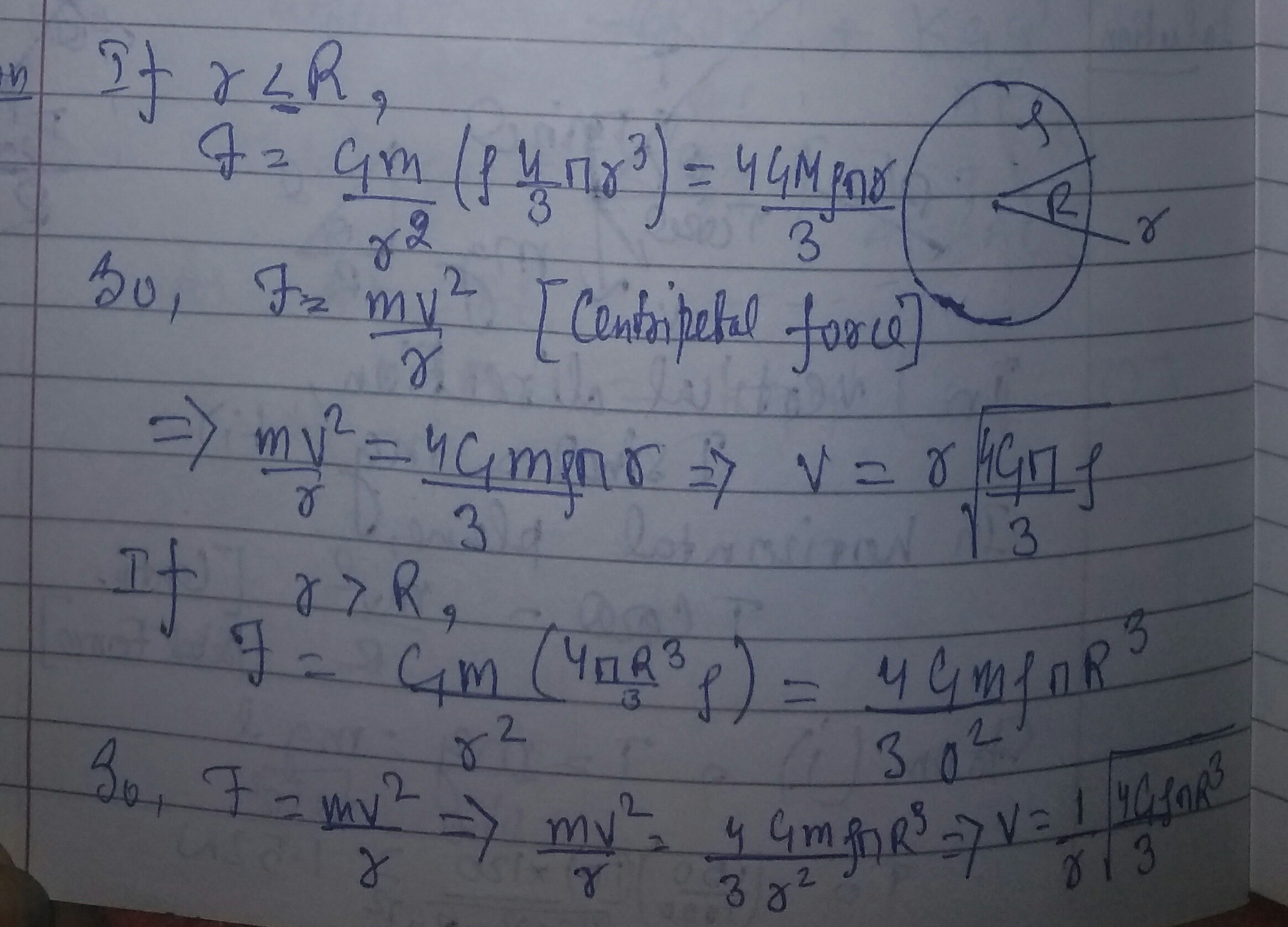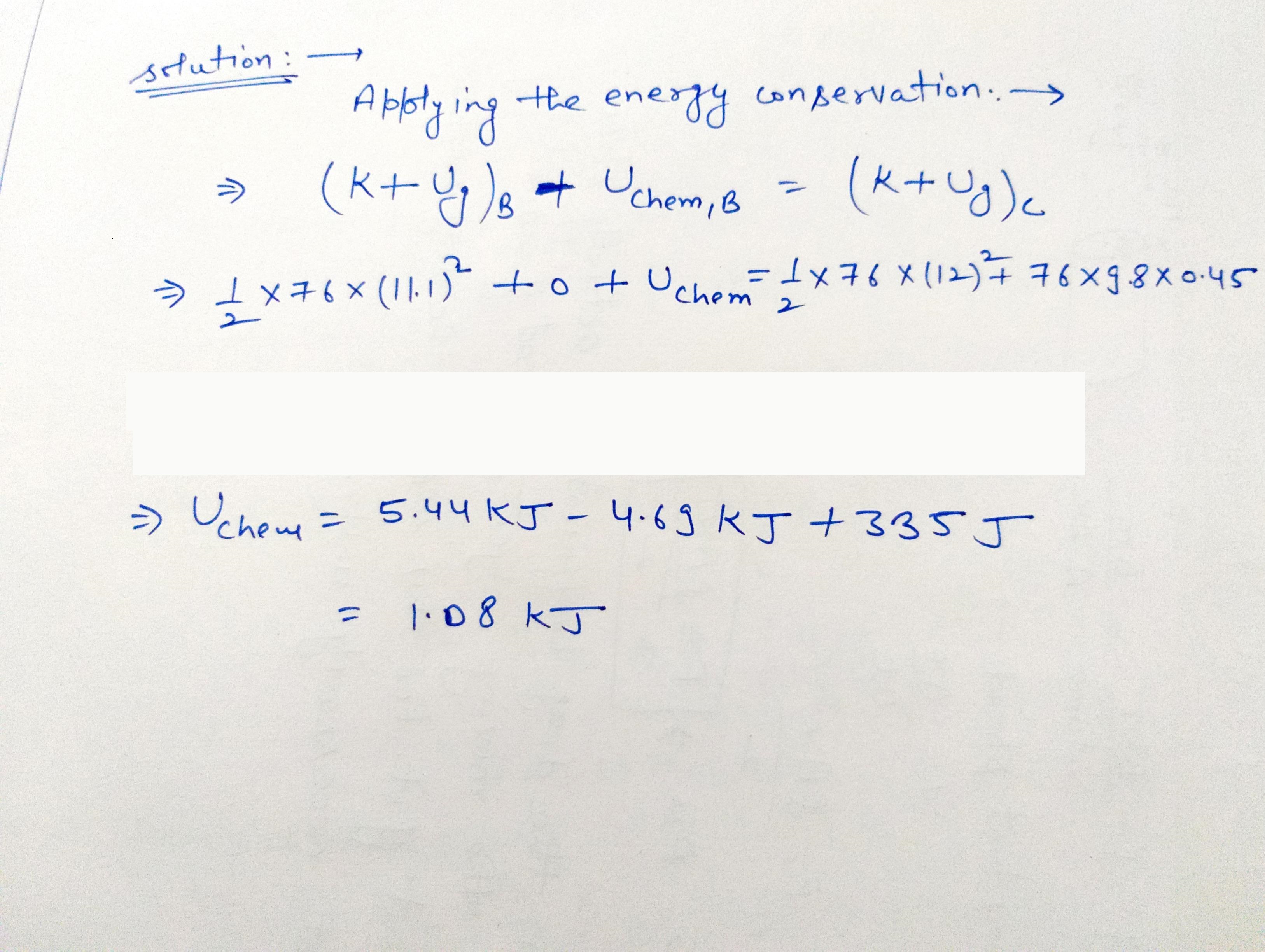Laws Of Motion - Class 11 Engineering Physics - Extra Questions
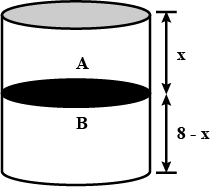
A thermally isolated cylindrical closed vessel of height 8m is kept vertically. It is divided into two equal parts by a diathermic (perfect thermal conductor) frictionless partition of mass 8.3kg. Thus the partition is held initially at a distance of 4m from the top, as shown in the schematic figure below. Each of the two parts of the vessel contains 0.1 mole of an ideal gas at temperature 300K. The partition is now released and moves without any gas leaking from one part of the vessel to the other. When equilibrium is reached, the distance of the partition from the top (in m) will be _______. (take the acceleration due to gravity =10ms−2 and the universal gas constant =8.3J mol−1K−1)
Distinguish between : Force and momentum.
The S.I unit of momentum is __________ .
Fill in the blanks with suitable words:
Newtons first law of motion is also called law of ________________.
The momentum of a massive object at rest is ________.
i) very large ii) very small iii) zero iv) infinity
An object of mass 1 kg is dropped from a height of 20 m. It hits the ground and rebounds with the same speed. Find the change in momentum. (Take g=10 m/s2)
Why we are hurt less when we jump on a muddy floor in comparison to a hard floor?
Why are seat belts designed in cars to stretch somewhat in a collision?
A force 0.7N acts on a body for 0.1 sec, then impulse is __________
Define : Acceleration.
Calculate the momentum of a toy car of mass 200g moving with a speed of 5m/s.
State Newton's third law of motion.
A ball of mass 0.5 gram is hit by battery switch giving an impulse of 0.075 N with what velocity does the ball move?
State first law of motion and explain it.
Momentum is a .............its unit is..........?
What is mass?
