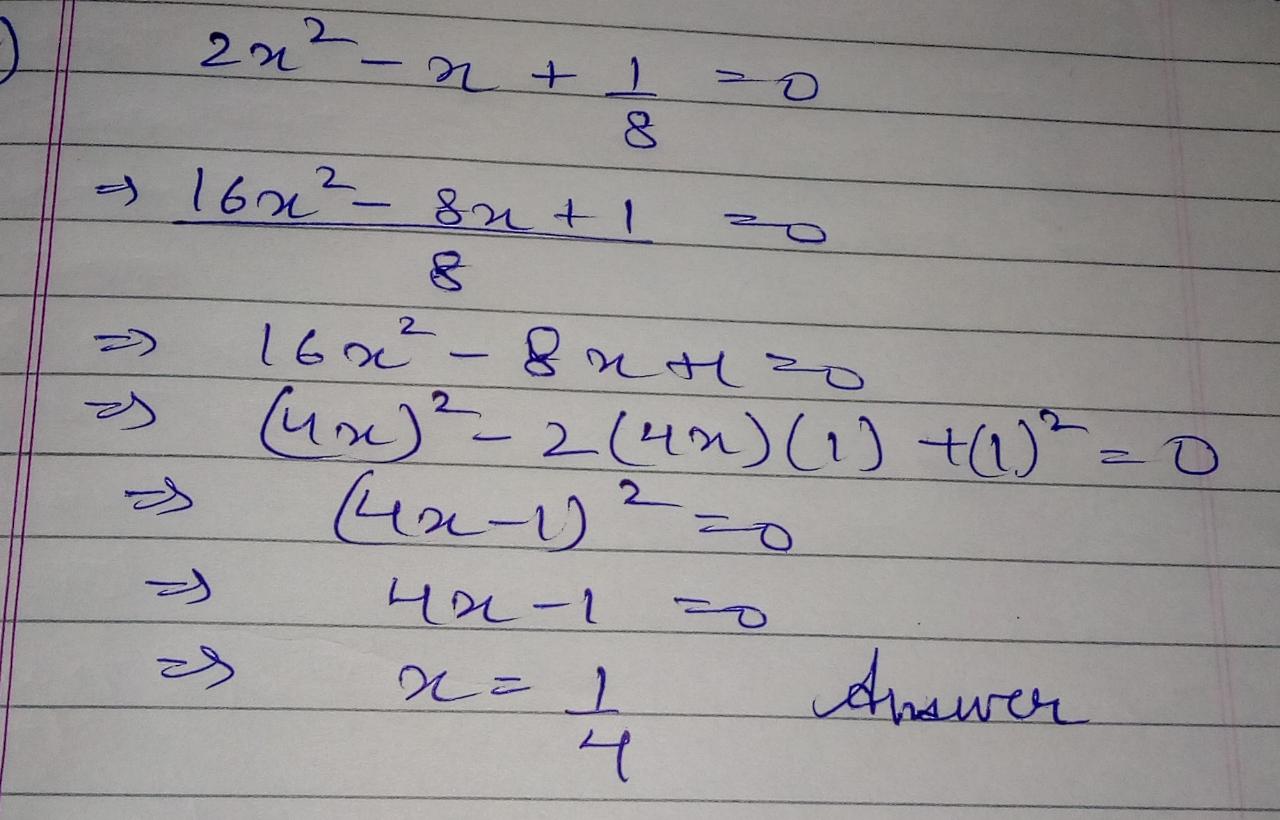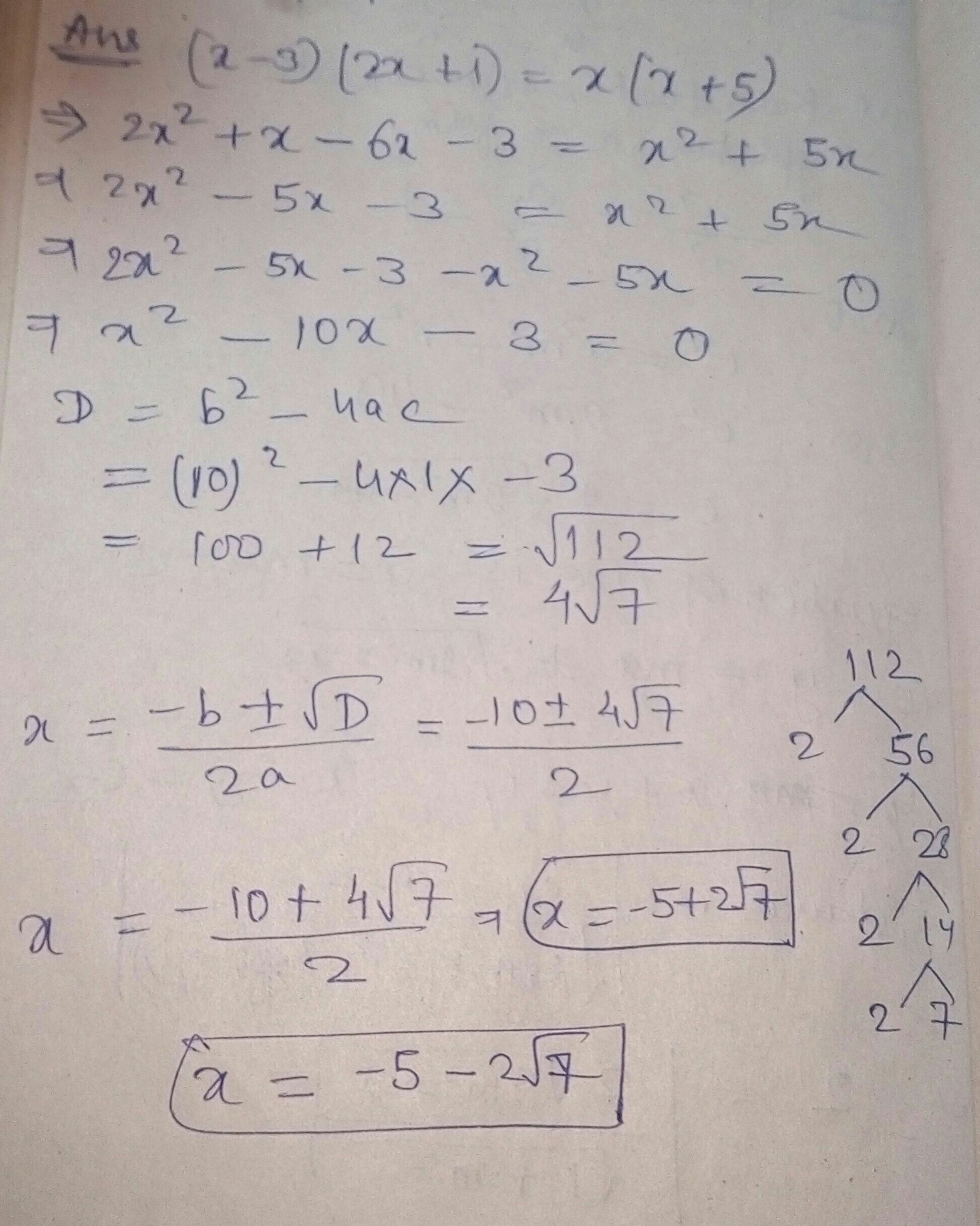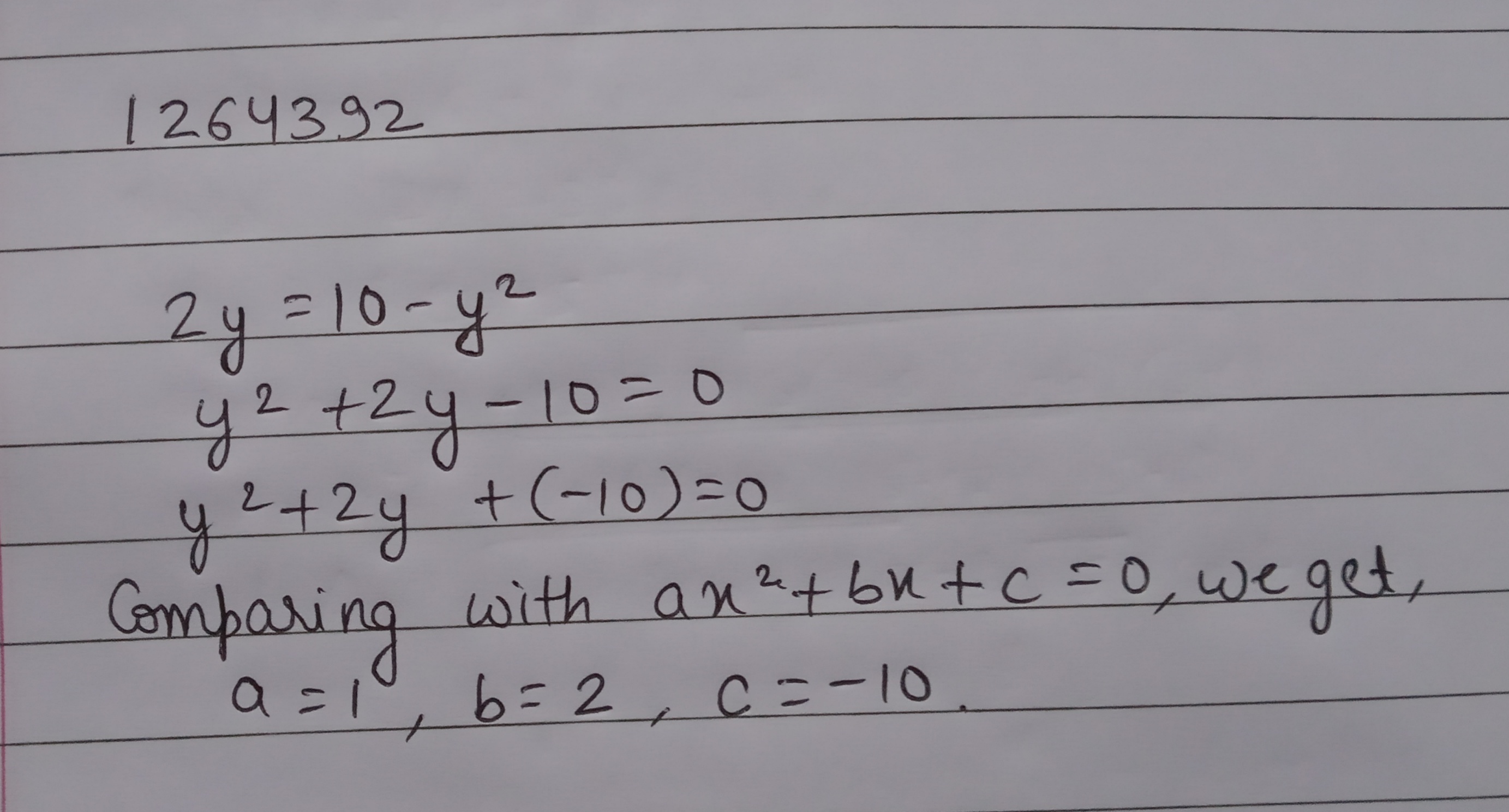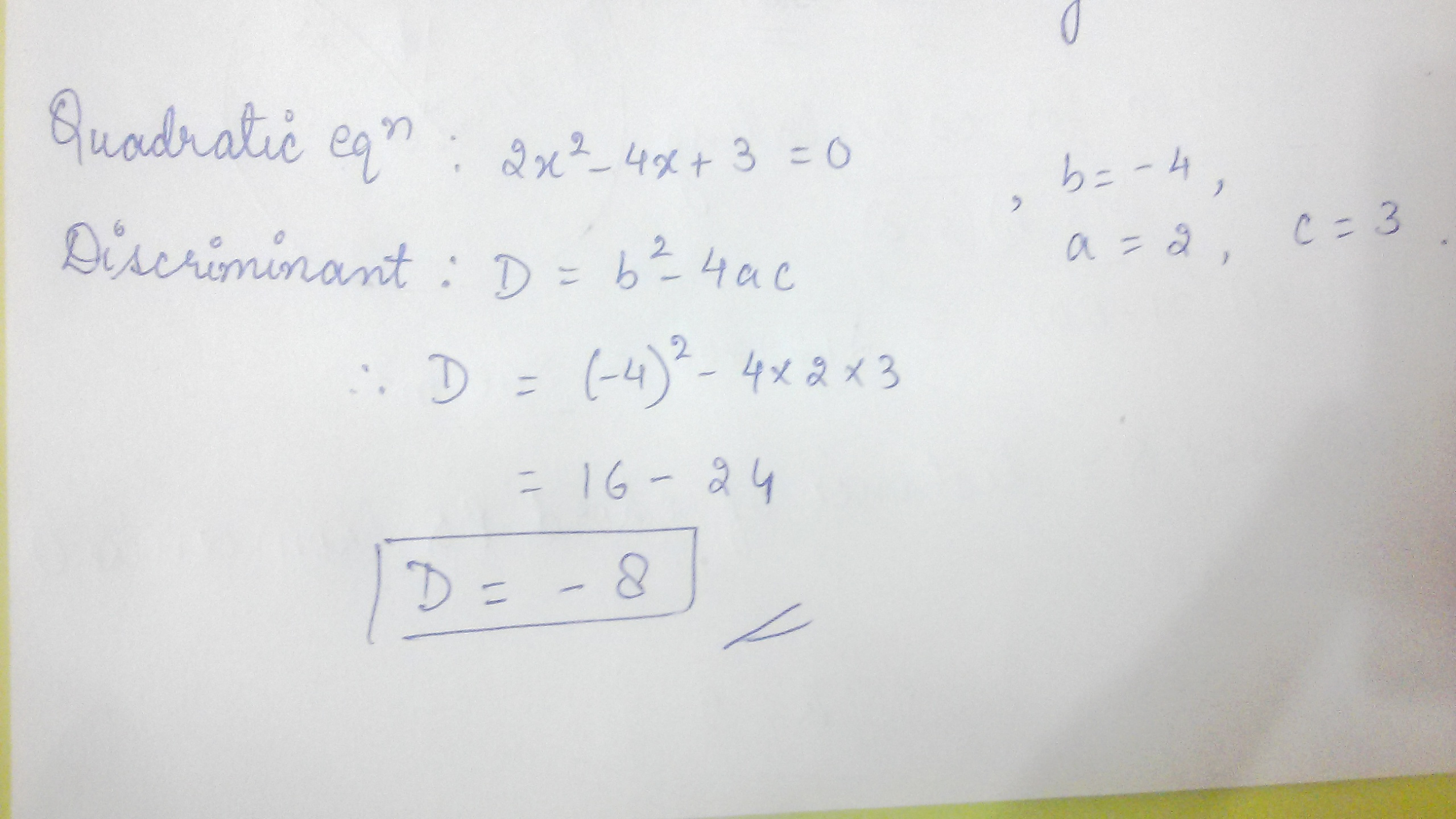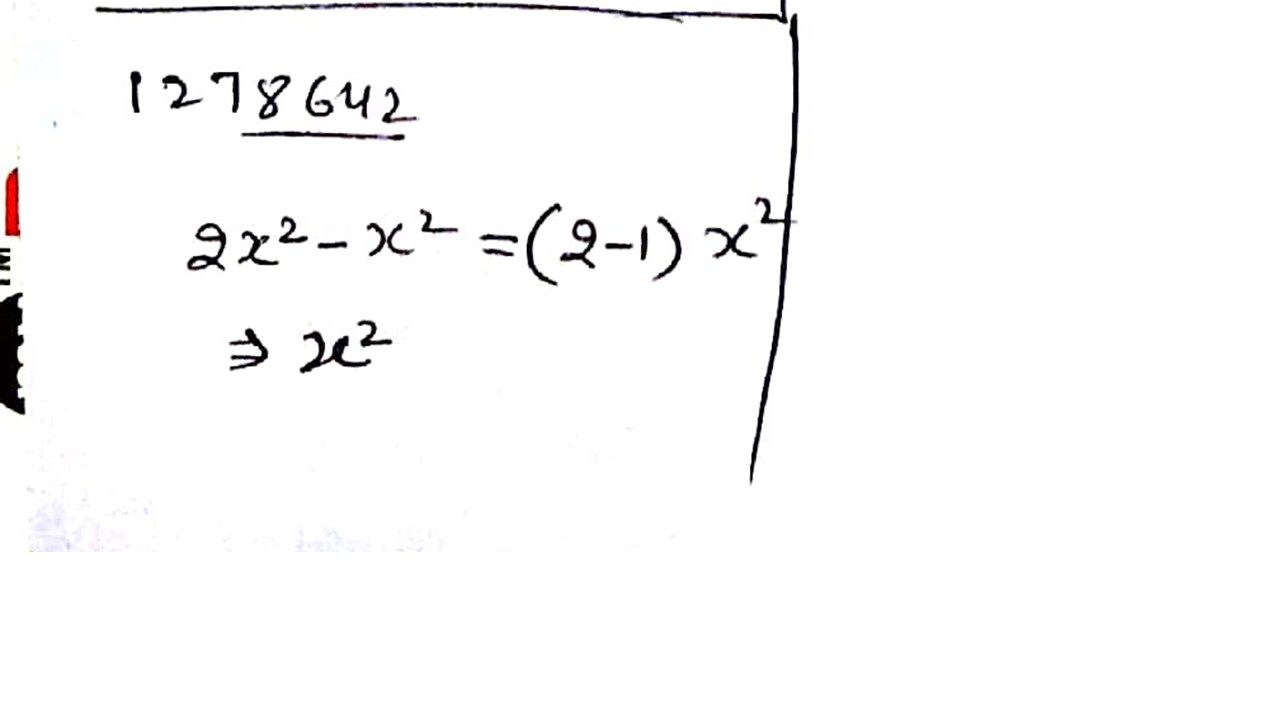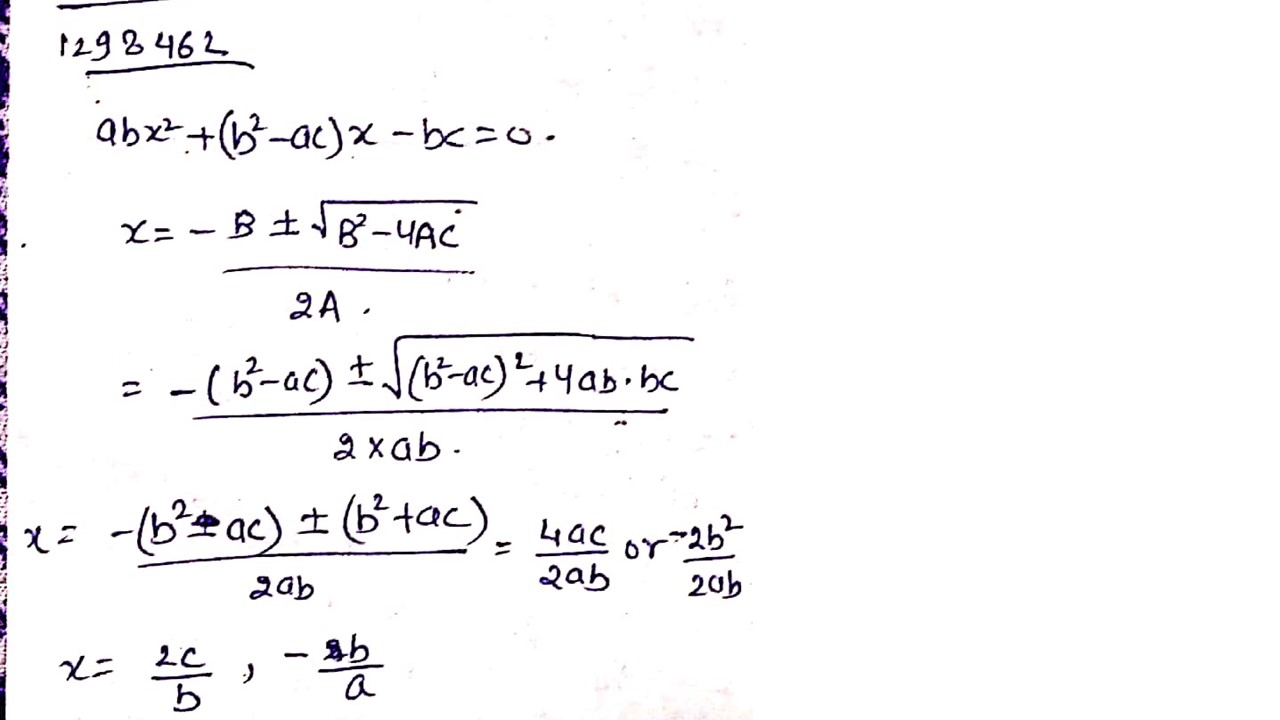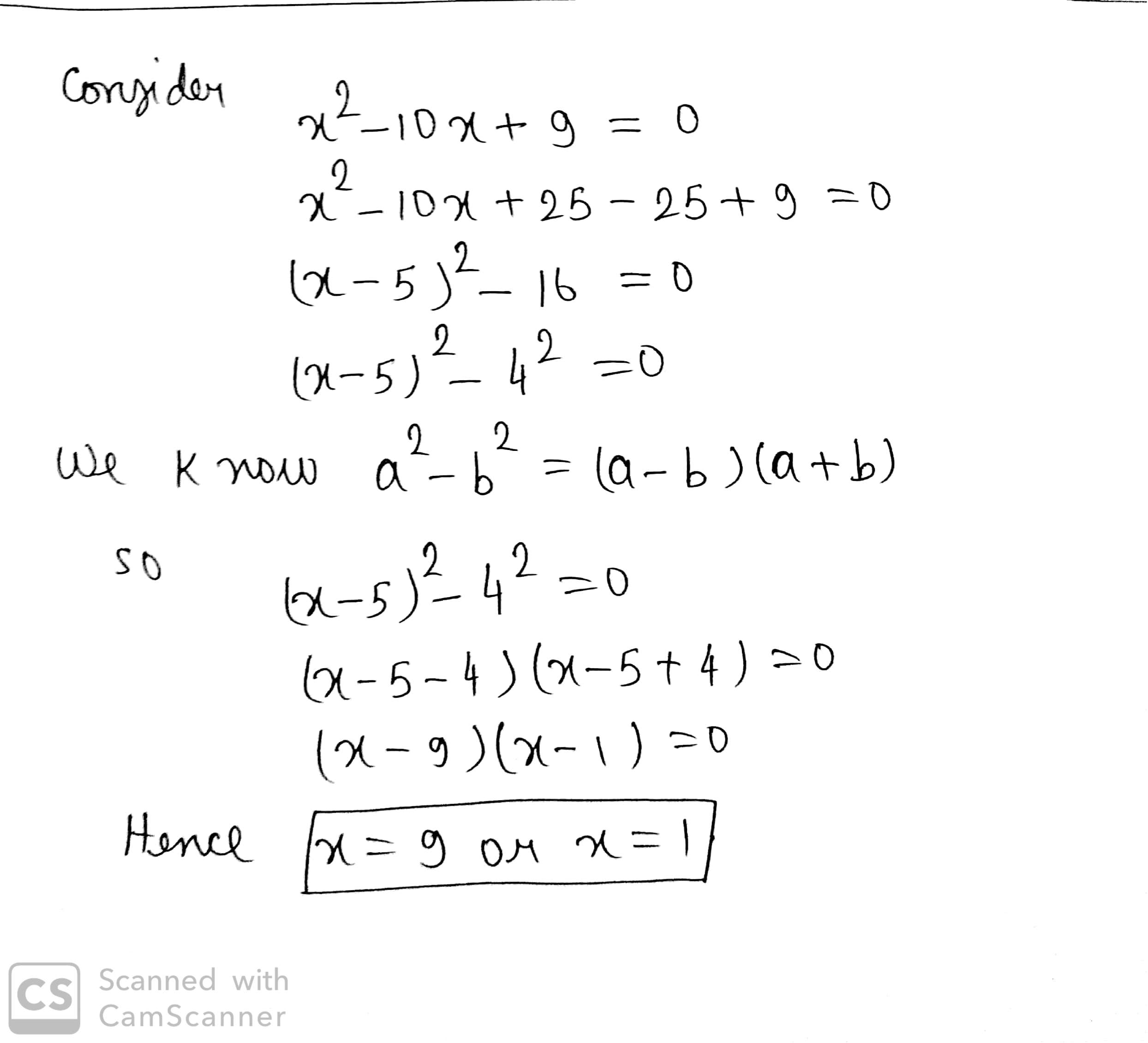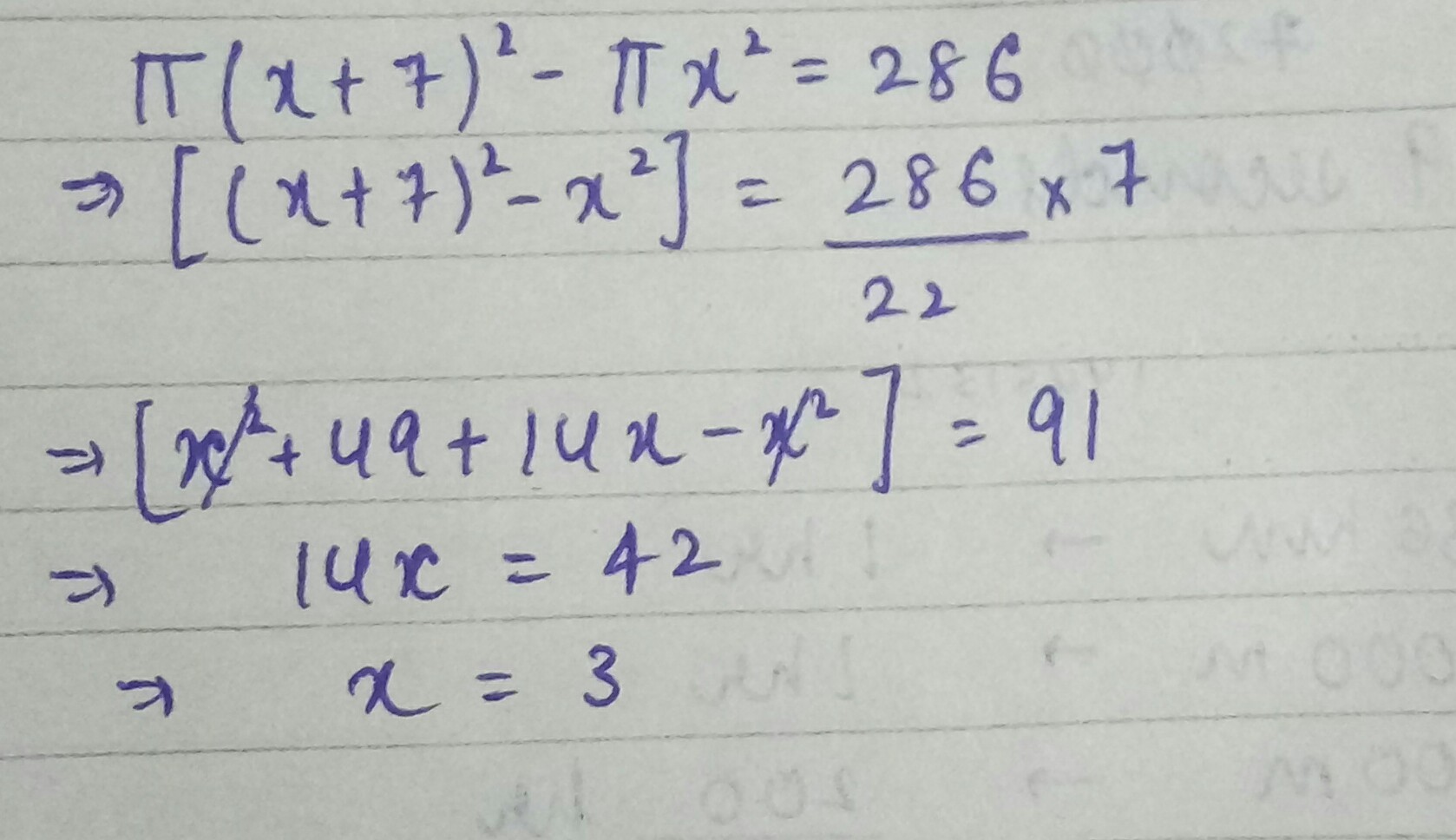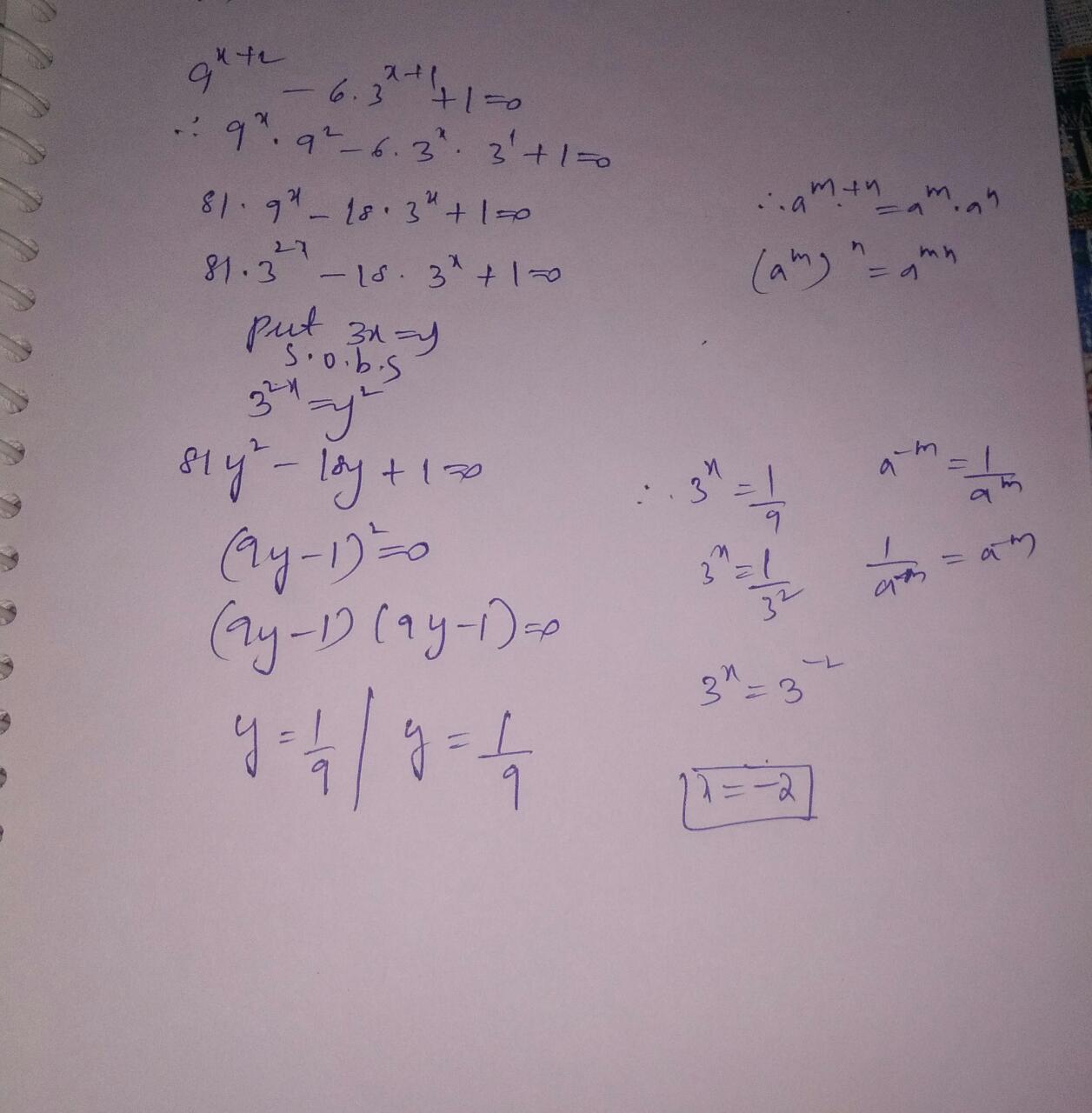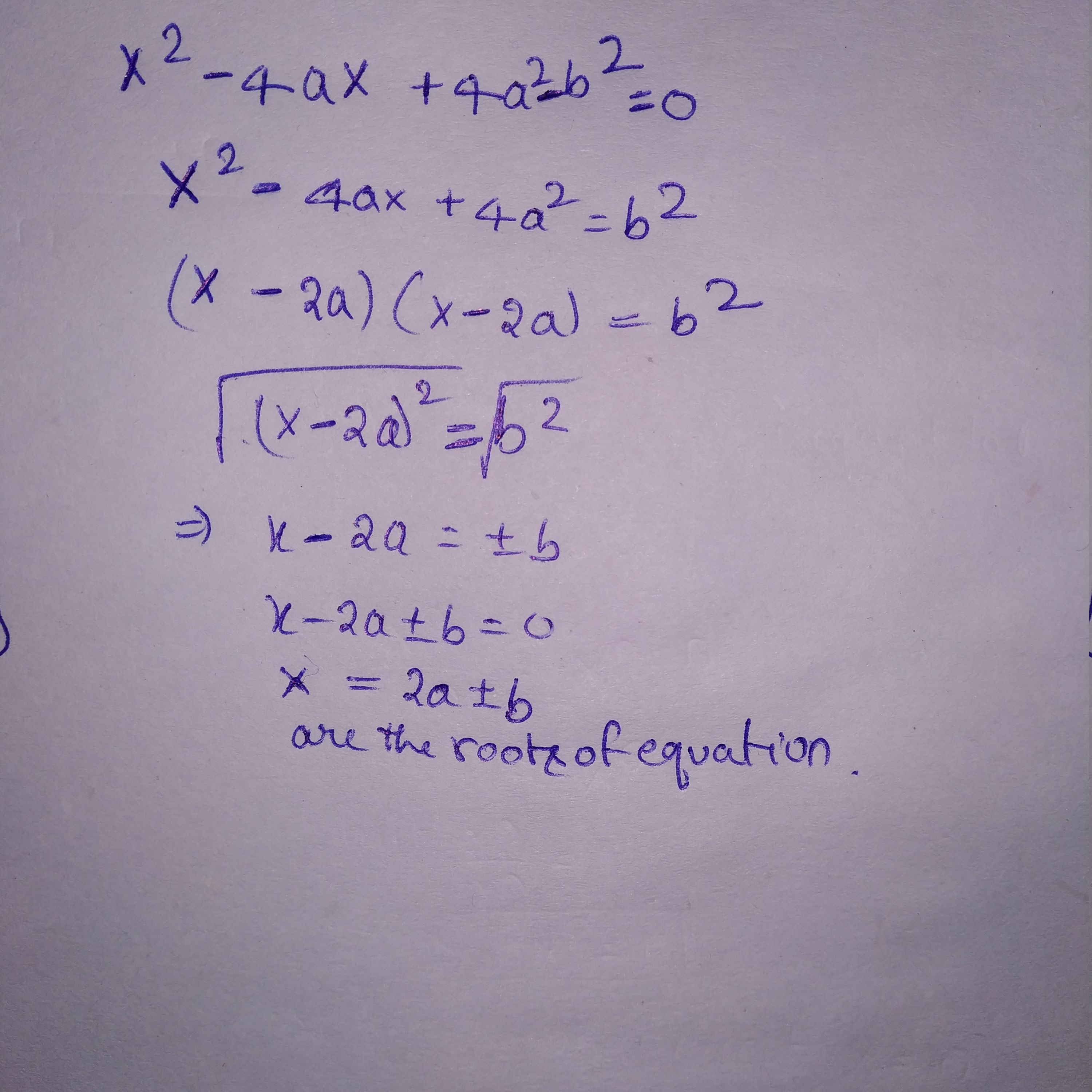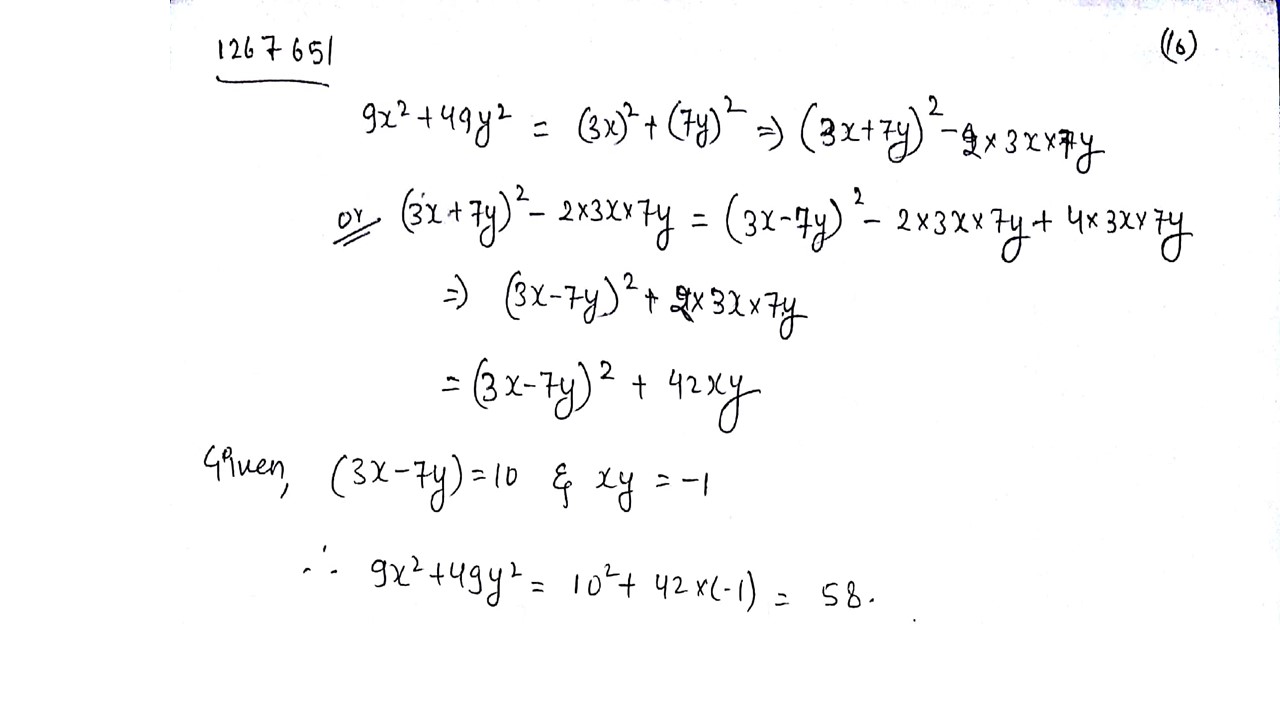