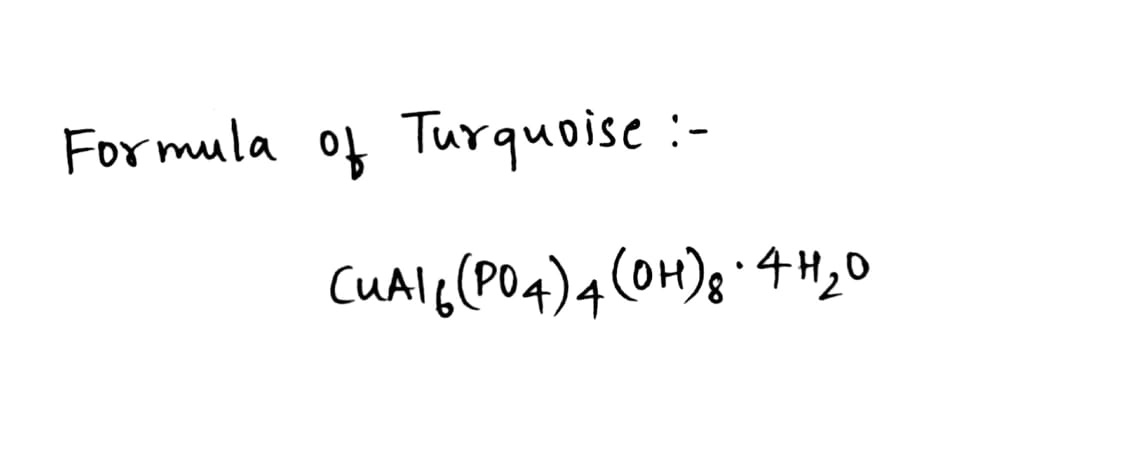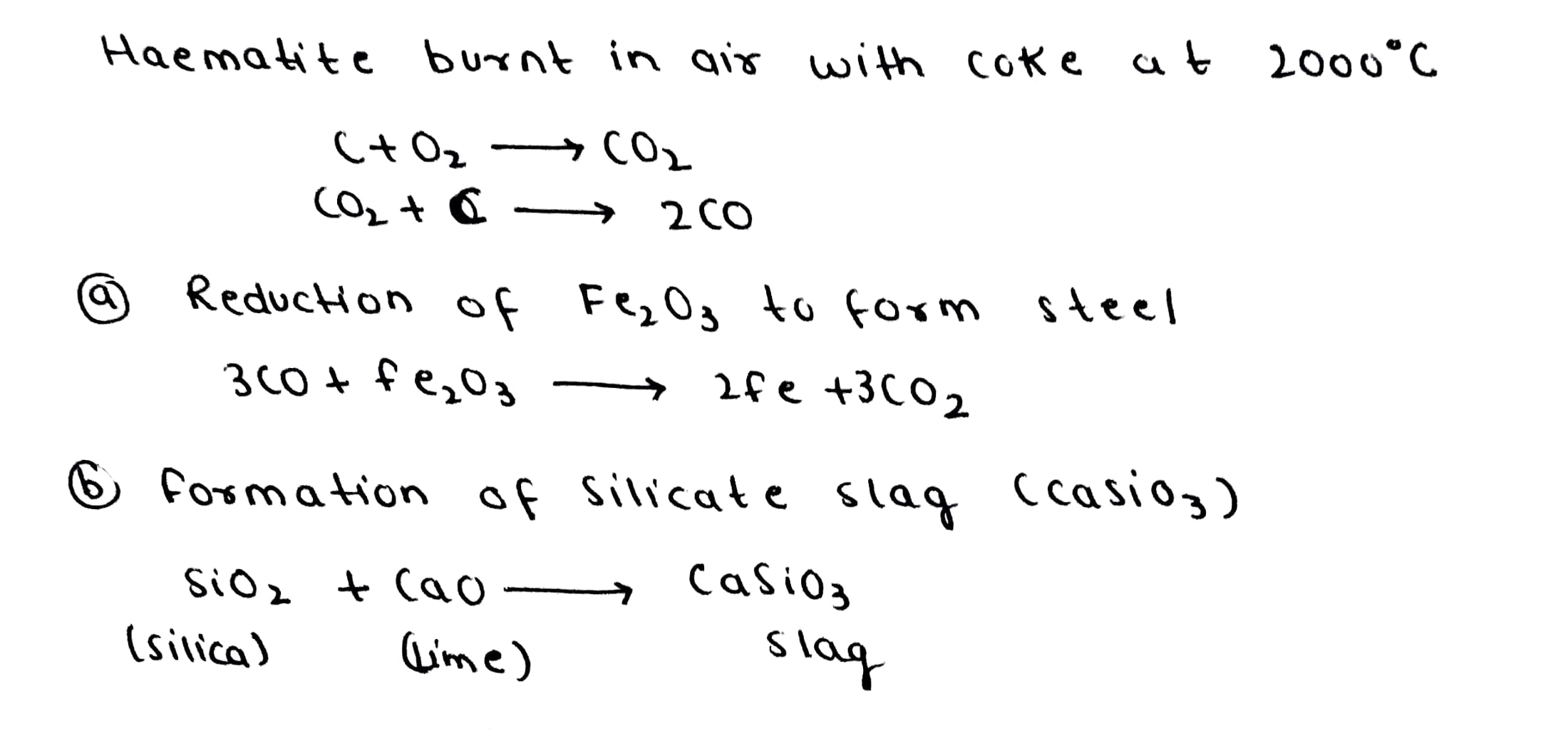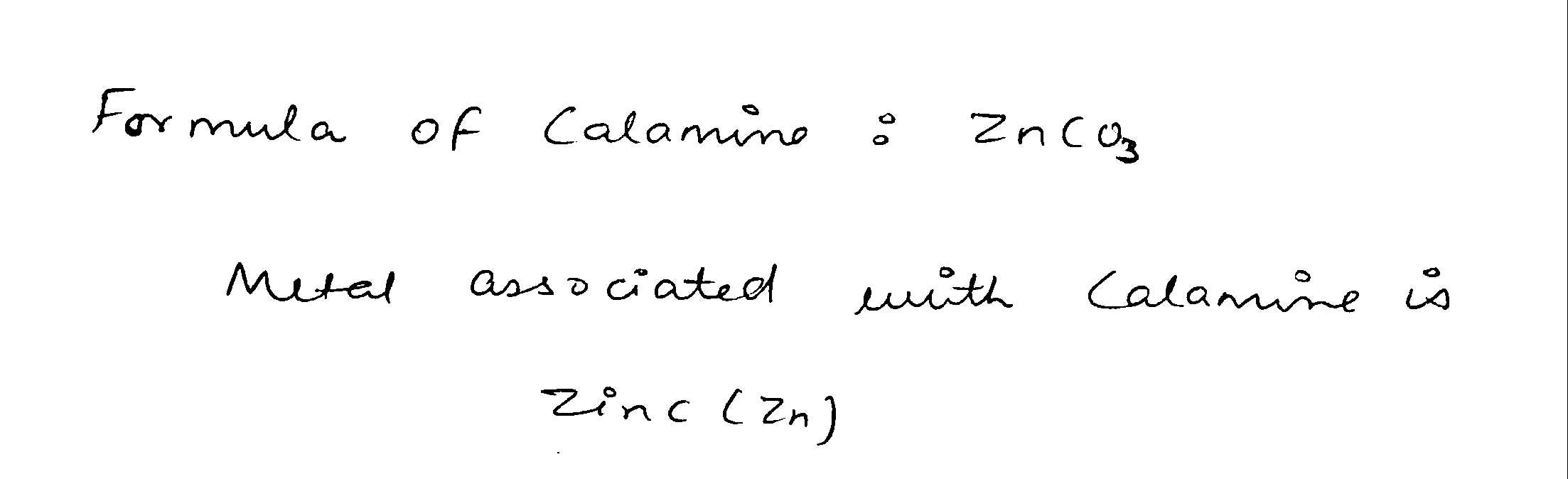General Principles And Processes Of Isolation Of Elements - Class 12 Medical Chemistry - Extra Questions
Write 'two' names and their chemical formulae of ores of zinc.
Explain the extraction of zinc from its chief ore.
Ellingham diagram in the extraction of zinc.
Explain the extraction of zinc from its important ore.
While extracting iron from its ore,out of slag and molten iron, which one floats at the surface?
A metal M found in nature as sulphide ore ($$M_2S$$) is one of the good conductors of heat and electricity and used in making electric wires. The metal M is _______ .
We have $$CuSO_4$$ solutions (blue) in two beakers A and B. In beaker A we add Ag pieces and in B we add Zn pieces. What will happen in B?