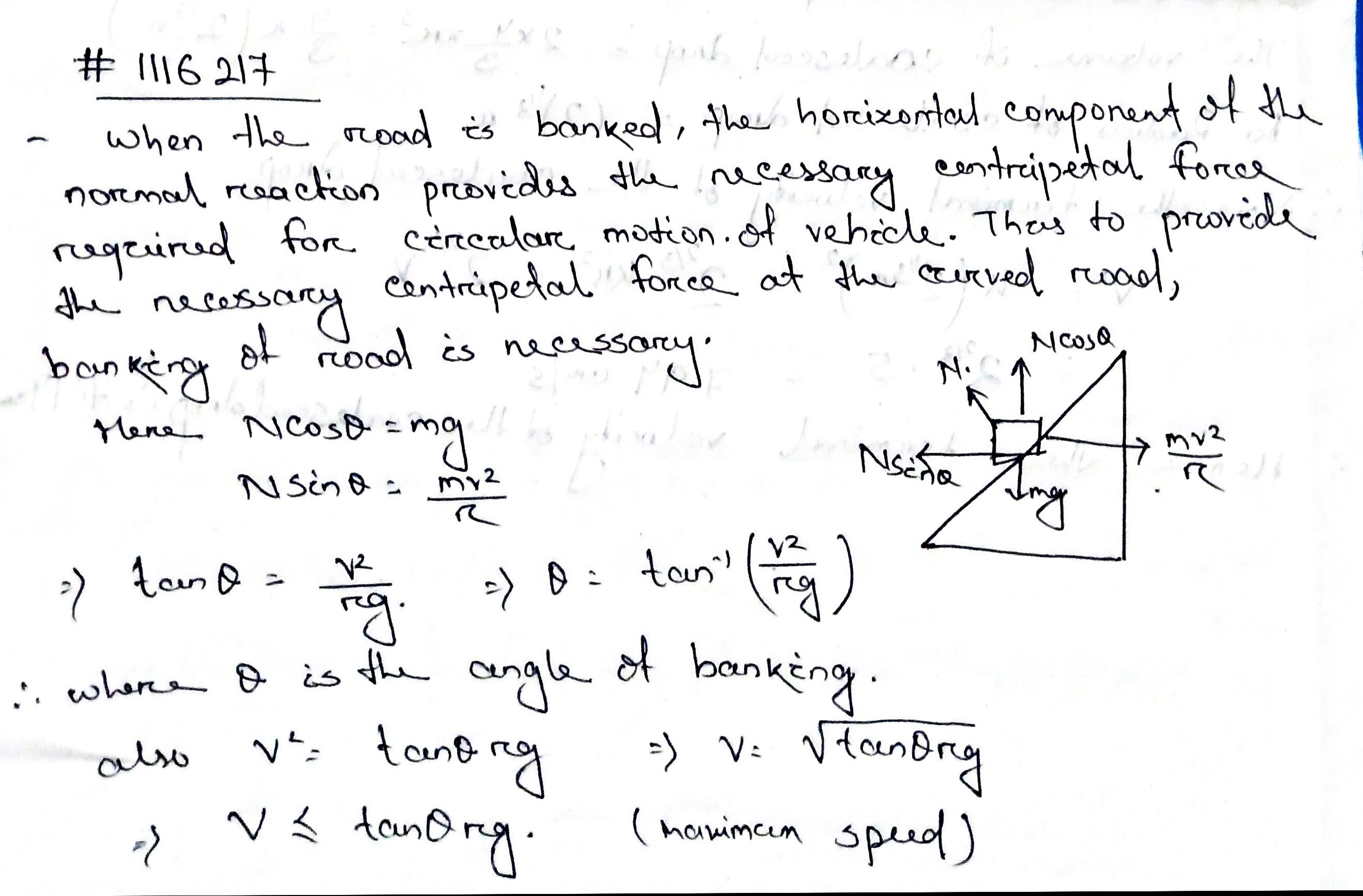
What is banking of roads? Give an example of it.
Define the following
Angular momentum
State reason
We are able to walk on the ground without slipping.
Give reason :-Hay or sponges are used while packing glassware. This helps to avoid breaking of glasswares due to collision.
Is the Galileo principle adopted by Newton is known as law of inertia?
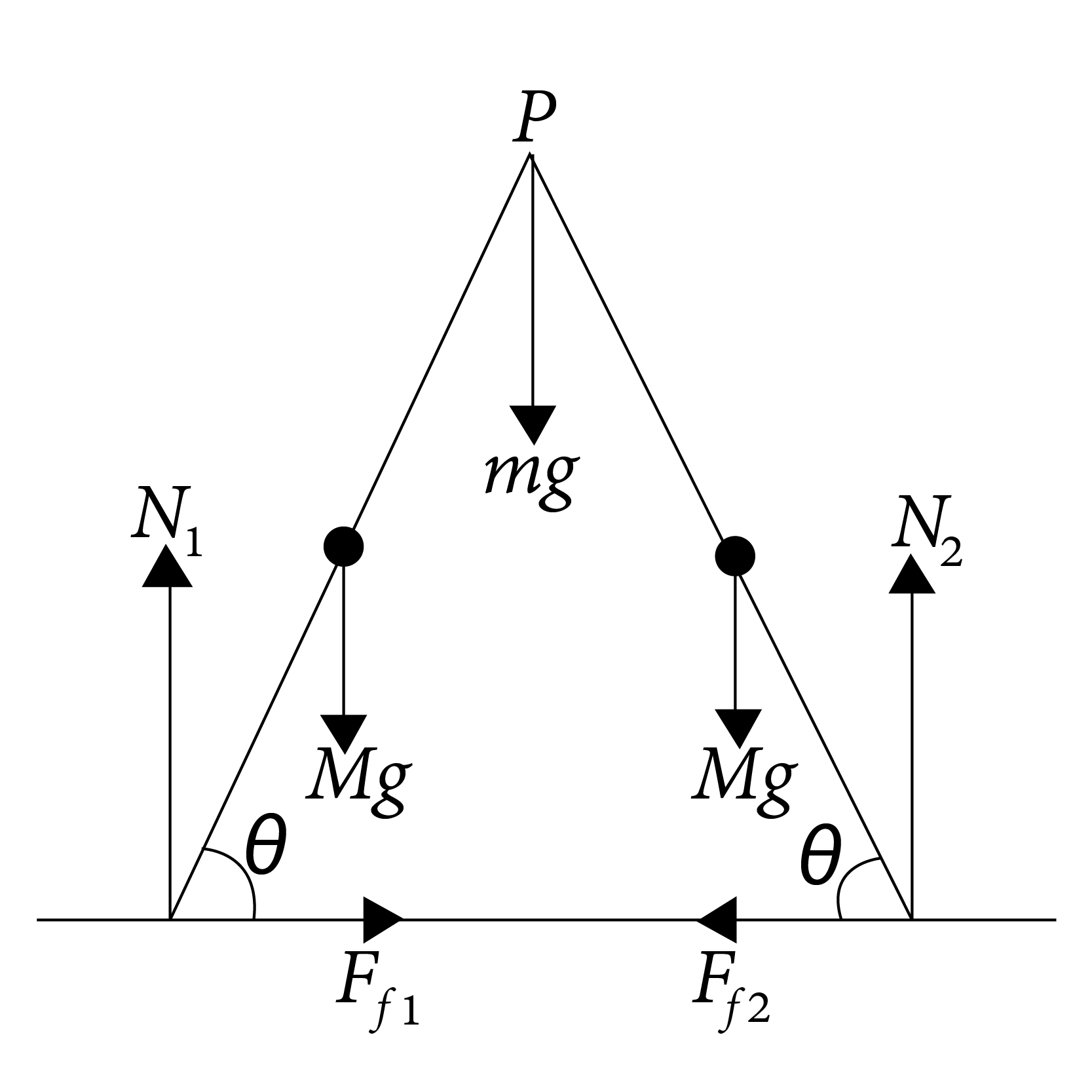
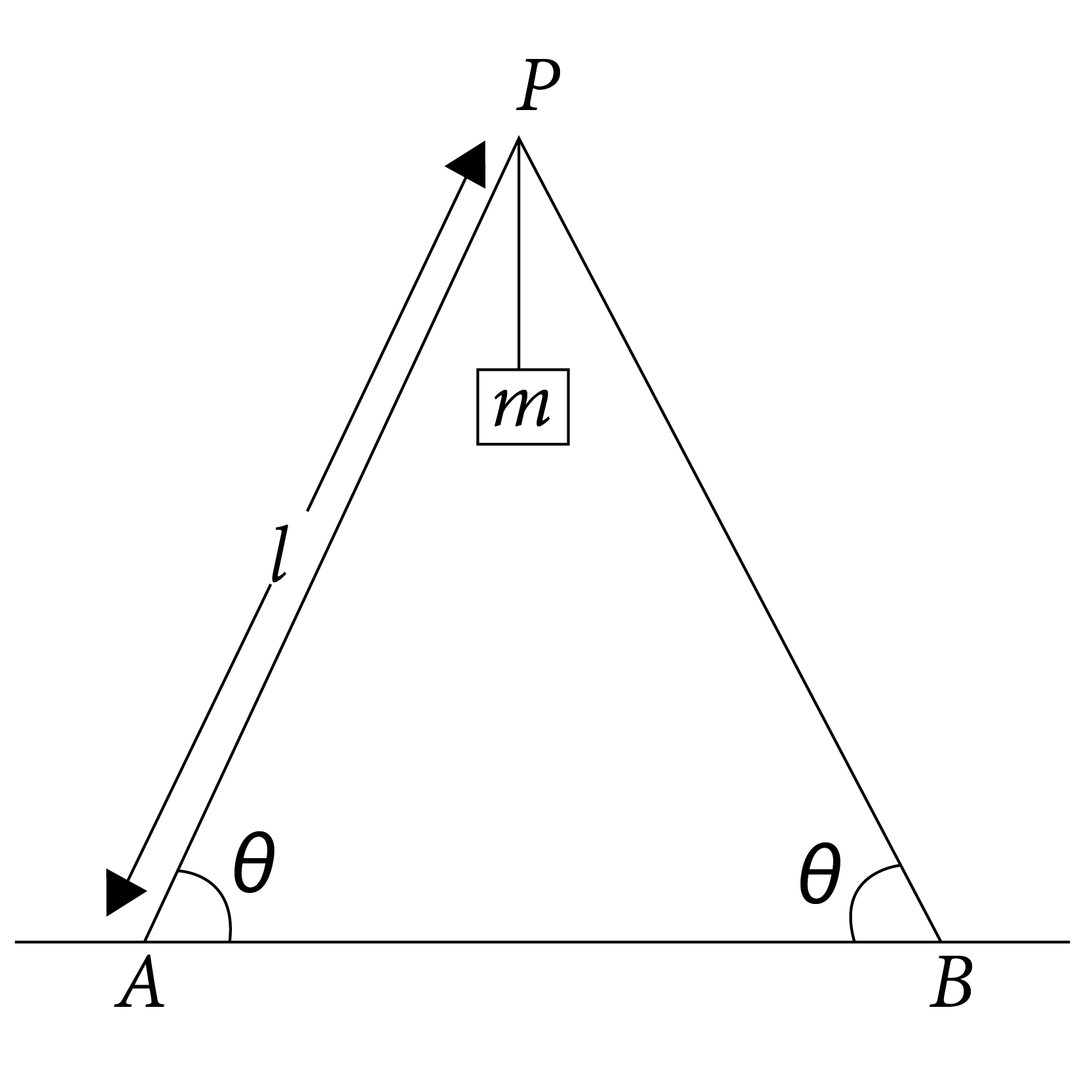
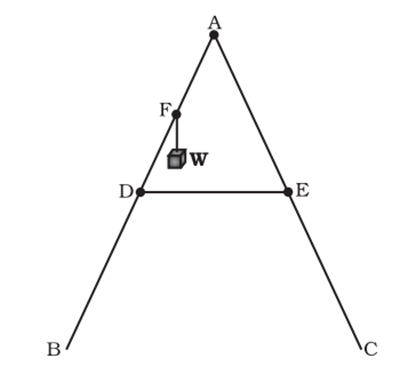
Two identical ladders, each of mass M and length l are resting on a rough horizontal surface as shown in Fig. A block of mass m hangs from P. If the system is in equilibrium, find the magnitude and the direction of frictional force at A and B
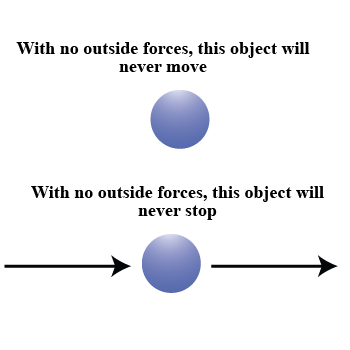
According to Newton's first law of motion, an object has a tendency to remain in its current position unless an external force is applied. Type 1 for true and 0 for false
Newton's 3rd Law states that to every action, there's an equal and opposite reaction, which means action and reaction are equal and opposite. State True or False.
