MCQ Questions for Class 12 Maths Quiz with Answers Chapter Wise PDF Download
CBSE Multiple Choice Type Questions for 12th Class Maths PDF formatted study resources are available for free download. These Grade 12 Maths CBSE MCQ Mock Test helps you learn & practice the concepts in a fun learning way.
Class 12 Maths MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers
Here are the chapterwise CBSE MCQ Quiz Test Questions for Class 12th Maths in pdf format that helps you access & download so that you can practice online/offline easily.
- Application Of Derivatives Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Questions
- Application Of Integrals Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Questions
- Continuity And Differentiability Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Questions
- Determinants Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Questions
- Differential Equations Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Questions
- Integrals Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Questions
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Questions
- Linear Programming Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Questions
- Matrices Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Questions
- Probability Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Questions
- Relations And Functions Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Questions
- Three Dimensional Geometry Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Questions
- Vector Algebra Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Questions
Application Of Derivatives Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Quiz

Application Of Derivatives Questions and Answers
| Application Of Derivatives Quiz Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| The curve for which the ratio of the length of the segment by any tangent on the $$Y-$$axis to the length of the radius vector is constant $$(K)$$, is | $$(y+\sqrt {x^2 +y^2})x^{k-1}=c$$ |
| The points on the curve $$9 y^{2} = x^{3}$$, where the normal to the curve makes equal intercepts with the axes are ........... | $$\left ( 4, \dfrac{-8}{3} \right )$$ |
| The angle between the tangents at ant point P and the line joining P to the original, where P is a point on the curve in $$(x^{2}+y^{2})=c \tan ^{-1}\dfrac{y}{x},c$$ is a constnt, is | independent of x |
| The slope of the tangent to the curve at a point $$(x,y) $$ on it is proportional to $$(x-2).$$ If the slope of the tangent to the curve at $$(10,-9)$$ on it is $$-3$$. The equation of the curves is . | $$y=\dfrac{-3}{16}(x-2)^2+3$$ |
| The tangent at the point $$(2, -2)$$ to the curve, $$x^2y^2-2x=4(1-y)$$ does not pass through the point. | $$(-2, -7)$$ |
| If the tangent to the conic, $$y - 6 = x^2$$ at (2, 10) touches the circle, $$x^2 + y^2 + 8x - 2y = k$$ (for some fixed k) at a point $$(\alpha, \beta)$$; then $$(\alpha, \beta)$$ is; | $$\displaystyle \left( -\frac{8}{17}, \frac{2}{17} \right)$$ |
| Let b be a nonzero real number. Suppose $$f : R \rightarrow R$$ is a differentiable function such that $$f(0) = 1$$. If the derivative f' of f satisfies the equation $$f'(x) = \dfrac{f(x)}{b^2 + x^2}$$ for all $$x \in R$$, then which of the following statements is/are TRUE? |
$$f\left( x \right) f\left( -x \right) =1$$ for all $$x\in R$$ |
| What is the $$x$$-coordinate of the point on the curve $$f(x) = \sqrt {x}(7x - 6)$$, where the tangent is parallel to $$x$$-axis? | $$\dfrac {2}{7}$$ |