The following reactions take place during the extraction of copper from copper ore:
(a) $$2Cu_2S(l)\,+\,3O_2(g)\, \rightarrow\, 2Cu_2O(l)\, 2Cu_2O(l)\, +\, 2SO_2(g)$$
(b) $$2Cu_2O(l)\, +\, Cu_2S(l)\, \rightarrow\, 6Cu(l)\, +\, SO_2(g)$$
If $$Cu_2O$$ and $$Cu_2S$$ act as oxidising and reducing agent respectively in reaction (b) then enter 1 else 0.
Consider following reactions:
(a) $$2ZnS\,+\, 3O_2\, \rightarrow\, 2ZnO\, +\, 2SO_2$$
$$ZnO\,+\, C\, \rightarrow\, Zn \, +\, CO$$
(b) $$2ZnS\,+\,C\, \rightarrow\, 2Zn\, +\, CS_2$$A
B
A and B are same
None
Sulphide ore is converted into pure metal (say $$Cu$$) by following steps.
Bessemerisation $$\rightarrow$$ Roasting $$\rightarrow$$ Electrolysis
The transition metal present in the alloy gun metal is Cu.
Match column A with column B and select the correct option-
Why is the extraction of copper from pyrites more difficult than that from its oxide ore through reduction?
Which reducing agent is employed to get copper from the leached low grade copper ore?
Describe the role of the following:
(i) $$Si{O}_{2}$$ in the extraction of copper from copper matte.
(ii) $$NaCN$$ in froth floatation process.
Write the names of any two ores of iron.
Zinc can displace __________ from $$CuSO_4$$ solution, but cannot displace _______ from $$MgSO_4$$ solution.
In the extraction of zinc from zinc blende:
How is impure zinc finally electro-refined?
Draw the labelled diagram of vertical retort method used in extraction of zinc and write only equation of chemical reaction in the extraction of zinc from zinc blende?
What is the action of carbon on the following metal oxide.
$$Fe_2O_3$$ in blast furnace.
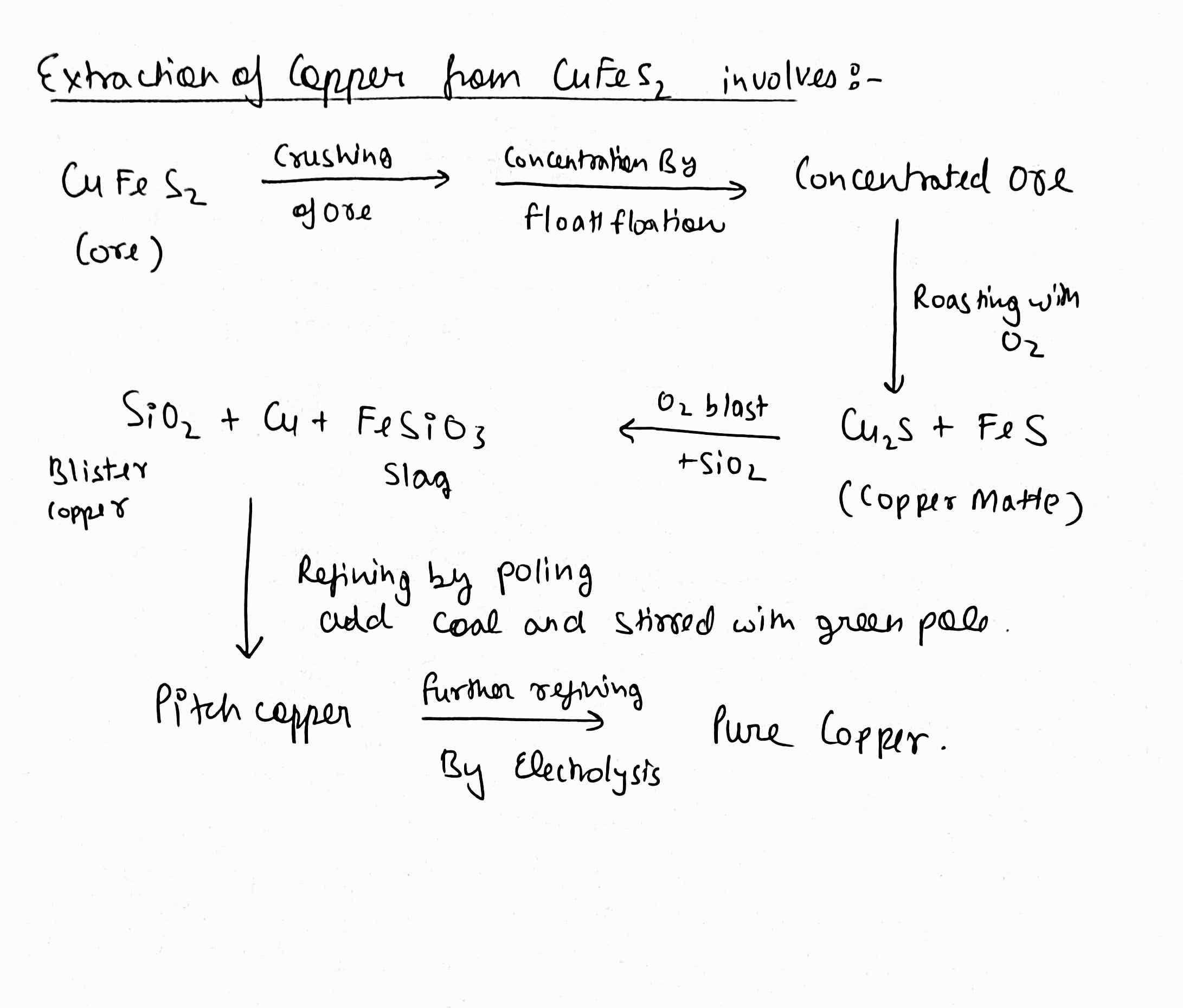
Name the sulphide ore of Copper. Describe how pure copper is extracted from this ore.
