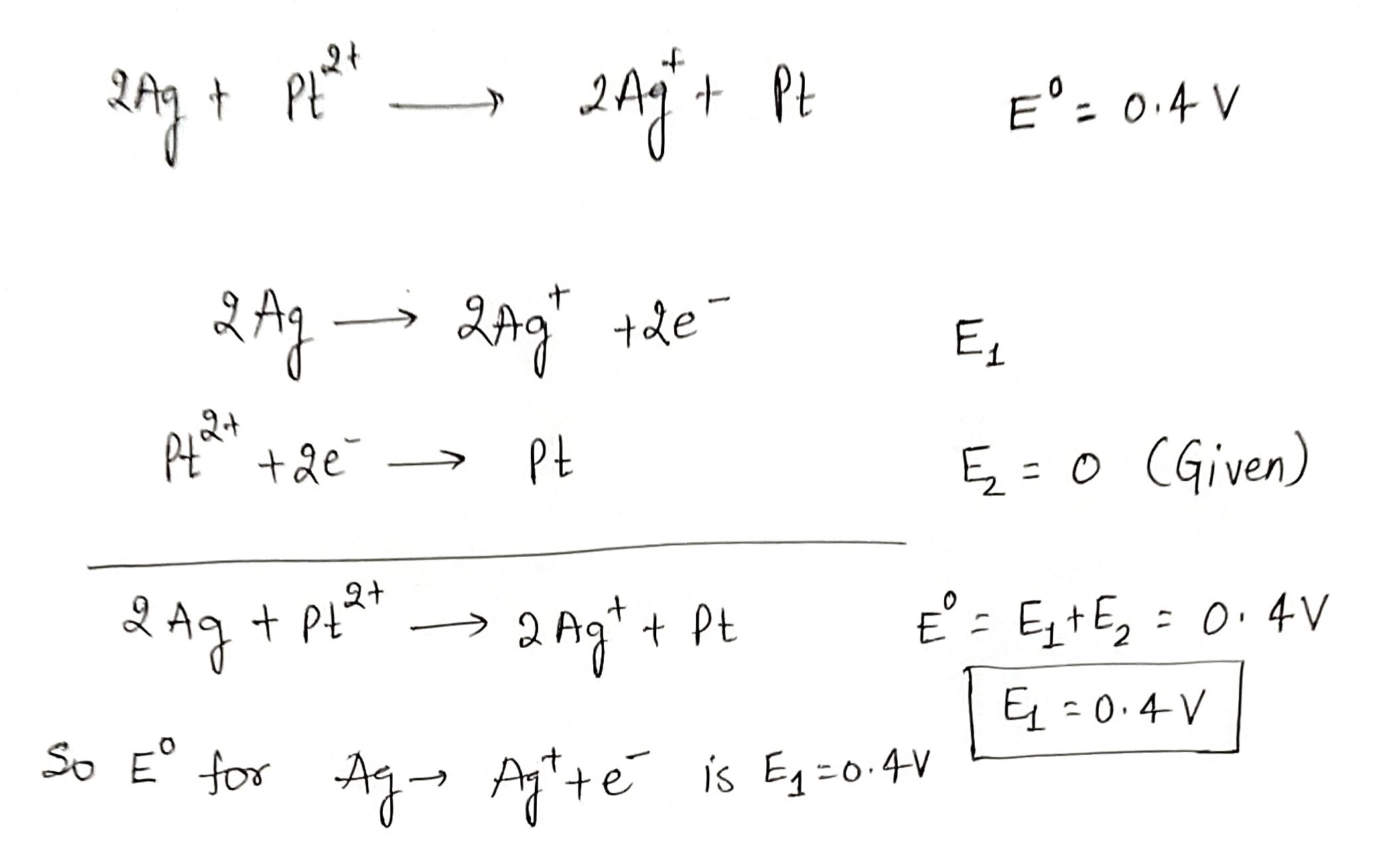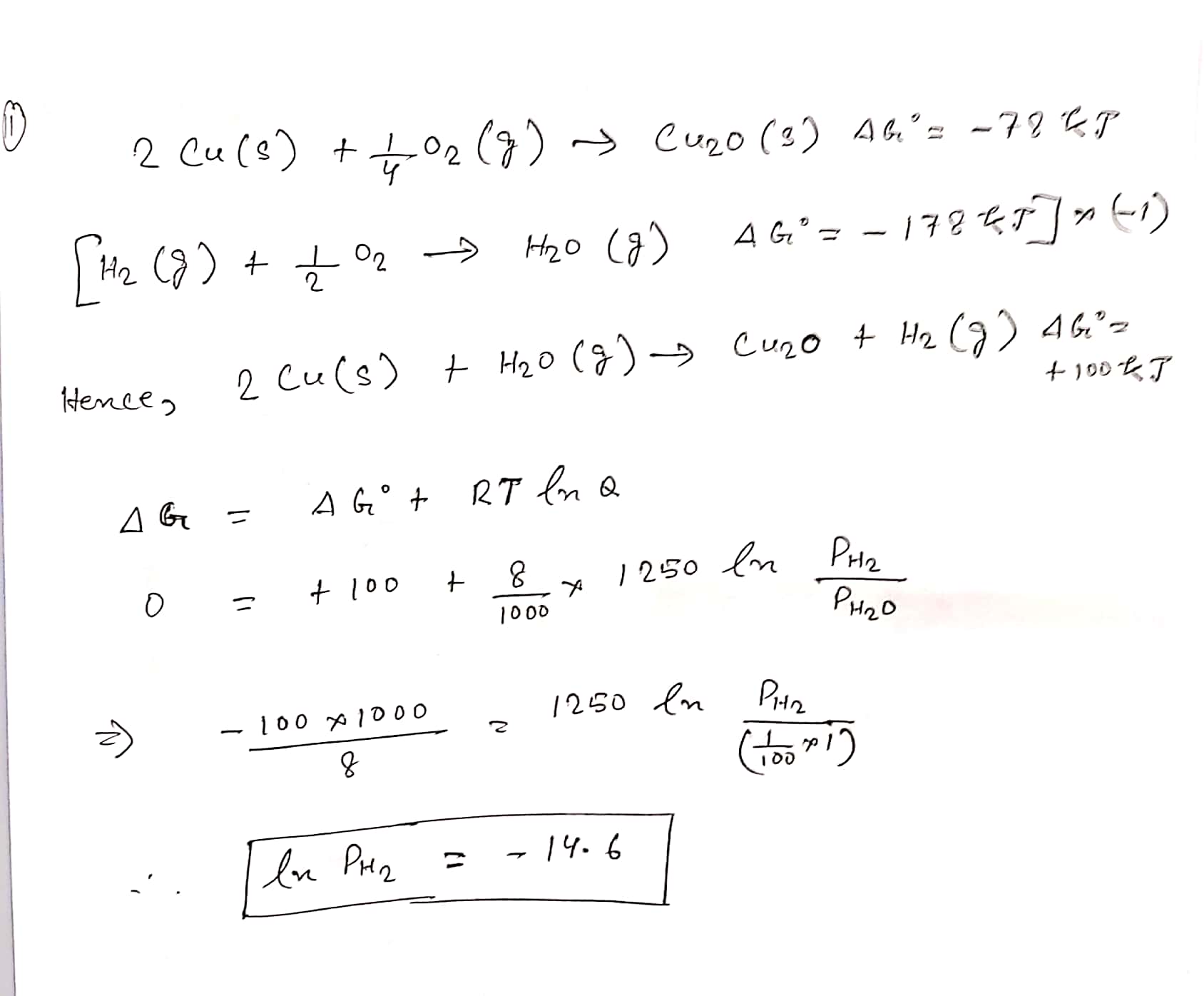Electrochemistry - Class 12 Medical Chemistry - Extra Questions
Lead is able to displace silver from AgNO$$_3$$ solution because its standard oxidation potential is higher than that of silver. If true enter 1, else enter 0
Calculate $$ E^{\ominus}_{cell} $$:
Given : $$E^{\ominus}_{Ag^{\oplus}\, |\, Ag}\, =\, 0.80$$.