| Consider the following statements in respect of the function $$f(x) = x^{3} - 1, \quad x\epsilon [-1, 1]$$ I. $$f(x)$$ is increasing in $$[-1, 1]$$ II. $$f'(x)$$ has no root in $$(-1, 1)$$. Which of the statements given above is/ are correct? |
Only I |
| If $$\dfrac{x^2}{f(4a)}=\dfrac{y^2}{f(a^2-5)}$$ respresents and ellipse with major axis as y-axis and $$f$$ is a decreasing function, then | $$a \in (-1, 5)$$ |
Application Of Integrals Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Quiz

Application Of Integrals Questions and Answers
| Application Of Integrals Quiz Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Area of the region bounded by the curve $$( y - x ) ^ { 2 } = x ^ { 3 }$$ and the line $$x = 1$$ is | $$\frac {4} {3}$$ |
| Area bounded by the curves $$y=\log _{ e }{ x } \quad$$ and $$y={ \left( \log _{ e }{ x } \right) }^{ 2 }$$ is ? |
$$e-2$$ |
| Area enclosed by the curve $$y = f ( x )$$ defined parametrical as $$x = \frac { 1 - t ^ { 2 } } { 1 + t ^ { 2 } } , y = \frac { 2 t } { 1 + t ^ { 2 } }$$ | $$\pi$$ sq. units |
| The area (in sq units) of the region bounded by the curve $$y=\sqrt { x } $$ and the lines $$y=0,y=x-2$$, is | $$\frac { 10 }{ 3 } $$ |
| The area bounded by the curve y=$${ x }^{ 3 },$$ x-axis and two ordinates x=1 to x=2 equal to | 15/4 sq.unit |
| Area enclosed by the graph of the function $$y=l{ n }^{ 2 }x-1$$ lying in the $${ 4 }^{ th }$$ quadrant is | $$\frac { 4 }{ e } $$ |
| Area bounded by the curves $$y = \sin x ,$$ tangent drawn to it at $$x = 0$$ and the line $$x = \frac { \pi } { 2 }$$ is equal to | $$\frac { \pi ^ { 2 } - 2 } { 2 }$$ sq.units |
| Area bounded by curves $$ x=\sqrt{y-1} $$ and y=x+1 is - |
$$ \frac{1}{6} s q \cdot u n i t $$ |
| The area of the region bounded by the curves $$y = x^2$$ and $$y = |x|$$ is | $$\dfrac{1}{3}$$ |
| The area enclosed by the line y = x + 1, X- axis and the lines x = -3 and x = 3 is | 10 |
Continuity And Differentiability Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Quiz

Continuity And Differentiability Questions and Answers
| Continuity And Differentiability Quiz Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Let $$f\left( x \right)=x\left| x \right| ,g\left( x \right)=sinx$$ and $$h\left( x \right) =\left( gof \right) \left( x \right) .$$ Then | $$h'\left( x \right) $$ is not differentiable at x=0 |
| If $$f(x)=0$$ for $$x<0$$ and $$f(x)$$ is differentiable at $$x=0$$, then for $$x\ge 0, f(x)$$ may be | $$-x^{3/2}$$ |
| $$\frac { d }{ dx } (\sin ^{ -1 }{ \{ \frac { \sqrt { 1+x } +\sqrt { 1-x } }{ 2 } \} } )=$$ | $$\frac { -1 }{ 2\sqrt { 1-{ x }^{ 2 } } } $$ |
| If $$\mathrm{f}(\mathrm{x})$$ is a differentiable function and $$\mathrm{g}(\mathrm{x})$$ is a double differentiable function such that $$|\mathrm{f}(\mathrm{x})|\leq 1$$ and $$\mathrm{f}'(\mathrm{x})=\mathrm{g}(\mathrm{x})$$. If $$\mathrm{f}^{2}(0)+\mathrm{g}^{2}(0)=9$$such that there exists some $$\mathrm{c}\in(-3, 3)$$ such that $$\mathrm{g}(\mathrm{c}).\ \mathrm{g}''(\mathrm{c})<0$$, True or false |
True |
| Let $$f : R \rightarrow R$$ and $$g : R \rightarrow R$$ be functions satisfying $$f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) + f(x)f(y)$$ and $$f(x) = xg(x)$$ for all $$x, y \in R$$. If $$\underset{x \rightarrow 0}{\lim} g(x) = 1$$, then which of the following statements is/are TRUE? | The derivative $${ f }^{ \prime }\left( 0 \right) $$ is equal to $$1$$ |