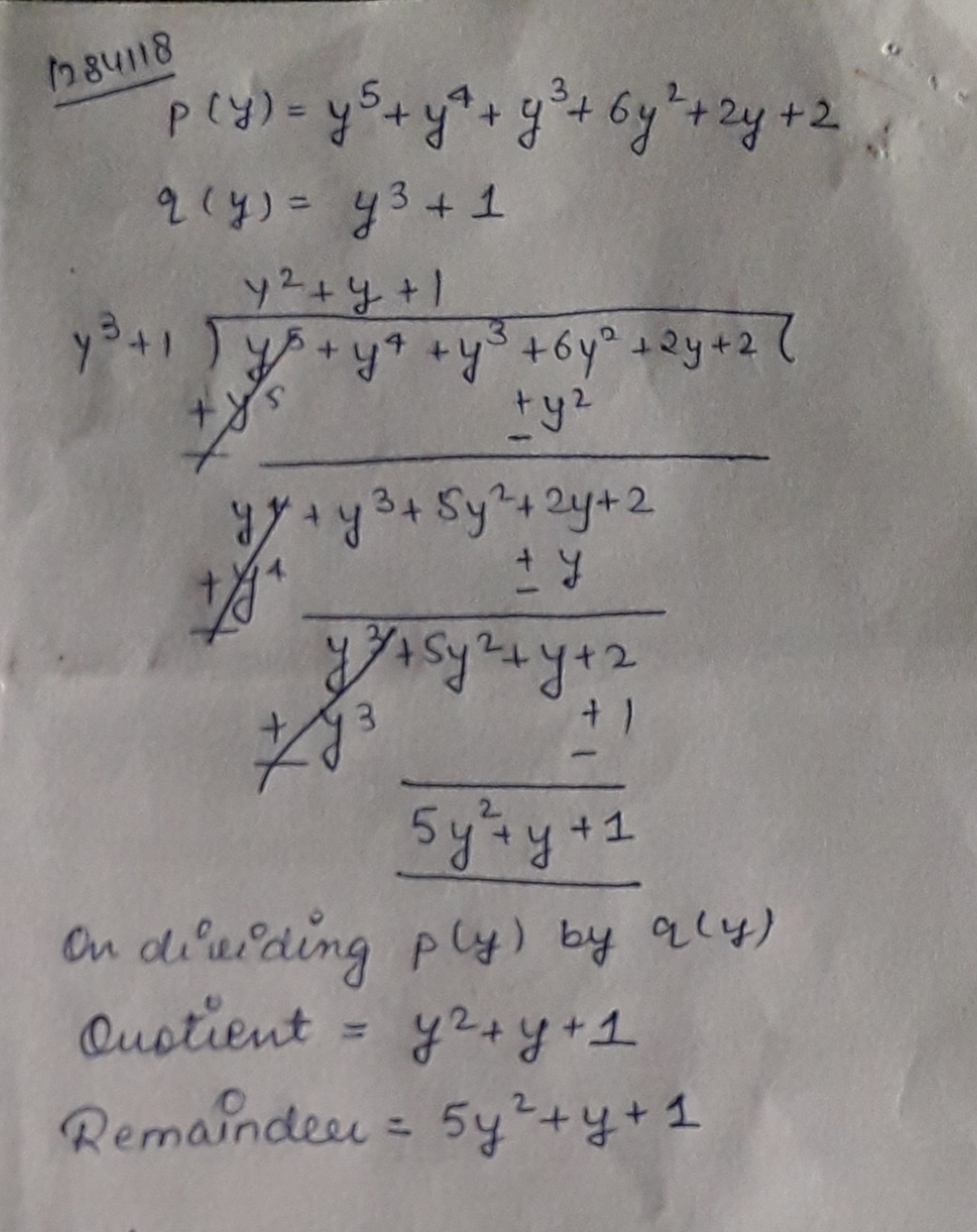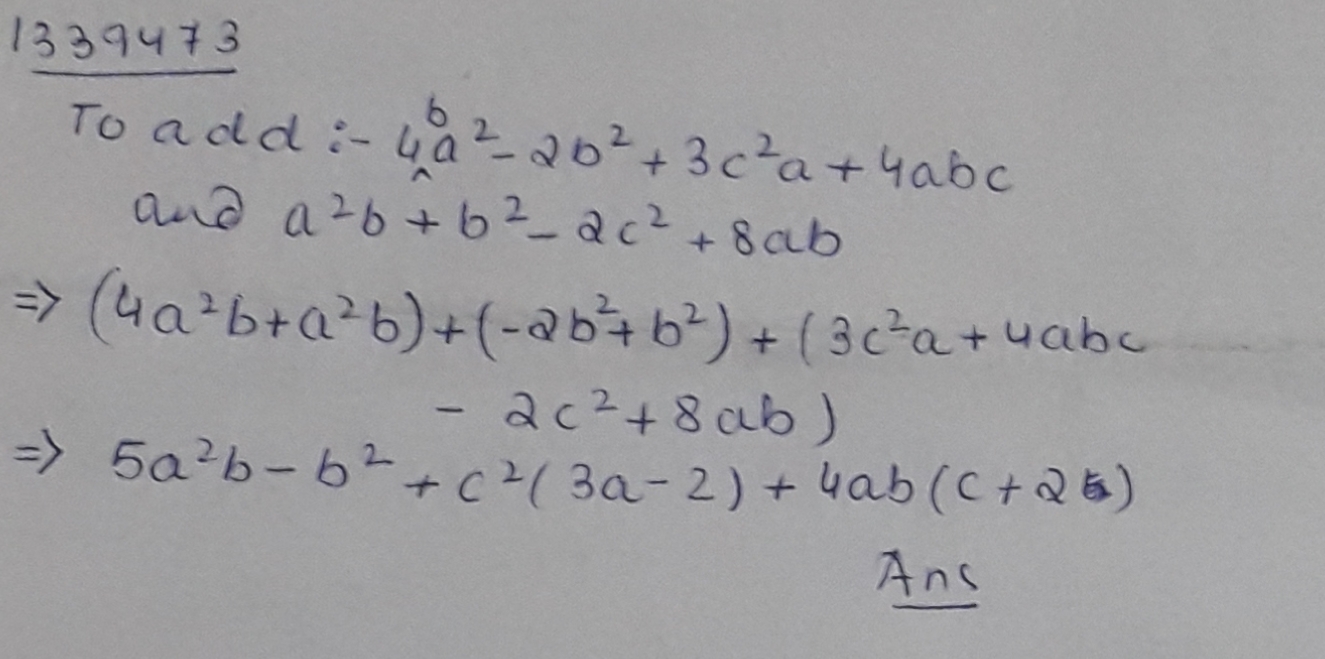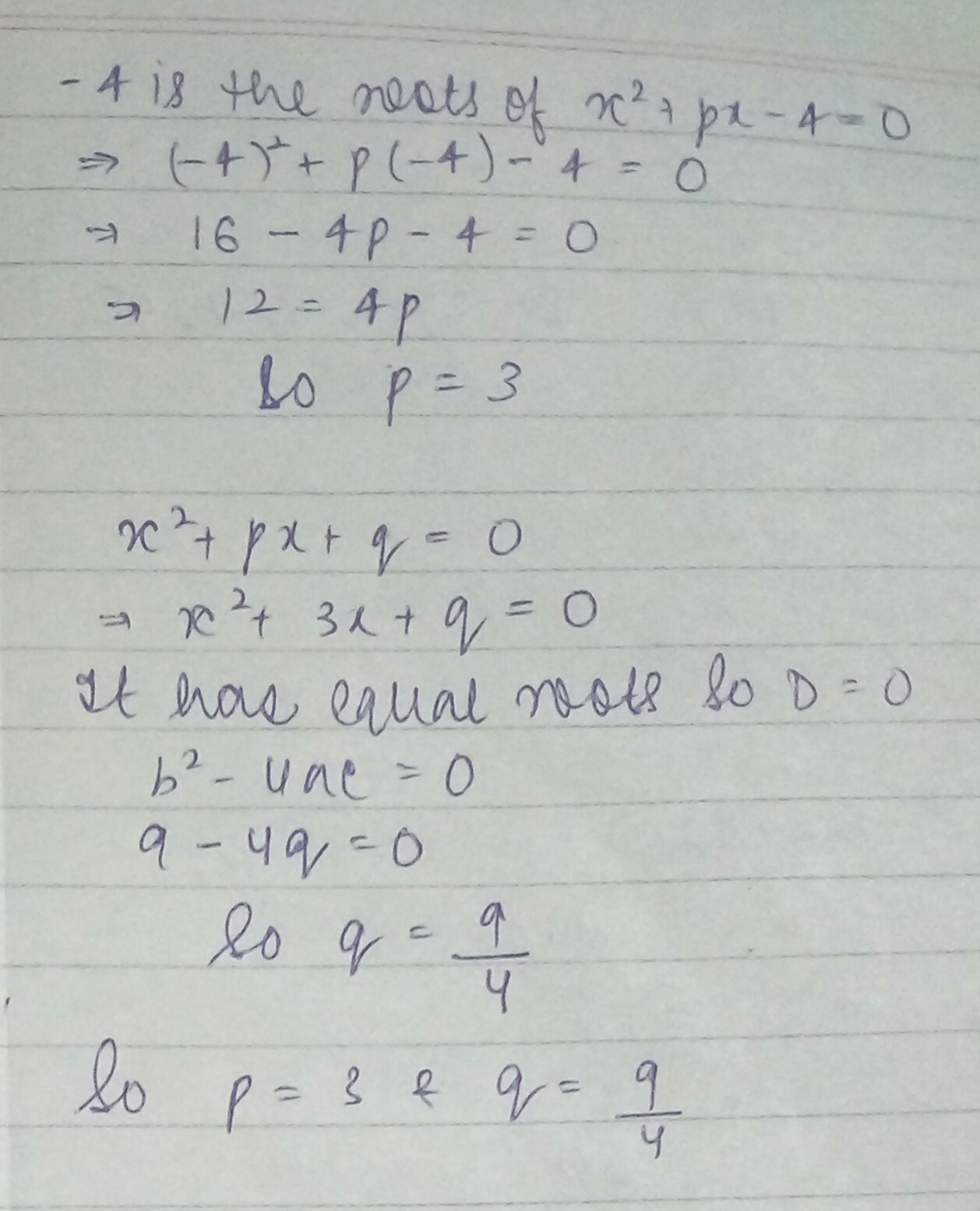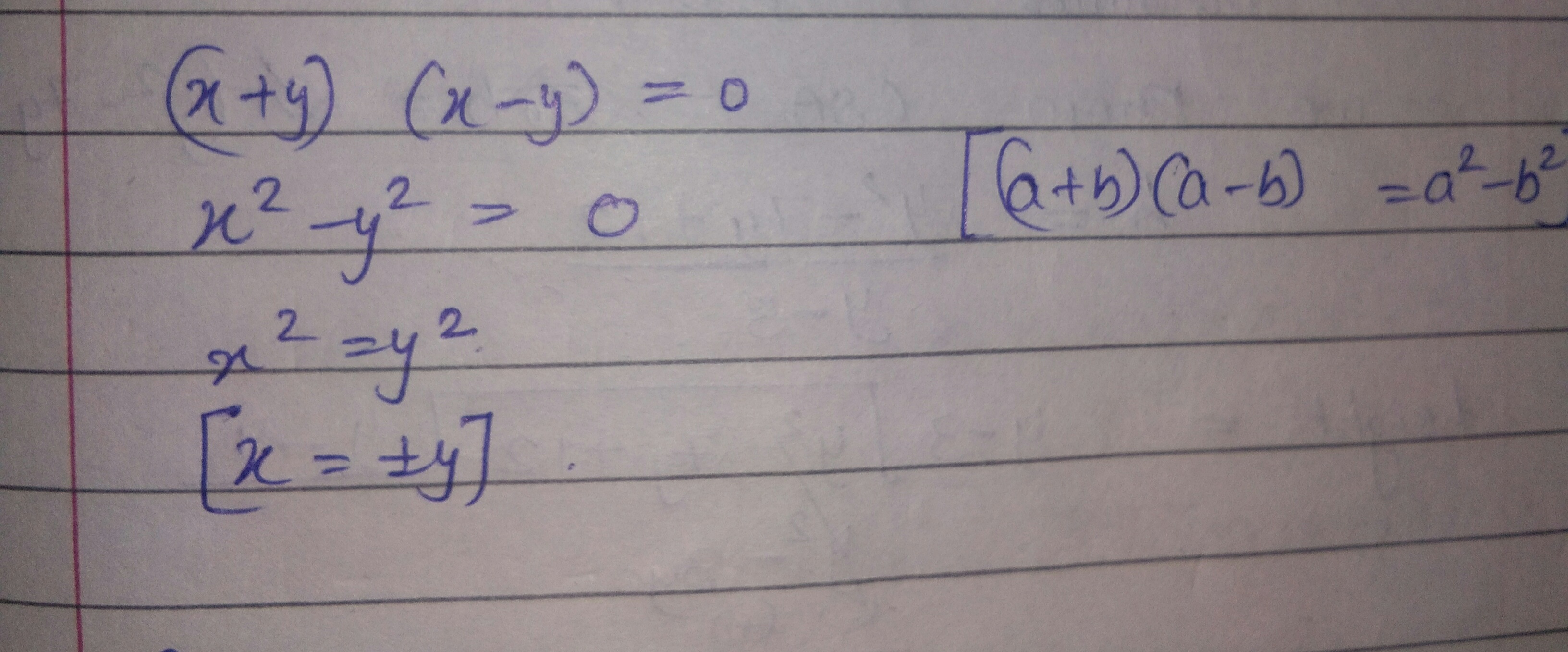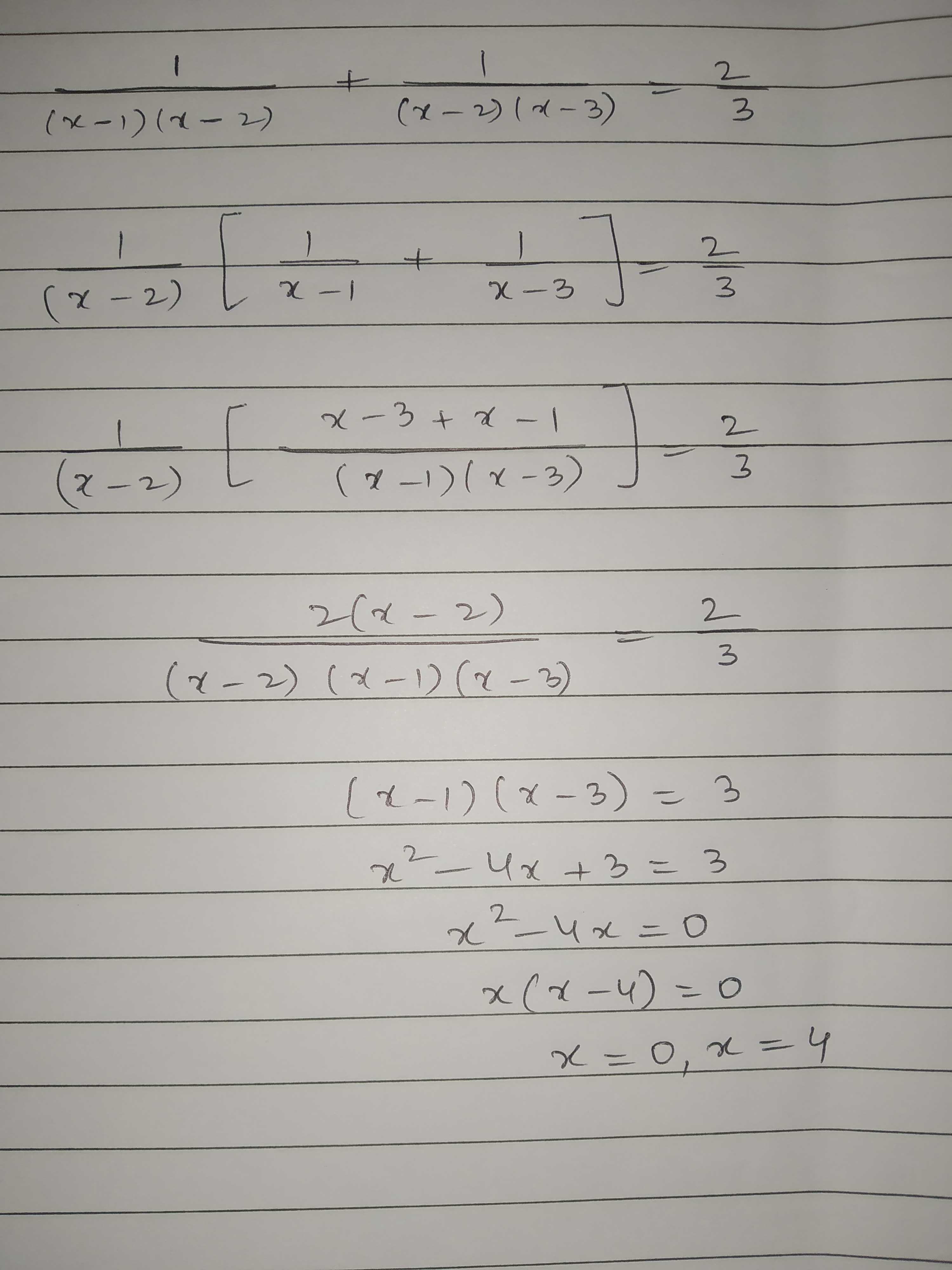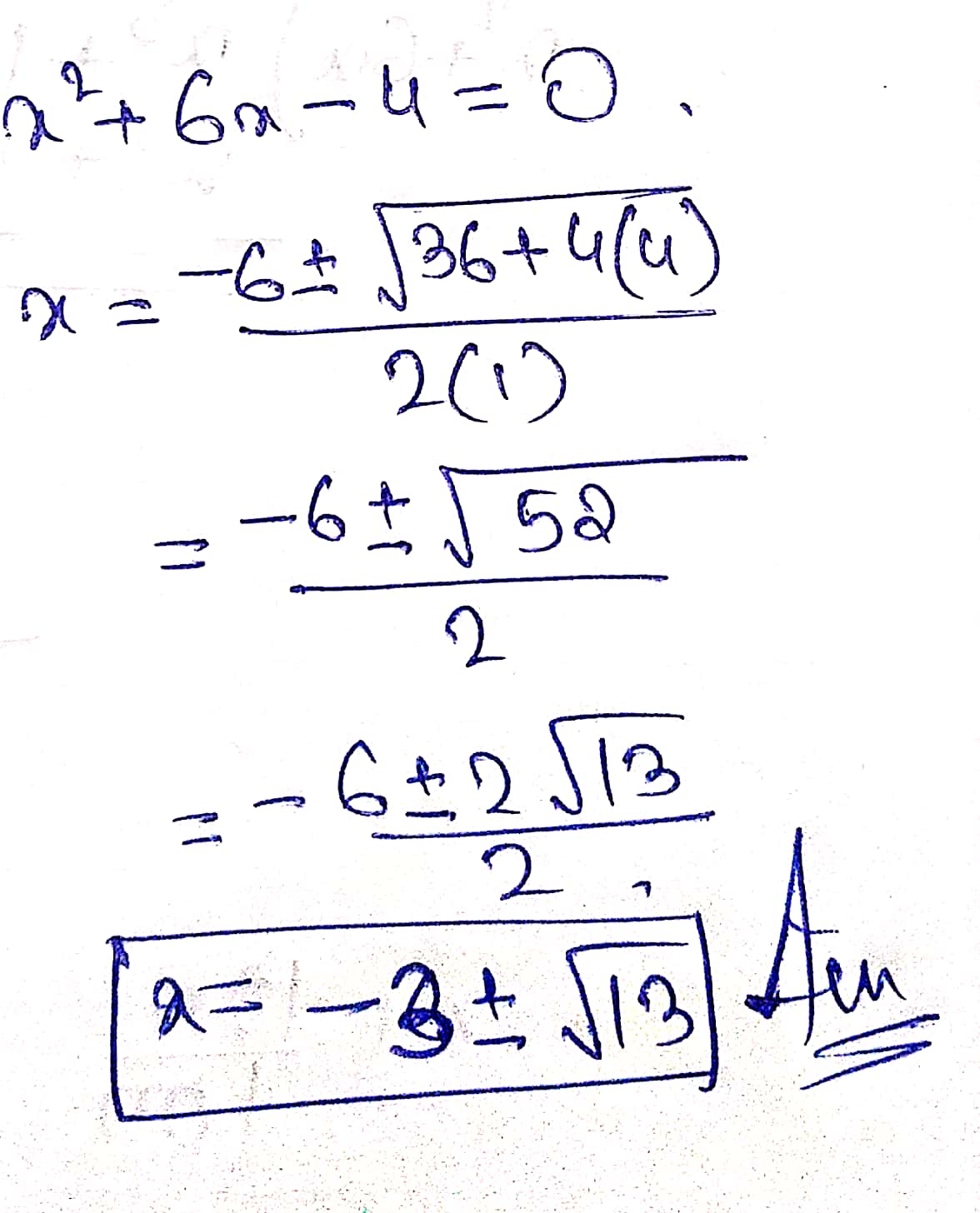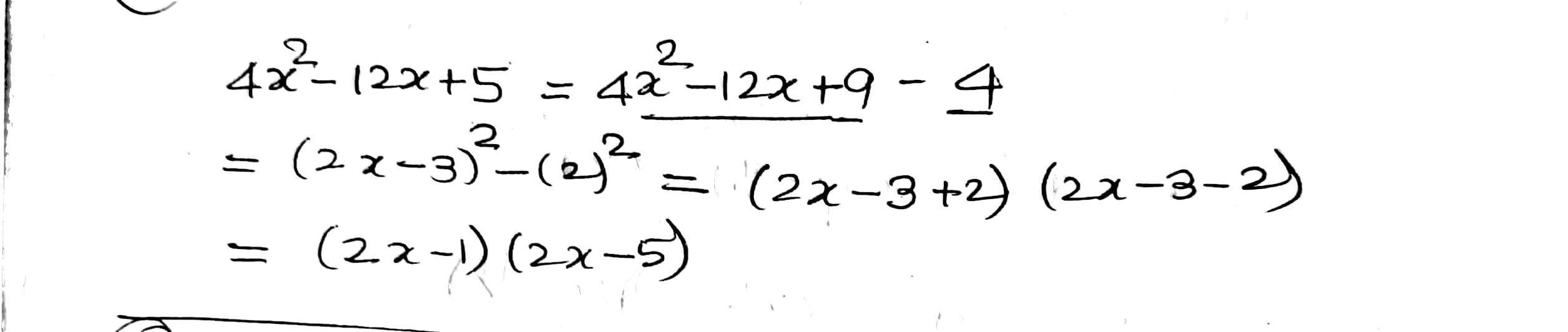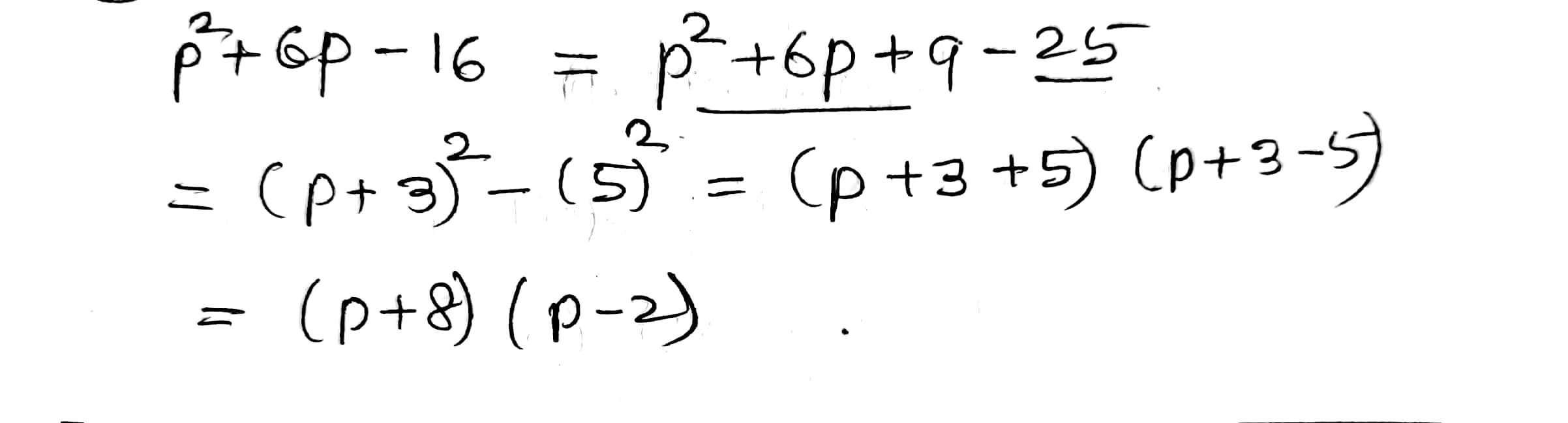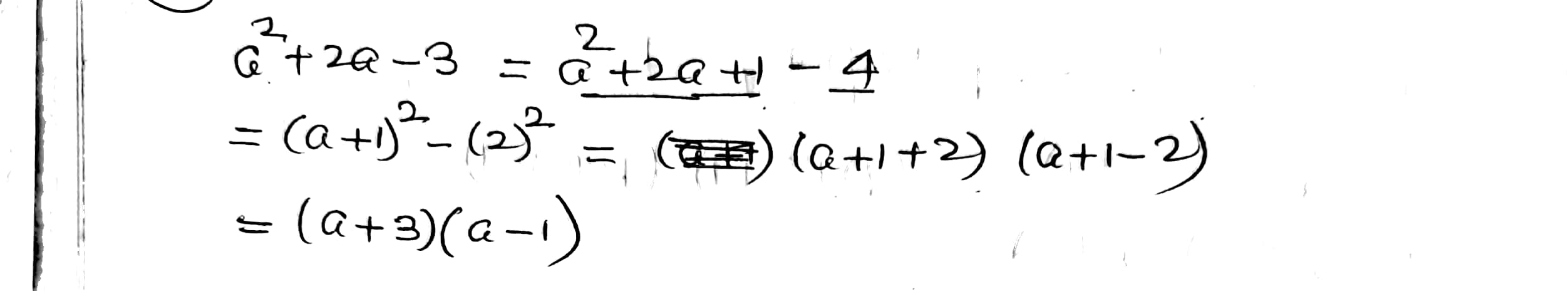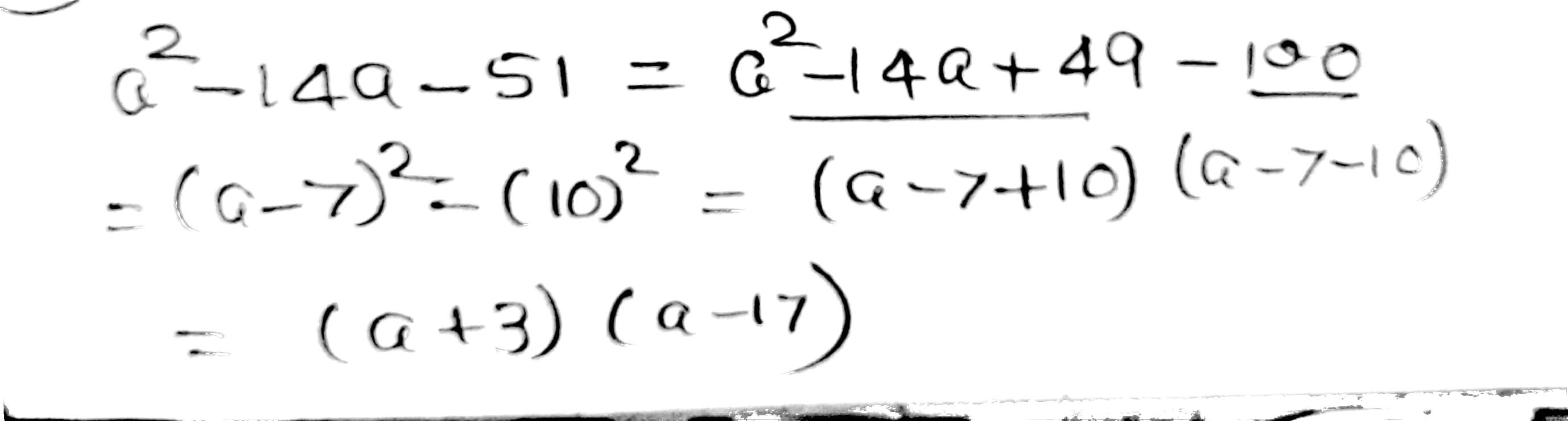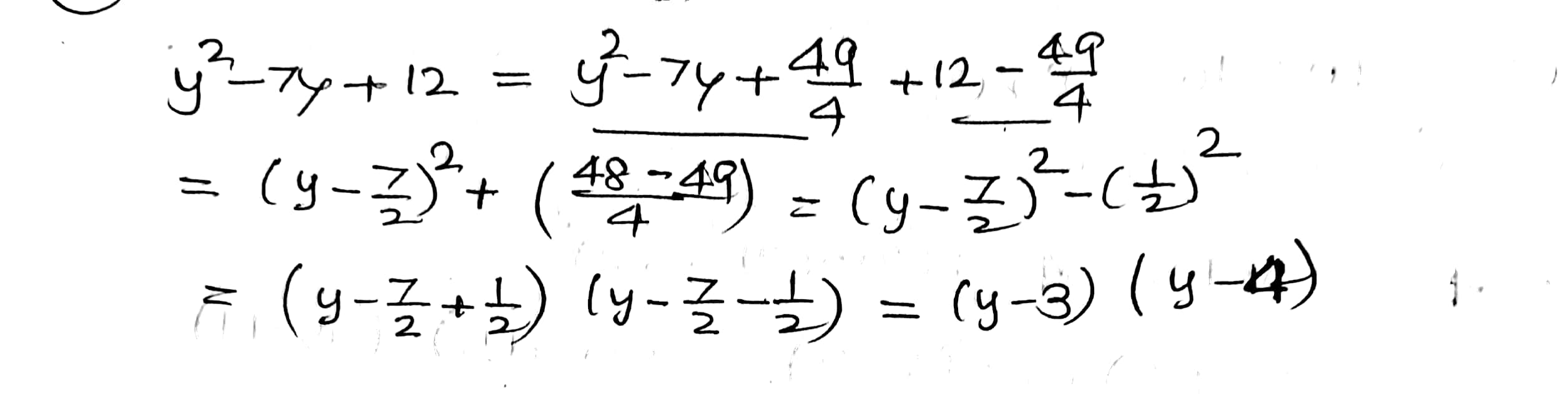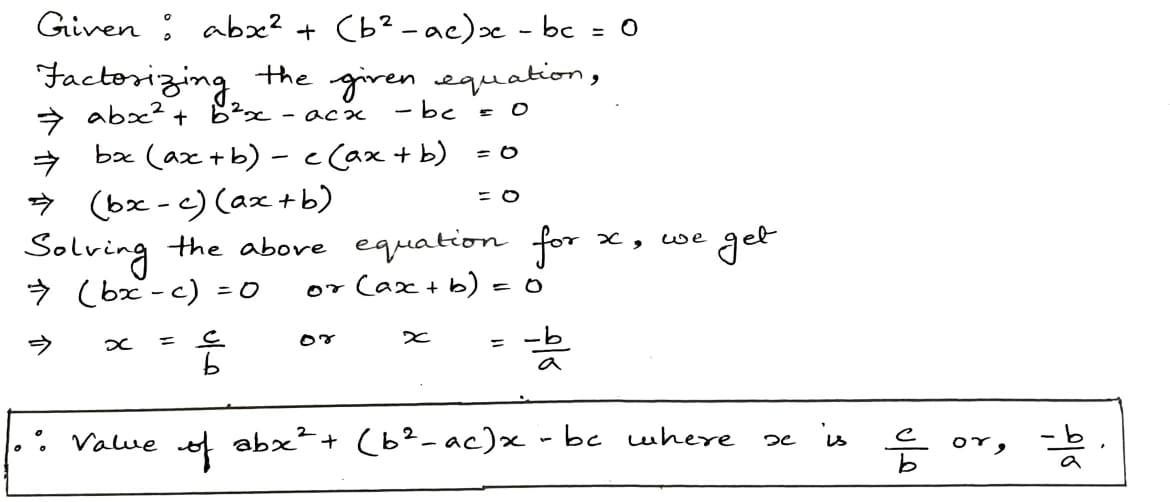