Q.1.
Technique used to detect the DNA in a clone is
-
0%
Polymerase chain reaction
-
0%
Gel electrophoresis
-
0%
Chromatography
-
0%
Autoradiography
Q.2.
Bacteria genetically engineered to express a gene from a plant will
-
0%
Synthesise a protein with the same sequence of amino acids as in the plant and, therefore, the protein will have the same structure and function as in the plant.
-
0%
Synthesis a protein with essentially the same sequence of amino acids as in the plant with differences relating to different colon wobble rules between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
-
0%
Not be able to synthesise a protein due to the presence of exon splicing sequences in the DNA sequence from the plant
-
0%
Not be able to synthesise a protein because transaction is coupled with transaction and posttranscriptional processing does not occur in it.
Q.3.
You discovered a novel eukaryotic organism that glows in the dark. You believe this trait is due to a single gene, and you wish to clone the gene. which of the following strategies is most likely to be successful?
-
0%
Isolate the genomic DNA from the organism, digest with a restriction endonuclease, insert into a plasmid vector and transform into a plasmid
-
0%
Isolate the genomic DNA from the organism, digest with a restriction endonuclease, insert into a plasmid vector and transform into bacteria. Screen colonies for for the ability to glow in the dark.
-
0%
Isolate mRNA from the organism, reverse transcribe and generate cDNA, insert into a plasmid vector and transform into bacteria. Screen colonies for the ability to glow in the dark.
-
0%
Isolate mRNA from the organism, reverse transcribe and genetate cDNA, Insert into a plasmid vector and transform into eukaryotic cells such as yeast. Screen colonies for the ability to glow in the dark.
Q.4.
Gel electrophoresis is a
-
0%
Technique of separation of charged molecules under the influence of magnetic field.
-
0%
Technique of incorporation of DNA molecules Into the cell through transient pore made due to electrical impulses.
-
0%
Technique of separation and isolation of DNA fragments through the pores of agarose.
-
0%
Technique of separation and purification of gene products.
Q.5.
Select the incorrect Statement regarding DNA replication with respect to the template strand
-
0%
Leading strand is formed in 5 $$\rightarrow$$ 3 direction.
-
0%
Okazaki fragments are formed in 5 $$\rightarrow$$ 3 direction.
-
0%
DNA polymerase catalyses polymerisation in 5 $$\rightarrow$$ 3 direction.
-
0%
DNA polymerase catalyses palymerisation in 3 $$\rightarrow$$ 5 direction.
Q.6.
Bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs), cosmids, phages, plasmids and yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) are all commonly used cloning vectors that differ in their cloning capacities, with a range from approximately 100 bp to 1000 kb. Which of the following is the increasing cloning capacity?
-
0%
BAC, cosmid, phage, plasmid, YAC
-
0%
YAC, BAC, cosmid, phage, plasmid
-
0%
Plasmid, phage, cosmid, BAC, YAC
-
0%
Plasmid, Cosmid, phage, BAC, YAC
Q.7.
A doctor while operating on an HIV(+)ve patient accidentally cuts himself with a scalpel. Suspecting himself to have contracted the virus which test will he take to rule out/confirm his suspicion?
-
0%
PCR
-
0%
Routine urine examination
-
0%
TLC
-
0%
DLC
Q.8.
The plasmid derived from E.coli is
-
0%
PBR $$327$$
-
0%
PBR $$322$$
-
0%
Phagemid
-
0%
None of the above
Q.9.
The term 'molecular scissors' generally refers to
-
0%
DNA polymerases
-
0%
RNA polymerases
-
0%
restriction endonucleases
-
0%
DNA ligases
Q.10.
In the $$PCR$$ technology the $$DNA$$ segment is replicated over a billion times. This repeated replication is catalyzed by the enzyme.
-
0%
$$DNA$$ polymerase
-
0%
Taq polymerase
-
0%
$$DNA$$ dependent $$RNA$$ polymerase
-
0%
Primase
Q.11.
The usual source of restriction endonucleases used in gene cloning is
-
0%
fungi
-
0%
bacteria
-
0%
plants
-
0%
viruses
Q.12.
In a genetic engineering experiment, restriciton enzymes can be used for
-
0%
bacterial DNA only
-
0%
viral DNA only
-
0%
any DNA fragment
-
0%
eukaryotic DNA only
Q.13.
The figure below shows three steps $$(A, B, C)$$ of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Select the option giving correct identification together with what it represents?


-
0%
B - denaturation at a temperature of about $$98^0$$C separating the two DNA strands.
-
0%
A - denaturation at a temperature of about $$50^0$$C
-
0%
C - extension in the presence of heat stable DNA polymerase.
