Q.1.
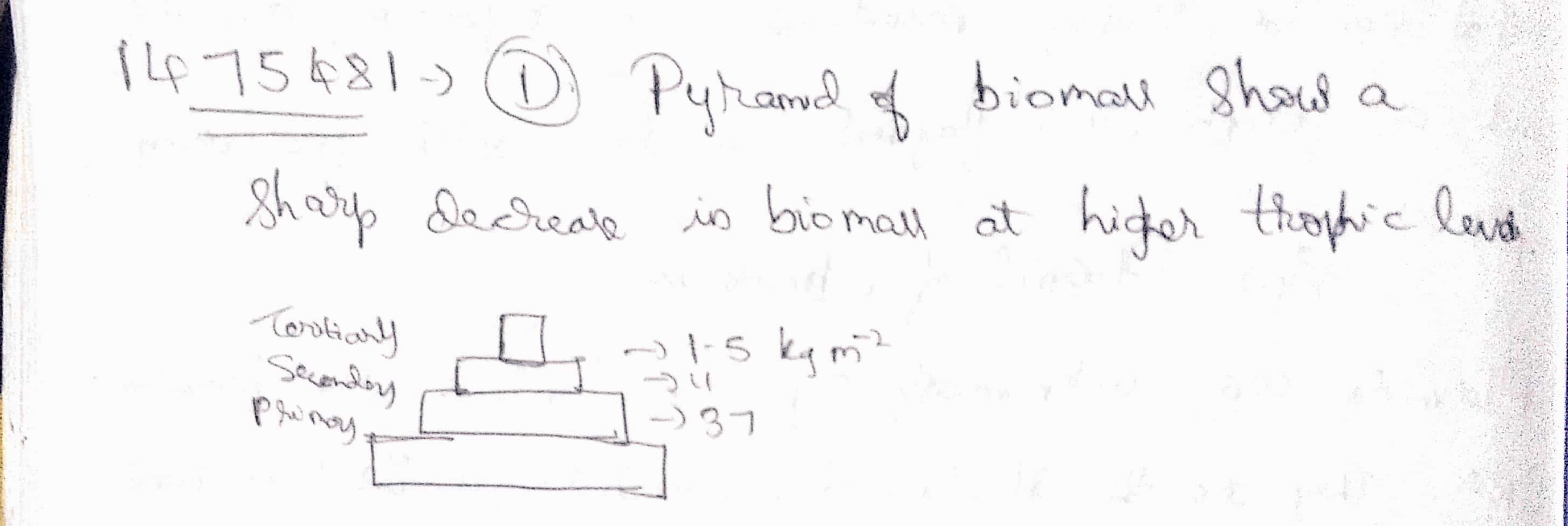
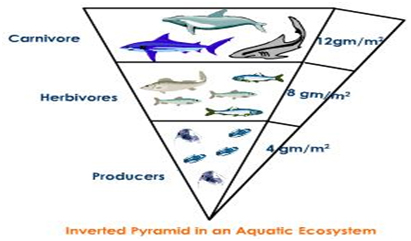
In a pyramid of biomass, it the total dry weight $$(kgm^{-2})$$ primary producers is about $$809$$. It will decrease at tertiary consumer level upto.
-
50%
$$37kgm^{-2}$$
-
50%
$$11kgm^{-2}$$
-
0%
$$5kgm^{-2}$$
-
0%
$$1.5kgm^{-2}$$
Q.2.
Flg can maintain community structure during food scarcity in tropical deciduous forest these are act as:
-
0%
Exotic species
-
0%
Pioneer species
-
33%
Edge species
-
67%
Key stone species
Q.3.
A climax community is recognized by _______________.
-
50%
Grass,herbs and shrubs
-
50%
Trees
-
0%
High biomass
-
0%
Uniform composition
Q.4.
The primary producers convert how much energy in the sunlight available to them into NPP?
-
0%
$$10\%$$
-
0%
$$42\%$$
-
100%
$$50\%$$
-
0%
$$1\%$$
Q.5.
How many statements are correct
(a) Pyramid of biomass in sea is also generally inverted
(b) Pyramid of energy is never inverted
(c) In terrestrial ecosystem a much larger fraction of energy flows through detritus food chain
(d) Humus is highly resistant to microbial action and undergoes decomposition at an extremely slow rate.
(a) Pyramid of biomass in sea is also generally inverted
(b) Pyramid of energy is never inverted
(c) In terrestrial ecosystem a much larger fraction of energy flows through detritus food chain
(d) Humus is highly resistant to microbial action and undergoes decomposition at an extremely slow rate.
-
50%
One
-
0%
Two
-
50%
Three
-
0%
All of these
Q.6.
Primary succession starts in an area where ___________________.
-
0%
No living organisms ever exicted
-
0%
All the living organisms that existed there, lost due to any reason
-
0%
No living organism are there
-
100%
Both A and C
Q.7.
How many statements are incorrect regarding succession?
