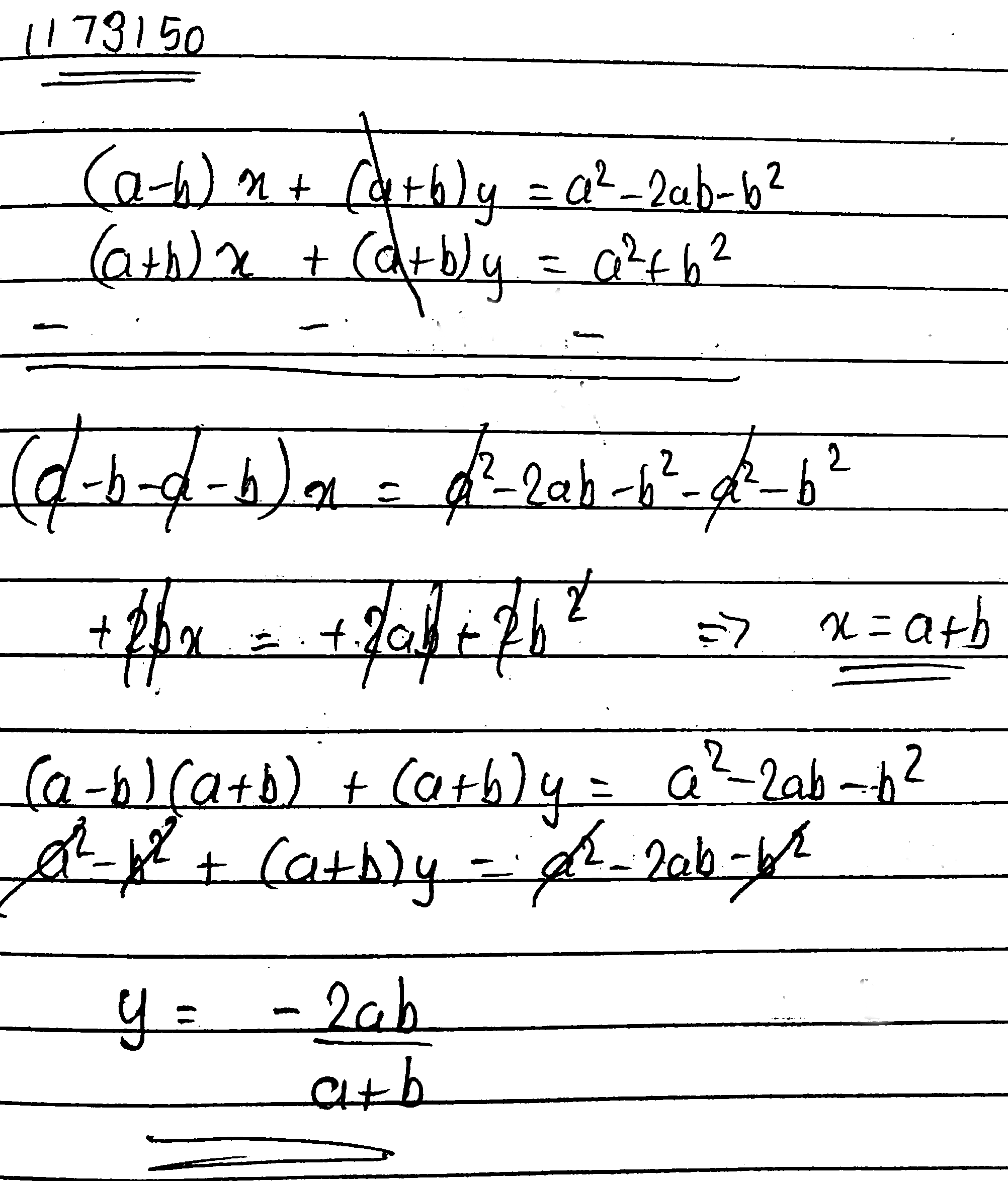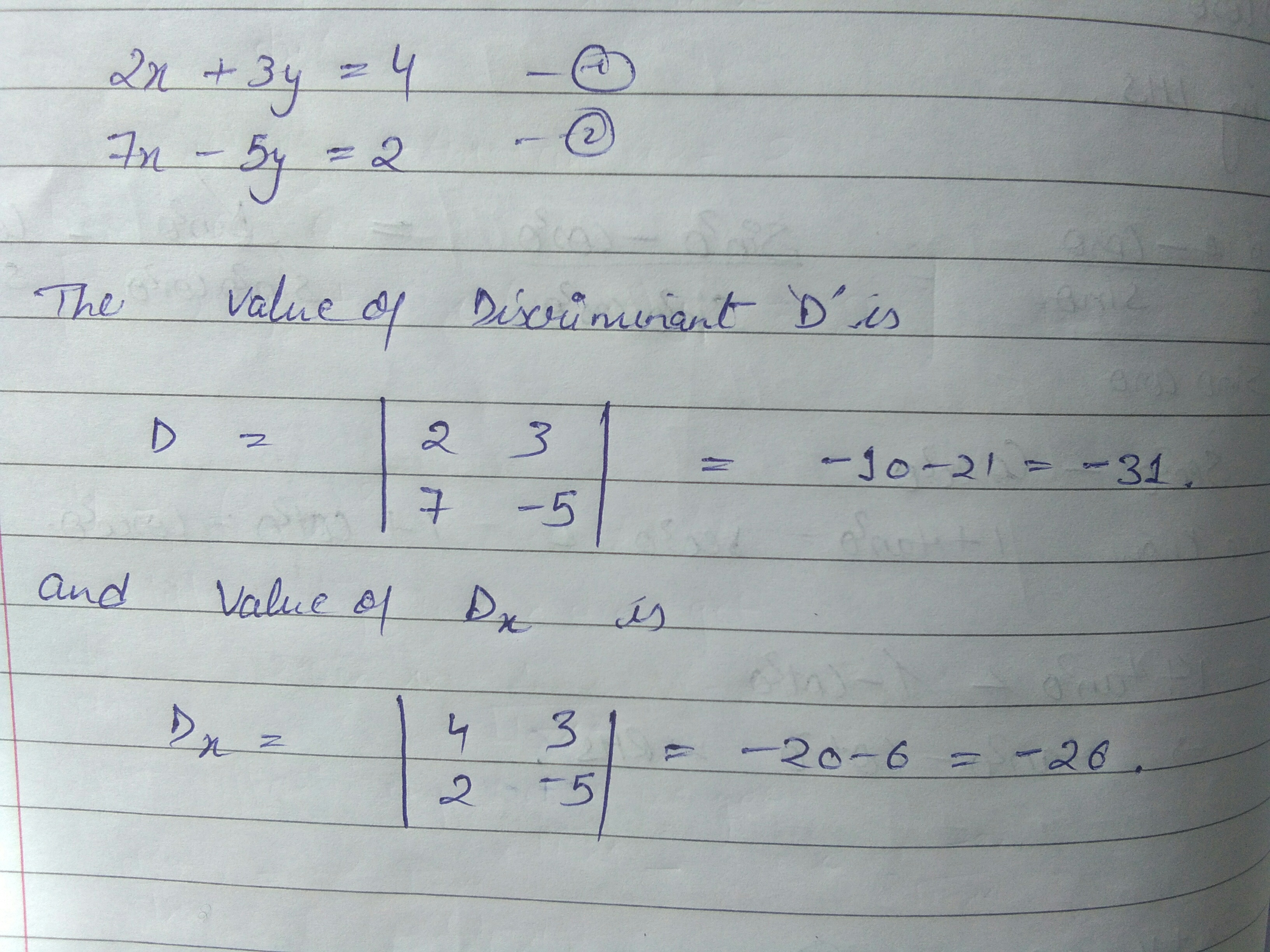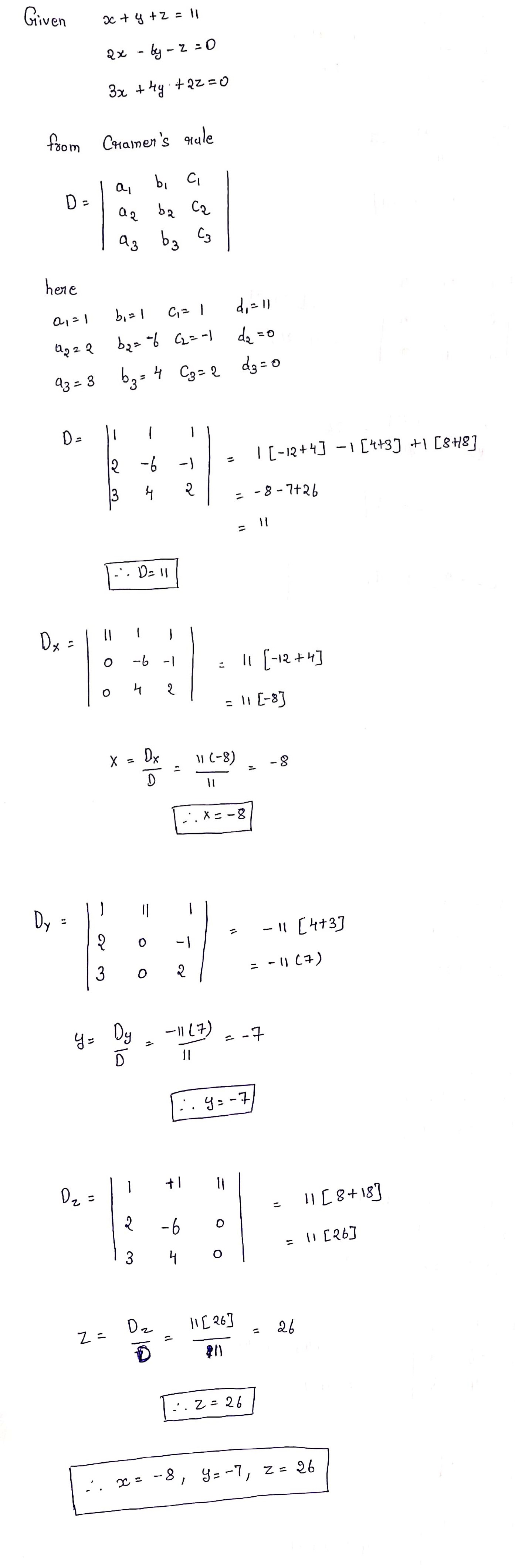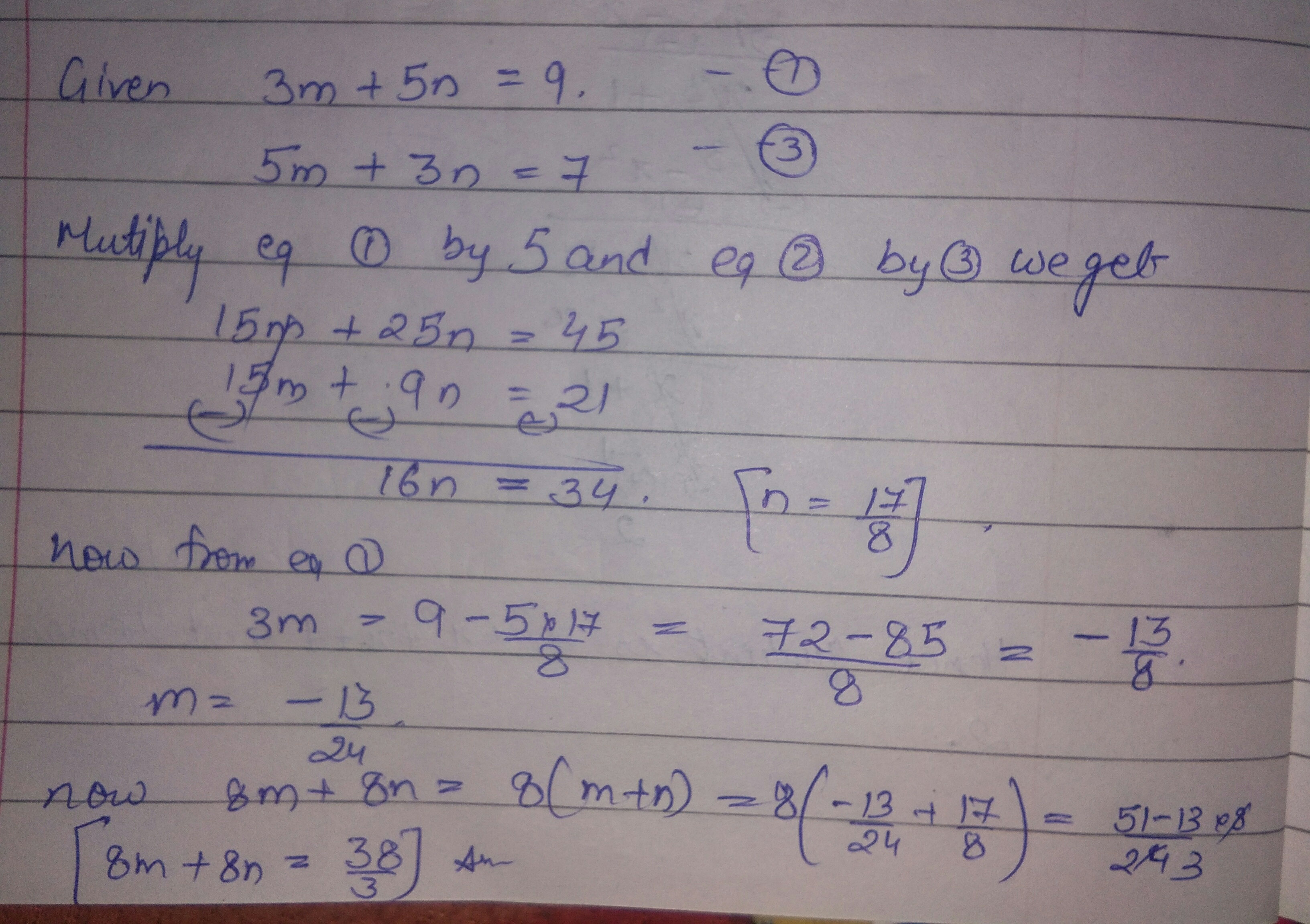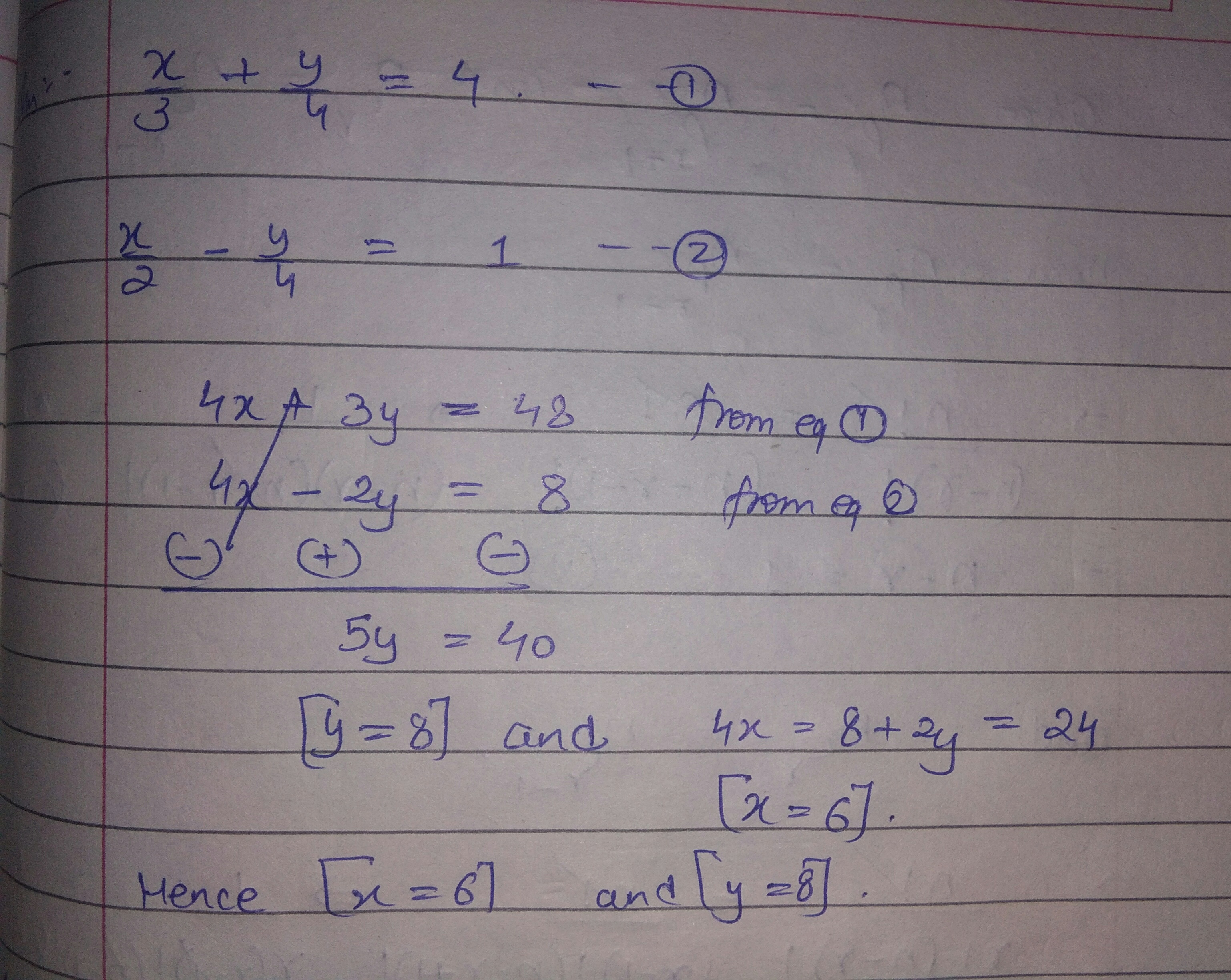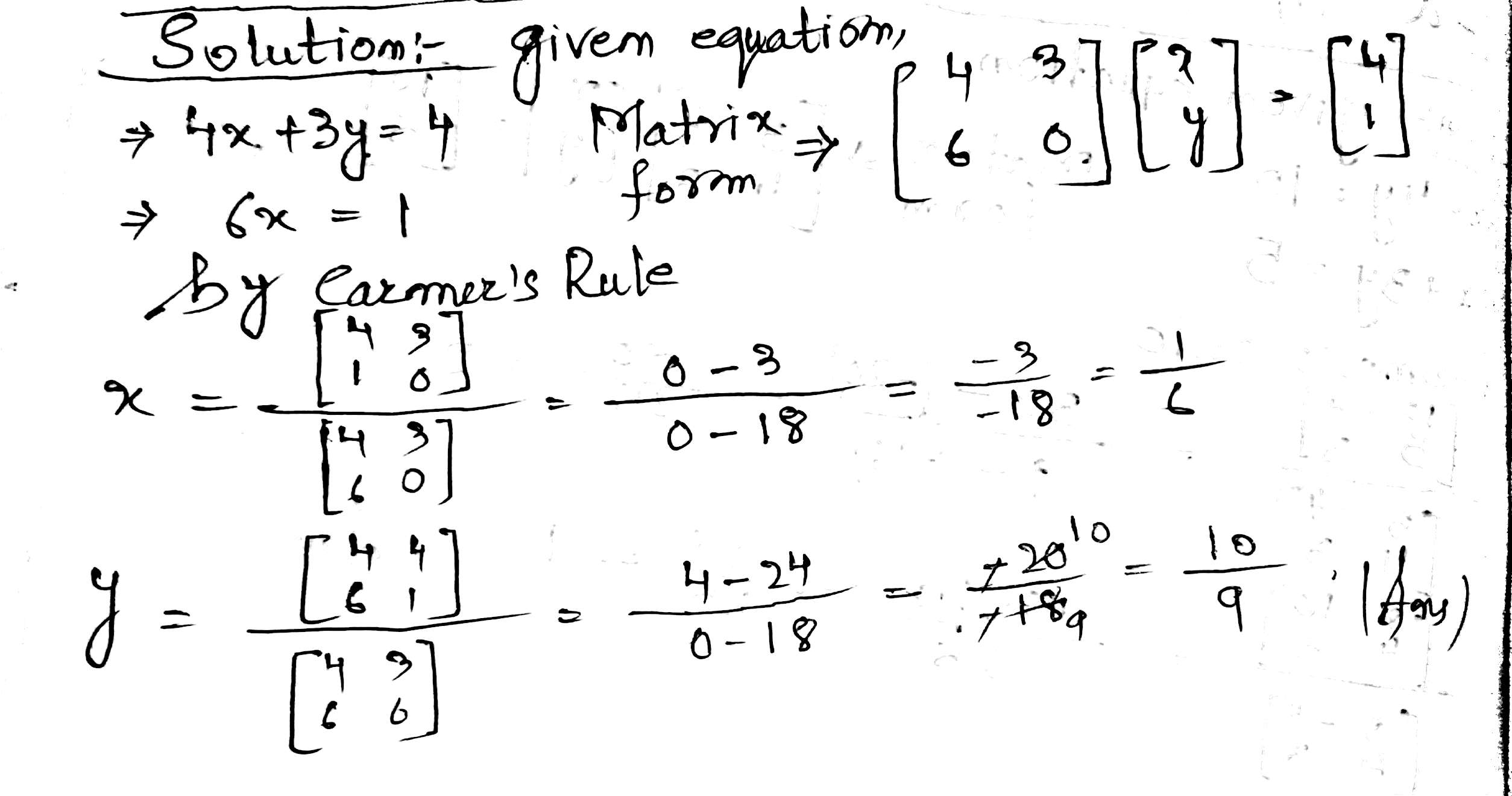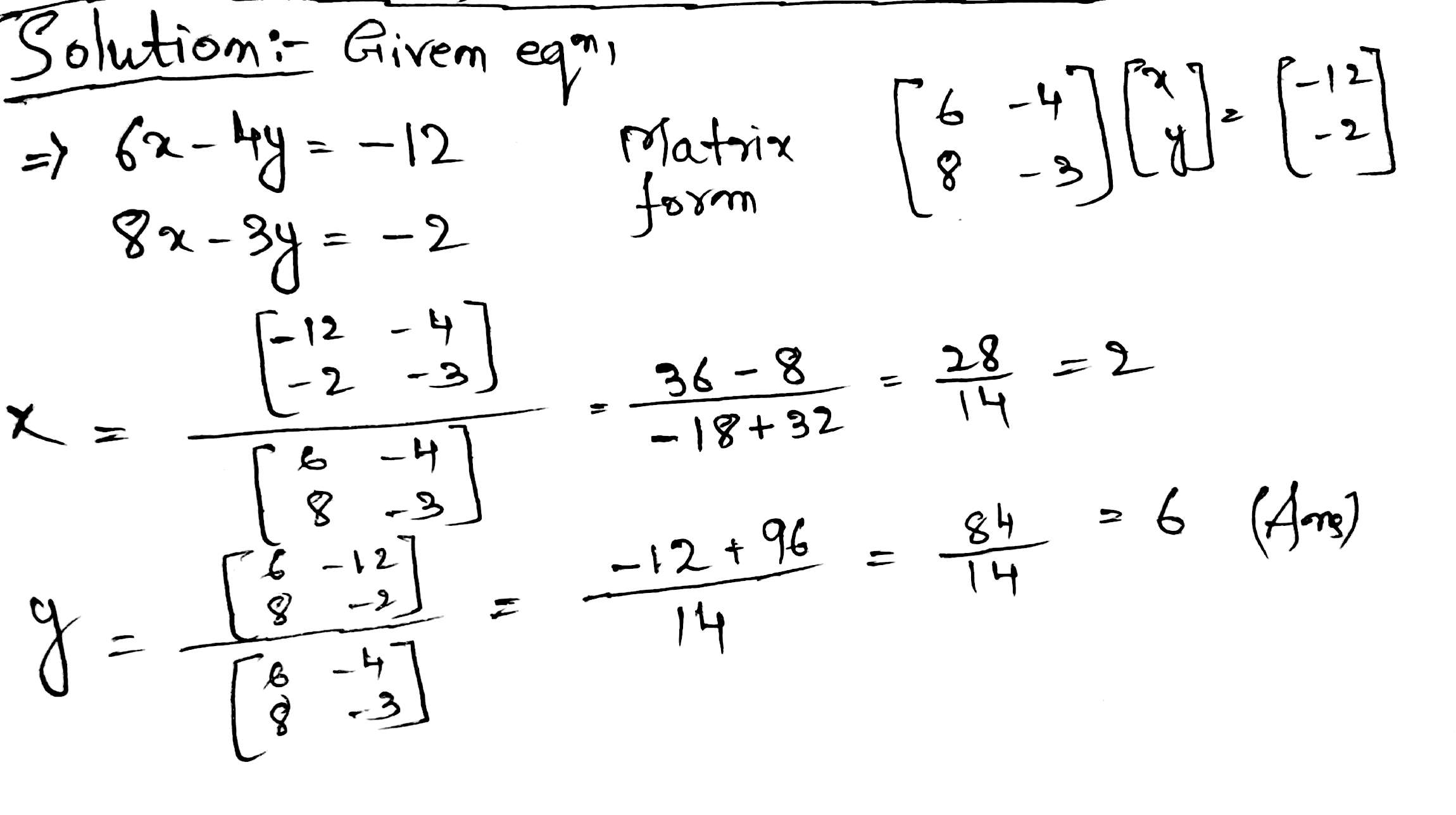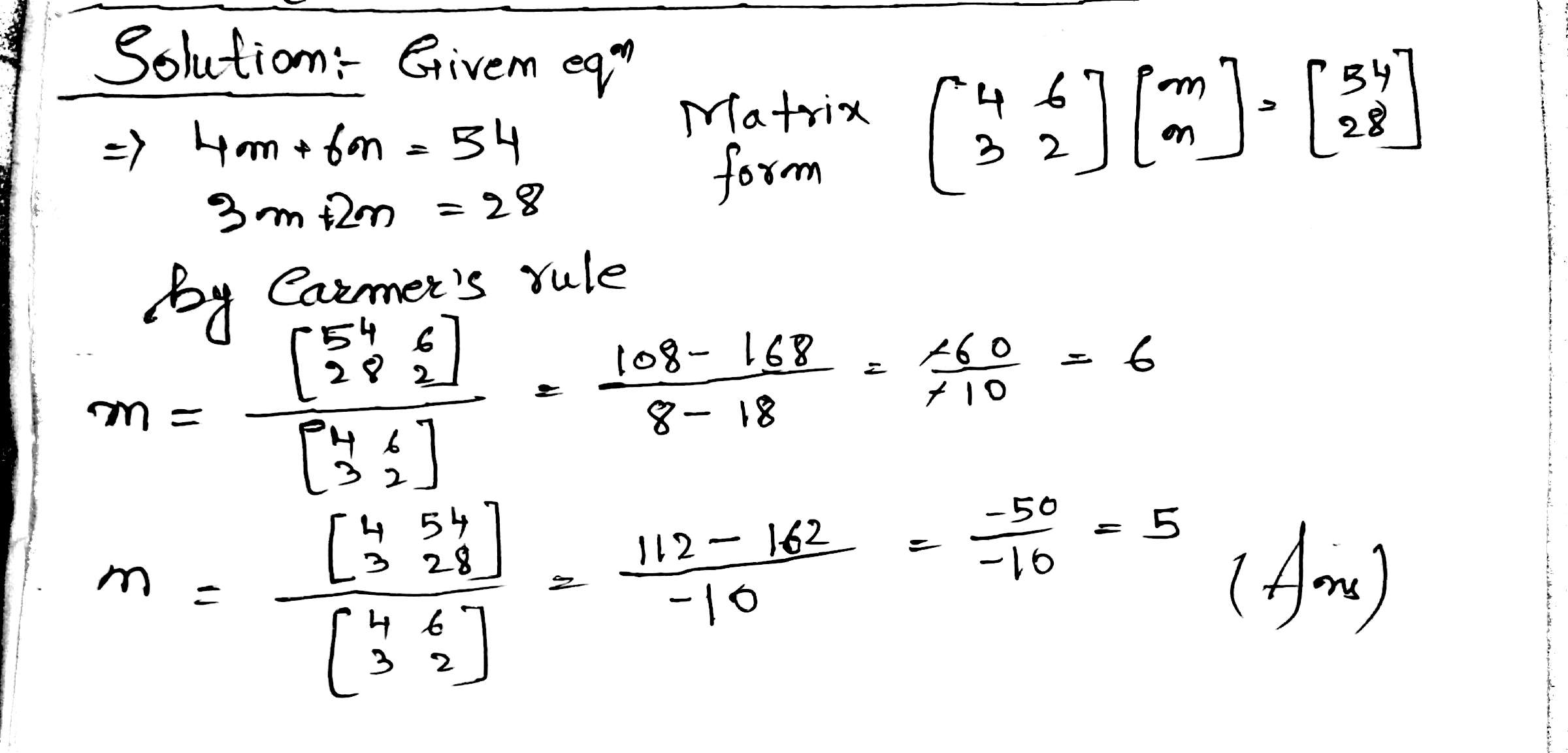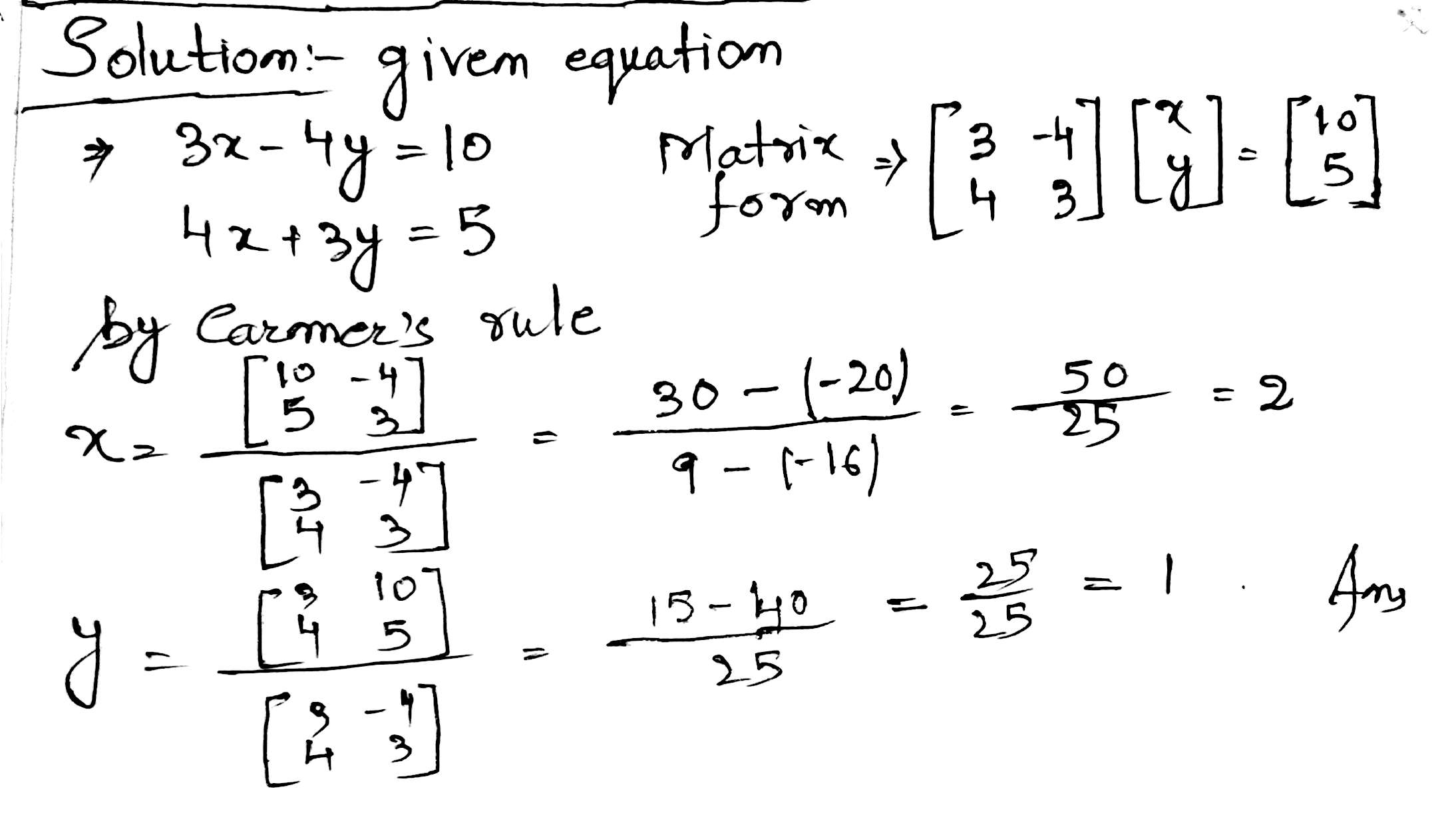