Q.1.
One of the types of connection is
-
0%
single point
-
0%
two point
-
0%
three point
-
0%
multipoint
Q.2.
A star topology does not allow direct traffic between devices.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.3.
Which of the following is not the requirement level?
-
0%
Required
-
0%
Accepted
-
0%
Elective
-
0%
Limited use
Q.4.
IAB stands for
-
0%
International Architecture Bureau
-
0%
Internet Architecture Bureau
-
0%
International Architecture Board
-
0%
Internet Architecture Board
Q.5.
IETF is the technical advisor to the ISOC.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.6.
What is a server in a computer network?
-
0%
The name for a large number of computer cables
-
0%
Someone who manages the network
-
0%
A powerful computer that provides a service, such as centralised file storage
Q.7.
A computer network is ___ connected together.
-
0%
One computer
-
0%
Two or more
-
0%
Three or more
-
0%
Four or more
Q.8.
What is an advantage of a LAN?
-
0%
You can save money by sharing peripherals like printers.
-
0%
It is limited to a small area.
-
0%
Can cover near infinite geographical distance.
-
0%
Expensive to setup.
Q.9.
is a needed requirement to make an internet connection?
-
0%
Pencil
-
0%
Table
-
0%
Modem
-
0%
Camera
Q.10.
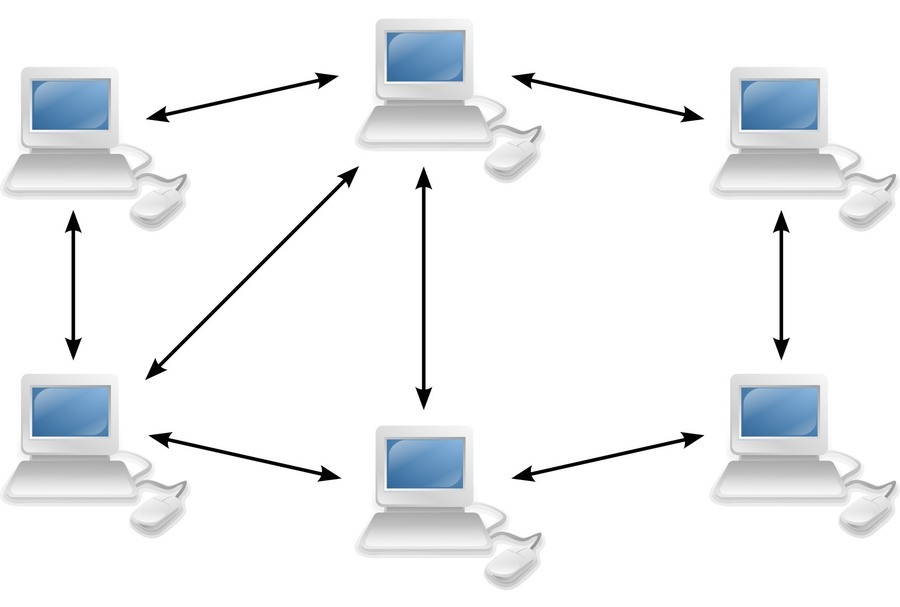
This is a client-server network?

