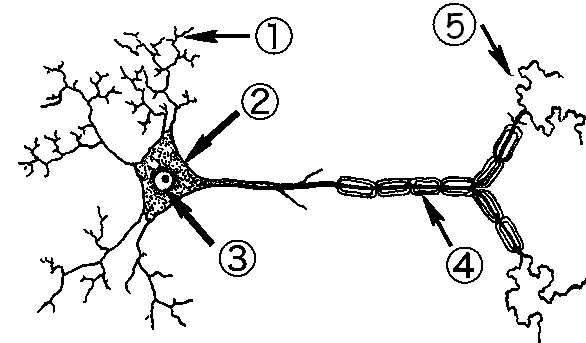
Tissues - Class 9 Biology - Extra Questions
State the different types of neurons. Explain their functions.
A tendon connects a .......... to a ..........
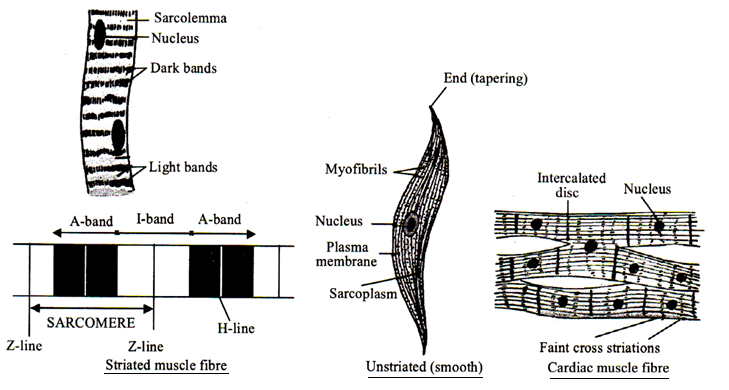
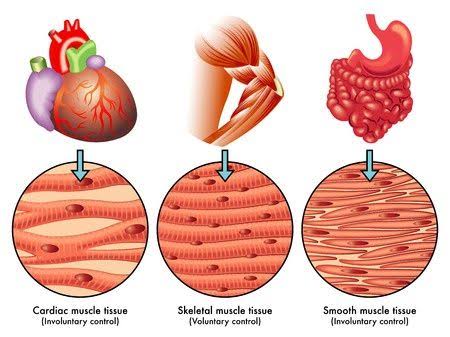
Differenciate between striated and unstriated muscles on the basis of their function and location in the body. Also compare their structure.
Human cheek cells stained and mounted in glycerine were observed with the help of a compound microscope. Name the stain used and name the components of the cell which would be seen:
Choose the ODD one out from the following terms given and name the CATEGORY to which the others belong.
Example: Nose, Tongue, Arm, Eye
Answer: Odd Term- Arm, Category- Sense organs
Dendrites, Medullary Sheath, Axon, Spinal cord.
The basic structural unit of the nervous system is ...........................
Name the location of Nissl's granules
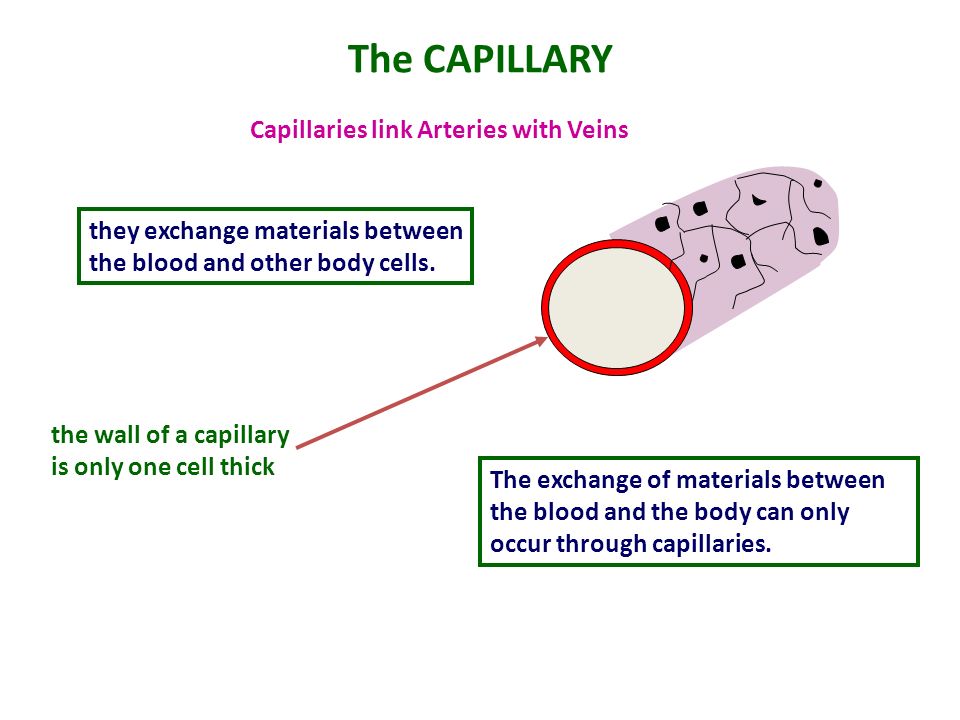
Name the site of exchange of material between the blood and the surrounding cells.
Short Answer
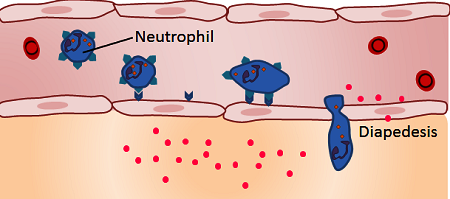
Why are white blood cells called the soldiers of body ?