Column I contains physical quantity/process while column II contains formula/principle. Match column I and II such that the formula/principle is correct corresponding to the quantity in column I.
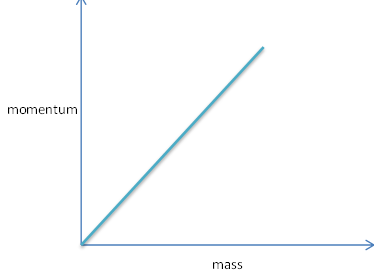
What is momentum? Write its SI unit. Interpret force in terms of momentum. Represent the following situation graphicallyMomentum versus mass when velocity is constant
Momentum versus mass when velocity is constant
A cyclist is riding with a speed of 27 km/h. As he approaches a circular turn on the road of radius 80 m, he applies brakes and reduces his speed at the constant rate of 0.50 m/s every second. What is the magnitude and direction of the net acceleration of the cyclist on the circular turn ?
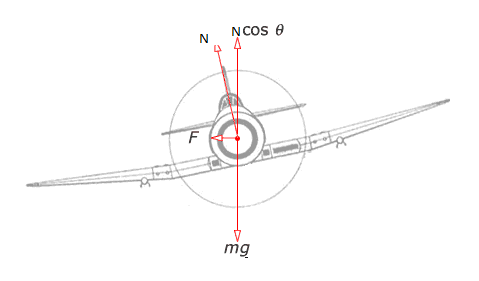
An aircraft executes a horizontal loop at a speed of 720 km/h with its wings banked at 150. What is the radius of the loop?
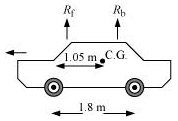
A car weighs 1800 kg. The distance between its front and back axles is 1.8 m. Its centre of gravity is 1.05 m behind the front axle. Determine the force exerted by the level ground on each front wheel and each back wheel.
Friction is much lesser in _____ than in sliding.
How much momentum will a dumb-bell of mass 10kg transfer to the floor if it falls from a height of 80cm ? Take its downward acceleration to be 10m s−2
A cricket ball of mass 120 g is moving with a velocity of 12ms−1, it turns back and move with a velocity of 20ms−1 when hit by a bat. Find the impulse and the force, if the force acts for 0.02 s.
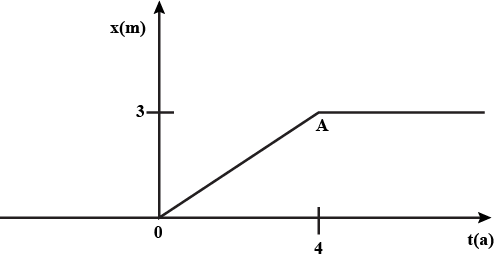
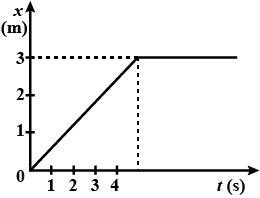
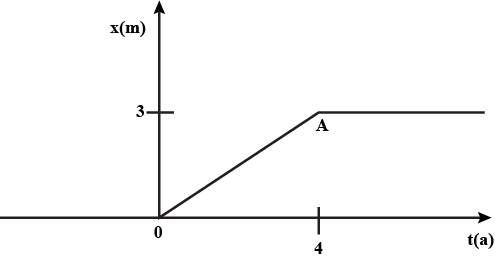
Figure given below shows the position-time graph of a particle of mass 4 kg. Find the impulse at t = 0 and t = 4 s. The motion may be considered one dimensional.

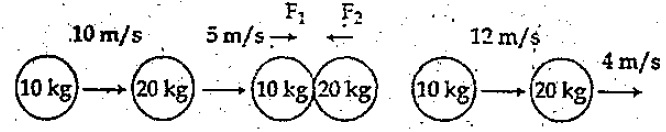
The figure represents two bodies of masses 10 kg and 20 kg and moving with an initial velocity of 10ms−1 and 5ms−1, respectively. They are colliding with each other, After collision, they are moving with velocities 12ms−1,4ms−1, respectively. The time of collision is 2s. Then calculate F1 and F2.
Two objects of same mass, namely A and B hit a man with a speed of 20 km/hr and 50 km/hr respectively and comes to rest instantaneously. Which object will exert more force on that man? Justify your answer.
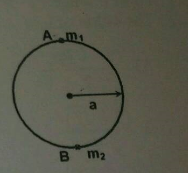
Two beads of masses m1 and m2 are threaded on a smooth circular wire of radius ′a′ fixed in a vertical plane. B is stationary at the lowest point when A is gently dislodged from rest at the highest point. A collides with B at the lowest point. The impulse given to B due to collision is just great enough to carry it to the level of the centre of the circle while A is immediately brought to rest by the impact. Find m1:m2
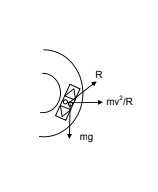
A train runs an unbanked circular bend of radius 30 m at a speed of 54 km/hr. The mass of the train is 106kg. What provides the necessary centripetal force required for this purpose. The engine or required to prevent wearing out of the rail?
A smooth wire is bent into a vertical circle of radius a. A bead P can slide smoothly on the wire. The circle is rotated about vertical diameter AB as axis with a constant speed as shown in figure. The bead P is at rest w.r.t the wire in the position shown. Then ω2 is equal to:

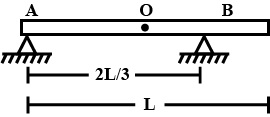
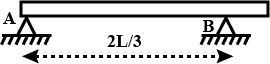
A uniform rod of length L and mass 2M rests over two supports A and B. A particle having mass, M is placed at the right end. Determine the reactions at supports A and B.