-
0%
A - annealing with two sets of primers.
Q.14.
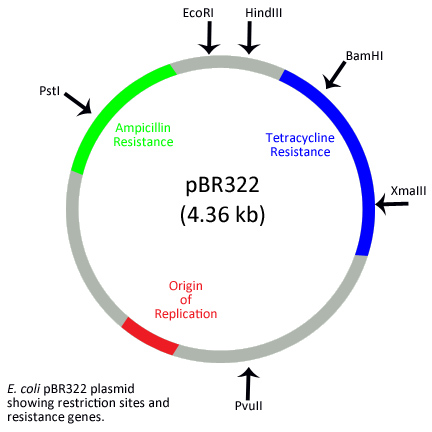
The given figure is the diagrammatic representation of the $$E.coli$$ vector $$pBR \,322$$. Which one of the given options correctly identifies its certain components?

-
0%
$$ori - $$original restriction enzyme
-
0%
$$rop - $$reduced osmotic pressure
-
0%
$$Hin \,d \,III,\, Eco \,R\, I$$ - selectable markers
-
0%
$$amp^{R}, tet^{R}$$ - antibiotic resistance genes
Q.15.
Which one is a true statement regarding $$DNA$$ polymerase used in $$PCR$$
-
0%
it is used to ligate introduced $$DNA$$ in recipient cell
-
0%
it serves as a selectable marker
-
0%
it is isolated from a virus
-
0%
it remains active at high temperature
Q.16.
The taq polymerase enzyme is obtained from
-
0%
Thiobacillus ferroxidans
-
0%
Bacillus subtilis
-
0%
Pseudomonas putida
-
0%
Thermus aquaticus
Q.17.
$$Eco \,RI$$ cleaves the $$DNA$$ strands to produce
-
0%
blunt ends
-
0%
sticky ends
-
0%
satellite ends
-
0%
ori replication end
Q.18.
How many copies of the DNA sample are produced in PCR technique after 6-cycle?
-
0%
$$4$$
-
0%
$$32$$
-
0%
$$64$$
-
0%
$$16$$
Q.19.
Ideally, in a process of genetically modifying an organism, a vector should have
-
0%
Recognition site
-
0%
Tetracycline resistant site
-
0%
Kanamycin resistant site
-
0%
Chloramphenicol resistant site
Q.20.
The cutting of DNA at specific locations became possible with the discovery of
-
0%
restriction enzymes
-
0%
probes
-
0%
selectable markers
-
0%
ligases
Q.21.
DNA fragments generated by the restriction endonucleases in a chemical reaction can be separated by
-
0%
electrophoresis
-
0%
restriction mapping
-
0%
centrigugation
-
0%
polymerase chain reaction
Q.22.
Commonly used vectors for human genome sequencing are ?
-
0%
T-DNA
-
0%
BAC and YAC
-
0%
expression vectors
-
0%
T/A cloning vectors
Q.23.
Which of the following restriction enzymes produces blunt ends?
-
0%
Sal I
-
0%
Eco RV
-
0%
Xho
-
0%
Hind III
Q.24.
Foreign DNA is also called
-
0%
vehicle DNA
-
0%
Passenger DNA
-
0%
r-DNA
-
0%
Vector DNA
Q.25.
In reference to DNA polymerase III, which statement is wrong?
-
0%
It requires ATP For polymerase action.
-
0%
Required for PCR
-
0%
More active than DNA Pol I & II
-
0%
Requires a previously made template to work on
Q.26.
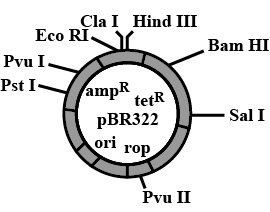
Observe the diagram of pBR322 and select the INCORRECT statement.

-
0%
They have antibiotics resistant gene for tetracycline and amipicillin.
-
0%
It has a Origin of replication.
-
0%
It has rop gene.
-
0%
None of the above
Q.27.
Which of the following is not necessary to execute polymerase chain reaction successfully?
-
0%
All four DNA bases
-
0%
Short DNA base pairs
-
0%
DNA polymerase
-
0%
DNA library
Q.28.
Identify the INCORRECT statement.
-
0%
The first restriction endonuclease enzyme, which has been isolated and characterized was Hind III.
-
0%
EcoRI recognize 5` GAATTC-3`, and cut the DNA between G and A
-
0%
The genes of plasmids encoding resistance to antibiotics like ampicillin, tetracycline, etc are considered useful selectable markers for Coli.
-
0%
pUC19 also encodes for an ampicillin resistance gene.
Q.29.
Which of the following is not a method of introducing alien DNA into host cells?