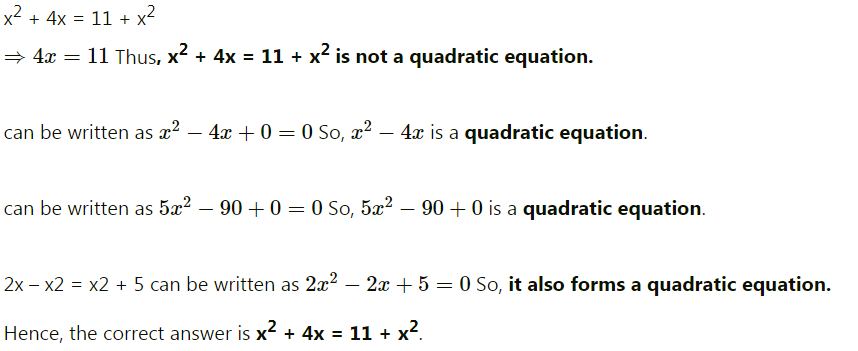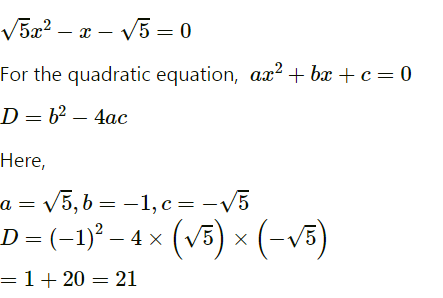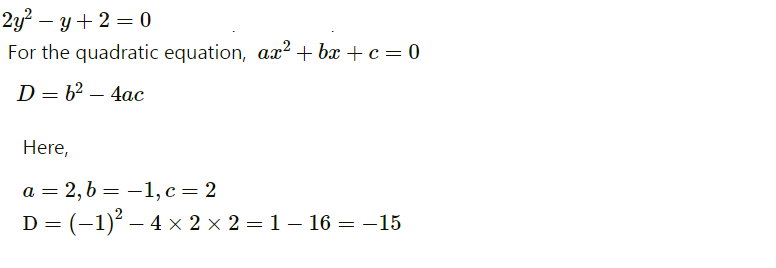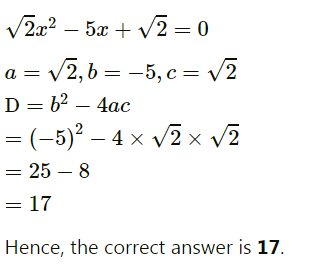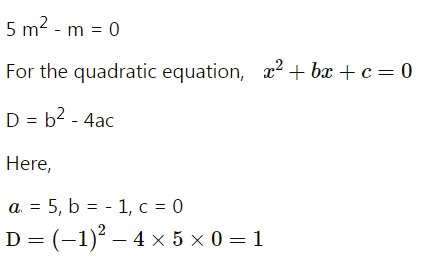Quadratic Equations - Class 10 Maths - Extra Questions
If the roots of the equation $$(b-c)x^{2}+(c-2)x+(a-b)=0$$ are equal, then prove that $$2b=a+c$$
Is the given equation quadratic? Enter 1 for True and 0 for False.
$$n\,-\, 3\, =\, 4n^{2}$$
Solve: $$\displaystyle 25x^{2}-30x+9=0$$
Solve the equation :
$$\displaystyle { 27x }^{ 2 }-10x+1=0$$
Solve the equation : $$\displaystyle { x }^{ 2 }-2x+\frac { 3 }{ 2 } =0$$
Solve the equation $$\displaystyle \sqrt { 2 } { x }^{ 2 }+x+\sqrt { 2 } =0$$
Solve the equation $$\displaystyle { 21x }^{ 2 }-28x+10=0$$
Solve the equation $$\displaystyle { x }^{ 2 }+\frac { x }{ \sqrt { 2 } } +1=0$$
Solve the equation $$\displaystyle { x }^{ 2 }+3x+5=0$$ for $$x$$.
