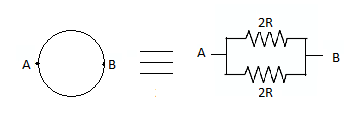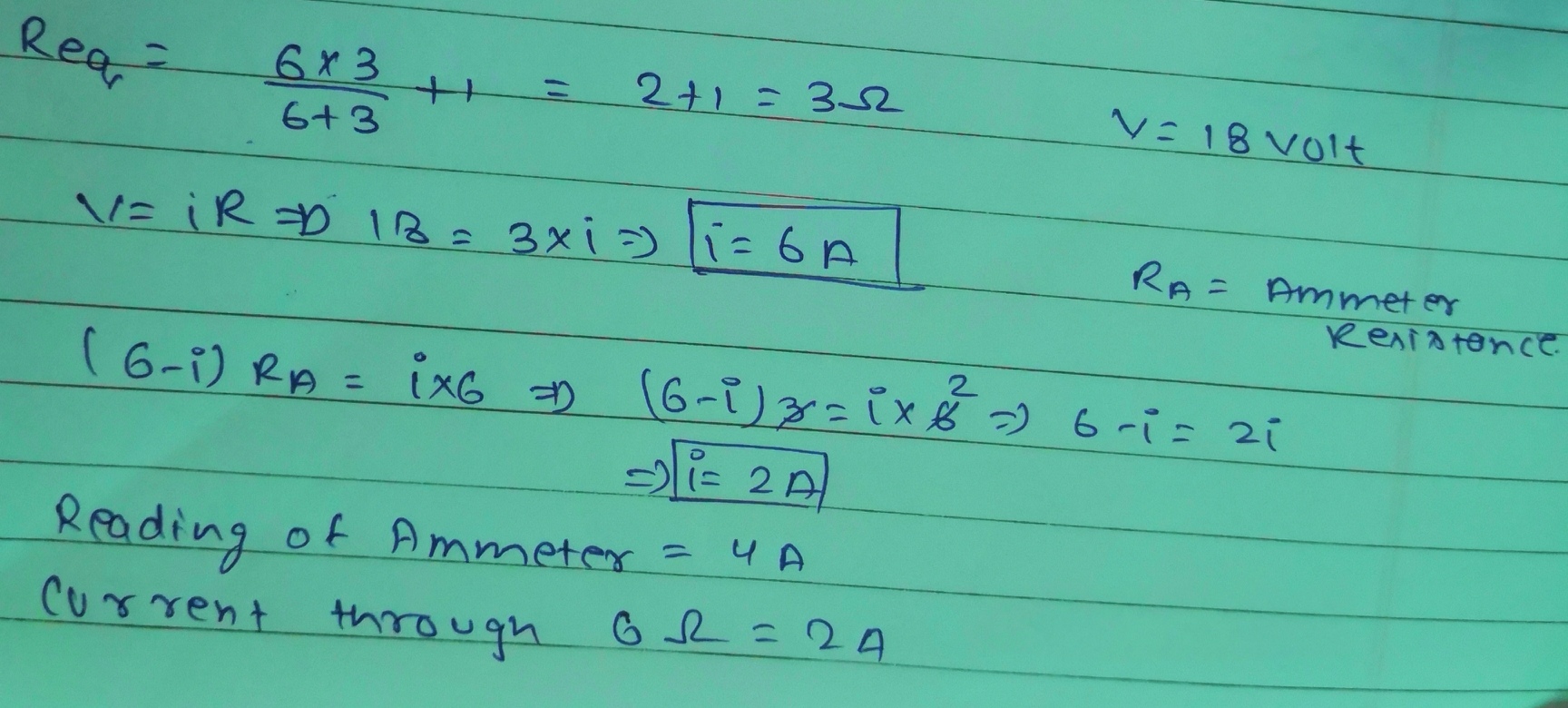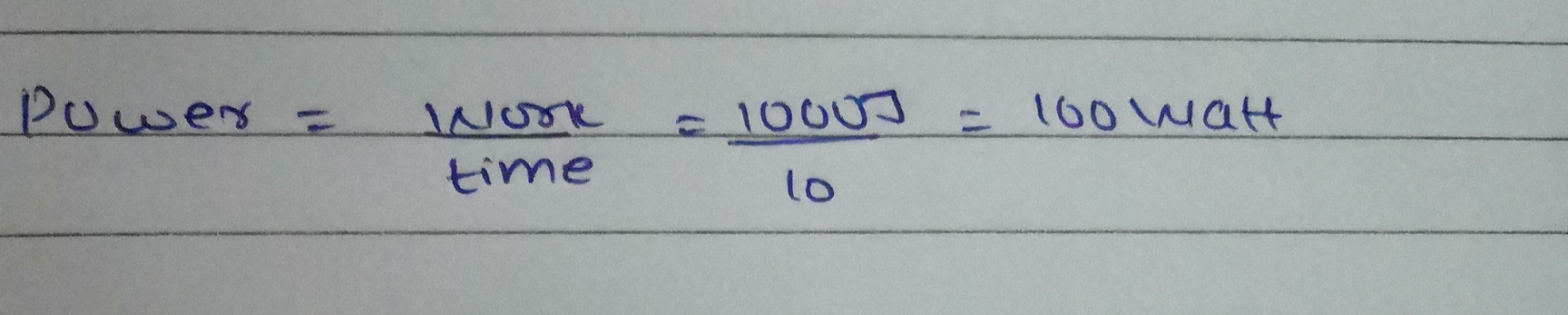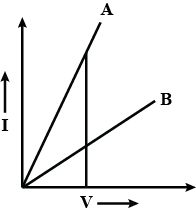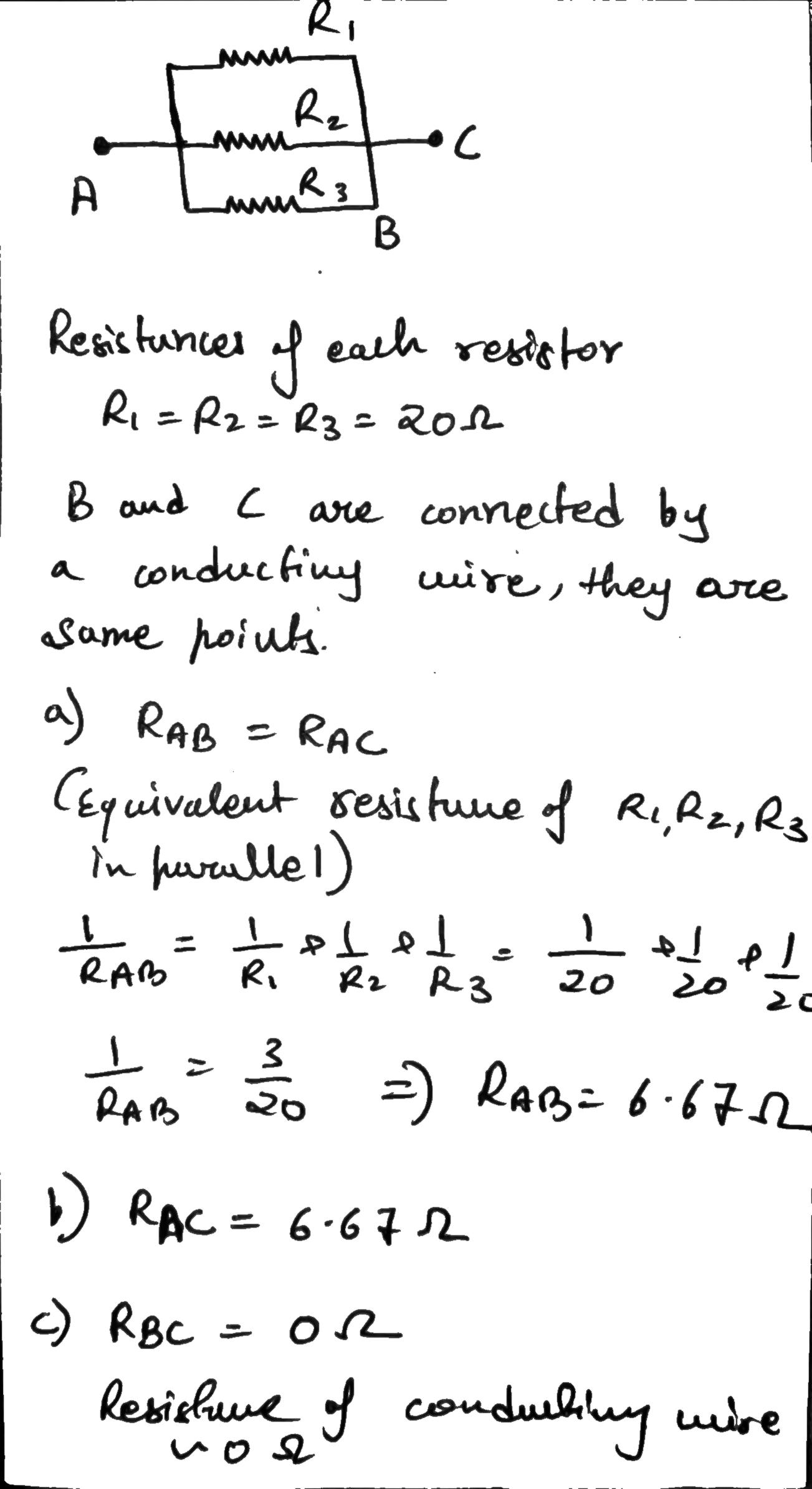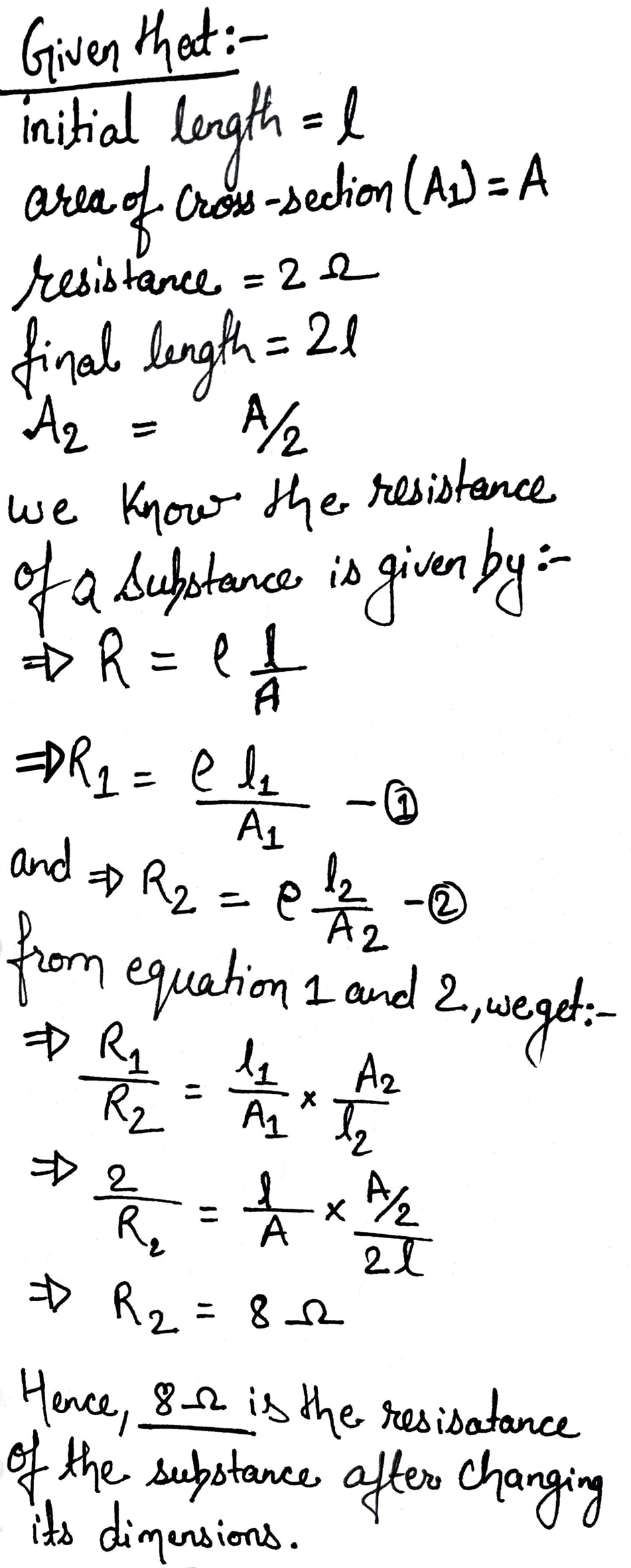Electricity - Class 10 Physics - Extra Questions
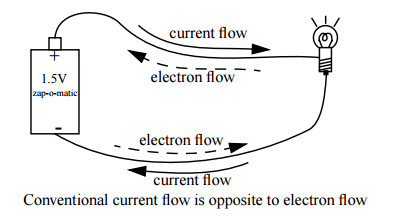
The electronic current flows opposite to the conventional current. True/False?
