Q.1.
To what depth must a rubber ball be taken in deep sea so that its volume is decreased by $$0.1$$%
(Take density of sea water $${ 10 }^{ 3 }kg\quad { m }^{ -3 }$$, bulk modulus of rubber $$=9\times { 10 }^{ 8 }N{ m }^{ -2 },g=10m{ s }^{ -2 }$$)
(Take density of sea water $${ 10 }^{ 3 }kg\quad { m }^{ -3 }$$, bulk modulus of rubber $$=9\times { 10 }^{ 8 }N{ m }^{ -2 },g=10m{ s }^{ -2 }$$)
-
0%
$$9m$$
-
0%
$$18m$$
-
0%
$$90m$$
-
0%
$$180m$$
Q.2.
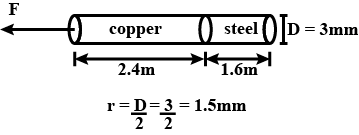
A copper wire of length $$2.4m$$ and a steel wire of length $$1.6m$$, both the diameter $$3mm$$, are connected end to end. When stretched by a load, the net elongation is found to be $$0.7mm$$. The load applied is
$$\left( { Y }_{ copper }=1.2\times { 10 }^{ 11 }N\quad { m }^{ -2 },{ Y }_{ steel }=2\times { 10 }^{ 11 }N\quad { m }^{ -2 } \right) $$
$$\left( { Y }_{ copper }=1.2\times { 10 }^{ 11 }N\quad { m }^{ -2 },{ Y }_{ steel }=2\times { 10 }^{ 11 }N\quad { m }^{ -2 } \right) $$
-
0%
$$1.2\times { 10 }^{ 2 }N$$
-
0%
$$1.8\times { 10 }^{ 2 }N$$
-
0%
$$2.4\times { 10 }^{ 2 }N$$
-
0%
$$3.2\times { 10 }^{ 2 }N$$
Q.3.
The volume change of a solid copper cube $$10cm$$ on an edge, when subjected to a pressure of $$7MPa$$ is then
(Bulk modulus of copper $$=140GPa$$)
(Bulk modulus of copper $$=140GPa$$)
-
0%
$$5\times { 10 }^{ -2 }{ cm }^{ 3 }$$.
-
0%
$$10\times { 10 }^{ -2 }{ cm }^{ 3 }$$
-
0%
$$15\times { 10 }^{ -2 }{ cm }^{ 3 }$$
-
0%
$$20\times { 10 }^{ -2 }{ cm }^{ 3 }$$
Q.4.
Which of the following apparatus is used to determine the Young's modulus of the material of a given wire?
-
0%
Searle
-
0%
sonometer
-
0%
Metre bridge
-
0%
Resonance tube
Q.5.
A copper wire of length $$2.4m$$ and a steel wire of length $$1.6m$$, both the diameter $$3mm$$, are connected end to end. The ratio fo elongation of steel to the copper wires is then
$$\left( { Y }_{ copper }=1.2\times { 10 }^{ 11 }N\quad { m }^{ -2 },{ Y }_{ steel }=2\times { 10 }^{ 11 }N\quad { m }^{ -2 } \right) $$
$$\left( { Y }_{ copper }=1.2\times { 10 }^{ 11 }N\quad { m }^{ -2 },{ Y }_{ steel }=2\times { 10 }^{ 11 }N\quad { m }^{ -2 } \right) $$
-
0%
$$\cfrac { 5 }{ 2 } $$
-
0%
$$\cfrac { 2 }{ 5 } $$
-
0%
$$\cfrac { 3 }{ 2 } $$
-
0%
$$\cfrac { 2 }{ 3 } $$
Q.6.
The relation between $$Y, \eta$$ and $$B$$ where $$Y, \eta ,B$$ are Young's Modulus, Shear modulus and bulk modulus respectively.
-
0%
$$\cfrac { 1 }{ Y } =\cfrac { 1 }{ 3\eta } +\cfrac { 1 }{ 9B } $$
-
0%
$$\cfrac { 9 }{ Y } =\cfrac { 1 }{ 3\eta } +\cfrac { 3 }{ B } $$
-
0%
$$\cfrac { 1 }{ \eta } =\cfrac { 1 }{ B } +\cfrac { 1 }{ Y } $$
-
0%
$$\cfrac { 9 }{ Y } =\cfrac { 3 }{ \eta } +\cfrac { 1 }{ B } $$
Q.7.