The standard electrode potential $$(E^{\circ})$$ for Daniel cell is $$+1.1\ V$$. Calculate $$\Delta G^{\circ}$$ for the reaction.
$$Zn(s) + Cu_{(aq)}^{2+} \rightarrow Zn_{(aq)}^{2+} + Cu(s)$$
$$(1\ F = 96500\ C/mol)$$
Jamila started noticing some kind of reddish brown particles around a photo frame, which is an old one. Why it could have happened and what is it?
(a) Explain the effect of temperature and catalyst on the rate of a reaction.
(b) State Faraday's first law of electrolysis.
A solution of $$CuSO_4$$ is Electrolysed for 10 minutes with a current of 1.5 amperes. What is the mass of copper deposited at the cathode?
State Faraday's laws of electrolysis.
Resistance of a conductivity cell filled with 0.15 mol $$L^{-1}$$ NaCl solution is 50 $$\Omega$$. If resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.02 mol $$L^{-1}$$ NaCl solution is 500 $$\Omega$$, calculate the conductivity of 0.02 mol $$L^{-1}$$ NaCl solution. (The conductivity of 0.15 mol $$L^{-1}$$ NaCl solution is 1.5 s/m).
Distinguish between electrolytic cell and galvanic cell.
State Faraday's first law of electrolysis. For the electrode reaction $$Zn^{2+}+2e^- \rightarrow Zn_{(s)}$$, what quantity of electricity in coulombs required to deposit one mole of zinc?
Define : Standard electrode potential.
Define corrosion. What is meant by rust? Write the chemical formula of rust.
Use $$E^{\circ}$$ values to calculate $$\triangle G^{\circ}$$ for the reaction
$$Fe^{2+} + Ag^{+}\rightarrow Fe^{3+} + Ag$$
$$E^{\circ}_{Ag^{+}/Ag} = 0.80\ volt$$ and $$E^{\circ}_{Pt/ Fe^{3+}, Fe^{2+}} = 0.77\ volt$$.
Solutions of two electrolytes $$A$$ and $$B$$ each having concentration of 0.2 M have conductivities $$2 \times {10^{ - 2}},4 \times {10^{ - 4}}{\text{S/cm}}$$ respectively. Which will offer greater resistance to the file of current and why?
What are galvanic cells? Explain the construction and working of galvanic cell with an example?
If the density of copper is $$8.94 g/cm^3$$, the quantity of elctricity required to plate an area $$100CM^2$$ of the thickness of $$10^{-2}$$ cm using $$CuSO_4$$ solution as electrolyte is:
Explain the term corrosion with examples.
For the cells$$2Ag+Pt^{2+}\rightarrow 2Ag^++Pt; E^0=0.4$$V$$2Ag+F_2\rightarrow 2Ag^++2F^-; E^0=2.07$$V.If the potential for the reaction $$Pt\rightarrow Pt^{2+}+2e^-$$ is assigned as zero, determine the potential for the following electrodes.$$Ag \rightarrow Ag^+ + e^-$$
An electron beam can undergo diffraction by crystals. Through what potential should a beam of electrons be accelerated so that its wavelength becomes equal to $$1.54\overset{o}{A}$$?
Resistance of a conductivity cell filled with $$0.1 M KCl$$ solution is 100 $$\Omega$$. If the resistance of the same cell when filled with $$0.02 M KCl$$ solution is 520 $$\Omega$$. Calculate the conductivity and molar conductivity of 0.02 M $$KCl$$ solution. [Given conductivity of 0.1 M KCl is 1.29 $$sin^{-1}$$]
The resistance of a solution 'A' is 50 ohm and that of the solution 'B' is 150 ohm, both solution being taken in the same conductivity cell. If equal volumes of solution A and B are mixed, what will be the resistance of the mixture using the same cell? (Assume that there is no increase in the degree of dissociation of A and B on mixing)
If you leave a piece of iron in the open area for a few days, it acquires a film of brownish substance, called rust.a) Do you think rust is different from iron?b) Can you change rust back into iron by some simple method?
Which two metals do not corrode easily ? Give example in each case to support that
Corrosion of some metals is a serious problem.
Which two metals do not corrode easily ? Give example in each case to support that
Corrosion of some metals is an advantage.
Among $$Zn$$ and $$Cu$$, which would occur more readily in nature as metal and which as ion?