| For the curve $$x = t^2 - 1, y = t^2 - t$$, tangent is parallel to $$x$$ - axis where, |
$$t=\dfrac{1}{2}$$ |
| Let F(x) = $$\left( f\left( x \right) \right) ^{ 2 }+\left( f\left( x \right) \right) ^{ 2 },F\left( 0 \right) -6$$ where f(x) is a differential function such that $$\left| f\left( x \right) \right| \le 1\forall x\notin \left[ -1,1 \right] $$ then choose the correct statement (s) | For some $$c\in \left( -1,1 \right) $$, $$F'\left( c \right) \ge 6,F"\left( c \right) \le 0$$ |
| If $$f(x)={ sin }^{ -1 }\left[ \dfrac { 2x }{ 1+{ x }^{ 2 } } \right] $$,then $$f(x)$$ is differentiable on | R-{-1,1} |
| $$\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}(\tan ^{-1}x)$$ | $$ \displaystyle \frac{1}{1+x^{2}}.$$ |
| If $$\displaystyle x+y=x^{y}$$ then $$\displaystyle \frac{dy}{dx}\ equals-$$ | $$\displaystyle \frac{yx^{y-1}-1}{1-x^{y}\log x}$$ |
Determinants Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Quiz

Determinants Questions and Answers
| Determinants Quiz Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| If A is a singular matrix, then adj A is | singular |
| If $$A = \left( \begin{array} { l l } { 1 } & { 2 } \\ { 3 } & { 5 } \end{array} \right), $$ then the value of the determinant $$\left| A ^ { 2009 } - 5 A ^ { 2008 } \right|$$ is | $$- 6$$ |
| If $$A=\begin{bmatrix} -4 & -1 \\ 3 & 1 \end{bmatrix}$$ then the determinant of the matrix $$\left( {A}^{2016}-2{A}^{2015}-{A}^{2014} \right) $$ is | $$-2016$$ |
| If $$A=A=\left[ \begin{matrix} a & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & a & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & a \end{matrix} \right]$$,then $$\left| A \right| \left| AdjA \right|$$ is equal to | $${a}^{9}$$ |
| If $$A$$ is a square matrix $$(adj \,A)' - (adj \,A')$$ | $$2A$$ |
| If adj B = A, |P| = |Q| = 1, then adj $$\left( { Q }^{ -1 }{ BP }^{ -1 } \right) $$ is | PAQ |
| There are $$12$$ points in a plane. The number of the straight lines joining any two of them when $$3$$ of them are collinear is. | $$64$$ |
| If $$A$$ is singular matrix, then $$A.(adj\,A)$$ is | $$singular$$ |
| If $$A$$ is $$4\times 4$$ matrix and if $$\left| \left| A \right| adj\left( \left| A \right| A \right) \right| ={ \left| A \right| }^{ n }$$, then $$n$$ is | $$11$$ |
| If $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 5a & -b \\ 3 & 2 \end{bmatrix}$$ and $$A(adj\, A)=A{A}^{T}$$ then $$5a+3b$$ is equal to | $$5$$ |
Differential Equations Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Quiz

Differential Equations Questions and Answers
| Differential Equations Quiz Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| The solution of $$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=2^{x-y}$$ is: | $$2^{x}-2^{y}=c$$ |
| The solution of $$(x^{2}+x)\frac{dy}{dx}=1+2x$$ is: | $$e^{y}=c(x^{2}+x)$$ |
| $$\displaystyle e^{x-y}dx+e^{^{y-x}}dy=0$$ Solve the differential equations. |
$$\displaystyle e^{2x}+e^{2y}=-k$$ |
| The solution to the differential equation $$y\ln y \, +\, xy'\, =\, 0\,$$ where$$\, y(1)\, =\, e$$, is: | $$x(\ln y)\, =\, 1$$ |
| $$x^{\frac{b-c}{bc}} . x^{\frac{c-a}{ca}} . x^{\frac{a-b}{ac}}=$$ |
1 |
| The solution of $$x^{2} \cfrac{dy}{dx}=2$$ is |
$$y=-\cfrac{2}{x}+c$$ |
| Which of the following differential equation is linear ? | $$(1+x)\dfrac{dy}{dx}-xy=1$$ |
| Degree of $$\dfrac{d^{3}y}{dx^{3}}+2\left ( \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right )^{4}+\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\cos x $$ is | $$1$$ |
