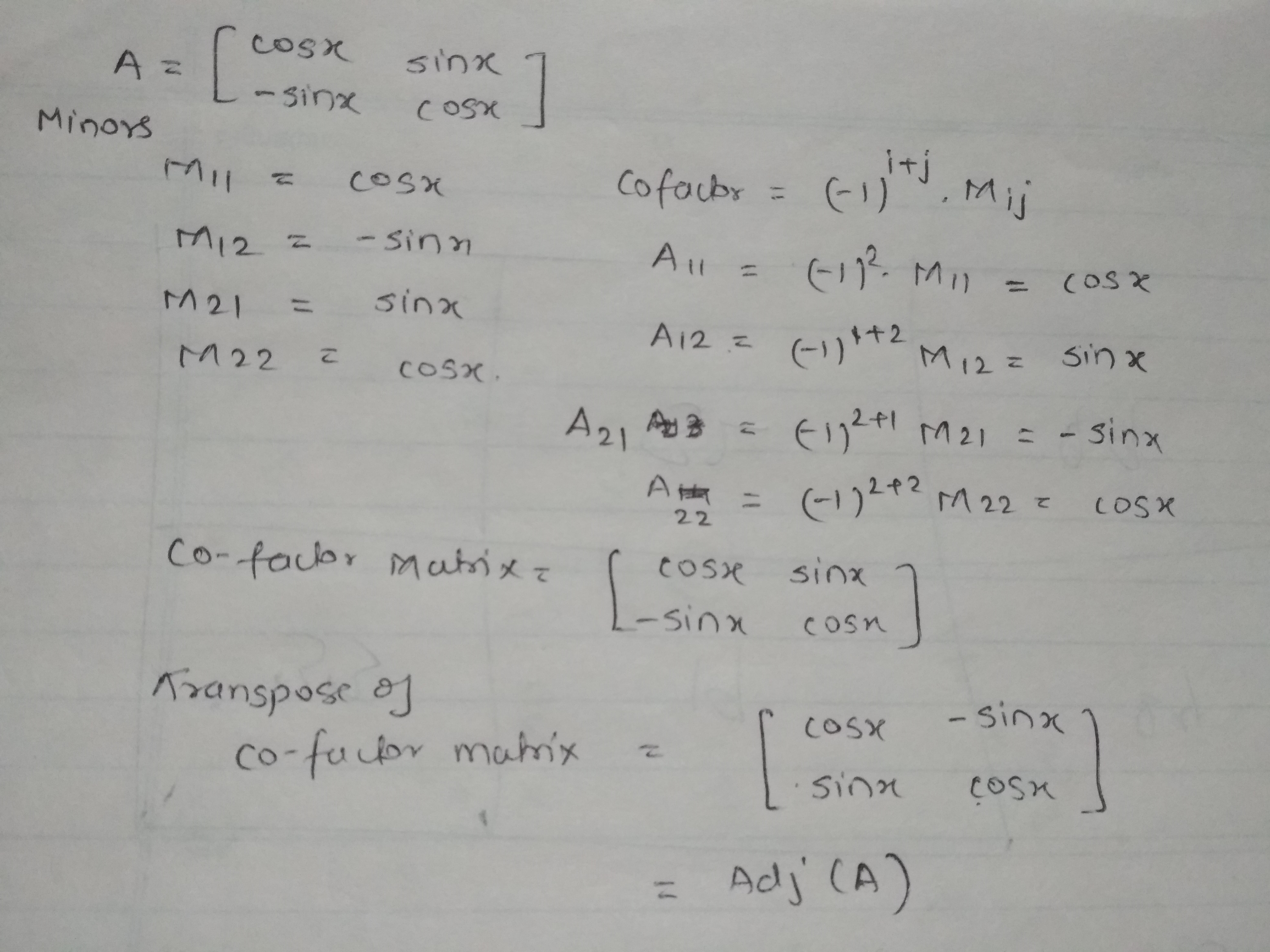Determinants - Class 12 Engineering Maths - Extra Questions
Find the value of determinant $$\begin{vmatrix} 2 & 4 \\ -5 & -1 \end{vmatrix}$$.