Unscramble the jumbled word.
Isecsum
What is the function of Lymphocytes?
Name one place where the following tissue is located:
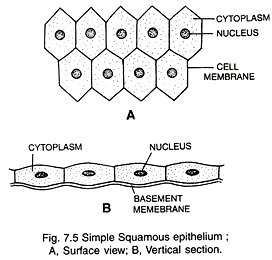
Squamous epithelium
Answer the following:
Name the major site where RBCs are formed.
The longest cell in animals.
Mention the components of the transport system in highly organized plants. State the functions of these components.
What is visceral muscle? Where is it found?
Why do we consider blood as a connective tissue?
What is the role of epidermis in plants?
Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body.
Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres.
What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
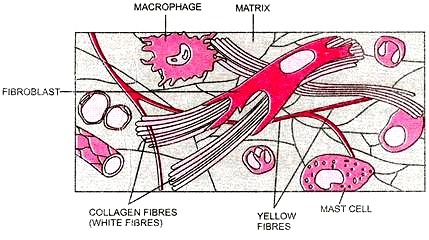
What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Name the following:
(a) Primary functional unit of brin:
(b) The small gap between the consecutive neurons:
(c) Part of the brain that coordinates the voluntary functions:
Name the following :
(i) The cell body of a nerve cell.
(ii) The waxy layer on the epidermis of the leaf meant to reduce transpiration.
(iii) A non-biodegradable pesticide.
(iv) The physical expression of genes in an individual.
(v) Knot-like mass of blood capillaries inside the bowman's capsule.
Answer the following questions.
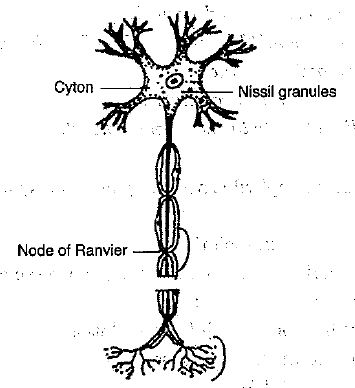
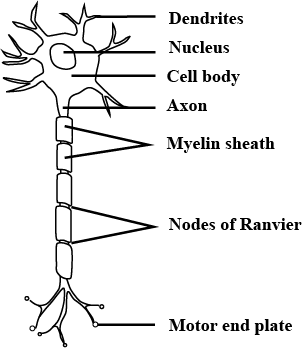
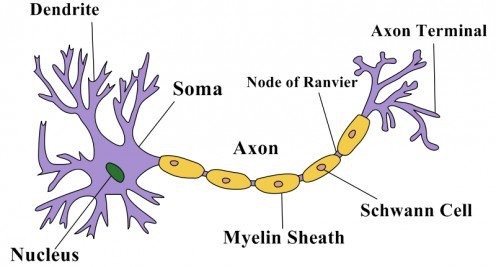
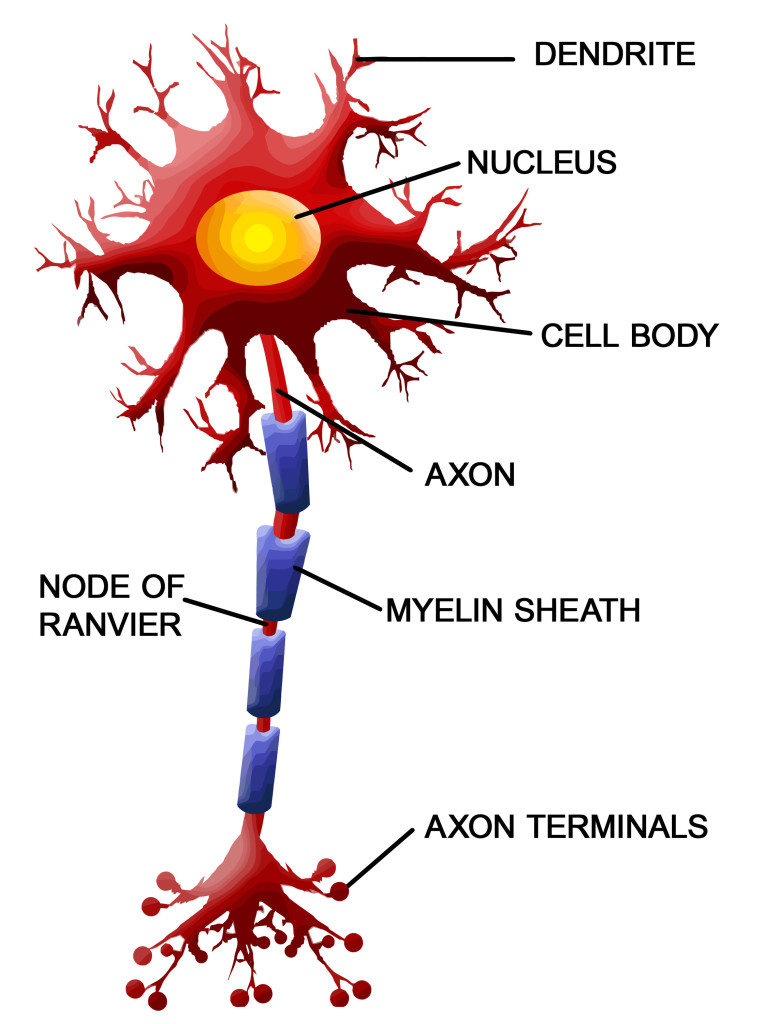
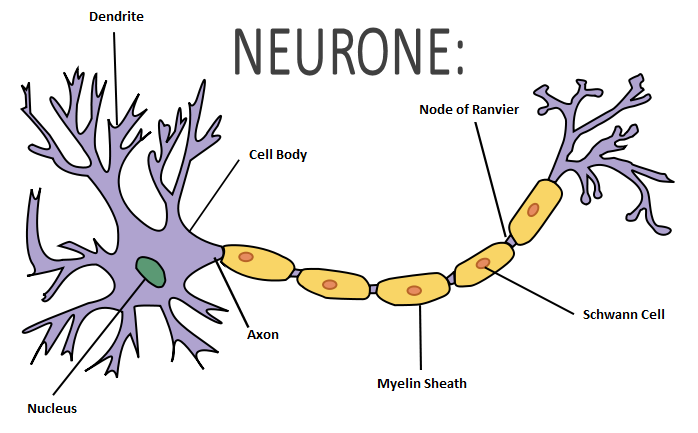
i) Draw a well labelled diagram of a neuron and name the following parts.