Give one word or a phrase for the following statement :
The process by which sulphide ore is concentrated :
The process by which sulphide ore is concentrated :
Given below is the steps for extraction of Copper from its ore. Write the reactions involved.(a) Roasting Copper (I) Sulphide.(b) Reduction of Copper (I) oxide with Copper (I) sulphide
A metal M which is one of the best conductor of heat and electricity used in making electric wires is found in the nature as sulphide ore $$M_2S$$? Which process will be suitable for extraction of this metal M from its ore, $$M_2S$$? Write a balance chemical reaction involved in the process of extraction.
$$CuFeS_{x}$$ (copper pyrite) is an ore of copper. What is the value of '$$X$$' here?
Give the balanced equation for the conversion of argentite into metallic silver.
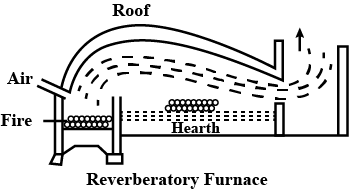
Write the chemical reaction involved in the extraction of copper from copper pyrites using a limited supply of air in a reverberatory furnace.
A metal 'X' acquires a green color coating on its surface on exposure to air.
(i) Identify the metal 'X' and name the process responsible for the change.
(ii) Name and write chemical formula of the green coating formed on the metal.
(iii) List any two important methods to prevent the process.
Explain what is galvanization. What purpose is served by it?
What is calcination?
State what difference will be seen if pure zinc is added in the distillation flask 'X' instead of granulated zinc.
Explain the recovery of copper from solution using scrap iron.
Write balanced equations for "the extraction of copper from copper pyrites by self-reduction."
Write the balanced equation for the extraction of copper from copper pyrites by self-reduction.
In extractive metallurgy of zinc, partial fusion of ZnO with coke is called __________ and reduction of the ore to molten metal is called ________. (smelting, calcining, roasting, sintering)
Which of the following metals can be obtained by the electrolytic reduction of aqueous solution of their salts $$Al, Na, Cu$$ and $$Ag$$?
Describe the principle of extraction of each of the following:$$Zn$$ from $$ZnO.$$
Iron is $$....th$$ most abundant in the earth crust.
Give the balanced equations for the:
Extraction of zinc from zinc blende.
Name two principal ores of each of the following metals:
Copper
Name two principal ores of each of the following metals:
Zinc
Give formula of the following:
Turquoise
Turquoise
Write short notes on the following:
Types of iron
Types of iron
How will obtain:
Copper from copper sulphide.
Answer the following questions:
What is the role of silica in the metallurgy of copper?
Answer the following questions:
Indicate the principle behind the method used for the refining of zinc.
Describe how the following changes are brought about:
Zinc oxide into metallic zinc.
(i) Given below are the steps for extraction of copper from its ore. Write the reaction involved.
(a) Roasting of copper (I) sulphide
(b) Reduction of copper (I) oxide with copper (I) sulphide.
