Q.1.
Permanent tissues differ from meristematic tissue in
A. Inability to divide
B. Attainment of definite size and shape
C. Performing a distinct function
D. Ability to divide
B. Attainment of definite size and shape
C. Performing a distinct function
D. Ability to divide
-
0%
A and B
-
0%
A, C and D
-
0%
B, C and D
-
100%
A, B and C
Q.2.
Which of the following elements of xylem helps in lateral conduction of water?
-
100%
Xylem tracheids
-
0%
Xylem parenchyma
-
0%
Xylem vessels
-
0%
Xylem fibres
Q.3.
The type of tissue found at the apex of root or stem is called
-
0%
Lateral meristem
-
100%
Apical meristem
-
0%
Intercalary meristem
-
0%
None of the above
Q.4.
Select the incorrect pair from the following.
A. Parenchymatous tissue have intercellular spaces.
B. Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent.
C. Aerenchymatous is specialized for photosynthesis.
D. Collenchymatous tissues are irregularly thickened at the corners.
B. Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent.
C. Aerenchymatous is specialized for photosynthesis.
D. Collenchymatous tissues are irregularly thickened at the corners.
-
0%
A and C
-
0%
A and D
-
100%
B and C
-
0%
B and D
Q.5.
Which of the following helps in increasing the height of plant?
-
100%
Apical meristem
-
0%
Cambium
-
0%
Vascular bundle
-
0%
None of these
Q.6.
Auxin inhibits the growth of_______________
-
0%
Apical buds
-
0%
Parthenocarpic development of fruits
-
100%
Lateral axillary buds
-
0%
Roots of cuttings
Q.7.
Cells which take part in secondary growth are named as _______
-
0%
Phloem
-
0%
Xylem
-
100%
Cambium
-
0%
Medullary ray
Q.8.
If the cut end of a tree is put in eosin solution then,
-
0%
Leaves remain fresh but ascent of sap stops
-
100%
Phloem gets colored because of the ascent of sap
-
0%
Xylem elements get stained showing ascent of sap
-
0%
Ascent of sap stops
Q.9.
Tracheary elements are involved in
-
0%
Mechanical strength
-
0%
Food trasnlocation
-
0%
Conduction of minerals
-
100%
Both A and C
Q.10.
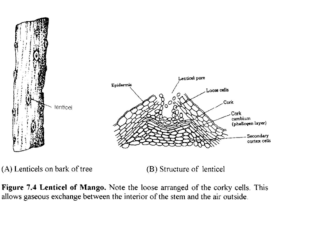
The small aerating pores seen on cork layer of woody stem are
-
100%
Guard cells
-
0%
Subsidiary cells
-
0%
Trichomes
-
0%
Lenticels
Q.11.
Buds which grow into flowers are called as
-
0%
Apical buds
-
100%
Floral buds
-
0%
Axillary buds
-
0%
Vegetative buds
Q.12.
Which of the following would you consider to prove that a plant is a monocot?
-
0%
Leaves with reticulate venation
-
100%
Taproot system
-
0%
Vascular bundles are closed
-
0%
Presence of cambium
Q.13.
The length of stem increases due to________
-
0%
Cambial activity
-
0%
Apical meristem
-
100%
Lateral meristem
-
0%
Cork cambium
Q.14.
Which of the following plant tissues is not a simple permanent tissue ?
-
100%
Xylem
-
0%
Collenchyma
-
0%
Sclerenchyma
-
0%
Parenchyma
Q.15.
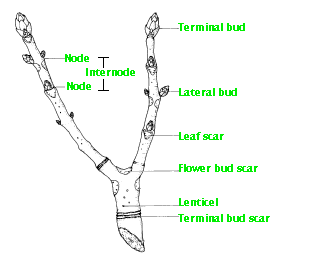
The point where the leaves grow on branch is called
-
0%
Node
-
100%
Stem
-
0%
Bud
-
0%
Root nodule
Q.16.
Tissue is formed by a combination of
-
0%
Organs
-
100%
Organ systems
-
0%
Cell
-
0%
All of the above
Q.17.
Conjoint, closed type of vascular bundles are characteristic of
-
100%
Monocot stem
-
0%
Dicot stem
-
0%
Monocot root
-
0%
Dicot root
Q.18.
Potato and sugarcane give rise to new plants through
-
0%
Eggs
-
0%
Seeds
-
100%
Stem
-
0%
Roots
Q.19.
Cells appear like pipeline arranged in continuous pattern below the cambium under microscope.
It could be _____ type cell.
-
0%
Xylem vessel
-
100%
Parenchyma
-
0%
Collenchyma
-
0%
Sclerenchyma
Q.20.
Lateral meristem is also called ______
-
0%
Xylem
-
0%
Phloem
-
0%
Vascular bundle
-
100%
Cambium
Q.21.
In beet _____ tissue stores food.
-
100%
Phloem
-
0%
Xylem.
-
0%
Parenchyma
-
0%
Aerenchyma
Q.22.
Most of the plant tissues are ______ cells.
-
0%
Dead
-
100%
Alive
-
0%
Minute
-
0%
Large
Q.23.
Apical meristem is located near the _____ of roots and stems.
-
0%
Lower surface
-
0%
Intermediate
-
0%
Lateral
-
100%
Tip
Q.24.
If a stem is girdled
-
0%
Root dies first
-
0%
Shoot dies first
-
100%
Both die together
-
0%
None of the above would die
Q.25.
Cork cambium results in the formation of cork, which becomes impermeable to water due to the accumulation of
-
0%
Resins
-
100%
Suberin
-
0%
Lignin
-
0%
Tannin
Q.26.
