uA>uB
-
0%
EA>EB
-
0%
LA>LB
Q.16.
In the Geiger-Marsden experiment, the force that scatters particles is
-
0%
nuclear force
-
0%
coulomb force
-
0%
both A and B
-
0%
gravitational force
Q.17.
In Rutherford's experiment the number of α particles scattered through an angle 60o is 112 per minute, then the number of α particles scattered through an angle of 900 per minute by the same nucleus is:
-
0%
28 per minute
-
0%
112 per minute
-
0%
12.5 per minute
-
0%
7 per minute
Q.18.
The radius of hydrogen atom, when it is in its second excited state ,becomes _ its ground state radius.
-
0%
half
-
0%
double
-
0%
four times
-
0%
nine times
Q.19.
The main defect of Bohr's atom model is :
-
0%
mixing of classical and quantum theories
-
0%
exclusion of nuclear motion
-
0%
failed to explain the fine structure of spectral lines
-
0%
failed to explain larger atoms
Q.20.
The electron is present in an orbit of energy state −1.51 eV, then angular momentum of the electron is
-
0%
2h/π
-
0%
h/π
-
0%
3h/2π
-
0%
7h/π
Q.21.
The possible values of principal quantum number can be:
-
0%
1,2,3...8
-
0%
0,1,2...8
-
0%
only zero
-
0%
only odd numbers
Q.22.
Atomic hydrogen is excited to the nth energy level.The maximum number of spectral lines which it can emit while returing to the ground state, is
-
0%
12n(n−1)
-
0%
12n(n+1)
-
0%
n(n+1)
-
0%
n(n−1)
Q.23.
If An is the area enclosed in the nth orbit in a hydrogen atom then the graph log (AnA1) against log n
-
0%
will have slope 2 (straightline)
-
0%
will have slope 4 (straightline)
-
0%
will be a monotonically increasing non linear curve
-
0%
will be a circle
Q.24.
If an electron is revolving round the hydrogen nucleus at a distance of 0.1 nm, the speed should be :
-
0%
2.188×106m/s
-
0%
1.094×106m/s
-
0%
4.376×106m/s
-
0%
1.59×106m/s
Q.25.
When an electron jumps from higher orbit to the second orbit in hydrogen, the radiation emitted out will be in (R=1.09×107m−1)
-
0%
ultraviolet
-
0%
visible region
-
0%
infrared region
-
0%
X-ray region
Q.26.
The maximum number of photons emitted by an H-atom, if atom is excited to states with principal quantum number four is
-
0%
4
-
0%
6
-
0%
2
-
0%
1
Q.27.
The velocity of a helium nucleus travelling in a curved path in a magnetic field is V. The velocity of a proton moving in the same curved path in the same magnetic field is :
-
0%
V
-
0%
4V
-
0%
2V
-
0%
V/2
Q.28.
There are only three hydrogen atoms in a discharge tube. The analysis of spectrum shows that in all the hydrogen atoms, electrons are de-exciting from the fourth orbit. What should be the maximum number of spectral lines?
-
0%
6
-
0%
1
-
0%
4
-
0%
5
Q.29.
Rydberg atoms are the hydrogen atoms in higher excited states such atoms are observed in space.The orbit number for such an atom with radius about 0.01 mm should be :
-
0%
1
-
0%
435
-
0%
13749
-
0%
117
Q.30.
The radius of shortest orbit in one electron system is 18 pm.It may be.
-
0%
11H
-
0%
12H
-
0%
He+
-
0%
Li+
Q.31.
The threshold wavelength for a surface having a threshold frequency of 0.6×1015 Hz in (A˚) is
-
0%
100
-
0%
2000
-
0%
5000
-
0%
400
Q.32.
In one revolution round the hydrogen nucleus, an electron makes five crests .The electron belongs to
-
0%
1^{st} orbit
-
0%
4^{th} orbit
-
0%
5^{th} orbit
-
0%
6^{th} orbit
Q.33.
The ratio of momenta of an electron and a \alpha -particle which is accelerated from rest by a potential difference of 100 V is:
-
0%
1
-
0%
\displaystyle \sqrt {\dfrac{{2{m_e}}}{{{m_\alpha }}}}
-
0%
\displaystyle \sqrt {\dfrac{{{m_e}}}{{{m_\alpha }}}}
-
0%
\displaystyle \sqrt {\dfrac{{{m_e}}}{{2{m_\alpha }}}}
Q.34.