-
0%
Micro injection
-
0%
Electroporation
-
0%
Being placed along with the cell into a gene gun
-
0%
Gel electrophoresis
Q.30.
A DNA sequencing reaction was performed with the fragment $$5-XXXGCGATCGYYYY-3'$$ as the template, dideoxy GTP, all the four $$dNTPs$$, and the required primers and enzyme. $$XXXX$$ and $$YYYY$$ in the given DNA fragment represent primer binding sites. The set of fragments obtained during the reaction will be (the primers are not shown in the amplified fragments).
-
0%
$$5'-CGATCGC-3'$$ only
-
0%
$$5'-CG-3', 5'-CGCTAG-3', 5'-CCCTAGC-3'$$
-
0%
$$5'-CG-3', 5'-CGATCG-3', 5'-CGATCGC-3'$$
-
0%
$$5'-G-3', 5'-GCG-3', 5'-GCGATCG-3'$$
Q.31.
Most important part if Ti-plasmid at which desired gene is put to target into plant cell is
-
0%
Ti-gene
-
0%
Vir gene
-
0%
T- DNA
-
0%
Ori site
Q.32.
Polymerisation of DNA is in
-
0%
$$3' \rightarrow 5'$$ direction
-
0%
$$5' \rightarrow 3'$$ direction
-
0%
Both $$3' \rightarrow 5'$$ and $$5' \rightarrow 3'$$ direction
-
0%
None of the above
Q.33.
A bacterial plasmid ________
-
0%
Does not replicate
-
0%
Can replicate independently
-
0%
Replicates, but with some association with chromosome
-
0%
Shows independent assortment (like in Mendelian Genetics)
Q.34.
The basic procedure involved in the construction of a recombinant DNA molecule is depicted. The mistake in the procedure is?
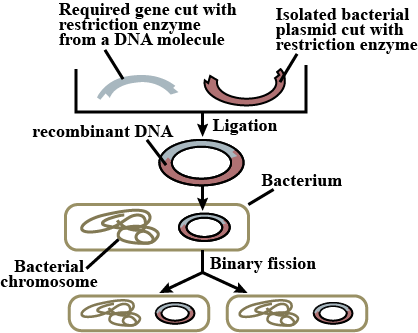

-
0%
Enzyme polymerase is not included
-
0%
Mammalian DNA is used
-
0%
Two different restriction enzymes are used
-
0%
The cut ends of vector and chromosomal DNA have staggering ends
Q.35.
Which of the following statements is incorrect about plasmids?
-
0%
They are extrachromosomal DNA
-
0%
They are used in genetic engineering
-
0%
They help in the replication of nucleoid
-
0%
They are small, circular and confer certain unique phenotypic characters to some bacteria like resistance to antibiotics
Q.36.
During heat shock to the bacterium , the temperature used for giving thermal shock is:
-
0%
$$82^oC$$
-
0%
$$109^oC$$
-
0%
Liquid nitrogen
-
0%
$$42^oC$$
Q.37.
Identify the correct sequence of steps in the construction of recombinant DNA.
$$(1)$$ use restriction enzymes
$$(2)$$ use DNA ligase
$$(3)$$ remove plasmid from parent bacterium
$$(4)$$ introduce plasmid into new host bacterium.
$$(1)$$ use restriction enzymes
$$(2)$$ use DNA ligase
$$(3)$$ remove plasmid from parent bacterium
$$(4)$$ introduce plasmid into new host bacterium.
-
0%
$$1-2-3-4$$
-
0%
$$4-3-2-1$$
-
0%
$$3-1-2-4$$
-
0%
$$2-3-1-4$$
Q.38.
Selected the vectors which have the ability to incomplete a foreign DNA in chromosomal DNA of plant cell.
-
0%
Disarmed Ti plasmid
-
0%
$$pBR322$$
-
0%
Bacteriophage
-
0%
Both (1) and (2).
Q.39.
How many fragments will be generated in total upon digestion of a closed circular DNA molecule and liner DNA molecule with a same restriction enzyme having six recognition sites on both DNA molecules?
-
0%
$$13$$
-
0%
$$14$$
-
0%
$$12$$
-
0%
$$6$$
Q.40.