(A) During succession climax community is always mesophytes
(B) Future seral communities can't be predicted
(C) Increases net community productivity
(D) Increases species diversity, Biomass and humus content.
(E) Gradual replacement from long lived to short lived plant.
(A) During succession climax community is always mesophytes
(B) Future seral communities can't be predicted
(C) Increases net community productivity
(D) Increases species diversity, Biomass and humus content.
(E) Gradual replacement from long lived to short lived plant.
-
0%
$$1$$
-
0%
$$2$$
-
0%
$$4$$
-
0%
None of the above
Q.8.
In ecological succession the climax community is best recognised by the following state.
-
0%
P$$=$$R
-
0%
P$$>$$R
-
0%
P$$<$$R
-
0%
P$$\neq$$R
Q.9.
How many statements are incorrect regarding succession ?
-
0%
During succession climax community is always mesophytes
-
0%
Future seral communities can't be predicted
-
0%
Increases net community productivity
-
0%
Increases species diversity, Biomass and humus content.
-
0%
Gradual replacement from long lived to short lived plant
Q.10.
All the statements are correct regarding ecological succession except
-
0%
It is a random process
-
0%
Species diversity increases as succession proceeds
-
0%
The food chain relationships becomes more complex
-
0%
The role of decomposers becomes more and more important
Q.11.
More solar radiation is received at the:
-
0%
Earth
-
0%
Top of the atmosphere
-
0%
North and south poles
-
0%
None of above
Q.12.
Which of the following statement is incorrect regarding ecological pyramids?
-
0%
The pyramid of energy is inverted in ocean ecosystem.
-
0%
The pyramid of biomass is inverted in aquatic ecosystem.
-
0%
The pyramid of numbers is upright in grassland ecosystem.
-
0%
The pyramid of biomass is upright in grassland ecosystem.
Q.13.
Net primary productivity (NPP) in an ecosystem is
-
0%
GPP - R = NPP
-
0%
GPP + R = NPP
-
0%
GPP - NPP = R
-
0%
R - NPP = GPP
Q.14.
Succession initiated on large sand deposits or deserts is called
-
0%
Hydrosere
-
0%
Psammosere
-
0%
Xerosere
-
0%
Oxylosere
Q.15.
In meteorology, the word insolation refers to:
-
0%
A well-constructed, energy-efficient home
-
0%
The solar constant
-
0%
Incoming solar radiation
-
0%
An increase in solar output
Q.16.
A set of organisms that resemble one another in appearance and behaviour is called a ____________
-
0%
Exons
-
0%
Prions
-
0%
Species
-
0%
Guilds
Q.17.
Solar radiation reaches the earth's surface as:
-
0%
Visible radiation only
-
0%
Ultraviolet radiation only
-
0%
Infrared radiation only
-
0%
Ultraviolet, visible, and infrared radiation
Q.18.
The pyramid of numbers in a single tree is
-
0%
Upright
-
0%
Inverted
-
0%
Spindle shaped
-
0%
None of these
Q.19.
Which of the following provides a measure of the average speed of air molecules?
-
0%
Pressure
-
0%
Temperature
-
0%
Density
-
0%
Heat
Q.20.
Which of the following gases has role an important in maintaining atmospheric temperature?
-
0%
Nitrogen
-
0%
Oxygen
-
0%
Argon
-
0%
Carbon dioxide
Q.21.
What are examples of man subsidized solar powered ecosystem?
-
0%
Coastal estuary, tropical rain forest
-
0%
Agriculture and Aquaculture
-
0%
Oceans
-
0%
Tropical Rain forest
Q.22.
Major 'reservoirs' of $$CO_{2}$$ are:
-
0%
Land, water, plants
-
0%
Fossil fuel, soil, , oceans
-
0%
Volcanic Eruption
-
0%
Deforestation
Q.23.
The areas where soil is washed away into streams, transported into rivers and finally lost to the sea are called
-
0%
Ecologically sensitive areas
-
0%
Grasslands
-
0%
Delta
-
0%
Biologically sensitive areas
Q.24.
An ecosystem gradually merges with an adjoining one through a transitional zone is called the _____________
-
0%
Ecological niche
-
0%
ecological footprint
-
0%
ecotone
-
0%
shore effect
Q.25.
Which chemical is used in air conditions and refrigerators?
-
0%
CFCs
-
0%
Chlorine
-
0%
Fluorine
-
0%
Carbon
Q.26.
The formation of a climax community from an abandoned farm land is a an example of
-
0%
Autogenic succession
-
0%
Allogenic succession
-
0%
Primary succession
-
0%
Secondary succession
Q.27.
Which among the following is mobile in nature?
-
0%
Primary productivity
-
0%
Secondary productivity
-
0%
GPP
-
0%
NPP
Q.28.
____________ is a mixture of 50 - 90% of methane
-
0%
Natural gas
-
0%
Air
-
0%
Water
-
0%
Bio diesel
Q.29.
Graphical representation of trophic structure and function is known as
-
0%
Ecological Pyramid
-
0%
Ecosystem
-
0%
Ecological Function
-
0%
Environment
Q.30.
