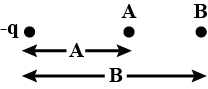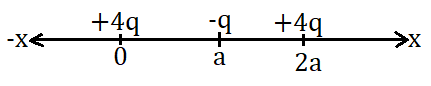Q.1.
Equipotential surfaces are
-
0%
Surfaces that are perpendicular to gravitational fields
-
0%
Surfaces that have same mass on top of it
-
0%
Surface that have same radius of curvature
-
0%
Surfaces that have same gravitational field on it
Q.2.
In the figure a capacitor of capacitance $$2\mu F$$ as is connected to a cell of eml 20 volt. The plates of the capacitors are drawn apart slowly to double the distance between them, The work done by the external agent on the plates is:

-
0%
$$-200 \mu J$$
-
0%
$$200 \mu J$$
-
0%
$$400 \mu J$$
-
0%
$$-400 \mu J$$
Q.3.
The electrostatic potential energy of two point charges, $$1$$ $$\mu$$C each, placed $$1$$ meter apart in air is?
-
0%
$$9\times 10^3$$J
-
0%
$$9\times 10^9$$J
-
0%
$$9\times 10^{-3}$$J
-
0%
$$9\times 10^{-3}$$eV
Q.4.
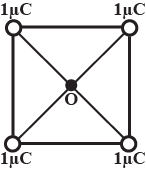
Charges $$1\mu C$$ are placed at each of the four corners of a square of side $$2\sqrt {2}m$$. The potential at the point of intersection of the diagonals is _____ $$(K = 9\times 10^{9} SI\ unit)$$.
-
0%
$$18\times 10^{3}V$$
-
0%
$$1800\ V$$
-
0%
$$18\sqrt {2}\times 10^{3}V$$
-
0%
None of these
Q.5.
The potential energy of system of two equal negative point charges of $$2\mu C$$ each held 1 m apart in air is ($$k = 9 \times 10^9\, SI \,unit$$)
-
0%
$$36 \,J$$
-
0%
$$3.6 \times 10^{-3}\, J$$
-
0%
$$3.6 \,J$$
-
0%
$$3.6 \times 10^{-2}\, J$$
Q.6.
A hollow metal sphere of radius $$10$$cm is charged such that the potential on its surface becomes $$80$$V. The potential at the centre of the sphere is?
-
0%
$$80$$V
-
0%
$$800$$V
-
0%
$$8$$V
-
0%
Zero
Q.7.
A hollow metal ball carrying an electric charge produces no electric field at points.
-
0%
Outside the sphere
-
0%
On its surface
-
0%
Inside the sphere
-
0%
At a distance more than twice
Q.8.
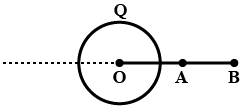
A uniformly charged fixed ring Q of radius R has a small charge $$-q$$ on its axis at a point A ( OA$$=$$d and d $$ < < $$R). When the charge was released, the distance AO was covered in time T. Then which of the following statements is/are true.

-
0%
For OB$$=2$$d, if charge was released from B, then the distance AO would be covered in a time $$T/6$$.
-
0%
For OB$$=\sqrt{2}$$d if charge was released from B then the distance AO would be covered in a time $$T/2$$
-
0%
If Q is doubled, then T doubles
-
0%
If R is doubled, then T decreases
Q.9.
The ratio of momentum of an electron and an alpha particle which are accelerated from rest by potential difference of 100 V is:
-
0%
$$\sqrt{\dfrac{m_{\alpha}}{m_e}}$$
-
0%
$$\sqrt{\dfrac{m_e}{m_{\alpha}}}$$
-
0%
$$\dfrac{2m_e}{m_{\alpha}}$$
-
0%
$$\sqrt{\dfrac{m_e}{2m_{\alpha}}}$$
Q.10.