| The solution of $$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=e^{logx}$$ is: | $$2y=x^{2}+c$$ |
| Check whether the function is homogenous or not. If yes then find the degree of the function $$g(x)=4-x^2$$. |
Not homogenous |
Integrals Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Quiz

Integrals Questions and Answers
| Integrals Quiz Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| $$\int { { e }^{ x^{ 3 } }+{ x }^{ 2-1 }(3{ x }^{ 4 }+{ 2x }^{ 3 }+{ 2x }^{ 2 }\quad x=h(x)+c } $$ then the value of $$h(1)h(-1)$$. | 1 |
| $$\displaystyle \int \frac { 1 - x ^ { 2 } } { \left( 1 + x ^ { 2 } \right) \sqrt { 1 + x ^ { 4 } } } d x$$ is equal to |
$$\frac { 1 } { \sqrt { 2 } } \sin ^ { - 1 } \left\{ \frac { \sqrt { 2 } x } { x ^ { 2 } + 1 } \right\} + c$$ |
| Let $$ 1 _ { n } = \int _ { 0 } ^ { \frac { 1 } { 2 } } \frac { 1 } { \sqrt { 1 - x ^ { n } } } d x $$ where $$ n > 2 , $$ then |
$$ I _ { n } < \frac { \pi } { 6 } $$ |
| If $${ I }_{ m }=\overset { e }{ \underset { 1 }{ \int } } (lnx)^{ m }dx,$$ where $$m\epsilon N,$$then $${ I }_{ 10 }+10{ I }_{ 9 }$$ is equal to- | e |
| If for every integer n, $$\int _{ n }^{ n+1 }{ f(x)dx={ n }^{ 2 } } $$, then the value of $$\int _{ -2 }^{ 4 }{ f(x)dx } $$ is - | 16 |
| $$\int _{ 0 }^{ 4036 }{ \dfrac { { 2 }^{ x } }{ { 2 }^{ x }+{ 1 }^{ 4036-x } } } dx=............$$ | 4035 |
| If $${ I }_{ 1 }=\int _{ x }^{ 1 }{ \cfrac { 1 }{ 1+{ t }^{ 2 } } } dt$$ and $${ I }_{ 2 }=\int _{ 1 }^{ 1/x }{ \cfrac { 1 }{ 1+{ t }^{ 2 } } } dt$$ for x > 0, then | $${ I }_{ 1 }={ I }_{ 2 }$$ |
| $$\frac { 1 }{ \pi } \int _{ -2 }^{ 2 }{ \frac { 1 }{ 4+{ x }^{ 2 } } dx= } $$ | $$\frac { 1 }{ 4 } $$ |
| $$\displaystyle \int_{-1}^{1}\dfrac{x^4}{1+e^{x^7}}dx$$ is | $$1/5$$ |
| Evaluate: $$\int { \sqrt { \dfrac { x }{ 4-{ x }^{ 3 } } } } dx$$ | $$2\sin ^{ -1 }{ \left( \dfrac { { x }^{ \dfrac { 3 }{ 2 } } }{ 2 } \right) +c } $$ |
Inverse Trigonometric Functions Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Quiz
Inverse Trigonometric Functions Questions and Answers
| Inverse Trigonometric Functions Quiz Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| $$if\quad x>0\quad then\quad { tanh }^{ -1 }\left( \frac { { x }^{ 2 }-1 }{ { x }^{ 2 }+1 } \right) $$ | $${ log }_{ e }x$$ |
| If $$\cos^{-1}x-\cos^{-1}(\dfrac {y}{2})=\alpha$$ $$ax^{2}-4xy\cos \alpha +y^{2}=$$ | $$4\sin^{2}\alpha$$ |
| $${\cot}^{-1}\left(\sqrt{\cos\alpha}\right) -{\tan}^{-1}\left(\sqrt{\cos\alpha}\right) =x$$, then $$\sin x$$ is equal to | $$\displaystyle {\tan}^{2}\frac{\alpha}{2}$$ |
| $${ cos }^{ -1 }(\frac { x }{ 3 } )+{ cos }^{ -1 }(\frac { y }{ 2 } )=(\frac { \theta }{ 2 } )$$ , then the value of $${ 4x }^{ 2 }$$-12xy cos$$(\frac { \theta }{ 2 } )$$+$${ 9y }^{ 2 }$$ is equal to | $$18(1-cos\theta )$$ |
| $$\cos ^{ -1 }{ \left\{ \dfrac { 1 }{ 2 } { x }^{ 2 }+\sqrt { { 1-x }^{ 2 } } .\sqrt { 1\dfrac { { x }^{ 2 } }{ 4 } } \right\} } =\cos ^{ -1 }{ \dfrac { x }{ 2 } } -\cos ^{ -1 }{ x } $$ holds for | $$0\le x\le 1$$ |
| $$tan^{-1}y=tan^{-1}x+tan^{-1}(\frac{2x}{1-x^{2}})$$ where $$|x| < \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}$$. Then a value of y is: | $$\dfrac{3x-x^{3}}{1-3x^{2}}$$ |
| $$4\tan ^{ -1 }{ \frac { 1 }{ 5 } } -\tan ^{ -1 }{ \frac { 1 }{ 70 } } +\tan ^{ -1 }{ \frac { 1 }{ 99 } } =$$ | $$\pi $$ |
| $$\cos ^{ -1 }{ \left( \cos { \dfrac { 7\pi }{ 6 } } \right) } $$ is equal to | $$\dfrac {5\pi}{6}$$ |