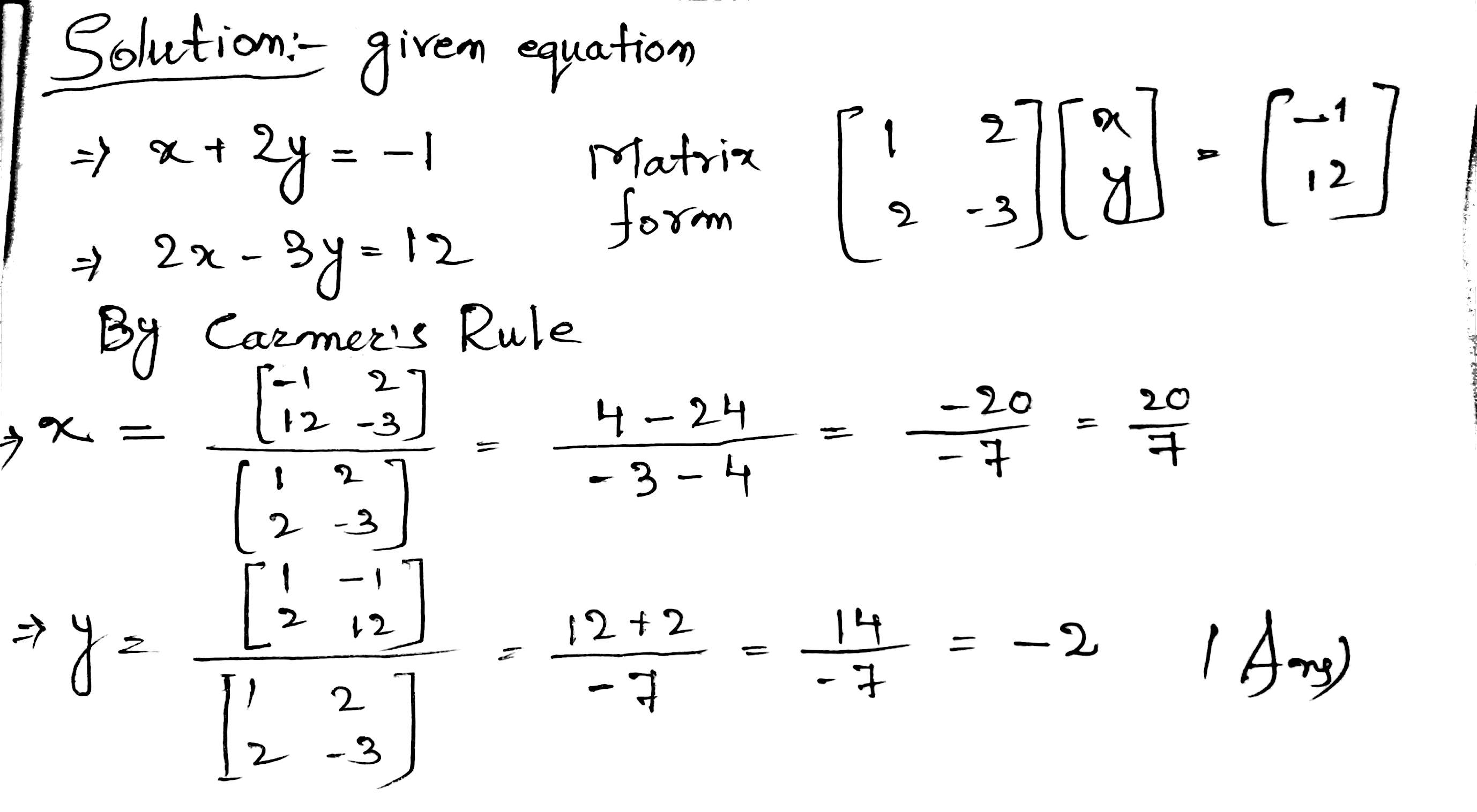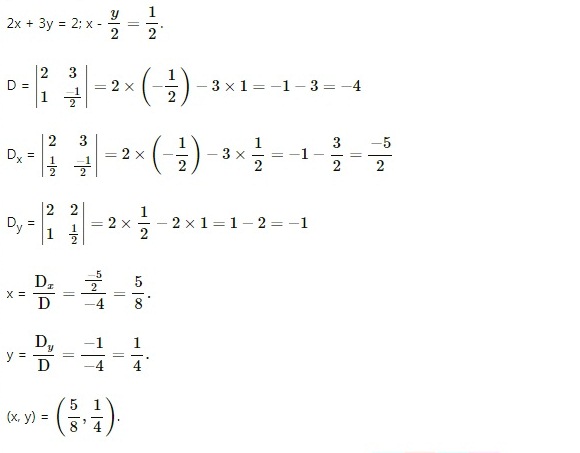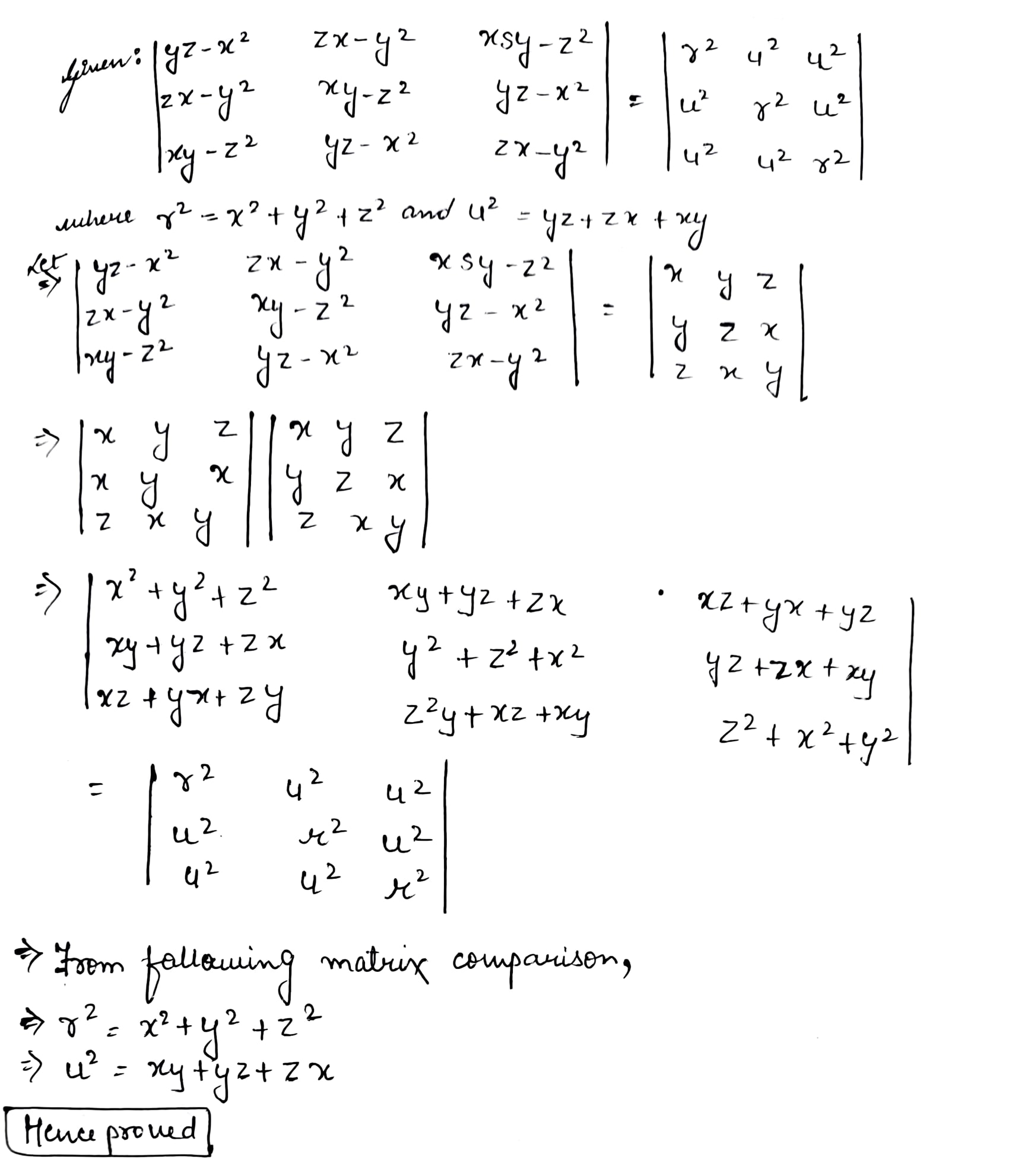Determinants - Class 12 Commerce Applied Mathematics - Extra Questions
If $$D_x\, =\, -18$$ and $$ D =\, 3$$ are the values of the determinants for certain simultaneous equations in $$x$$ and $$y$$, Find $$-x$$.