Give equation to show the chemical reactions of zinc and lead where it displaces copper from its compound.
Why should we paint the iron bars of window?
Give reasons for the following statements.
$$\bullet$$ Tamarind is not stored in aluminium vessels.
$$\bullet$$ It is a common practice to apply oil on iron articles and tools.
$$\bullet$$ Stainless steel knives instead of iron knives are preferred for cutting citrus fruits.
Is there any advantage, if iron nails are kept inside kerosene. Why?
The e.m.f. of the cell $$Cd\begin{vmatrix}Cd Cl_2\\ 1M\end{vmatrix} \begin{vmatrix}AgCl(s)\\ \end{vmatrix}Ag$$ is 0.675 volt at 25$$^o$$C. The temperature coefficient of the cell is $$-6.5 \times 10^{-4} Volt \space K^{-1}$$. If heat of the reaction is $$x$$ kJ then $$-100x$$ is :
$$E^o_{cell}$$ for reaction,
$$4Al(s) + 3O_2(s) + 6H_2O + 4OH^- \rightarrow 4 [Al(OH)_4^-]$$ is 2.73 V.
If $$\triangle{G}_f^o$$ for $$OH^-$$ and $$H_2O$$ are - 157 kJ mol$$^{-1}$$ and - 237.2 kJ mol$$^{-1}$$. If $$\triangle{G}_f^o$$ for $$[Al(OH)_4]^-$$ is $$x$$ kJ.
$$-x$$ is:
If $$E^o_1, E^o_2$$ and $$E^o_3$$ are standard oxidation potentials for $$Fe | Fe^{2+} , Fe^{2+} | Fe^{3+}$$ and $$Fe| Fe^{3+}$$, then $$E^o_3 = \displaystyle \frac{E^o_2 + 2E^o_1}{n}$$. The value of n is:
If for the following half-cell reactions :
$$Cu^{2+}\, +\, e^{-}\, \rightarrow\, Cu^{\oplus}$$;
$$E^{\oplus}\, =\, 1.77\, V$$
$$Cu^{2+}\, +\, 2e^{-}\, \rightarrow\, Cu$$;
$$E^{\ominus}\, =\, -\, 0.34$$
The $$E^{\ominus}$$ of the half-cell reaction will be (in V)
$$Cu^{\oplus}\, +\, e^{-}\, \rightarrow\, Cu$$
$$\Delta G$$ for the reaction, $$\displaystyle \frac{4}{3} Al + O_2 \rightarrow \frac{2}{3} Al_2O_3,$$ is -772 kJ mol$$^{-1}$$ of $$O_2$$. The minimum E.M.F. in volts required to carry out electrolysis of $$Al_2O_3$$ is:
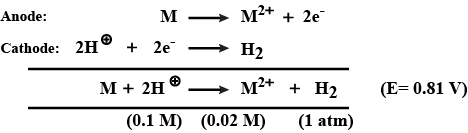
If the EMF of a cell :
$$M\, |\, M^{2+}\, (0.02\, M)\, ||\, H^{+}\, (0.1\, M)\, |\, H_{2}$$ (1 atm)
at $$25^{\circ}\, C$$ is 0.81V. Find the standard reduction potential of $$M$$.(Write a value to the nearest integer. If an answer is negative then write its magnitude)
$$M\, |\, M^{2+}\, (0.02\, M)\, ||\, H^{+}\, (0.1\, M)\, |\, H_{2}$$ (1 atm)
at $$25^{\circ}\, C$$ is 0.81V. Find the standard reduction potential of $$M$$.
(Write a value to the nearest integer. If an answer is negative then write its magnitude)
The resistance of a solution A is 50 ohms and that of solution B is 100 ohms, both solutions being taken in the same conductivity cell. If equal volumes of solution A and B are mixed, the resistance (in ohms) of the mixture using the same cell will be $$13x+2$$. Then $$x$$ is:
Assume that there is no increase in the degree of dissociation of A and B on mixing. (write the value to the nearest integer)
In the button cells widely used in watches and other devices the following reaction takes place:
$$Zn(s) + Ag_{2}O(s) + H_{2}O(l) \rightarrow Zn^{2+}(aq) + 2Ag(s) + 2OH^{-}(aq)$$
Determine $$\Delta_{r} G^{\theta}$$ and $$E^{\theta}$$ for the reaction.