| The value of $$\sin ^{ -1 }{ (\cos { (\cos ^{ -1 }{ (\cos { x } ) } +\sin ^{ -1 }{ (\sin { x } ) } ) } ) } ,\quad where\quad x\in (\frac { \pi }{ 2 } ,\pi )$$, is equal to | $$-\frac { \pi }{ 2 } $$ |
| The value of $$\sin^{-1}(\sin 3)+\cos^{-1}(\cos 7)-\tan^{-1}(\tan 5)$$ is | $$\pi-1$$ |
Linear Programming Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Quiz



Linear Programming Questions and Answers
| Linear Programming Quiz Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Solution of LPP to minimize z = 2x + 3y, such that $$x \geq 0, y \geq 0, 1 \leq x + 2y \leq 10 $$ is | $$x = 0, y = \dfrac{1}{2}$$ |
| The point which provides the solution to the linear programming problem : Max P= 2x+3y subject to constraints :$$x\geq 0, y\geq 0,2x+2y\leq 9,2x+y\leq 7,x+2y\leq 8,$$ is | (1,3.5) |
| Feasible region is the set of points which satisfy | all the given constraints |
| If the corner points of the feasible solution are (0, 10), (2, 2) and (4, 0), then the point of minimum z = 3x + 2y is | (2, 2) |
| Minimise $$Z=\sum _{ j=1 }^{ n }{ \sum _{ i=1 }^{ m }{ { c }_{ ij }.{ x }_{ ij } } } $$ Subject to $$\sum _{ i=1 }^{ m }{ { x }_{ ij } } ={ b }_{ j },j=1,2,......n$$ $$\sum _{ j=1 }^{ n }{ { x }_{ ij } } ={ b }_{ j },j=1,2,......,m$$ is a LPP with number of constraints |
$$m+n$$ |
| The solution of the set of constraints of a linear programming problem is a convex (open or closed) is called ______ region. | feasible |
| Solving an integer programming problem by rounding off answers obtained by solving it as a linear programming problem (using simplex), we find that | The value of the objective function for a maximization problem will likely be less than that for the simplex solution. |
| If a = b then ax = ........... | bx |
| The bar graph shows the grades obtained by a group of pupils in a test. If grade C is the passing mark, how many pupils passed the test? 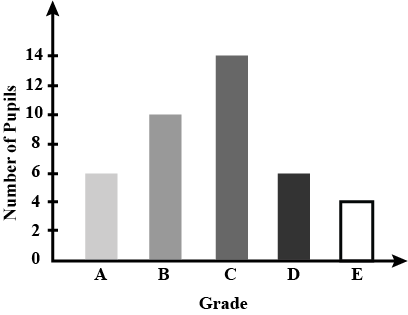 |
30 |
| An iso-profit line represents | An infinite number of solutions all of which yield the same profit |
Matrices Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Quiz


Matrices Questions and Answers
| Matrices Quiz Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| If $$\displaystyle A=\left[ \begin{matrix} 3 & 1 \\ -1 & 2 \end{matrix} \right] $$ and $$\displaystyle I=\left[ \begin{matrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{matrix} \right] $$, then the correct statement is: | $$\displaystyle { A }^{ 2 }-5A+7I=O$$ |
| If AB = AC then | B need not be equal to C |
| If $$\mathrm{A}^{2}=\mathrm{A},\ \mathrm{B}^{2}=\mathrm{B},\ \mathrm{A}\mathrm{B}=\mathrm{B}\mathrm{A}=O$$ (Null Matrix), then $$(\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{B})^{2}=$$ |
$$\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{B}$$ |
| $$I$$ $$A=\left[\begin{array}{ll} 0 & 1\\ 1 & 0 \end{array}\right]$$, $$A^{4}=$$ ($$I$$ is an identity matrix.) |
$$I$$ |
| lf $$\mathrm{A}= \left[\begin{array}{lll} o & c & -b\\ -c & o & a\\ b & -a & o \end{array}\right]\mathrm{a}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{d}$$ $$ \mathrm{B}=\left[\begin{array}{lll} a^{2} & ab & ac\\ ab & b^{2} & bc\\ ac & bc & c^{2} \end{array}\right],$$ then $$\mathrm{A}\mathrm{B}=$$ |
$$\mathrm{O}$$ |
| lIf $$\mathrm{A} =\left[\begin{array}{ll} a & 0\\ a & 0 \end{array}\right],\ \mathrm{B}=\left[\begin{array}{ll} 0 & 0\\ b & b \end{array}\right],$$ then $$\mathrm{A}\mathrm{B}=$$ |
$$O$$ |
| If $$A=\left[\begin{array}{lll} 1 & -2 & 3\\ -4 & 2 & 5 \end{array}\right]$$ and $$B=\left[\begin{array}{ll} 2 & 3\\ 4 & 5\\ 2 & 1 \end{array}\right],$$ then |