If the value of determinants $$\begin{vmatrix} x& -5\\ 3 & 4\end{vmatrix}$$ is $$31$$, then find the value of $$x$$
Find the value of the determinant: $$\begin{vmatrix} 4& -2\\ 3 & 1\end{vmatrix}$$
If $$D=7,{D}_{x}=35$$ and $${D}_{y}=42$$ are the values of the determinants for certain simultaneous equations in $$x$$ and $$y$$, then find the values of $$x$$ and $$y$$.
Find the value of the following determinant
$$\begin{vmatrix}7 & 2\\ 5 &4 \end{vmatrix}$$
solve the following simultaneous equations by using Cramer's rule:
$$x+y=7,x-y=5$$
If $${ D }_{ x }=18,{ D }_{ y }=15$$ and $$D=3$$ are the values of the determinants for certain simultaneous equations in $$x$$ and $$y$$, then find the values of $$x$$ and $$y$$.
Find the value of the following determinant $$\begin{vmatrix} 4 & 3\\2 & 7\end{vmatrix}$$.
Find the value of following determinant
$$\begin{vmatrix} 5& 2\\ 7 & 4 \end{vmatrix}$$
If $${D}_{x}=30,{D}_{y}=42$$ and $$D=6$$ are the values of the determinants for certain simultaneous equations in $$x$$ and $$y$$, then find the values of $$x$$ and $$y$$.