If in the above question, the Young's modulus of the material is Y, the value of extension x is:
-
0%
$$\left ( \frac{El}{YA} \right )^{1/3}$$
-
0%
$$\left ( \frac{YA}{Wl} \right )^{1/3}$$
-
0%
$$\frac{1}{l}\left [ \frac{WA}{Y} \right ]^{1/3}$$
-
0%
$$l\left [ \frac{W}{YA} \right ]^{1/3}$$
Q.8.
A metal wire of length $$L_1$$ and area of cross section A is attached to a rigid support. Another metal wire of length $$L_2$$ and of the same cross-sectional area is attached to the free end of the first wire. A body of mass M is then suspended from the free end of the second wire. If $$Y_1$$ and $$Y_2$$ are the Young's moduli of the wires respectively, the effective force constant of the system of two wires is
-
0%
$$\frac{Y_1Y_2A}{2(Y_1L_2+Y_2L_1)}$$
-
0%
$$\frac{Y_1Y_2A}{2(L_1L_2)^{1/2}}$$
-
0%
$$\frac{Y_1Y_2A}{(Y_1L_2+Y_2L_1)}$$
-
0%
$$\frac{(Y_1Y_2)^{1/2}A}{2(L_1L_2)^{1/2}}$$
Q.9.
The maximum load a wire can withstand without breaking, when its length is reduced to half of its original length, will
-
0%
be double
-
0%
be half
-
0%
be four times
-
0%
remains same
Q.10.
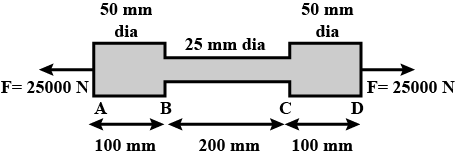
A steel bar $$ABCD$$ $$40cm$$ long is made up of three parts $$AB, BC$$ and $$CD$$, as shown in the figure The rod is subjected to a pull of $$25kN$$. The total extension of the rod is (Young's modulus for steel $$2\times { 10 }^{ 11 }N{ m }^{ -2 }$$:

-
0%
$$0.0637mm$$
-
0%
$$0.0647mm$$
-
0%
$$0.0657mm$$
-
0%
$$0.0667mm$$
Q.11.
The mean distance between the atoms of iron is $$3\times10^{-10}m$$ and interatomic force constant for iron is $$7 N m^{-1}$$. The Young's modulus of electricity for iron is
-
0%
$$2.33\times 10^5 Nm^{-2}$$
-
0%
$$23.3\times 10^{10} Nm^{-2}$$
-
0%
$$2.33\times 10^{9} Nm^{-2}$$
-
0%
$$2.33\times 10^{10} Nm^{-2}$$
Q.12.
Find the stress developed inside a tooth cavity filled with copper when hot tea at temperature of $$ 57^o C $$ is drunk. (Take temperature of tooth to be $$ 37^o C,\alpha =1.7\times { 10 }^{ -5 }{ }{ /^o C} $$ and bulk modulus for copper $$ =140\times { 10 }^{ 9 }N{ m }^{ -2 } $$ )
-
0%
$$ 1.43\times { 10 }^{ 8 }N{ m }^{ -2 } $$
-
0%
$$ 4.13\times { 10 }^{ 8 }N{ m }^{ -2 } $$
-
0%
$$ 2.12\times { 10 }^{ 4 }N{ m }^{ -2 } $$
-
0%
$$ 3.12\times { 10 }^{ 4 }N{ m }^{ -2 } $$
Q.13.