$$\mathrm{A}\mathrm{B},\ \mathrm{B}\mathrm{A}$$ exist and are not equal |
| $$A=\left[\begin{array}{lll} 0 & 1 & -2\\1 & 0 & 3\\2 &-3 & 0 \end{array}\right]$$ then $$\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{A}^{\mathrm{T}}=$$ |
$$\left[\begin{array}{lll} 0 & 2 & 0\\ 2 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0 \end{array}\right]$$ |
| $$\left[\begin{array}{ll} x & 0\\ 0 & y \end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{ll} a & b\\ c & d \end{array}\right]=$$ |
$$\left[\begin{array}{ll} ax & b_{X}\\ yc & dy \end{array}\right]$$ |
| If $$\mathrm{A}=\left[\begin{array}{lll} 1 & -3 & -4\\ -1 & 3 & 4\\ 1 & -3 & -4 \end{array}\right]$$, then $$\mathrm{A}^{2}=$$ |
Null matrix |
Probability Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Quiz


Probability Questions and Answers
| Probability Quiz Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Three number are chosen at random without replacement from {1,2,3,...8}. The probability that their minimum is 3, given that their maximum is 6 is | $$\frac{3}{28}$$ |
| Difference between sample space and subset of sample space is considered as | complementary events. |
| If A and B are two events in a sample space S such that $$P\left ( A \right )\neq 0$$, then $$P\left ( \frac{B}{A} \right )= $$ | $$\frac{P\left ( A\cap B \right )}{P\left ( A \right )}$$ |
| Let A and E be any two events with positive probabilities : Statement - 1 : $$P \left (\displaystyle \frac{E}{A} \right) \geq P \left (\displaystyle \frac{A}{E} \right ) P(E)$$ Statement - 2 : $$P \left (\displaystyle \frac{A}{E}\right ) \geq P(A\cap E)$$ |
Both the statement are true |
| If $$\mathrm{C}$$ and $$\mathrm{D}$$ are two events such that $$\mathrm{C}\subset \mathrm{D}$$ and $$\mathrm{P}(\mathrm{D})\neq 0$$, then the correct statement among the following is |
$$P\left(\dfrac{C}{D}\right) \geq \mathrm{P}(\mathrm{C})$$ |
| If $$A$$ and $$B$$ are any two events such that $$P(A) = \dfrac {2}{5}$$ and $$P(A\cap B) = \dfrac {3}{20}$$, then the conditional probability, $$P(A|(A'\cup B'))$$, where A' denotes the complement of $$A$$, is equal to: | $$\dfrac {5}{17}$$ |
| It is given that the events A and $$B$$ are such that $$P(A)=\displaystyle \frac{1}{4},\ P(A|B)=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}$$ and $$P(B|A)=\displaystyle \frac{2}{3}$$. Then $$P(B)$$ is |
$$\displaystyle \frac{1}{3}$$ |
| Assertion is False, Reason is True | |
| One of the two boxes, box $$I$$ and box $$II$$, was selected at random and balls are drawn randomly out of this box. The ball was found to be red.If the probability that this red ball was drawn from box $$II$$ is $$\dfrac{1}{3}$$, then the correct option options with the possible values of $$n_1,n_2,n_3$$ and $$n_4$$ is (are) |
$$n_1 = 3, n_2=6,n_3=10,n_4=50$$ |
A fair die is rolled repeatedly until a six is obtained. Let X denote the number of rolls required. The conditional probability that $$X \geq 6$$ given $$X > 3$$ equals |
$$\displaystyle \frac{25}{36}$$ |
Relations And Functions Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Quiz


Relations And Functions Questions and Answers
| Relations And Functions Quiz Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| If $$f:N\rightarrow N,f(x)=x+3$$, then $$\quad { f }^{ -1 }(x)=.....$$ | does not exist |
| If $$f(x)=8x^3$$ and $$g(x)=x^{1/3}$$ then $$(g o f)(x)=?$$ | $$2x$$ |
| Which of the following functions are one-one? |
