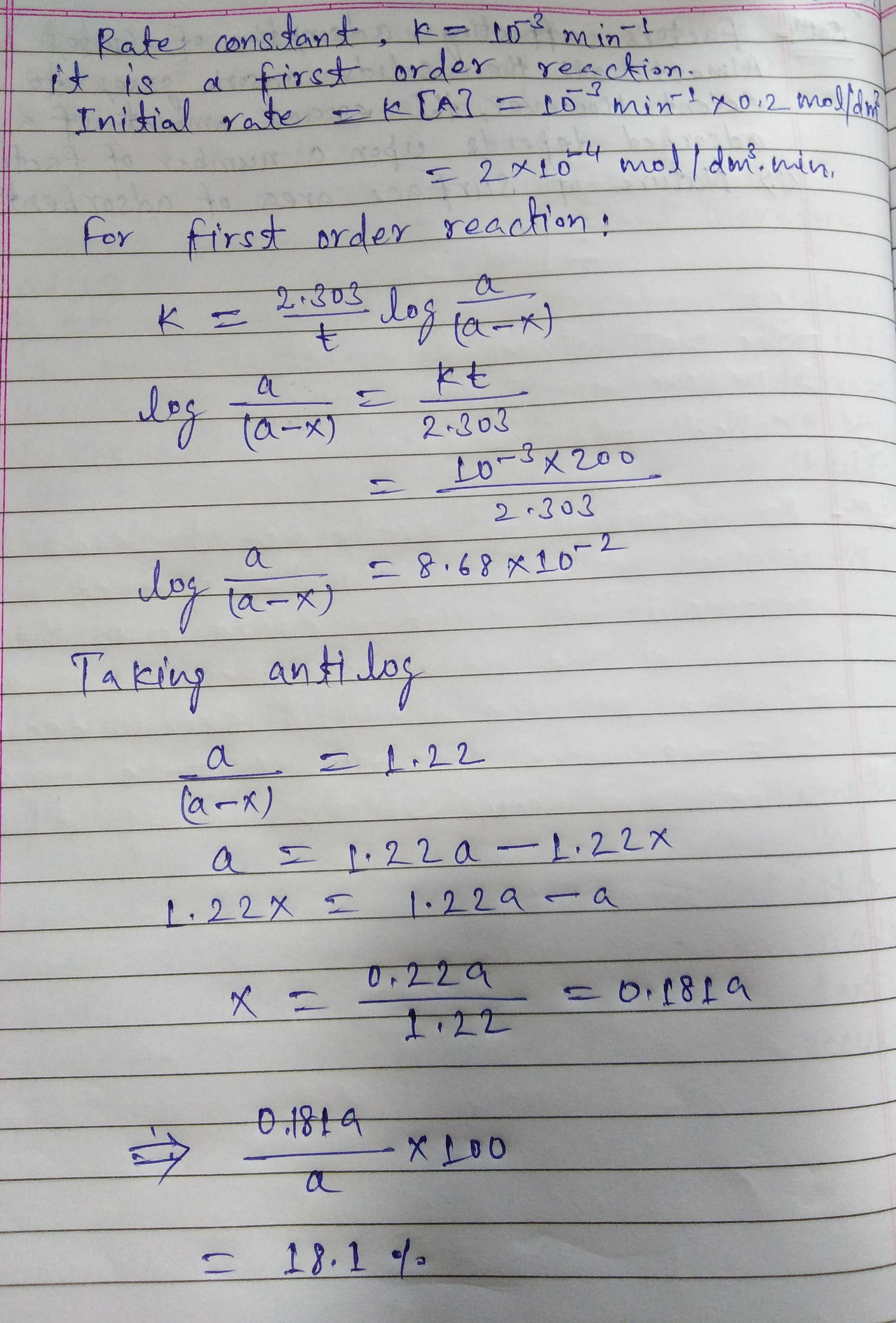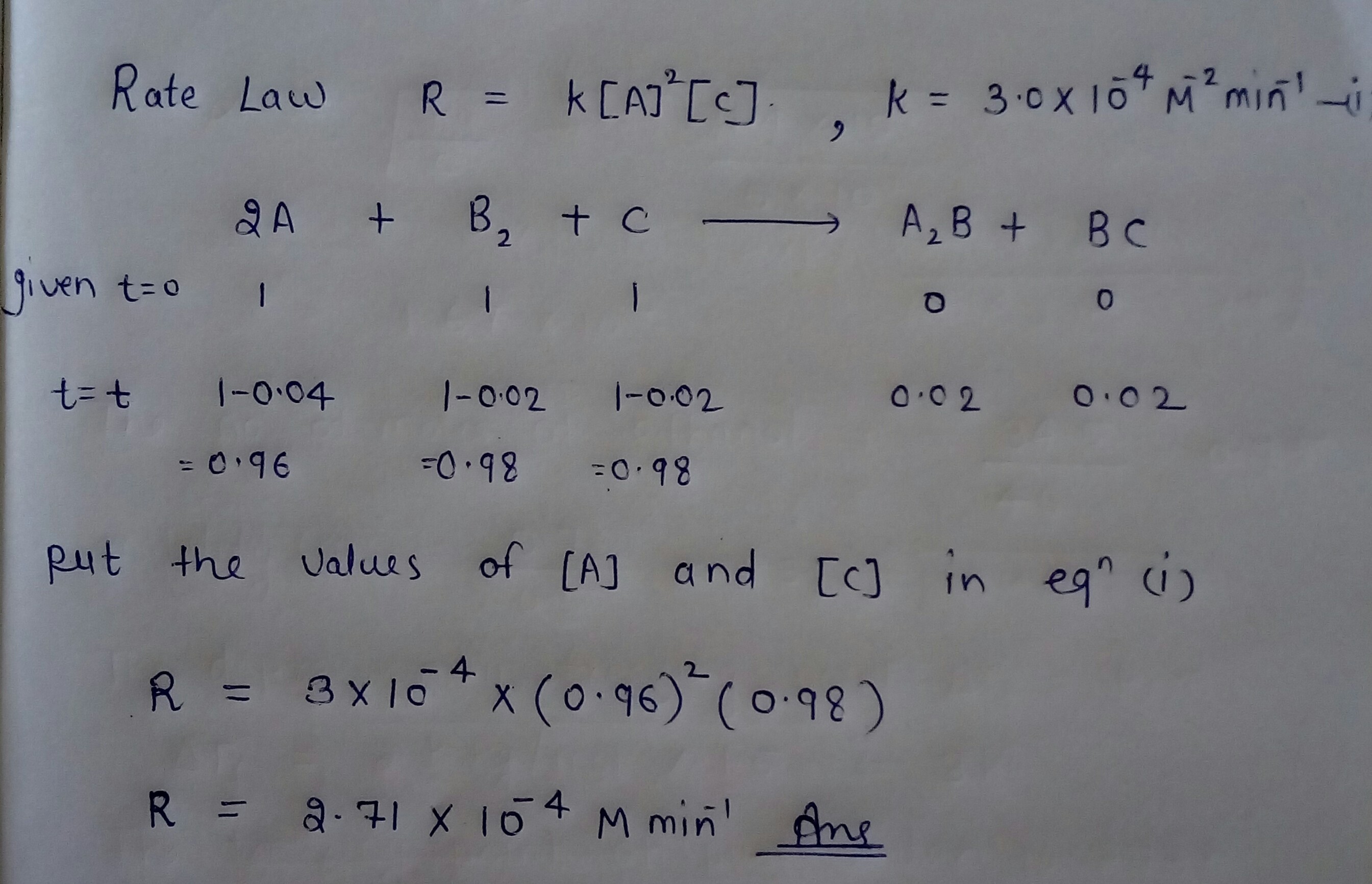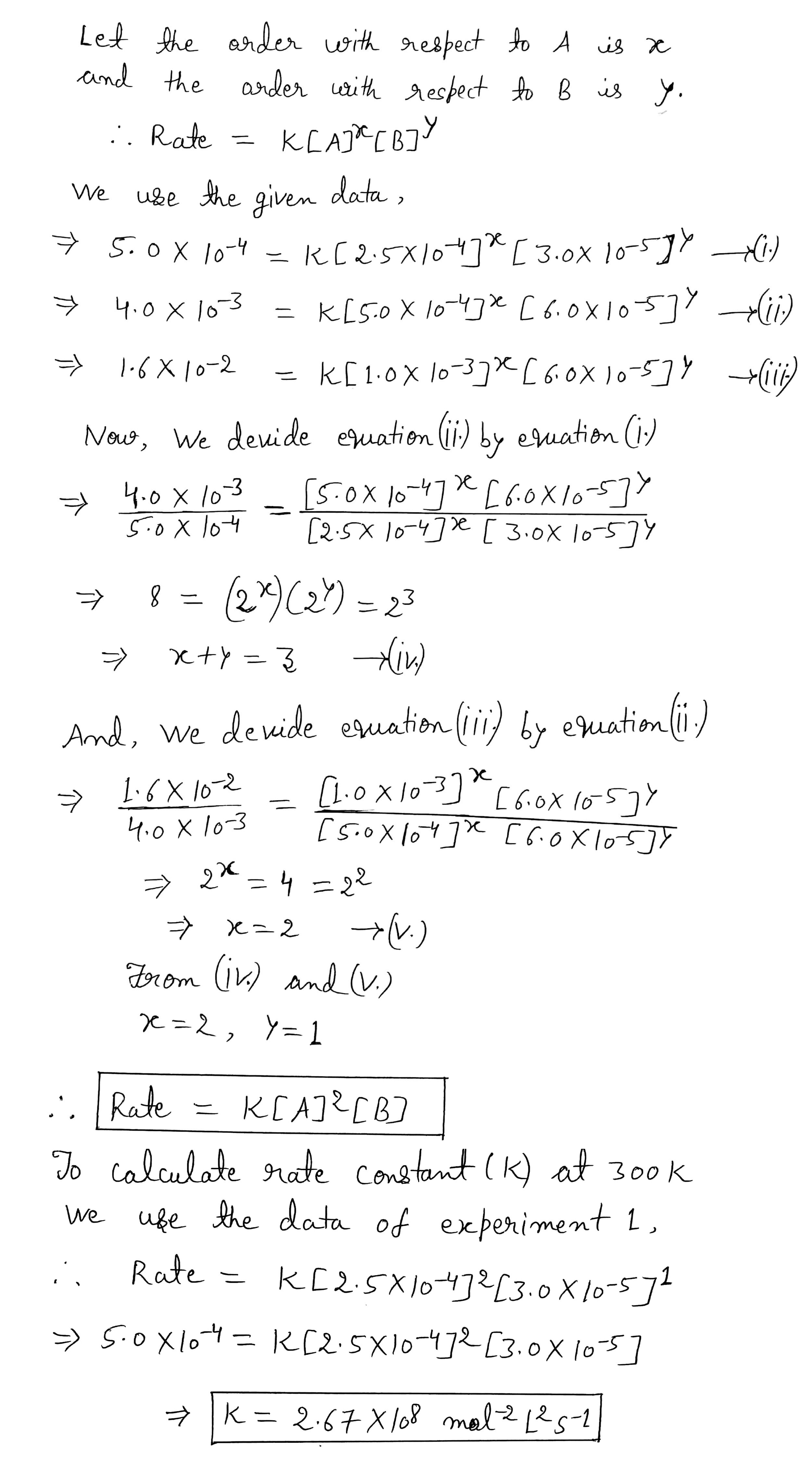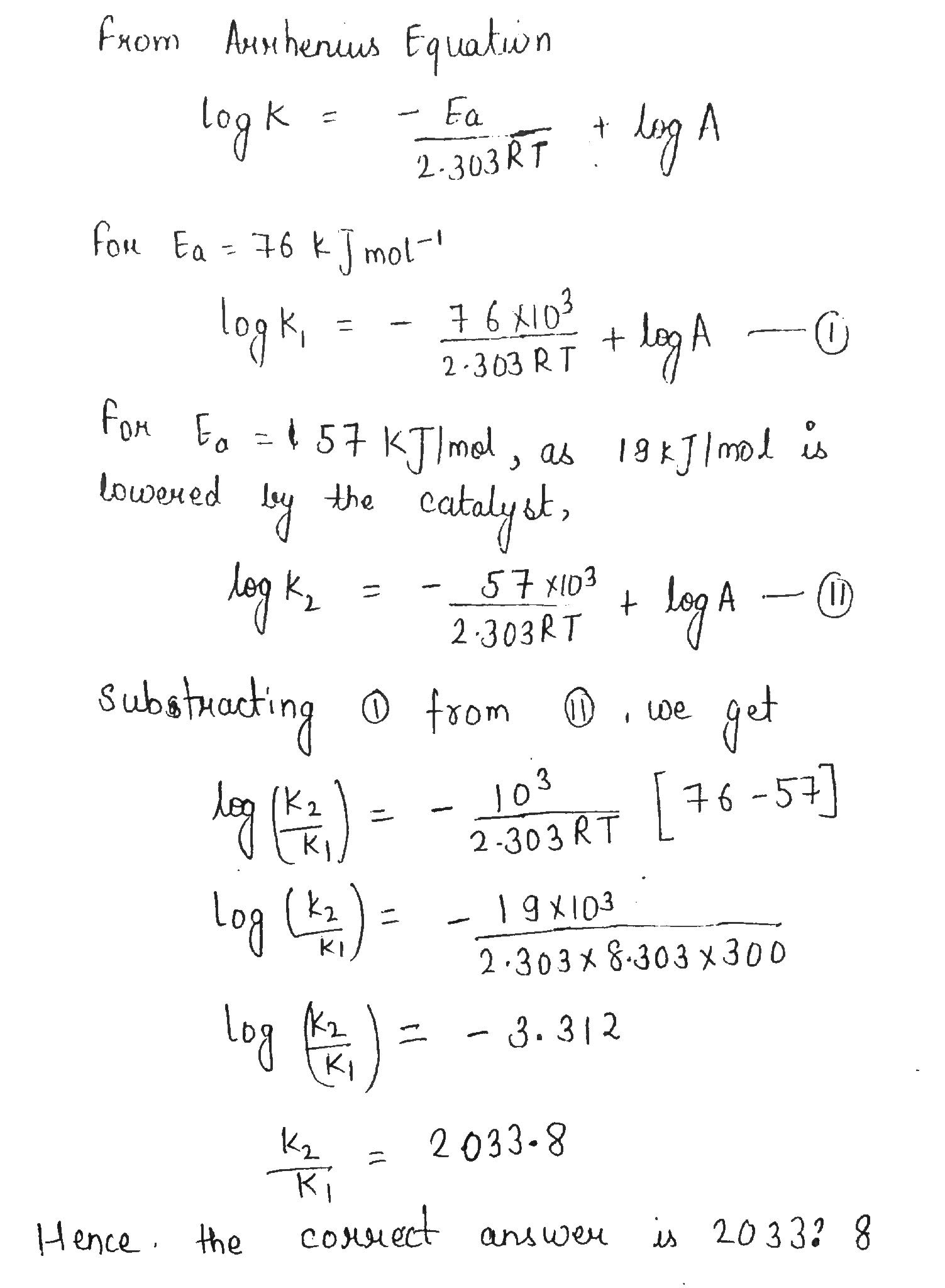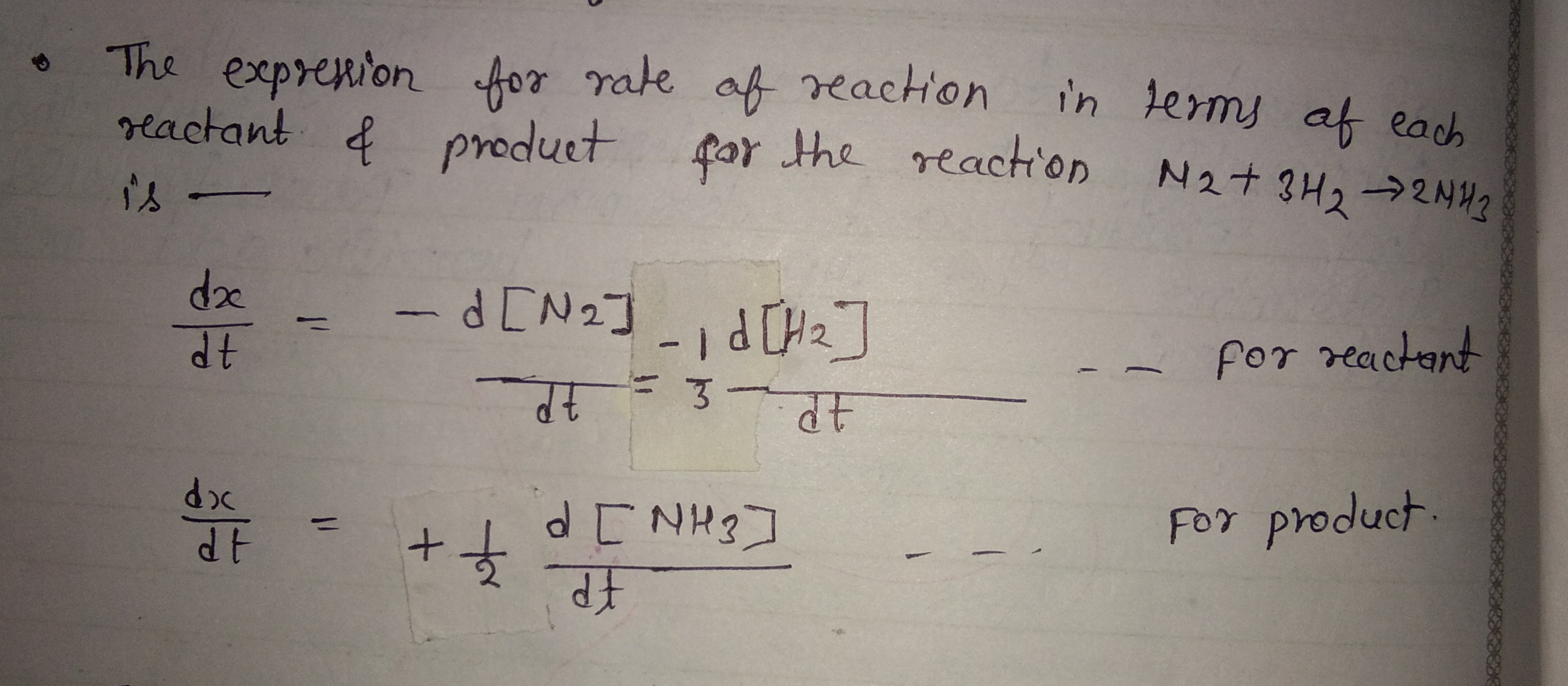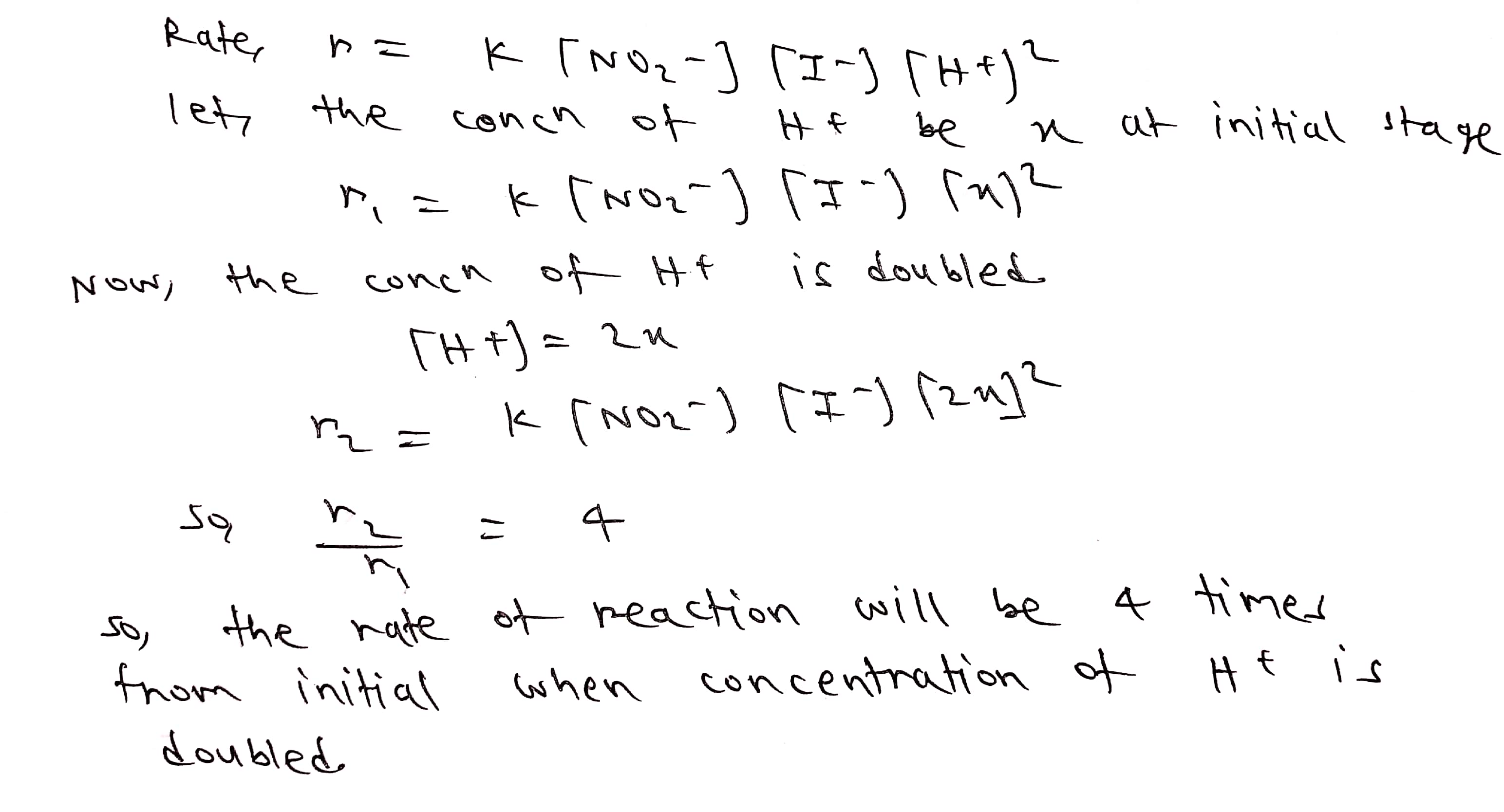Chemical Kinetics - Class 12 Medical Chemistry - Extra Questions
Every chemical reaction has its own characteristic rate. It is affected by some important factors. The most important factors are 1 , temperature, 2 , 3 and surface area out of these factors rise/decrease in temperature, light quantity, rise in the concentration of