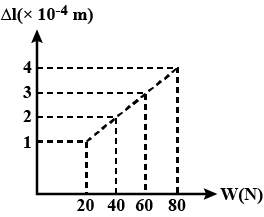
The adjacent graph shows the extension ($$\Delta l$$) of a wire of length $$1m$$ suspended from the top of a roof at one end and with a load $$W$$ connected to the other end. If the cross-sectional area of the wire is $${ 10 }^{ -6 }{ m }^{ 2 }$$, the Young's modulus of the material of the wire is

-
0%
$$2\times { 10 }^{ 11 }N{ m }^{ 2 }$$
-
0%
$$2\times { 10 }^{ -11 }N{ m }^{ 2 }$$
-
0%
$$3\times { 10 }^{ -12 }N{ m }^{ 2 }$$
-
0%
$$2\times { 10 }^{ -13 }N{ m }^{ 2 }$$
Q.14.
The ratio of diameters of two wires of same material is n:The length of each wire is 4 m. On applying the same load, the increases in the length of the thin wire will be (n > l)
-
0%
$$n^2$$ times
-
0%
n times
-
0%
2n times
-
0%
(2n + 1) times
Q.15.
The dimensions of four wires of the same material are given below. In which wire the increase in the length will be maximum?
-
0%
Length 100 cm, diameter 1 mm
-
0%
Length 200 cm, diameter 2 mm
-
0%
Length 300 cm. diameter 3 mm
-
0%
Length 50 cm, diameter 0.5 mm
Q.16.
A rubber ball of bulk modulus B is taken to a depth h of a liquid of density p. Find the fractional change in the radius of the ball.
-
0%
$$ \, \dfrac{\rho gh}{4B}$$ -
0%
$$ \, \dfrac{\rho gh}{3B}$$ -
0%
$$\, \dfrac{\rho gh}{2B}$$ -
0%
$$ \dfrac{\rho gh}{5B}$$
Q.17.
A wire is stretched 1 mm by a force of 1 kN. How far would a wire of the same material and length but of four times that diameter he stretched by the same force?
-
0%
$$\dfrac{1}{2}$$mm
-
0%
$$\dfrac{1}{4}$$mm
-
0%
$$\dfrac{1}{8}$$mm
-
0%
$$\dfrac{1}{16}$$mm
Q.18.
A steel wire is stretched by 1 kg wt. If the radius of the wire is doubled, its Young's modulus will:
-
0%
remain unchanged
-
0%
become half
-
0%
become double
-
0%
become four times
Q.19.
Plastic deformation results from the following
-
0%
Slip
-
0%
Twinning
-
0%
Both slip and twinning
-
0%
creep
Q.20.
A gas undergoes a process in which its pressure $$p$$ and value $$v$$ are related as $$Vp^2 =$$ constant. The bulk modulus for the gas in this process is:
-
0%
$$\dfrac{p}{2}$$
-
0%
$$2p$$
-
0%
$$2pv$$
-
0%
$$3p$$
Q.21.
A wire has a tensile strength of 70MPa, and breaks under 100N of force. What is the cross-sectional area of the wire just before breaking?
-
0%
$$14.2 \times 10^{-6} m^2$$
-
0%
$$1.42 \times 10^{-6} m^2$$
-
0%
$$ 1.42 \times 10^{-3} m^2$$
-
0%
$$ 1.42 \times 10^{-2} m^2$$
Q.22.
A thin metal sheet is being bent by or pounded in to a new shape. The process of being elastic to plastic behaviour is known as
-
0%
Yield
-
0%
Creep
-
0%
Welding
-
0%
Tinkering
Q.23.
An elastic spring is given a force of 1000 N over an area of $$0.2 m^2.$$
-
0%
$$3000 N m^{-2}$$
-
0%
$$5000 N m^{-2}$$
-
0%
$$500 N m^{-2}$$
-
0%
$$2500 N m^{-2}$$
Q.24.
The plasticity behaviour of a material determines the
-
0%
elastic behavior of the material
-
0%
resistance of the material to electric fields
-
0%
viscous behavior of the material and is irrecoverable.
-
0%
resistance of the material to magnetic fields
Q.25.
Substances that elongate considerably and undergo plastic deformation before they break are known as
-
0%
brittle substances
-
0%
breakable substances
-
0%
ductile substances
-
0%
all of these
Q.26.
Plastic deformation in a material begins at
-
0%
Q point
-
0%
Yield point
-
0%
Proportionality limit
-
0%
Elastic limit
Q.27.
At yield point, Hooke's law doesn't hold good
-
0%
True
-
0%
False
Q.28.
