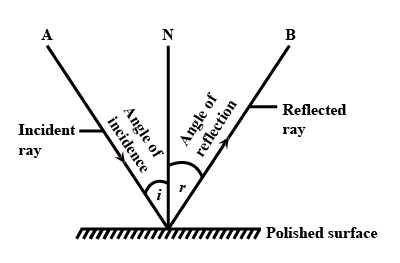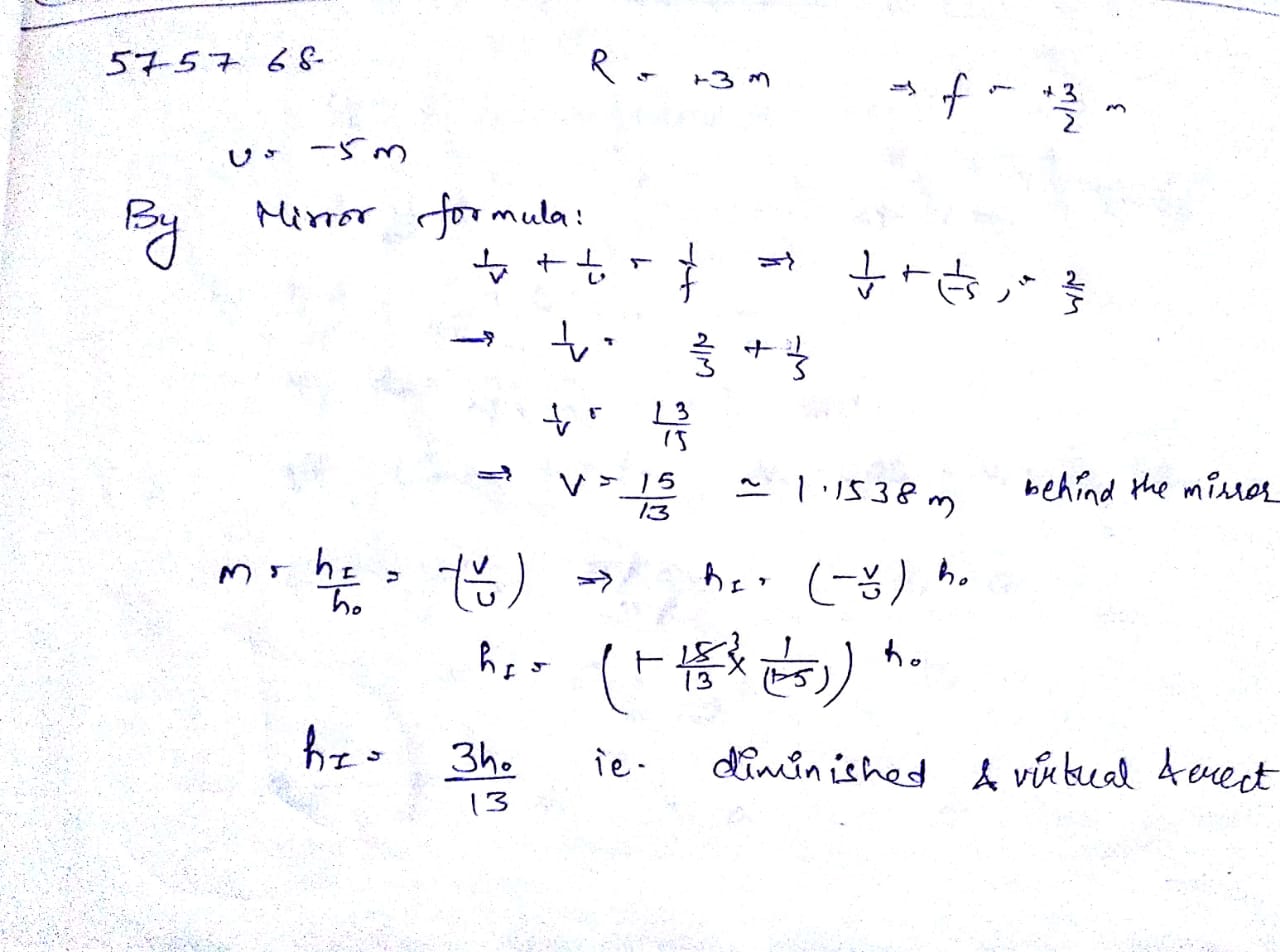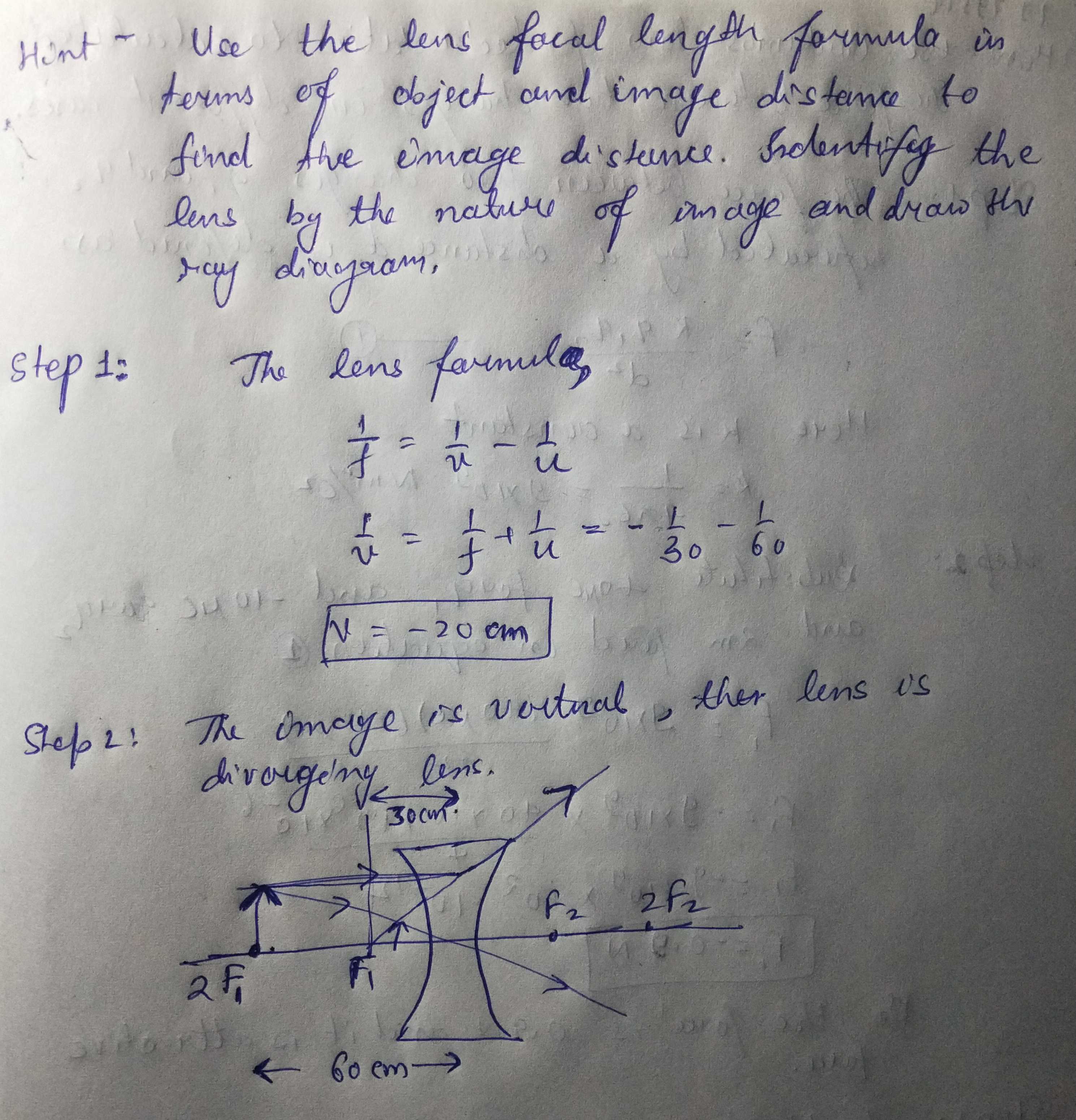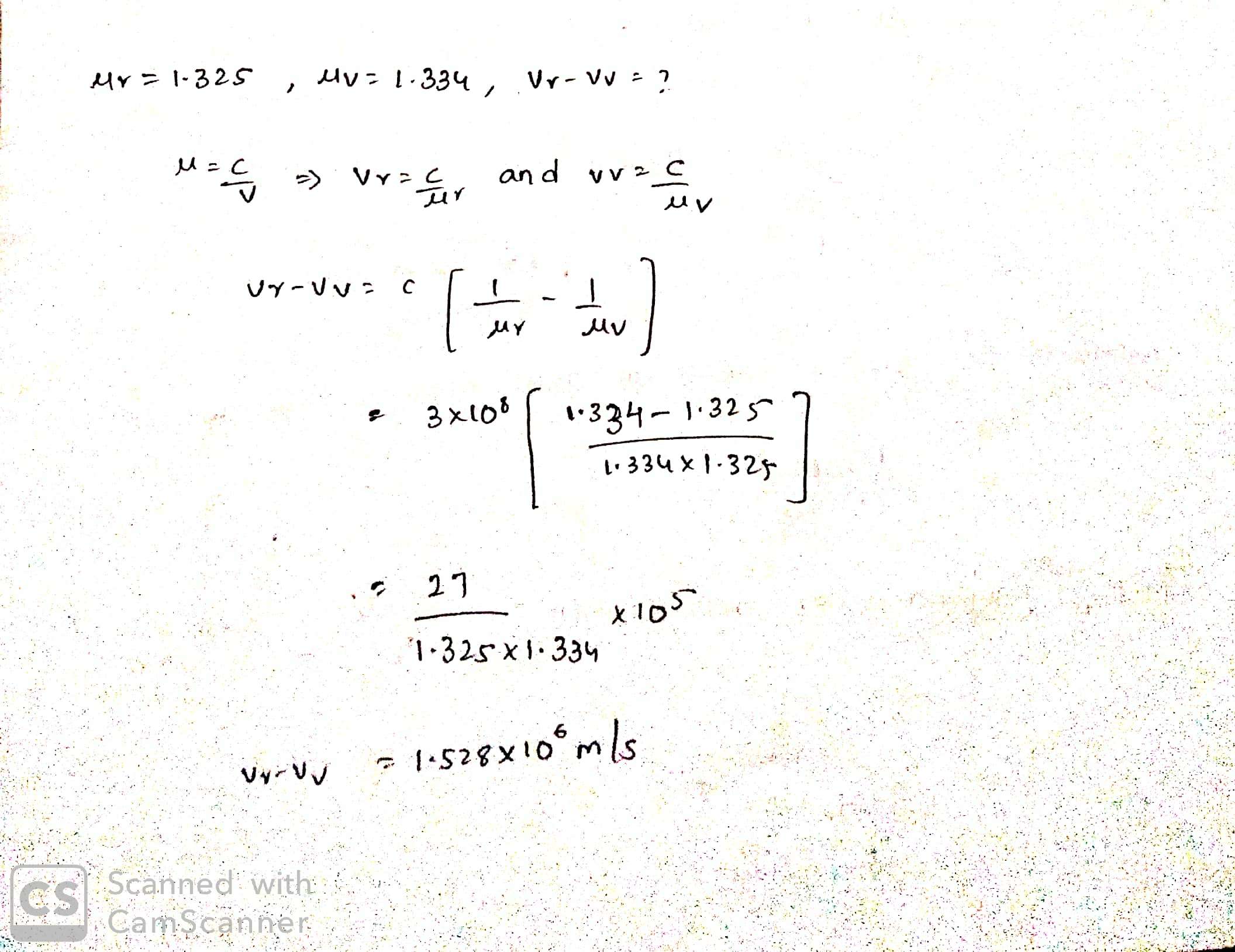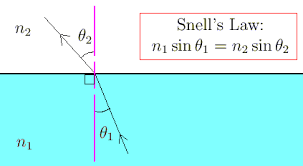Light Reflection And Refraction - Class 10 Physics - Extra Questions
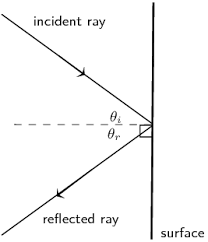
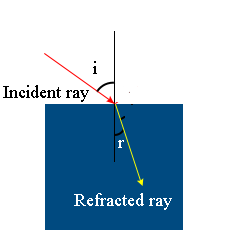
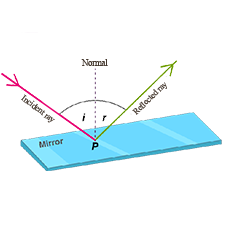
Angle of reflection is the angle between reflected ray and the ........(incident ray, normal).