1) Node of Ranvier
2) Nissil granules
3) Cyton
ii) Name the part of the human brain which is concerned with the following.
Seat of memory
Coordinates muscular activity
iii. Mention any three major activities of the WHO.
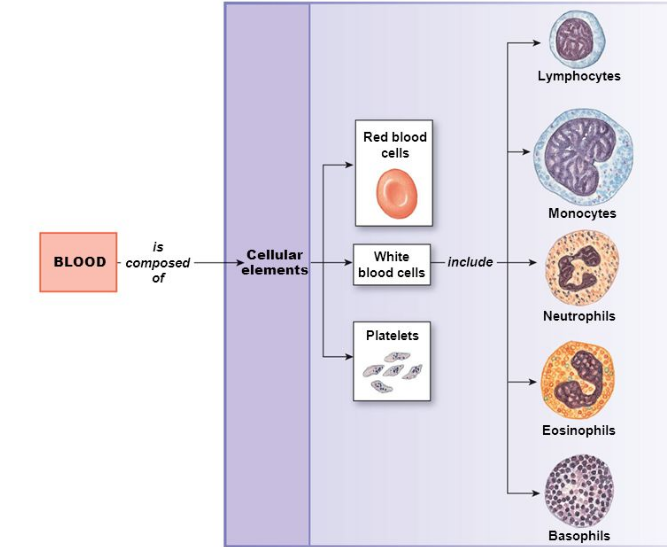
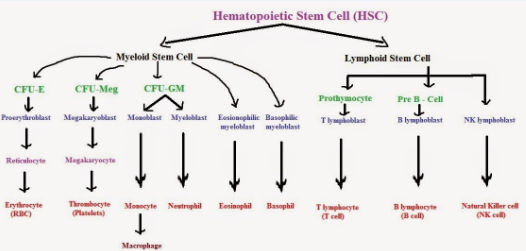
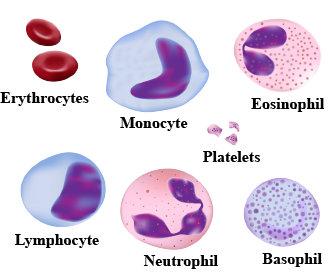
Give an account on cellular components of blood.
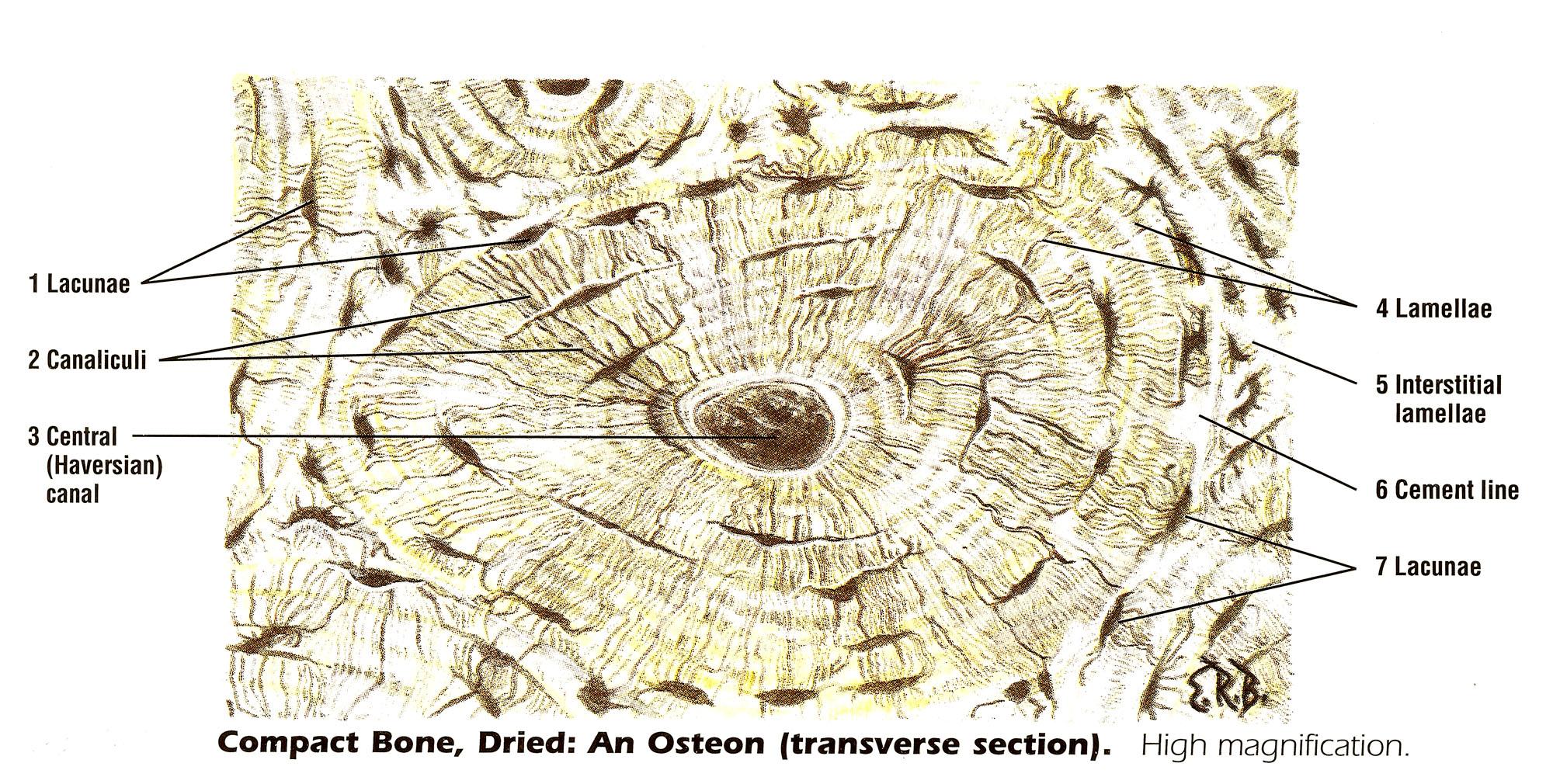
Draw a labelled diagram of the T.S. of bone
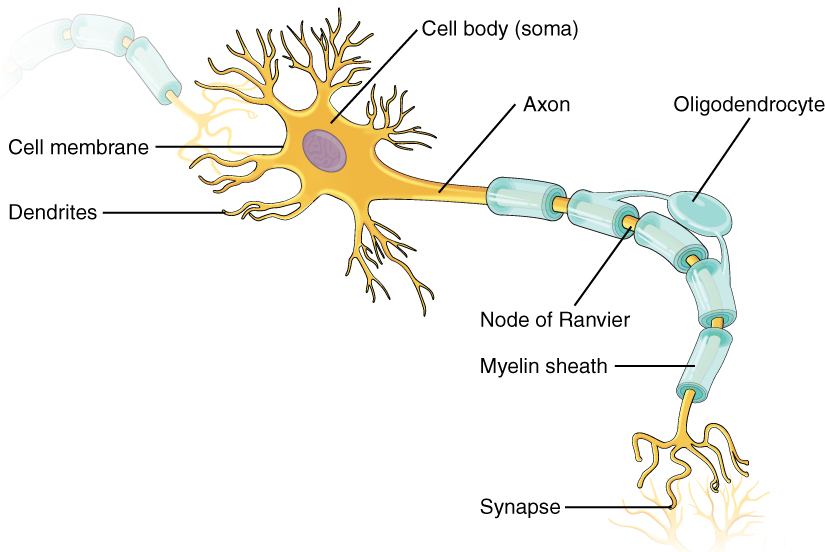
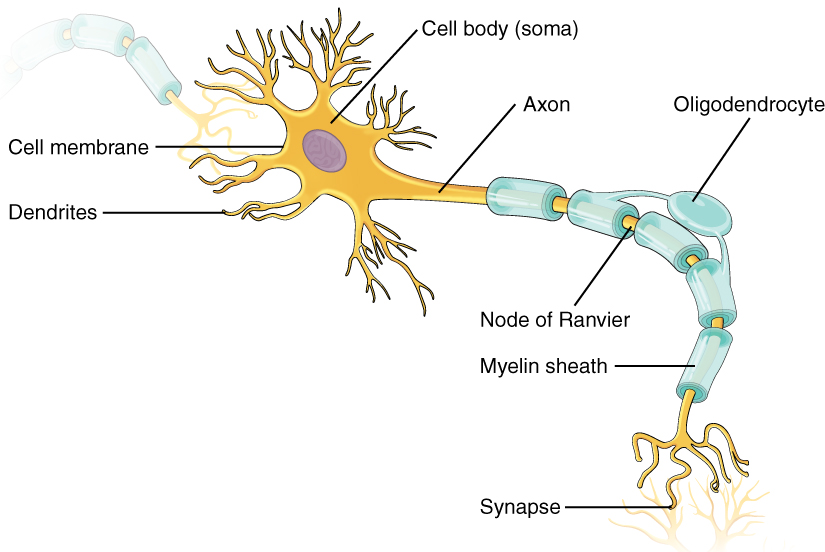
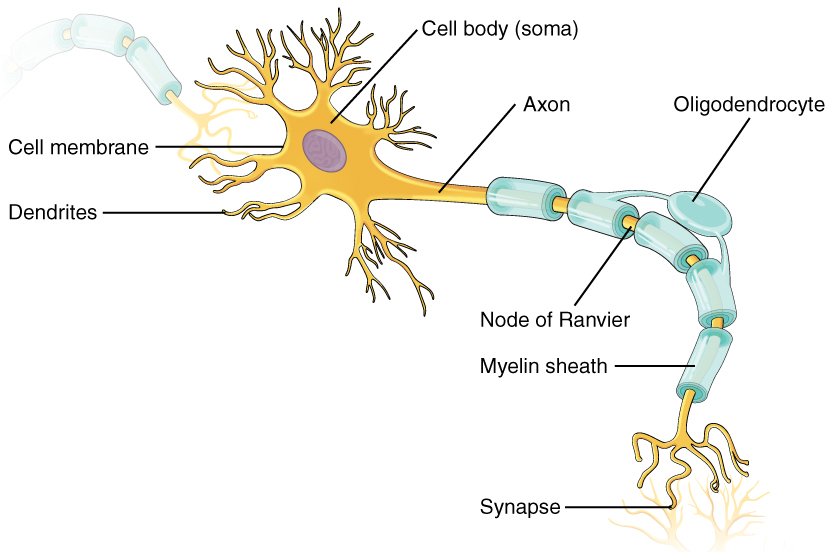
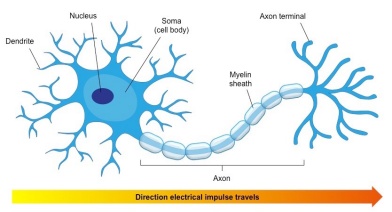
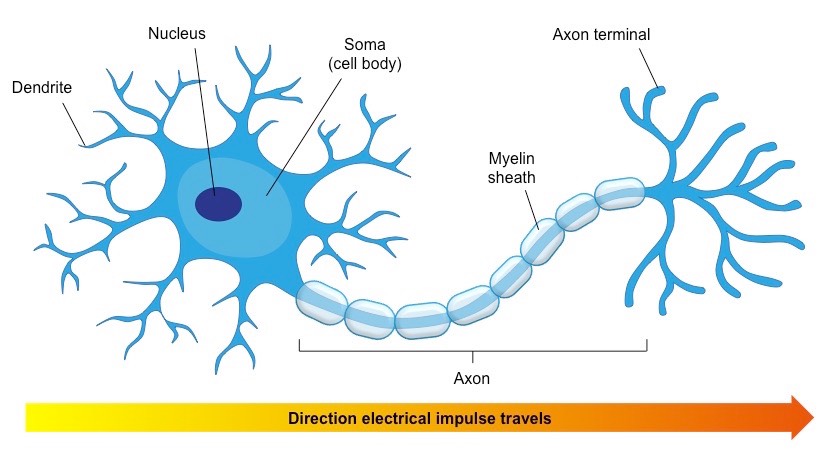
Explain the structure and function of neuron.
Explain the structure of neuron.
Draw the diagram of neuron and label any two parts.