A charged particle 'q' is shot with speed v towards another fixed charged particle Q. It approaches Q upto a closest distance r and then returns. If q were given a speed $$2v$$, the closest distance of approach would be.
-
0%
r
-
0%
$$2r$$
-
0%
$$r/2$$
-
0%
$$r/4$$
Q.11.
The electric potential at a point in free space due to a charge Q coulomb is $$Q\ \times { 10 }^{ 11 }$$ V. The electric field at that point is:
-
0%
12 $$\pi { \varepsilon }_{ 0 }Q \times { 10 }^{ 22 }\ V { m }^{ -1 }$$
-
0%
4$$\pi { \varepsilon }_{ 0 }Q \times { 10 }^{ 22 }\ V { m }^{ -1 }$$
-
0%
12$$\pi { \varepsilon }_{ 0 }Q \times { 10 }^{ 20 }\ V { m }^{ -1 }$$
-
0%
$$4\pi{ \varepsilon }_{ 0 }Q \times { 10 }^{ 20 }\ V { m }^{ -1 }$$
Q.12.
The area of the plates of a parallel plante capacitor is $$A$$ and the gap between them is $$d$$. The gap is filled with a non-homogeneous dielectric whose dielectric constant varies with the distance $$y$$ from one plate as:$$K=\lambda \sec { \left( \cfrac { \pi y }{ 2d } \right) } $$, where $$\lambda$$ is a dimensionless constant. The capacitance of this capacitor is
-
0%
$$\cfrac { \pi { \varepsilon }_{ 0 }\lambda A }{ 2d } $$
-
0%
$$\cfrac { \pi { \varepsilon }_{ 0 }\lambda A }{ d } $$
-
0%
$$\cfrac { 2\pi { \varepsilon }_{ 0 }\lambda A }{ d } $$
-
0%
None
Q.13.
A capacitor is charged by a battery and then the battery is disconnected. A dielectric slab is introduced between the plates. The result is
-
0%
P.d between the plates increases, charge on the plate decreases
-
0%
P.d between the plates decreases, charge remains same
-
0%
P.d increases, charge remain constant
-
0%
P.d decreases, charge increases
Q.14.
Which one of the following gives the resultant capacitor when capacitors are joined in series?
-
0%
The sum of the individual capacitors
-
0%
The reciprocal of the sum of the reciprocals of the individual capacitors
-
0%
The reciprocal of the sum of the capacitors
-
0%
The sum of the reciprocals of the individual capacitors
Q.15.
A system consists of two charges 4 $$\mu C$$ and -3 $$\mu C$$ with no external field placed at (-5 cm, 0, 0) and (5 cm, 0, 0) respectively. The amount of work required to separate the two charges infinitely away from each other is
-
0%
1.1 J
-
0%
2 J
-
0%
2.5 J
-
0%
3 J
Q.16.
The potential at a point due to a charge of 5 x $${ 10 }^{ -7 }$$ C located 10 cm away is:
-
0%
3.5 x $${ 10 }^{ 5 }$$ V
-
0%
3.5 x $${ 10 }^{ 4 }$$ V
-
0%
4.5 x $${ 10 }^{ 4 }$$ V
-
0%
4.5 x $${ 10 }^{ 5 }$$ V
Q.17.
Which of the following statement is true about the relation between electric field and potential?
-
0%
Electric field in the direction in which the potential decreases steepest
-
0%
Magnitude of electric field is given by the change in the magnitude of potential per unit displacement normal to the equipotential surface at that point.
-
0%
In the region of strong electric field, equipotential surfaces are far apart.
-
0%
Both the statements (a) and (b) are correct.
Q.18.
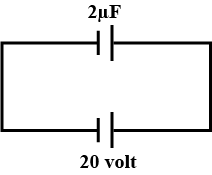
There is a -ve charge -$$q$$ as shown in the figure. Take the potential to be zero at infinity. If $$A$$ and $$B$$ are two points in the charge's vicinity, then the potential at-
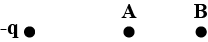
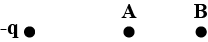
-
0%
$$A$$ is less than at $$B$$
-
0%
$$A$$ is more than that at $$B$$
-
0%
$$A$$ is greater in magnitude than at $$B$$
-
0%
$$A$$ is smaller in magnitude than at $$B$$
Q.19.