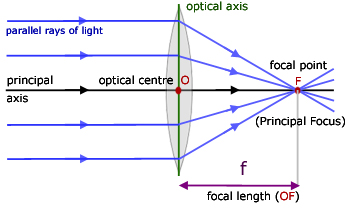
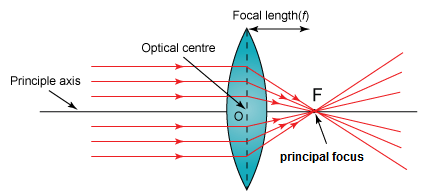
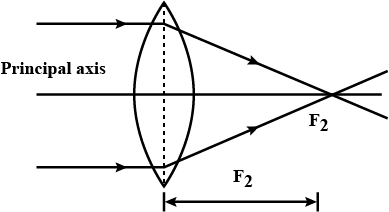
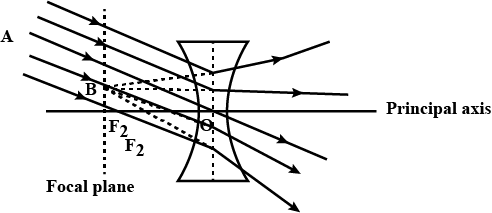
Define focal length of a spherical lens.
What is reflection? Give two examples.
Define normal.
The process of sending back the light rays into the same medium is called _________.
State the characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror.
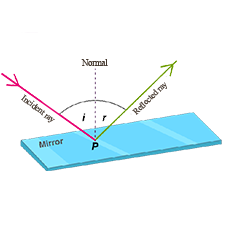
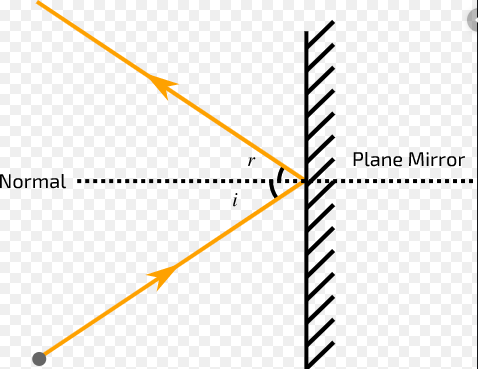
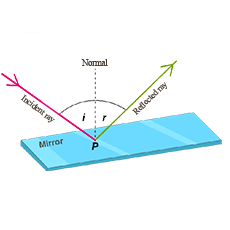
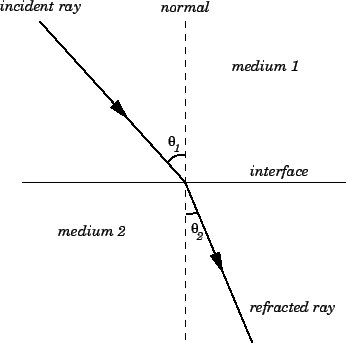
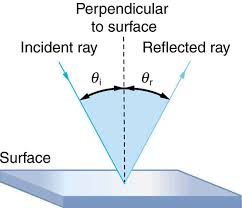
What is reflection of light ? Also write the laws of reflection.
Angle of reflection is the angle between ________ and the ________.
The magnification produced by a mirror is - 1.What does it signify about the image formed ?
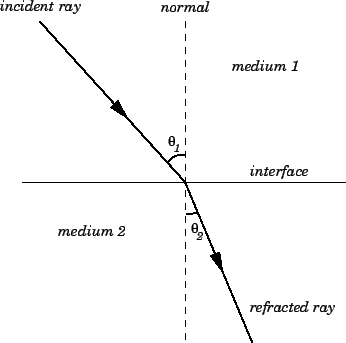
- The incident ray, refracted ray, and the normal to the interface of any two given media, all lie in the same plane
- This is a part of the laws of refraction of light. Type $$1$$ for true and $$0$$ for false.
In refraction through a glass slab with parallel faces, incident ray and emergent ray are parallel. Type 1 for true and 0 for false.
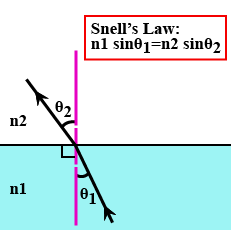
Snell's law of refraction is $$\mu_{1}\sin\theta_{1} = \mu_{2}\sin\theta_{2}$$.Type 1 for true and 0 for false.