$$h:R\rightarrow R$$ given by $$ h(x)={ x }^{ 3 }+4$$ for all $$\quad x\in R$$ |
| A mapping function $$f:X\rightarrow Y$$ is one-one, if |
$$f({ x }_{ 1 })=f({ x }_{ 2 })\Rightarrow { x }_{ 1 }={ x }_{ 2 }$$ for all $${ x }_{ 1 },{ x }_{ 2 }\in X$$ |
| Let $$R$$ be a relation from a set $$A$$ to a set $$B$$,then |
$$\displaystyle R\subseteq A\times B$$ |
| Number of one-one functions from A to B where $$n(A)=4, n(B)=5$$. | $$120$$ |
| Find the value of $$\displaystyle \left( g\circ f \right) \left( 6 \right) $$ if $$\displaystyle g\left( x \right) ={ x }^{ 2 }+\frac { 5 }{ 2 } $$ and $$\displaystyle f\left( x \right) =\frac { x }{ 4 } -1$$. |
2.75 |
| The first component of all ordered pairs is called | Domain |
| Find the correct expression for $$\displaystyle f\left( g\left( x \right) \right) $$ given that $$\displaystyle f\left( x \right) =4x+1$$ and $$\displaystyle g\left( x \right) ={ x }^{ 2 }-2$$ | $$\displaystyle 4{ x }^{ 2 }-7$$ |
| The second component of all ordered pairs of a relation is | Range |
Three Dimensional Geometry Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Quiz

Three Dimensional Geometry Questions and Answers
| Three Dimensional Geometry Quiz Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| The equation of a plane passing through the points $$A(a, 0, 0), B(0, b, 0)$$ and $$C(0, 0, c)$$ is given by? | $$\dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b}+\dfrac{z}{c}=1$$ |
| The direction consines of the line drawn from $$P\left ( -5,3,1 \right )\,to\,Q\left ( 1,5,-2 \right )$$ is | $$\left ( \dfrac {6}{7},\dfrac {2}{7},-\dfrac {3}{7} \right )$$ |
| If a straight line makes an angle of $$60^\circ$$ with each of the X and Y axes, the angle which it makes with the Z axis is | $$\dfrac {3\pi}{4}$$ |
| The points $$(p+1, 1), (2p+1, 3)$$ and $$(2p+2,2p)$$ are collinear if | $$p=-\dfrac{1}{2}$$ |
| In a plane there are 10 points, no three are in same straight line except 4 points which are collinear, then the number of straight lines are | 45 |
| The st lines whose direction cosines satisfy: $$al+bm+cn=0$$ and $$fmn+gnl+hlm=0$$ are perpendicular if: |
$$\dfrac {f}{a}+\dfrac {g}{b}+\dfrac {h}{c}=0$$ |
| The equation of the plane which passes through the x-axis and perpendicular to the line $$\dfrac {(x - 1)}{cos\theta} = \dfrac {(y + 2)}{sin\theta} = \dfrac {(z - 3)}{0}$$ is | $$x\, cos\theta + y\,sin\theta = 0$$ |
| If $$l_1$$, $$m_1$$, $$n_1$$ and $$l_2$$, $$m_2$$, $$n_2$$ are the direction cosines of two perpendicular lines, then the direction cosine of the line which is perpendicular to both the lines , will be | ($$m_1$$$$n_2$$ - $$m_2$$$$n_1$$), ($$n_1$$$$l_2$$ - $$n_2$$$$l_1$$), ($$l_1$$$$m_2$$ - $$l_2$$$$m_1$$) |
| The point collinder with (1,-2,-3) and (2,0,0) amoung the following is | (0, -4, -6) |
| A line with direction ratio 2,7,-5 is drawn to intersect the lines $$\frac { x-y }{ 3 } =\frac { y-7 }{ -1 } =\frac { z+2 }{ 1 } $$ and $$\frac { x+3 }{ -3 } =\frac { y-3 }{ 2 } =\frac { z-6 }{ 4 } $$ at P and Q respectively, then length of PQ is- | $$\sqrt { 78 } $$ |
Vector Algebra Class 12 Engineering Maths MCQ Quiz


Vector Algebra Questions and Answers
| Vector Algebra Quiz Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| The position vector of A is $$2\vec { i } +3\vec { j } +4\vec { k } $$$$\vec { AB } =5\vec { i } +7\vec { j } +6\vec { k } $$, then the position vector of B is | $$-7\vec { i } -10\vec { j } -10\vec { k } $$ |