reactants and surface area 4 the rate of reaction. Whereas as 5 alter the rate of reaction.
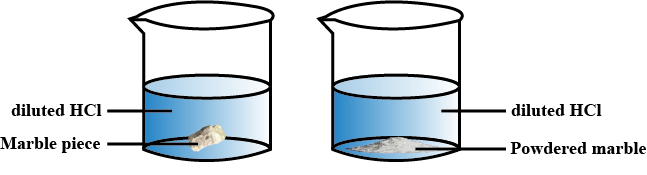
A gas is formed by the reaction between marble pieces and dilute $$HCl$$.
(a) Which gas is formed as a result of this reaction?
(b) Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
(c) Suggest two ways of increasing the speed of the chemical reaction.
Equal lengths of magnesium ribbons are taken in test tubes A and B. Hydrocloric acid is added to test tube A, while acetic acid is added to test tube B. The amount and concentration taken for both the acids are same. In which test tube does the reaction occur more vigourously and why?
The temperature coefficient of the rate of a reaction is $$2.3.$$ How many times will the rate of the reaction increase if the temperature is raised by $$25 K$$?
$$(8.02 times)$$
What will be the initial rate of a reaction if its rate constant is $${10^{ - 3}}{\min ^{ - 1}}$$ and the concentration of reaction is $$0.2$$ $$mold{m^{ - 3}}$$.How much of reactant will be converted into products in $$200$$ min.
