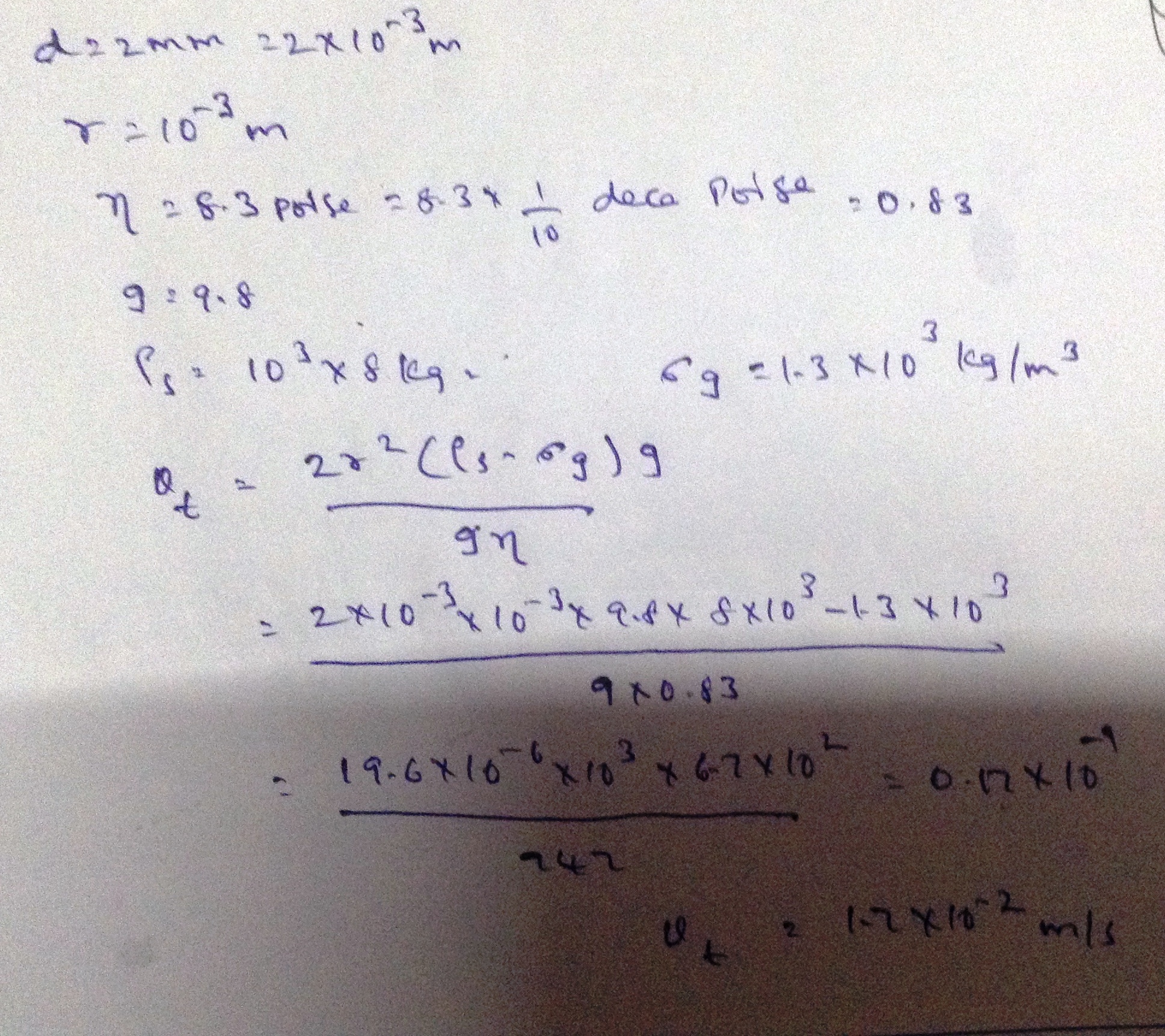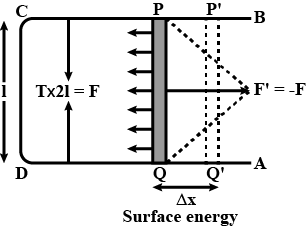Mechanical Properties Of Fluids - Class 11 Medical Physics - Extra Questions
The height of a mercury column in a barometer at a place is 74 cm. If a liquid of density $$5.44 g cm^{-3}$$ is used then find the height of the liquid column.
Barometric height used as a unit to express the atmospheric pressure because atmospheric pressure holds the mercury in the tube, so the height of mercury is used as a unit to express the atmospheric pressure.Type 1 for true and 0 for false
Barometer can be used to forecast the weather by checking pressure fluctuations. Type 1 for true and 0 for false
Why does the atmospheric pressure go on decreasing as we go higher up above the earth's surface?