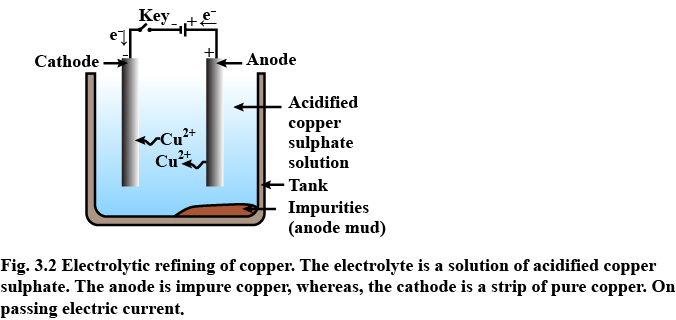
(c) Electrolytic refining
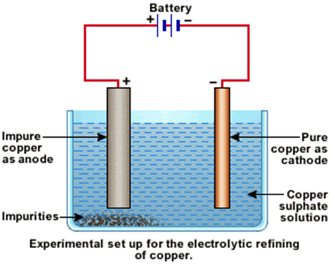
(ii) Draw a neat and well labelled diagram for electrolytic refining of copper
How are the following metallic oxides reduced? Write equations.(a) Iron(II) oxide
(b) Zinc oxide
(b) Zinc oxide
Write chemical equation for the event.
Iron filings are dropped in aqueous solution of copper sulphate.
A to F below relate to the source and extraction of either zinc or aluminium:A. Bauxite
B. Coke
C. Cryolite
D. Froth floatation
E. Sodium hydroxide solution.
F. Zinc blend
(i) Write down the three letters each from the above list which are relevant to:
ZincAluminium
(ii) Fill in the blanks using the most appropriate words from A to F.
The ore from which aluminum is extracted must first be treated with........so that pure aluminium oxide can be obtained.
B. Coke
C. Cryolite
D. Froth floatation
E. Sodium hydroxide solution.
F. Zinc blend
(i) Write down the three letters each from the above list which are relevant to:
ZincAluminium
(ii) Fill in the blanks using the most appropriate words from A to F.
The ore from which aluminum is extracted must first be treated with........so that pure aluminium oxide can be obtained.
Iron is extracted from its oxide ores:
How do you obtain the Wrought form of iron ?
While adding the raw materials into the blast furnace for the extraction of iron, it is forgotten to mix limestone with the charge.
Give reason for this result.
Iron is extracted from its oxide ores:
Name the purest form of iron.
While adding the raw materials into the blast furnace for the extraction of iron, it is forgotten to mix limestone with the charge.
Predict the result of this mistake.
Write name and chemical formula of sulphide and oxide ore of copper.
Explain with equation how does copper purify by electrolytic method?
Write name and chemical formula of sulphide and oxide ores of zinc.
Haematite , magnetite , iron pyrites , etc. are the minerals of iron. Which are the ores of iron among these minerals ?
Which reducing agent is used to extract copper from copper ore (scrap copper), which has very low amount of copper in it? Explain.
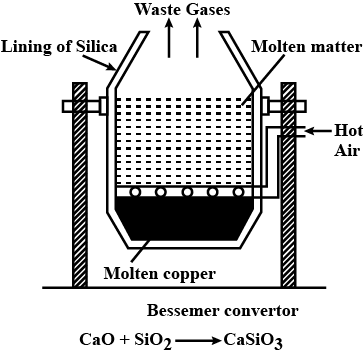
Why silica lines are used in Bessemer convertor in reduction of copper oxide? Write chemical reaction of it and draw labelled diagram.
Complete the following reactions:
(i) $$2Cu_{2}O + Cu_{2}S \rightarrow$$ _____ $$+$$ _____.
(ii) $$Ag_{2}S + NaCN \rightarrow$$ ____ $$+$$ _____.
(iii) $$Al_{2}O_{3} + NaOH\rightarrow$$ ____ $$+$$ ____.
(iv) $$CuFeS_{2} + O_{2}\rightarrow$$ ____ $$+$$ _____.
(v) $$Cu_{2}S +$$ ____ $$+$$ _____ $$Cu + SO_{2}$$.
Which metals have sulfides ores?
Draw labelled diagram and reaction of furnace which is used in metallurgy of copper ore.
How is iron extracted industrially?
Complete the table given below.
Ore of iron Raw material fed into the blast
furnace The compound used for reducing
haematite Gangue Flux Slag Equation of formation of slag
| Ore of iron | |
| Raw material fed into the blast furnace | |
| The compound used for reducing haematite | |
| Gangue | |
| Flux | |
| Slag | |
| Equation of formation of slag |
Given below are the equations for the reaction taking place inside the blast furnace.
$$ C + O_2 \rightarrow CO_2 $$
$$ CO_2 + C \rightarrow 2CO $$
$$ CaCO_3 + SiO_2 \rightarrow CaSiO_3 $$
$$ Fe_2O_3 + 3CO \rightarrow 2 Fe + 3 CO_2 $$
Name the ore of iron.