| Line passing through $$ (3,4,5) $$ and $$ (4,5,6) $$ has direction ratios $$ \ldots $$ | $$ 1,1,1 $$ |
| In a parallelogram ABCD, $$|\overrightarrow{AB}| = a, |\overrightarrow{AD}| = b$$ and $$|\overrightarrow{AC}| = c$$, then $$\overrightarrow{DB}.\overrightarrow{AB}$$ has the value | $$\displaystyle \frac{1}{2} (a^2 + b^2 - c^2)$$ |
| If $$|\overrightarrow{C}|^2=60$$ and $$\overrightarrow{C} \times (\widehat{i}+2\widehat{j}+5\widehat{k})=\overrightarrow{0}$$, then a value of $$\overrightarrow{C}\cdot (-7 \widehat{i}+2\widehat{j}+3\widehat{k})$$ is : |
$$12\sqrt{2}$$ |
| If $$\vec{a} \times \vec{b} = \vec{b} \times \vec{a}$$, then | $$\mathrm{\vec{a}}=k\mathrm{\vec{b}}$$ |
| Let $$P,\ Q,\ R$$ and $$S$$ be the points on the plane with position vectors $$-2\hat{i}-\hat{j},\ 4\hat{i},\ 3\hat{i}+3\hat{j}$$ and $$-3\hat{i}+2\hat{j}$$ respectively. The quadrilateral $$PQRS$$ must be a |
parallelogram, which is neither a rhombus nor a rectangle |
| Statement -$$1$$ is True, Statement -$$2$$ is False | |
| $$ABCD$$ is a parallelogram and $$AC, BD$$ be its diagonals Then $$ \vec{AC} +\vec{BD}$$ is |
$$2\vec{BC} $$ |
| The triangle $$ABC$$ is defined by the vertices $$A= (0,7,10)$$ , $$B=(-1,6,6)$$ and $$C=(-4,9,6)$$. Let $$D$$ be the foot of the attitude from $$B$$ to the side $$AC$$ then $$BD$$ is |
$$-\overline{i}+2\overline{j}+2\overline{k}$$ |
| The point $$C=(\dfrac{12}{5}, \dfrac{-1}{5},\dfrac{4}{5})$$ divides the line segment $$AB$$ in the ratio $$3:2$$. If $$B=(2,-1,2)$$ then $$A$$ is |
$$(3, 1,-1)$$ |
Maths MCQ Questions for Class 12 - Practice Test with Solutions
Do you want to overcome your drawbacks while attempting the quizzes or MCQ tests like time consumption, approaching questions, etc.? Take the advantage of practicing with MCQExams.com MCQ Questions for Standard 12 Maths Test. As it is a time-based approach and also provides answers to all questions.
One should practice the MCQs in this way for a better assessment of their preparation level. All chapters CBSE Class 12 Maths MCQ Quiz Questions with Solutions PDF free download links are available for easy access & quick reference.
How to Use MCQExams.com Chapterwise 12th Maths MCQ Interactive Quiz?
Guys do you love to share your practice hacks and tips with your friends? If yes, then our 12tth standard CBSE Maths MCQ interactive quiz help you do the same. Excited to know the process then jump into the below steps right away:
- Go with the respective chapter class 12 Maths MCQ quiz link from the above
- Now, you will find the MCQ quiz boxes for the Application Of Derivatives chapter along with the interactive quiz windows.
- Click on the CBSE 12th Class Application Of Derivatives MCQ Interactive Quiz and it will redirect you to another window where it displays the questions with options in stories format.
- Answer the question one after another and learn the answers right away this helps you to do a quick assessment of your knowledge.
- You can also share this cool MCQ Interactive Quiz Questions of Plus Two Maths topicwise with your friends by just tapping on the send arrow located at the top left corner of the story.
- After clicking the button, you can opt for the copy link option and easily paste the link on your friend's chat or else in your whatsapp story too. Isn’t it cool!!
- Keep passing this interesting approach of practicing Plus Two CBSE Maths Application Of Derivatives MCQ Questions to your co-students and help them in attempting the entrance exams like JEE & NEET.