Elasticity is defined as the ability of a body to
-
0%
Resist linear motion in a hard surface
-
0%
Resist rolling motion in a hard surface
-
0%
Resist a distorting influence and to return to its original size and shape when that influence or force is removed.
-
0%
Resist electric current in a magnetic field
Q.29.
Which of the following is the dimension of Bulk Modulus?
-
0%
$$[M^1L^{-1}T^{-1}]$$
-
0%
$$[M^1L^{-1}T^{-2}]$$
-
0%
$$[M^1L^{1}T^{2}]$$
-
0%
$$[M^1L^{1}T^{-1}]$$
Q.30.
Longitudinal strain is calculated using the formula
-
0%
Change in length/ original length
-
0%
Original length/Change in length
-
0%
Original length $$\times $$ Change in length
-
0%
Original length - Change in length
Q.31.
Poisson' ratio is defined as the ratio of
-
0%
longitudinal stress and longitudinal strain
-
0%
longitudinal stress and lateral stress
-
0%
lateral stress and longitudinal stress
-
0%
lateral stress and lateral strain
Q.32.
The difference between pressure and stress is
-
0%
pressure and stress have different units
-
0%
pressure and stress have different dimensions
-
0%
Force cannot be determined using stress, but in pressure it can be done
-
0%
Pressured is applied to a body, while stress is induced
Q.33.
Which one of the following is true about Bulk Modulus of elasticity?
-
0%
It is the ratio of compressive stress to volumetric strain
-
0%
It is the ratio of compressive stress to linear strain
-
0%
It is the ratio of tensile stress to volumetric strain
-
0%
It is the ratio of tensile stress to linear strain
Q.34.
A force of 10 N is applied to an object, whose area is $$5 cm^2$$ at an angle of 30 degrees with the vertical. What kind of stress can be found from this data
-
0%
Normal and areal stress can be found
-
0%
only normal stress can be found
-
0%
only areal stress can be found
-
0%
Stress cannot be found from this data, since applied force is neither along the horizontal or vertical
Q.35.
A steel wire is suspended from a fixed end, while the other end is loaded with a weight W. This produced an extension x. As the weight is increased, the extension was also increased. A plot of extension vs load within elastic limits will give rise to
-
0%
a curve
-
0%
an ellipse
-
0%
a straight line
-
0%
a hyperbola
Q.36.
The radius of a copper wire is 4 mm. What force is required to stretch the wire by 20% of its length, assuming that the elastic limit is not exceeded (Y=$$12 \times 10^{10} N / m^2$$
-
0%
$$7.23 \times 10^5 N$$
-
0%
$$7.23 \times 10^7 N$$
-
0%
$$7.23 \times 10^6 N$$
-
0%
$$7.23 \times 10^8 N$$
Q.37.
A wire of length L can support a load W. If the wire is broken in to two equal parts , then how much load can be suspended by one of those cut wires?
-
0%
Half
-
0%
Same
-
0%
Double
-
0%
One fourth
Q.38.
A rubber cord 10 m long is suspended vertically. How much does it stretch under its own weight. ( [Density of rubber is $$1500 (kg / m^3), Y = 5 \times 10^8 N/m^2)$$
-
0%
0.3 mm
-
0%
0.15 mm
-
0%
0.015 mm
-
0%
0.03 mm
Q.39.
When the temperature of a gas is $$20^0C$$ and pressure is changed from $$P_1=1.01\times 10^{5}\, Pa$$ to $$P_2=1.165\times 10^5\,Pa$$, then the volume changes by $$10$$%. The bulk modulus is
-
0%
$$1.55\times10^5 \,Pa$$
-
0%
$$1.05\times10^5 \,Pa$$
-
0%
$$1.4\times10^5 \,Pa$$
-
0%
$$0.115\times10^5 \,Pa$$
Q.40.
A student measures the poisson's ratio to be greater than 1 in an experiment. The meaning of this statement would be
-
0%
An increase in length would also result in decrease in area of cross section of the wire
-
0%
An increase in length would also result in increase in area of cross section of the wire
-
0%
An decrease in length would also result in decrease in area of cross section of the wire
-
0%
An increase in length will not change the area of cross section of the wire
Q.41.