Find the Adjoint matrix of the matrix $$\begin{vmatrix} 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 2 & 3 & 2 \\ 3 & 3 & 4 \end{vmatrix}$$
If $$\omega$$ is one of the imaginary cube roots of unity, find the value of
$$\begin{vmatrix}1 & \omega^{3} & \omega^{2}\\ \omega^{3} & 1 &\omega \\ \omega^{2} & \omega & 1\end{vmatrix}$$.
Find determinant $$Dc=\begin{vmatrix} 1 & 1 & -2 \\ 1 & -2 & 3 \\ 2 & -1 & -1 \end{vmatrix}$$
Find the relation between $$a$$ and $$b$$. If the points $$P(1,2),Q(0,0)$$ and $$P(a,b)$$ are collinear
If the matrix $$A$$ = $$\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}6 & x & 2\\2 & { - 1} & 2\\{ - 10} & 5 & 2\end{array}} \right]$$is a singular matrix. Find the value of x.
Find $$'x'$$ if
$$\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}4&x&6\\2&3&4\\1&1&1\end{array}} \right| = 10$$
If $$\triangle = \begin{vmatrix} 3 & 5 & 7 \\ 2 & -3 & 1 \\ 1 & 1 & 2 \end{vmatrix} $$, find it's value.
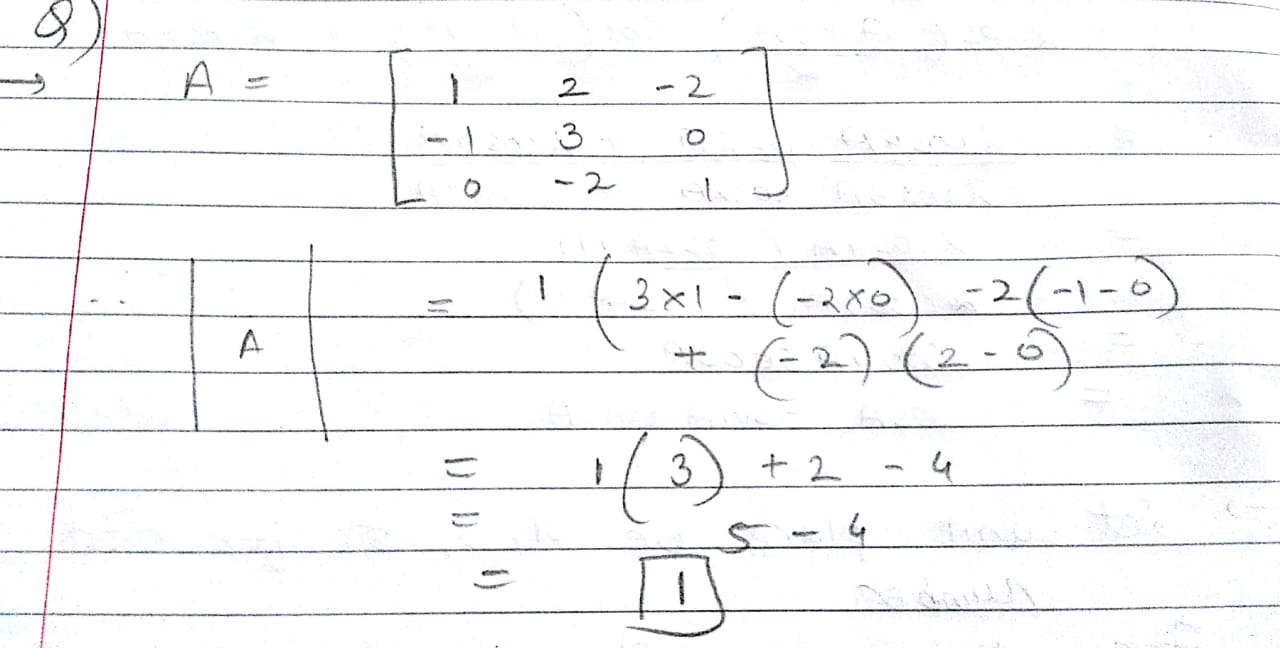
How do I find
$$A=\left[ \begin{matrix} 1 & 2 & -2 \\ -1 & 3 & 0 \\ 0 & -2 & 1 \end{matrix} \right] =\left| A \right| =?$$
Find ad-joint of
$$A=\begin{bmatrix} \cos x & \sin x \\ -\sin x & \cos x \end{bmatrix}$$
Find the values of x, if
$$\begin{vmatrix} x+1 & x-1 \\ x-3 & x+2 \end{vmatrix}=\begin{vmatrix} 4 & -1 \\ 1 & 3 \end{vmatrix}$$
Find the values of x, if $$\begin{vmatrix} 2x & 5 \\ 8 & x \end{vmatrix}=\begin{vmatrix} 6 & 5 \\ 8 & 3 \end{vmatrix}$$
Expand:$$ \begin{vmatrix} 1 & -7 & 3 \\ 5 & -6 & 0 \\ 1 & 2 & -3 \end{vmatrix}$$
Find the values of x, if
$$\begin{vmatrix} x+1 & x-1 \\ x-3 & x+2 \end{vmatrix}=\begin{vmatrix} 4 & -1 \\ 1 & 3 \end{vmatrix}$$