The energy of a hydrogen atom in the ground state is 13.6 eV. The energy of He+ ion in the first excited state will be
-
0%
-13.6 eV
-
0%
-27.2 eV
-
0%
-54.4 eV
-
0%
-6.8 eV
Q.35.
According to Bohr's theory of hydrogen atom, for an electron in the n^{th} allowed orbit, then
-
0%
linear momentum is proportional to (1/n)
-
0%
radius is proportional to n
-
0%
the kinetic energy is proportional to (1/n^2)
-
0%
the angular momentum is proportional to n
Q.36.
When a hydrogen atom is in its first excited level, its radius is
-
0%
four times its ground state radius
-
0%
twice times its ground state radius
-
0%
same times its ground state radius
-
0%
half times its ground state radius.
Q.37.
Hydrogen atom is excited from ground state to another state with principal quantum number equal to 4. Then the number of spectral lines in the emission spectra will be.
-
0%
2
-
0%
3
-
0%
5
-
0%
6
Q.38.
Gold is chosen by Rutherford for his \alpha-ray scattering experiment because:
-
0%
gold has high malleability
-
0%
gold has high ductility
-
0%
gold has high density
-
0%
gold is the least reactive element
Q.39.
Rutherford's alpha (\alpha) particle scattering experiment resulted in discovery of:
-
0%
electron
-
0%
proton
-
0%
nucleus in the atom
-
0%
atomic mass
Q.40.
The time taken by a photo-electron to come out after the photon strikes is approximately
-
0%
10^{-6} sec
-
0%
10^{-4} sec
-
0%
10^{-10} sec
-
0%
10^{-16} sec
Q.41.
Rutherford's model explains :
-
0%
Atom is a planetary model.
-
0%
Electrons never loose nor gain energy.
-
0%
Electron revolves around the nucleus with high velocities to counterbalance the forces of electrostatic forces of attraction between protons and electrons.
-
0%
Electrons do not move at all.
Q.42.
When a hydrogen atom emits a photon of energy 12.1 eV, its orbital angular momentum changes by
-
0%
1.05 \times 10^{-34}Js
-
0%
2.11 \times 10^{-34}Js
-
0%
3.16 \times 10^{-34}Js
-
0%
4.22 \times 10^{-34}Js
Q.43.
The fine structure of hydrogen spectrum can be explained by
-
0%
the presence of neutrons in the nucleus.
-
0%
the finite size of nucleus.
-
0%
the orbital angular momentum of electrons.
-
0%
the spin angular momentum of electrons.
Q.44.
In the hydrogen atom in the ground state
-
0%
the kinetic energy of the electron is less than the potential energy which is positive
-
0%
the potential energy is less than the kinetic energy which is positive
-
0%
the potential energy is negative and the kinetic energy numerically less than the numerical value of potential energy
-
0%
the total energy is negative
Q.45.
Rutherford experiment of scattering of \alpha particles showed for the first time that the atom has:
-
0%
electrons
-
0%
only protons
-
0%
nucleus
-
0%
None of the above
Q.46.
A small positively charged nucleus is present in the center. Which observations tells about this?
-
0%
Most of the \alpha \ - particles passed straight
-
0%
Most of the \alpha \ - particles rebounded after hitting the atoms
-
0%
Only a few \alpha \ - particles deflected away from their path
-
0%
Very few \alpha \ - particles rebounded
Q.47.
Which of the following products in a hydrogen atom is independent of principal quantum number n ?
-
0%
v_r
-
0%
v_n
-
0%
E_r^{2}
-
0%
E_n
Q.48.
When a photomultiplier tube was used , the photo current recorded is 60 \mu A. The actual photo current is
-
0%
\displaystyle > 60 \mu A
-
0%
\displaystyle = 60 \mu A
-
0%
\displaystyle < 60 \mu A
-
0%
None of these
Q.49.
Cathode ray oscillograph is used for
-
0%
Taking X-ray photographs
-
0%
Showing pictures
-
0%
Demonstrating electrical pulses
-
0%
Producing elementary particles
Q.50.
Rutherford's scattering experiment is related to the size of the:
-
0%
nucleus
-
0%
atom
-
0%
electron
-
0%
neutron