The theoretical limits of poisson's ratio lies between -1 to 0.5 because
-
0%
Shear modulus and bulk's modulus should be positive
-
0%
Bulk's modulus is negative during compression
-
0%
Shear modulus is negative during compression
-
0%
Young's modulus should be always positive
Q.42.
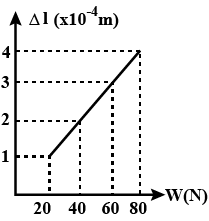
A $$1$$m long metal wire of cross sectional area $$10^{-6}m^2$$ is fixed at one end from a rigid support and a weight W is hanging at its other end. The graph shows the observed extension of length $$\Delta l$$ of the wire as a function of W. Young's modulus of material of the wire in SI units is?

-
0%
$$5\times 10^4$$
-
0%
$$2\times 10^5$$
-
0%
$$2\times 10^{11}$$
-
0%
$$5\times 10^{11}$$
Q.43.
A uniform wire (Young's modulus $$2\times 10^{11}Nm^{-2}$$ ) is subjected to longitudinal tensile stress of $$5\times 10^7\ Nm^{-2}$$. If the overall volume change in the wire is $$0.02\%$$, the frictional decrease in the radius of the wire is close to
-
0%
$$1.0 \times 10^{-4}$$
-
0%
$$1.5 \times 10^{-4}$$
-
0%
$$0.25 \times 10^{-4}$$
-
0%
$$5 \times 10^{-4}$$
Q.44.
The ratio of the coefficient of volume expansion of glass container to that of a viscous liquid kept inside the container is $$1:4$$. What fraction of the inner volume of the container should the liquid occupy so that the volume of the remaining vacant space will be same at all the temperature?
-
0%
$$2/5$$
-
0%
$$1/4$$
-
0%
$$1/64$$
-
0%
$$1/8$$
Q.45.
A metal rod of Young's modulus $$Y$$ and coefficient of thermal expansion $$\alpha$$ is held at its two ends such that its length remains invariant. If its temperature is raised by $${t}^{o}C$$, the linear stress developed in it is:
-
0%
$$1/\left( Y\alpha t \right) $$
-
0%
$$\alpha t/Y$$
-
0%
$$Y/\alpha t$$
-
0%
$$Y\alpha T$$
Q.46.
For which material the poisson's ratio is greater than 1
-
0%
Steel
-
0%
Copper
-
0%
Aluminium
-
0%
None of the above
Q.47.
The maximum strain energy that can be stored in a body is known as:
-
0%
impact energy
-
0%
toughness
-
0%
proof resilience
-
0%
none of the above
Q.48.
A rubber ball is taken to depth $$1$$ km inside water so that its volume reduces by $$0.05\% $$.What is the bulk modulus of the rubber:
-
0%
$$2 \times 10^{10} N/m^2$$
-
0%
$$2 \times {10^{9\,}}\,N/{m^2}$$
-
0%
$$2 \times 10^{7}N/m^2$$
-
0%
$$2 \times {10^{11\,}}\,N/{m^2}$$
Q.49.
The proportional limit of steel is $$8\times { 10 }^{ 8 }N/{ m }^{ 2 }$$ and its Young's modulus is $$2\times { 10 }^{ 11 }N/{ m }^{ 2 }$$. The maximum elongation, a one metre long steel wire can be given without exceeding the proportional limit is
-
0%
2 mm
-
0%
4 mm
-
0%
1 mm
-
0%
8 mm
Q.50.
Overall changes in volume and radii of a uniform cylindrical steel sire are $$0.2\%$$ and $$0.002\%$$ respectively when subjected to some suitable force. Longitudinal tensile stress acting on the wire is :-
$$(Y=2.0\times 10^{11}\ NM^{-2})$$
$$(Y=2.0\times 10^{11}\ NM^{-2})$$
-
0%
$$3.2\times 10^{9}\ Nm^{-2}$$
-
0%
$$3.2\times 10^{7}\ Nm^{-2}$$
-
0%
$$3.6\times 10^{9}\ Nm^{-2}$$
-
0%
$$3.9\times 10^{8}\ Nm^{-2}$$