State two functions of areolar tissue.
Find the odd one and also write down the common features of others.(a) Dendrite, Cell body, Axon, Nephron
(b) Epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, Mumps, Alzheimer's disease(c) Melatonin, Insulin, Glucagon, Ethylene
Create a poster/flowchart to depict all that you have learnt in this chapter about plant tissues.
What are the two main types of nerves? Write their functions.
Fill in the blank
RBC: Carrier of oxygen; WBC: ...............
Which blood cells are without nuclei? What is the advantage of this condition?
Write a note on erythrocytes.
What do you mean by fractured bone?
Why are fractured bones plastered?
What makes the blood look red?
What is cavity in bones?
Describe the structure of the multipolar neuron.
Neurons are packed around with some cells. What are these cells called?
Differentiate between :
Myelinated and non-myelinated axons
Differentiate between :
Dendrites and axons.
Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them ?
Draw a labelled diagram of a neuron with a myelin sheath.
Given appropriate biological/ technical terms for the following:
Cellular components of blood containing haemoglobin.
Write one word for each of the following :
(a) A group of similar cells that perform specific function.
(b) Least specialized cells in plants
(c) Cells responsible for increase in diameter of the stem and root of dicot plants.
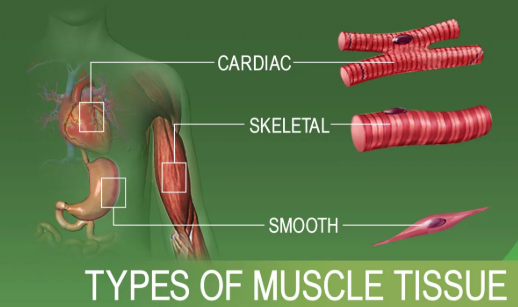
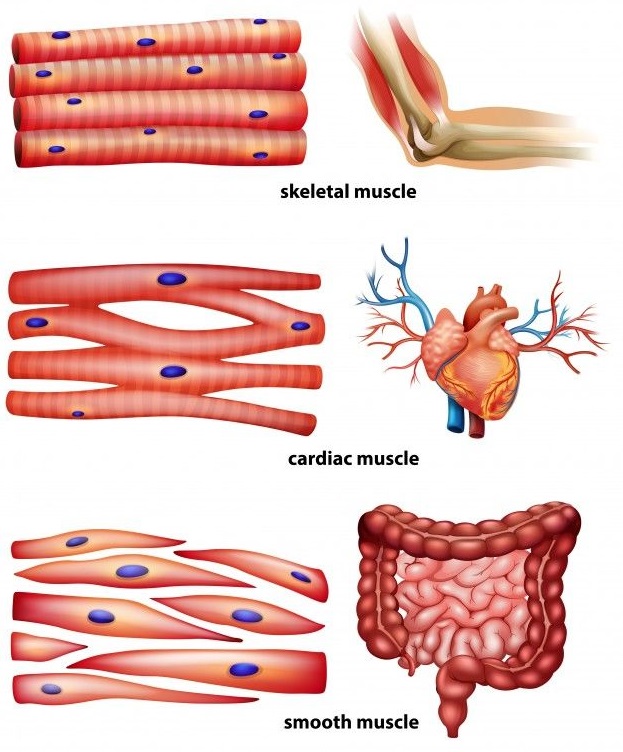
Name the three kinds of muscles in the human body giving one example of each.