In the following schematic diagram for the preparation of hydrogen as as shown in given figure, what would happen if the following changes are made?
(a) In place of zinc granules, same amount of zinc dust is taken in the test tube.
(b) Instead of dilute sulphuric acid, dilute hydrochloric acid is taken
(c) In place of zinc, copper turnings are taken
(d) Sodium hydroxide is taken in place of dilute sulphuric acid and the tube is heated.

Why does the rate of a reaction increase with rise in temperature ?
What is the effect of temperature on the reactions?
(i) $$N_2 (g) + 3H_2 (g) \ \overset{\rightharpoonup}{\leftharpoondown} \ 2 NH_3 (g) + Heat$$
(ii) $$N_2 (g) + O_2 (g) \ \overset{\rightharpoonup}{\leftharpoondown} \ 2 NO_3 (g) - Heat$$
Why does the rate of any reaction generally decrease during the course of the reaction ?
The rate of which reaction increases when the concentration of nitrogen is increased? Forward reaction / Backward reaction.
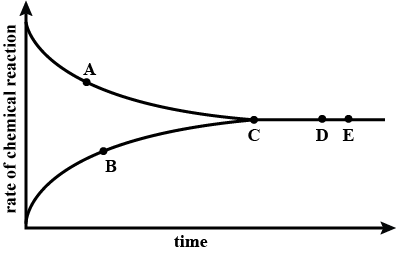
The graph showing the progress of the reaction $$N_{2}+3H_{2}\rightleftharpoons 2NH_{3}$$ is given
Identify the reactions represented by $$B$$ and $$C$$?

Find out the relation between Temperature and rate of a reaction?