-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.11.
What one is true, about a peer to peer network?
-
0%
Shares a local server
-
0%
Files not stored on a local server
Q.12.
WAP stands for?
-
0%
Wireless Accessible Points
-
0%
Wireless Access Point
-
0%
Wired Able Place
-
0%
Wired Able Point
Q.13.
What is needed if the computer does not have a built-in network chip on its motherboard
-
0%
NIC
-
0%
WAP
-
0%
Router
-
0%
Switch
Q.14.
What does NIC stand for?
-
0%
Network Interface Career
-
0%
Network Interface Card
-
0%
Network Intermittent Card
-
0%
New Interface Card
Q.15.
what is the task of the DNS?
-
0%
translate a domain name into the correct IP address
-
0%
translate an IP address into a domain name
-
0%
Gives names to websites which aren't named
-
0%
Leaves websites alone
Q.16.
Which of these is NOT an advantage of networks?
-
0%
Sharing peripheral devices such as printers and scanners
-
0%
Possible to communicate globally
-
0%
Can protect against viruses
-
0%
PCs can be backed up and updated by one central PC
Q.17.
P2P stands for...
-
0%
Peer-to-Peer
-
0%
Peer-to-Peripheral
-
0%
Peripheral-to-Peer
Q.18.
Data is stored where, in a client-server network?
-
0%
Centrally
-
0%
On each PC
-
0%
In the switch
-
0%
In the hub
Q.19.
A MAC address is
-
0%
A unique identifier for all devices on a network
-
0%
A set of numbers that identify a computer on a network
-
0%
A unique identifier for computers on a network
Q.20.
Which device filters data packets and only sends to those that require the data?
-
0%
Router
-
0%
Switch
-
0%
Hub
-
0%
WAP
Q.21.
What is a client?
-
0%
Powerful Computers that provide services to other computers
-
0%
Computers that ask for the services a server provides
-
0%
Physical connection between devices
-
0%
A circuitboard with the components to send/receive data
Q.22.
What is a server?
-
0%
Powerful Computers that provide services to other computers
-
0%
Computers that ask for the services a server provides
-
0%
Physical connection between devices
-
0%
A circuitboard with the components to send/receive data
Q.23.
Connecting to a network is good because...
-
0%
You can share an internet connection
-
0%
You can share files and folders
-
0%
You can share printers
-
0%
All of these!
Q.24.
Which of these is a disadvantage of the ring topology?
-
0%
If one cable is disabled the whole network can crash
-
0%
If the central hub crashes the whole network breaks
-
0%
Only four computers can be attached to the ring
-
0%
Everyone has to sit facing each other
Q.25.
What is a communication media?
-
0%
Powerful Computers that provide services to other computers
-
0%
Computers that ask for the services a server provides
-
0%
Physical connection between devices
-
0%
A circuitboard with the components to send/receive data
Q.26.
What is a network adapter?
-
0%
Powerful Computers that provide services to other computers
-
0%
Computers that ask for the services a server provides
-
0%
Physical connection between devices
-
0%
A circuitboard with the components to send/receive data
Q.27.
What is a resource?
-
0%
Any peripheral device
-
0%
A person that uses a client
-
0%
Rules for networks and communications
-
0%
A circuitboard with the components to send/receive data
Q.28.
What is a user?
-
0%
Any peripheral device
-
0%
A person that uses a client
-
0%
Rules for networks and communications
-
0%
A circuitboard with the components to send/receive data
Q.29.
What is a protocol?
-
0%
Any peripheral device
-
0%
A person that uses a client
-
0%
Rules for networks and communications
-
0%
A circuitboard with the components to send/receive data
Q.30.
What is TCP used for?
-
0%
To send information across the internet in packets
-
0%
To ensure that information is sent to the correct computer
-
0%
To send mail across the internet
-
0%
To transmit webpages across the internet
Q.31.
What is IP used for?
-
0%
To send information across the internet in packets
-
0%
To ensure that information is sent to the correct computer
-
0%
To send mail across the internet
-
0%
To transmit webpages across the internet
Q.32.
What are HTTP[S] used for?
-
0%
To send information across the internet in packets
-
0%
To ensure that information is sent to the correct computer
-
0%
To send mail across the internet
-
0%
To transmit webpages across the internet
Q.33.
What is FTP used for?
-
0%
To send information across the internet in packets
-
0%
To ensure that information is sent to the correct computer
-
0%
To send mail across the internet
-
0%
To copy files from one computer to another
Q.34.
Which of these are mail protocols?
-
0%
SMTP and POP
-
0%
TCP and FTP
-
0%
FTP and SMTP
-
0%
POP and IP
Q.35.
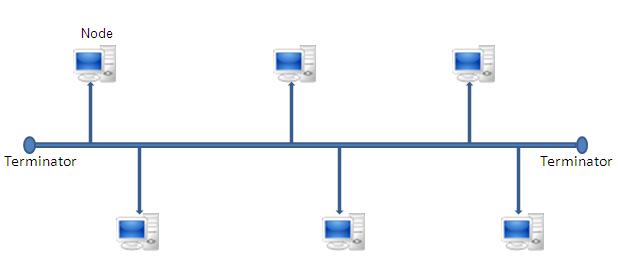
Which topology is this?

-
0%
Bus
-
0%
Star
-
0%
Ring
-
0%
Wave
Q.36.
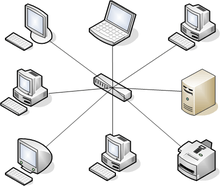
Which topology is this?