Can you consider a cluster of eggs as a tissue? Why?
Short answer
Name the muscle found in the human heart?
Given is a diagram of a human blood smear. Study the diagram and answer the question that follows.
Name the components numbered 1 to 4.

Give appropriate biological or technical terms for the following.
Squeezing out of blood cells from the capillaries into the surrounding tissues.
What are bones made of ? Are the bones living or non-living ? Give reason.
What is the difference between ligament and tendon? What are their functions?
Define the term 'Tissue.'
Name different types of WBCs.
Name a simple living mechanical tissue.
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
Root hairs are formed from extensions of the ..........
Root hairs are formed from extensions of the ..........
"Abnormally large number of WBC's in the blood are usually an indication of some infection in our body." Comment on the statement.
Name the tissue which connects muscle to a bone.
Very short answer type.
What is a ligament?
Very short answer type.
Mark the odd one in the given series.
areolar tissue, blood, neuron, tendon
Very short answer type.
How many types of muscles occur in the body of a vertebrate?
Differentiate between erythrocytes and leucocytes of mammals.
Which type of WBCs are called granulocytes and why?
Differentiate between.
Hemopoiesis and hemolysis.
What are the characteristics of cardiac muscle? Describe its specific function.
Very short answer type.
Mark the odd one in each series.
neurolemma, dendrite, Z-band, myelin
Give two main differences between unstriped and striped muscular tissues and give examples of each.
Describe the structure and the functions of three types of muscular tissue
What roles do the dendrites, cell body, and axon play in communication of signals?
Name the kind of tissue that forms the inner lining of blood vessels.
Differentiate between.
Neuron and nephron
Short/ Long answer type questions.
Give four differences between red and white muscle fibres.
Give the other name for white bloods cells.
What is epidermis?
Describe briefly the structure of a nerve cell.
Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Why do the thigh muscles get tired soon, but not the muscles of the heart?
Describe the functions of the following components of the transport system.
(i) Blood(ii) Lymph
What is the function of myelinated sheath in a neuron?
What is the use of tissues in multicellular organisms?
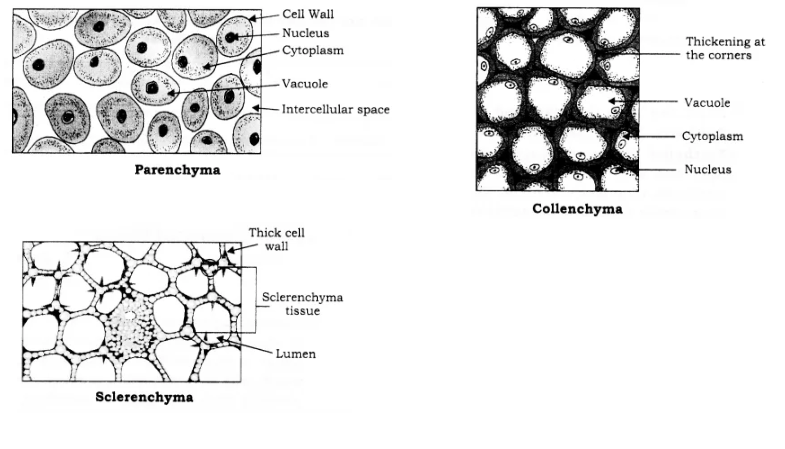
What is a complex permanent tissue? Write the different types of complex permanent tissues.
Give a brief account on neurons.
What are the types of muscular tissue? Explain in detail.
Draw a flow chart to show the types of blood cells.
Why are the voluntary muscles also called striated muscles?
Tissue that stores fat in our body is ________
Name the part of the neuron where information is acquired.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of non- straited muscle.
Explain the basic criteria for classification of permanent tissue of the plant.
Explain the structure of muscle fiber seen in walls of visceral organs
Draw a neat labelled diagram of non-striated muscle.
Classify simple epithelial cells on the basis of shape and position in the body.
Describe location, structure and function of the nervous tissue.
Write a note on areolar connective tissue
Name a layer of large flat cells which fits closely as to edge like tiles in a floor.
I) What are the different types of muscular tissues?
ii) Write two differences between these tissues.
iii) What are unique characters of cardiac muscles?
From which organ do erythrocytes originate?
Pneumocyte Type-1 of alveoli are example of _________.
Write a note on Cardiac Muscles?
What are WBC, RBC and platelet?
Differentiate between the white blood cells and red blood cells.
Write a note on aerolar connective tissue.
The number of bones in an adult human body is _________.
What is the main function of white blood corpuscle?
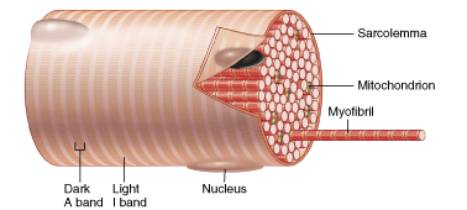
Explain Structure of striated muscle tissue.