What are insulators? Define on the basis of atomic structure. Give four examples of insulators.
State three characteristics of a series circuit?
A heating element is marked $$210 V$$, $$630 W$$. Find the resistance of the element when connected to a $$210 V$$ dc source.
The wattage of an electric heater which draws 5 A current when connected to a 220 V supply is _____________.
...................... does not conduct electricity.
A 1000 W heater has more resistance than a 100 W bulb.
The current drawn by a bulb rated 40 W, 220 V when it is connected to a 220 V supply is ___________.
State the characteristics required in a material to be used as an effective fuse wire.
Two copper wires are of the same length, but one is thicker than the other.
Which wire will have more resistance?
Match the following:
Write the differences between static electricity and electric current.
$$(i)$$ What happens to the resistivity of semi-conductors with the increase of temperature?
$$(ii)$$ For a fuse, higher the current rating ________ is the fuse wire. (Thicker / Thinner)
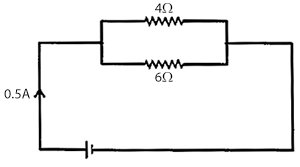
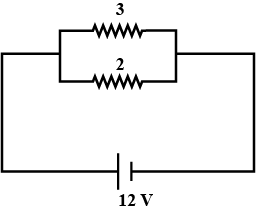
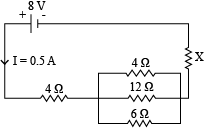
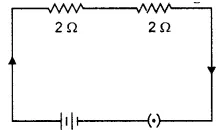
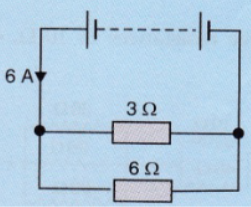
Two resistors of $$4\Omega$$ and $$6\Omega$$ are connected in parallel to a cell to draw $$0.5\ A$$ current from the cell.
Draw a labelled circuit diagram showing the above arrangement
The SI units of current is .........
(i) Which particles are responsible for current in conductors?
(ii) To which wire of a cable in a power circuit should the metal case of a geyser be connected?
(iii) To which wire should the fuse be connected ?
Write three safety measures in using electricity.
An electric bulb is rated $$200V - 100W$$. Find the resistance of the bulb.
Murugan measured the electric current. What unit should he use?
Write the S.I. unit of electric power.
Equivalent resistance when $$2$$ and $$3$$ ohm resistances are connected in series is _______.
Give two examples each of conductors and insulators of heat.
Explore and answer :
Does pure water conduct electricity? If not, what can we do to make it conduct?
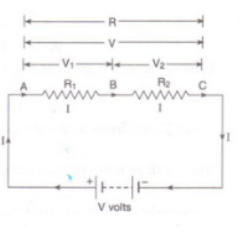
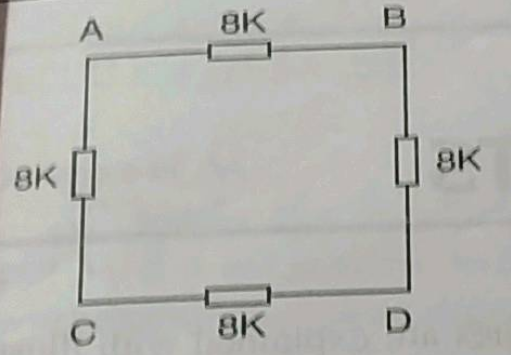
Write equivalent resistance of given circuit.
Though same current flows the wire and the filament of a bulb, yet only the filament glows.Why?
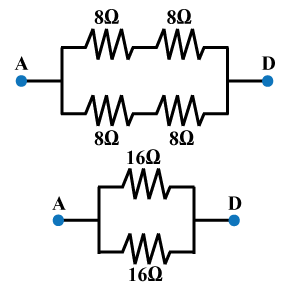
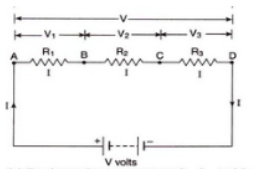
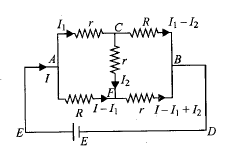
Calculate the resistance across points AD.
Define electric current. What is its $$SI$$ unit?
Power of a lamp is $$60\ W$$. Find the energy in joules consumed by it in $$1\ s$$.?
Define $$1$$ ampere.
Name and define the SI unit of current
Name and define unit for electric current.
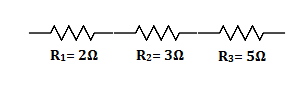
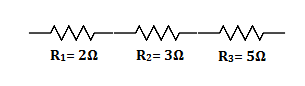
$$6\Omega,8\Omega$$ and $$10\Omega$$ resistance are connected in series. Find total resistance of the circuit.
Two resistance 3 ohm and 2 ohm are in parallel connection and a potential difference of 12 V is applied across them.Find
a) The equivalent resistance of the parallel combinations.
b) The circuit current and
c) The branch currents.
What are conductors of electricity ?
How much current flows through a $$10\ \Omega$$ resistor when it is connected to a battery of $$3\ v $$ ?
Define electric current.
Name the quantity whose unit is (i) kilowatt , and (ii) kilowatt - hour.
What is the unit of electric charge ?
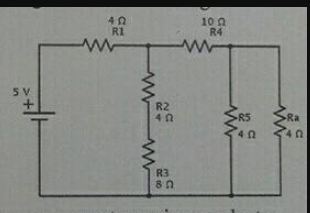
Find the total resistance in the given circuit.
By what name is the physical quantity coulomb / second called ?
What is the unit of electric current ?
What is meant by electrical resistivity of a material?
A wire of length L and resistance R is stretched so that the length is doubled and area of cross section halved. How will (i) resistance change and (ii) resistivity change.
Why does the cord of an electric heater not glow while the heating element does ?
What is the total resistance of 5 resistors each of resistance 5$$\Omega $$ connected in parallel?
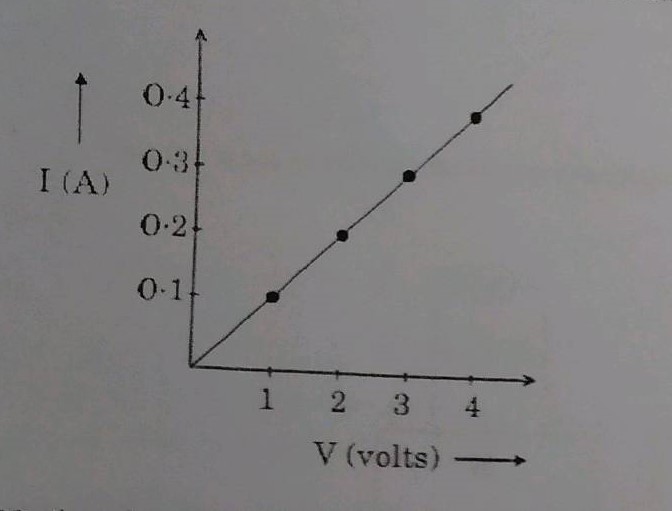
The voltage - current $$(V-I)$$ graph of a metallic conductor at two different temperature $$T_{1}$$ and $$T_{2}$$ is shown below. At which temperature is the resistance higher?

Match the entries in column A with appropriate ones from column B.
A current of 8 A flows through a 25 V car headlight bulb. Calculate the electric power (in Watts).
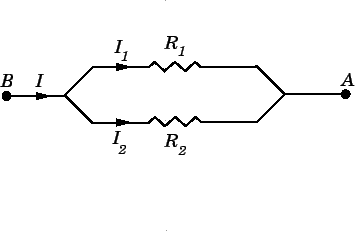
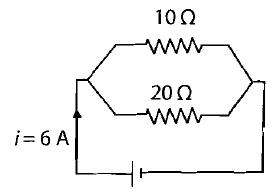
Two resistors of resistances $$10 \Omega$$ and $$20 \Omega$$ are connected in parallel. A battery supplies $$6 A$$ of current to the combination. Calculate the current in each resistor.
Explain the following.
(a) Why is the tungsten used almost exclusively for filament of electric lamps?
(b) Why are the conductors of electric heating devices, such as bread-toasters and electric irons, made of an alloy rather than a pure metal?
(c) Why is the series arrangement not used for domestic circuits?
(d) How does the resistance of a wire vary with its area of cross section?
(e) Why are copper and aluminium wires usually employed for electricity transmission?
A certain household has consumed $$250\ units$$ of energy during a month. How much energy is this in Joules?