-
0%
Bus
-
0%
Star
-
0%
Ring
-
0%
Wave
Q.37.
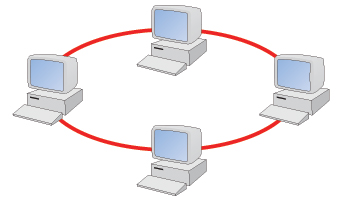
Which topology is this?

-
0%
Bus
-
0%
Star
-
0%
Ring
-
0%
Wave
Q.38.
Which of these is an advantage of the bus topology?
-
0%
It is easy and cheap to set up
-
0%
It is useful for large companies
-
0%
You can pick people up
-
0%
Anyone can join
Q.39.
Which of these is an advantage of the star topology?
-
0%
Devices do not rely on each other to function
-
0%
It looks nice
-
0%
A central server is not needed
-
0%
Only one cable is needed to connect everything together
Q.40.
What is different about WiFi and MiFi?
-
0%
One begins with W and the other with M
-
0%
MiFi strictly uses wireless networks, WiFi does not?
-
0%
WiFi is only used at home
-
0%
No-one uses MiFi
Q.41.
What does a computer network allow computers to share?
-
0%
Electricity
-
0%
Resources
-
0%
Mice
Q.42.
To log onto a network, what do you usually need?
-
0%
A user ID and password
-
0%
A fast connection
-
0%
Specialist software
Q.43.
Which of the following statements about a network is FALSE?
-
0%
Resources such as printers can be shared
-
0%
Viruses can spread to other computers throughout a computer network
-
0%
Files cannot be shared between users
Q.44.
Which of these statements is TRUE about a LAN?
-
0%
A LAN connects computers in a small area such as an office
-
0%
A modem is needed to connect a computer to a LAN
-
0%
A LAN consists of only one computer
Q.45.
Which of the following networks is LEAST likely to be a WAN?
-
0%
The Internet
-
0%
A school network
-
0%
A network of bank cash dispensers
Q.46.
Which type of network needs 'terminators' to function correctly?
-
0%
Bus
-
0%
Ring
-
0%
Star
Q.47.
Which type of network needs a 'hub' or 'switch'?
-
0%
Star
-
0%
Ring
-
0%
Bus
Q.48.
What is a data collision?
-
0%
When two devices on a network transmit data at the same time
-
0%
When one device on a network transmits data
-
0%
When two devices on a network transmit at separate times
Q.49.
Which of the following is not a network?
-
0%
LAN
-
0%
Stand-alone computer
-
0%
Internet
-
0%
Intranet
Q.50.
A LAN does not consist of a collection of computers in a
-
0%
Building
-
0%
Department
-
0%
School
-
0%
Country
Q.51.
LAN means
-
0%
Local Area Network
-
0%
Local Access Network
-
0%
Laser Assisted Network
-
0%
Logical Area Network
Q.52.
Networks allow computers to share
-
0%
Electricity
-
0%
Cables
-
0%
Resources
-
0%
Mice
Q.53.
A LAN is a worldwide networks of networks
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.54.
WAN means
-
0%
Wireless Area Network
-
0%
Wide Access Network
-
0%
Wide Area Network
-
0%
Worldwide Access Network
Q.55.
MAN means
-
0%
Metropolis Area Network
-
0%
Micro Access Network
-
0%
Mid-sized Area Network
-
0%
Metropolitan Area Network
Q.56.
Computers are prone to tampering and corruption when part of a LAN
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.57.
A network consists of only one computer
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.58.
The internet is an example of a WAN
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.59.
Computers experience less viruses when part of a network
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.60.
A MAN usually has slow connection speeds
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.61.
The most popular LAN cable is
-
0%
Fibre optic cable
-
0%
Twisted pair
-
0%
Coaxial
-
0%
Infrared
Q.62.
Which of these networks is LEAST likely to be a WAN
-
0%
The internet
-
0%
A school network
-
0%
A network of bank cash dispensers
Q.63.
UWI has computers being used in Barbados, Jamaica and Trinidad & Tobago. The network used is
-
0%
LAN
-
0%
MAN
-
0%
WAN
Q.64.
Life Insurance Company occupies several floors at Baobab Towers. The network used is
-
0%
LAN
-
0%
MAN
-
0%
WAN
Q.65.
A LAN usually requires a login to access the network
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.66.
A WAN only uses satellites to connect computers
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.67.
Which network covers a small geographical area?
-
0%
LAN
-
0%
WAN
Q.68.
The internet is an example of _________________
-
0%
LAN
-
0%
WAN
Q.69.
Star Topology is a slow topology
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.70.
A computer that stores and manages files for multiple users on a network is called as a ______________________
-
0%
File Server
-
0%
Web Server
Q.71.
Ring Topology uses a device known as HUB
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.72.
The Bus topology requires less cabling
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.73.
Which piece of equipment allows your home to connect to the internet?
-
0%
Router
-
0%
Switch
-
0%
Tablet
-
0%
Encryption
Q.74.
What is added to each part of a message to get it to the correct destination?
-
0%
IP Address
-
0%
Router
-
0%
ISP
-
0%
DNS
Q.75.
What happens to a file when it is sent?
-
0%
Sent as a single piece
-
0%
A copy is split up into many parts
-
0%
A copy is made and sent
-
0%
The original is sent
Q.76.
Do all the parts of a file sent have to go the same route?
-
0%
Yes
-
0%
No
Q.77.
What keyword means that your information is being kept secret?
-
0%
Encryption
-
0%
IP Address
-
0%
DNS
-
0%
ISP
Q.78.
The speed of your connection is called:
-
0%
Bandwidth
-
0%
Latency
Q.79.
This is a...
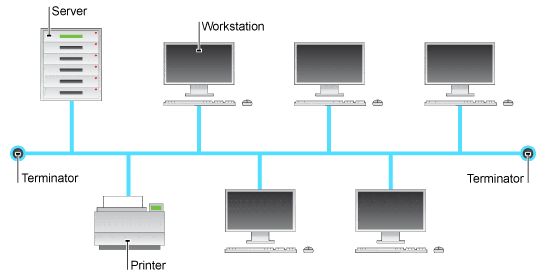