Solve the following simultaneous equations by using Cramer's rule:
$$x - 2y = -18$$
$$2x - y = 9$$
Find $$D_{x}$$ for the following simultaneous equations: $$3x + 4y = 8, x - 2y = 5$$
If $${ D }_{ x }=24,{ D }_{ y }=32$$ are the values of the determinants for certain simultaneous equations in $$x$$ and $$y$$, then find the values of $$x$$ and $$y$$
Solve the following equations by Cramer's rule:
$$3x+y+z=2,2x-4y+3z=-1,4x+y-3z=-11\quad $$
Find the ratios of $$x : y : z$$ from the equations
$$7x = 4y + 8z, 3z = 12x + 11y$$.
If $$A=\left[ \begin{matrix} 1 & -1 & 2 \\ 3 & 0 & -2 \\ 1 & 0 & 3 \end{matrix} \right] $$ verify that $$A(adj\ A)=\left| A \right| I$$.
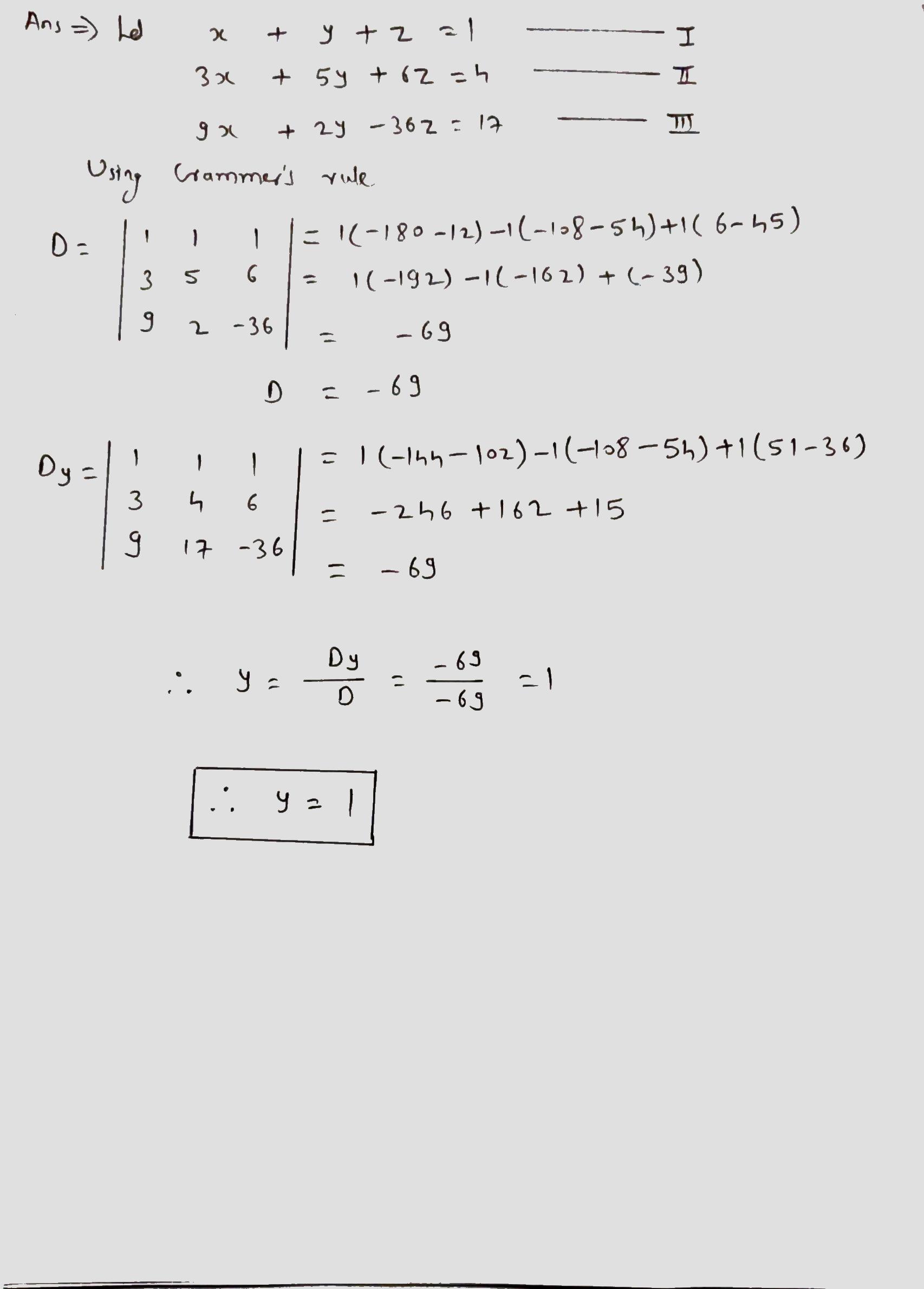
If$$x + y + z = 1$$
$$3x + 5y + 6z = 4$$
$$9x + 2y - 36z = 17$$Then find $$y$$
Solve the equation $$\dfrac{x}{a}\, + \,\dfrac{y}{b}\, = \,2\,,\,ax\, - \,by\, = \,{a^2} - \,{b^2}$$
Solve the system of linear equation $$ 3x-2y=13$$ and $$ 4x+y=21$$
Solve the following simu1taneous equations.
(1) $$5x-3y=8;$$ $$3x+y=2$$
Solve: (i)$$4x+5y-62=0$$
(ii)$$3x+2y-36=0$$
Solve.
$$3x-2y=1$$ and $$2x+y=3$$.
Solve the given pair of linear equations:
$$(a-b)x+(a+b)y={a}^{2}-2ab-{b}^{2}$$
$$(a+b)(x+y)={a}^{2}+{b}^{2}$$
Find co-factors of elements of the matrices $$\begin {bmatrix} -1 & 2 \\ -3 & 4\end {bmatrix}$$
Solve the following equation by cramer's method:
$$7x+3y=15 , 12y-5x=39$$
Find the value of: $$\begin{vmatrix} -3 & -5 \\ -2 & -1 \end{vmatrix}$$
Find $${D}_{x}$$ and $$D$$ for the equation $$2x+3y=4;7x-5y=2$$
Solve the following simultaneous equations. 2x - y = 5 ; 3x + 2y = 11
Solve the following simultaneous equations. x + y = 11 ; 2x - 3 y =7
Solve by Cramer's rule
$$x+y+z=6$$
$$x-y+z=2$$
$$3x+2y-4z=-5$$. The value of x is
If $$D_y\, =\, -15$$ and $$D\, =\, -5$$ are the values of the determinants for certain simultaneous equations in $$x$$ and $$y$$, find $$y$$.
If $$ \displaystyle a_{1}f_{1}\left ( x \right )+a_{2}f_{2}\left ( x \right )+a_{3}f_{3}\left ( x \right )=0 $$ where $$a_1,a_2,a_3$$ are constants (not all zero) and $$ \displaystyle f_{1},f_{2},f_{3} $$ are twice differentiable functions.Then $$ \displaystyle D=\begin{vmatrix}f_{1}\left ( x \right ) &f_{2}\left ( x \right ) & f_{3}\left ( x \right )\\ Df_{1}\left ( x \right ) & Df_{2}\left ( x \right ) & Df_{3}\left ( x \right )\\ D^{2}f_{1} \left ( x \right )& D^{2}f_{2}\left ( x \right ) & D^{2}f_{3}\left ( x \right )\end{vmatrix} $$ is equal to $$ \displaystyle Df_{1}\left ( x \right )=\frac{d}{dx}f_{1} $$
If the polynomial $$\displaystyle f\left ( x \right )=2x^{3}+mx^{2}+nx-14$$ has $$\displaystyle \left ( x-1 \right )$$ and $$\displaystyle \left ( x+2 \right )$$ as its factors find the value of $$\displaystyle m\times n$$
For what value of $$k$$ will the following pair of linear equations have no solution?
$$2x + 3y = 1 $$ and $$(3k - 1)x +(1 - 2k) y = 2k + 3$$
If $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 3 & 1 \\ -1 & 2 \end{bmatrix}$$, show that $${ A }^{ 2 }-5A+7I=O$$. Hence find $${ A }^{ -1 }$$
If $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 2 & -1 & 1 \\ -1 & 2 & -1 \\ 1 & -1 & 2 \end{bmatrix}$$, verify that $${ A }^{ 3 }-{ 6A }^{ 2 }+9A-4I=0$$. Hence find $$ { A }^{ -1 }$$
For the matrix $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 & 1 \\ 1 & 2 & -3 \\ 2 & -1 & 3 \end{bmatrix}$$, show that $${ A }^{ 3 }-{ 6A }^{ 2 }+5A+11I=0$$. Hence find $${ A }^{ -1 }$$
Given, $$-3x + 4y = 20$$ and $$6x +3y =15$$
If $$(x, y)$$ is the solution to the system of equations above, what is the value of $$x$$ ?