What is the angle between electric field and equipotential surfaces ?
-
0%
90 always
-
0%
0 always
-
0%
0 to 90
-
0%
0 to 180
Q.20.
Which of the following statement is not true?
-
0%
Electrostatic force is a conservative force.
-
0%
Potential at a point is the work done per unit charge in bringing a charge from infinity to that point in an electric field.
-
0%
Electrostatic force is non-conservative.
-
0%
Potential is the ratio of work to charge.
Q.21.
A capacitor of capacitance $${ C }_{ 1 }$$ is charged to a potential V and then connected in parallel to an uncharged capacitor of capacitance $${ C }_{ 2 }$$. The final potential difference across each capacitor will be
-
0%
$$ \dfrac { { C }_{ 1 }V }{ { C }_{ 1 }+{ C }_{ 2 } }$$
-
0%
$$ \dfrac { { C }_{ 2 }V }{ { C }_{ 1 }+{ C }_{ 2 } }$$
-
0%
$$ 1+\dfrac { { C }_{ 2 } }{ { C }_{ 1 } }$$
-
0%
$$ 1-\dfrac { { C }_{ 2 } }{ { C }_{ 1 } }$$
Q.22.
An infinite cylinder of radius $${ r }_{ 0 }$$ carrying linear charge density $$\lambda$$. The equation of the equipotential surface for this cylinder is
-
0%
$$\displaystyle r={ r }_{ 0 }{ e }^{ \pi { \varepsilon }_{ 0 }\left\lfloor V(r)+V({ r }_{ 0 }) \right\rfloor \lambda }$$
-
0%
$$\displaystyle r={ r }_{ 0 }{ e }^{ 2\pi { \varepsilon }_{ 0 }\left\lfloor V(r)-V({ r }_{ 0 }) \right\rfloor { \lambda }^{ 2 } }$$
-
0%
$$\displaystyle r={ r }_{ 0 }{ e }^{ -2\pi { \varepsilon }_{ 0 }\left\lfloor V(r)-V({ r }_{ 0 }) \right\rfloor /\lambda }$$
-
0%
$$\displaystyle r={ r }_{ 0 }{ e }^{ -2\pi { \varepsilon }_{ 0 }\left\lfloor V(r)-V({ r }_{ 0 }) \right\rfloor \lambda }$$
Q.23.
The charge on 3$$\mu F$$ capacitor shown in the figure is
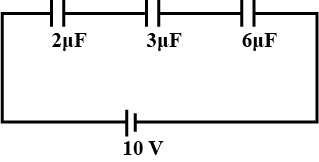

-
0%
2 $$\mu C$$
-
0%
10 $$\mu C$$
-
0%
6 $$\mu C$$
-
0%
8 $$\mu C$$
Q.24.
The figure show several equipotential lines. Comparing between points $$A$$ and $$\mathrm { B }$$ , pick up the best possible statement
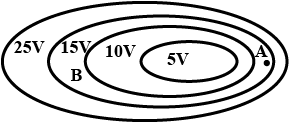

-
0%
the electric field has a greater magnitude at point $$\mathrm { A }$$ and is directed to left.
-
0%
the electric field has a greater magnitude at point $$\mathrm { A }$$ and is directed to right.
-
0%
the electric field has a greater magnitude at point $$\mathrm { B }$$ and is directed to left.
-
0%
the electric field has a greater magnitude at point $$\mathrm { B }$$ and is directed to lright.
Q.25.