Solve the equation $$\displaystyle { 2x }^{ 2 }+x+1=0$$
Check whether $$2x + x^2 + 1 = 0$$ a quadratic equations.
Solve the quadratic equation $$3{x}^{2}+5x+2=0$$ using formula method.
Solve the following quadratic equation by completing square method
$$x^2 + 11x + 24 = 0$$
Check whether $$6x^3 + x^2 = 2$$ is a quadratic equations
Solve the quadratic equation $$2{x}^{2}+5x+3=0$$ using formula method.
Decide whether $$\cfrac{3}{y}-4=y$$ is a quadratic equation or not.
Solve the equation $$3y^{2} + 8y + 5 = 0$$ by using formula method
Solve the following quadratic equation by using formula method
$$3y^2 + 7y + 4 = 0$$
If $$a = 1, b = 8$$ and $$c = 15$$, then find the value of $$b^2-4ac =$$
Solve the following quadratic equation using the formula method:
$$4{x}^{2}+7x+2=0$$
Solve the following quadratic equation by using the formula method: $$m^{2} - 3m - 10 = 0$$
The discriminant of the quadratic equation $$px^{2} + qx + r = 0$$ is ________
Solve $$x^2 + 6x - 7 = 0$$ by the method of completing the square
Write the discriminant of the equation $$ax^2 + bx + c = 0$$.
Decide whether $$m^{2} + m + 2 = 4m$$ is a quadratic equation
Solve the quadratic equation $$2x^{2} + x - 4 = 0$$ by completing the square
Solve the quadratic equation $$x^{2} - 4x + 2 = 0$$ by formula method.
If $$x=\cfrac { \sqrt { 3 } -\sqrt { 2 } }{ \sqrt { 3 } +\sqrt { 2 } } ,y=\cfrac { \sqrt { 3 } +\sqrt { 2 } }{ \sqrt { 3 } -\sqrt { 2 } } $$, find the value of $$3{ x }^{ 2 }-5xy+3{ y }^{ 2 }$$
Solve the equation by using the formula:
$${m}^{2}-2m=2$$
The formula of discriminant of quadratic equation $$ax^{2} + bx + c = 0$$ is $$D =$$ ______.
Find the value of $$k$$ for which the given equations has real and equal roots:
(i) $$(k - 12)x^{2} + 2(k - 12)x + 2 = 0$$
(ii) $$k^{2}x^{2} - 2(k - 1)x + 4 = 0$$.
Solve the equation $$a^2x^2-3abx+2b^2=0$$ by completing the square.
An equation whose maximum degree of variable is two is called ............... equation.
Check whether the given equation is a quadratic equation or not:$$x(x + 1) + 8 = (x + 2)(x - 2)$$
Find the roots of the following quadratic equation (if they exist) by the method of completing the square.
$$x^2 \, - \, 4ax \, + \, 4a^2 \, - \, b^2 \, = \, 0$$
Show that the roots of the equation $$x^2 - 2x + 3 = 0$$ are imaginary.
Simplify $$\cfrac { \left( { x }^{ 2 }+1 \right) \left( { x }^{ 2 }+2 \right) }{ \left( { x }^{ 2 }+3 \right) \left( { x }^{ 2 }+4 \right) } =$$
Find the root of the following quadratic equation (if they exist) by the method of completing the square.
$$\sqrt{3}x^2 \, + \, 10x \, + \, 7\sqrt{3} \, = \, 0$$
Write standard form of quadratic equation and find the roots of the equations $$3x^2+5\sqrt{2}+2=0$$ using general formula.
Write the discriminant of the given quadratic equation
$${ x }^{ 2 }+px+2q=0\quad $$
Solve $$4ab=2(a^2-b^2)\sqrt-1$$
Find the roots of the following quadratic equation, $$2x^2+x-4=0$$
Solve the following quadratic equations by the method of perfect the square.
$$3x^2-5x+2=0$$
If $$\alpha$$ and $$\beta$$ are the zeros of $$x^{2}+x-2$$ then find value of $$\dfrac{1}{\alpha}-\dfrac{1}{\beta}$$
Solve the following quadratic equations by the method of perfect the square.
$$5x^2-6x-2=0$$
Solve the following quadratic equations by the method of perfect the square.
$$2x^2+x+4=0$$
$$x^{2}+3\left| x \right| +2=0$$ Find the value of $$x$$.
Find a quadratic equation with real co-efficient whose one root is $$3-2i$$.
Solve the following quadratic equations by the method of perfect the square.
$$4x^2+3x+5=0$$
Solve$${ x }^{ 2 }+5x-2=0$$
Solve $${x}^{2}-3x+12=5$$
Factorise : $$2\sqrt{2}x^2 + 9x + 5 \sqrt{2}=0$$
Check whether the following is quadratic equation.
$$(x+1)^2=2(x-3)$$
The equation $$x^2 + 2(m-1)x + (x + 5) = 0$$ has real and equal roots. Find the value of $$m$$.
The quadratic equation $$ax^2 + bx + c = 0$$, ($$a\ne 0$$) has atmost _____ roots.
$$2\sqrt{5}{x}^{2}-3x-\sqrt{5}=0$$ Find $$x$$.
Find the values of a : $$7{a^2} + 7a - 20=0$$
Find the co-ordinates points where the graph of polynomial $${x^2} + x + 12$$ intersects the x-axis.
Check whether the following is quadratic equation.
$$x^2+3x+1=(x-2)^2$$
Solve the following quadratic equation by completing the square method.
$$x^2+2\ x-5=0$$
Find the nature of the roots of the following quadratic equations. If roots are real, find them.
$$5x^{2}-3x+2=0$$
Check whether the following is quadratic equation.
$$(x+2)^3=2x(x^2-1)$$
Check whether the following is quadratic equation.
$$x^2-2x=(-2)(3-x)$$
Check whether the following in quadratic equation.
$$(x-3)(2x+1)=x(x=5)$$
Check whether the following is quadratic equation.
$$(x-2)(x+1)=(x-1)(x+3)$$
Solve the quadratic equation : $$4x^2-4ax+(a^2-b^2)=0$$
Solve each of the following equation by using the method of completing the square:
$$\dfrac {2}{x^{2}}-\dfrac {5}{x}+2=0$$
$$(x + 2)(x + 3) + (x - 3)(x - 2) - 2x(x + 1) = 0$$
Solve each of the following equation by using the method of completing the square:
$$8x^{2}+14x-1=0$$ ?
Factorise:
$${x}^{2}-x-12$$
Solve each of the following equation by using the method of completing the square:
$$5x^{2}+6x-2=0$$ ?
Solve the quadratic equation :$$4x^2+4bx-(a^2-b^2)=0$$
Solve each of the following equation by using the method of completing the square:
$$3x^{2}-2x-1=0$$
Find the roots of given equation $$2y^{2}-y-1=0$$
Solve $$\sqrt 5 {x^2} + x + \sqrt 5 = 0$$.
Find the roots of the equations by the method of completing the square.
$$x^{2}+7x-6=0$$
Solve each of the following equation by using the method of completing the square:
$$x^{2}-(\sqrt {2}+1)x+\sqrt {2}=0$$
Solve each of the following equation by using the method of completing the square:
$$\sqrt {2}x^{2}-3x-2\sqrt {2}=0$$
Solve $$2x^2-5x+3=0$$.
Solve:$$2x^2+x+4=0$$.
Solve $${x^2} - 4x + 1 = 0$$ by completing square method.
Write the equation by the method of completing the square.
$$x^{2}+7x-6=0$$
Find the roots of the equations by the method of completing the square.
$$x^{2}-10x+9=0$$
Find the factor of the polynomial given below.
$$12x^{2}+16x+77$$
Solve the quadratic equation.
$$ 8 x ^ { 2 } - 22 x - 21 = 0 $$
solve:
$$\dfrac{20\pm \sqrt{400-4(5)(18)}}{2(5)}$$=?
Find the values of $$'k'$$ $$2x^{2}+kx+3=0$$ so that they have two equal roots ?
Evaluate
$$6x+29=\dfrac{5}{x}$$
$$ (2x-1) (x-3) = (x+5)(x-1) $$
Solve the above equations
Solve using formula.
$$5x^{2} + 13x + 8 = 0$$.
Find the roots of the equation $$2x^2 - x + \dfrac {1}{8} = 0 $$
Solve the quadratic equation $$(x-2)^{2}+1=17$$
Solve using formula.
$$5m^{2} - 4m - 2 = 0$$.
Solve using formula.
$$x^{2} - 3x - 2 = 0$$.
Solve using the Quadratic formula.
$$3m^{2} + 2m - 7 = 0$$.
Is $$x=-2$$ a solution of the equation $${ x }^{ 2 }-2x+8=0$$?
Find the roots of $$ax^2 + bx + c = 0 (a \neq 0)$$ by the method of completing the square.
How can solve by completing square method $$x^2 - 5x + 5 = 0$$
Solve $$(x^{2}-2x+1)^{n+1}=1$$
$$5x( x+2) = 3$$
The sum of a natural number and its positive square root is $$132$$. Find the number.
The sum of a natural number and its square is $$156$$. Find the number.
Solve:
$${ x }^{ 2 }+8x+16= ?$$
For $$p=99$$ then find the value of $$p^3+3p^2+3p$$
Find the roots of the equation $$5x^{2}-6x-2=0$$.
simplify :
$$\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {2x + 1} \right) = x\left( {x + 5} \right)$$
Find the value of k for which the following equations has equal roots.$$x^{2}+4kx+(k^{2}-k+2)=0.$$
Solve $$ {{x}^{2}}-12x+36=0 $$
Factorise $$ 8x ^{2}-34x +30=0$$
Find factors of $$x ^ { 4 } + 2 x ^ { 3 } - 7 x ^ { 2 } - 8 x + 12$$
$$x^{2}-5x+4$$ =
Solve:
$$9x^2-3x-2=0$$
Find the roots of the quadratic equation $$x - \dfrac{1}{x} = 3$$.
Find the roots of $$5x^2+13x+8=0$$ by using quadratic formula.
If $$ (x^{2}-2x+1)$$=0 then the value of x is
What is the formula to solve general form of quadratic equation and what is its discriminant value.
Write the following quadratic equation in the form of $$ax^2 + bx + c$$, then write the values of a,b,c:
$$2y=10-y^2$$
Find the roots of the following quadratic equation (if they exist ) by the method of completing the square.
$$4x^{2}+4\sqrt {3}x+3=0$$
Solve: $$4x^2-2(a^2+b^2)x+a^2b^2=0$$
Find the discrimination of the quadratic equation $$2x^{2}-4x+3=0$$
Solve:
$$\sqrt { 2 } x ^ { 2 } + 7 x + 5 \sqrt { 2 } = 0$$
What must be subtracted from $$3a^{2}-6ab-3b^{2}-1$$ to get $$4a^{2}-7ab-4b^{2}$$.
Solve: $$2x^2 - x^2 =$$?
Solve using quadratic formula,
$$3x^{2}+2(3+2a)\ x+8a=0$$
Equation $$y = x ^ { 2 } + 7 x - 5$$ can be written in the form $$y = ( x + a ) ^ { 2 } + $$ $$b$$. Find the value of $$a$$ and $$b$$.
Solve for $$x$$:
$$x ^ { 2 } + 21 x - 100=0$$
Solve :
$$\sqrt {2x+\sqrt {2x+4}}=4$$
Check whether the following is Quadratic equations:
$${\left( {x + 1} \right)^2} = 2\left( {x - 3} \right)$$
Solve:
$$2x^{2}+5x+3=$$?
Solve :
$$\sqrt {2x+9}+x=13$$
Solve:
$$\sqrt {3x^{2}-2}+1=2x$$
Solve the following by using the method of completing square.
$$3y^{2}-7y-20=0$$
Solve the following by using the method of completing square.
$$6x^{2}-11x+3=0$$
Write constant term
$$7x^2-11$$
Obtain the roots of the following quadratic equation by using the general formula the solution:
$$3x^{2}-2x+2=0$$
Solve for x: $$4x^{2}+14x+6$$
Solve the following by using the method of completing square.
$$5x^{2}-4x-10=0$$
Solve the following.
$$ab{x^2} + ({b^2} - ac)x - bc = 0$$
Solve : $$x^{2}-8x+15=0$$ by completing a square method.
Write constant term
$$3y^2+5y-7$$
Solve.
$$\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{9} - \dfrac{2}{3}x + 1 = 0$$
Find the value of $$x$$ : $$x ^ { 2 } + 2 x - 7$$
solve.
$$21{x^2} - 8x - 4 = 0$$
Solve : $$3x^{2}-4x+\dfrac{20}{3}=0$$
Solve:
$$f(x)=x^{2}-11x+28$$
Simplify $$\frac{a}{{x - a}} + \frac{b}{{x - b}} = \frac{{2c}}{{x - c}}$$
Obtain the roots of the following quadratic equation by using the general formula the solution:
$$\sqrt {3}\ x^{2}+10x-8\sqrt {3}=0$$
Is $$\sqrt{2}x^{2} +7x+5\sqrt{2}=0$$ quadratic equation. If yes then give reason.
Solve :$$3x^{2}-6x+3=0$$
Solve:$$9m^{2}-10m+1$$
Solve the following quadratic equation $${ x }^{ 2 }+4x-5=0$$ by completing the square method.
Find the discriminant of quadratic equation $$x^{2}-4x+1=0$$.
Solve : $${ x }^{ 2 }-8x+15=0$$ by completing a square method.
Factorize :$$y^{2}-10y+25$$
By using the formula, find the roots of the following quadratic equation, $$\left(x +7\right)\left(x + 3\right) = 5\left(x+4\right) \left(x +2\right) + 17x$$
Find the value of k for which the quadratic equation $$(k+4)x^{2}+(k+1)x+1=0$$ has equal roots.
Solve $$x^{2}-5x-36=0$$.
Given reason whether the following is an equation or not:$$(x-2)^2=x^2-4x+4$$.
If $$a^{2}+\dfrac {1}{a^{2}}=23$$, find the value of $$\left(a+\dfrac {1}{a}\right)$$
Solve for $$x:$$$$x^2-5x+6=0$$.
$$ \frac{x-a}{x-b}+\frac{x-b}{x-a}= $$
Solve :$$x^{2}+10x+25=0$$
Solve :$$x^{2}+4x+4=0$$
Solve
$$x^2+$$ $$4x$$ $$-8$$ = 0
Find $$\displaystyle x^2 + 5x$$ at $$x=3$$
For what value of $$k$$ does the quadratic equation $$(k-5)x^{2}+2(k-5)x+2=0$$ have equal roots?
Check whether the following are Quadratic equations
$${ x }^{ 2 }+3x+1={ \left( x-2 \right) }^{ 2 }$$
Check whether the following is a quadratic equation or not.$$(x+1)^2=2(x-3)$$
Write the discriminant of the following equation :$$x^{2}-4x+2=0$$
If $$x^{2}+\dfrac {1}{x^{2}}=51$$, find the value of $$\left(x-\dfrac {1}{x}\right)$$
If m = 2, find the value of $$m^2-m+1$$
Solve:
$$x^2=9$$
Solve:
$$x^2+2xy \cot2 \alpha -y^2=0$$
Solve :$$x^{2}-8x+16=0$$
Solve:$${x}^{2}-4x+1+3=0$$
If $$\alpha$$ and $$\dfrac{1}{\alpha }$$ are zeroes of $$4x^{2}-17x+k-4$$, find value of k.
Factorise the polynomial by the method of completing the square.
$$p^2+6p -16$$
Write the coefficient of $$m^{2}$$ in $$-4m^{2}+3m-7$$
Find the roots of the quadratics equation $$3{ x }^{ 2 }-4\sqrt { 3 }x +4=0$$.
Solve the given equation by the method of completing the squares:
$$x^{2}+12x-45=0$$
Find the roots of the following quadratic equation, if they exist, by the method of completing the square:
$$2{x}^{2}+x-4=0$$
Evaluate:$$\dfrac { 1 }{ \sqrt{ { x }^{ 2 }+2x+9 } }=1$$
Find the discriminant of the quadratic equation $$4\sqrt{2}{x}^{2}+8x+2\sqrt{2}=0$$
Factorise $$ x ^ { 2 } - 10 x + 9 = 0 $$ using completing square method.
$$\Pi \left( x+7 \right) ^{ 2 }-\Pi { x }^{ 2 }=286$$
Find which of the following equations are quadratic:
$$ x^{2}+5 x-5=(x-3)^{2} $$
Find which of the following equations are quadratic:
$$ 7 x^{3}-2 x^{2}+10=(2 x-5)^{2} $$
Find which of the following equations are quadratic:
$$ 5 x^{2}-8 x=-3(7-2 x) $$
Find which of the following equations are quadratic:
$$ (\mathbf{x}-\mathbf{1})^{2}+(\mathbf{x}+\mathbf{2})^{2}+3(\mathbf{x}+\mathbf{1})=0 $$
$$ a(2a-b) -b^2 $$
Find whether the following equations are quadratic or not:
$$ (3 x-1)^{2}=5(x+8) $$
Find the roots of the following quadratic equation, if they exist, by the method of completing the square:
$$4{x}^{2}+4\sqrt{3x}+3=0$$
Find which of the following equations are quadratic:
$$ (x-4)(3 x+1)=(3 x-1)(x+2) $$
If the roots of the equation $$(a^{2}+b^{2})x^{2}-2(ac+bd)x+(c^{2}+d^{2})=0$$ are equal, then prove that $$\dfrac{a}{b}=\dfrac{c}{d}$$.
If $$ P\left( x \right) ={ ax }^{ 2 }+bx+c $$ and $$ Q\left( x \right) =-{ ax }^{ 2 }+bx+c $$ , where $$ ac\neq 0 $$ , then show that $$ P\left( x \right) Q\left( x \right) $$=0 has at least two real roots.
If the equation $$ { ax }^{ 2 }+2bx+c=0$$ has real roots, $$a,b,c$$ being real numbers and if $$m$$ and $$n$$ are real number such that $$ { m }^{ 2 }>n>0$$ then show that the equation $$ { ax }^{ 2 }+2mbx+nc=0$$ has real roots.