A ball of mass 1kg dropped from 9.8m height strikes the ground and rebounds to a height of 4.9m. If the time of contact between ball and ground is 0.1s, then find impulse and average force acting on ball.
Assuming frictionless contacts, determine the magnitude of external horizontal force P applied at the lower end for equilibrium of the rod as shown in figure. The rod is uniform and its mass is ′m′.

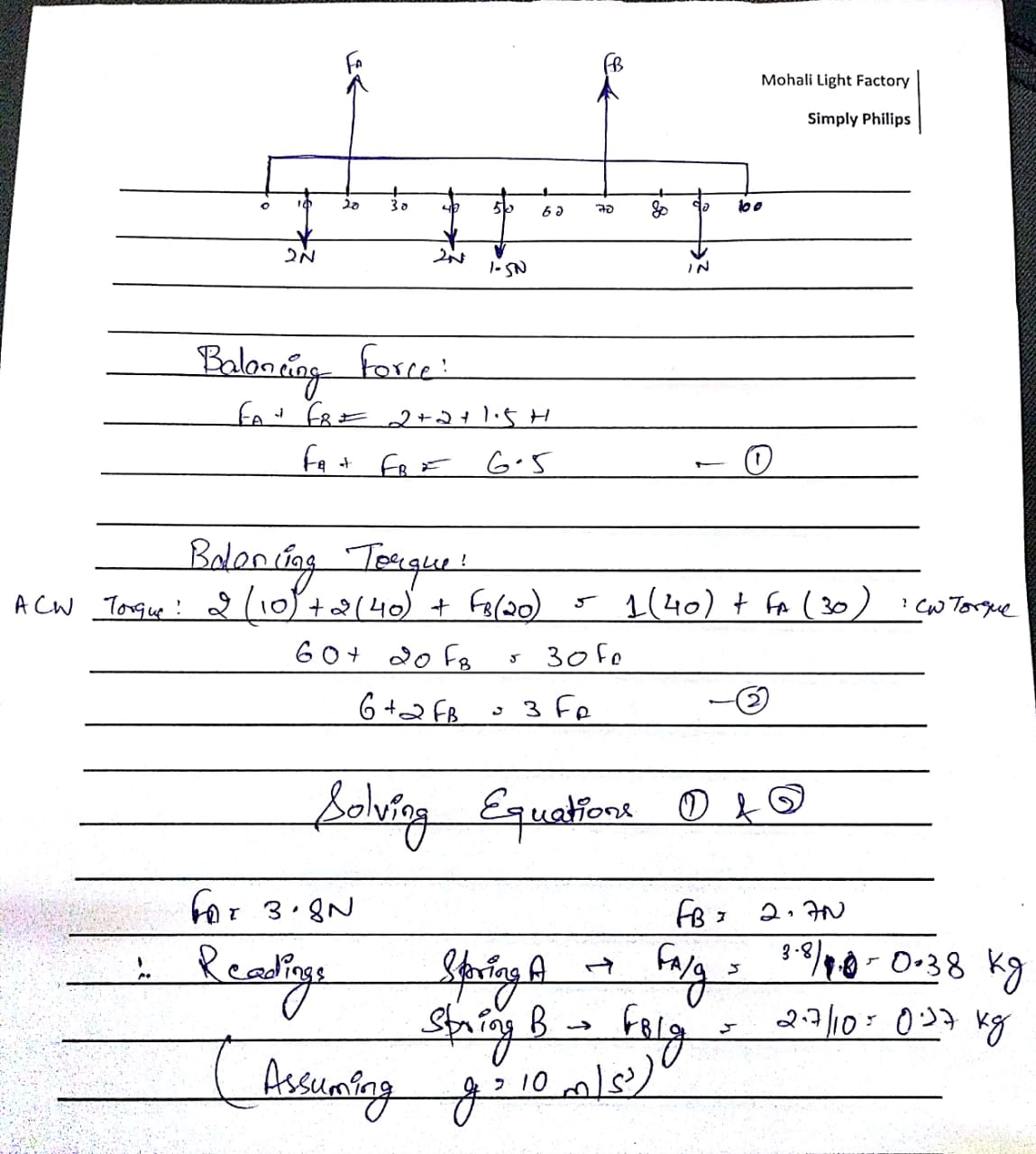
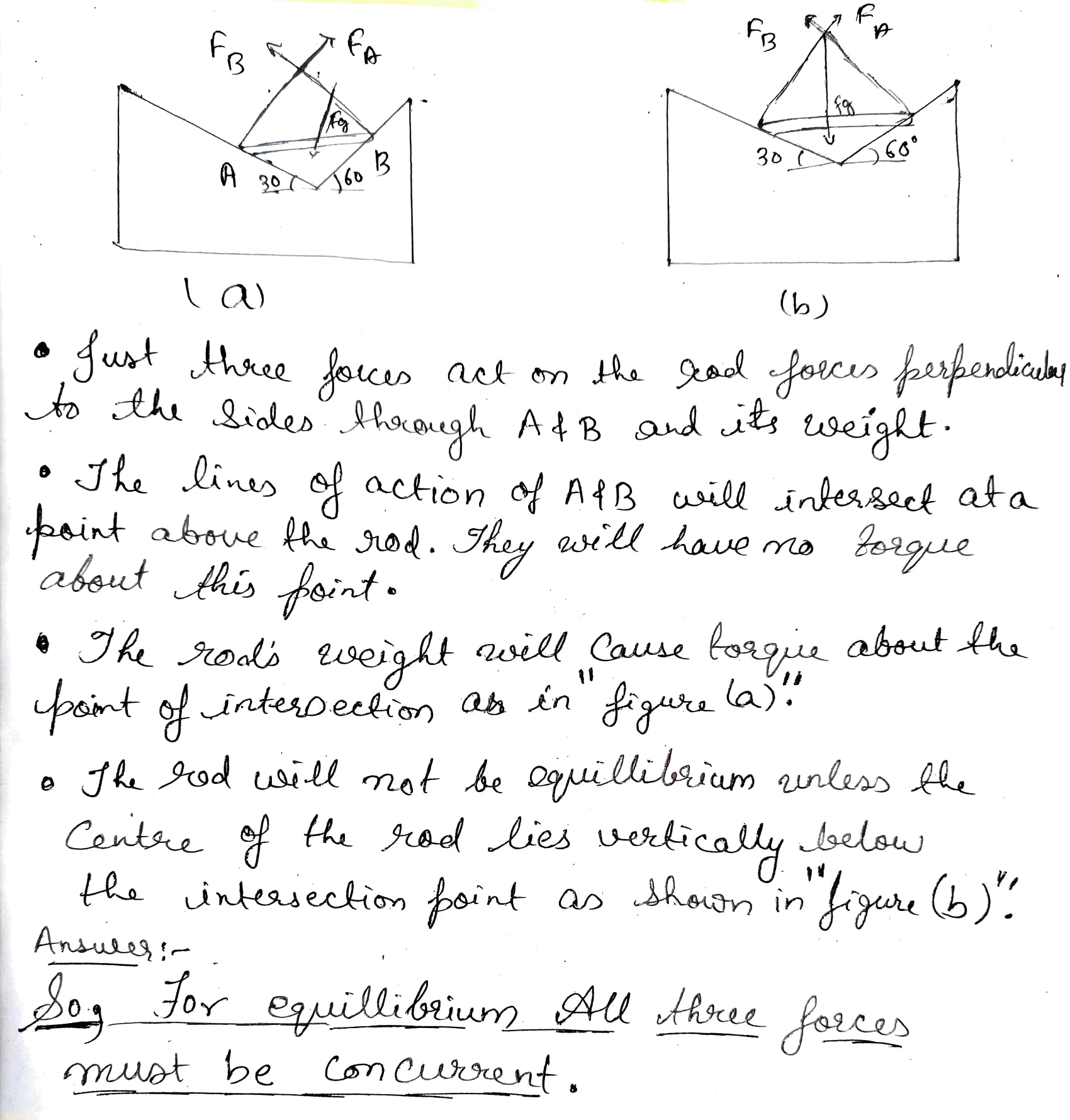
A meter stick is hung from two spring balances A and B of equal lengths that are located at the 20cm and 70cm marks of the meter stick. Weights of 2.0N are placed at the 10cm and 40cm marks, while a weight of 1.0N is placed at the 90cm mark. The weight of the uniform meter stick is 1.5N. Determine the scale readings of the two balances A and B.
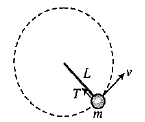
A block of mass 1 kg is tied to a string length 1m, the other end which is fixed. The block is moved on a smooth horizontal table with constant speed 10ms−1. Find the tension in the string.
A small block of mass 2m initially rests at the bottom of a fixed circular , vertical task ,which has a radius of R. The contact surface between the mass and loop is frictionless. A bullet of mass m strikes the block horizontally with initial speed v0 and remain embedded in the block as the block and the bullet circle the loop. Determine each of the following in terms of m, v0, R and g.
a)The speed of the masses immediately after the impact.
b)The minimum initial speed of the bullet if the block and bullet are to successfully execute a complete ride on the loop.

A 150g cricket ball moving at a speed of 12m/s is hit by a bat and turned back at a speed of 20m/s. The duration of impact is 0.1s. What is the average force exerted on the ball by the bat?
An aircrafts executes a horizontal loop at a speed of 720km/h with its wings banked at 15o. What is the radius of the loop?
A point source of light is placed at the centre of curvature of a hemispherical surface. The radius of curvature is r and the inner surface is completely reflecting. Find the force on the hemisphere due to the light falling on it if the source emits a power W.
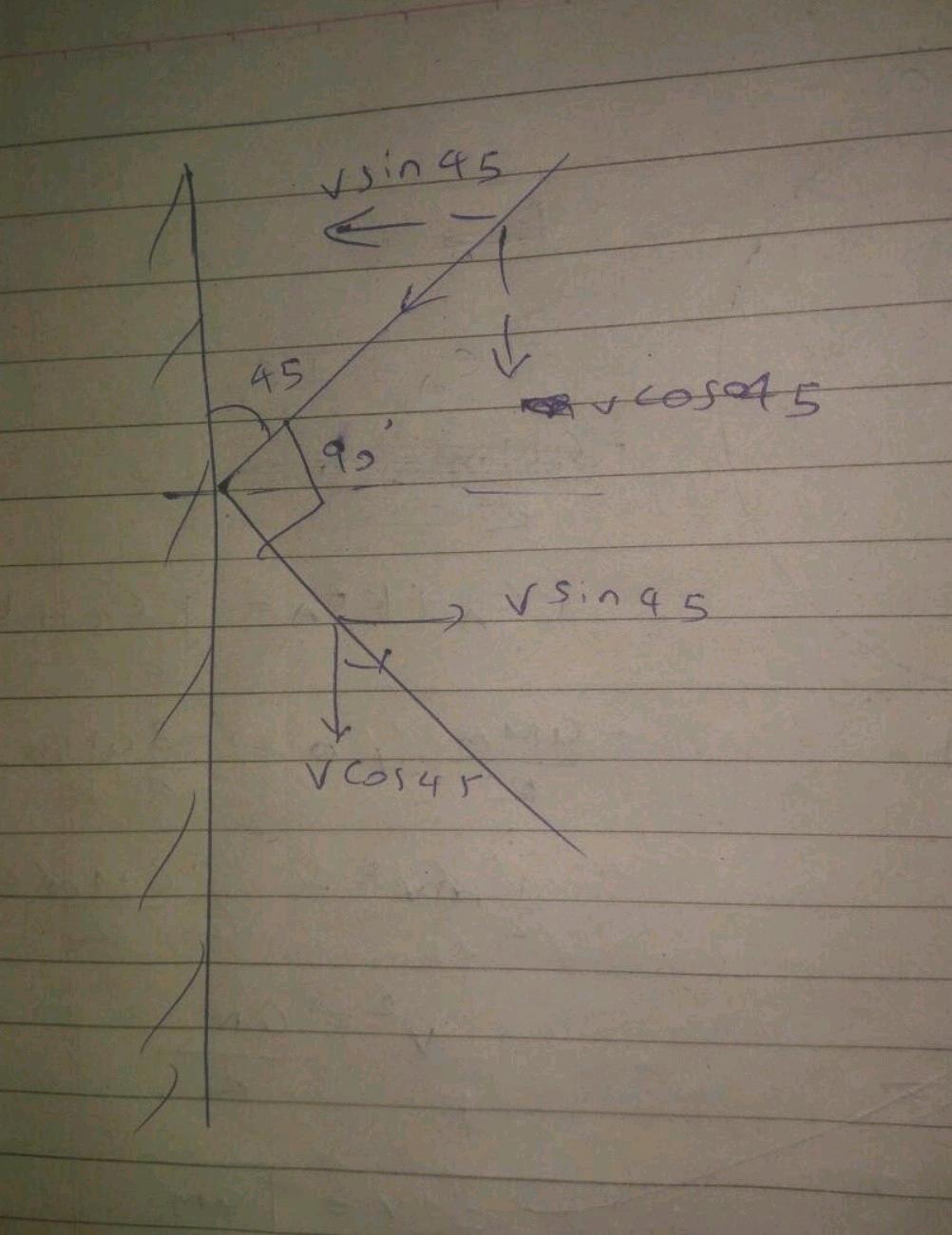
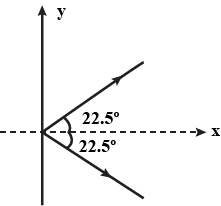
A ball of mass 20g hits a wall at an angle 45∘ with a velocity of 15ms−1. If the ball rebounds at 90∘ to the direction of incidence, calculate the impulse received by ball.
A bullet of mass 0.1 kg moving horizontally with a velocity of 20 m/s strikes a target and brought to rest in 0.1 s. Find the impulse and average force of impact.
A ball of mass 5 Kg strikes against wall at an angle of 45o and is reflected at the same angle. Find the change in momentum.
State and explain the Newton's first law of motion.
State and prove the law of conservation of momentum.
A train runs along an unbanked circular track of radius 30m at a speed of 54km/h. The mass of the train is 106kg. What provides the centripetal force required for this purpose-the engine or the rails? What is the angle of banking required to prevent wearing out of the rail?
A cyclist turns around a curve at 15 km/hr if he turns at double the speed the tendency to overturn is.
A bullet of mass 0.1kg moving horizontally with a velocity of 20m/s strikes a stationary target & is brought to rest in 0.1s. find the impulse & average force of impact
A ball of mass 100 gm is hit by hockey stick giving an impulse of 0.083Nm, with what velocity does the ball move?