Answer the following, in short, using a maximum $$30$$ words.
Explain Faraday's first law of electrolysis.
A galvanic cell consists of a metallic. zinc plate immersed in 0.1 M $${\text{Zn}}{\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{2}}}$$ solution and metallic plate of lead in 0.02 M $${\text{Pb}}{\left( {{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}} \right)_{\text{2}}}$$ solution. Calculate the emf of the cell write the chemical equation for the electrode reactions and represent the cell. (Given $${\text{E}}{^\circ _{Z{n^{2 + }},Zn}} = - 0.76V,\,E{^\circ _{P{b^{2 + }},Pb}} = 0.13V$$)
According to the equation $$Cu^{2+}+2e^- \rightarrow Cu$$, how much moles of copper are deposited when $$965C$$ of electricity is passed through a solution of $$Cu^{2+}$$ ions? $$(1F=96500\,C)$$
Why is an external emf of more than $$2.2\ V$$ required for the extraction of $$Cl_{2}$$ from brine?
The electrical resistance of a column of 0.05 M $$NaOH$$ solution of diameter 1 cm and length 50 cm is $$5.55 \times 10^3$$ ohm.Calculate its conductance, resistivity, conductivity and molar conductivity.
The surface of copper gets tarnished by the formation of copper oxide. $$N_2$$ gas was passed to prevent the oxide formation during heating of copper at $$1250$$ K. However, the $$N_2$$ gas contains 1 mole per cent of water vapour as an impurity. The water vapour oxidises copper as per the reaction given below:
$$2Cu(s) + H_2O(g) \rightarrow Cu_2O(s) + H_2(g)$$
$$ P_{H_2}$$ is the minimum partial pressure of $$H_2$$ (1 bar) needed to prevent the oxidation at 1250 K. The value of In$$(P_{H_2})$$ is .......
[Given: Total pressure = 1 bar, $$R$$ (universal gas constant) = $$8 J K^{-1} mol^{-1}, ln (10) = 2.3, CuO(s)$$ and $$Cu_2O(s)$$ are mutually immiscible.
At 1250 K: $$2Cu(s) + \dfrac{1}{2}O_2(g) \rightarrow Cu_2O(s), \Delta G^0 = -78,000 \ J mol^{-1}$$
$$H_2(g) + \dfrac{1}{2}O_2(g) \rightarrow H_2O(g); \Delta G^0 = 1,78,000 \ J mol^{-1}$$
What is electrode potential?
A strip of nickel metal is placed in a $$ 1 $$ molar solution of $$ Ni(NO_3)_2 $$ and a strip of silver metal is placed in a $$ 1$$ molar solution of $$ AgNO_3 $$ . An electrochemical cell is created when the two solutions are connected by a salt bridge and the two strips are connected by wires to a voltmeter .
(i) Write the balanced equation for the overall reaction occurring in the cell and calculate the cell potential .
(ii) Calculate the cell potential , E at $$ 25^{\circ} \,C $$ for the cell if the initial concentration of $$ Ni(NO_3)_2 $$ is $$ 0.100 $$ molar and the initial concentration of $$AgNO_3 $$ is $$ 1.00 $$ molar .
$$ [E^{\circ}_{Ni^{2+} / Ni} = - 0.25\,V ; E^{\circ}_{Ag/Ag} = 0.80 \,V , log \, 10^{-1} = -1] $$
Class 12 Medical Chemistry Extra Questions
- Alcohols, Phenols And Ethers Extra Questions
- Aldehydes, Ketones And Carboxylic Acids Extra Questions
- Biomolecules Extra Questions
- Chemical Kinetics Extra Questions
- Chemistry In Everyday Life Extra Questions
- Coordination Compounds Extra Questions
- Electrochemistry Extra Questions
- General Principles And Processes Of Isolation Of Elements Extra Questions
- Haloalkanes And Haloarenes Extra Questions
- Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Extra Questions
- Polymers Extra Questions
- Solutions Extra Questions
- Surface Chemistry Extra Questions
- The D-And F-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The P-Block Elements Extra Questions