Why are our bodies not crushed by the large pressure exerted by the atmosphere.
A solid weighs $$32\ gf$$ in air and $$28.8\ gf$$ in water. Find: the volume of solid
A solid weighs $$32\ gf$$ in air and $$28.8\ gf$$ in water. Find: $$R.D.$$ of solid.
Define Density and relative density.
Define turbulent flow.
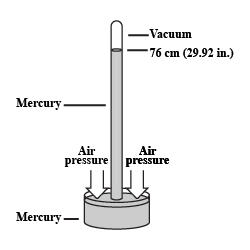
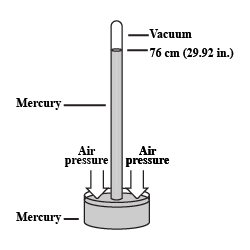
What is a barometer? How will you construct a simple barometer?
Explain how is the height of mercury column in tube of a simple barometer is a measure of the atmospheric pressure.
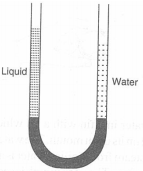
A U-tube is partially filled with mercury. Some water is poured in its one arm and a liquid in the other arm so that the level of mercury in both arms is same. What is the ratio of lengths of water and liquid in the two arms of the U-tube?
Density of water $$=1000\;kg\,m^{-3}$$ and density of liquid $$=900\;kg\,m^{-3}$$.
The commonly used barometric liquid in a barometer is ______
If the velocity of water near the surface of a $$6$$m deep river is $$6$$ m$$/$$s, assuming uniform velocity gradient along the depth, find the shear stress between the horizontal layers of water (coefficient of viscosity of water $$=10^{-2}$$ poise).
A tank with a small orifice contains oil on top of water. It is immersed in a large tank of the same oil. Water flows through the hole. Assuming the level of oil outside the tank above orifice does not change. a. What is the velocity of this flow initially? b. When the flow stops, what would be the position of the oil-water interface in the tank? c. Determine the time at which the flow stops? Density of oil $$=800\ kg/{ m }^{ 3 }$$.

Two spherical bodies having masses $$m_{1},m_{2}$$ respectively falling in viscous medium the ratio of terminal velocities is$$\dfrac{v_{1}}{v_{2}}=(\dfrac{m_{1}}{m_{2}})^{2/3}$$.
If area of cross section of one end of tube is $$8$$cm and velocity of liquid flow is $$1.5ms^{-1}$$. What is the speed of ejection of the liquid if the life area of cross reaction of the other end is $$4.0$$cm.
Write the formula terminal velocity
A block of wood is so loaded that it just floats in water at room temperature. What change will occur in the state of floatation,if water is heated? Give reason.
The terminal velocity of a steel ball 2 mm in diameter falling through glycerin is $$ 44\times10^{-2} cm/s $$ (Given that specific gravity of steel = 8, specific gravity of steel =8, specific gravity of glycerin a 1.3, viscosity of glycerine 8.3 poise.)
When a ball is dropped from a height, its speed increases gradually.Name the force which causes this change in speed.
State the SI unit of density ? Relate it with its cgs unit.
A body of volume $$V$$ and density $$\rho s$$, floats with volume $$v$$ inside a liquid of density $$\rho_1$$. Show that $$\dfrac{v}{V}=\dfrac{\rho s}{\rho L}$$
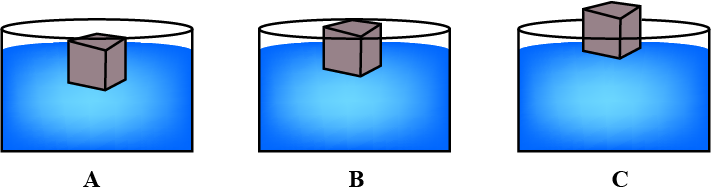
Figure shows the same block of wood floating in three different liquids $$A,B\ and\ C$$ of densities $$\rho1,\rho 2$$ and $$\rho 3$$ respectively. Which of the liquid has the highest density? Give reason for your answer.
When a piece of wood is suspended from the hook of a spring balance, it reads $$70gf$$. The wood is now lowered into the water which results in floating the wood. What reading do you expect on the scale of spring balance?
What is the unit of relative density ?
Why is a force needed to keep a block of wood inside water?
Define the term density
A sphere of iron and another of wood, both of same radius are placed on the surface of water. State which of the two will sink? Give reason to your answer.
