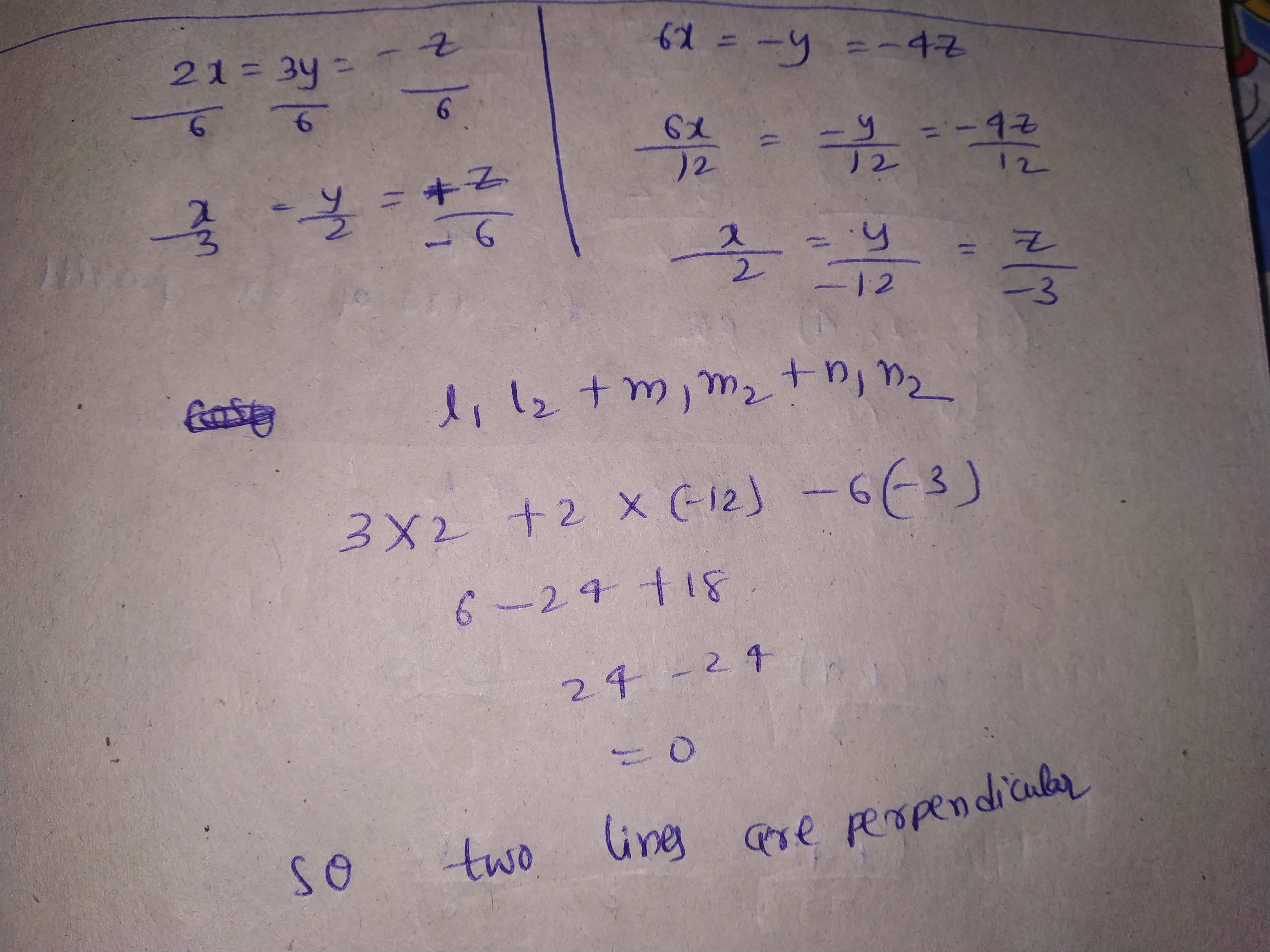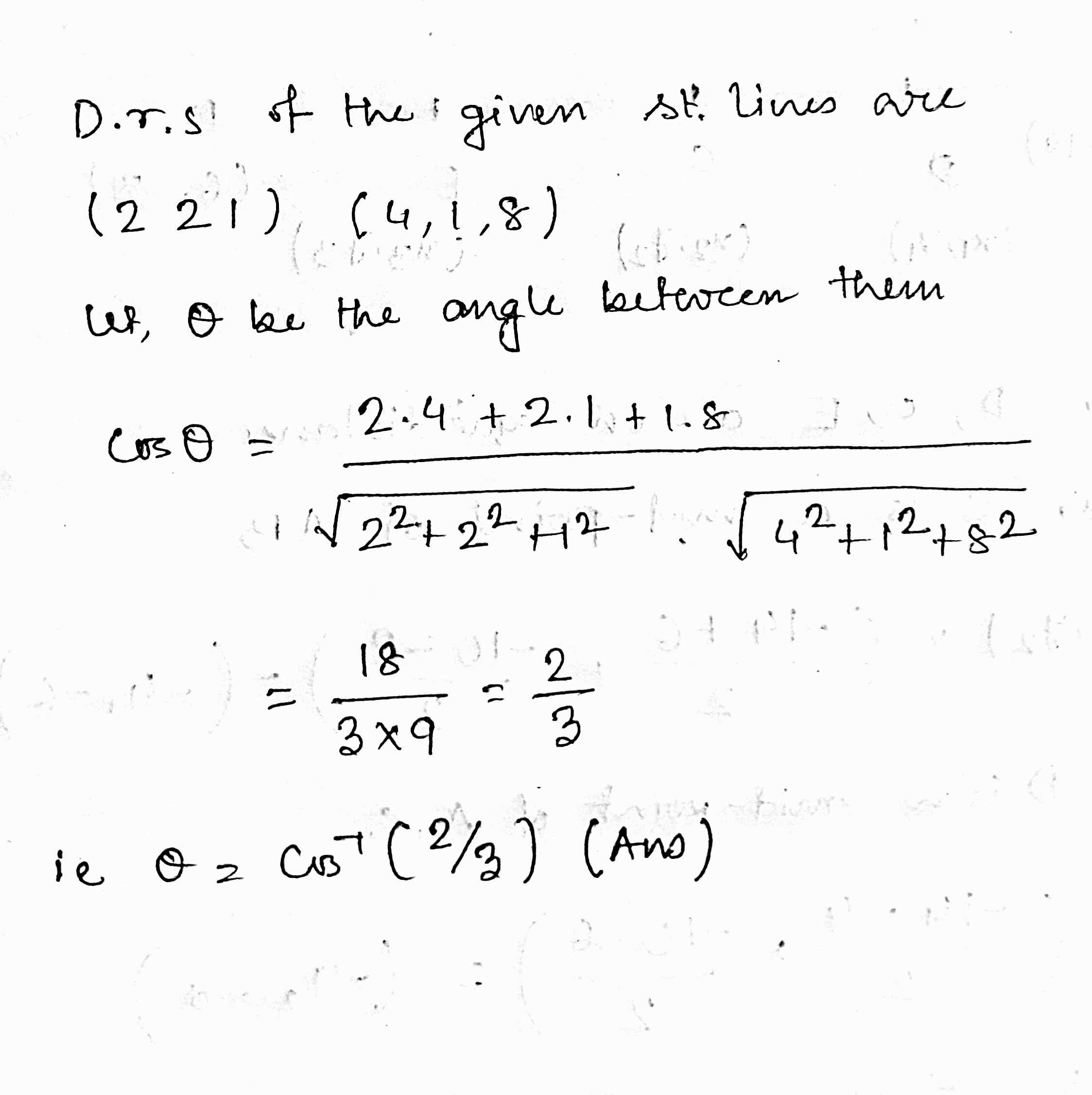Three Dimensional Geometry - Class 12 Engineering Maths - Extra Questions
If the coordinates of the points $$A,B,C,D$$ be $$(1,2,3), (4,5,7), (-4,3,-6)$$ and $$(2,9,2)$$ respectively, then find the angle between the lines $$AB$$ and $$CD$$
Angle between lines whose direction cosine satisfy $$l+m+n=0, {l}^{2}+{m}^{2}-{n}^{2}=0$$.
Find the vector equation of the plane passing through the points $$4\overline{i} - 3\overline{j} - \overline{k}, 3\overline{i} +7 \overline{j}-10\overline{k}$$ and $$2\overline{i} + 5\overline{5} - 7\overline{k}$$ and find if the point $$\overline{i} + 2\overline{j} - 3\overline{k}$$ lies on the plane.
Find the angle between two lines, one of which has direction ratios $$2, 2, 1$$ while the other one is obtained by joining the points $$(3, 1, 4)$$ and $$(7, 2, 12)$$.
Find the angle between the lines $$y-\sqrt{3}x-5=0$$ and $$\sqrt{3}y-x+6=0$$.