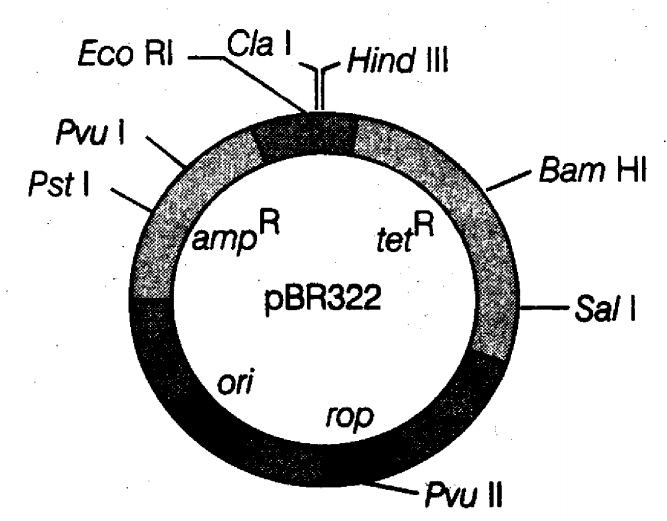
Which of the following is not a feature of plasmid $$pBR322$$?
-
0%
Double stranded circular DNA
-
0%
Autonomous replication
-
0%
Integrates with chromosomal DNA in host cell
-
0%
Absence of histones
Q.41.
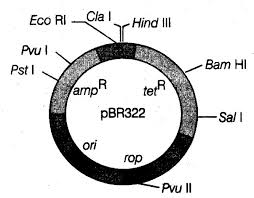
E.coli cloning vector pBR322 showing restriction sites, ori and antibiotic resistance genes is given below. Select the correct option.
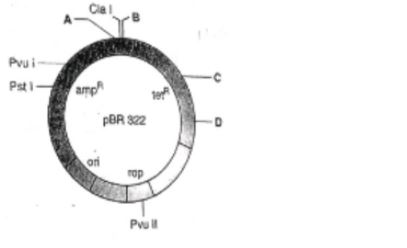

-
0%
A-Hind III,B-Eco RI, C-Bam H I, D-Sal I
-
0%
A-Eco RI, B-Hind III, C-Bam HI, D-Sal I
-
0%
A-Eco RI, B-BamH I, C-Hind III, D-Sal I
-
0%
None of these
Q.42.
Column I Column II
I. Agarose A. PCR
II. Opines B. Gene gun
III. Biolistic C. Ti plasmid
iv. Thermal cycler D. Sea weeds
I. Agarose A. PCR
II. Opines B. Gene gun
III. Biolistic C. Ti plasmid
iv. Thermal cycler D. Sea weeds
-
0%
$$I-D,II-A,III-B,IV-C$$
-
0%
$$I-D,II-C,III-B,IV-A$$
-
0%
$$I-D,II-A,III-C,IV-B$$
-
0%
$$I-A,II-D,III-B,IV-C$$
Q.43.
Which of the following techniques can be used to introduce foreign DNA into the cell?
-
0%
Using disarmed pathogen
-
0%
Microinjection
-
0%
Gene gun
-
0%
All of these
Q.44.
Insertional inactivation is related to
-
0%
Microinjection
-
0%
Gene gun
-
0%
Gel electrophoresis
-
0%
Selection of recombinations
Q.45.
The areas of application of PCR include
A. Production of monoclonal antibodies
B. Insertion of recombinant DNA into an organism
C. Diagnosis of specific mutation
D. Detection of plant pathogens
B. Insertion of recombinant DNA into an organism
C. Diagnosis of specific mutation
D. Detection of plant pathogens
-
0%
A, B
-
0%
B, C
-
0%
C, D
-
0%
A, B, C, D
Q.46.
X technique is now routinely used to detect HIV in suspected AIDs patients. It is being used to detect mutations in genes in suspected cancer patients too. It is a powerful technique to identify many other genetic disorders. Identify X-
-
0%
X=PCR
-
0%
X=DNA fingerprinting
-
0%
X-Bioinformatic
-
0%
X-X-ray defreaction
Q.47.
The first plasmid used for recombinant DNA technology is obtained from
-
0%
Bacillus thuringiensis
-
0%
Thermus aquaticus
-
0%
Salmonella typhimurium
-
0%
E. coli
Q.48.
Which of the following is not a source of restriction endonuclease?
-
0%
Haemophilus influenza
-
0%
Escherichia coli
-
0%
Agrobacterium tumefaciens
-
0%
Bacillus amyloli
Q.49.
In E.coli, a finished polypeptide has $$162$$ amino acids of which the first amino acid is not methionine compound. How many nucleotides of DNA are required to code this polypeptide?
-
0%
$$486$$
-
0%
$$54$$
-
0%
$$489$$
-
0%
$$492$$
Q.50.
The technique in which a foreign DNA is precipitated on the surface of the tungsten or gold particle and shot into target cells is known as?
-
0%
Microinjection
-
0%
Chemical - mediated genetic transformation
-
0%
Electroporation
-
0%
Biolistic method