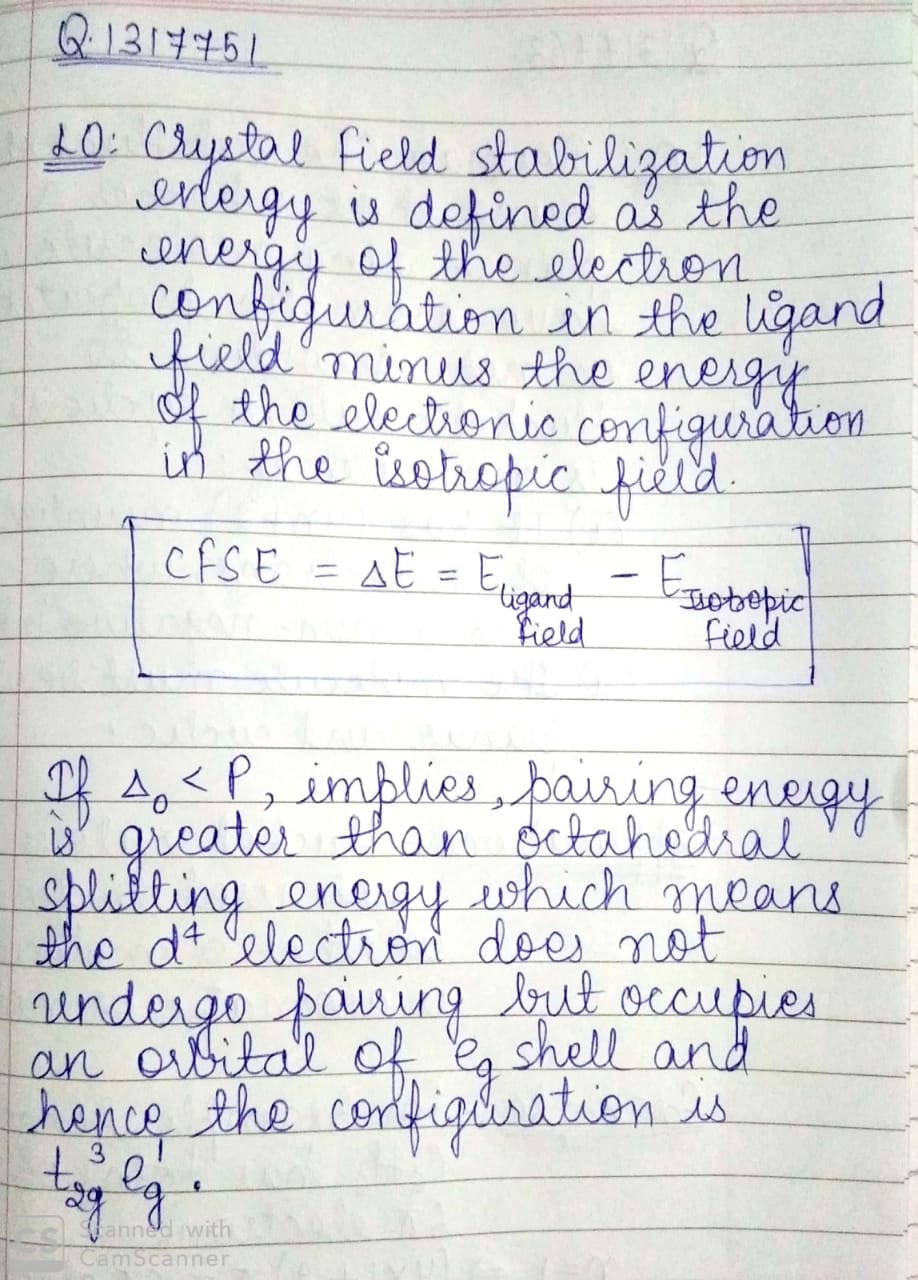Coordination Compounds - Class 12 Medical Chemistry - Extra Questions
On the basis of crystal field theory write the electronic configuration for $${d}^{4}$$ if $${\Delta}_{0}< P$$.