Classify the following into cells, tissue, and organ.
skin, fat cell, RBC, blood, ear, muscle
skin, fat cell, RBC, blood, ear, muscle
Which one is largest and smallest
(a) Eosinophil
(b)Basophil
(c)Neutrophil
(d)Monocyte
(e) T-lymphocyte
Write a note on squamous epithelium.
Name of the protein present in the bone matrix.
Full form of RBCs
Write name of muscle responsible for movement of hairs.
At intervals, myelinated nerve fibres possess unmyelinated areas called ______.
Name the three kinds of blood cells.Which amongst them has nucleus?
Draw a diagram of the human nerve cell. Justify its shape with regards to its function.
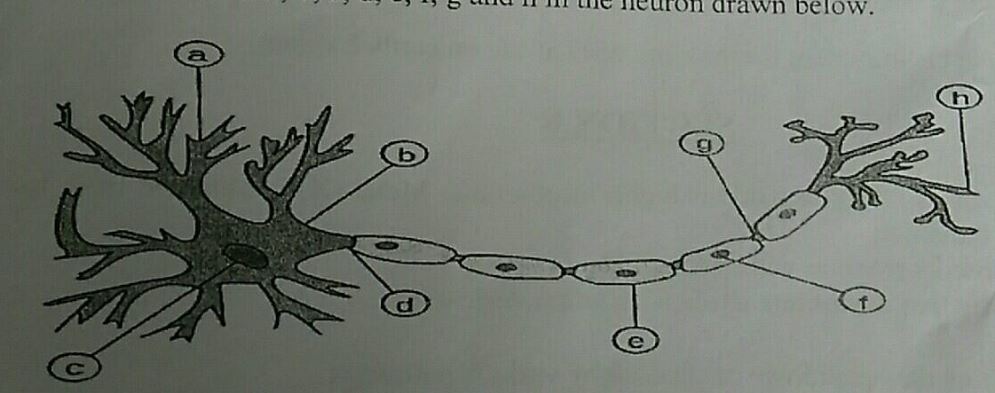
Name the parts labelled a,b,c,d,e,f,g and h in the neuron drawn below.
Identify the odd word and explain why it is odd:
Cartilage, Bone, Tendon, Cardiac Muscle
Give reasons for this sentence:
A mature erythrocyte lacks nucleus and mitochondria.
Give reasons for the following
Leukocytes are called soldiers of our body.
Name the tissue responsible for the movement in our body.
Define the term tissue with respect to plants.
If there is increase in RBC's count in Ramesh's blood, then he is suffering from which condition?
Give one word for the following.
An iron containing protein present on the surface of red blood cells.
How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
What is erythroblastosis?
Name the muscle which is commonly found in visceral organs.
Distinguish between red muscle fibres and white muscle fibres.
Write the function of the following.
Chordae tendineae.
How many muscles are present in human body approximately?
Give importance/functions of Erythrocytes.
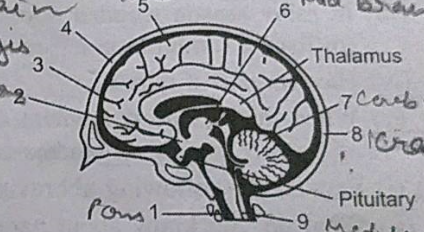
The diagram given alongside is the external view of the human brain. Study the same and answer the question that follow.
What is the structural and functional unit of nervous system?
Name the type of muscle fibers that has automatic rhythmicity.
Give appropriate biological/technical terms for the following.
The tissue which stores fat.
Find out the correct matches:
| Group 'A' | Group 'B' |
| Heart beats | a. 350 ml |
| RBC | b. 7.4 |
| WBC | c. 37oC |
| Blood Donation | d. 72 |
| Normal body | e. 4-6 millions/mm3 |
| pH of oxygenated blood | f. 5000-6000 / mm2 |
Name the following :
Tissue that connects muscle to bone in human.
Name the following:
Tissue that stores fat in our body.
What different types of cells will you see when you observe a drop of blood under a microscope? What are their functions?
What are the component of the transport system in human beings? What are the functions of these components?
Which structure protects the plant body against the invasion of parasites?
Xylen & phloem are described as ________
Distiguish between the following pairs of terms:
Thrombocyte and Erythrocyte
Fill in the blanks.
Lining of blood vessels is made up of _____ tissue.
Write a short note.
Meristematic tissue.
Meristematic tissue.
The following statement is wrong. Rewrite it correctly by changing either one or two words.
Simple squamous epithelium is present in respiratory tract.
Simple squamous epithelium is present in respiratory tract.
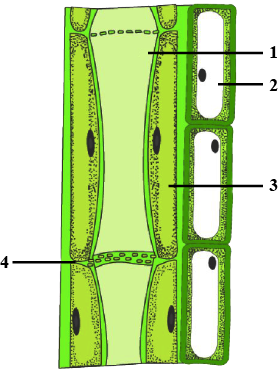
Why are xylem and phloem called complex tissues? How are they different from one other?
Sclerenchyma is a _____________ permanent tissue.
Why is epidermis important for the plants?
Name any two simple and two complex permanent tissues in plants.
Write the name of the following tissue.
The tissue lining the inner surface of the mouth.
The tissue lining the inner surface of the mouth.
Why do we get a crunchy and granular feeling when we chew pear fruit?
Differentiate between meristematic and permanent tissues in plants.
Fill in the blanks:
Bone possesses a hard matrix composed of _______ and _______.