-
0%
BUS
-
0%
RING
-
0%
STAR
-
0%
MESH
Q.80.
A problem with a bus network is...
-
0%
There are data crashes
-
0%
It stops if a single computer stops working
-
0%
It is expensive
-
0%
You can't add a printer
Q.81.
A problem with a ring network is...
-
0%
There are data crashes
-
0%
It stops if a single computer stops working
-
0%
It is expensive
-
0%
You can't add a printer
Q.82.
A problem with a star network is...
-
0%
There are data crashes
-
0%
It stops if a single computer stops working
-
0%
It is expensive
-
0%
You can't add a printer
Q.83.
This is a...
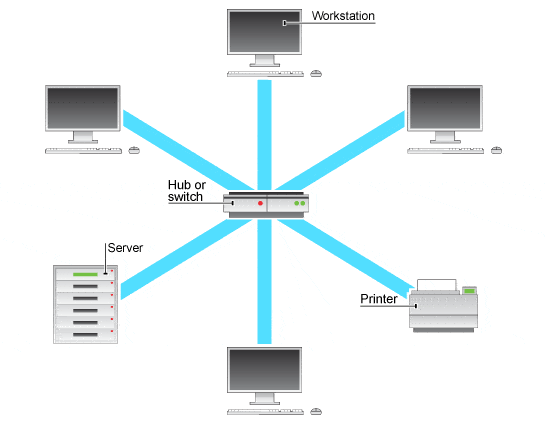

-
0%
BUS
-
0%
RING
-
0%
STAR
-
0%
MESH
Q.84.
This is a...
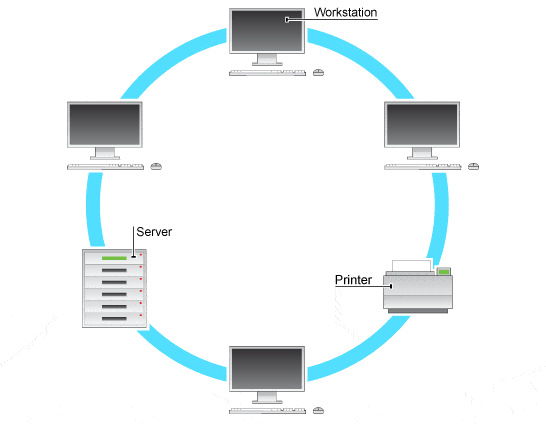

