Structure Of The Atom - Class 9 Chemistry - Extra Questions
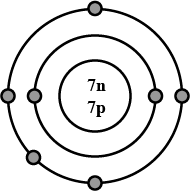
Draw the electronic configuration of the following element clearly stating the number of neutrons and protons in their nucleus.
Nitrogen.
What is Mass number?
On the basis of Rutherford's model of an atom, which subatomic particle is present in the nucleus of an atom?
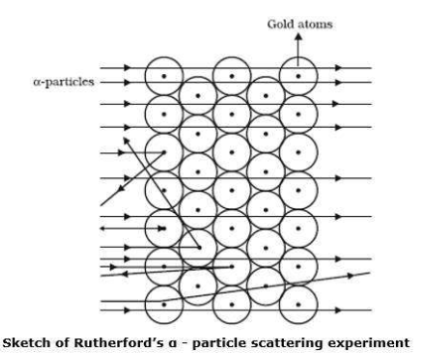
Which metal did Rutherford select for his $$\alpha-$$ particle scattering experiment and why?
State one major drawback of Rutherford's model.
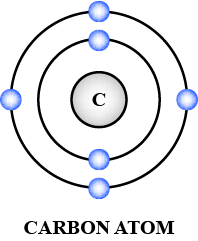
In the figure given alongside:
A, B and C are orbits of electron in the atom.
Name $$X$$ and state the charge on it.
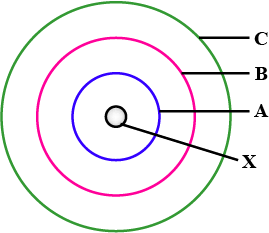
Write the relationship between mass number and atomic number?
How do you represent an atom symbolically with atomic number and mass number ?
Give reason for the following:
Ernest Rutherford selected a gold foil for his experiments.
Explain the important features of Rutherford's Planetary model and write its defects.
An element X has a mass number 4 and atomic numberWrite the valency of this element?
Name two particles found inside the nucleus. What are they collectively called?
Define the following term:
(i) Nucleons
(i) Nucleons
The following data represent the distribution of electrons, protons and neutrons in atoms of elements $$P, Q, R$$ and $$S$$.
| Element | Protons | Neutrons | Electrons |
| $$P$$ | $$19$$ | $$22$$ | $$19$$ |
| $$Q$$ | $$17$$ | $$18$$ | $$17$$ |
| $$R$$ | $$17$$ | $$20$$ | $$17$$ |
| $$S$$ | $$18$$ | $$22$$ | $$18$$ |
The composition of two atomic particles is given below:
| X | Y | |
| Protons: | 8 | 8 |
| Neutrons: | 8 | 9 |
| Electrons: | 8 | 8 |
The composition of two atomic particles is given below:
| X | Y | |
| Protons: | 8 | 8 |
| Neutrons: | 8 | 9 |
| Electrons: | 8 | 8 |
The composition of two atomic particles is given below:
| X | Y | |
| Protons: | 8 | 8 |
| Neutrons: | 8 | 9 |
| Electrons: | 8 | 8 |
The following data represent the distribution of electrons, protons and neutrons in atoms of elements $$P, Q, R$$ and $$S$$.
| Element | Protons | Neutrons | Electrons |
| $$P$$ | $$19$$ | $$22$$ | $$19$$ |
| $$Q$$ | $$17$$ | $$18$$ | $$17$$ |
| $$R$$ | $$17$$ | $$20$$ | $$17$$ |
| $$S$$ | $$18$$ | $$22$$ | $$18$$ |
The atom of an element is made up of $$4$$ protons, $$5$$ neutrons and $$4$$ electrons. What is its atomic number and mass number ?
$$\text{ With reference to period 3 of the periodic table-State}$$
The number of electrons in the penultimate shell of the element with valency -1.
The composition of two atomic particles is given below:
| X | Y | |
| Protons: | 8 | 8 |
| Neutrons: | 8 | 9 |
| Electrons: | 8 | 8 |
Name the scientist who discovered that electrons are present in an atom in discrete orbits
What is isobar?
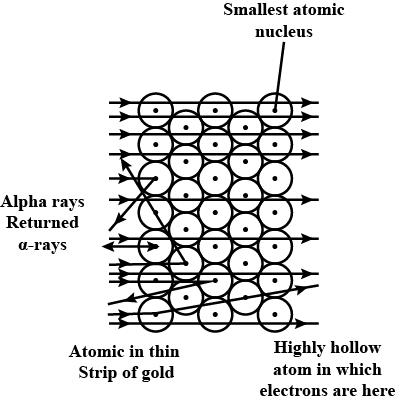
Answer the following questions, which help you understand the difference between Thomson's model and Rutherford's model better.