How many $$176\ \Omega$$ resistors (in parallel) are required to carry 5A on a 220V line?
A toaster produces more heat than an electric lamp when they are connected in parallel. Which of the two has the greater resistance?
Which of the following bulbs offers more resistance?
(A) 60 W - 220 V(B) 100 W - 250 V
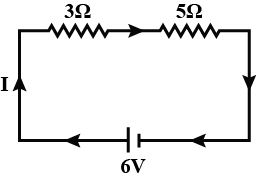
A resistance of $$3\ ohms$$ is connected in series with another resistance of $$5\ ohms$$. A potential difference of $$6$$ volts is applied across the combination. Calculate the current through the circuit and potential difference across the $$3\ ohm$$ resistance.
Give examples for good conductors solid and liquid.
The potential difference between the ends of a conductor is 40V. If the conductor draws a current of 4A from the source, what current will the conductor draw if the potential difference is increased to 100V ?
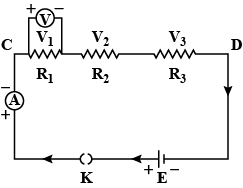
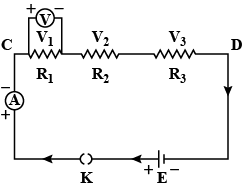
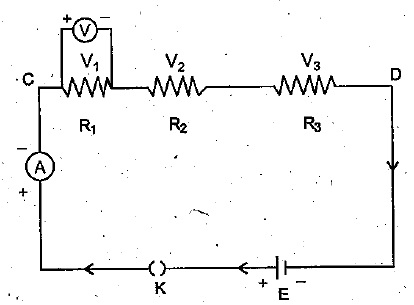
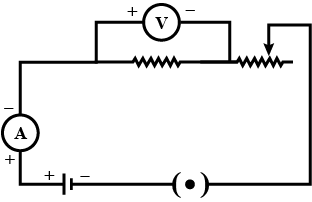
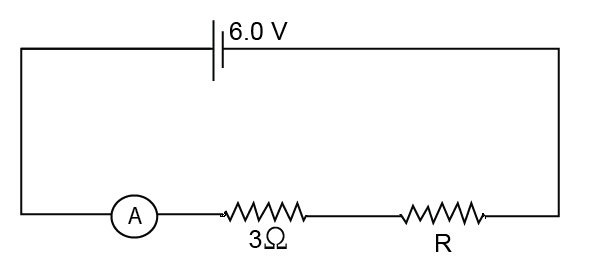
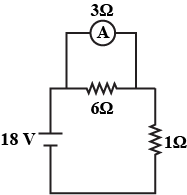
The figure shows a circuit
When the circuit is switched on, the ammeter reads $$0.5 A$$.
(i) Calculate the value of the unknown resistor $$R$$.
(ii) Calculate the charge passing through the $$3 \Omega$$ resistor in $$120 s$$.
(iii) Calculate the power dissipated in the $$3 \Omega$$ resistor.
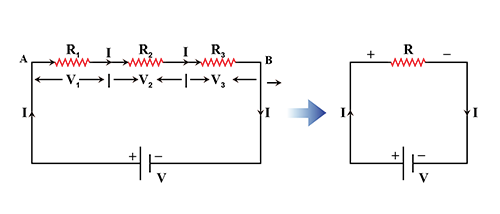
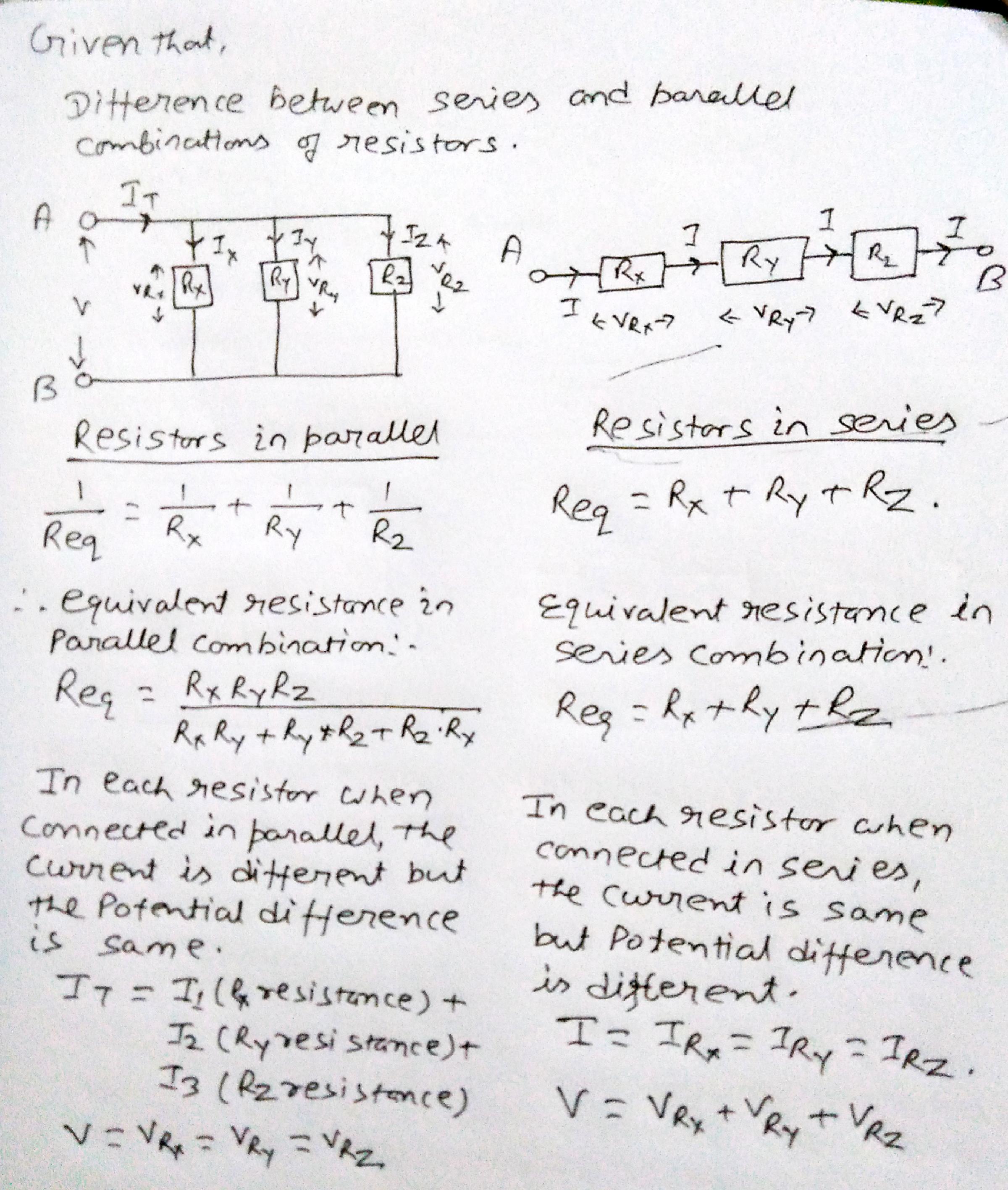
Deduce the expression for the the equivalent resistance of three resistors connected in series.
How do you verify that resistance of a conductor is proportional to the length of the conductor for constant cross section area and temperature?
(i) Name the device used to protect the electric circuits from overloading and short circuits.
(ii) On what effect of electricity does the above device work?
Deduce the expression for the the equivalent resistance of three resistors connected in Parallel.
An unknown circuit draws a current of 2A from a 12V battery equivalent resistance is.......
Three resistors of values $$2 \Omega, 4\Omega, 6 \Omega$$ are connected is series. The equivalent resistance of combination of resistors is............
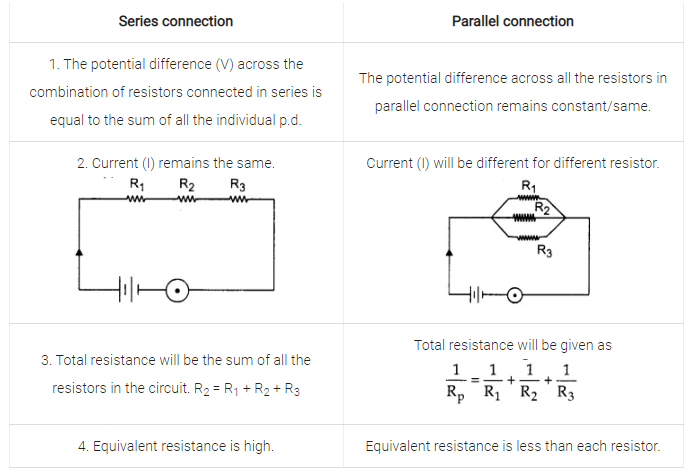
Difference between resistances in series and parallel.
Find the expression for the resistors connected in series. Write any two characteristics of series combination of resistors.
With a neat labeled diagram, derive the equation for three resistance connected in parallel.
Find the expression for the resistors connected in series and state its two characteristics. (Draw figure).
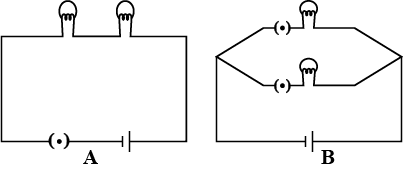
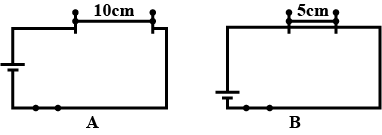
A student connected two bulbs in two different combinations as shown in figure A and B. Observe the figure and answer the following questions:
a. Name the type of combination of the bulbs in figure A.
b. Name the type of combination of the bulbs in figure B.
c. State the combination in which the resistance will be decreased.
When do you say that the resistors are connected in series? Find the expression for the resistors connected in this way. (Draw circuit diagram).
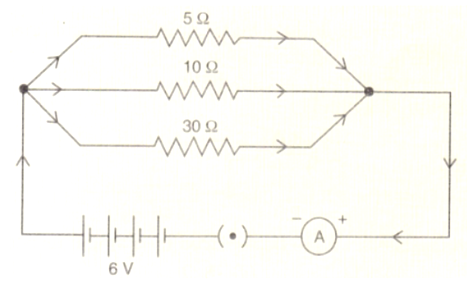
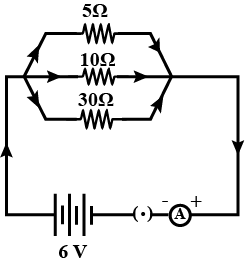
Three resistances having the values 5$$\Omega$$, 10$$\Omega$$, 30$$\Omega$$ are connected in parallel with each other. Calculate the total circuit resistance.
A domestic electric circuit has a fuse of $$5A$$. What is the maximum number of $$100 W ( 220 V )$$ bulbs that can be safely used in the circuit?