Select the materials from the list above
Sodium the sulphate, Test tube, dil $$HCl,Cu,Mg$$ ribbon, Beaker, Water, Spirit lamp, boding Tube
A graph given below deals with the reversible reaction.
What inference can be drawn about the concentration of the reactants and products at the point $$D$$ and $$E$$?
Describe an experiment to prove that nature of the reactants affects the rate of chemical reaction.
Is there any difference in the mass of the marble ?
What happens if the concentration of ammonia is increased?
A graph given below deals with the reversible reaction.
What happen to the forward and backward reactions as time passes?

Why rate of reaction increases when concentration increases ?
What about the concentration of acids in both the reactions ?
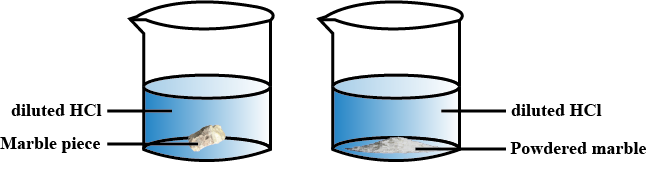
Some materials available in the laboratory are given below. Magnesium ribbon, marble powder , marble pieces , dilute HCl , concentrated HCl.
Which materials will you choose for the preparation of more $$CO_2$$ is less time ?
Giving reasons in brief, indicate whether the following statement is TRUE or FALSE:
The rate of an exothermic reaction increases with increasing temperature.
The experiment conducted by two students are given below.
Experiment 1 : $$2\,mL$$ of sodium thiosulphate solution is taken in a test tube, heated and to it $$2mL $$ of Hg solution is added.
Experiment 2 : $$2\,mL $$ of sodium thiosulphate solution is taken in a test tube and to it $$2\,m$$ of $$HCl$$ solution is added.
In which experiment is the precipitate formed quickly ? Justify your answer.
The experiment conducted by two students are given below.
Experiment 1 : $$2\,mL$$ of sodium thiosulphate solution is taken in a test tube, heated and to it $$2mL $$ of Hg solution is added.
Experiment 2 : $$2\,mL $$ of sodium thiosulphate solution is taken in a test tube and to it $$2\,m$$ of $$HCl$$ solution is added.
Write the balanced equation for the reaction.
Mention the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
For a given reaction $$A+B\to P$$, the ordes w.r.t $$A$$ and $$B$$ are $$1$$ and $$2$$ respectively. Fill in the blanks from the following data:
Rate $$(M s^{-1})$$ $$[A]$$ $$[B]$$ $$0.10$$ $$1.0\ M$$ $$0.20\ M$$ ... $$2.0\ M$$ $$0.20\ M$$ ... $$2.0\ M$$ $$0.40\ M$$
| Rate $$(M s^{-1})$$ | $$[A]$$ | $$[B]$$ |
| $$0.10$$ | $$1.0\ M$$ | $$0.20\ M$$ |
| ... | $$2.0\ M$$ | $$0.20\ M$$ |
| ... | $$2.0\ M$$ | $$0.40\ M$$ |
One mole of a gas $$A$$ and two moles of a gas $$B$$ are introduced into one vessel and $$2$$ moles of $$A$$ and $$1$$ mole of $$B$$ a second vessel having the same capacity. The temperature is the same in both vessels. Will the rate of reaction $$A$$ and $$B$$ in these vessel differ if its expressed by the equation.
rate $$=k[A][B]$$
The rate law of the reaction,
$$CH_3COOC_2H_5 +H_2O \xrightarrow []{[H^+]} CH_3COOH+C_2H_5OH$$ is
$$\dfrac {dx}{dt}=k[CH_3COOC_2H_5] [H_2O]^o$$
What will be the effect on the rate if the concentration of $$H^+$$ is tripled?
The rate law of the reaction,
$$CH_3COOC_2H_5 +H_2O \xrightarrow []{[H^+]} CH_3COOH+C_2H_5OH$$ is
$$\dfrac {dx}{dt}=k[CH_3COOC_2H_5] [H_2O]^o$$
What will be the effect on the rate if the concentration of the ester is doubled?
How many times will the rate of the reaction $$2A+B\to A_2B$$ change if the concentration of substance $$A$$ is doubled and that of substance $$B$$ is halved?
One mole of a gas $$A$$ and two moles of a gas $$B$$ are introduced into one vessel and $$2$$ moles of $$A$$ and $$1$$ mole of $$B$$ a second vessel having the same capacity. The temperature is the same in both vessels. Will the rate of reaction $$A$$ and $$B$$ in these vessel differ if its expressed by the equation.
rate $$=k[A]^2 [B]$$ ?
For the reaction: $$2A+B_2+C\rightarrow A_2B+BC$$, the rate law expression has been determined experimentally to be $$R=k[A]^2[C]$$ with $$k=3.0\times 10^{-4}M^{-2}min^{-1}$$.
Determine the rate after $$0.04$$ mole per litre of A has reacted.