Is the given equation quadratic? Enter 1 for True and 0 for False.
$$x^{2} +\, 4x\, =\, 11$$
Is the given equation quadratic? Enter 1 for True and 0 for False.
$$x^{2} +\, 4x\, =\, 11$$
Find the value of discriminant for the following equation.$$x^{2}\, -\, 3x\, +\, 2\, =\, 0$$
Find the value of discriminant for $$\sqrt3x^{2}\, +\, 2\sqrt2x\, -\, 2\sqrt3\, =\, 0$$
If $$z^{2}\, +\, 4z\, -\, 7\, =\, 0$$, then $$z\, =\, -\, 2\, \pm\, \sqrt{11}$$.
If true then enter $$1$$ and if false then enter $$0$$
Is the following equation quadratic? Enter 1 for True and 0 for False.
$$m\, -\, \displaystyle \frac{5}{m}\, =\, 4m\, +\, 5$$
Find the value of discriminant for the following equation.$$x^{2}\, -\, 6x\, +\, 7\, =\, 0$$
Discuss the nature of the roots of the equation $$\displaystyle 4x^{2}-2x+1=0 $$
Solve the equation $$\displaystyle { x }^{ 2 }-x+2=0$$
Roots of the quadratic equation $$\displaystyle 3x^{2}-2\sqrt{15}x-2=0$$ are $$\dfrac{\sqrt{15}\pm \sqrt{21}}{3}$$. If true answer is 1,else 0
Solve the equation : $$\displaystyle { 3x }^{ 2 }-4x+\frac { 20 }{ 3 } =0$$
Find the roots of the following quadratic equations, if they exist, by the method of completing the square:
(i) $$\displaystyle 2{ x }^{ 2 }-7x+3=0$$
(ii) $$\displaystyle 2{ x }^{ 2 }+x-4=0$$
(iii) $$\displaystyle 4{ x }^{ 2 }+4\sqrt { 3x } +3=0$$
(iv) $$2x^{2}+x+4=0$$
Check whether the following are quadratic equations :
(i) $$\displaystyle { \left( x+1 \right) }^{ 2 }=2\left( x-3 \right) $$
(ii) $$\displaystyle { x }^{ 2 }-2x=\left( -2 \right) \left( 3-x \right) $$
(iii) $$\displaystyle \left( x-2 \right) \left( x+1 \right) =\left( x-1 \right) \left( x+3 \right) $$
(iv) $$\displaystyle \left( x-3 \right) \left( 2x+1 \right) =x\left( x+5 \right) $$
(v) $$\displaystyle \left( 2x-1 \right) \left( x-3 \right) =\left( x+5 \right) \left( x-1 \right) $$
(vi) $$\displaystyle { x }^{ 2 }+3x+1={ \left( x-2 \right) }^{ 2 }$$
(vii) $$\displaystyle { \left( x+2 \right) }^{ 3 }=2x\left( { x }^{ 2 }-1 \right) $$
(viii) $$\displaystyle { x }^{ 3 }-4{ x }^{ 2 }-x+1={ \left( x-2 \right) }^{ 3 }$$
Find the roots of the following equations:
(i) $$\displaystyle x-\dfrac { 1 }{ x } =3,x\neq 0$$
(ii) $$\displaystyle \dfrac { 1 }{ x+4 } -\dfrac { 1 }{ x-7 } =\dfrac { 11 }{ 30 } ,x\neq -4,7$$
Find the value of $$\sqrt {a + \sqrt {a + \sqrt {a + ...... \infty}}}$$
Solve the given quadratic equation by completing the square, $$4x^2 - 20x + 9 = 0$$.
Solve the quadratic equation $$x^2 + 6x - 7 = 0$$ by completing the square.
Check whether $$3x - 10 = 0$$ is a quadratic equation or not?
Check whether $$x^2 - y^2 = 0$$ is a quadratic equation.
Check whether $$x^2 - \dfrac{29}{4} x + 5= 0$$ is a quadratic equation
Check whether $$x(x+1) + 8 = (x+ 2) (x-2)$$ is a quadratic equation.
Solve $$3x^2 - 5x + 2 = 0$$ by completing the square method.
Check whether $$x^3 - 10x + 74 = 0$$ is a quadratic equation.
Check whether $$\left( x + \dfrac{3}{4} x \right ) (x - 8 ) + 10 = 0$$ is a quadratic equations
Check whether $$5 - 6x = \dfrac{2}{5} x^2$$ is a quadratic equation.
Solve the given quadratic equation by completing the square, $$2x^2 + 5x - 3 = 0$$
Solve the following equation and calculate the answer correct to two decimal places.
$$x^2-5x-10=0$$.
Solve the given quadratic equation by completing the square, $$x^2 - 3x + 1 = 0$$
Solve the given quadratic equation by completing the square, $$x^2 + 16 x - 9 = 0$$
Solve for $$x$$ using the quadratic formula. Write your answer correct to two significant figures. $$(x - 1)^{2} - 3x + 4 = 0$$
Solve the quadratic equation $$x^{2} - 3(x + 3) = 0$$; Given your answer correct to two significant figures.
Solve the given quadratic equation by completing the square, $$4x^2 + x - 5 = 0$$
Solve the following equation and give your answer correct to 3 significant figures
$$5x^2-3x-4=0$$
Solve the quadratic equation $$2{ x }^{ 2 }+5x+2=0$$
Solve the quadratic equation $$2{x}^{2}+3x+1=0$$ using formula method.
Solve the following quadratic equation by completing square method
$$x^2 + 11 x + 30 =0 $$
Solve the following quadratic equation using formula method $$3x^2+7x+4=0$$.
Solve the following quadratic equation by completing square method
$$x^2 + 10 x + 24 = 0$$
Solve the following quadratic equation by completing the square method:
$${m}^{2}-3m-1=0$$
Solve the following quadratic equation using formula method:
$$6x^{2} - 7x - 1 = 0$$
Solve the following quadratic equation by completing square method
$$x^2 + 10 x + 21 = 0$$
Solve the following quadratic equation by using quadratic formula method: $$x^{2} + 4x + 1 = 0$$
Solve the following quadratic equation by completing square method
$$5y^2 - 4y - 1 = 0$$
Solve the following quadratic equation by the formula method : $$3{x}^{2}+7x+2=0$$.
Compare quadratic equation $${x}^{2}+3x-1=0$$ with the general form $$a{x}^{2}+bx+c=0$$ and write the value of '$$a$$' and '$$b$$'.
Find the roots of equation $$2x^2 - x - 4 = 0$$ by the method of completing the square.
State whether the given equation is quadratic or not. Give reason.
$$\displaystyle\frac{5}{4}m^2-7=0$$.
Solve the quadratic equation for x :
$$4{ x }^{ 2 }-4{ a }^{ 2 }x+\left( { a }^{ 4 }-{ b }^{ 4 } \right) =0$$
Let $$a, b, c$$ be the sides of a triangle. No two of them are equal and $$\lambda \epsilon R$$. If the roots of the equation $$x^{2} + 2(a + b + c)x + 3\lambda (ab + bc + ca) = 0$$ are real then.
Solve the equation $$4x^2-5x-3=0$$.
Number of solutions of the equations $$|2x^2 + x -1| = |x^2+ 4x + 1|$$
Find the value of $$p$$ in the equation $$2{ x }^{ 2 }+3x-p=0$$ if the roots are real and equal.
Solve the equation $$3x-\displaystyle\frac{3}{x}=-8$$ by formula method.
Solve the quadratic equation $$5x^2-6x-2=0$$ by completing the square.
Solve the following quadratic equation by formula method-
$$3x^{2} + 8x - 3 = 0$$
Write standard form of quadratic equation and find the roots of the equation $$3x^2 + 5 \sqrt 2 x + 2 = 0$$ using general formula.
Find the value of discriminant $$(\Delta)$$ for the quadratic equation: $$x^2+3x+1=0$$.
Solve the following equation:
$$2{ x }^{ 2 }-13x+15=0$$
Find the smallest solution in positive integers of $${ x }^{ 2 }=41{ y }^{ 2 }-1$$.
Find the general solution in positive integers of $${ x }^{ 2 }-17{ y }^{ 2 }=-1$$.
Find a general formula to express two positive integers which are such that the result obtained by adding their product to the sum of their squares is a perfect square.
Find the general solution in positive integers of $${ x }^{ 2 }-5{ y }^{ 2 }=1$$.
If the product of all solution of the equation $$\dfrac{(2009)x}{2010}=(2009)^{\log_x(2010)}$$ can be expressed in the lowest form as $$\dfrac{m}{n}$$ then the value of $$(m+n)$$ is
Show that the roots of the equation
$$(x - a)(x - b)(x - c) - f^{2}(x - a) - g^{2}(x - b) - h^{2}(x - c) + 2fgh = 0$$ are all real.
Solve $$x^2+7x=7$$ and give your answer correct to two decimal places.
Solve the following equation:
$$\displaystyle\, \left ( \left ( \sqrt[5]{27} \right )^{x/4 - \sqrt{x/3}} \right )^{x/4 + \sqrt{x/3}} = \sqrt{27}$$
Check if the equation $$x \, + \, \dfrac{1}{x} \, = \, x^2 , \, x \, \neq \, 0$$ is quadratic.
Solve the following equations.
$$\displaystyle log \, (5 \, - \, x) \, + \, log \,(3 \, - \, x) \, = \, 1.$$
Find the roots of the quadratic equation (if they exist) by the method of completing the square.
$$2x^2 + x + 4 = 0$$
$$2x^2 + x + 4 = 0$$
Discriminant of the following quadratic equation is :
$$2x^2$$ - 5x + 3 = 0
Discriminant of the following quadratic equation is zero for k equal to:
$$x^2$$ - 2x + k = 0, k $$\epsilon$$ R
Verify the equation $$(x+1)^2=2(x-3)$$ is a quadratic equation
Discriminant of the following quadratic equation is :
$$\sqrt{3}x^2 \, + \, 2\sqrt{2}x \, - \, 2\sqrt{3} \, = \, 0$$
Two pipes running together can fill a tank in $$11\dfrac{1}{9}$$ minutes. If one pipe takes $$5$$ minutes more than the other to fill the tank , find the product of the time in which each pipe would fill the tank .
Negative of Discriminant of the following quadratic equation is :
$$x^2$$ - x + 1 = 0
Discriminant of the following quadratic equation is :
$$x^2 -2x - 4 = 0$$
Solve $$2x^2+x-6$$ by completing square method
Find the Discriminant of the equation :
$$(x - 1)(2x - 1) = 0$$
If the roots of the equation $$(b - c)x^2 + (c - a)x + (a - b) = 0$$ are equal, then prove that $$2b = a + c$$.
$$(7 \, - \, 4 \sqrt 3)^{x^2 \, - 4x \, + \, 3} \, + \, (7 \, + \, 4 \sqrt 3)^{x^2 \, - 4x \, + \, 3} \, = \, 14$$
(a) Prove that the roots of
$$(x-a)(x-b)+(x-b)(x-c)+(x-c)(x-a)=0$$
are always real and they will be equal if and only if $$a=b=c$$.
(b) Examine the nature of the roots of the quadratic $${ \left( b-x \right) }^{ 2 }-4(a-x)(c-x)=0$$ where a,b,c are real.
(c) Discuss the nature of the roots of the equation $${ x }^{ 2 }+2(3\lambda +5)x+2(9{ \lambda }^{ 2 }+25)=0$$
Using the Completing Square Method convert the following quadratic equation in the form of $$(x+p)^2=q$$ and then find out its roots.
$$5x^2-6x-2=0$$
If the roots of the equation
$$({ c }^{ 2 }-ab){ x }^{ 2 }-2({ a }^{ 2 }-bc)x+({ b }^{ 2 }-ac)=0$$
be equal, prove that either $$a=0$$
or $${ a }^{ 3 }+{ b }^{ 3 }+{ c }^{ 3 }+=3abc$$.
$${x^2} - (\sqrt 2 + 1)x + \sqrt 2 = 0$$
Solve the following equations :
$$\sqrt{3x+1}$$$$-$$ $$\sqrt{x-1}$$ = $$2$$
Using the Completing Square Method, find the roots of the following quadratic equations
$$4x^2+4\sqrt{3}x+3=0$$
Write the zeroes of the polynomial :
$$x^2+2x+1$$
If $$\alpha, \beta$$ are the roots of $$x^2 \, + \, ax \, + \, b \, = \, 0$$. Then prove that $$\dfrac{\alpha }{\beta }$$ is a root of the equation $$bx^2 \, +\, (2b \, - \,a^2) \, x \, + \, b \,= \, 0$$.
Solve the equation $$2{ x }^{ 2 }-5x+3=0$$ by the method of completing square.
Check whether the given equation is a quadratic equation.
$$x+\cfrac { 3 }{ x } ={ x }^{ 2 }$$
Check whether the given equation is a quadratic equation.
$${ x }^{ 2 }-6x+4=0$$
Find the roots of the given equation $$4{ x }^{ 2 }+4bx-\left( { a }^{ 2 }-{ b }^{ 2 } \right) =0$$ by the method of completing the square.
Solve the quadratic equation $$9{ x }^{ 2 }-15x+6=0\quad $$ by the method of completing the square.
By using the method of completing the square, show that the equation $$4{ x }^{ 2 }+3x+5=0$$ has no real roots.
Find the roots of the equation $$5{ x }^{ 2 }-6x-2=0,$$ by the method of completing the square.
Solve:$$4x^2+4\sqrt{3}x+3=0$$.
Find the value of $$'K'$$ if $$Q.E$$
$$(2k+1){x}^{2}+2(k+3)x+(k+5)=0$$ has equal roots
$$x=\sqrt {6+\sqrt {6}+\sqrt {6}...}$$
Check whether the following is quadratic equation.
$$(2x-1)(x-3)=(x+5)(x-1)$$
Is the mathematical statement $$(a+4)(a+2)=a^{2}+8$$ correct? given the reasons to support your answer.
An equation is condition on a _________
For what value of $$'k',\ (k^2 - 4)x^2 + 2x - 9=0$$ can not be quadratic equation?
Solve $${x^2} - 15x + 54$$
Find the value of $$\sqrt{6+\sqrt{6+\sqrt{6+......to \infty}}}$$
If $$x=3+i$$ then prove that $$x^2-6x+13=0$$.
Solve the following
Find the roots of quadratic equation $$2x^{2}-4x+3=0$$ by completing the square find the roots of quadratic equation by using the formula
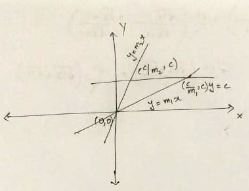
Show that the area of the triangle formed by the lines $$y = m_1\ x, y = m_2\ x \ and \ y = c$$ is equal to $$\dfrac{c^2}{4} (\sqrt{33} + \sqrt{11}),$$ where $$m_1, m_2$$ are the roots of the equation $$x^2 + (\sqrt {3} + 2)x + \sqrt {3} - 1 = 0$$.
Solve the equation: $$11{x^2} - 21x - 92 = 0$$
Solve for x : $$\sqrt 2 {x^2} + 7x + 5\sqrt 2 = 0$$
Solve:
$$abx^2+(b^2-ac)x-bc=0$$
Find the value of $$k$$ if $$x=4;y=-2$$ is a solution of the equation $$5x+4y=k$$
Solve:
$$(4x+2)\sqrt{x^2+x+1}$$
Solve the following equations$$16x - \dfrac{{10}}{x} = 27$$
$$\dfrac{1}{x} - \dfrac{1}{{x - 2}} = 3,\,x \ne 0,2$$
$$x - \dfrac{2}{x} = 3,\,x \ne 0$$
$$\dfrac{1}{x} - \dfrac{1}{{x - 2}} = 3,\,x \ne 0,2$$
$$x - \dfrac{2}{x} = 3,\,x \ne 0$$
The roots of the quadratic equation
$${x^2} - .2ax + {a^2} + {b^2} - {c^2} = 0$$ are where a,b,c $$ \in \,R:$$
Multiply:
$$\left( {\frac{1}{3}{x^2} - \frac{1}{2}x + 5} \right)\,by\,\left( {\frac{1}{2}{x^2} - \frac{1}{3}x + 1} \right)$$
$$yx^{2}-12x+k$$ is a perfect square find the numerical nature of $$k$$
Find the value of a and b.
$$\frac{{7 + \sqrt 5 }}{{7 - \sqrt 5 }} - \frac{{7 - \sqrt 5 }}{{7 + \sqrt 5 }} = a + \frac{7}{{11}}\sqrt 5 b$$
Hence factorise the polynomial : $$24{x^2} - (a + 41)x + (b + 11)$$
Find the roots of the equation:
$$x - \dfrac{1}{x} =3,x \ne 0$$
$$x - \dfrac{1}{x} =3,x \ne 0$$
Solve $$2 \cos^{2} \theta-\sqrt{3} \sin \theta +1=0$$
If $$\frac{{{x^2} + 1}}{x} = 2\frac{1}{2}$$ , find the value of:
$$x - \frac{1}{x}$$
Check whether the following is quadratic equation.
$$x^3-4x^2-x+1=(x-2)^3$$
Solve the following quadratic equation by completing the square method.
$$m^2-5m=-3$$
Solve the following quadratic equation by completing the square method.
$$5x^2=4x+7$$
Solve the following quadratic equation by completing the square method.
$$9y^2-12y+2=0$$
If $$p,q,r \in R$$ and the quadratic equation $$p{x^2} + qx + r = 0$$ has no real root, then
$$\left(\frac{1}{4}a-\frac{1}{2}b+1\right)^2$$
Solve the following quadratic equation by completing the square method.
$$x^2+x-20=0$$
Write one quadratic polynomial that has one zero?
Solve : $$5x - 4x^2 + 3$$
Find quadratic equation such that its roots are square of sum of the roots and square of difference of the roots of equation
$$2{x}^{2}+2(p+q)x+{p}^{2}+{q}^{2}=0$$
Find the roots of the following equation:
$$27- 125a^2- 135 a+ 225a^2$$
Find the roots of the equation $$5{x}^{2}-6x-2$$ by completing the square method
What constant number must be added or subtracted to $$4x^{2}+12x+8=0$$ to solve it by method of completing the square?
The set of values of 'c' for which the equation $${x^2} - 4x - c - \sqrt {8{x^2} - 32x - 8c} = 0$$ has exactly two distinct real solution is $$(a, b)$$ then find the value of $$(b - a)$$.
Solve each of the following equation by using the method of completing the square:
$$4x^{2}+4\sqrt {3}x+3=0$$ ?
By using the method of completing the square show that $${4x}^{2}+3x+5=0$$ has no real roots.