Two lamps one rated $$60\ W$$, $$220\ V$$ and the other $$40\ W$$, $$220\ V$$ are connected in parallel to a $$220\ V$$ electric supply mains. What is the total current drawn from the electric mains if the voltage of the electric supply is $$220\ V$$?
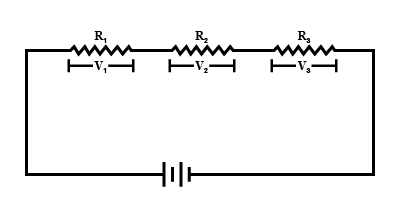
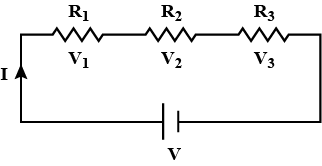
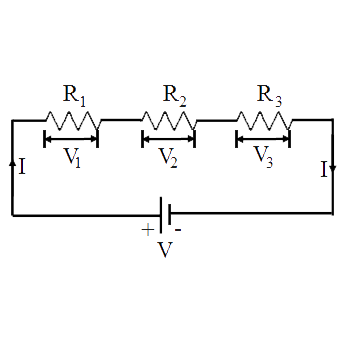
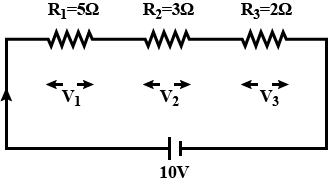
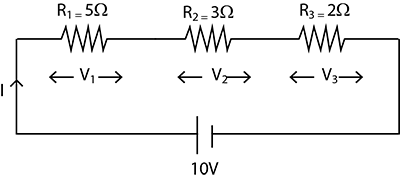
Three resistors are connected in series with $$10 V$$ supply as shown in the figure. Find the voltage drop across each resistor, and effective resistance of series combination.
My mother was operating the washing machine on Sunday morning. Suddenly, she saw a spark coming out of the electric board and the electric current in the house failed. An electrician was called to look into the matter. What should he have noticed?
Show that the effective resistance of series combination in a circuit is equal to the sum of their resistances.
A wire of resistance $$4 R$$ is bent in the form of a circle. What is the effective resistance between the ends of the diameter?
Explain series connections of Resistors and drive the formula of equivalent resistance.
With the help of a circuit diagram, obtain the expression for equivalent resistance of two resistors connected in parallel.
Nichrome and copper wire of same length and same radius are connected in series. Current $$I$$ is passed through them. Which wire gets heated up more? Justify your answer.
Name the device used to protect the electric circuits from overloading and short circuits.
Vani's hairdryer has a resistance of $$50 \Omega$$ when it is first turned on.
i) How much current does the hairdryer draw from the $$230\ V$$ line in Vani's house?
ii) What happens to the resistance of the hairdryer when it runs for a long time?
The commercial unit of electrical energy is _____.
One Kwh is equal to ___________J.
Give the definition of electric current and define its unit.
What is equivalent resistance? Derive the expression for effective resistance of two resistors connected in parallel.
Three resistors $$R_1, R_2, R_3$$ are joined in series. Draw labelled diagram and obtain expression of its equivalent resistance.
The safety device based on the heating effect of electric current is called a ___________(fuse, heater).
Commercial unit of electric energy is kilowatt hour (kWh). Convert 1 kWh into Joule.
Resistors are sometimes joined together and they have several applications in electronics. Obtain the expression for the effective resistance in the combination of two resistors $${R}_{1}$$ and $${R}_{2}$$ in parallel.
Name any two effects of electric current.
What do you understand by the thermal effect of electric current?
Calculate the resultant resistance when three resistances of $$3\Omega$$ are connected in parallel?
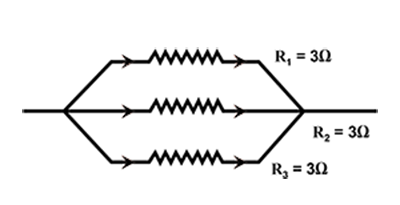
Resistors are sometimes joined together and they have several applications in electronics. Draw a series combination of three resistors $${R}_{1}$$, $${R}_{2}$$ and $${R}_{3}$$.
On which factors does the heat produced depend when the current is flown through a conducting wire and explain it.
You have three resistors of values $$2\Omega, 3\Omega$$ and $$5\Omega$$. How will you join them so that the total resistance is more than $$7\Omega$$? Draw a diagram for the arrangement.
You have three resistors of values $$2\Omega, 3\Omega$$ and $$5\Omega$$. How will you join them so that the total resistance is more than $$7\Omega$$? Calculate the equivalent resistance.
An electric lamp of resistance $$100\Omega$$, a toaster of resistance $$50\Omega$$ and a water filter of resistance $$500\Omega$$ are connected in parallel to a $$220V$$ source. What is the resistance of an electric iron connected to the same source and takes as much current as all three appliances and what is the current through it ?
A resistance coil is made by joining in parallel two resistances each of 10$$\Omega $$. An emf of 1V is applied between the two ends of coil for 5 minutes. Calculate the heat produced in calories.
If the value of resistance is $$10.845 \Omega $$ and the value current is $$3.23$$ A, the potential difference is $$35.02935\,\,V$$. Find its value in significant number.
A copper wire has diameter $$0.5 \ mm$$ and resistivity of $$1.6\times { 10 }^{ -8 }\Omega m$$. What will be the length of this wire to make its resistance $$10\ \Omega $$?
Explain and derive equivalent Resistance formula for 3 Resistors connected in Pure Series. Generalize the formula?
When an electric current is passed through an electric bulb, it becomes warm when touched. Give reasons.
Heat energy is being produced in a resistance in a circuit at the rate of $$100\ W$$. The current of $$2\ A$$ is flowing in the circuit. what must be the value of the resistance (in $$\Omega$$)?
Two resistances when connected in parallel give resultant value of $$2\Omega$$. When connected in series the value becomes $$9\Omega$$. Calculate the value of each resistance.
Find the reading of ammeter. Is this the current thought $$6\Omega $$?
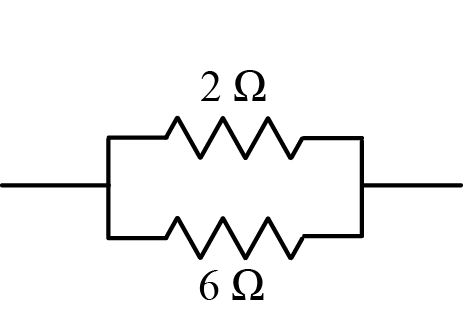
Calculate combined resistance of resistances $$3 \Omega $$ and $$6 \Omega$$ connected in parallel.
Calculate the power of soldering iron with a hot resistance $$4$$ $$K\Omega$$ and operating voltage of $$200$$ $$V$$.
In the above question, Find individual power consumed.
Given $$R_1=1 \ k \Omega$$ and $$R_2=0.5\ k\Omega$$
Judge the equivalent resistance when the following are connected in parallel
(i) $$1 \Omega$$ and $$10^6 \Omega$$
(ii) $$1 \Omega, 10^3 \Omega $$ and $$ 10^6 \Omega.$$
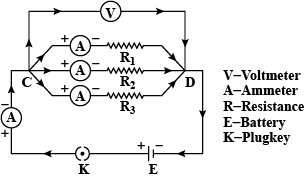
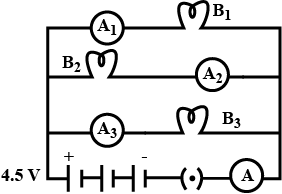
$$B_1, B_2$$ and $$B_3$$ are three identical bulbs connected as shown in Figure 12.When all the three bulbs glow, a current of 3A is recorded by the ammeter A.
What happens to the reading of $$A_1, A_2, A_3$$ and A when the bulb $$B_2$$ gets fused?
Resistors having resistances of $$15\Omega$$, $$20\Omega$$, and $$10\Omega$$ are connected in parallel. What is the effective resistance in the circuit.
$$B_1, B_2$$ and $$B_3$$ are three identical bulbs connected as shown in Figure 12.When all the three bulbs glow, a current of 3A is recorded by the ammeter A.
How much power is dissipated in the circuit when all the three bulbs glow together?
A wire of resistance 5 ohm is bend in the form of closed circle. What is the resistance between 2 points at the ends of any diameter of the circle?
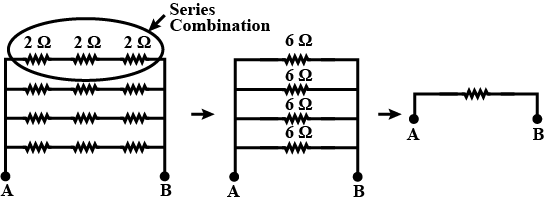
A combination consists of three resistors in series. Four similar sets are connected in parallel. If the resistance of each resistor is $$2\ \Omega$$. Find the equivalent resistance of the combination.
A conductor connected to a battery is heated, explain how.