Show $$\begin{vmatrix}
ax & by & cz\\
x^2 & y^2 & z^2\\
1 & 1 & 1
\end{vmatrix}=\begin{vmatrix}
a & b & c\\
x & y & z\\
yz & zx & xy
\end{vmatrix}$$
For a fixed positive integer n, if $$D=\begin{vmatrix}
n! & (n+1)! & (n+2)!\\
(n+1)! & (n+2)! & (n+3)!\\
(n+2)! & (n+3)! & (n+4)!
\end{vmatrix}$$ then show$$\left [\frac {D}{(n!)^3}-4\right ]$$ is divisible by n.
If $$u=ax^2+2bxy+cy^2, u'=a'x^2+2b'xy+c'y^2$$, then prove that $$\begin{vmatrix}
y^2 & -xy & x^2\\
a & b & c\\
a' & b' & c'
\end{vmatrix}=\begin{vmatrix}
ax+by & bx+cy\\
a'x+b'y & b'x+c'y
\end{vmatrix}=-\frac {1}{y}\begin{vmatrix}
u & u'\\
ax+by & a'x+b'y
\end{vmatrix}$$
If $$\omega$$ is one of the imaginary cube roots of unity, find the value of
$$\begin{vmatrix}1 & \omega & \omega^{2}\\ \omega & \omega^{2} & 1\\ \omega^{2} & 1 & \omega\end{vmatrix}$$.
Prove the following :
$$\left| \begin{matrix} 2ab & a^{ 2 } & { b }^{ 2 } \\ a^{ 2 } & { b }^{ 2 } & 2ab \\ { b }^{ 2 } & 2ab & a^{ 2 } \end{matrix} \right| =-{ \left( { a }^{ 3 }+{ b }^{ 3 } \right) }^{ 2 }.$$
Let A be the matrix of order $$ 3 \times 3$$ such that $$|A| = 1,$$ $$B = 2A^{-1}$$ and $$C = \frac{(adj A)}{\sqrt[3]{2}}$$, then the value of $$|AB^2 . C^3|$$ is
[Note : |A| represent determinant value of matrix A.]
Prove the following :
$$\left| \begin{matrix} \dfrac { { a }^{ 2 }+{ b }^{ 2 } }{ c } & c & c \\ a & \dfrac { { b }^{ 2 }+{ c }^{ 2 } }{ a } & a \\ b & b & \dfrac { { c }^{ 2 }+{ a }^{ 2 } }{ b } \end{matrix} \right| =4abc$$
If A = $$\begin{bmatrix}
a \\[0.3em]
b \\[0.3em]
-a
\end{bmatrix}_{3\times1} \begin{bmatrix}
a & b & -a \\[0.3em]
\end{bmatrix}_{1\times3}$$ then find wheather $$A^{-1}$$ exists or not.