From the following data for the reaction between A and B:
$$[A]$$, mol $$L^{-1}$$ $$[B]$$, mol $$L^{-1}$$ Initial rate, mol $$L^{-1}s^{-1}$$, at Initial rate, mol $$L^{-1}s^{-1}$$, at $$300$$ K $$320$$K $$2.5\times 10^{-4}$$ $$3.0\times 10^{-5}$$ $$5.0\times 10^{-4}$$ $$2.0\times 10^{-3}$$ $$5.0\times 10^{-4}$$ $$6.0\times 10^{-5}$$ $$4.0\times 10^{-3}$$ - $$1.0\times 10^{-3}$$ $$6.0\times 10^{-5}$$ $$1.6\times 10^{-2}$$ -
Calculate the rate constant at $$300$$K.
| $$[A]$$, mol $$L^{-1}$$ | $$[B]$$, mol $$L^{-1}$$ | Initial rate, mol $$L^{-1}s^{-1}$$, at | Initial rate, mol $$L^{-1}s^{-1}$$, at |
| $$300$$ K | $$320$$K | ||
| $$2.5\times 10^{-4}$$ | $$3.0\times 10^{-5}$$ | $$5.0\times 10^{-4}$$ | $$2.0\times 10^{-3}$$ |
| $$5.0\times 10^{-4}$$ | $$6.0\times 10^{-5}$$ | $$4.0\times 10^{-3}$$ | - |
| $$1.0\times 10^{-3}$$ | $$6.0\times 10^{-5}$$ | $$1.6\times 10^{-2}$$ | - |
Calculate the rate constant at $$300$$K.
The rate constant for an isomerisation reaction $$A\rightarrow B$$ is $$4.5\times 10^{-3}$$ $$min^{-1}$$. If the initial concentration of A is $$1$$M, calculate the rate after $$1$$ h.
The activation energy of a certain uncatalysed reaction at $$300\ K$$ is $$76\ kJ\ mol^{-1}$$. The activation energy is lowered by $$19\ kJ\ mol^{-1}$$ by the use of catalyst. By what factor, the rate of catalysed reaction is increased?
The order of the reaction $$2A+B+C\rightarrow Product$$, is found to be 1, 2 and 0 w.r.t A, B and C respectively. If the concentration of each reactant is increased by two times, what will be the effect on the rate of the reaction?
Thermodynamic feasibility of the reaction alone cannot decide the rate of the reaction . Explain with the help of one example .
A reaction is second order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of the reactant doubled?
For the reaction :
$$ 2A + B \rightarrow A_{2}B $$
The rate $$ = k \left [ A \right ]\left [ B \right ]^{2} $$ $$ k= 2.0 \times 10 ^{-6} $$ $$ mol^{-2} L ^{2} s^{-1} $$ .
Calculate the initial rate of the reaction when $$ \left [ A \right ] = 0.1 mol L^{-1} , \left [ B \right ] = 0.2 molL^{-1}$$
How many types of reactions are there on the basis of speed?
Mention the factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
In a reaction between A and B, the initial rate of reaction ($$r_0$$) was measured for different initial concentrations of A and B as given below:
What is the order of the reaction with respect to A and B?
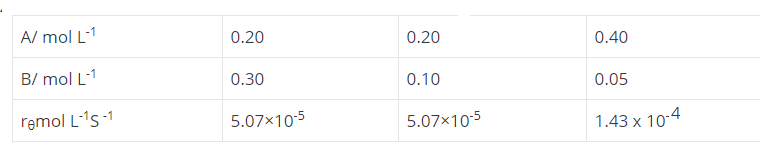
A reaction first order in A and second order in B.
How is the rate affected on increase the concentration of B three times ?
The reaction between A and B is first order with respect to A and Zero order with respect to B .
Fill in the blanks in the following table :
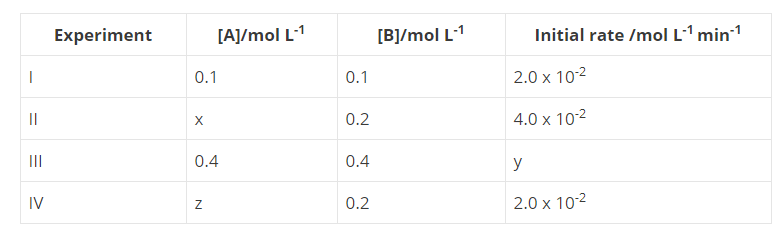
Write the expression for rate of reaction in terms of each reactant and product for the reaction, $$N_2 +3H_2 \rightarrow 2NH_3$$
What is the effect of a temperature on the rate constant of a reaction? How can this temperature affect on rate constant be represented quantitatively.
Name the factors on which the rate of a particular reaction depends.
For an elementary reaction,
$$2 A + B \rightarrow 3 C$$
the rate of appearance of C at time 't' is $$1.3 \times 10^{-4} mol\ L^{-1} s^{-1}$$. Calculate at this time
1) Rate of the reaction.
A reaction is second order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of the reactant reduced to half?
A reaction first order in A and second order in B.
How is the rate affected when the concentration of a both A and B are doubled ?
Coldwater is taken in one test tube an hot water in another one. Mg ribbon with same size is dropped in each of the test tubes.
Which factor influences the rate of reaction? Explain the reason.
The rate law for a reaction is found to be.
Rate $$= K [NO^{-}_{2}][I^{-}][H^{+}]^{2}$$
How would the rate of reaction change when
Concentration of $$H^{+}$$ is doubled
Prepare a write up for finding the relation between temperature and rate of a reaction.