Affinity of hemoglobin for CO is two hundred times more considerable than:
-
0%
$$O_{2}$$
-
0%
$$CO_{2}$$
-
0%
Sox
-
0%
Nox
Q.31.
What are examples of primary succession?
-
0%
Estuaries, Forests
-
0%
Island, Sand or silt bed
-
0%
Mangroves, Deserts
-
0%
Forests, Wetland
Q.32.
What is percentage of S, Ca and K?
-
0%
2%
-
0%
3%
-
0%
7%
-
0%
8%
Q.33.
Which ecological succession is involved in migration, aggregation and competition?
-
0%
Initial causes
-
0%
Ecesis
-
0%
stabilizing causes
-
0%
Unstable Causes
Q.34.
Increased volcanic activities, reducesd :
-
0%
Solar gain
-
0%
High Sun radiations
-
0%
Oceans ability
-
0%
Both a and c
Q.35.
Most of solar radiation is reflected by
-
0%
Atmospheric clouds
-
0%
dust
-
0%
gases
-
0%
All of above
Q.36.
How many types of ecological succession are there?
-
0%
3
-
0%
2
-
0%
5
-
0%
4
Q.37.
Chemical energy that is stored in primary producers is in form of
-
0%
Organic molecules
-
0%
Inorganic compounds
-
0%
Green plants and Algae
-
0%
Omnivores
Q.38.
Which type of ecosystem has low productivity and capacity?
-
0%
Naturally subsidized solar powered ecosystem
-
0%
Unsubsidized natural solar powered ecosystem
-
0%
Man subsidized solar power ecosystem
-
0%
Fuel power ecosystem
Q.39.
Write true or false for the following statement.
The green plants capture about 10% of the energy of sunlight that falls on their leaves and convert it into food energy.
The green plants capture about 10% of the energy of sunlight that falls on their leaves and convert it into food energy.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.40.
The pyramid biomass of the sea is?
-
0%
Inverted
-
0%
Upright.
-
0%
Stable.
-
0%
Can be either inverted or upright
Q.41.
Match the two sets.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| I | Pioneers | A | Vegetation which modifies its own environment and thus, causing its own replacement |
| II | Autogenic succession | B | Replacement of existing community by external conditions |
| III | Allogenic succession | C | Establishment |
| IV | Ecesis | D | Primary colonisers |
-
0%
I- D, II- A, III- B, IV- C
-
0%
I- A, II- B, III- C, IV- D
-
0%
I- B, II- A, Ill- D, IV- C
-
0%
I- A, II- D, Ill- C, IV- B
Q.42.
Which one of the following is a major link in decomposer food chain?
-
0%
Anthracoceros
-
0%
Gyps
-
0%
Anser
-
0%
Pavo
Q.43.
Biogeochemical cycles can be traced in
-
0%
Ecosystems
-
0%
Biomes
-
0%
Only water
-
0%
Both A and B
Q.44.
The possibilities of presence of coal or fossil fuels in a particular area can be guessed by the study of
-
0%
Protozoans
-
0%
Pollen grains analysis (paleobotany)
-
0%
Both of the above
-
0%
Sulphur cycle
Q.45.
Edaphic nutrient cycle includes
-
0%
Gaseous types
-
0%
Partial sedimentary types
-
0%
Total sedimentary types
-
0%
All of the above
Q.46.
The carbon and nitrogen atoms circulating in the biogeochemical cycles are the same atoms that were in
-
0%
Insects of cenozoic era
-
0%
Dinosaurs, insects and trees of mesozoic era
-
0%
Mammals of cenozoic era only
-
0%
All of the above
Q.47.
Choose the correct set.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| I. | Gross primary productivity | A. | Total assimilation |
| II. | Secondary productivity | B. | Remains mobile and does not remain in situ |
| III. | Transducers | C. | Green plants |
| IV. | Food web | D. | Interlocking pattern |
-
0%
I- A, II- B, III- C, IV- D
-
0%
I- B, II- C. Ill- D, IV- A
-
0%
I- C, II- D, III- A, IV- B
-
0%
I- A, II- C, Ill- B, IV- D
Q.48.
Eltonian pyramids of numbers are upright in which one of the following ecosystems?
-
0%
Grassland
-
0%
Tree
-
0%
Pond
-
0%
Both A and C
Q.49.
Match the columns.
| Column I | Column II |
| I. Circulation of water | A. Dust water and gases above the earth |
| II. Circulation of nitrogen | B. Food chain |
| III. Circulation of food material | C. Hyrdrological cycle |
| IV. Troposphere | D. Nitrogen cycle |
-
0%
I-A, II-B, III-C, IV-D
-
0%
I-A, II-D, III-C, IV-B
-
0%
I-C, II-D, III-B, IV-A
-
0%
I-C, II-A, III-D, IV-B
Q.50.
The pyramid of number in a grassland ecosystem is:
-
0%
Always erect
-
0%
Always inverted
-
0%
Either erect or inverted
-
0%
Irregular