The mass of a block made of a certain material is $$13.5\ kg$$ and its volume is $$15\times 10^{-3}\ m^3$$. What will be the upthrust on block with floating? Take density of water$$=1000\ kg\ m^{-3}$$.
A block of wood of mass $$24kg$$ floats on water. The volume of wood is the volume of block below the surface of water,(Density of water $$= 1000\ kg\ m^{3}$$)
Explain the following:
Icebergs floating in sea are dangerous for ships.
The mass of a block made of a certain material is $$13.5\ kg$$ and its volume is $$15\times 10^{-3}\ m^3$$
Will the block float or sink in water when released? Give reason for your answer.
Explain how is the height of mercury column in the tube of a simple barometer,a measure of the atmospheric pressure.
How you will show there in vaccum above the surface of mercury in a barometer ? What name is given to this vaccum?
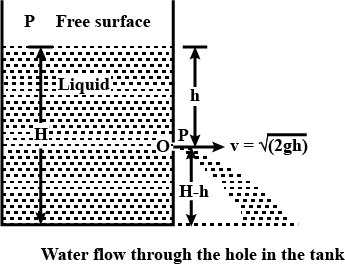
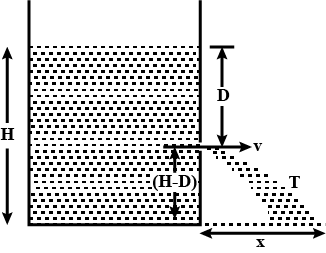
A water tank is filled with water upto height H. There is a orifice in the wall of water tank at a depth D from the water surface. If water is emerging from orifice to ground then find out the horizontal range of water on the ground.
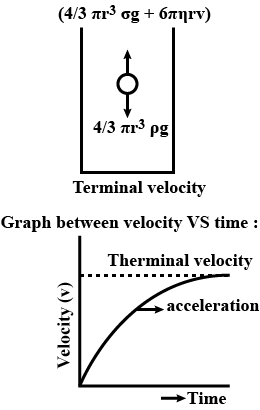
Derive expression for the terminal velocity of a small body falling through a viscous liquid.
Water is flowing through a non-uniform cross-sectional pipe. Where the radius of pipe is 2 cm, velocity of water is 20 cm/s. If another place, where radius of the pipe is 6 cm, find out the velocity of the water.
Derive a relation between surface tension and surface energy.
Find out the speed of efflux at a height h from the side of a container both when its top is closed and open. Hence derive Torricell's law.
Find out the terminal velocity of rain water drop of radius 1 mm. Viscous coefficient for air is $$ 1.8 \times 10^{-5} \space Ns/m^{2}$$ and density $$1.2 kg/m^{3}$$, density of water is $$10^{3} kg/m^{3}$$, ($$g = 10 \space m/s^{2}$$).
The mass of a spherical glass ball is M. It is falling down through a viscous fluid with terminal velocity V. Find out the terminal velocity of another spherical glass ball of mass 8M in the same medium.
A raindrop of mass $$m$$ at a height $$h$$ starts from rest and initially accelerates under gravity. Due to viscous drag of air, its motion is resisted and it finally it acquires a constant terminal velocity $$v_{T}$$ and hits the ground. Neglect the buoyancy, assume acceleration due to gravity $$g$$ and no wind. Find the magnitude of the average viscous force on the rain drop during the entire downward trip.
A barometer is constructed with its tube having radius $$1.0$$mm. Assume that the surface of mercury in the tube is spherical in shape. If the atmospheric pressure is equal to $$76$$cm of mercury, what will be the height raised in the barometer tube? The contact angle of mercury with glass $$=135^o$$ and surface tension of mercury $$=0.465$$ N $$m^{-1}$$. Density of mercury $$=13600$$ kg $$m^{-3}$$.
Two balls A and B have radii in the ratio 1:What will be the ratio of their terminal velocities in a liquid?
The gravitational force exerted on a solid object is $$5.00\ N$$. When the object is suspended from a spring scale and submerged in water, the scale reads $$3.50\ N$$. Find the density of the object.
Class 11 Medical Physics Extra Questions
- Gravitation Extra Questions
- Kinetic Theory Extra Questions
- Laws Of Motion Extra Questions
- Mechanical Properties Of Fluids Extra Questions
- Mechanical Properties Of Solids Extra Questions
- Motion In A Plane Extra Questions
- Motion In A Straight Line Extra Questions
- Oscillations Extra Questions
- Systems Of Particles And Rotational Motion Extra Questions
- Thermal Properties Of Matter Extra Questions
- Units And Measurement Extra Questions
- Waves Extra Questions
- Work, Energy And Power Extra Questions