Ectophloic siphonostele is found in
-
0%
Osmunda and Equisetum
-
0%
Marsilea and Botrychium
-
0%
Adiantum and Cucurbita
-
100%
Dicksonia and Maidenhair fern
Q.27.
Which among the permanent tissues is impermeable to water?
-
0%
Parenchyma
-
0%
Collenchyma
-
0%
Both A and B
-
100%
Sclerenchyma
Q.28.
What is the function of sclerenchymatous tissue?
-
0%
Flexibilty
-
0%
Tenderness
-
0%
Strength
-
100%
All of the above
Q.29.
Xylems can classified as
-
0%
Xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres
-
100%
Tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres
-
0%
Vessels and xylem fibres
-
0%
None of the above
Q.30.
Name the essential element in xylem.
-
0%
Tracheids
-
0%
Vessels
-
0%
Xylem parenchyma
-
100%
Both A and B
Q.31.
The sclerenchyma cells are thick walled due to the presence of
-
0%
Acetone
-
100%
Lignin
-
0%
Lipids
-
0%
None of the above
Q.32.
Plant stem cells have the ability to
-
0%
Divide
-
0%
Differentiate
-
0%
Self renew
-
100%
All of the above
Q.33.
The cells of sclerenchyma can be classified as:
-
0%
Fibers and fibroids
-
0%
Ligaments and fibers
-
100%
Fibers and sclereids
-
0%
None of the above
Q.34.
Which does not contain cytoplasm?
-
0%
Liver cell
-
0%
Palisade tissue
-
100%
Red blood cell
-
0%
Xylem vessel
Q.35.
Interfasicular cambium is a
-
100%
Primary meristematic tissue
-
0%
Primordial meristem
-
0%
Type of protoderm
-
0%
Secondary meristematic tissue
Q.36.
Exarch and polyarch condition is found in
-
0%
Monocot stem
-
100%
Dicot stem
-
0%
Monocot root
-
0%
Dicot root
Q.37.
The bark of woody plant is dead but the inner layers inside the bark are living. How do these inner layers get oxygen and release carbon dioxide?
-
100%
Lenticels
-
0%
Stomata
-
0%
Pneumatophores
-
0%
Tendrils
Q.38.
Vascular bundles in root, stem, leaves are
-
0%
Continuous
-
0%
Discontinous
-
100%
Both A and B
-
0%
None of these
Q.39.
Which one of the following is not true about monocotyledons?
-
0%
Embryo has single cotyledon
-
0%
Leaves show parallel venation
-
0%
Flowers are generally trimerous
-
100%
Vascular bundle are conjoint, collateral and open
Q.40.
Phloem is a type of ________
-
0%
Connective tissue
-
100%
Vascular tissue
-
0%
Epidermal tissue
-
0%
All of the above
Q.41.
Name the element which is a living cell.
-
0%
Xylem fibres
-
100%
Xylem parenchyma
-
0%
Tracheids
-
0%
Vessels
Q.42.
Which of the following statements describes monocotyledons?
-
0%
They have fibrous roots
-
100%
Their leaves have parallel venation
-
0%
Their seeds have only one cotyledon
-
0%
All of the above
Q.43.
Non-living cells that transports water in vascular plant is
-
0%
Tracheids and vessel elements
-
0%
Guard cells
-
0%
Parenchyma cells
-
0%
Sieve tube members and companion cells
-
100%
Sclerenchyma cells
Q.44.
Sclerenchyma is a simple permanent tissue with thick secondary lignified cell walls. Which of the following cells have the secondary cell walls?
-
0%
The cells containing cytoplasm only.
-
0%
The cells with protoplast.
-
0%
The cells which are living at maturity.
-
100%
The cells which are non living at maturity.
Q.45.
The cellular organization between a single cell and an entire organism is controlled by:
-
100%
Hormones
-
0%
Tissues
-
0%
Enzymes
-
0%
Proteins
Q.46.
Which of these cells are the storage sites for sugar and starches in stems and roots?
-
0%
Tracheids and Vessel elements
-
0%
Guard cells
-
0%
Parenchyma cells
-
100%
Sieve tube members and Companion cells
-
0%
Sclerenchyma cells
Q.47.
Cork Cambium of dicot stem originates from
-
100%
Dedifferentiated parenchyma cells of cortex
-
0%
Dedifferentiated collenchyma cells of cortex
-
0%
Parenchyma cells of medullary ray
-
0%
Parenchyma cells of pericycle
Q.48.
Identify the correct pair of statements from the following.
(I) Pericycle of dicot root parenchymatous but sclerenchymatous in mature monocot root.
(II) Pericycle cells of both dicot ancimonocot roots actively divide to produce lateral toots during secondary growth.
(III) All cells of endodermis are passage cells in dicot.
(IV) Xylem always produced in a centripetal manner in the roots of fruit bearing plants.
(I) Pericycle of dicot root parenchymatous but sclerenchymatous in mature monocot root.
(II) Pericycle cells of both dicot ancimonocot roots actively divide to produce lateral toots during secondary growth.
(III) All cells of endodermis are passage cells in dicot.
(IV) Xylem always produced in a centripetal manner in the roots of fruit bearing plants.
-
0%
(III), (IV)
-
0%
(I), (II)
-
0%
(I), (IV)
-
100%
(II), (III)
Q.49.
The study of tissue is known as:
-
100%
Histology
-
0%
Cytology
-
0%
Dermatology
-
0%
Cardiology
Q.50.
Collocytes which provide mechanical strength to the plants are present in
-
100%
Dicotyledonous stem
-
0%
Monocotyledonous leaf
-
0%
Monocotyledonous stem
-
0%
Dicotyledonous root