Name any two simple and two complex permanent tissues in plants.
Write a short note on RBCs.
Give reasons.
Muscles should be strong and efficient.
Muscles should be strong and efficient.
What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Grey matter is present in which organ?
How are simple tissues different from complex tissues, in plants?
Define Tissues? Describe the simple tissues found in plants with a diagram?
Write a short note on xylem.
The stomatal pore is guarded by two kidney shaped guard cells. Name the epidermal cells surrounding the guard cells. How does a guard cell differ from an epidermal cell? Use a diagram to illustrate your answer.
What are the two basic types of plant tissues?
Write the appropriate type of tissues in Column B according to the function mentioned in Column A:
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Secretion and absorption | ---- |
| (b) Protective covering | ---- |
| (c) Linking and supporting framework | ---- |
Product of photosynthesis is transported from the leaves to various parts of the plants and stored in some cell before being utilised. What are the cells/ tissues that store them?
Epidermal cells are often modified to perform specialized functions in plants. Name some of them and the function they perform.
A major percentage (97%) of O2 is transported by RBCs in the blood. How is the remaining percentage (3%) of O2 transported?
What is the epidermal cell modification in plants which prevents water loss?
Name the plant tissue which helps in carrying the food to different parts.
What do xylem vessels carry?
Why is it easier to culture meristems compared to permanent tissues?
Write one speciality of Striated muscle
Name one place each in living organisms where the following tissue is located:
Meristematic tissue
Give one word for the following:
A group of similar cells performing a specific function.
Give the technical term for the following:
The category of plant tissues that have lost their ability to multiply.
Write one speciality of each one of the following:
Bone
Give the technical terms for the the type of tissues which are involved in the upward movement of water and dissolved materials from the roots to other parts of the plant
Write one speciality of each one of the following:
Cardiac muscle
Give the location of the following muscle :
Unstriated muscles
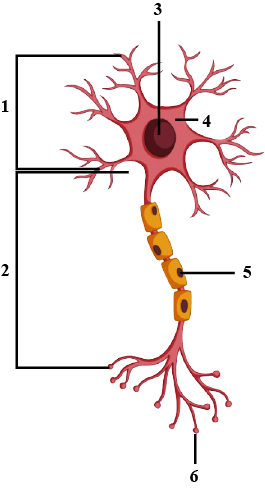
Study the diagram given below and the answer the questions that follow:
(a) Identify the cell.
(b) Name the parts labelled 1,2,3,4,5, and 6.
(c ) Where is this cell likely to be found in the human body and what is its function?
Name the three kinds of muscles found in the human body. In each case, name one region in the body where they are found.
Differentiate between cells of:
Meristematic tissue and permanent tissue
Name the kinds of cells found in the surface of the human skin.
Name the kinds of cells found in the following places:
Brain
Study the diagram given below and then answer the questions that follow:
(a) Identify the tissue and give a reason to support your answer.
(b) Name the parts labelled 1,2,3 and 4.
(c) Where is this tissue likely to be found in the plant?
(d) State the function of the parts labelled 1,2,3 and 4.
Write in brief about arrector pili muscle.
Differentiate between cells of:
Fibers of voluntary muscle and cardiac muscle
Name the following:
The tissue concerned with upward conduction of water in plants.
Write the medical significance of Differential Leukocyte Count.
Explain the role of ESR in disease diagnosis.
What is the color and shape of white blood cells?
Where RBC is formed?
What is used for total leucocyte count?
What is apothorax?
How many vertebrae make up the spinal cord?
Our body contains a large number of cells L which are the longest cells in the body. L has long and short branches called M and N respectively. There is a gap O between two L cells, through which nerve impulse transfer by the release of chemical substance P.
(i) Name the cells L
(ii) What are M and N?
(iii) What is the gap O?
(iv) Name the chemical substance P
What is cartilage? Give two functions.
Mark the odd one in each series.
(a) Areolar tissue; blood; neuron; tendon
(b) RBC; WBC; platelets; cartilage
(c) Exocrine; endocrine; salivary gland; ligament
(d) Maxilla; mandible; labrum; antennae
(e) Protonema; mesothorax; metathorax; coxa
Identify the type of tissue in the following: Skin, Bark of tree, Bone , Lining of kidney tubule, Vascular bundle.
Distinguish between cardiac muscle and striated muscle.
Name the following.
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth. (b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans. (c) Tissue that transports food in plants. (d) Tissue that stores fat in our body. (e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix. (f) Tissue present in the brain.
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth. (b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans. (c) Tissue that transports food in plants. (d) Tissue that stores fat in our body. (e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix. (f) Tissue present in the brain.
Classify the type of neurons and state their functions.
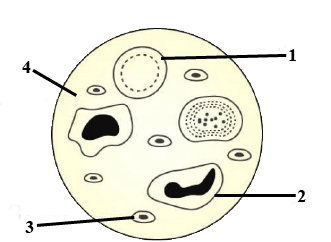
Given below is a diagram of a smear of human blood. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
a. Name the parts 1, 2, 3 and 4 indicated by guidelines.
b. Mention two structural differences between the parts labelled '1' and '2'.
c. What is the main function of the parts labelled 1, 2 and 3 respectively?
d. What is the life span of the part labelled '1'?
e. Name a soluble protein found in '4' which helps in the clotting of blood.
Why xylem is a type of complex tissue?
Value-based questions. Name the tissues where the following structure occurs:
Canaliculi
Canaliculi