A circular road of radius 50m has the angle of banking equal to 30o. At what speed should a vehicle go on this road so that the friction is not used?
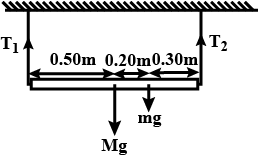
A uniform metre stick of mass 200 g is suspended from the ceiling through two vertical strings of equal lengths fixed t the ends. A small object of the mass 20 g is placed on the stick at the distance of 70 cm from the left end. Find the tension in two strings.
What is the need for banking a road ? Obtain an expression for the maximum permissible speed with which a car can safely turn on a curved road banked at an angle θ.
What is impending motion?
Determine the maximum acceleration of the train in which a box lying on its floor will remain stationary μ=0.15.
Does force of gravity act on dust particles?
A man is pushing a cart down in slope. Suddenly the cart starts moving faster and he wants to slow it down. What should he do?
While sieving grains, small pieces fall down. Which force pills them down?
A turn of radius 600 m is banked for a vehicle of mass 200 kg going with a speed of 1800 kmh−1. Determine the banking angle of its path.
An object of mass m1 moving with speed v collides with another object of mass m2 at rest and stick to it. Find the impulse to the second object.
Two cars A and B start from the same starting point. A is starting from rest and moving with constant acceleration 2 m/s2 and car B is starting with a constant velocity 40 m/s. After what time both cars will meet each other?
Fill the following table
| S. No | physical Quality | Formula | Units |
| 1 | Force | Newton | |
| 2 | Momentum | p = mv | Newton field |
| 3 | Impulse | Newton. sec | |
| 4 | Acceleration | v−ut | Newton first |
A sperically symmetric granitational syatem of particles has a mass density s { ρ for r ≤ R & O for r > R } where ρ is a const.
A test mass can undergo circular motion under the influence of granitational field of particles. Its speed is v as a function of hit r from centre of system is represented by
An object mass m1 moving with speed v collides with another object of mass m2 at rest and stick to it. Find the impulse imparted to the second object.
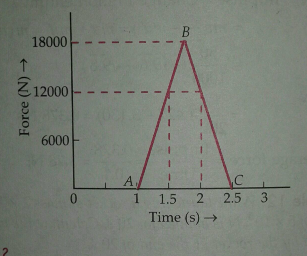
The figure shows an estimated force time graph for a baseball stuck by a bat.
From the curve determine:(i) impulse delivered to the ball (ii) force exerted on the ball(iii) the max. force on the ball.
A bullet of mass 60g moving with the velocity of 500m/s is brought to rest in 0.01s. Its impulse will be?
An electron is moving in a circular path with a radius of 10 cm with a constant speed of 5∗106 m/s. The current constituted in the circular path is
Can the coefficient of the friction be grater than one?
State the expression of kinetic energy of a rolling body on the horizontal surface. Hence deduce its expression for a disc rolling with velocity v on the surface.
An athlete runs for a certain distance before taking long jump, Why?
Why is it difficult for a fireman to hold a hose, with ejects large amount of water at a high velocity ?
The position-time graph of a body of mass 2 kg is as given in the figure. Calculate the impulse on the body at t=0 second and t=4 second.
Write the S.I. unit of momentum .
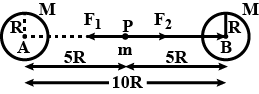
Two identical heavy spheres are separated by a distance of 10 times their radius. will an object placed at the midpoint of the line joining their centers be in stable equilibrium or unstable equilibrium ? Give reason for your answer.
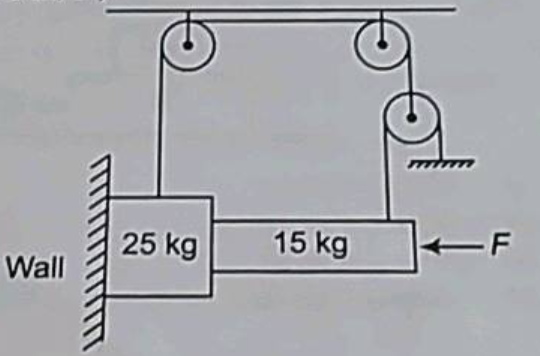
If coefficient of friction between all surfaces is 0.4, then find the minimum force F to have equilibrium of the system. (Take g = 10ms2 )
The troops (soldiers) equipped to be dropped by parachutes from an aircraft are called paratroopers. Why do paratroops roll on landing?
Explain how, a karate player can break a pile of tiles with a single blow of his hand.
A ball is moved on a horizontal table with some velocity. The ball stops after moving some distance. Which external force is responsible for the change in the momentum of the ball ?
A park has a radius of 10m. If a vehicle goes round it at an average speed of 18km/hr. what should be the proper angle of banking?
With which physical quantity should the speed of a running bull be multiplied so as to obtain its momentum?
Newton's first law of motion is also called Galileo's law of......
Explain why it is easier to stop a tennis ball than a cricket ball moving with the same speed.
What is the other name of Newton's first law of motion?
Name the physical quantity that is considered to be a measure of the quantity of motion of a body.
What name is given to the product of mass and velocity of a body?
Name the physical quantity whose unit is kg.m/s.
What is the change in momentum of a car weighing 1500 kg when its speed increases from 36 km/h to 72 km/h uniformly?
Why the road accidents at high speeds very much worse than road accidents at low speeds?

State Newton's third law of motion and give two examples to illustrate the law.
A moving bicycle comes to rest after sometime if we stop pedalling it.But Newton's first law of motion says that a moving body should continue to move for ever, unless some external force acts on it.How do you explain the bicycle case?
Explain why,a person travelling in a bus falls forward when the bus stops suddenly.
Which physical quantity corresponds to the rate of change of momentum?
What is the momentum in kg.m/s of a 10 kg car travelling at (a) 5 m/s (b) 20 cm/s and (c)36 km/h?
A plastic ball and a clay ball of equal masses, travelling in the same direction with equal speeds,strike against a vertical wall.from which ball does the wall receive a greater amount of momentum?
To every action,there is an.......... and ............. reaction
State Newton's first low of motion.Give two examples to illustrate Newton's first law of motion.
Calculate the momentum of the following:
a an elephant of mass 2000 kg moving at 5 m/s
b) a bullet of mass 0.02 kg moving at 400 m/s.

A bowler runs a long distance before bowling from the bowling line. Why?
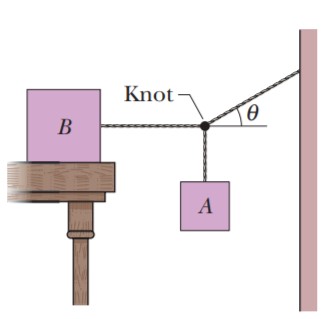
Block B in Fig. weighs 711 N.The coefficient of static friction between the block and the table is 0.25; angle θ is 30∘; assume that the cord between B and The knot is horizontal. Find the maximum weight of block A for which the system will be stationary.
Why does your foot hurt more when you kick a stone than when you hit a football?
Two rods of the same weight and equal length have different thicknesses. They are held vertically on the surface of sand as shown in Figure. Which one of them will sink move? Why?
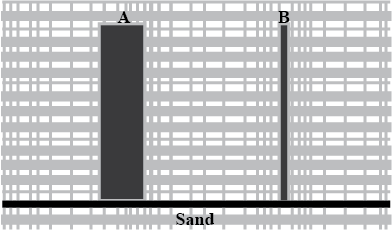
A ball of dough is rolled into a flat chapatti. Name the force
exerted to change the shape of the dough.
A piece of paper can be jerked out from under a book quickly without moving the book. Why?
Two blocks of iron of different masses are kept on a cemented floor as shown in Figure. Which one of them would require a larger force to move it from the rest position?
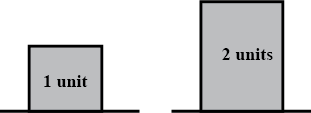
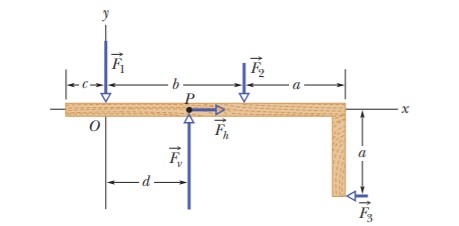
Forces →F1,→F2 and →F3 act on the structure of Figure, shown in an overhead view. We wish to put the structure in equilibrium by applying a fourth force, at a point such as P. The fourth force has vector components →Fh and →Fv.We are given that a=2.0m,b=3.0m,c=1.0m,F1=20N,F2=10N, and F3=5.0N. Find (a) Fh, (b) Fv, and (c) d.
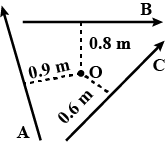
A.B and C are the three forces each of magnitude 4 n acting in the plane of the paper as shown in the figure. The point O lies in the same plane.
Which force has the least moment about O? Give a reason.
A woman throws an objects of mass 500 g with speed of 25 ms−1.
(a) What is the impulse imparted to the objects?
(b) If the object hits a wall and rebounds with half the original speed, what is the change in momentum of the object?
Two friends on roller skates are standing 5 m apart facing each other. One on the left throws a ball of 2 kg towards the other, who catches it. How will this activity affect the position of the one on the right?
Fill in the blanks:
The force of friction acting between two bodies in contact while at rest is known as _______ friction.
What do you mean by the equilibrium of a body?
State Newton's first law of motion. Why is it called the law of inertia?
Why does a child feel more pain when she/he falls down on a hard cement floor than when she/he falls on the soft muddy ground in the garden?
Explain the following :
When a train suddenly moves forward, the passenger standing in the compartment tends to fall backwards.
State the condition when a body is in (i) static (ii) dynamic. equilibrium. Give one example
each of static and dynamic equilibrium.
State Newton's first law of motion.
Two equal and opposite forces act on a moving object. How is its motion affected? Give reason.
Why does a coin placed on a card, drop into the tumbler when the card is flicked with the finger?
Name the factor on which inertia of a body depends and state how it depends on the factor stated by you.
Give one example of each of the following :
Inertia of rest,
State two condition for a body acted upon by several forces to be in equilibrium.
Give qualitative definition of force on the basis of Newton's first law of motion.
A body of mass 5kg is moving with the velocity with 2m/s. Calculate its linear momentum.
A force of 10N acts on a body of mass 2kg for 3s, initially at rest. Calculate:
change in momentum of the body.
A car is moving with a uniform velocity of 30m/s. It is stopped in 2s by applying a force of 1500N through its brakes. Calculate: (a) the change in momentum of car,
The linear momentum of a ball of mass 50g is 0.5kg m/s. Find its velocity.