What is $$pK$$ value of the complex $$[PtCl_4]$$ if__________.
$$Pt^{4+}+Cl^-\rightarrow [PtCl]^{3+}$$ $$K_1=10^{-2}$$
$$[PtCl]^{3+}+Cl^-\rightarrow [PtCl_2]^{2+}$$ $$K_2=10^{-3}$$
$$[PtCl_2]^{2+}+Cl^-\rightarrow [PtCl_3]^+$$ $$K_3=10^{-4}$$
$$[PtCl_3]^++Cl^-\rightarrow [PtCl_4]$$ $$K_4=10^{-4}$$
Which of the following is more stable complex and why? $${ \left[ Co{ \left( N{ H }_{ 3 } \right) }_{ 6 } \right] }^{ 3+ }$$ and $${ \left[ Co{ \left( en \right) }_{ 3 } \right] }^{ 3+ }$$
How many moles of $$AgCl$$ will be precipitated when an excess of $$AgNO_3$$ solution is added to one molar solution of $$[CrCl(H_2O)_5]Cl_2$$?
Which isomerism is shown by $$[Co(NH_{3})_{6}]Cl_3$$. Write name?
Which one is more stable in the following pairs of complexes? Give reasons.
i) $$[Co(NO_{2})_{6}]^{4-}$$ and $$[Co(NO_{2})_{6}]^{3-}$$
ii) $$K_{4}[Fe(CN)_{6}]$$ and $$K_{3}[Fe(CN)_{6}]$$.
(iii)$$[CO(H_{2}O)_{6}]^{2+}$$ and $$[CO(NH_{3})_{6}]^{2+}$$
The hexaaquomanganese (II) ion contains five unpaired electrons while the hexacyano ion contains only one unpaired electron. Explain using Crystal Field Theory.
Which of the following is not correctly matched?
| Complex ion | CFSE | |
| a | $$[Co(NH_3)_6]^{3+}$$ | $$24 \ Dq$$ |
| b | $$[Cr(NH_3)_6]^{3+}$$ | $$12 \ Dq$$ |
| c | $$[FeF_6]^{3-}$$ | $$4 \ Dq$$ |
| d | $$[Fe(CN)_6]^{3-}$$ | $$20 \ Dq$$ |
If crystal field stabilization energy of $$[ML_6]^{+n}$$ is $$-0.8 \triangle_0$$. Find minimum number of electrons in $$t_{2g}$$ orbitals of metal ion?
On the basis of crystal field theory write the electronic configuration for $$d^{4}$$ ion, if $$\Delta_{0} < P$$.
What is crystal field stabilization energy?On the basic of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration for $$d^{4}$$ ion if $$\Delta_{o}<P$$