The rate law for a reaction is found to be,
Rate $$= K [NO^{-}_{2}][I^{-}][H^{+}]^{2}$$
How would the rate of the reaction change when the concentration of $$H^{+}$$ is doubled?
Rate $$= K [NO^{-}_{2}][I^{-}][H^{+}]^{2}$$
How would the rate of the reaction change when the concentration of $$H^{+}$$ is doubled?
For an elementary reaction,$$2 A + B \rightarrow 3 C$$the rate of appearance of C at time 't' is $$1.3 \times 10^{-4} mol\ L^{-1} s^{-1}$$. Calculate at this timea) Rate of disappearance of A.
The rate constant for a first order reactions is $$ 60 s^{-1}$$ . How much time will it take to reduce the initial concentration of the reactant to its 1/16 the value ?
The rate law for a reaction is found to be.
Rate $$= K [NO^{-}_{2}][I^{-}][H^{+}]^{2}$$ How would the rate of reaction change when
Concentration of each of $$NO_{2}, I^{-}$$ and $$H^{+}$$ are tripled?
What happens to the rates of forward and backward reactions as time progresses?
What will be the effect of removing ammonia continuously from the system ?
Why rate of a reaction increase when temperature increases?
Write an experiment to prove that concentration of reactants affect the rate of reactions.
Complete the table writing the effect of change in concentration in the system at equilibrium.
| Action | Change of concentration | Change in rate |
| $$\bullet$$ More hydrogen is added | $$\bullet$$ Increase the concentration of reactant. | $$\bullet$$ Rate the forward reaction increases. |
| $$\bullet$$ More ammonia is added | $$\bullet$$ Increase the concentration of product. | $$\bullet$$ .............. |
| $$\bullet$$ Ammonia is removed | $$\bullet$$ Decrease the concentration of product. | $$\bullet$$ .............. |
| $$\bullet$$ More nitrogen is added | $$\bullet$$ Increase the concentration of reactant. | $$\bullet$$ ................ |
Write your observation
Test tube 1 : ............
Test tube 2 : ............
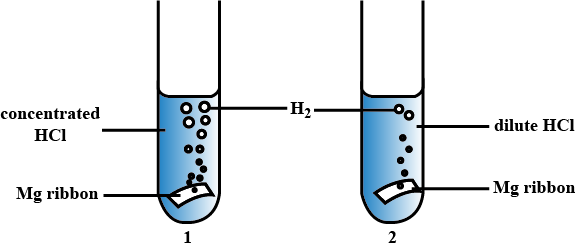
Mention the factor that affect the rate of a chemical reaction .
A reaction is second order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of the reactants is doubled?
Is there any difference in the rate of reaction in the two beakers ?
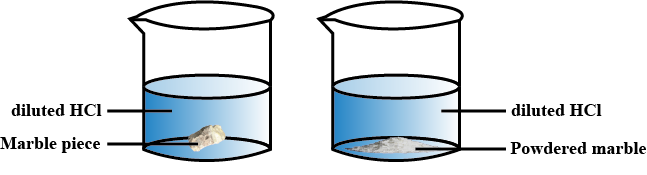
Write an experiment to prove the relation between temperature and rate of reaction.
In which of the following tubes is the precipitate formed faster ?
What is the color of the precipitate formed ?
Some materials available in the laboratory are given below. Magnesium ribbon, marble powder , marble pieces , dilute HCl , concentrated HCl.
Write the balanced chemical equation of the reaction.
A reaction is second order with respect to a reactant. How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of the reactants is reduced to $$\dfrac{1}{2}$$?
Some apparatus and chemical are given.
Zn , Mg , dilute HCl, $$ CaCO_3$$ , test tube , water.
(a) Design an experiment to prove that the nature of reactants can influence the rate of reaction.
(b) Write the equations for the chemical reactions.
(c) Write the expression for the rate of the reaction.
Sulfur pieces do not react with cold concentrated nitric acid. But sulfur powder reacts.
Explain the reason why the rate of chemical reaction is increased here ?
A reaction is first order with respect to A and second order with respect B.
How is the rate affected when the concentration of both A and B is doubled.
How is the rate affected when the concentration of both A and B is doubled.
Sulfur pieces do not react with cold concentrated nitric acid. But sulfur powder reacts.
Suppose you want to increase the rate of reaction again. Which way you would choose ? Give reason.
A reaction is first order with respect to A and second order with respect B.
How is the rate affected when the concentration of B is tripled ?
How will the rate of the reaction be affected when
(a) Surface area of the reactant is reduced,
(b) Catalyst is added in a reversible reaction, and
(c) Temperature of the reaction is increased?
Class 12 Medical Chemistry Extra Questions
- Alcohols, Phenols And Ethers Extra Questions
- Aldehydes, Ketones And Carboxylic Acids Extra Questions
- Biomolecules Extra Questions
- Chemical Kinetics Extra Questions
- Chemistry In Everyday Life Extra Questions
- Coordination Compounds Extra Questions
- Electrochemistry Extra Questions
- General Principles And Processes Of Isolation Of Elements Extra Questions
- Haloalkanes And Haloarenes Extra Questions
- Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Extra Questions
- Polymers Extra Questions
- Solutions Extra Questions
- Surface Chemistry Extra Questions
- The D-And F-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The P-Block Elements Extra Questions