-
0%
BUS
-
0%
RING
-
0%
STAR
-
0%
MESH
Q.85.
This piece of equipment is used for a....
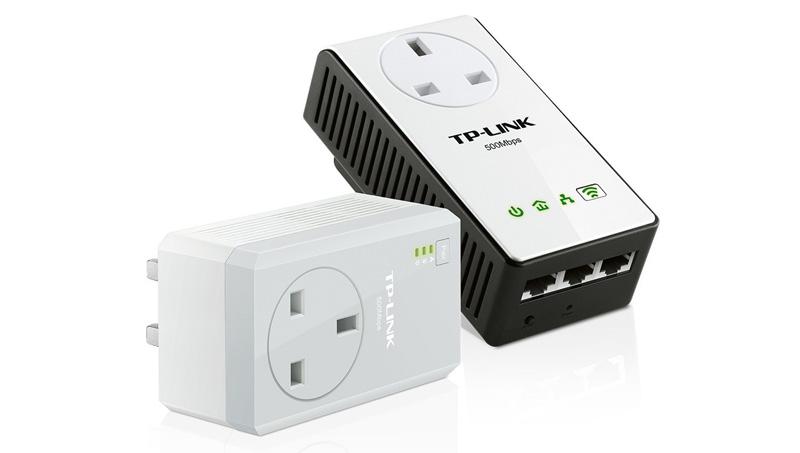


-
0%
Wired Network Adapter
-
0%
Wireless Network Adapter
-
0%
PowerLine Network Adapter
-
0%
Phone Network Adapter
Q.86.
The best use of wired connections is for...
-
0%
Security and gaming
-
0%
Portable devices
-
0%
Getting a connection in difficult to reach areas
Q.87.
The best use of wireless connections is for...
-
0%
Security and gaming
-
0%
Portable devices
-
0%
Getting a connection in difficult to reach areas
Q.88.
The best use of powerline connections is for...
-
0%
Security and gaming
-
0%
Portable devices
-
0%
Getting a connection in difficult to reach areas
Q.89.
This is the name of the school's network...
-
0%
LAN
-
0%
WAN
-
0%
MAN
-
0%
PAN
Q.90.
When you create a HOTSPOT from your phone, you are creating which network type?
-
0%
LAN
-
0%
WAN
-
0%
MAN
-
0%
PAN
Q.91.
The type of network for a home network is usually:
-
0%
Peer to Peer
-
0%
Client-Server
Q.92.
School's network is an example of:
-
0%
Peer to Peer
-
0%
Client-Server
Q.93.
Which is the advantage of peer to peer?
-
0%
Each device is unique
-
0%
If the server is turned off, the system no longer works.
-
0%
It's less secure
-
0%
Client PC can be low power
Q.94.
What do you need to access cloud computing?
-
0%
A cloud
-
0%
An internet connection
-
0%
Updated software
-
0%
Lots of storage space
Q.95.
What does WAN stand for ?