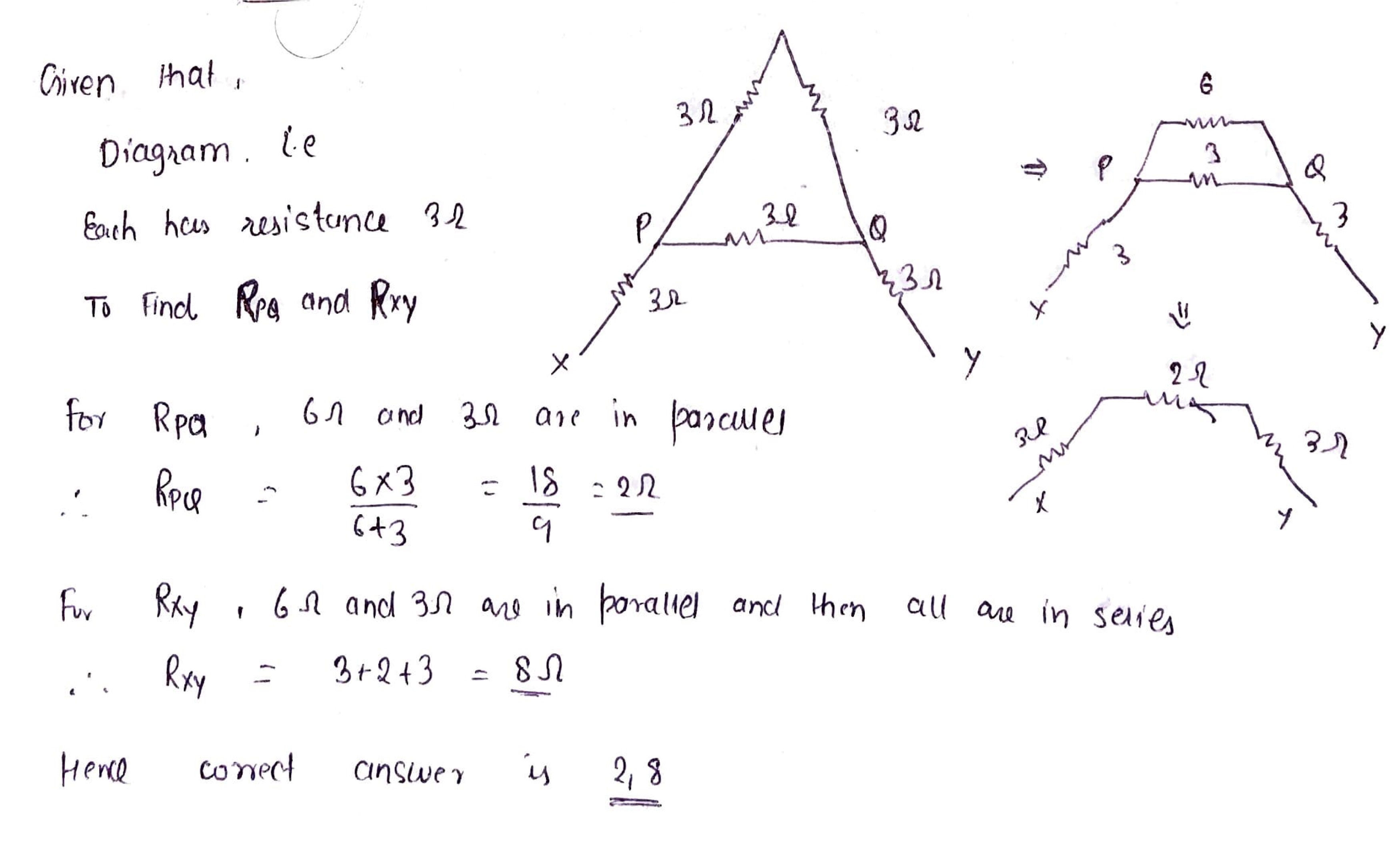
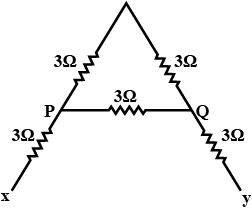
Find the resistor each $$ 3 \Omega$$ are connected as shown, calculate the resistance
a) between the paint p and q
2) between the paint x and y
How many bulbs of power $$60\ W$$ can be connected in parallel across a $$240\ V$$ source if current rating of the circuit is $$5A$$? What is the resistance of each bulb?
Two lamps of rating $$100 W$$, $$220V$$ and $$60 W$$ , $$220V$$ are joined in parallel with $$220 V$$ line. How much current will flow through the circuit?
What is the ratio of heat generation in two resistors having resistances $$R$$ and $$2R$$ in same time $$t$$.
Find the total resistance in the circuit.?

An electric heater of power 3 kW is used for one minute.Find the energy supply by the heater.
A lamp consumes $$1000\ J$$ of electrical energy in $$10\ s$$. What is its power?
What is the resistance of an ideal voltmeter?
A piece of wire of resistance R is cut into five equal parts. When these parts are connected in parallel. Then the equivalent resistance of this combination is R' .The ratio $$\frac{R}{R'}$$ is
An electric bulb consumes $$7.2\ kJ$$ of electrical energy in $$2\ min$$. What is the power of the electric bulb?
State the relation between the commercial unit of energy and SI unit of energy.
Find the followings -a) total resistance of the circuit,
b) the value of resistor R
c) the current flowing through R.
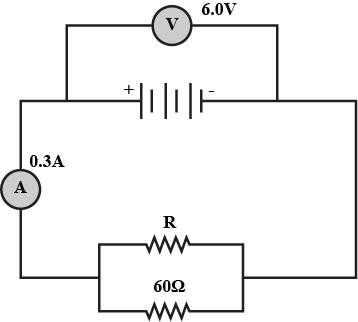
A constantan wire of length $$50\ cm$$ and $$0.4\ mm$$ diameter is used in making a resistor. If the resistivity of constantan is $$5\times 10^{-7} \ \Omega-m$$, calculate the value of the resistance.
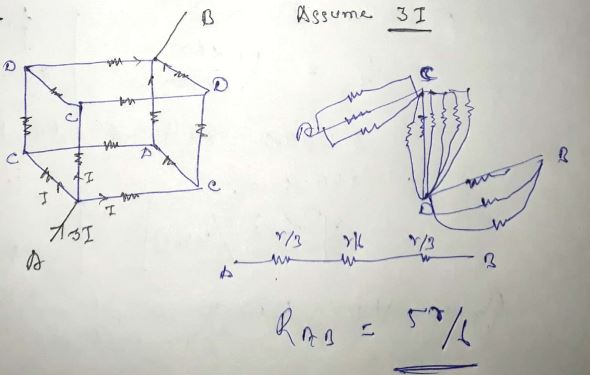
Twelve wires, each of resistance 'r' are joined to from a skeleton cube. Find the effective resistance between two diagonally opposite ends of the cube.
A common device which can supply small electric current continuously for a sufficient time
Classify the following into good conductors, resistors and insulators :
Rubber, Mercury, Nichrome, Polythene, Aluminium, Wood, Manganin, Bakelite, Iron, Paper, Thermocol, Metal coin.
Give S.I. unit and commercial unit of energy
A voltage of 30 V is applied across a colour coded carbon resister with first, second and third rings of blue, black and yellow colours. What is the current flowing through the resistor?
An electric heater which is connected to a 220 V supply line has two resistance coils. A and B of $$ 24 \Omega $$ resistance each. these coils can be used separately (one at a time), in series or in parallel. calculate the current drawn when:- Only one coil A is used
- coils A and B are used in series
- Only one coil A is used
- coils A and B are used in series
A uniform wire with a resistance of $$ 27 \Omega $$ is divided into three equal pieces and then they are joined in parallel . find the equivalent resistance of the parallel combination.
If two resistors with resistance 5 $$\Omega$$ and 10 $$\Omega$$ respectively , are connected to a battery of emf 6V, then determine the strength of the total resistance and current in the circuit when connected in
(a) parallel combination and (b) series combination
An electric bulb is rated $$220\ V$$ and $$100\ W$$. When it is operated on $$110\ V$$, what will be the power consumed?
What is an electric fuse? State its purpose in the household electrical circuit?
(i)What is an electric fuse? (ii)An electric fuse of rating 3 ampere is connected in a circuit in which an electric iron of power 1 kw is connect which operates at 220 V. What would happen, Explain?
How does the heat $$H$$ produced by a current passing through a fixed resistance wire depend on the magnitude of current $$I$$?
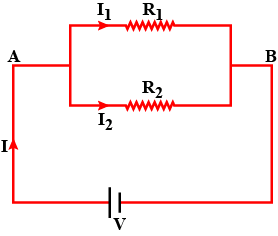
With the help of labelled circuit diagram derive a formula to find combined resistance (R) when two or more resistance $$(R_1,R_2,R_3.....)$$ are connected in parallel taking symbols potential difference $$(V)$$ and current $$(I)$$.
An electric lamp of resistance $$20 \, \Omega$$ and a conductor of resistance $$4\, \Omega$$ are connected to a $$6\, V$$ battery as shown in the circuit. Calculate:
(a) The total resistance of the circuit
(b) The current through the circuit
(c)The potential difference across the (i) Electric lamp and (ii) Conductor, and
(d) Power of the lamp.
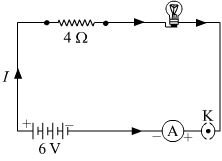
Two Metallic resistors are connected first in series and then in parallel across a d c supply. Plot of I-V graph is shown for the two cases. Which one represents a parallel combination of the resistors and why?
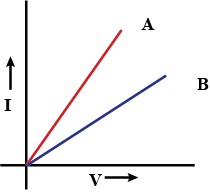
Define resistivity.
(i)Draw a circuit diagram to show three resistors connected in parallel with a cell and a key. (ii)Write formula for the equivalent resistance $$R$$ of these combination if the individual resistance of the resistance are $$R_1, R_2$$ and $$R_3$$.
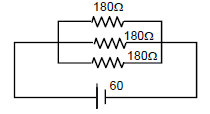
Three bulbs, each having a resistance of $$180 \Omega$$, are connected in parallel to an ideal battery of emf $$60 V$$. Find the current delivered by the battery when
(a) all the bulbs are switched on,
(b) two of the bulbs are switched on and
(c) only one bulb is switched on.
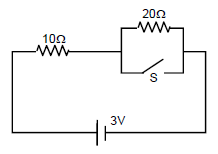
Consider the circuit shown in figure. Find the current through the $$10 \Omega$$ resistor when the switch $$S$$ is (a) open (b) closed.
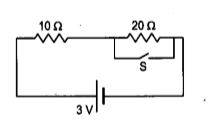
A resistor $$ R_1$$ consumes electrical power $$ P_1 $$ when connected to e.m.f. e. when resistor $$ R_2 $$ is connected to the same e.m.f. it consumes electrical power $$ P_2 $$ in terms of $$ P_1 $$ and $$ P_2 $$ what is the total electrical power consumed when they are both connected to this e.m.f. source.
a. in parallel
b. in series ?
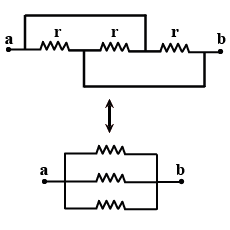
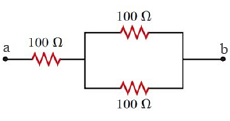
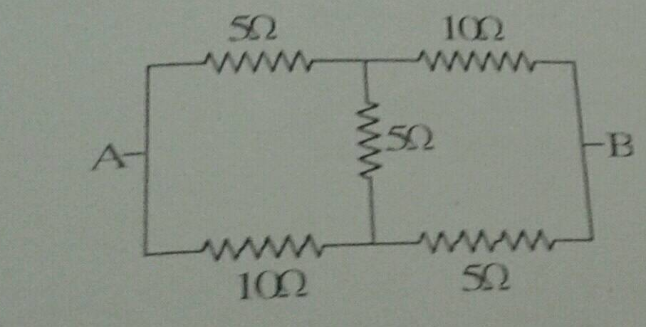
Find the equivalent resistance of the network shown in figure between the points $$a$$ and $$b$$.

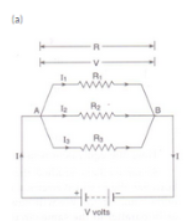
(a) What is meant by the "resistance of a conductor" ? Write the relation between resistance, potential difference and current.
(b) When a $$12 \,V$$ battery is connected across an unknown resistor , there is a current of $$2,5 \,mA$$ in the circuit. Calculate the value of the resistance of the resistor.
