Q.1.
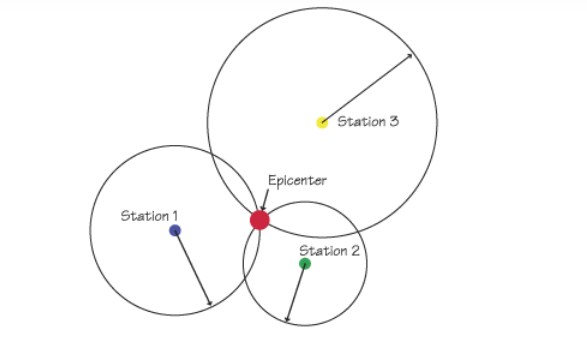
How many seismograph stations are used to locate the epicentre of an earthquake?
-
29%
$$4$$
-
29%
$$2$$
-
29%
$$3$$
-
14%
$$9$$
Q.2.
Name the scale on which the destructive energy of an earthquake is measured.
-
0%
Temperature scale
-
0%
Vector scale
-
100%
Richter scale
-
0%
Energy scale
Q.3.
A Seismograph is a device that is used to measure the:
-
0%
thunderstorm frequency
-
100%
earthquake magnitude
-
0%
lightning frequency
-
0%
lightning intensity
Q.4.
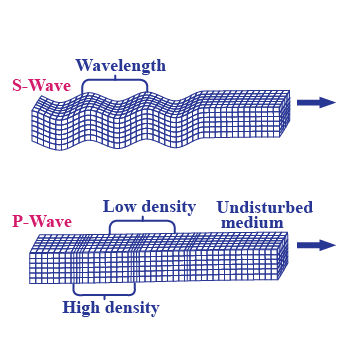
Choose the correct statement.
-
40%
'P' waves are slower than 'S' waves.
-
40%
Both 'P' and 'S' waves have same speed.
-
20%
'S' waves are slower than 'P' waves.
-
0%
None of the above.
Q.5.
What are seismic waves caused by?
-
0%
Aerial explosion
-
0%
Traffic
-
100%
Earthquakes
-
0%
Heavy rain
Q.6.
The weather department has predicted that a thunderstorm is likely to occur on a certain day. Suppose you have to go out on that day. Should you carry an umbrella?
-
20%
Yes
-
60%
No
-
0%
Ambiguous
-
20%
Data insufficient
Q.7.
A seismograph is also known as:
-
20%
Seismogram
-
0%
Seismology
-
80%
Seismometer
-
0%
Seismocity
Q.8.
How do we record seismic waves?
-
0%
With the help of an oscilloscope.
-
80%
With the help of a seismograph.
-
20%
With the help of an anemometer.
-
0%
None of the above.
Q.9.
Rub an empty ball pen refill on a polythene sheet and hold it on top of small pieces of paper. What will be your observation?
-
100%
Pieces of paper are attracted.
-
0%
Pieces of paper are repelled.
-
0%
Pieces of paper are neither attracted nor repelled.
-
0%
Pieces of paper are either attracted or repelled.
Q.10.
Fill in the blanks:
-
20%
downward, upward
-
80%
upward, downward
-
0%
downward, downward
-
0%
upward, upward
Q.11.
On which principle does a seismograph work?
-
40%
Principle of inertia.
-
20%
Principle of conservation of momentum.
-
40%
Principle of gravitational force.
-
0%
None of the above.
Q.12.
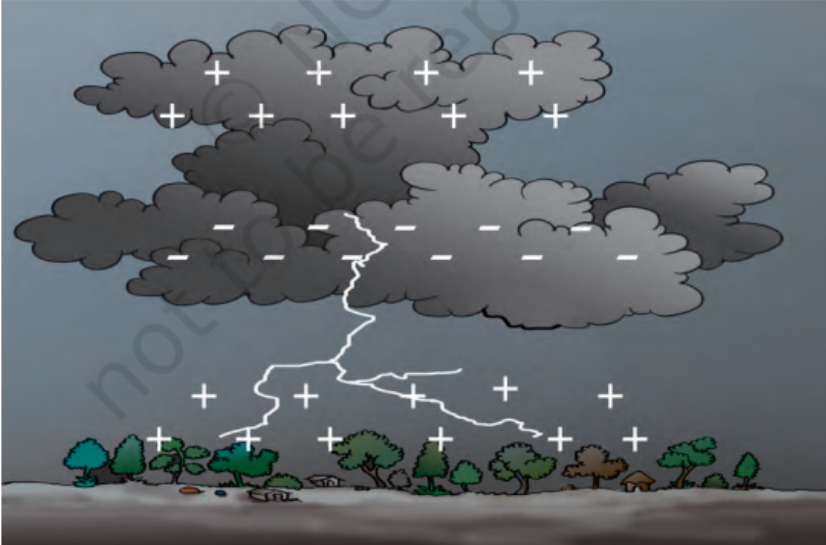
Accumulation of charges causes ________ in the clouds.