-
0%
Weak Access Node
-
0%
Working Area Network
-
0%
Wide Area Network
-
0%
World Access Net
Q.96.
Which one of these items is not an advantage of a client-server network?
-
0%
No central point of failure
-
0%
Central control of security
-
0%
Easier to supervise network performance
-
0%
Easier to perform software upgrades
Q.97.
Which one of these items is true of a peer-to-peer network?
-
0%
No network wide security in place
-
0%
Central control of security
-
0%
Has a central point of failure
-
0%
Easier to perform network wide backups
Q.98.
Which one of these items is true of a client-server network?
-
0%
Needs a network manager to run the network
-
0%
No centralised management
-
0%
All computers have equal status
-
0%
No dependency on a server
Q.99.
In this image what are the B's known as?
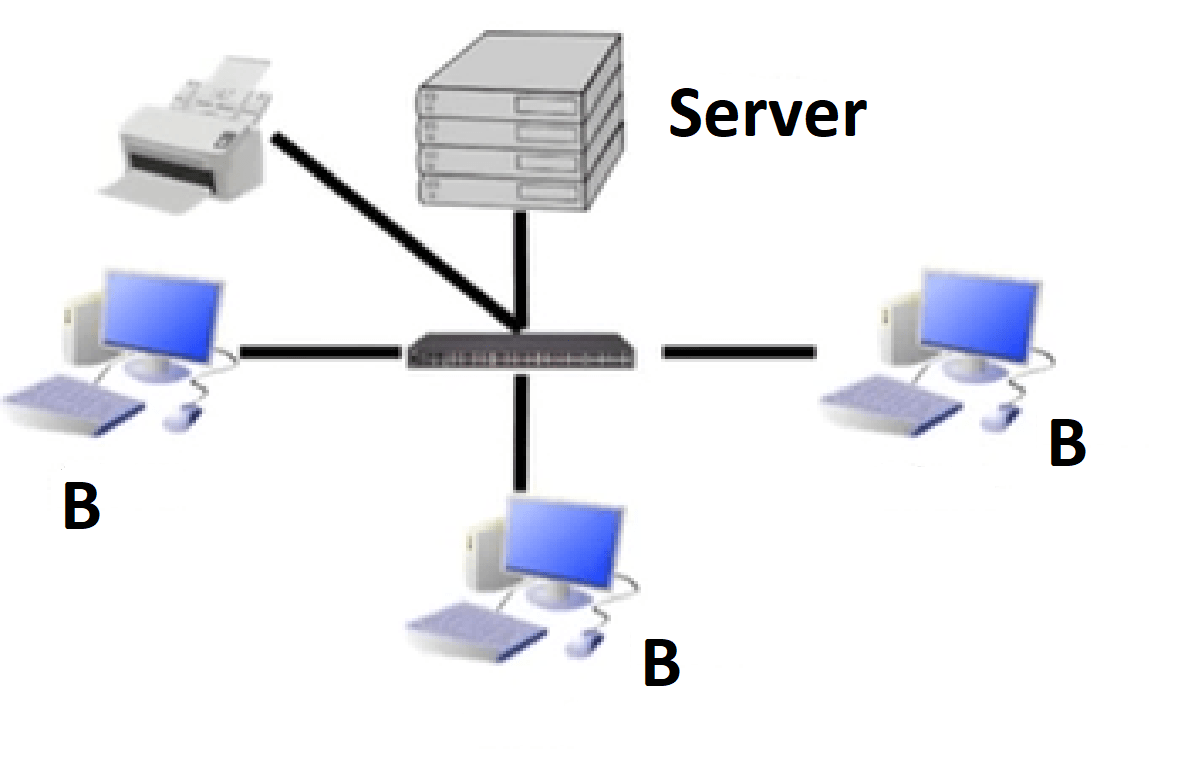

-
0%
Servers
-
0%
Peers
-
0%
Clients
-
0%
Hardware
Q.100.
You must have this to connect to a network...
-
0%
Network Interface Card
-
0%
Wireless Application Protocol
-
0%
Wi-Fi
-
0%
Ethernet Cable
Q.101.
What does TCP stand for?
-
0%
Transcript Control Protocol
-
0%
Transition Control Protocol
-
0%
Transmit Control Protocol
-
0%
Transmission Control Protocol
Q.102.
Which protocol holds the email until you actually delete it?
-
0%
POP3
-
0%
IMAP
-
0%
SMTP
-
0%
FTP
Q.103.
What does HTTPS stand for?
-
0%
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
-
0%
Hyper Text Transport Protocol Secure
-
0%
Hyper Text Transport Protocol
-
0%
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure
Q.104.
Which protocol is responsible for transferring computer files between client and server on a computer network?
-
0%
SMTP
-
0%
FTP
-
0%
TCP/IP
-
0%
HTTP
Q.105.
What type of network topology shown in the picture?
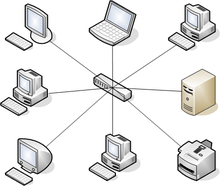

-
0%
Bus topology
-
0%
Ring topology
-
0%
Star topology
-
0%
Tree topology
Q.106.
What type of network topology shown in the picture?
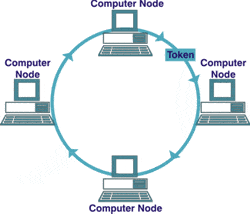

-
0%
Bus topology
-
0%
Ring topology
-
0%
Star topology
-
0%
Tree topology
Q.107.
Base on the picture given, determined whether the statement below is TRUE or FALSE"For data to be sent from one computer to the other, the sending computer must have a token"
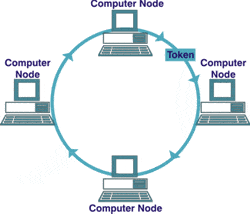