(a) Give two examples of substances which are good conductors of electricity. Why do you think they are good conductors of electricity ?
Calculate the resistance of a copper wire $$1.0 \,km$$ long and $$0.50 \,mm$$ diameter if the resistivity of copper is $$1.7 \times 10^{-8} \,\Omega m.$$
Distinguish between good conductors , resistors and insulators . Name two good conductors , two resistors and two insulators.
A resistance of $$20 \,ohms$$ has a current of $$2$$ amperes flowing in it. What potential difference is there between its ends ?
Which of the following equation shows the correct relationship between electrical units ?
$$1 \,A = 1 \,C/s $$ or $$1 \,C = 1 \,A/s$$
(a) In which direction does conventional current flow around a circuit ?
(b) In which direction do electron flow ?
(a) Give one example to show how the resistance depends on the nature of material of the conductor.
(b) Calculate the resistance of an aluminium cable of length $$10 \,km$$ and diameter $$2.0 \,mm$$ if the resistivity of aluminium is $$2.7 \times 10^{-8} \,\Omega m.$$
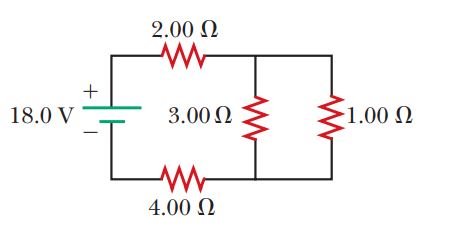
In the circuit given below :
(a) What is the combined resistance ?
(b) What is the p.d. across the combined resistance ?
(c) What is the p.d. across the $$3 \,\Omega$$ resistor ?
(d) What is the current in the $$3 \,\Omega$$ resistor ?
(e) What is the current in the $$6 \,\Omega$$ resistor ?
The electrical resistivities of four materials A, B, C, and D are given below :
Which material is : (a) good conductor (b) resistor (c) insulator, and (d) semiconductor?
$$A=110\times 10^{-8}\ \Omega m$$$$B=1.0\times 10^{10}\ \Omega m$$
$$C=10.0\times 10^{-8}\ \Omega m$$
$$D=2.3\times 10^{3}\ \Omega m$$
$$A=110\times 10^{-8}\ \Omega m$$
$$B=1.0\times 10^{10}\ \Omega m$$
$$C=10.0\times 10^{-8}\ \Omega m$$
$$D=2.3\times 10^{3}\ \Omega m$$
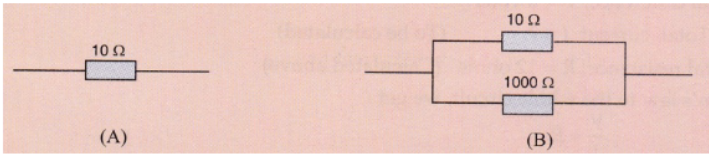
Which of the following resistor arrangement , A or B , has the lower combined resistance ?
How should the two resistances of $$2$$ ohms each be connected so as to produce an equivalent resistance of $$1$$ ohm ?
If five resistances , each of value $$0.2 \,ohm ,$$ are connected in series , what will be the resultant resistance ?
State the law of combination of resistances in parallel.
If $$3$$ resistances of $$3$$ ohm each are connected in parallel , what will be their total resistance ?
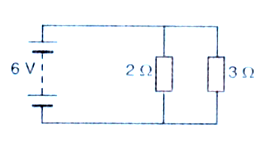
The figure given below shows an electric circuit in which current flows from a $$6 \,V$$ battery through two resistors.
(a) Are the resistors connected in series with each other or in parallel ?
(b) For each resistor , state the p.d. across it.
(c) The current flowing through from the battery is shared between the two resistors. Which resistor will have bigger share of the current ?
(d) Calculate the effective resistance of the two resistors.
(e) Calculate the current that flows from the battery.
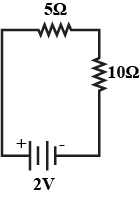
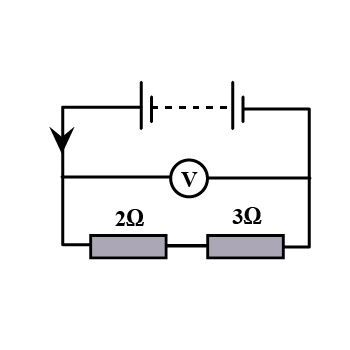
In the circuit shown below , the voltmeter reads $$10 \,V.$$
(a) What is the combined resistance ?
(b) What current flows ?
(c) What is the p.d. across $$2 \,\Omega$$ resistor ?
(d) What is the p.d. across $$3 \,\Omega$$ resistor ?
A potential difference of 6 V is applied to two resistors of 3$$\Omega$$ and 6 $$\Omega$$ connected in parallel. Calculate : (a) the combined resistance (b) the current flowing in the main circuit (c) the current flowing in the 3 $$\Omega$$ resistor
(a) Explain with the help of a labelled circuit diagram, how you will find the resistance of a combination of three resistors of resistances $$R_1 , R_2 $$ and $$R_3$$ joined in parallel.
(b) In the diagram shown below , the cell and the ammeter both have negligible resistance . The resistors are identical.
With the switch K open , the ammeter reads $$0.6 \,A$$ . What will be the ammeter reading when the switch is closed ?
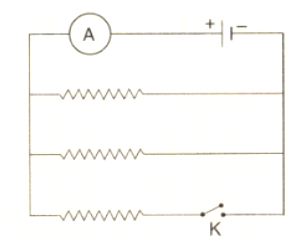
If the current passing through a conductor is doubled , what will be the change in heat produced ?
A resistor of 8 ohms is connected in parallel with another resistor X. The resultant resistance of the combination is $$4.8\,ohms$$. What is the value of the resistor X ?
(a) With the help of a diagram , derive the formula for the resultant resistance of three resistors connected in series.
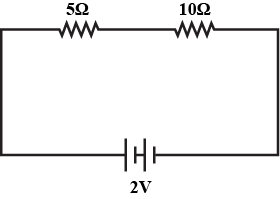
(b) For the circuit shown in the diagram given below :
Calculate :
(i) the value of current through each resistor.
(ii) the total current in the circuit.
(iii) the total effective resistance of the circuit.
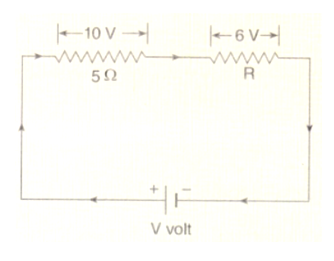
(a) With the help of a circuit diagram , deduce the equivalent resistance of two resistances connected in series.
(b) Two resistances are connected in series as shown in the diagram:
(i) What is the current through the 5 ohm resistance ?
(ii) What is the current through R ?
(iii) What is the value of R ?
(iv) What is the value of V ?
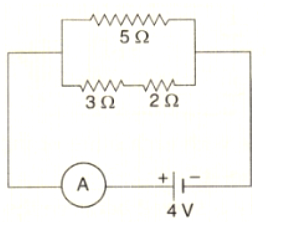
State whether an electric heater will consume more electrical energy or less electrical energy per second when the length of its heating element is reduced. Give reasons for your answer.
(a) With the help of a circuit diagram , obtain the relation for the equivalent resistance of two resistances connected in parallel.
In the circuit diagram shown below , find :
(i) Total resistance
(ii) Current shown by the ammeter A
The resistors $$R_1 , R_2 , R_3$$ and $$R_4$$ in the figure given below are all equal in value.
What would you expect the voltmeters A , B and C to read assuming that the connecting wires in the circuit have negligible resistance ?
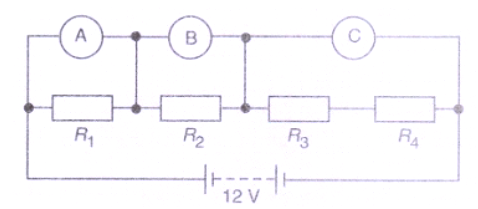
Four resistances of 16 ohms each are connected in parallel. Four such combinations are connected in series.
What is the total resistance ?
Name two effects produced by electric current.
$$(a)$$ What current is taken by a $$3\ kW$$ electric geyser working on $$240\ V$$ mains?$$(b)$$ What size fuse should be used in the geyser circuit?
What is the usual capacity of an electric fuse used in the lighting circuit.
Three appliances are connected in parallel to the same source which provides a voltage of $$220\ V$$. A fuse connected to the source will blow if the current from the source exceeds $$10\ A$$. If the three appliances are rated at $$60\ W, 500\ W$$ and $$1200\ W$$ at $$220\ V$$, will the fuse blow?
Which of the following circuits will still be dangerous even if the fuse blows off and electric iron stops working during a short circuit?
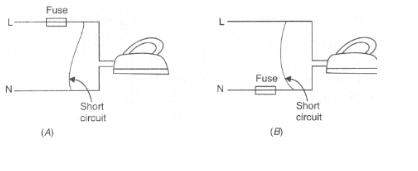
A vacuum cleaner draws a current of $$2\ A$$ from the mains supply. What will happen if a $$13\ A$$ fuse is fitted in its circuit?
A vacuum cleaner draws a current of $$2\ A$$ from the mains supply.
What is the appropriate value of the fuse to be fitted in its circuit?
What is the usual capacity of an electric fuse used In the power, circuit, of a small house?
State three factors on which the heat produced by an electric current depends. How does it depend on these factors ?
Is electric current a scalar or vector quantity? State the standard unit of electric current.
An electric fan/ motor becomes warm when continuously used for a long time. Why?
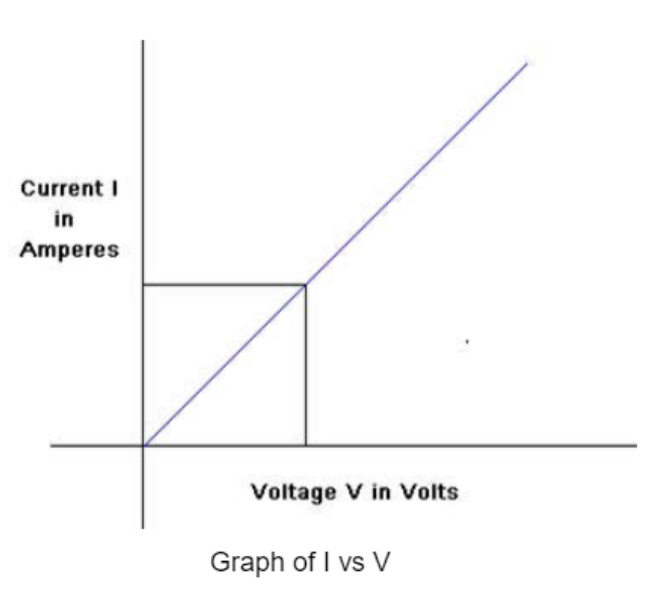
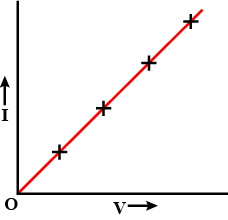
Present the relationship between the voltage applied across a conductor and the current flowing through it graphically.