A parallel plate capacitor of capacitance 5 $$\mu F$$ and plate separation 6 cm is connected to a 1 V battery and charged. A dielectric of dielectric constant 4 and thickness 4 cm is introduced between the plates of the capacitor. The additional charge that flows into the capacitor from the battery is
-
0%
2 $$\mu C$$
-
0%
3 $$\mu C$$
-
0%
5 $$\mu C$$
-
0%
10 $$\mu C$$
Q.26.
A parallel capacitor plate is charged and then isolated. The effect of increasing of plate separation on charge, potential, capacitance respectively are
-
0%
constant, decreases, decreases
-
0%
increase, decreases, decreases
-
0%
constant, decreases, increases
-
0%
constant, increases, decreases.
Q.27.
A capacitor has some dielectric between its plates, and the capacitor is connected to a dc source. The battery is now disconnected and then the dielectric is removed, then
-
0%
capacitance will increase.
-
0%
energy stored will decrease.
-
0%
electric field will increase.
-
0%
Voltage will decrease.
Q.28.
In a parallel plate capacitor, the capacity increases if:
-
0%
area of the plate is decreased
-
0%
distance between the plates is increases
-
0%
area of the plate is increased
-
0%
dielectric constant decreases.
Q.29.
Two identical capacitors are joined in parallel, charged to a potential V, separated and then connected in series, the positive plate of one is connected to the negative of the other. Which of the following is true?
-
0%
The charges on the free plated connected together are destroyed.
-
0%
The energy stored in the system increases.
-
0%
The potential difference between the free plates is 2 V.
-
0%
The potential difference remains constant.
Q.30.
A parallel plate capacitor has two square plates with equal and opposite charges. The surface charge densities on the plate are $$+\sigma$$ and $$-\sigma$$ respectively. In the region between the plates the magnitude of electric field is:
-
0%
$$\dfrac { \sigma }{ 2{ \varepsilon }_{ 0 } } $$
-
0%
$$\dfrac { \sigma }{ { \varepsilon }_{ 0 } } $$
-
0%
0
-
0%
none of these
Q.31.
A parallel plate air capacitor is charged to a potential difference of V volts. After disconnecting the charging battery the distance between the plates of the capacitor is increased using an insulating handle. As a result the potential difference between the plates:
-
0%
increases
-
0%
decreases
-
0%
does not change
-
0%
becomes zero
Q.32.
A capacitor consists of two metal plates each $$10{\text{ }}cm$$ by $$20{\text{ }}cm;$$ they are separated by a $$2.0{\text{ }}mm$$ thick insulator with dielectric constant $$4.1$$ and dielectric strength 6.0107 V/m. What is the capacitance in $$pF\left( {{{10}^{ - 12}}F} \right)?$$
-
0%
75
-
0%
100
-
0%
240
-
0%
360
Q.33.
The electric potential at a point in free space due to a charge $$Q$$ coulomb is $$Q\times { 10 }^{ 11 }V$$. The electric field at that point is
-
0%
$$12\pi { \varepsilon }_{ 0 }Q\times { 10 }^{ 22 }V{ m }^{ -1 }$$
-
0%
$$4\pi { \varepsilon }_{ 0 }Q\times { 10 }^{ 22 }V{ m }^{ -1 }$$
-
0%
$$12\pi { \varepsilon }_{ 0 }Q\times { 10 }^{ 20 }V{ m }^{ -1 }$$
-
0%
$$4\pi { \varepsilon }_{ 0 }Q\times { 10 }^{ 20 }V{ m }^{ -1 }$$
Q.34.
The potential at a point due to a charge of $$5\times { 10 }^{ -7 }C$$ located $$10cm$$ away is:
-
0%
$$3.5\times { 10 }^{ 5 }V$$
-
0%
$$3.5\times { 10 }^{ 4 }V$$
-
0%
$$4.5\times { 10 }^{ 4 }V$$
-
0%
$$4.5\times { 10 }^{ 5 }V$$
Q.35.