-
0%
FALSE
-
0%
TRUE
Q.108.
What type of network topology shown in the picture?
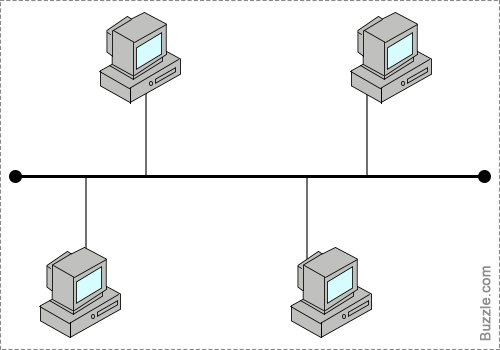

-
0%
Bus topology
-
0%
Ring topology
-
0%
Star topology
-
0%
Tree topology
Q.109.
What is the correct description for the type of topology shown in the picture?
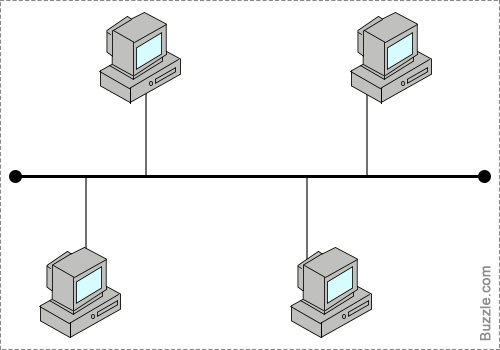

-
0%
All of the nodes in the network must be connected to each other for the network to work.
-
0%
All nodes must be connected to a centeral communication device
-
0%
The network consists of a single central cable (backbone), to which all computers and other devices connect.
-
0%
a cable forms a closed loop with all computers and devices arrangedalong the ring.
Q.110.
What Can't a Firewall Do?
-
0%
Can't protect against viruses.
-
0%
Stop hackers from accessing your computer.
-
0%
Determines which programs can access the Internet.
Q.111.
Firewalls can be configured to block data from certain locations (i.e., computer network addresses), applications, or ports while allowing relevant and necessary data through
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.112.
The full form of W.W.W is _____________________
-
0%
wide web worry
-
0%
work wide web
-
0%
World Wide Web
-
0%
online work web
Q.113.
A computer network is ______ connected together.
-
0%
One computer
-
0%
Two or more computers
-
0%
At least three or more computers
Q.114.
What does WAN stands for?
-
0%
Wide Area Network
-
0%
World Area Network
-
0%
Wide Arena Network
-
0%
World Arena Network
Q.115.
What does LAN stands for?
-
0%
Local Area Network
-
0%
Local Arena Name
-
0%
Local Arena Network
-
0%
Local Area Name
Q.116.
What does WLAN stands for?
-
0%
Wired Local Area Network
-
0%
Wireless Local Area Network
-
0%
Wired Local Arena Network
-
0%
Wireless Local Arena Network
Q.117.
A wired network that connect computers within a building is called a ______ ?
-
0%
LAN
-
0%
WAN
-
0%
WLAN
Q.118.
The internet is this kind of network.
-
0%
LAN
-
0%
WLAN
-
0%
WAN
Q.119.
A WAN covers a wider area than a LAN. True or False?
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.120.
Which of the device below is also called a Repeater?
-
0%
Hub
-
0%
Bridge
-
0%
Switch
-
0%
Router
-
0%
Modem
Q.121.
Which of the device below creates a WLAN?
-
0%
Network cable
-
0%
Access Points
-
0%
Modem
-
0%
Router
Q.122.
Which of the device below is also called a smarter hub?
-
0%
Hub
-
0%
Bridge
-
0%
Switch
-
0%
Router
-
0%
Access Point
Q.123.
What am I?


-
0%
Sound card
-
0%
Switch
-
0%
Network Interface card
-
0%
Ethernet cable
Q.124.
What am I?