(a) Is the average angle of deflection of $$\alpha$$-particles by a thin gold foil predicted by Thomson's model much less, about the same, or much greater than that predicted by Rutherford's model?
(b) Is the probability of backward scattering (i.e., scattering of $$\alpha$$-particles at angles greater than $$90^\circ$$) predicted by Thomson's model much less, about the same, or much greater than that predicted by Rutherford's model?
(c) Keeping other factors fixed, it is found experimentally that for small thickness $$t$$, the number of $$\alpha$$-particles scattered at moderate angles is proportional to $$t$$. What clue does this linear dependence on $$t$$ provide?
(d) In which model is it completely wrong to ignore multiple scattering for the calculation of average angle of scattering of $$\alpha$$-particles by a thin foil?
(b) Is the probability of backward scattering (i.e., scattering of $$\alpha$$-particles at angles greater than $$90^\circ$$) predicted by Thomson's model much less, about the same, or much greater than that predicted by Rutherford's model?
(c) Keeping other factors fixed, it is found experimentally that for small thickness $$t$$, the number of $$\alpha$$-particles scattered at moderate angles is proportional to $$t$$. What clue does this linear dependence on $$t$$ provide?
(d) In which model is it completely wrong to ignore multiple scattering for the calculation of average angle of scattering of $$\alpha$$-particles by a thin foil?
It is now believed that protons and neutrons (which constitute nuclei of ordinary matter) are themselves built out of more elementary units called quarks. A proton and a neutron consist of three quarks each. Two types of quarks, the so-called 'up' quark (denoted by u) of charge + (2/3) e, and the 'down' quark (denoted by d) of charge (-1/3) e, together with electrons build up ordinary matter. (Quarks of other types have also been found which give rise to different unusual varieties of matter.) Suggest a possible quark composition of a proton and neutron.
If $$Z=3$$, what would be the valency of the element? Also, name the element.
What are the limitations of Rutherford's model of the atom?
State True or False.
In the $$\alpha$$-ray scattering experiment, some $$\alpha$$-rays get deflected due to the attraction of electrons.
In the $$\alpha$$-ray scattering experiment, some $$\alpha$$-rays get deflected due to the attraction of electrons.
Rutherford's atomic model could not explain the stability of atom. How do you account for this?
A lead block used to keep the source in $$\alpha$$ - ray scattering experiment. What is its purpose?
Where is the nucleus of an atom is situated ?
Could aluminium foil serve the purpose in $$\alpha$$ - ray scattering experiment. Explain the reason behind it.
Determine whether statements I and II are true or false.I: Most of the fast-moving $$\alpha$$--particles
passed straight through the gold foil.
II: Most of the space inside the atom is empty.
Almost all the mass of an atom is concentrated in a small region of space called the _________.
Define the terms: (a) atomic number, and (b) mass number.
From the given examples, form the pair of isotopes and the pair of isobars:
$$_{18}Ar^{40}, _{17}Cl^{35}, _{20}Ca^{40}, _{17}Cl^{37}$$
Why the nucleus is positively charged?
Describe Rutherford's atomic model and also explain its drawbacks.
Define Nucleus of an atom.
Define nucleus.
The ________ of an atom is very hard and dense.
On the basis of Rutherford's model of an atom, which subatomic particle is present in the nucleus of an atom?
What are the postulates of J.J Thomson? What are his drawbacks?
Give the main drawback of Rutherford's model.
How will you find the valency of sodium, chlorine and argon?
State True or False for following statement:
Rutherford's $$\alpha$$-particle scattering experiment gives the experimental evidence for deriving the conclusion that most of the space inside the atom is empty.
From Rutherford's $$\alpha-$$particle scattering experiment, give the experimental evidence for the conclusion that the nucleus of an atom is positively charged.
Write the important limitation of Rutherford's nuclear model of the atom.
In the words of Rutherford "this result was almost as incredible as if you fire a $$15-inch$$ shell at a piece of tissue paper and it comes back and hits you"
Discuss the concerning observation of the $$\alpha-$$scattering experiment made by Rutherford.
What is the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons present in the following elements?
(I) $$_{27}^{59}Co$$
(II) $${ _{ 47 }^{108}Ag }$$
(I) $$_{27}^{59}Co$$
(II) $${ _{ 47 }^{108}Ag }$$