-
0%
Rain
-
20%
Earthquake
-
80%
Lightning
-
0%
Storm
Q.13.
Seismometers can record motions in ________ directions.
-
0%
One
-
60%
All
-
40%
Opposite
-
0%
Same
Q.14.
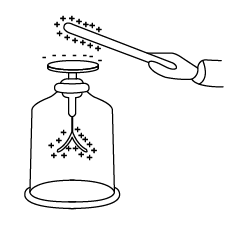
What will be the nature of charge on the metal paper clip of electroscope when a negatively charged body is brought in contact with it?
-
20%
Positive
-
60%
Negative
-
20%
Partially positive
-
0%
None of the above
Q.15.
Lightning is nothing but ________.
-
100%
electric discharge
-
0%
electricity
-
0%
electro - magnetic discharge
-
0%
magnetic effect
Q.16.
Fill in the blank:
-
50%
Accumulation
-
25%
Leakage
-
25%
Conduction
-
0%
Induction
Q.17.
Fill in the blank:
-
25%
Positive
-
0%
Neutral
-
75%
Negative
-
0%
None of the above
Q.18.
Fill in the blank:
-
25%
Negative
-
75%
Positive
-
0%
Neutral
-
0%
No
Q.19.
_________ was the first to discover that lightning is electric discharge.
-
0%
Thomas Alva Edison
-
0%
Nicolas Tesla
-
100%
Benjamin Franklin
-
0%
Isaac Newton
Q.20.
What happens when the end of the paper clip of electroscope is touched by hands?
-
25%
Electric current is produced
-
75%
Foil strips remain as it is
-
0%
Foil strips collapse
-
0%
None of the above
Q.21.
What is the frictional order of the following materials on rubbing:
ebonite, glass rod, wool, plastic
-
25%
Wool, glass rod, ebonite, plastic
-
50%
Glass rod, wool, plastic, ebonite
-
25%
Wool, glass rod, plastic, ebonite
-
0%
Glass rod, wool, ebonite, plastic
Q.22.
What kind of electric charge is acquired on a glass rod when it is rubbed with silk cloth?
-
75%
Positive charge
-
0%
Negative charge
-
25%
Partially positive charge
-
0%
Partially negative charge
Q.23.
When a plastic rod is rubbed with the fur, what charge does the plastic rod get?
-
75%
Positive
-
0%
Negative
-
25%
Neutral
-
0%
None of the above
Q.24.
When two bodies are charged by rubbing they acquire:
-
75%
equal and opposite charge
-
0%
equal and same charge
-
0%
negative charge
-
25%
positive charge
Q.25.
When a charged body is brought near an electroscope:
-
75%
the strips of foils opens up.
-
0%
the strips of foils close.
-
25%
the strips open and close simultaneously.
-
0%
the strips neither open nor close.
Q.26.
An electroscope is used:
-
75%
to detect presence of charge on a body.
-
0%
to determine the nature of charge on a body.
-
0%
to measure the exact amount of charge on a body.
-
25%
for both A and B.
Q.27.
Why does not a steel spoon get charged on rubbing with polythene or woollen cloth?
-
0%
Because steel is a poor conductor.
-
75%
Because steel is a good conductor.
-
25%
Because steel has high density.
-
0%
Because a steel spoon is shiny.
Q.28.
When plastic comb is used to comb dry hair, which type of charge does the comb acquire?
-
25%
Negative
-
50%
Positive
-
25%
Neutral
-
0%
None of the above
Q.29.
The device, which can be used to detect whether an object is charged, is:
-
0%
telescope
-
25%
microscope
-
75%
electroscope
-
0%
none of the above
Q.30.
When a body gains electrons it acquires
-
25%
Positive charge
-
50%
Negative charge
-
0%
Partially positive charge
-
25%
Partially negative charge