Write what are the limitation of crystal field theory.
How would you account for the following:
The $${d}^{1}$$ configuration is very unstable in ions.
List and explain the factors which affect the stability of coordination complexes.
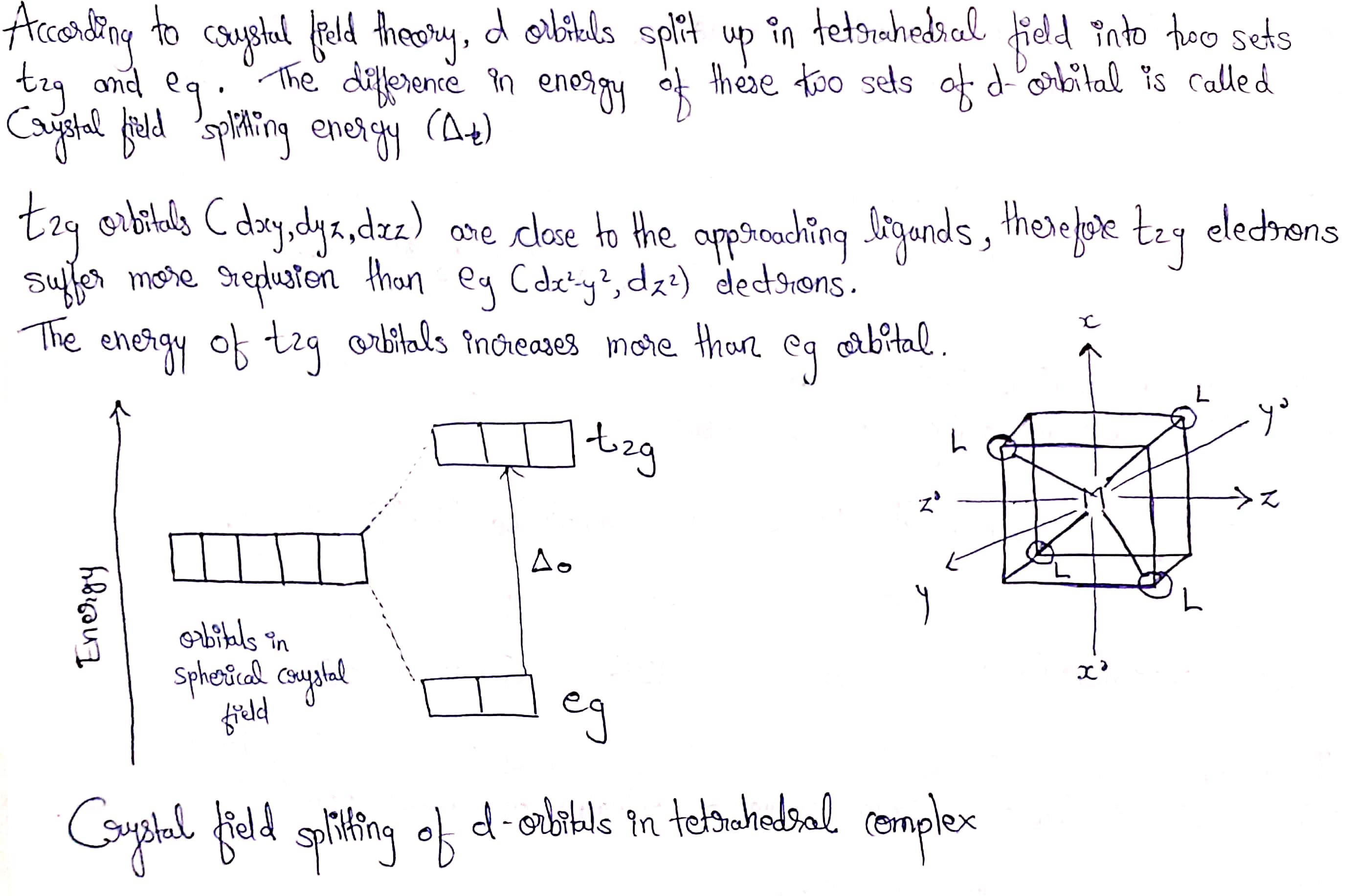
Draw an energy level diagram to show the lifting of the degeneracy of the 3d orbitals in a tetrahedral ligand field.
Explain, why $$Mn^{3+}$$ is less stable than $$Mn^{2+}$$ and $$Mn^{4+}$$ ions?
Explain, why $$Mn^{3+}$$ disproportionate into $$Mn^{2+}$$ and $$Mn^{4+}$$ ions?
Explain why $$[Cu(en)_2]^{2+}$$ is less stable than $$[Fe(EDTA)]^-$$?
Why is the complex $$[Co(en)_{3}]^{3+}$$ more stable than the complex $$[CoF_{6}]^{3-}$$?
What is spectrochemical series?
Which of the following complex is more stable and why ? $$[Co(NH_{3})_{6}]^{3+}$$ and $$[Co(en)_{3}]^{3+}$$
Why do compounds having similar geometry have different magnetic moment?
Arrange following complex ions in increasing order of crystal field splitting energy $$(\Delta_0)$$:
$$[Cr(Cl)_6]^{3-}, [Cr(CN)_6]^{3-}, [Cr(NH_3)_6]^{3+}$$
Ethylenediamine displaces $$H_2O$$ in the complex $$[Fe(H_2O)_6]^{3+}$$ in three steps.
$$[Fe(H_2O)_6]^{3+}+3en\rightarrow [Fe(en)_3]^{3+}+6H_2O$$
Stepwise formation constants are
$$log K_1=4.34$$
$$log K_2=3.31$$
$$log K_3=2.05$$
Overall formation constant is $$A\times 10^B$$.
$$A+B$$ is ............
Ethylenediamine displaces $$H_2O$$ in the complex $$[Fe(H_2O)_6]^{3+}$$ in three steps.
$$[Fe(H_2O)_6]^{3+}+3en\rightarrow [Fe(en)_3]^{3+}+6H_2O$$
Stepwise formation constants are:
$$\log K_1=4.34$$
$$\log K_2=3.31$$
$$\log K_3=2.05$$
Overall formation constant is $$A\times 10^{2B}$$.
$$\text{B}$$ in question is:
Which complex is more stable in each pair?