Complete the table.
Why is $$Fe$$ an abundant element on earth and why are the elements with high atomic numbers increasingly rare?
Given below are the equations for the reaction taking place inside the blast furnace.
$$ C + O_2 \rightarrow CO_2 $$
$$ CO_2 + C \rightarrow 2CO $$
$$ CaCO_3 + SiO_2 \rightarrow CaSiO_3 $$
$$ Fe_2O_3 + 3CO \rightarrow 2 Fe + 3 CO_2 $$
Which is the gangue in iron ore ?
Why is the cosmic abundance of $$Fe$$ very high?
Copper pyrites, $$CuFeS_2$$, is the important source of copper. 10 g of it was leached with dil. $$H_2SO_4$$ and solution diluted to 1 L. 10 mL of this solution required 10 mL of 0.02 M $$KMnO_4$$ in acidic solution. What is % of $$Fe$$ in $$CuFeS_2$$?
$$0.804$$ g sample of iron ore was dissolved in acid. Iron was oxidised to $$+2$$ state and it required $$47.2$$ mL of $$0.112\:N\:KMnO_4$$ solution for titration. If the percentage of $$Fe$$ in the ore (as nearest integer value) is $$6X+1$$. Then $$X$$ is:
What is the role of silica in the metallurgy of copper?
How is copper extracted from a low grade ore of it?
How is copper extracted from its sulphide ore? Explain the various steps supported by chemical equations.
Draw labelled diagram for the electrolytic refining of copper :
Write the steps involved in the extraction of pure metals in the middle of the activity series from their carbonate ores.
Name one chief ore each of copper and aluminium. Name the method used for concentration of these two ores.
Copper can be extracted by hydro-metallurgy but not zinc, Explain.
Write the name and chemical formula of any one ore of iron and zinc each
How is leaching carried out in the case of low grade copper ores? Name the method used for refining of copper metal.
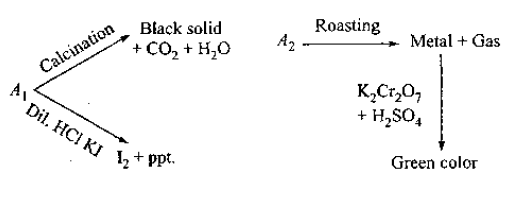
$$A_1$$ and $$A_2$$ are two ores of metal M. $$A_1$$ on calcination gives a black precipitate, $$CO_2$$ and water. Identify $$A_1$$ and $$A_2.$$
Answer the following question briefly:
(i) What is the actual reducing agent of haematite in the blast furnace?
(ii) Zinc not copper is used for the recovery of metallic silver from the complex $$[Ag(CN)_2]^- $$. Explain.
(iii) Why is chalcocite roasted and not calcinated during the recovery of copper?
When the ore haematite is burnt in air with coke around 2000K along with lime, the process not only produces steel but also produces a silicate slag that is useful in making building materials such as cement. Discuss the same and show through balanced chemical equations.
Describe the principle of extraction of each of the following:$$Cu$$ from $$CuFeS_2.$$
Name the metals with which the following ores/ minerals are associated :
Calamine
Give the balanced equations for the:
Extraction of copper from pyrites by self reduction.
How will you obtain Copper from its ore copper glance?
What is the role of limestone in the extraction of iron from its oxides?
You are provided with a sample of some impure metals such as zinc, copper and germanium. Which method would you recoment for the purification of each of these metals?
Answer the following question in details.
Explain extraction of iron.
Predict the mode of occurrence of the following metal:
Moderately reactive (i.e Fe)
Class 12 Medical Chemistry Extra Questions
- Alcohols, Phenols And Ethers Extra Questions
- Aldehydes, Ketones And Carboxylic Acids Extra Questions
- Biomolecules Extra Questions
- Chemical Kinetics Extra Questions
- Chemistry In Everyday Life Extra Questions
- Coordination Compounds Extra Questions
- Electrochemistry Extra Questions
- General Principles And Processes Of Isolation Of Elements Extra Questions
- Haloalkanes And Haloarenes Extra Questions
- Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Extra Questions
- Polymers Extra Questions
- Solutions Extra Questions
- Surface Chemistry Extra Questions
- The D-And F-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The P-Block Elements Extra Questions