Solve the following equation by using the method of completing the square:
$$x^{2}-4x+1=0$$
Solve the quadratic equation : $$4x^2-4a^2x+(a^4-b^4)=0$$
Solve the following equation by using the method of completing the square:
$$x^{2}-6x+3=0$$
$$v_1+v_2=4$$ and $$v^2_1+v^2_2=16$$. Find value of $$v_1$$ and $$v_2$$.
Solve the equation $${3x}^{2}- 5x + 2 = 0$$ by the method of completing the square
Find the root of the following quadratic equation (if they exist) by the method of completing the square.
$$2x^2-7x+3=0$$.
Solve each of the following equation by using the method of completing the square:
$$7x^{2}+3x-4=0$$
Solve each of the following equation by using the method of completing the square:
$$4x^{2}+4bx-(a^{2}-b^{2})=0$$
Find the root of the following quadratic equation (if they exist) by the method of completing the square.
$$4x^2+4\sqrt{3}x+3=0$$.
Solve the equations by completing the square
$$x^{2}+7x-6=0$$
If $$6x-x^2=1$$, then the value of $$\left(\sqrt{x}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}}\right)$$ is?
Find the roots of the following quadratic equation, if they exist, by the method completing the square: $$2x^2-7x + 3=0$$
If the roots of the given equation $$(a-b)x^2+(b-c)x+(c-a)=0$$ are equal, prove that $$b+c=2a$$.
Solve the following Quadratic equation:$$x^{2} + 6x - (a^{2} + 2a - 8) = 0$$.
If $$a-b=1$$ and $$ab=12$$, find the value of $$(a^2+b^2)$$.
Find the discriminant of the quadratic equation $$ 32 \sqrt { 3 } x ^ { 2 } + 21 x - \sqrt { 3 } = 0 $$.
$$\sqrt { { 3x }^{ 2 }-7x-30 } -\sqrt { { 2x }^{ 2 }-7x-5 } =x-5$$
Find the roots of $$4x^{2}+3x+5=0$$ by the method of completing the square.
Solve $${x}+{\dfrac {1}{x}}=25{\dfrac {1}{25}}$$
Find the roots of the equations by the method of completing the square.
$$5x^{2}-6x-2=0$$
The equation $$4\sin ^{ 2 }{ x } -2\left( \sqrt { 3 } +1 \right) \sin { x } +\sqrt { 3 } =0$$ has -
Find the roots of the quadratic equation $$\sqrt{2x^{2}+1}$$
Solve using formula.
$$x^{2} + 6x + 5 = 0$$.
Solve the equation: $$2{ \left( x-3 \right) }^{ 2 }+3(x-2)(2x-3)=8(x+4)(x-4)-1$$
prove that $${a^3}{\left( {b - c} \right)^3} + {b^3}{\left( {c - a} \right)^3} + {c^3}{\left( {a - b} \right)^3} =$$ $${{a}^{3}}\left( c-b \right)+{{b}^{3}}\left( a-c \right)+{{c}^{3}}\left( b-a \right) $$
Solve $$8{x^2} - 10x - 3=0$$.
Solve using formula.
$$y^{2} + \dfrac {1}{3}y = 2$$.
Solve the following equation $$y^{2}-2y=5$$ which number should be added in given equation therefore, equation becomes complete square.
Solve:
$$x^2-4x-5$$
Solve the given problem and find value of x :-$$\dfrac{1}{x} + \dfrac{1}{{x - 2}} = 3 ; x \ne 0,2$$
Check whether the equation $$5{x^2} - 6x - 2 = 0$$ has real roots and if it has, find them by the method of completing the square. Also verify that roots obtained satisfy the given equation.
Solve:$$c^2-3c-10= 0$$
Solve the given equation and find the value of $$x$$ -
$$ {x^2} + 2ab = (2a + b)x $$
Solve for x :-$$\sqrt 3 {x^2} - 2\sqrt 2 x - 2\sqrt 3 = 0$$
If the discriminant of $$3{x^2} + 2x + a = 0$$ is double the discriminant of $${x^2} - 4x + 2 = 0$$ then find $$'a'$$.
If $$\alpha$$ and $$\beta$$ are the roots of the equation $$3{x^2} - 6x + 4 = 0$$, fid the value of $${\alpha}^2$$ + $${\beta}^2$$.
If $$x=-2$$ is the root of equation $$3{x^2} + 7x + p = 0$$ find the value of show that the root of equation $${x^2} + K\left( {4x + K - 1} \right) + p = 0$$ are equal.
Find the roots of the equation $$\begin{array} { l } { \frac { 1 } { x + 1 } + \frac { 2 } { x + 2 } } \\ { = \frac { 4 } { x + 4 } } \end{array}$$
If roots of quadratic equation $$(b-c){x}^{2}+(c-a)x+(a-b)=0$$ are real and equal then prove that $$2b=a+c$$.
Solve $$7{x}^{2}-30x-25=0$$ by completing square method
Solve:$$4+y-14y^2=0$$
$$\sqrt{x^{2}+1}$$
Solve:$$f(x)=\{(x-2)\}^2$$
Solve:$$x^2-3x-4= 0$$
$$\frac{1}{x(x^{4}-1)}$$
$$\sqrt{2}x^{2}+2x+5x+5\sqrt{2}=0$$
Solve the Quadratic Equation: $${b}^{2}-kb+ak$$
Solve :
$${x^2} + x - 2664 = 0$$
Solve for $$y$$:
$$5 y ^ { 2 } + 5 y - 10 = 0$$
Find the value of x, if $$4{ x }^{ 2 }-5x+20=0$$
Find $$x$$:
$$x^{2}+\left(\dfrac{a}{a+b}+\dfrac{a+b}{a}\right)x+1=0$$
Check whether $$(x+3)^3=x^3-8$$ is a quadratic equation?.
Solve for $$x : 9x^2-6ax+(a^2-b^2)=0.$$
Solve: $$\displaystyle {{98} \over {121}}{x^2} = {1 \over 2}$$
Evaluate
$$x^{2}-(\sqrt{2}+1)x+\sqrt{2}=0$$
Solve:
$${x}^{2}-5x+7=0$$
Using the quadratic formula, solve the equation $$9x^{2}+7x-2=0$$.
Solve the equation by the method of completing the squares:
$$x^{2}+12x-45=0$$
Solve:
$$3 x ^ { 2 } + 2 \sqrt { 5 } x - 5 = 0$$
Find the roots of the equation $$16x^2-27x-10 = 0$$.
Find the roots of $$x^{2}-4x-8=0$$ by the method of completing square.
$$\dfrac{1}{2(1-x)}\left[\dfrac{\sqrt{1-x}}{\sqrt{1+x}}+\dfrac{\sqrt{1+x}}{\sqrt{1-x}}\right]$$.
Find the value of discriminant of $$x^2 + 7x - 1 = 0$$
Find the root of the following quadratic equation (if they exist) by the method of completing the square.
$$\sqrt {2}x^{2}-3x-2\sqrt {2}=0$$
solve for x, $${9}^{x+2} - 6.{3}^{x+1} + 1=0 $$
Find the roots of the following quadratic equations (if they exist ) by the method of completing the square.
$$x^{2}-4ax+4a^{2}-b^{2}=0$$
If $$3x - 7y = 10$$ and $$xy = -1$$ then value of $$9x^2 + 49y^2$$ is?
Find the zeros of polynomial $$6x^{2}-3-7x$$.
If $$\displaystyle \frac {1}{a+b+x} = \frac{1}{a}+ \frac {1}{b}+ \frac {1}{x} $$, what is $$x = $$ ?
Solve:
$$x^2-2x-8$$
Find the roots of the following equation $$4x^2+4bx-(a^2-b^2)=0$$ by the method of completing the square.
Find the roots of the following quadratic equations, if they exist, by the method of completing the square :
(i) $$2 x ^ { 2 } - 7 x + 3 = 0$$ (ii) $$2 x ^ { 2 } + x - 4 = 0$$
(iii) $$4 x ^ { 2 } + 4 \sqrt { 3 } x + 3 = 0$$ (iv) $$2 x ^ { 2 } + x + 4 = 0$$
Find the roots
$$\sqrt 2 {x^2} - 3x + 2\sqrt 2 = 0$$
Find the roots of fraction $$\frac { x }{ (x+3)(x-4) } =1$$
Divide $$p(y)$$ by $$q(y)$$
$$P(y)=y^{5}+y^{4}+y^{3}+y6{2}+2y+2$$ and $$q(y)=y^{3}+1$$
Find the roots.
$$2{x^2} + {x} - 4 = 0$$
If $$x = \sin t$$ and $$y = \sin p t ,$$ prove that: $$\left( 1 - x ^ { 2 } \right) y _ { 2 } - x y _ { 1 } + p ^ { 2 } y = 0$$
Solve the equation $$a ^ { 2 } x ^ { 2 } - 3 a b x + 2 b ^ { 2 } = 0$$ by the method of completing the square.
Solve:$$x^2-135x+3500=0$$
Find the minimum value of $$\cos^{2}\theta+$$ $$\sec^{2}\theta$$
Obtain the roots of the following quadratic equation by using the general formula the solution:
$$p^{2}x^{2}+(p^{2}-q^{2})\ x-q^{2}=0$$
Add :- $$4{a}^{2}b-2{b}^{2}+3{c}^{2}a+4abc5$$ and $${a}^{2}b+{b}^{2}-2{c}^{2}+8ab$$
If $$-4$$ is a root of the equation $$x^{2}+px-4=0$$ and the equation $$x^{2}+px+q=0$$ has equal root, find the values of $$p$$ and $$q$$.
Find the root of the following quadratic equation, if they exist , by the method of completing the square:
$$2x^{2}-7x+3=0$$
Convert to quadratic equation $$16x-\dfrac{10}{x}=27$$.
Write the following equation in the form $$ax^{2}+bx+c=0$$.
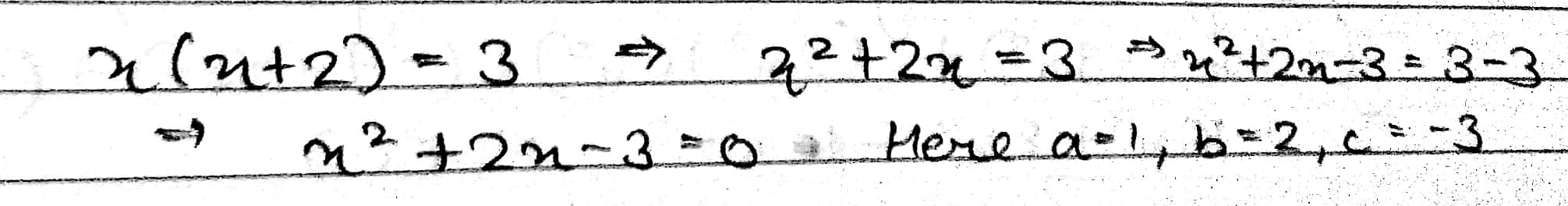
$$x(x+2)=3$$
Solve the following for $$x$$:
$$\dfrac {1}{2a+b+2x}=\dfrac {1}{2a}+\dfrac {1}{b}+\dfrac {1}{2x}$$
Find the product of the rational expressions $$\dfrac{3x^{2}+8x-3}{2x^{2}-x-6}$$ and $$\dfrac{x^{2}-4}{x+3}$$.
(x+y) (x-y) =0
What is a Quadratic Equation ?
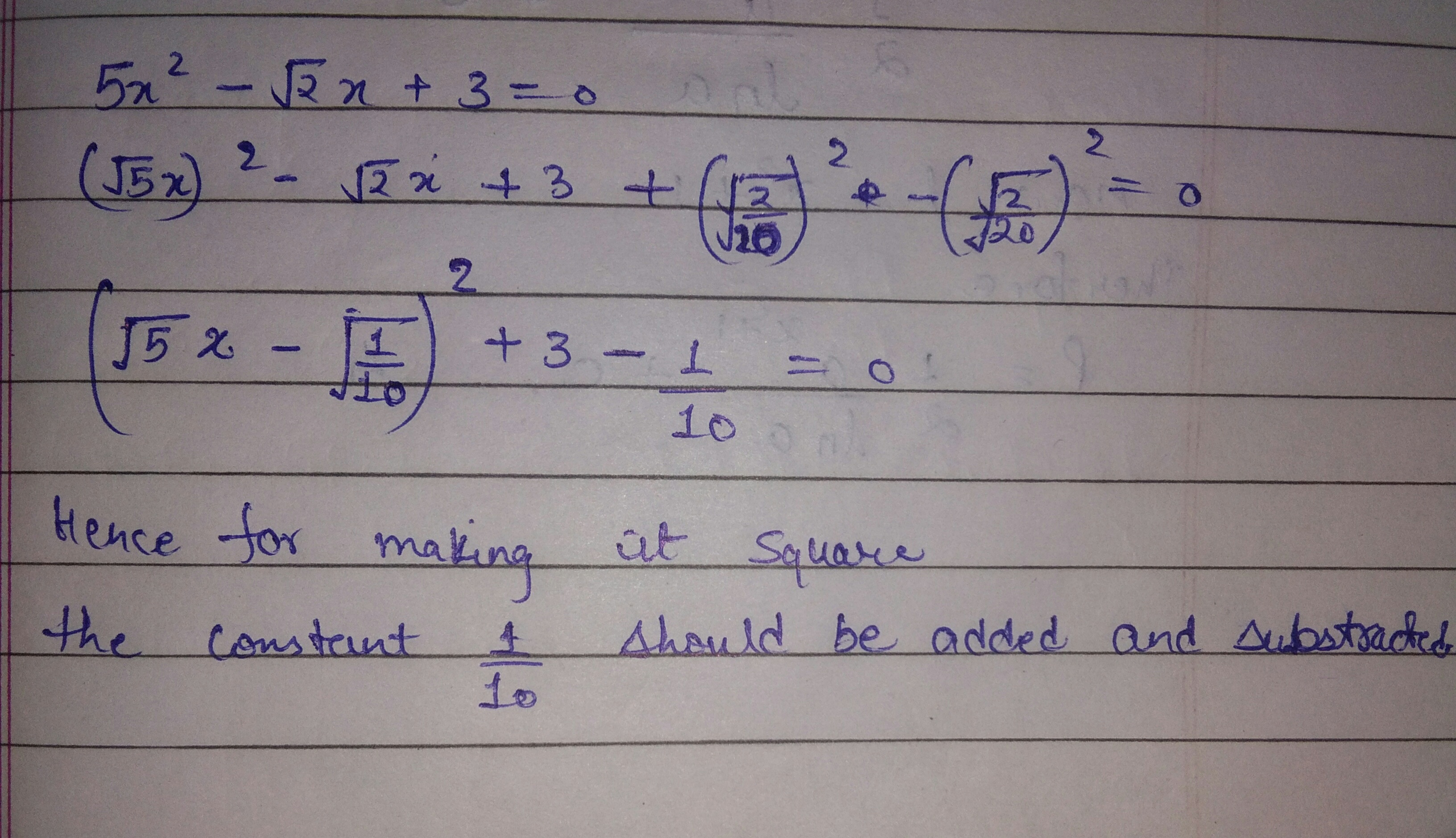
Which constant should be added and subtracted to solve the quadratic equation $$5x^{2}-\sqrt{2x}+3=0$$ by the method of completing the square?
Factorise:
$$4x^{4}-12x^{2}+9$$
Find the value of $$2{a}^{2}-3{b}^{2}+4{c}^{2}-5{d}^{2}$$ when $$a=3,\,b=0,c=2$$ and $$d=1$$
Find the value of $$k$$ if the quadratic equation $$3x^{2}-k\sqrt {3}x+4=0$$ equal roots.
Prove that the equation $$x^{2}(a^{2}+b^{2})+2x(ac+bd)+(c^{2}+d^{2})=0$$ has no real root, if $$ad \neq bc$$.
Find the roots of the following equation $$4x^{2}+4bx-(a^{2}-b^{2})=0$$ by the method of completing the square.
Verify:$$(a+b)^2-(a-b)^2=4ab$$, for $$a=4,b=3$$.
Solve: $${ 150x }^{ 2 }-750x-8=0$$
Find the roots of the quadratic equation $$2{x}^{2}+9x+10=0$$
Solve
$$2x^{2}-6x+3=0$$
Express $$\sqrt{3}y=2x$$ in standard form
Solve $$2 x ^ { 3 } y - 14 y ^ { 2 } x - 12 x ^ { 2 } y - 4 x ^ { 2 } y - 2 x y ^ { 2 }$$
If the discriminant of equation $$6x^{2}+bx+2=0$$ is $$1$$ then find the value of $$'b'$$.
Solve:$$2x^2-x+\dfrac{1}{8}=0$$.
Solve the following equation:
$$4 ( y - 5 ) = 16$$
Find the values of $$'k'$$ for which $$x^{2}-2x+k=0$$ has real roots.
The value of $$x$$ if $$x+\dfrac 1x=2$$
Check whether the equation $$ 6 x^{2}-7 x+2=0 $$ has real roots. If it has, find them by method of completing square.
If the quadratic equation $$x^{ 2 }-4x+k=0$$ has equal roots , then find the value of k,
Check whether the following are Quadratic equations
$${ \left( x+2 \right) }^{ 3 }=2x\left( { x }^{ 2 }-1 \right) $$
Find the roots of the equation $$5x^{2}-6x-2=0$$ by the method of completing the square.
Find the value of $$k$$ for which the quadratic equation $$x(x-k)+5=0$$ will have two real and equal roots.
Check whether the following is a quadratic equation:
$${ x }^{ 3 }-{ 4x }^{ 2 }-x+1={ \left( x-2 \right) }^{ 3 }$$
If $$4x^{ 2 }-4x+k=0$$ find $$x$$
If $$\tan \theta +\dfrac {1}{\tan \theta}=2$$, prove $$\tan^{2} \theta +\dfrac {1}{\tan^{2}\theta}=2$$
Show that
$$\left( 4x-9 \right) ^{ 2 }+144x=\left( 4x+9 \right) ^{ 2 }$$
Find the quadratic equation, if $$x=\sqrt{5+\sqrt{5+\sqrt{5+...\infty }}}$$ and x is a natural number.
Solve :
$$\dfrac { { x }^{ 2 } }{ \left( { x }^{ 2 }+2 \right) \left( { 2x }^{ 2 }+1 \right) } =1$$
Solve for x : $$\frac{1}{(x-1)(x-2)}+\frac{1}{(x-2)(x-3)}=\frac{2}{3},x\neq 1,2,3,$$
Solve the following quadratic equation for $$x:$$
$$x^{2}-4ax-b^{2}+4a^{2}=0$$
Solve
$$\dfrac {m}{n}x^ {2}+\dfrac {n}{m}=1-2x$$
Solve by completing square method:
$${ x }^{ 2 }+8x+5$$
If $$x^2-3x+3=0$$, then find the roots of the equation.