Find the angle between the following pairs of lines:
$$\dfrac {x - 5}{1} = \dfrac {2y + 6}{-2} = \dfrac {z - 3}{1}$$ and $$\dfrac {x - 2}{3} = \dfrac {y + 1}{4} = \dfrac {z - 6}{5}$$
Find the angle between the following pairs of lines:
$$\dfrac {5 - x}{-2} = \dfrac {y + 3}{1} = \dfrac {1 - z}{3}$$ and $$\dfrac {x}{3} = \dfrac {1 - y}{-2} = \dfrac {z + 5}{-1}$$
Find the angle between the following pairs of lines:
$$\dfrac {x - 1}{2} = \dfrac {y - 2}{3} = \dfrac {z - 3}{-3}$$ and $$\dfrac {x + 3}{-1} = \dfrac {y - 5}{8} = \dfrac {z - 1}{4}$$
Find the angle between the following pairs of lines:
$$\vec {r} = 3\hat {i} + \hat {j} - 2\hat {k} + \lambda (\hat {i} + \hat {j} - 2\hat {k})$$ and $$\vec {r} = 2\hat {i} - \hat {j} - 56\hat {k} + \mu (3\hat {i} - 5\hat {j} - 4\hat {k})$$.
Find the angle between the following pair of lines:
(i) $$\vec { r } =2\hat { i } -5\hat { j } +\hat { k } +\lambda \left( 3\hat { i } -2\hat { j } +6\hat { k } \right) $$ and $$\vec { r } =7\hat { i } -6\hat { k } +\mu \left( \hat { i } +2\hat { j } +2\hat { k } \right) $$(ii) $$\vec { r } =3\hat { i } +\hat { j } -2\hat { k } +\lambda \left( \hat { i } -\hat { j } -2\hat { k } \right) $$ and $$\vec { r } =2\hat { i } -\hat { j } -56\hat { k } +\mu \left( \hat { 3i } -5\hat { j } -4\hat { k } \right) $$
Find the angle between the following pair of lines:
(i) $$\cfrac{x-2}{2}=\cfrac{y-1}{5}=\cfrac{z+3}{-3}$$ and $$\cfrac{x+2}{-1}=\cfrac{y-4}{8}=\cfrac{z-5}{4}$$
(ii) $$\cfrac{x}{2}=\cfrac{y}{2}=\cfrac{z}{1}$$ and $$\cfrac{x-5}{4}=\cfrac{y-2}{1}=\cfrac{z-3}{8}$$
Find the angle between the two straight lines whose direction cosines are given by $$2l+2m-n=0$$ and $$mn+nl+lm=0$$.
Measure of angle between $$\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{2}=\dfrac{z}{1}$$ and $$\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{-1}=\dfrac{z}{-2}$$ is
The angle between the lines $$\dfrac{x-2}{3} = \dfrac{y+1}{-2} = z-2$$ and $$\dfrac{x-1}{1}= \dfrac{2y+3}{3} = \dfrac{z+5}{2}$$ is equal to:
Find the angle between the following pairs of lines:
$$\dfrac {x + 4}{3} = \dfrac {y - 1}{5} = \dfrac {z + 3}{4}$$ and $$\dfrac {x + 1}{1} = \dfrac {y - 4}{1} = \dfrac {z - 5}{2}$$
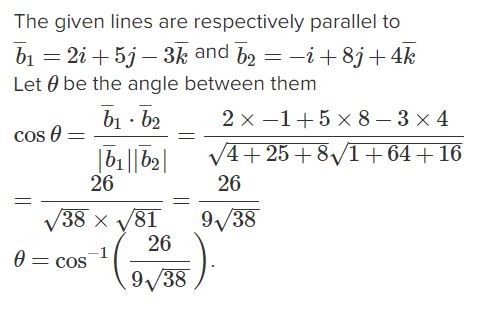
Find the angle between the lines $$\vec {r} = (2\hat{i} - 5\hat {j} + \hat {k}) + \lambda (3\hat {i} + 2\hat {j} + 6\hat {k})$$ and $$\vec {r} = 7\hat {i} - 6\hat {j} + \mu (\hat {i} + 2\hat {j} + 2\hat {k})$$.
Find the angle between the lines $$2x = 3y = -z$$ and $$6x = -y = -4z$$.
Find the angle between the following pair of lines:
$$\dfrac {x - 2}{2} = \dfrac {y - 1}{5} = \dfrac {z + 3}{-3}$$ and $$\dfrac {x + 2}{-1} = \dfrac {y - 4}{8} = \dfrac {z - 5}{4}$$.
Find the angle between the following pair of lines:
$$\dfrac {x}{2} = \dfrac {y}{2} = \dfrac {z}{1}$$ and $$\dfrac {x - 5}{4} = \dfrac {y - 2}{1} = \dfrac {z - 3}{8}$$.
Find the angle between the lines
$$\dfrac{x}{2}=\dfrac{y}{2}=\dfrac{z}{1}$$ and $$\dfrac{x-5}{4}=\dfrac{y-2}{1}=\dfrac{z-3}{8}$$
Class 12 Engineering Maths Extra Questions
- Continuity And Differentiability Extra Questions
- Determinants Extra Questions
- Differential Equations Extra Questions
- Integrals Extra Questions
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions Extra Questions
- Relations And Functions Extra Questions
- Three Dimensional Geometry Extra Questions
- Vector Algebra Extra Questions