Identify the type of combination in which $$R_1$$ and $$R_2$$ are connected in the given circuit diagram. Find the equivalent resistance in the given circuit.
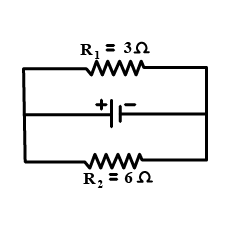
The potential difference between the terminals of an electric heater is $$60\ V$$ when it draws a current of $$4\ A$$ from the source. Find the resistance of the heater.
What is the commercial unit of electrical energy ? Convert it into joule . What is the other name of the commercial unit ? What is meant by a parallel combination of resistors ? Deduce an expression for the equivalent resistance when two resistors are connected in parallel.
Relate $$Watt$$ to $$Joule$$.
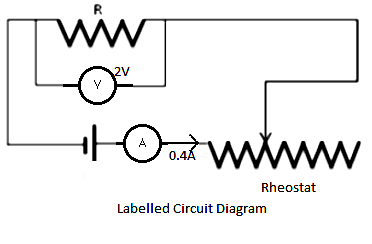
When a high resistance voltmeter is connected across a resistance R and its reading is $$2\ V$$. An electric cell is sending the current of $$0.4\ A$$ in the electric circuit in which a rheostat is connected to vary the current.
Find the resistance of the resistor.
Heat is generated continuously in an electric heater but the temperature of its element becomes constant after some time. Why?
Why is resistance less when resistors are joined in parallel?
How is the fuse connected in an electric circuit?
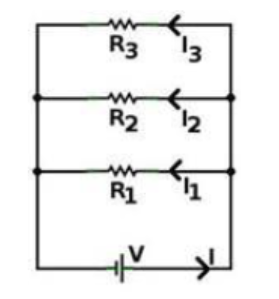
Figure shows three $$20.0\Omega $$ resistors. Find the equivalent resistance between points (a) A and B, (b) A and C, and (c) B and C. (Hint:
Imagine that a battery is connected between a given pair of points.)
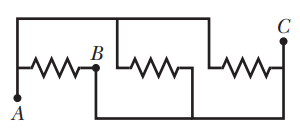
Two heated wires of the same dimensions are first connected in series and then in parallel to a source of supply.What will be the ratio of heat produced in the two cases?
In India, domestic power supply is at $$220 \ V$$, $$50 \ Hz$$; while in USA it is $$110 \ V$$, $$50 \ Hz$$. Give one advantage and one disadvantage of $$220 \ V$$ supply over $$110 \ V$$ supply.
Which physical quantity remains constant when resistances are connected in parallel?
A uniform wire of resistance $$50\ \Omega$$ is cut into $$5$$ equal parts. These parts are now connected in parallel. What is the value of the equivalent resistance of the combination?
Mention the commercial unit of energy. Express it in terms of joules. Calculate the energy in joule consumed by a device of $$60\,W$$ in $$1\,hour$$.
In series combination which remains constant, current or voltage?
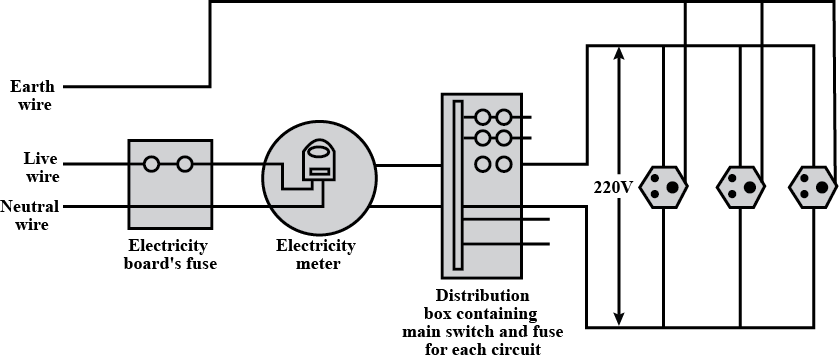
Draw an appropriate schematic diagram showing common domestic circuits and discuss the importance of fuse. Why is it that a burnt out fuse should be replaced by another fuse of identical rating?
Differentiate between watt and watt hour.
What does the slope of an $$I-V$$ graph of a linear resistor represent?
Name the factors on which the heat produced in a wire depends when current is passed in it,and state how does it depend on the factors stated by you.
Paheli does not have a night lamp in her room. She covered the bulb of her room with a towel in the night to get dim light. Has she taken the right step? Give one reason to justify your answer.
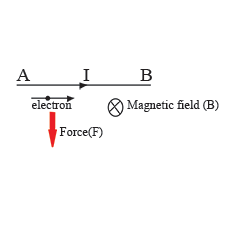
A fixed wire AB carries current I. An electron is moving parallel to the wire, in which direction does the electron tend to move?

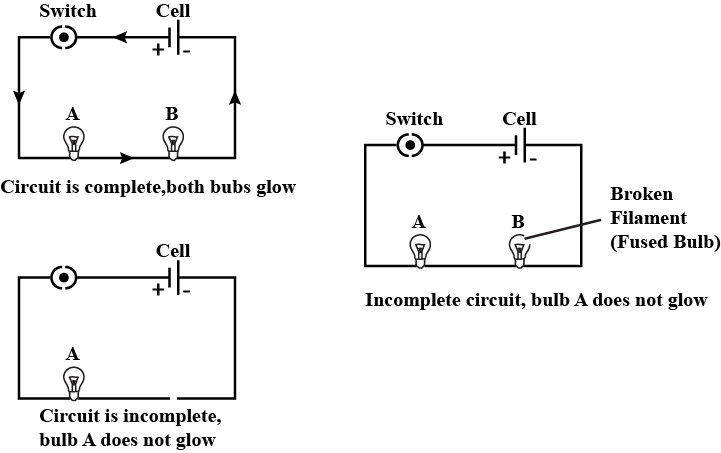
Describe an experiment to show that electricity flows only if the circuit is complete and it does not flow if the circuit is incomplete.
Draw a $$I-V$$ graph for a linear resistor.
What does the slope of $$V-I$$ graph for a conductor represent?
Paheli took a wire of length 10 cm. Boojho took a wire of 5 cm of the same material and thickness. Both of them connected the wires as shown in the circuit given in Figure 14.The current flowing in both the circuits is the same.
i) Will the heat produced in both the cases be equal? Explain.
ii) Will, the heat produced be the same if the wires taken by them are of equal lengths but of different thickness? Explain.
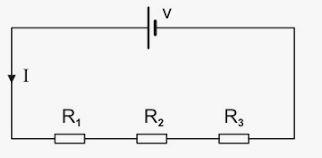
Calculate the total equivalent resistance for two resistors connected in series.

'A fuse is rated 8A'. Can it be used with an electrical appliance of rating 5kW,200 V?
State how are the two resistors joined with a battery when potential difference is same across each resistor
State how are the two resistors joined with a battery when equivalent resistance is less than either of the two resistances
Name the device used to protect the electric circuits from over loading and short circuit. On what effect of current does it work?
Two resistors having resistance $$4 \Omega$$ and $$6\Omega$$ are connected in parallel. Find their equivalent resistance.
Draw a graph to show current-voltage relationship of non-ohmic resistor.
State how are the two resistors joined with a battery when equivalent resistance is more than either of the two resistances.
Write the expression for the equivalent resistance $$R$$ of three resistors $$R_1$$, $$R_2$$ and $$R_3$$ joined in series.
State how are the two resistors joined with a battery when same current flows in each resistor
A resistor of $$6\Omega$$ is connected in series with another resistor of $$4 \Omega$$. A potential difference of $$20 \ V$$ is applied across the combination. Calculate the current in the circuit.
State two differences between a conductor and an insulator of electricity.
n electrons flow through a cross section of a conductor in time t. If charge on an electron is e, write an expression for the current in the conductor.
A particular resistance wire has a resistance of $$3.0$$ ohm per meter. Find the total resistance of three lengths of this wire each $$1.5 m$$ long joined in parallel.
Four resistors each of $$2 \Omega$$ are connected in parallel. What is the effective resistance?
The following figure shows the symbols for components used in the accompanying electrical circuit . Place them at proper places and complete the circuit.
Which law can you prove with the help of above circuit ?
The following table shows current in Amperes and potential difference in Volts. What will be the nature of the graph between the current and potential difference? (Do not draw a graph)
| V (Volts) | I (Amp) |
| 4 | 9 |
| 5 | 11.25 |
| 6 | 13.5 |
What is thermal effect of electric current ? Write down the names of any four appliances based on this effect.
Give reason -
In practice the unit kWh is used for the measurement of electrical energy rather than joule.
The following table shows current in Ampere and potential difference in Volts
| V (Volts) | I (Amp) |
| 4 | 9 |
| 5 | 11.25 |
| 6 | 13.5 |
Which law will the graph prove? Explain the law.
Solve the following example.
If a 1200 W electric iron is used daily for 30 minute, how much total is consumed in the month of April?
Solve the following problem.
The resistance of a 1m long nichrome wire is 6 $$\Omega$$. If we reduce the length of the wire to 70 cm. what will its resistance be ?
If $$10$$ milliampere current flows through a wire produces a potential difference of $$2.5 \,V$$ between its ends, then find the resistance of wire.
With the help of suitable diagram derive equivalent resistance of resistors in series combination.
What is the difference between series and parallel combinations of resistors ?
When the given resistances are connected in series, which physical quantity does not change.
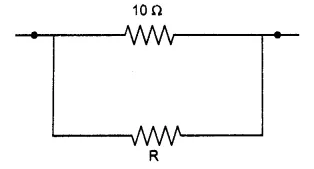
The combined resistance in the given circuit is $$5 \Omega.$$ What is the value of R ?
Find the maximum and minimum resistance by combination of three resistors of $$1\Omega, 2\Omega$$ and $$3\Omega.$$
For the circuit shown in the diagram given above:
Calculate total effective resistance of the circuit.
A circuit diagram is given below.
Calculate the total effective resistance.
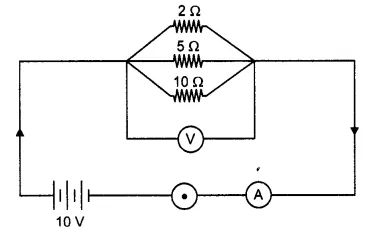
Give the difference in unit of electric energy and commercial unit of electric energy.
Give two disadvantages of the heating effect of current.