Find '$$m+n$$' for the following simultaneous equations:
$$3m+4n=7$$
and $$4m+3n=14$$
Solve the following simultaneous equations by using Cramer's Rule
$$3x + y = 1$$,
$$2x - 11 y = 3$$
If $$A=\begin{bmatrix} \cos^2\theta & \cos\theta \sin\theta\\ \cos\theta\sin\theta & \sin^2\theta\end{bmatrix}$$ and $$B=\begin{bmatrix}\cos^2\Phi & \cos\Phi \sin\Phi\\ \cos\Phi \sin\Phi & \sin^2\Phi\end{bmatrix}$$, show that AB is a zero matrix if $$\theta$$ and $$\Phi$$ differ by an odd multiple of $$\displaystyle\frac{\pi}{2}$$.
Solve the following simultaneous equations using Cramer's rule.
$$3x-2y=3$$;
$$2x+y=16$$.
Solve $$x + y + z = 11\\
2x - 6y - z = 0\\
3x + 4y + 2z = 0$$.
Solve the equations
$$x + 2y + 3z = 14$$
$$2x - y + 5z = 15$$
$$3x - 2y - 4z = -13$$
Find x and y using Cramer's Rule if :$$\dfrac{1}{2^x}+\dfrac{2}{3^y}=10,\dfrac{3}{2^x}-\dfrac{5}{3^y}=-3$$ ?
Find x and y using Cramer's Rule,if $$\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{2}{y}=6,\dfrac{3}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=8$$ ?
If $$A = \left[ \begin{array} { c c c } { 5 } & { 8 } & { 1 } \\ { 0 } & { 2 } & { 1 } \\ { 4 } & { 3 } & { - 1 } \end{array} \right] , B = \left[ \begin{array} { c } { 2 } \\ { - 1 } \\ { 3 } \end{array} \right]$$ and $$A X = B$$ then find $$X$$
Find $$ A^2$$ where A is given $$A= \begin {bmatrix}1 & 2 & 3 \\ 1 & 2 & 3\\ -1 & 2 & -3 \end{bmatrix}$$
Solve $$\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}1 & 1 & 1\\a & b & c\\{{a^3}} & {{b^3}} & {{c^3}}\end{array}} \right| = \left( {a - b} \right)\left( {b - c} \right)\left( {c - a} \right)\left( {a + b + c} \right)$$
For what value of k , the following pair of linear equations has infinite number of solutions :
$$5x + 2y = k ; 10x + 4y = 3$$
If 3m +5n =9 and 5m +3n =7 then find the value of 8m +8n.
Solve the following
$$\frac{x}{3}+\frac{y}{4}=4, \frac{x}{2}-\frac{y}{4}=1$$
Solve the following simultaneous equation using cramer's rule
$$4x+3y-4=0: 6x=1$$
Solve the following simultaneous equation using cramer's rule
$$6x-4y=-12: 8x-3y=-2$$
Solve the following simultaneous equation using cramer's rule
$$4m+6n=54 : 3m +2n =28$$
Solve the simultaneous equations.
$$\dfrac { x } { 3 } + \dfrac { y } { 4 } = 4 ; \quad \dfrac { x } { 2 } - \dfrac { y } { 4 } = 1$$
Solve the following simultaneous equations using Cramer's rule :
$$3x+y=7; \ 2x-11y=3.$$
Solve the following simultaneous equation using cramer's rule.
$$3x-4y=10:4x+3y=5$$
Solve the following simultaneous equation using cramer's rule
$$x+2y=-1: 2x-3y=12$$
Solve the following simultaneous equation using cramer's rule
2x + 3y = 2: x-$$\frac { y }{ 2 } =\frac{1}{2}$$
If $$A = \begin{bmatrix} 3& 2\\ 2 & 1\end{bmatrix}$$, verify that $$A^{2} - 4A - I = O$$, and hence find $$A^{-1}$$.
Show that the matrix $$A =\begin{bmatrix} -8& 5\\ 2 & 4\end{bmatrix}$$ satisifies the equation $$A^{2} + 4A - 42I = 0$$ and hence find $$A^{-1}$$.
If $$A = \begin{bmatrix} -1& -1\\ 2 & -2\end{bmatrix}$$, show that $$A^{2} + 3A + 4I_{2} = O$$ and hence find $$A^{-1}$$.
If $$A = \begin{bmatrix} 3& -2\\ 4 & -2\end{bmatrix}$$, find the value of $$\lambda$$ so that $$A^{2} = \lambda A - 2I$$. Hence, find $$A^{-1}$$.
Show that the $$A = \begin{bmatrix}1 & 0 & -2\\ -2 & -1 & 2\\ 3 & 4 & 1\end{bmatrix}$$ satisfied the equation $$A^{3} - A^{2} - 3A - I = O$$, and hence find $$A^{-1}$$.
Solve the following equation:
$$\begin{vmatrix} x & 3 & 7 \\ 2 & x & 2 \\ 7 & 6 & x \end{vmatrix}=0$$
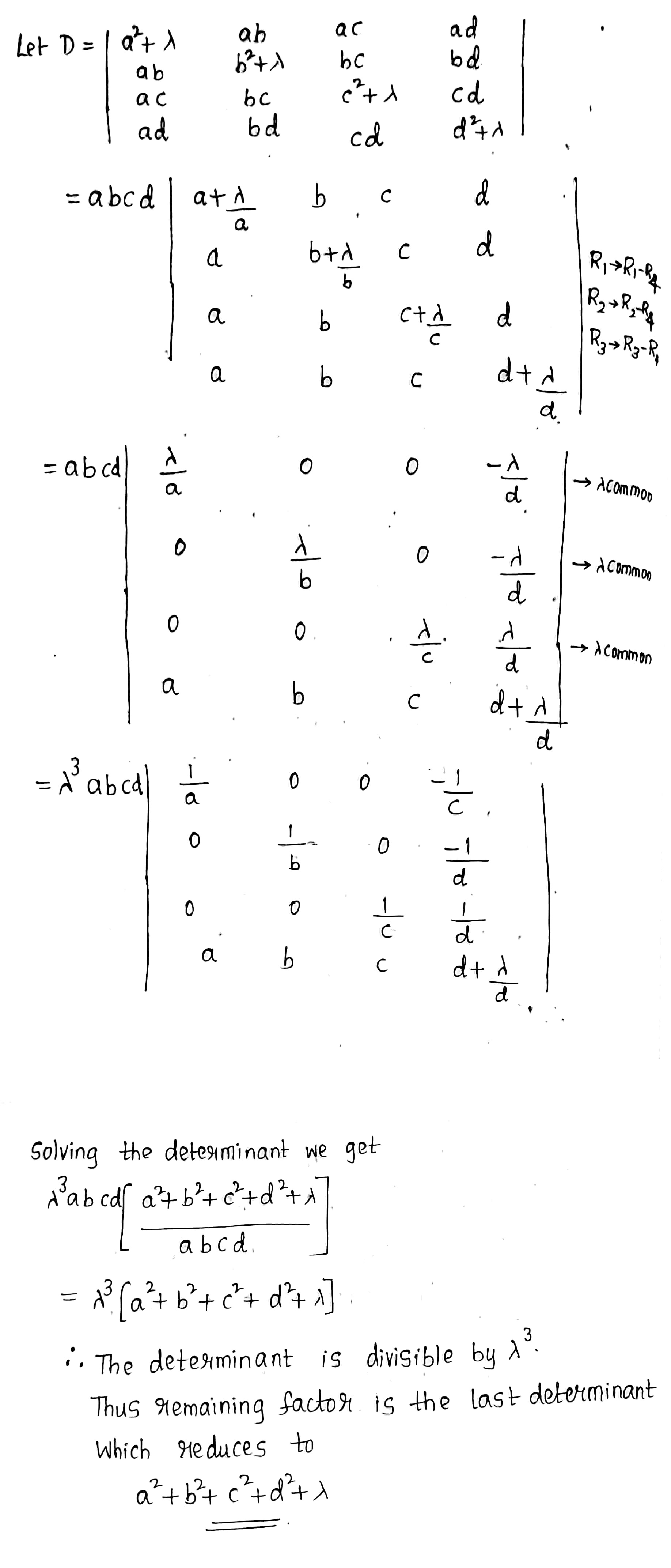
Show that $$\begin{vmatrix} a^2+\lambda & ab & ac & ad \\ ab & b^2+\lambda & bc & bd \\ ac & bc & c^2+\lambda & cd \\ ad & bd & cd & d^2+\lambda \end{vmatrix}$$
is divisible by $$\lambda^{3}$$ and find the other factor.