Explain the following :
Dust particles are removed from a carpet by beating it.
What Is banking of roads?
What is an impulsive force?
State Newton's first law of motion and give its one example.
Two billiard balls each of mass 0.05 kg moving in opposite directions with speed 6ms−1 collide and rebound at the same speed. What is the impulse imparted to each bail due to the other?
Explain Newton's first law of motion.
What is the resultant force of balanced forces?
Write an expression of impulse for force.
A batsman deflects a ball by an angle of 450 without changing its initial speed which is equal to 54 km/h. What is the impulse imparted to the ball? (Mass of the ball is 0.15 kg.)
Static friction is a self-adjusting force comment.
What provides the centripetal force for a car taking a turn on a level road.
What is angle of banking? Give the expression for it.
Can a moving body be in equilibrium?
What is the angle of banking for a curve road radius 180m suitable for a maximum speed of 30m? Calculate the maximum speed to be maintained when the angle of banking is θ=30o(g=9.8ms−2)
What is limiting friction?
Define Impulse of a force and Impulsive force.
Two heavy spheres each of mass 100 kg and radius 0.10 m are placed at the midpoint of the line joining the centres of the spheres ? is an object placed at that point in equilibrium ? if so , is the equilibrium stable or unstable?
Calculate the Impulse of a force of 50 N acting for 0.1s.
Find out the reasons
An athlete doing a long jump-start run from a distance.
Observe the figure and answer the question.
What is the law to which this property is related?
Bring the two marbles into contact and let them roll. What happens?
Find out reasons for the situations
Accidents that happen to passengers who do not wear seat belts are more fatal.
Move the first marble slightly back and roll forward. What happens?
If a tennis ball (mass 58.5 g) and a cricket ball (mass 163 g) are the reach a certain distance when hit with a cricket bat, which is to be hit with greater force? The tennis ball/ the cricket ball?
State the Newton's laws of motion. Write any two illustrations
A body is moving on a frictionless curved path of radius of 1.8 km with a speed of 30 ms−1. Find the banking angle required.
A bullet of mass 25kg is fired from a rifle of mass 2kg. Imagine
State reason
The moving parts of machines experience wear and tear.
A loaded lorry of mass 1500 kg moves with a velocity of 12 m/s. Within a small interval of the time, the velocity becomes 10 m/s
What is the change in momentum?
Observe the figure and answer the question.
How is this property related to the mass of the object?
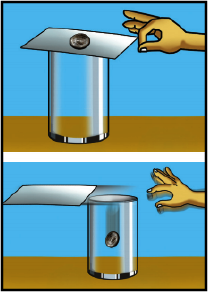
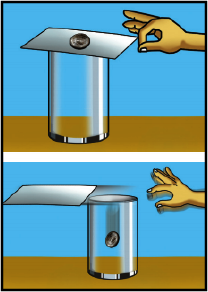
What are the balanced forces acting on a book at rest on a table?
Prepare and present an experiment to illustrate inertia of rest.
To remove the dust from a carpet, it is suspended and hit with a stick. What is the scientific principle behind it?
What is meant by momentum?
Find out situations form our daily life to explain the law of conversion of momentum and note them down.
You are standing on a saucer-shaped sled at rest in the middle of a frictionless ice rink. Your lab partner throws you a heavy Frisbee. You take six different actions in successive experimental trials. Rank the following situations according to your final speed from largest to smallest. If your final speed is the same in two cases, give them equal rank. (a) You catch the Frisbee and hold onto it. (b) You catch the Frisbee and throw is back to your partner. (c) You bobble the catch, just touching the Frisbee so that it continues in its original direction more slowly. (d) You catch the Frisbee and throw it so that it moves (e) You catch the Frisbee and throw it so that it moves vertically upward above your head. (f) You catch the Frisbee and set it down so that it remains at rest on the ice.
Can an object be in equilibrium if it is in motion? Explain.
The mass of a roller-coaster car, including its passengers, is 500kg. Its speed at the bottom of the track in above figure is 19m/s. The radius of this section of the track is r1=25m. Find the force that a seat in the roller-coaster car exerts on a 50kg passenger at the lowest point.

Which of the following options is correct to keep the ruler in equilibrium when 40 gf wt is shifted to 0cm mark?
F is shifted towards 0cm or
F is shifted towards 100cm.
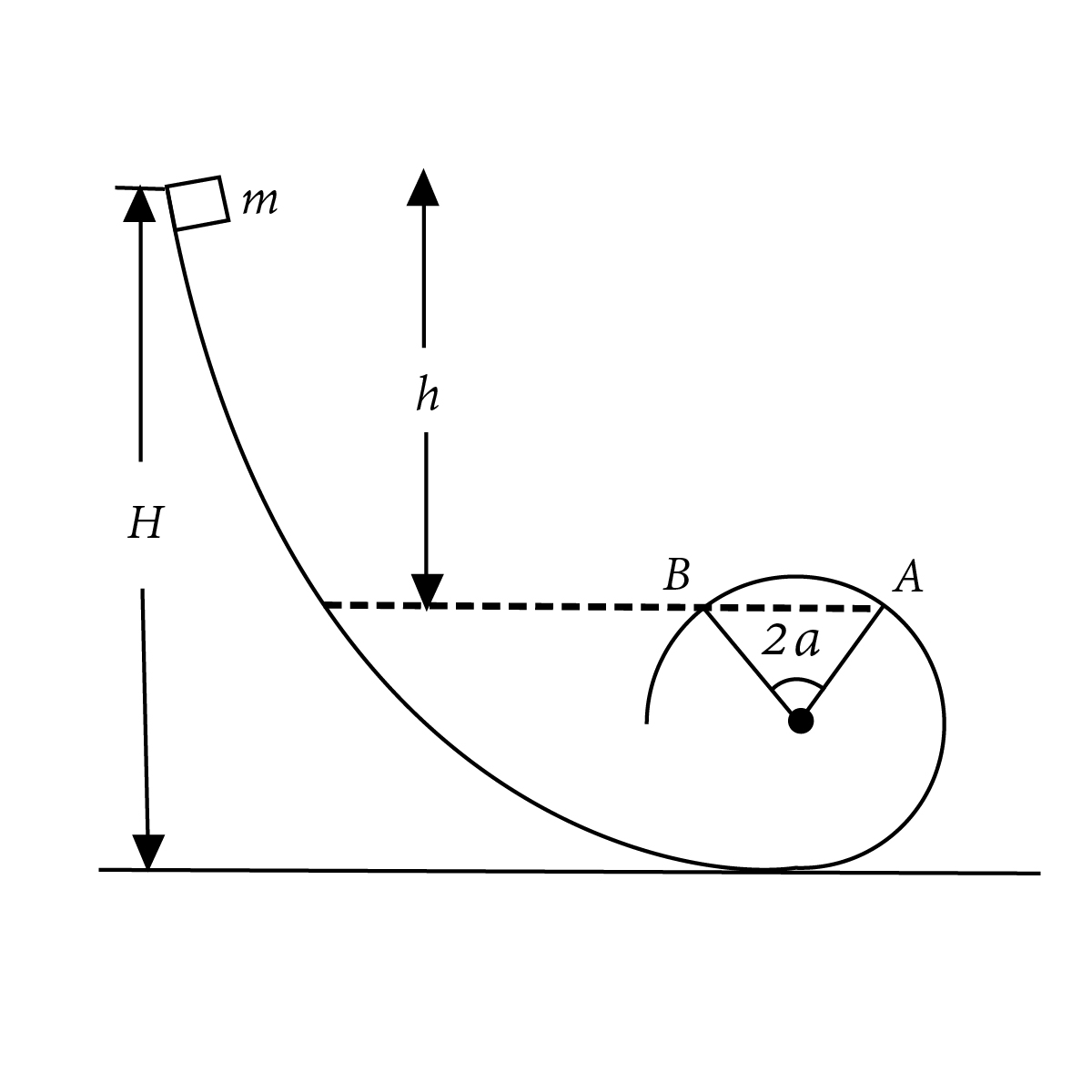
A small object slides without friction from the height H=50cm and then loops the vertical loop of radius r=20cm from which a symmetrical section of angle 2 α has been removed. Find angle α such that after losing contact at A and flying through air, the object will reach point B.
A 3 m long ladder weighing 20 kg leans on a frictionless wall. Its feet rest on the floor 1 m from the wall as shown in Fig. Find the reaction forces of the wall and the floor.
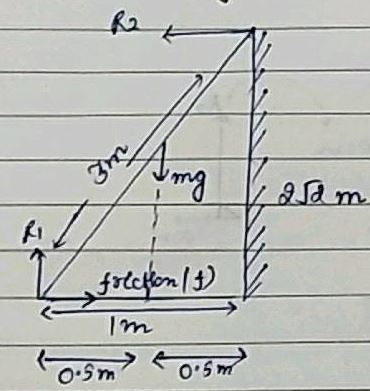
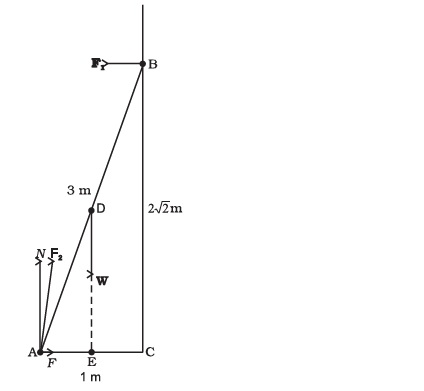
As shown in Fig., the two sides of a step ladder BA and CA are 1.6 m long and hinged at A. A rope DE, 0.5 m is tied half way up. A weight 40 kg is suspended from a point F, 1.2 m from B along the ladder BA. Assuming the floor to be frictionless and neglecting the weight of the ladder, find the tension in the rope and forces exerted by the floor on the ladder. (Take g = 9.8 m/s2) (Hint: Consider the equilibrium of each side of the ladder separately.)
What is banking of roads? Obtain an expression for the maximum safety speed of a vehicle moving along a curved horizontal road.
A 10kg block is pulled on the vertical plane along a frictionless surface in the form of an arc of a circle of radius 10m. The applied force is of 200N as shown in the figure. If the block started from rest at A, what is the velocity at B?
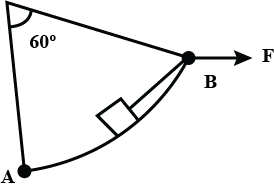
A sphere of mass m and radius R rests on sufficiently rough inclined plane in equilibrium as shown in the figure. Find the tension in the string.

Two balls of mass m and 2m are connected by a light inextensible string. The string is initially slack. The heavier ball is given velocity v0 towards the right. Find impulse by the string on the ball of mass m when the string becomes tight.