The top of the atmosphere is about $$400kV$$ with respect to the surface of earth, corresponding to an electric field that decreases with altitude. Near the surface of earth the field is about $$100V{m}^{-1}$$, but still don't get an electric shock, as we set out of our houses in to open because (assume the house is free from electric field)
-
0%
our body is a perfect insulator
-
0%
our body and ground form an equipotential surface
-
0%
the original euipotential surfaces of open air remain same
-
0%
none of these
Q.36.
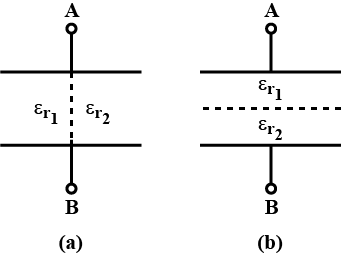
A parallel plate capacitor is given a definite potential difference. Keeping the potential difference same, a slab of thickness 3 mm is placed between the plates. To do this, the distance between the plates is increased by 2.4 mm. Calculate the dielectric constant of the slab.

-
0%
10
-
0%
15
-
0%
5
-
0%
8
Q.37.
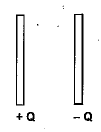
Consider a parallel plate capacitor having charge $$Q$$. Then

-
0%
There is no force acting on plates of the capacitor
-
0%
The electric field at outer side of plates is zero
-
0%
The electric field between the plates of the capacitor is $$\dfrac{\sigma}{in_0}$$
-
0%
The force between the plates is given by $$\dfrac{Q^2}{2A \in_0}$$
Q.38.
A capacitor of capacitance $$C$$ is connected to a cell of $$emf$$ V and when fully charged, it is disconnected. Now the separation between the plates doubled. The change in flux of electric field through a closed surface enclosing the capacitor is :
-
0%
Zero
-
0%
$$\dfrac{CV}{\varepsilon_0}$$
-
0%
$$\dfrac{CV}{2\varepsilon_0}$$
-
0%
$$\dfrac{2CV}{\varepsilon_0}$$
Q.39.
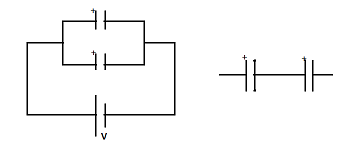
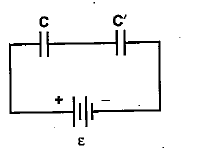
In a series combination of two capacitances $$C'$$ and $$C(C> C)$$ (as shown in the circuit)

-
0%
C' stores more energy than $$C$$
-
0%
$$C$$ stores more energy than $$C'$$
-
0%
potential difference across $$C$$ is more than that across $$C'$$
-
0%
potential difference across $$C'$$ is less than that across $$C$$
Q.40.
Two conducting plates A and B are placed parallel to each other. A is given $$Q_1$$ and B a charge $$Q_2$$. Then
-
0%
The charge on the outer plate A is $$\dfrac{Q_1 + Q_2}{2}$$
-
0%
The charge on the outer plate B is $$\dfrac{Q_1 + Q_2}{2}$$
-
0%
The charge on inner plate A is $$\dfrac{Q_1 - Q_2}{2}$$
-
0%
The charge on inner plate B is $$\dfrac{Q_1 - Q_2}{2}$$
Q.41.
Work done in moving an object through an equipotential surface is
-
0%
Positive
-
0%
Negative
-
0%
Zero
-
0%
Depends on the field direction
Q.42.
A parallel plate capacitor with air as dielectric is charged to a potential 'V' using a battery. Removing the battery, the charged capacitor is then connected across an identical uncharged parallel plate capacitor filled with wax of dielectric constant 'K' the common potential of both the capacitor is
-
0%
V volts
-
0%
kV volts
-
0%
(k + 1) V volts
-
0%
$$\dfrac{V}{{k + 1}}{\text{volts}}$$
Q.43.