Absolute value of the sum of roots of the equation
$$\begin{vmatrix} x+2 & 2x+3 & 3x+4 \\ 2x+3 & 3x+4 & 4x+5 \\ 3x+5 & 5x+8 & 10x+17 \end{vmatrix}=0$$ is
$$\begin{vmatrix} { x }^{ n } & { x }^{ n+2 } & { x }^{ n+4 } \\ { y }^{ n } & { y }^{ n+2 } & { y }^{ n+4 } \\ { z }^{ n } & { z }^{ n+2 } & { z }^{ n+4 } \end{vmatrix}=\left( \cfrac { 1 }{ { y }^{ 2 } } -\cfrac { 1 }{ { x }^{ 2 } } \right) \left( \cfrac { 1 }{ { z }^{ 2 } } -\cfrac { 1 }{ { y }^{ 2 } } \right) \left( \cfrac { 1 }{ { x }^{ 2 } } -\cfrac { 1 }{ { z }^{ 2 } } \right) $$ then $$n$$ is _____.
If $$ x=-4 $$ is a root of $$ \Delta = \left| \begin{matrix} x & 2 & 3 \\ 1 & x & 1 \\ 3 & 2 & x \end{matrix} \right| = 0 $$ then find the other two roots.
If $$ x = - 9 $$ is root of $$ \left| \begin{matrix} x & 3 & 7 \\ 2 & x & 2 \\ 7 & 6 & x \end{matrix} \right| =0 $$ then other two roots are _________
If $$ f(x) = \left| \begin{matrix} (1+x)^{17}& (1+x)^{19} &(1+x)^{23} \\ (1+x)^{23} & (1+x)^{29} & (1+x)^{34} \\ (1+x)^{41} & (1+x)^{43} & (1+x)^{47} \end{matrix} \right| = A +Bx +Cx^2 + ........then A $$ = ___________
Solve the following simultaneous equation.
$$3a + 5b = 26; a + 5b = 22$$
Solve the following simultaneous equation.
$$x + 7y = 10; 3x - 2y = 7$$
Solve the following simultaneous equation:
$$5m - 3n = 19; m - 6n = -7$$
Solve the following simultaneous equation:
$$5x + 2y = -3; x + 5y = 4$$
Solve the following simultaneous equations.
$$\frac{7x - 2y}{xy} = 5 ;\frac{8x + 7y}{xy} = 15$$
Solve the following simultaneous equation.
$$49x - 57y = 172; 57x - 49y = 252$$
Solve the following simultaneous equation.
$$\dfrac{1}{3}x + y = \dfrac{10}{3}; 2x + \dfrac{1}{4}y = \dfrac{11}{4}$$
Solve the following equation by Cramer's method.
$$3x - 2y = \frac{5}{2}; \frac{1}{3}x + 3y = - \frac{4}{3}$$
Solve the following simultaneous equations
$$\frac{148}{x} + \frac{231}{y} = \frac{527}{xy}; \frac{231}{x} + \frac{148}{y} = \frac {610}{xy}$$
Solve the following equations by Cramer's method.
4m - 2n = -4; 4m + 3n = 16
Solve the following simultaneous equations.
$$\frac{1}{2(3x + 4y)} + \frac{1}{5(2x - 3y)} = \frac{1}{4}; \frac{5}{(3x + 4y)} - \frac{2}{(2x - 3y)} = -\frac{3}{2}$$
Solve the following equations by Cramer's methd.
$$6x - 3y = -10; 3x + 5y - 8 = 0$$
Solve the following
simultaneous equation using Cramer's rule.
$$6x - 4y = -12$$
$$8x - 3y = -2$$
Solve the following simultaneous equations.
2x + y = - 2; 3x - y =7
Solve the following sets of simultaneous equations.
2y -x =0; 10x + 15y = 105
Solve the following simultaneous equations. x -2 y = -1 ; 2x - y =7
Solve the following simultaneous equations. x - 2y = - 2 ; x +2y =10
If $$a,b,c$$ are real, find the factors of the determination.
$$\Delta =\begin{vmatrix} b+c & c+a & a+b \\ c+a & a+b & b+c \\ a+b & b+c & c+a \end{vmatrix}$$
Solve the following system of equation by Cramer's rule:
$$2x-7y-13=0, 5x+6y-9=0$$
Use Cramer's rule to solve the following system of equations:
$$2x-y=17$$
$$3x+5y=6$$
Solve the following system of equation by Cramer's rule:
$$2x+3y=9, 3x-2y=7$$
Use Cramer's rule to solve the following system of equations:
$$3x+ay=4$$
$$2x+ay=2, a \ne 0$$
A determinant of second order is made with the elements 0 andFind the number of determinants with non-negative values.
Let $$A =\begin{bmatrix} 2&3 \\-1 &5 \end{bmatrix}$$. If $$A^{-1}=xA+yI$$, find $$x + 2y$$.
If $$A =\begin{bmatrix} 1&0 &0 \\0 &1 &1 \\0 &-2 &4 \end{bmatrix}$$, $$I=\begin{bmatrix} 1&0 &0 \\0 &1 &0 \\0 &0 &1 \end{bmatrix}$$ and
$$\displaystyle A^{-1}=\frac{1}{6}(A^2+\alpha A+\beta I)$$, find $$\beta/11 $$
The digit in the tens place of a two-digit number is three times that in the units place. If the digits are reversed, the new number will be $$36$$ less than the original number. Find the original number. Check your solution.
Find $$x$$ and $$y$$ using Cramer's Rule if :
$$\dfrac{1}{2x}+\dfrac{2}{3y}=10,\dfrac{3}{2x}-\dfrac{5}{3y}=-3$$
Prove that one root of the equation is x=2 and hence find the remaining roots $$\left| \begin{matrix} x \\ 2 \\ -3 \end{matrix}\begin{matrix} -6 \\ -3x \\ 2x \end{matrix}\begin{matrix} -1 \\ x-3 \\ x+2 \end{matrix} \right| =0$$
If S the set of distinct values of 'b' for which the following system of linear equations
x + y + z = 1
x + ay + z = 1
ax + by + z = 1
Use cramer's rule and solve $$3x+4y+5z=18$$$$2x-y+8z=13$$$$5x-2y+7z=20$$
Solve the following simultaneous equations using corner's rule.
(3) $$x+2y=-1;2x-3y=12$$
The value of $$\begin{vmatrix} 2{ x }_{ 1 }{ y }_{ 1 } & { x }_{ 1 }{ y }_{ 2 }+{ x }_{ 2 }{ y }_{ 1 } & { x }_{ 1 }{ y }_{ 3 }+{ x }_{ 3 }{ y }_{ 1 } \\ { x }_{ 1 }{ y }_{ 2 }+{ x }_{ 2 }{ y }_{ 1 } & 2{ x }_{ 2 }{ y }_{ 2 } & { x }_{ 2 }{ y }_{ 3 }+{ x }_{ 3 }{ y }_{ 2 } \\ { x }_{ 1 }{ y }_{ 3 }+{ x }_{ 3 }{ y }_{ 1 } & { x }_{ 2 }{ y }_{ 3 }+{ x }_{ 3 }{ y }_{ 2 } & 2{ x }_{ 3 }{ y }_{ 3 } \end{vmatrix}$$ is
Shew that $$\begin{vmatrix} yz-x^2 & zx-y^2 & xsy-z^2 \\ zx-y^2 & xy-z^2 & yz-x^2 \\ xy-z^2 & yz-x^2 & zx-y^2 \end{vmatrix}=\begin{vmatrix} r^2 & u^2 & u^2 \\ u^2 & r^2 & u^2 \\ u^2 & u^2 & r^2 \end{vmatrix}$$
where $$r^{2}=x^{2}+y^{2}+z^{2}$$ and $$u^{2}=yz+zx+xy$$
Prove that $$ \left| \begin{matrix} bc-a^2 & ca-b^2 & ab-c^2 \\ ca-b^2 & ab-c^2 & bc-a^2 \\ ab-c^2 & bc-a^2 & ca-b^2 \end{matrix} \right| $$ i divisible by $$ ( a+b+ c) $$ and find the quotient.
Class 12 Commerce Applied Mathematics Extra Questions
- Application Of Derivatives Extra Questions
- Applications Of Integrals Extra Questions
- Definite Integrals Extra Questions
- Determinants Extra Questions
- Differential Equations Extra Questions
- Indefinite Integrals Extra Questions
- Linear Equations Extra Questions
- Matrices Extra Questions
- Probability Distribution And Its Mean And Variance Extra Questions
- Quantification And Numerical Applications Extra Questions
- Standard Probability Distributions Extra Questions