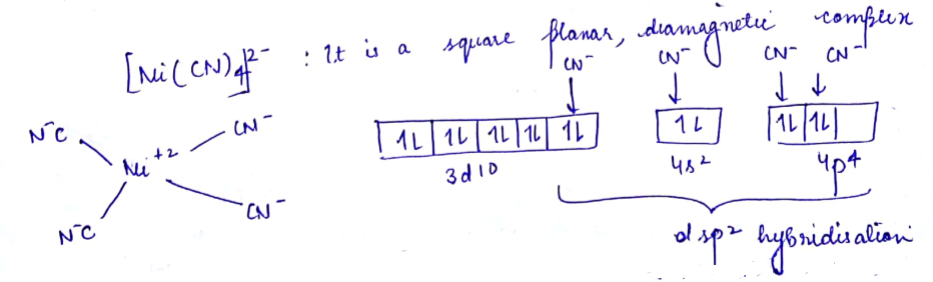
(a) $$[Ni(CN)_4]^{2-}$$ , $$[Pt(CN)_4]^{2-}$$.
What is crystal field splitting energy? How does the magnitude of $$\Delta_{0}$$ decide the actual configuration of d orbitals in a coordination entity?
What is meant by stability of a coordination compound in solution? State the factors which govern stability of complexes.
Find the crystal field stabilization energy (CFSE) (in kJ/mol) for complex, $${\left[ {Ti{{\left( {{H_2}O} \right)}_6}} \right]^{3 + }}$$. According to CFT, the first absorption maximum is obtained at $$20,3000\, cm^{-1}$$ for the transition
Explain hydrate (solvate) isomerism and linkage isomerism with suitable examples.
The step wise formation of $$[Cu(NH_{3})_{4}]^{2+} $$ is given below
$$Cu^{2+} + NH_{3} \overset{K_{1}} \rightleftharpoons [Cu(NH_{3})]^{2+} $$
$$[Cu(NH_{3})]^{2+} + NH_{3} \overset{K_{2}} \rightleftharpoons [Cu(NH_{3})_{2} ]^{2+} $$
$$[Cu(NH_{3})_{2}]^{2+} + NH_{3} \overset{K_{3}} \rightleftharpoons [Cu(NH_{3})_{3}]^{2+} $$
$$[Cu(NH_{3})_{3}]^{2+} + NH_{3} \overset{K_{4}} \rightleftharpoons [Cu(NH_{3})_{4}]^{2+} $$
The value of stability constants $$K_{1} , K_{2} , K_{3}$$ and $$K_{4}$$ are $$10^{4} , 1.58 \times 10^{3} , 5 \times 10^{2}$$ and $$10^{2} $$ respectively. The overall equilibrium constants for dissociation of $$[Cu(NH_{3})_{4}]^{2+} $$ is $$x \times 10^{-12} $$. The value of $$x$$ is _____________.
(Rounded off to the nearest integer)
$$Cu^{2+} + NH_{3} \overset{K_{1}} \rightleftharpoons [Cu(NH_{3})]^{2+} $$
$$[Cu(NH_{3})]^{2+} + NH_{3} \overset{K_{2}} \rightleftharpoons [Cu(NH_{3})_{2} ]^{2+} $$
$$[Cu(NH_{3})_{2}]^{2+} + NH_{3} \overset{K_{3}} \rightleftharpoons [Cu(NH_{3})_{3}]^{2+} $$
$$[Cu(NH_{3})_{3}]^{2+} + NH_{3} \overset{K_{4}} \rightleftharpoons [Cu(NH_{3})_{4}]^{2+} $$
The value of stability constants $$K_{1} , K_{2} , K_{3}$$ and $$K_{4}$$ are $$10^{4} , 1.58 \times 10^{3} , 5 \times 10^{2}$$ and $$10^{2} $$ respectively. The overall equilibrium constants for dissociation of $$[Cu(NH_{3})_{4}]^{2+} $$ is $$x \times 10^{-12} $$. The value of $$x$$ is _____________.
(Rounded off to the nearest integer)
Class 12 Medical Chemistry Extra Questions
- Alcohols, Phenols And Ethers Extra Questions
- Aldehydes, Ketones And Carboxylic Acids Extra Questions
- Biomolecules Extra Questions
- Chemical Kinetics Extra Questions
- Chemistry In Everyday Life Extra Questions
- Coordination Compounds Extra Questions
- Electrochemistry Extra Questions
- General Principles And Processes Of Isolation Of Elements Extra Questions
- Haloalkanes And Haloarenes Extra Questions
- Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Extra Questions
- Polymers Extra Questions
- Solutions Extra Questions
- Surface Chemistry Extra Questions
- The D-And F-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The P-Block Elements Extra Questions