A uniform chain of mass M and length L is held vertically in such a way that its lower end just touches the horizontal floor. The chain is released from rest in this position. Any portion that strike the floor comes to rest. Assuming that the chain does not form a heap on the floor, calculate the force exerted by it on the floor when a length x has reached the floor.
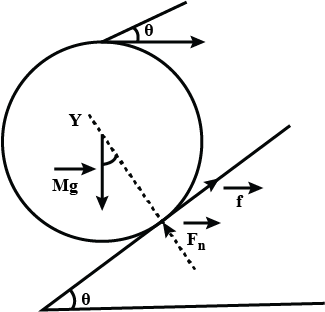
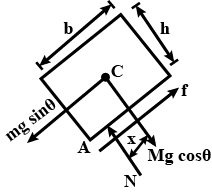
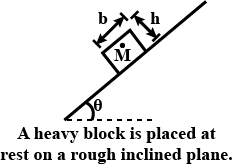
A heavy block of length b and height h is placed at rest on a rough inclined plane of inclination θ with the horizontal, as shown in figure.
(a) The normal reaction from the surface cannot pass through the centre mass.Why?
(b) If μ is the coefficient of friction between the block and the inclined plane, then discuss the conditions of translational and rational equilibrium of the block.
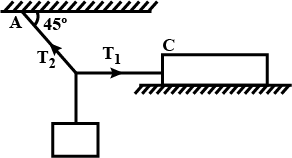
Define impulse. Two blocks of masses 10g and 30g are fastened to the ends of a cord which passes over a frictionless pulley. The 10g block rests on the table. What minimum force must be applied on the 10g block to keep it on the table? What will be the tension in the cord under this condition? What will be the acceleration of the system and the tension in the cord when the force is withdrawn?
(g=9.8ms−2)

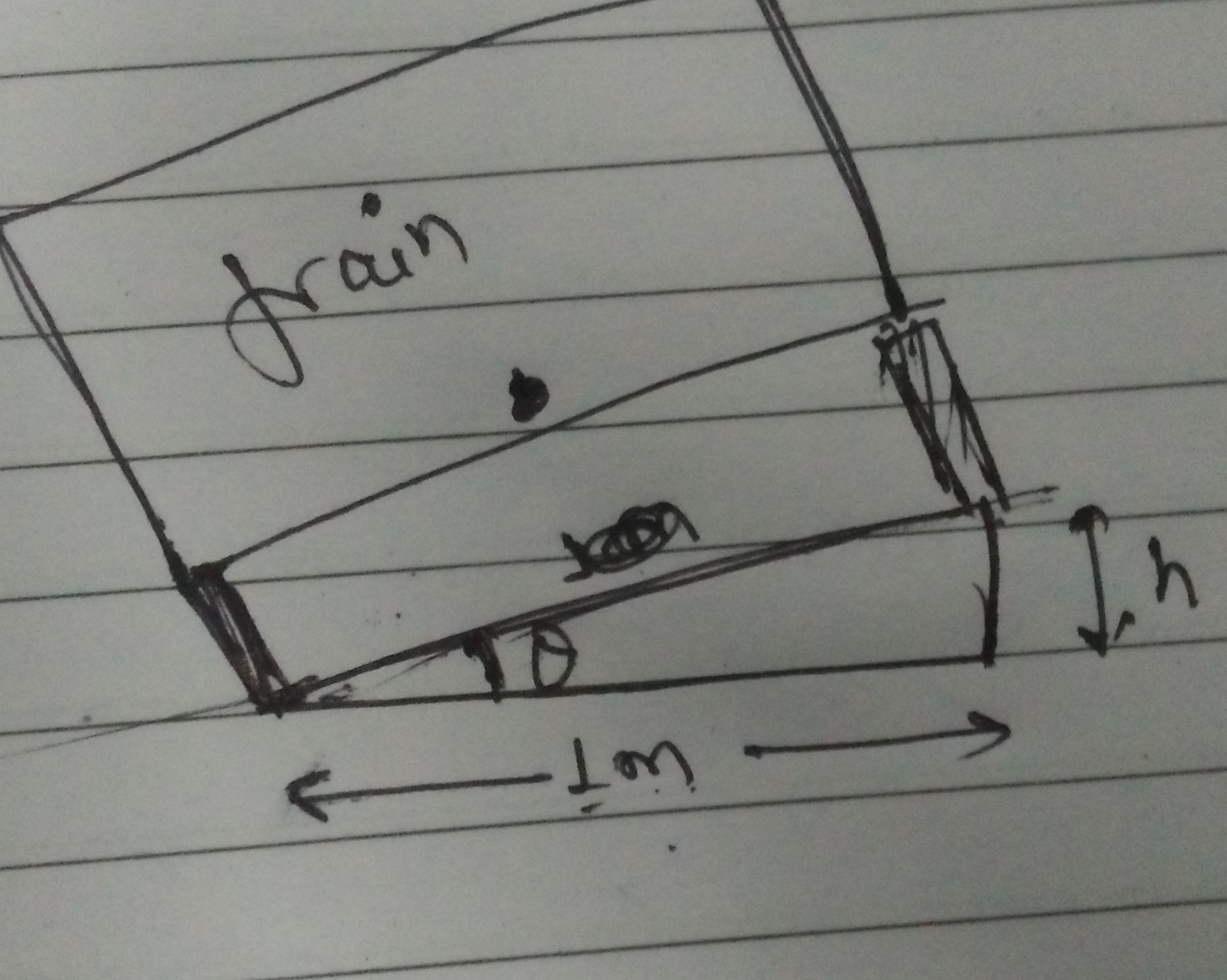
A train has to negotiate a curve of 400m. By how much should the outer sail be raised w.r.t. the inner rail for a speed of 48 km/h? (given: Distance between rail =1m].
A system is pushed by a force F as shown in figure. All surfaces are smooth except between B and C. Friction coefficient between B and C is μ. Minimum value of F to prevent block B from down ward slipping is

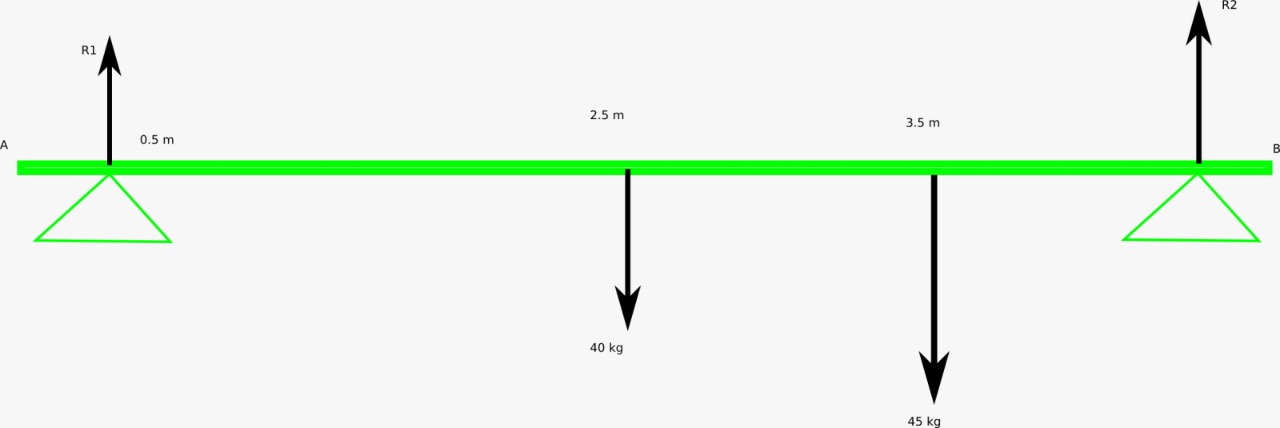
A uniform wooden plank 5 m long and weighting 40 kg is resting on two supports 0.5 m from each end. A boy weighting 45 kg stands 1.5 m from one end of the wooden plank. Find the reactions at the supports.
In the figure, a block of weight 60N is placed on a rough surface. The coefficient of friction between the block and the surface is 0.5. What should be the weight W such that the block does not slip on the surface?
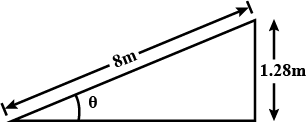
A road is 8 m wide. Its average radius of curvature is 40 m. The outer edge is above the lower edge by a distance of 1.28 m. Find the velocity of vehicle for which the road is most suited? (g=10m/s2
Define Newton's first law.
calculate the angle of banking of a smooth curved road of radius 100 m if vehicles can safely travel along it with a speed of 108km/h.