An example of an equipotential surface in earth is
-
0%
A line passing through the centre of the earth connecting two points along the diameter
-
0%
A plane that passes through the circular section of the hemisphere of the earth
-
0%
A spherical surface at a distance of 1km from the surface of the earth with its centre at centre of earth
-
0%
A plane on the surface of the earth, which is a tangent to the earth
Q.44.
The electric field due to the electric potential V = $$(2x^{2}-4x)$$ is
-
0%
$$(4x+4)\hat{i}$$
-
0%
$$(4x-4)\hat{i}$$
-
0%
$$(-4x+4)\hat{i}$$
-
0%
$$(-4x-4)\hat{i}$$
Q.45.
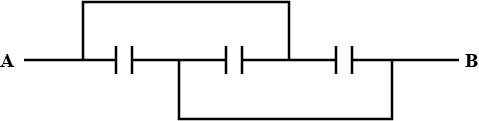
In the given figure each capacitor is equal to 45$$\mu F$$ then the equivalent capacity between A and B in the given circuit is:

-
0%
$$15
\mu F
$$ -
0%
$$10
\mu F
$$ -
0%
$$40
\mu F
$$ -
0%
$$135
\mu F
$$
Q.46.
Two insulated charged spheres of radii $${R}_{1}$$ and $${R}_{2}$$ having charges $${Q}_{1}$$ and $${Q}_{2}$$ respectively are connected to each other, then there is:
-
0%
no change in the energy of the sytem
-
0%
an increase in the energy of the system
-
0%
always a decrease in the energy of the system
-
0%
a decrease in energy of the system unless $${q}_{1}{R}_{2}={q}_{2}{R}_{1}$$
Q.47.
Select the correct statements.
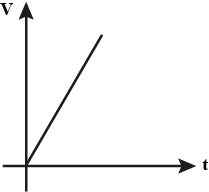

-
0%
The energy of a capacitor resides in the field between the plates
-
0%
The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor does not depend on the metal of the plates
-
0%
If the current charging a capacitor is kept constant, the potential difference V across the capacitor varies with time according to the adjacent graph
-
0%
All of the above
Q.48.
Electrons are caused to fall through a potential difference of 1500 volt. If they were initially at rest, their final speed is
-
0%
$$4.6 \times {10^7}m/s$$
-
0%
$$0.726 \times {10^7}m/s$$
-
0%
$$0.23 \times {10^2}m/s$$
-
0%
$$5.1 \times {10^9}m/s$$
Q.49.
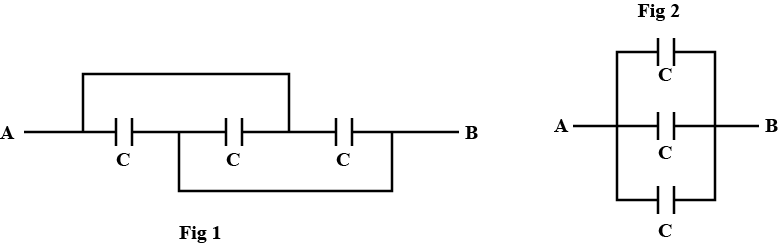
Three charges +4q,-q and +4q are kept on a straight line at position (0,0,0),(a,0,0) and (2a,0,0) respectively. Considering that they are free to move along the x-axis only
-
0%
All the charges are in stable equilibrium
-
0%
All the charges are in unstable equilibrium.
-
0%
Only the middle charge is in stable equilibrium.
-
0%
Only middle charge is in unstable equilibrium.
Q.50.
The earth has volume 'V' and surface area 'A'; then its capacitance would be:
-
0%
$$
4\pi \in _0 \dfrac{A}
{V}
$$ -
0%
$$
4\pi \in _0 \dfrac{V}
{A}
$$ -
0%
$$
12\pi \in _0 \dfrac{V}
{A}
$$ -
0%
$$
12\pi \in _0 \dfrac{A}
{V}
$$