-
0%
Access Point
-
0%
Switch
-
0%
Modem
-
0%
UFO
-
0%
Bridge
Q.125.
What am I? (Select best answer)
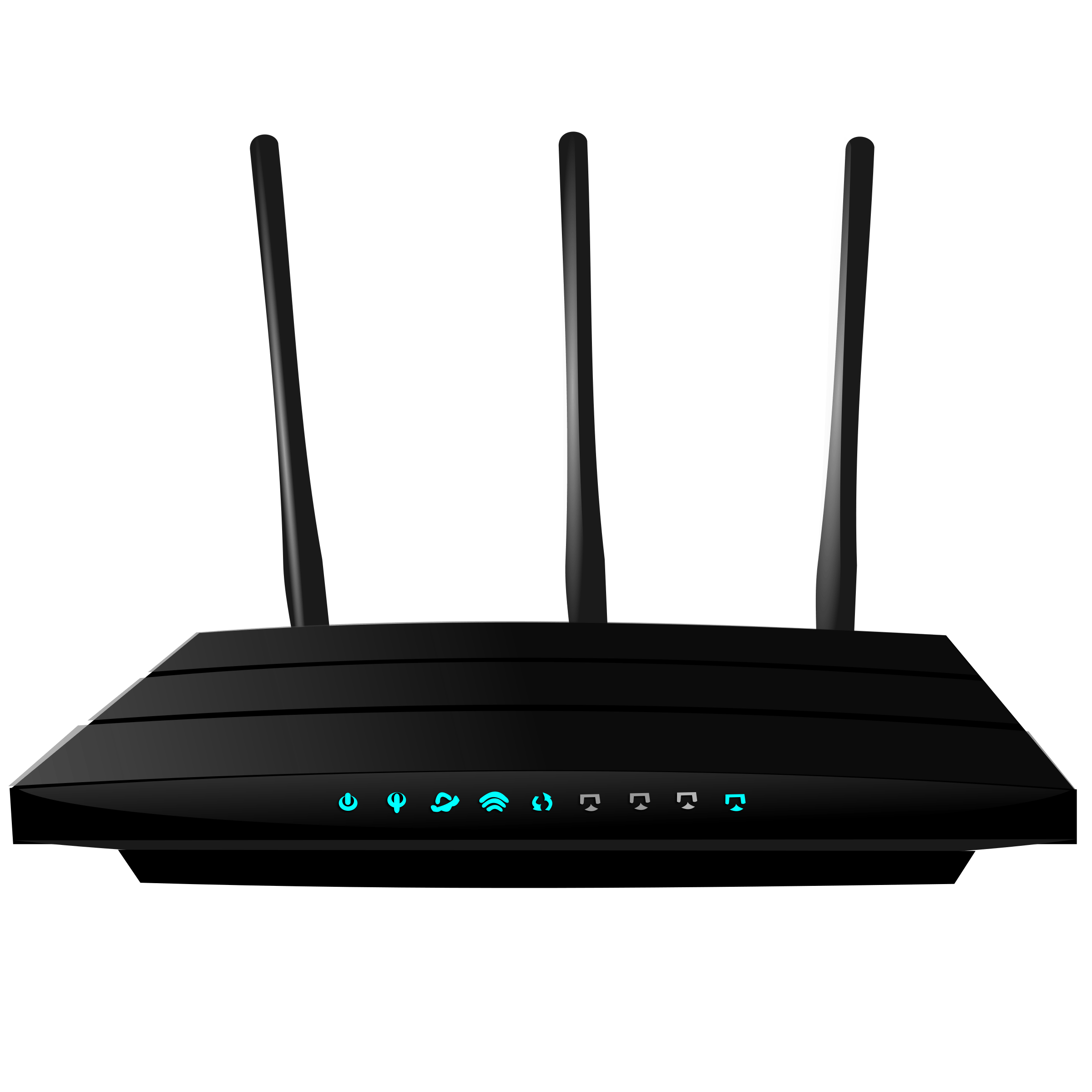


-
0%
Switch
-
0%
Wireless router
-
0%
NIC
-
0%
Modem
-
0%
Router
Q.126.
What is a disadvantage of a LAN?
-
0%
Site (software) licences are likely to be cheaper than buying several standalone licences.
-
0%
Security is good - users cannot see other users' files unlike on stand-alone machines.
-
0%
if the main cable fails or gets damaged the whole network will fail
-
0%
Purchasing the network cabling and file servers can be expensive.
Q.127.
is a web browser
-
0%
Internet
-
0%
DIS
-
0%
Google
-
0%
Google chrome
Q.128.
What does Protocol mean?
-
0%
Security
-
0%
Rules
-
0%
Orders
-
0%
Services
Q.129.
What is Hypertext used for?
-
0%
Creating websites
-
0%
Sending emails
-
0%
Saving programs
-
0%
Storing data
Q.130.
A group of 1024 megabytes is called a byte.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.131.
The smallest unit for storing data, either a 0 or a 1, is called a byte.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.132.
A bit generally consists of eight bytes.
-
0%
True
-
0%
False