Solve: $$\begin{vmatrix}x & x^2 & yz\\ y & y^2 & zx\\ z & z^2 & xy\end{vmatrix} = (x - y)(y - z)(z - x)(xy + yz + zx)$$.
Find the value of $$x$$ for which the determinant $$\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{2x - 3}&{x - 2}&{x - 1}\\{x - 2}&{2x - 2}&x\\{x - 1}&x&{2x - 1}\end{array}} \right|$$ vanishes if
Show that:$$\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}a&b&c\\{a - b}&{b - c}&{c - a}\\{b + c}&{c + a}&{a + b}\end{array}} \right| = {a^3} + {b^3} + {c^3} - 3abc$$
Find the maximum value of
$$\begin{vmatrix} 1 & 1 & 1 \\ 1 & 1+\sin { \theta } & 1 \\ 1 & 1 & 1+\cos { \pi } \end{vmatrix}$$
Find the equation of line passing through the points $$(3,2)$$ and $$(-1,3)$$ by using determinants.
Find the determinant of the matrix
$$\begin{bmatrix} 3 & 1 \\ 5 & 2 \end{bmatrix}$$
Find the value of the determinant $$\begin{vmatrix} 2i & -3i \\ i^3 & -2i^ s \end{vmatrix}$$ where $$i=\sqrt{-i}$$
prove that $$\left| \begin{matrix} x+1 & 3 & 5 \\ 2 & x+2 & 5 \\ 2 & 3 & x+4 \end{matrix} \right| ={ \left( x-1 \right) }^{ 2 }\left( x+9 \right)$$
If $$\begin{vmatrix} 2 & -4 \\ 9 & d-3 \end{vmatrix} =4$$, then find the value of d.
$$\begin{vmatrix} \cos15^{\circ} & \sin15^{\circ} \\ \sin75^{\circ} & \cos75^{\circ} \end{vmatrix}$$
Find the value of $$x$$ if$$ \begin{vmatrix} 3 & 4 &1 \\0 & x & 8\\ 3 & -1 & 4\end{vmatrix}=0$$
For what value of x the matrix A is singular?
$$A= \begin{bmatrix} 1+x & 7 \\ 3-x & 8 \end{bmatrix}$$
Evaluate the following determinant : $$ \begin{vmatrix} a & h & g \\ h & b & f \\ g & f & c \end{vmatrix}$$
$$\text { Prove that: }\left|\begin{array}{ccc}a+b+2 c & a & b \\c & b+c+2 a & b \\c & a & c+a+2 b\end{array}\right|=2(a+b+c)^{3}\\$$
If the point $$(x,y),(a,0),0,b)$$ are collinear, prove that
$$\cfrac { x }{ a } +\cfrac { y }{ b } =1$$
If $$D_r=\begin{vmatrix}
2^{r-1} & 2(3^{r-1}) & 4(5^{r-1})\\
x & y & z\\
2^n-1 & 3^n-1 & 5^n-1
\end{vmatrix}$$ then prove that $$\displaystyle \sum_{r=1}^nD_r=0$$
The trace of a square matrix is defined to be the sum of its diagonal entries. If $$A$$ is a $$2 \times 2$$ matrix such that the trace of $$A $$ is $$3$$ and the trace of $$A^3$$ is $$-18$$, then the value of the determinant of $$A$$ is ______.
Class 12 Engineering Maths Extra Questions
- Continuity And Differentiability Extra Questions
- Determinants Extra Questions
- Differential Equations Extra Questions
- Integrals Extra Questions
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions Extra Questions
- Relations And Functions Extra Questions
- Three Dimensional Geometry Extra Questions
- Vector Algebra Extra Questions