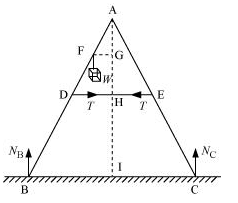
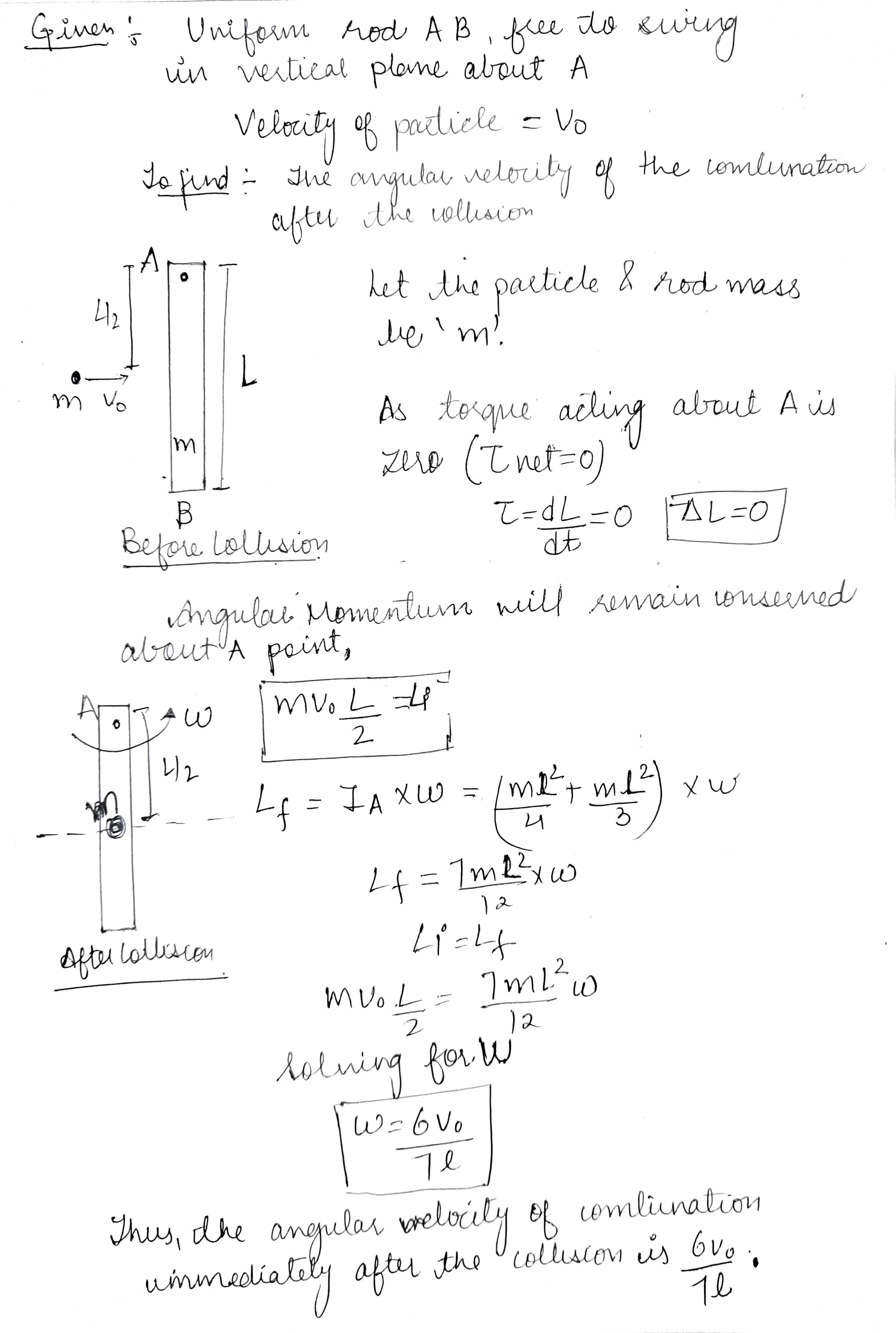
A uniform rod AB which is free to swing in the vertical plane about a horizontal axis through A, is hanging freely . A particle of equal mass strikes the rod with a velocity v0 and gets stuck ti it. Find the angular velocity of the combination immediately after the collision.
Does the angle of banking depends upon mass of the vehicle?
Obtain express for sensitivity of moving coil glavanometer
A scooter weighing 150 kg together with its rider moving at 36 km/hr is to take a turn of radius 30 m. If the horizontal force needed for the turn is to be supplied by the normal force by the road, what should be the proper angle of banking?
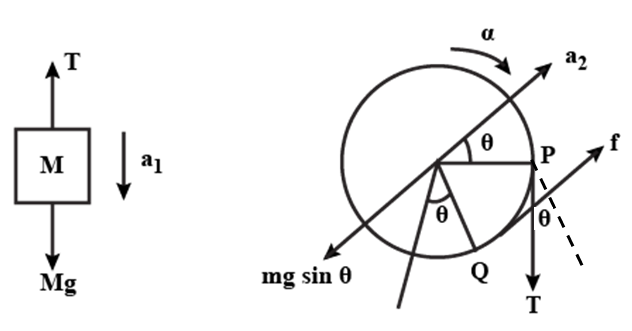
A cylinder of mass M=2.0kg is placed on two parallel rails inclined at an angle θ=37o to the horizontal (side view shown in the figure). A load of unknown mass is suspended from a light inextensible cord wound on the cylinder. The cylinder is held initially at rest and then released. If the cylinder starts rolling up the rails without slipping, what should mass of the load be?

The angle between the resultant contact force and the normal force exerted by a body on the other is called the angle of friction. Show that, if λ be the angle of friction and μ the coefficient of static friction, λ≤tan−1μ.
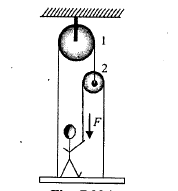
With what force F a man pull on a rope in order to support the platform on which he stands, if the mass of man is 60 kg and that at platform is 20 kg. With what force force N does the man press the platforms?
What is the maximum weight of the platform that the man can support?
(a) If a raindrop falls from such a height freely under gravity, what will be its speed? Also,calculate in km/h. (g=10m/s2)
(b) A typical raindrop is about 4mm diameter. Momentum is mass × speed in magnitude. Estimate its momentum when it hits the ground.
(c). Estimate the time required to flatten the drop.
(d) The rate of change of momentum is a force. Estimate how much force such a drop would exert on you.
(e) Estimate the order of magnitude force on the umbrella. The typical lateral separation between two raindrops is 5cm.(Assume that umbrella is circular and has a diameter of 1m and cloth is not pierced through!!)
Main concept used: F=madpdt=F
Eqn. of motion p=mv
mass =ρ× Volume
Column-1 shows certain situations and column-2 shows information about forces :
Figure shows the position-time graph of a particle of mass 4 kg. What is the
force on the particle for t < 0, t > 4 s, 0 < t < 4 s?
impulse at t = 0 and t = 4 s? (Consider one dimensional motion only)
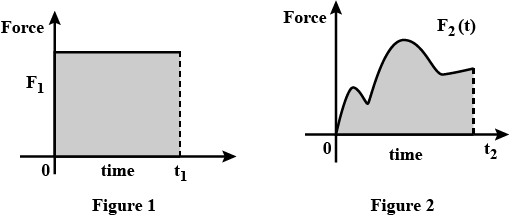
Define Impulse. What graphical methods can be used to calculate impulse in the following cases
constant force
variable force acting on a body
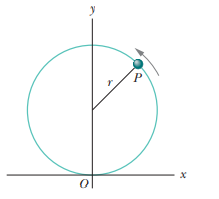
A particle P travels with constant speed on a circle of radius r=3.00m (Fig. 4-56) and completes one revolution in 20.0s. The particle passes through O at time t=0. State the following vectors in magnitude angle notation (angle relative to the positive direction of x). With respect to O, find the particles position vector at the times t of (a) 5.00s, (b) 7.50s, and (c) 10.0s. (d) For the 5.00s interval from the end of the fifth second to the end of the tenth second, find the particles displacement. For that interval, find (e) its average velocity and its velocity at the (f) beginning and (g) end. Next, find the acceleration at the (h) beginning and (i) end of that interval.
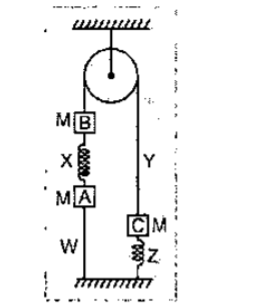
In the diagram strings, springs and the pulley are light and ideal. The system is in equilibrium with the strings taut (T > 0), match the column. Masses are equal.
How can Newton's first law of motion be obtained from the second law of motion?
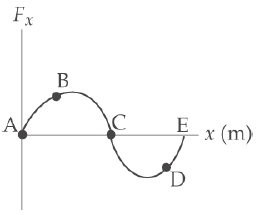
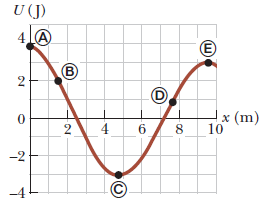
For the potential energy curve shown in above figure, (a) determine whether the force F_{x} is positive, negative, or zero at the five points indicated. (b) Indicate points of stable, unstable, and neutral equilibrium. (c) Sketch the curve for F_{x} versus x from x = 0 to x = 9.5 m.
Coriolis force F_{co\ r}=2m, [v'_C\omega], where v_C is the velocity of the body's centre of inertia in the rotating reference frame.
A skateboard with his board can be modeled as a particle of mass 76.0\ kg at his center of mass (which we will study in chapter 9) As show in figure the skateboard starts from rest in a crouching position at one lip of a half-pipe (point A)The half-pipe isa one half of a cylinder of radius 6.80\ m with its axis horizontal. On his descent, the skateboarder moves without friction so that his center of mass moves through one quarter of a circle of radius 6.30m Immediately after passing point B, he stands up and raises his arms, lifting his center of mass from 0.500m to 0.950 m above the concrete (point c). Next, the skateboarder gildes upward circle of radius 5.85\ m His body is horizontal when he passes point D, the far lip of the half-pipe. as he passes through point D, the speed of the skateboarder is 5.14 m/s. How much chemical potential energy in the body of the skateboarder was converted to mechanical energy in the skateboarder-Earth system when he stood up at point B?
A hammer of mass 1 kg moving with a speed of 6 \ ms^{-1} strikes a wall and comes to rest in 0.1 s. Find the
Impulse
Retarding force on the hammer
Retardation
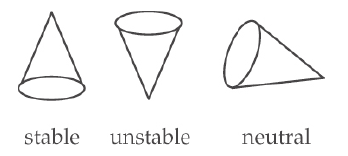
A right circular cone can theoretically be balanced on a horizontal surface in three different ways. Sketch these three equilibrium configurations and identify them as positions of stable, unstable, or neutral equilibrium.
A child lying on her back experiences 55.0 N tension in the muscles on both sides of her neck when she raises her head to look past her toes. Later, sliding feet first down a water slide at terminal speed 5.70 m/s and riding high on the outside wall of a horizontal curve of radius 2.40 m, she raises her head again to look forward past her toes. Find the tension in the muscles on both sides of her neck while she is sliding.
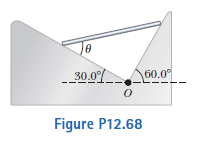
A uniform rod of weight F_g and length L is supported at its ends by a frictionless trough as shown in the Figure 12.68.
Is the equilibrium of the rod stable or unstable?
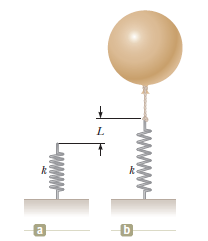
A light spring of constant k=90.0\ N/m is attached vertically to a table (Fig. P14.65a). A 2.00-g balloon is filled with helium (density =0.179\ kg/m^{3}) to a volume of 5.00\ m^{3} and is then connected with a light cord to the spring, causing the spring to stretch as shown in Figure P14.65b. Determine the extension distance L when the balloon is in equilibrium.
Class 11 Engineering Physics Extra Questions
- Gravitation Extra Questions
- Kinetic Theory Extra Questions
- Laws Of Motion Extra Questions
- Mechanical Properties Of Fluids Extra Questions
- Mechanical Properties Of Solids Extra Questions
- Motion In A Plane Extra Questions
- Motion In A Straight Line Extra Questions
- Oscillations Extra Questions
- Physical World Extra Questions
- Systems Of Particles And Rotational Motion Extra Questions
- Thermal Properties Of Matter Extra Questions
- Units And Measurement Extra Questions
- Waves Extra Questions
- Work,Energy And Power Extra Questions