Find the discriminant of $$2{ x }^{ 2 }+10x+21=0.$$
Solve:
$$x^2-2xy+y^2-2^2$$
Simplify the following expressions:
$${(x+y+z)}^{2}+{ \left( x+\cfrac { y }{ 2 } +\cfrac { z }{ 3 } \right) }^{ 2 }-{ \left( \cfrac{x}{2}+\cfrac { y }{ 3 } +\cfrac { z }{ 4 } \right) }^{ 2 }$$
Classify the following polynomial as linear, quadratic, cubic and biquadratic polynomial:
$$2x + x^{2}$$.
Classify the following polynomial as linear, quadratic, cubic and biquadratic polynomial:
$$x + x^{2} - 4$$.
Simplify the following products:
$$(2{x}^{4}-4{x}^{2}+1)(2{x}^{4}-4{x}^{2}-1)$$
Find the roots $$x^{2}+6x-4=0$$
Factorize the following quadratic polynomial by using the method of completing the square.
$$4x^2-12x+5$$.
Solve the following equations by using the method of completing the square:
$$8x^2-14x-15=0$$
Solve the following equations by using the method of completing the square:
$$3x^2-x-2=0$$
Solve the following equations by using the method of completing the square:
$$x^2+8x-2=0$$
Factorize the following quadratic polynomial by using the method of completing the square.
$$p^2+6p-16$$.
Factorize the following quadratic polynomial by using the method of completing the square.
$$a^2+2a-3$$.
Factorize the following quadratic polynomial.
$$x^2+12x+20$$.
Factorize the following quadratic polynomial by using the method of completing the square.
$$a^2-14a-51$$.
Factorize the following quadratic polynomial by using the method of completing the square.
$$y^2-7y+12$$.
Check whether the following is quadratic equation in $$x$$?$$\sqrt{2}x^{2}+7x+5\sqrt{2}=0$$
Find the discriminant of each of the following equations:
$$2x^2-7x+6=0$$
Check whether the following is quadratic equation in $$x$$?$$1/3x^{2}+1/5x-2=0$$
What is the highest degree of the quadratic equation in $$x$$?
$$2x^{2}+5/2 x-\surd{3}=0$$
Find the discriminant of each of the following equation:
$$\surd 3 x^2 +2\surd 2 x-2\surd 3=0$$
Find the discriminant of each of the following equations:
$$3x^2 -2x+8=0$$
Solve the following equation by using the method of completing the square:
$$2/x^2-5/x+2=0$$
Solve the following equation by using the method of completing the square:
$$5x^2-6x-2=0$$
Find the discriminant of each of the following equation:
$$2x^2-5\sqrt 2x+4=0$$
What is the degree of the quadratic equation in $$x$$?
$$x^{2}-x+3=0$$
Find the roots of each of the following equation, if they exist, by applying the quadratic formula:
$$16x^2 -24x-1=0$$
Find the roots of each of the following equations, if they exist, by applying the quadratic formula:
$$2x^2 +x-4=0$$
Check whether the following is quadratic equation in $$x$$?$$x-6/x=3$$
Find the discriminant of each of the following equation:
$$(x-1)(2x-1)=0$$
Find the roots of equation, if they exist, by applying the quadratic formula:
$$25x^2 +30x+7=0$$
Find the roots of each of the following equation, if they exist, by applying the quadratic formula:
$$x^2- 6x+4=0$$
Find the roots of each of the following equations, if they exist, by applying the quadratic formula:
$$x^2 -4x-1=0$$
By using the method of completing the square, show that the equation $$2x^2+x+4=0$$ has no real roots:
Solve the following equation by using the method of completing the square:
$$\sqrt 3 x^2 +10x+7\sqrt 3 =0$$
Find the discriminant of each of the following equation:
$$1-x=2x^2$$
Find the roots of the following equation, by applying the quadratic formula:
$$2x^2 -2\sqrt2 x+1=0$$
Check whether the following is quadratic equation in $$x$$?
$$x+2/x=x^{2}$$
Find the roots of each of the following equation, if they exist, by applying the quadratic formula:
$$\surd 3 x^2 +10x-8\surd 3=0$$
Find the roots of each of the following equations, if they exist, by applying the quadratic formula:
$$3x^2 -2\surd 6 x+2=0$$
Find the roots of each of the following equation, if they exist, by applying the quadratic formula:
$$\surd 2 x^2 +7x+5\surd 2=0$$
Find the roots of each of the following equations, if they exist, by applying the quadratic formula:
$$2\surd 3 x^2 -5x+\surd 3=0$$
Find the roots of the following equation if they exist by applying the quadratic formula:
$$15x^2-28=x$$
Find the roots of each of the following equation, if they exist, by applying the quadratic formula:
$$2x^2 +6\surd 3 x-60=0$$
Find the roots of the following equation, if they exist, by applying the quadratic formula:
$$4\sqrt 3\ x^2 +5x-2\sqrt 3 =0$$
Find the roots of each of the following equations, if they exist, by applying the quadratic formula:
$$\surd 3\ x^2 -2\surd 2 x- 2\surd 3=0$$
Solve by using quadratic formula
(i) $$256 x^{2}-32 x+1=0$$
(ii) $$25 x^{2}+30 x+7=0$$
Is the following equation a quadratic equation in $$x$$?
$$(x+2)^{3}=x^{3}-8$$
Solve by using quadratic formula
(i) $$2 x^{2}-7 x+6=0$$
(ii) $$2 x^{2}-6 x+3=0$$
Solve by using quadratic formula
(i) $$x^{2}+7 x-7=0$$
(ii) $$(2 x+3)(3 x-2)+2=0$$
Check whether the following equation is quadratic equation in $$x$$ or not?
$$x^{2}-1/x^{2}=5$$
Is the following equation a quadratic equation in $$x$$?
$$(x+1/x)^{2}=2(x+1/x)+3$$
Is the following equation a quadratic equation in $$x$$?
$$(2x+3)(3x+2)=6(x-1)(x-2)$$
Solve by using formula
(i) $$2 \mathbf{x}^{2}+\sqrt{5} \mathbf{x}-5=0$$
(ii) $$\sqrt{3 x^{2}+10 x-8 \sqrt{3}=0}$$
If the equation $$ 2 x^{2}+4 x y+7 y^{2}-12 x-2 y+t=0 $$ where 't' is a parameter has exactly one real solution of the form $$ (x, y) $$, then find the value of $$ (x+y) $$.
Solve by using formula
(i) $$\mathbf{a}\left(\mathbf{x}^{2}+\mathbf{1}\right)=\left(\mathbf{a}^{2}+\mathbf{1}\right) \mathbf{x}, \mathbf{a} \neq \mathbf{0}$$
(ii) $$4 x^{2}-4 a x+\left(a^{2}-b^{2}\right)=0$$
Solve the following equations by using the quadratic formula and give your answer correct to 2 decimal places:
(i) $$4 x^{2}-5 x-3=0$$
(ii) $$2 x-\dfrac 1x=1$$
Solve by using formula
$$(\mathbf{i}) \mathbf{x}-\mathbf{1} / \mathbf{x}=\mathbf{3}, \mathbf{x} \neq \mathbf{0}$$
(ii) $$1 / x+1 /(x-2)=3, x \neq 0,2$$
Find the value of the discriminant of the quadratic equation $$ 2 x^{2}-4 x+3=0 $$.
Using quadratic formula, solve the following equation for $$x:ab{x}^{2}+({b}^{2}-ac)x-bc=0$$
Solve by using formula
$$(i) \dfrac{x-2}{x+2}+\dfrac{x+2}{x-2}=4$$
$$(i i) \dfrac{x+1}{x+3}=\dfrac{3 x+2}{2 x+3}$$
Solve by using formula
$$\dfrac{1}{x-2}+\dfrac{1}{x-3}+\dfrac{1}{x-4}=0$$
Solve the equation $$5 x^{2}-3 x-4=0$$ and give your answer correct to 3 significant figures:
$$ 2x^2 +13xy - 24y^2 $$
Solve the equation $$x^2-12x+27=0$$ by using formula.
$$ 5x^2 +17xy - 12y^2 $$
$$ x^4 +9x^2y^2 + 81y^4 $$
$$ 9x^2 + 12x +4 -16 y^2 $$
$$ x^2 -6xy -7y^2 $$
Solve $$ 2 x^{2}-5 x+3=0 $$ by using formula.
Find the zeros of the polynomial $$p(x)=x^2-15x+50$$
$$ 21x^2 - 59 xy + 40 y^2 $$
$$ 6x^2 -5xy -6y^2 $$
Check whether the following are quadratic equations:
$$x(x+1)+8=(x+2)(x-2)$$
Check whether the following is a quadratic equation or not:
$$(x+2)^3=x^3-4$$
Check whether the following are quadratic equations:
$$x^2-\dfrac{1}{x^2}=8$$
Check whether the following are quadratic equations:
$$2x^2-3\sqrt{x}+5=0$$
Check whether the following are quadratic equations:
$$(x+1)(x-1)=(x+2)(x+3)$$
Check whether the following are quadratic equations:
$$(x-1)^2=(x+1)^2$$
Check whether the following are quadratic equations:
$$x-\dfrac{1}{x}=8$$
Check whether the following are quadratic equations:
$$x^2+\dfrac{1}{x}=5$$
Check whether the following are quadratic equations:
$$x(2x+3)=x^2+1$$
Find the roots of the following quadratic equations,if they exist by the method of completing the square: $$5x^2-6x-2=0$$
Solve the following equations by the method of completion of a square $$5x^2-24x-5=0$$
Find the roots of the following quadratic equations,if they exist by the method of completing the square: $$x^2-9x+18=0$$
Solve the following equations by the method of completion of a square $$15x^2+53x+42=0$$
Solve the following equations by the method of completion of a square $$7x^2-13x-2=0$$
Find the roots of the following quadratic equations,if they exist by the method of completing the square: $$x^2-6x+4=0$$
Find the roots of the following quadratic equations,if they exist by the method of completing the square: $$\sqrt{5}x^2+9x+4\sqrt{5}=0$$
Find the roots of the following quadratic equations,if they exist by the method of completing the square: $$2x^2+\sqrt{15}x+\sqrt{2}=0$$
Find the roots of the following quadratic equations,if they exist by the method of completing the square: $$2x^2-5x+3=0$$
Find the roots of the following quadratic equations,if they exist by the method of completing the square: $$x^2+x+3=0$$
Find the roots of the following quadratic equations,if they exist by the method of completing the square: $$9x^2-15x+6=0$$
Write the discriminate of each of the following quadratic equation: $$x^2+4x+3=0$$
Write the discriminate of each of the following quadratic equation: $$$$4x^2+5x+7=0$$
Solve the following equations by the method of completion of a square $$7x^2+2x-5=0$$
Write the discriminate of each of the following quadratic equation: $$2x^2+4x+5=0$$
Write the discriminate of each of the following quadratic equation: $$3x^2+5x+6=0$$
Solve the following quadratic equation by completing the square method.
$$ x^{2}+x-20=0 $$
Decide whether the following equation is a quadratic equation or not.$$ y^{2}+\dfrac{1}{y}=2 $$
Write any two quadratic equation
One of the roots of equation $$ 5{m}^{2}+2 {m}+{k}=0 $$ is $$ \dfrac{-7}{5} $$ Complete the following activity to find the value of '$$k$$'.
Solve the following quadratic equation by completing the square method.
$$ x^{2}+2 x-5=0 $$
Find the value of discriminant.
$$2y^{2} - 5y + 10 = 0$$
Find the value of discriminant.
$$x^{2} + 7x - 1 = 0$$
Solve the following quadratic equation by completing the square method.
$$ 9 y^{2}-12 y+2=0 $$
Solve the following quadratic equation by completing the square method.
$$ 2 y^{2}+9 y+10=0 $$
Solve the following quadratic equation by completing the square method.
$$ 5 x^{2}=4 x+7 $$
Solve the following quadratic equation by completing the square method.
$$ m^{2}-5 m=-3 $$
Find the value of discriminant.
$$\sqrt{2}x^{2} + 4x + 2 \sqrt{2} = 0$$
Solve using formula.
$$ 5 m^{2}-4 m-2=0 $$
Choose the correct answer for the following question.
Out of the following equations which one is not quadratic equation?
$$x^{2} + 4x = 11 + x^{2}$$
$$x^{2} = 4x $$
$$5x^{2} = 90 + 5$$
$$2x - x^{2} = x^{2}$$
is the following equation quadratic?
$$x^{2} + 2x + 11 = 0$$
Find the value of discriminant of the following equation.
$$\sqrt{5}x^{2} - x - \sqrt{5} = 0 $$
Find the value of discriminant of the following equation.
$$2y^{2} - y + 2 = 0$$
Write the formula to find the roots of Quadratic equation $$ap^2 + bp + c = 0$$.
Choose the correct answer for the following question.
For $$\sqrt{2}x^{2} - 5x + \sqrt{2} = 0$$ find the value of the discriminant.
-5
17
$$\sqrt{2}$$
$$2\sqrt{2} - 5$$
Is the following equation quadratic?
$$\left(x + 2 \right)^{2} = 2x^{2}$$
Find the value of discriminant of the following equation.
$$5m^{2} - m = 0$$
Test, whether the following equation is quadratic equation.
$$x(x+1)+8=(x+2)(x-2)$$
is the following equation quadratic?
$$x^{2} - 2x + 5 = x^{2}$$
Solve the following equations by the method of completing square.
$$5x^2-6x-2=0$$
Solve the following equations by the method of completing square.
$$3x^2-5x+2=0$$
Solve the following equations by the method of completing square.
$$4x^2+3x+5=0$$
Solve the following equations by the method of completing square.
$$2x^2+x-4=0$$
Solve the following equations by the method of completing square.
$$4x^2+4bx-(a^2 -b^2)=0$$
Solve the following equations by the method of completing square.
$$2x^2+x+4=0$$
Solve the following equations by the method of completing square.
$$4x^2+4\sqrt 3 x+3=0$$
Solve for $$x$$;
$$x^2 -4ax-b^2+4a^2 +4a^2=0$$.
Test, whether the following equation is quadratic equation.
$$x+\dfrac 1x+x^2, x\neq 0$$
Solve for $$x$$ the quadratic equation $$x^2-4x-8=0$$
Give your answer correct to three significant figures.
Find the value of $$k$$ for which the quadratic equation $$kx(x - 2) + 6 = 0 $$ has two equal roots.
Using completing the square method, show that the equation $$x^{2} - 8x + 18 = 0 $$ has no solution.
Solve the following equations.
$$3x^{2} + 7x - 5 = 0 $$
Show all your working and give your answer correct to $$2$$ decimal places.
Examine the nature of the roots of the quadratic $$\displaystyle \left ( b-x \right )^{2}-4\left ( a-x \right )\left ( c-x \right )=0$$ where a, b, c are real.
Find the number of real solutions of the quadratic equation $${x}^{2}+2=x+5$$.
Find the number of real solution to the rational equation
$$\dfrac {2}{(x+1)}-\dfrac {1}{(x-2)}=-1$$ find value of $$x^2$$
Check whether $$x^2 - x = 0$$ is a quadratic equation.
Find the values (s) of $$k$$ so that the quadratic equation $$3x^2 - 2kx + 12 = 0$$ has equal roots.
Check whether $$\sqrt 3 x = \dfrac{22}{13}$$ is a quadratic equation.
Check whether $$x^2 + \dfrac{1}{2} x = 0$$ is a quadratic equation.
Check whether $$\sqrt{2}x^2+3x =0$$ is a quadratic equation.
Check whether $$x^2 = 8$$ is a quadratic equation.
Solve $$x + 2 + y + 3 + \sqrt {(x + 2)(y + 3)} = 39$$.
$$(x + 2)^{2} + (y + 3)^{2} + (x + 2)(y + 3) = 741$$.
Solve the given quadratic equation by completing the square, $$t^2 + 3t = 7$$
If the difference between the roots of $${ x }^{ 2 }+2px+q=0$$ be same as that between the roots of $${ x }^{ 2 }+2qx+p=0$$ $$\left( p\neq q \right)$$, then $$p+q$$ is equal to
Solve each of the following equation by using the method of completing the square:
$$x^{2}-8x-2=0$$ ?
Solve the equation by completing the square method:
$$x^{2}-10x+9=0$$
Solve the following equation by using the general formula , if the equation has a solution R :
i)$${1 \over x} - {1 \over {x - 3}} = 3,x \ne 0,2$$
ii)$$x + {1 \over x} = 3,x \ne 0$$iii)$$3{x^2} + 2\sqrt {5x} - 5 = 0$$
iv)$$\sqrt 3 {x^2} - 2x + \sqrt 3 = 0$$
v)$${1 \over {x + 1}} + {2 \over {x + 2}} = {4 \over {x + 4}}{\rm{ ;x}} \ne {\rm{1, - 2, - 4}}$$
vi)$$\sqrt 2 {x^2} + 7x + 5\sqrt {2 = 0} $$
Solve each of the following equation by using the method of completing the square:
$$2x^{2}+5x-3=0$$ ?
Solve each of the following equation by using the method of completing the square:
$$3x^{2}+x-2=0$$ ?
Solve the equations by completing the square
$$x^{2}-5x+5=0$$
$$x^{2} - (2b - 1)x + (b^{2} - b - 20) = 0$$.
If $$x^2-(5m-2)x+4m^2 +10m+25=0$$ were to be a perfect square then find the value of $$m$$?
Find the value of $$k$$ for which the quadratic equation $$(k-2)x^ {2}+(2k-3)x+(5k-6)=0$$ has equal roots.
Solve the following equation $$x^2+\dfrac{x}{\sqrt{2}}+1=0$$.
Determine whether the values given against the quadratic equation are the roots of the quadratic equation or not:
$$2{m^2} - 5m = 0,m = 2,\dfrac{5}{2}$$
Check whether the following equation is quadratic equation in $$x$$ or not?
$$x^{2}-3x-\sqrt{x}+4=0$$
Expand : $$( 3 x + 2 ) ^ { 2 }$$
Class 10 Maths Extra Questions
- Areas Related To Cricles Extra Questions
- Arithmetic Progressions Extra Questions
- Circles Extra Questions
- Constructions Extra Questions
- Coordinate Geometry Extra Questions
- Introduction To Trigonometry Extra Questions
- Pair Of Linear Equations In Two Variables Extra Questions
- Polynomials Extra Questions
- Probability Extra Questions
- Quadratic Equations Extra Questions
- Real Numbers Extra Questions
- Some Applications Of Trigonometry Extra Questions
- Statistics Extra Questions
- Surface Areas And Volumes Extra Questions
- Triangles Extra Questions