A battery of $$10 \,V$$ is connected in a circuit with $$3 \Omega, 4\Omega, 6\Omega$$ resistors connected in series. How much current will flow through $$6\Omega$$ resistor ?
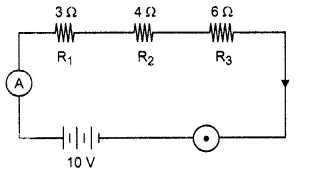
For the circuit shown in the diagram given above:
Calculate: the value of current through each resistor.
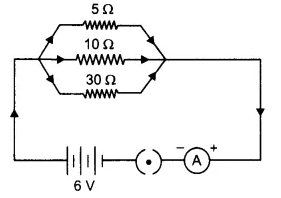
Study the above circuit and answer the questions that follows:
(a) State the type of combination of the two resistors in the circuit.
(b) How much current is flowing through
(i) $$10 \Omega$$ and
(ii) $$15 \Omega$$ resistor ?
(c) What is the ammeter reading ?
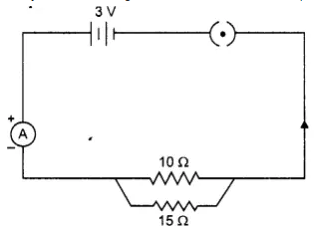
Give the differences between series and parallel connections of resistors.
Calculate the area of cross section of a wire of length $$1.0 \,m,$$ its resistance is $$23\Omega$$ and the resistivity of the material of the wire is $$1.84 \times 10^{-6} m$$
What is heating effect of electric current ? Find the expression for calculating 'Heat'.
What is the commercial unit of energy? Define it.
Give advantages and disadvantages of series and parellel connection of resistors.
Bigger unit of energy is _______.
What would be the values of $$\dfrac V I$$ ratios when the potential difference is $$0.5 \,V, 1.5 \,V$$ and $$2.0\,V$$ respectively ? What conclusion do you draw from these value..
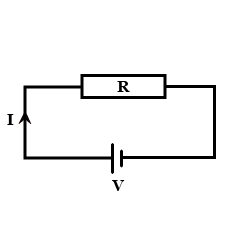
In a residence, $$4$$ tube lights: each of them of $$40$$ W are operated daily for $$5$$ hours and $$3$$ fans: each of $$120$$ W are operated daily for $$4$$ hours. Calculate the electricity bill at Rs. $$5$$ per unit for September month.
An electrical appliance of 100 W is used for 3 h per day. Calculate the units of energy consumed per day and for a month.
Define $$1\ kWh$$.
Show how you would connect three resistors, each of resistance $$6\Omega$$, so that the combination has a resistance of
(i) $$9\Omega$$,
(ii) $$4\Omega$$.
What is meant by heating effect of electric current?
Give examples where we find heating of electric current.
What factors does the heat produced in a wire depend on?
Fill in the blanks:
When current is switched on in a room heater, it .......................
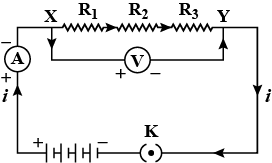
Is the direction of current in the circuit between $$A$$ and $$B$$ from $$A$$ to $$B$$ or from $$B$$ to $$A$$?
Judge the equivalent resistance when the following are connected in parallel
(a)$$1\Omega$$ and $$10^{6}\Omega$$
(b)$$1\Omega$$ and $$10^{3}\Omega$$ and $$10^{6}\Omega$$
Heat is generated in accordance with the equation $$H = I^2Rt.$$ If the current $$I$$ is reduced to half, how much will be the reduction in heat?
Heat is generated in accordance with the equation $$H = I^2Rt.$$ In that case what are the methods to reduce the heat generated ?
Convert $$1$$ Kilowatt-hour of electric energy into joules.
What is the unit of current ?
Heat is generated in accordance with the equation $$H = I^2Rt.$$ In that case
How can we reduce the current without change in power ? Find out on the basis of the equation $$P = V \times I.$$
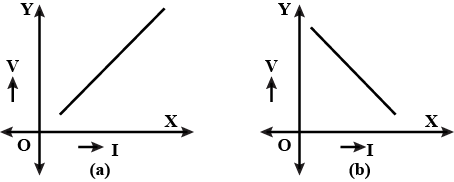
In the given graphs which is the graph depicting Ohm's Law ? justify your answer.
In a household electric circuit, where is the MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) connected?
According to Ohm's Law, V/I must be a constant (resistance R). If so, what is the reason for the change in the ammeter readings?
When the circuit was switched on, was the temperature of the bulb low or high?
Heat is generated in accordance with the equation $$H = I^2Rt.$$ In that case if current (I) is reduced to $$\dfrac{1}{10}$$ times how much will be the reduction in heat?
In this case which form of energy was converted into heat energy?
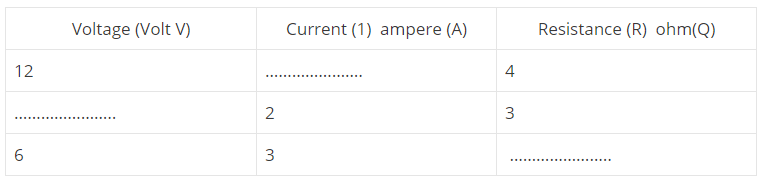
Complete the following table based on Ohm's Law
Is there any difference in the amount of heat energy thus obtained and the work done by the current?
According to Joule's Law, more heat will be produced when an electric current is increased. What happens to the fuse wire due to this?
A current of 0.4 A flows through an electric bulb working at 230 V. What is the power of the bulb?
0.5 A current flows through an electric heating device connected to 230 V supply.
How much is the power of the heating device connected to the circuit if we ignore the resistance of the circuit wire?
$$10$$ resistors of $$2 \ \Omega$$ each are connected in parallel. Calculate the effective resistance.
Complete the following table on the basis of Joule's Law.
| Resistance of conductor $$R \ (\Omega)$$ | Intensity of Current $$I \ (A)$$ | Time for which current flows $$t \ (s)$$ | Heat generated $$I^2R t \ (J)$$ | Change in Heat $$(H)$$ |
| $$2 \ R$$ | $$I$$ | $$t$$ | $$2 \ I^2 Rt$$ | Twice $$(2 H)$$ |
| $$R$$ | $$2 \ I$$ | $$t$$ | ................. | ................... |
| $$\dfrac{R}{2}$$ | $$I$$ | $$t$$ | ................. | ................... |
| $$R$$ | $$\dfrac{I}{2}$$ | $$t$$ | ................. | ................... |
| $$R$$ | $$I$$ | $$2 t$$ | ................. | ................... |
| $$R$$ | $$I$$ | $$\dfrac{t}{2}$$ | ................ | ................... |
When ni-chrome wire become red hot while passing electricity through the circuit, how does this energy change occur?
Name the part in which electrical energy changes into heat energy.
0.5 A current flows through an electric heating device connected to 230 V supply.
How much is the resistance of the circuit?
A potential difference of 6V is applied across a conductor having $$12\Omega $$. How much current will pass through it? How many times will the current increase if length if length of resistor is halved and potential difference is double ?
| Electrical device | Operating voltage (V) | Power of the device (P) | Current through the circuit $$I = P/V$$ | The amperage of the fuse to be used in the circuit (A) |
| Water heater | 230V | 4370 W | 20 A | |
| Air conditioner (AC) | 230V | 3335 W | 15 A | |
| Television (LED-TV) | 230V | 57.5 W | 0.3 A | |
| Computer (Laptop) | 230V | 28.75 W | 0.2 A |
If the resistance of two soldering irons working in 250 V are 500 $$\Omega$$ and 750 $$\Omega$$.
a. Calculate which one of these will carry more current.
b. Find out which soldering iron has more power.
c. Calculate the heat produced in 5 minutes in the soldering iron having resistance 750 $$\Omega$$.
When a 12 V battery is connected to resistor, 2.5 mA current flows through the circuit. If so what is the resistance of the resistor?
Operating voltage
Resistance of the device (R) Currents flowing in the device
$$I = V/R$$ Heat generated per second, Heat
$$H = V \times I \times t$$ Power given by the device
$$P = V \times I$$ or $$P = H/t$$ Reason for the change in power 230V 57.5 $$\Omega$$ 4A 920J 920W Difference in resistance 230V 11.5 $$\Omega$$ 2A 460J 460W Difference in resistance 230V 230 $$\Omega$$ 1A 230J 230W Difference in resistance 115V 57.5 $$\Omega$$ 2A 230J 230W Difference in resistance 460V 57.5 $$\Omega$$ 8A 3680J 3680W Difference in resistance
The table shows details of an electric heating device designed to work in 230 V. Complete the table by calculating the change in the heat and power on changing the voltage and resistance of the device. Analyze the table and answer the following question.
What change happens to power on increasing the resistance without changing the voltage?
| Operating voltage | Resistance of the device (R) | Currents flowing in the device $$I = V/R$$ | Heat generated per second, Heat $$H = V \times I \times t$$ | Power given by the device $$P = V \times I$$ or $$P = H/t$$ | Reason for the change in power |
| 230V | 57.5 $$\Omega$$ | 4A | 920J | 920W | Difference in resistance |
| 230V | 11.5 $$\Omega$$ | 2A | 460J | 460W | Difference in resistance |
| 230V | 230 $$\Omega$$ | 1A | 230J | 230W | Difference in resistance |
| 115V | 57.5 $$\Omega$$ | 2A | 230J | 230W | Difference in resistance |
| 460V | 57.5 $$\Omega$$ | 8A | 3680J | 3680W | Difference in resistance |
An electric heater conducts 4 A current when 60 V is applied across its terminals. What will be the current if the potential difference is 120 V?
Given below questions are related with heating of an electric iron box. Answer them.
a. Which is the part that produces heat in an electric iron?
b. Which nature of this part is made use in the above situation?
c. What is the relation between intensity of electric current and heat energy generated?
d. What are the factors that affect the heat generated in such heating appliances?
e. What is the relation connecting these factors with the heat generated?
f. What is this law known as?
g. Name a device that works on this law used for ensuring safety in electric circuits?
| Electric appliance | Energy change (electrical energy $$\to$$) | Effect of electric current |
| Bulb | .......a....... | Lighting effect |
| Electric Fan | Mechanical Energy | ........b......... |
| Electric Iron box | ........c....... | Heating effect |
| Strong battery (While charging) | Chemical Energy | .........d......... |
A 800 W electrical device is designed to work in 200 V. What will be its power if the device is working in 100 V?
If we apply 220 V for a device having 230 V and 400 W, what will happen to the power of the device?
(increases, decreases, doesn't change)
| Electric current intensity is made three times | Heat produced becomes ....(1).... |
| In a circuit, fuse wire is connected in | ......(2)..... |
| Electric current intensity is reduced to $$1/4$$ | Heat produced becomes ....(3).... |