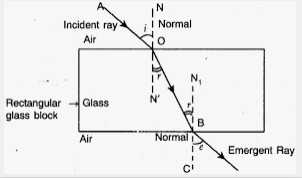
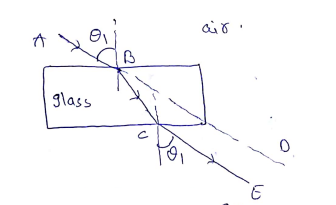
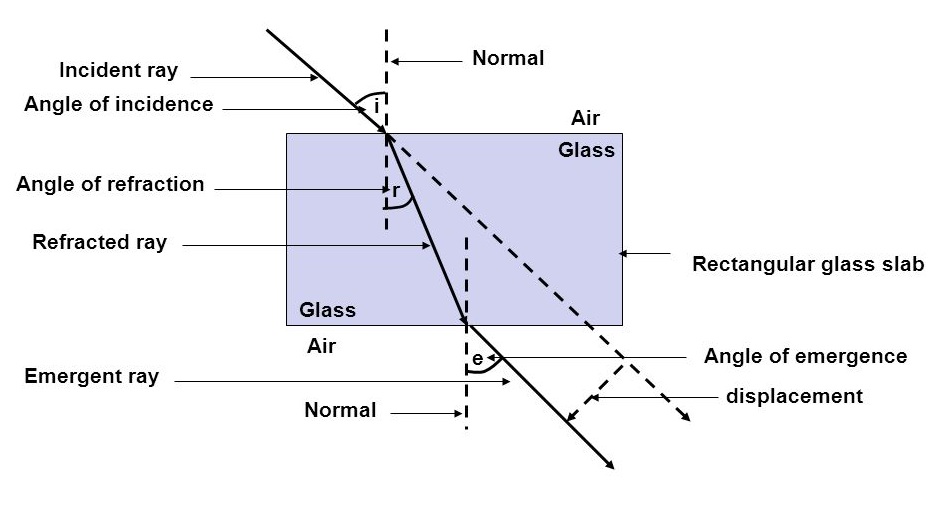
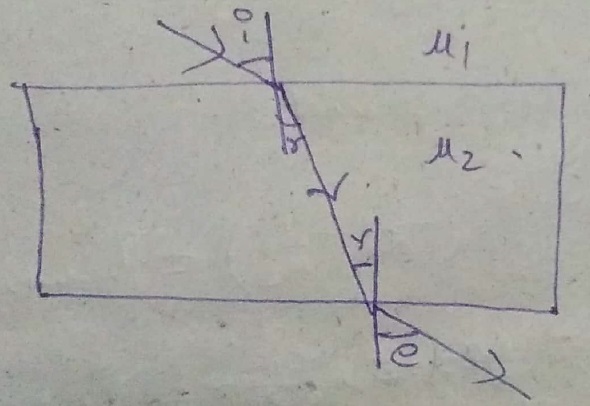
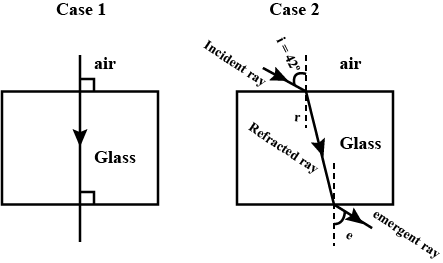
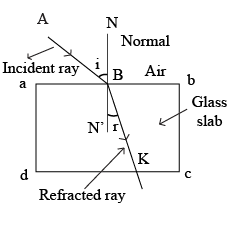
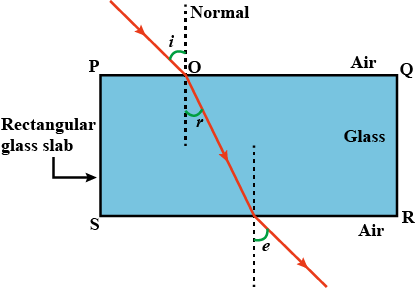
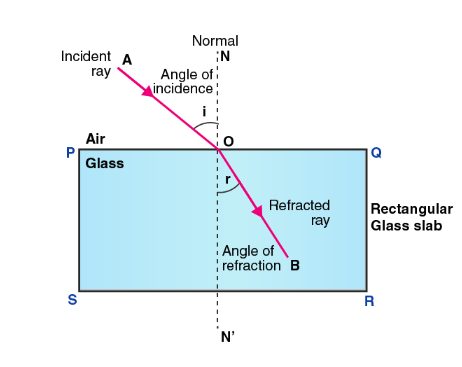
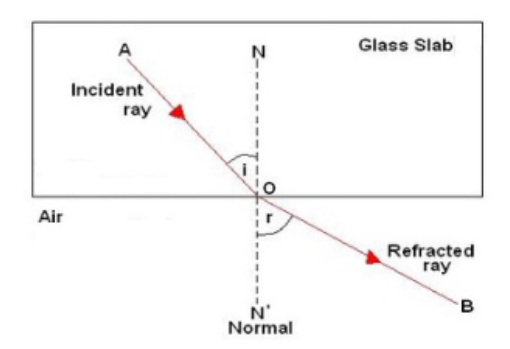
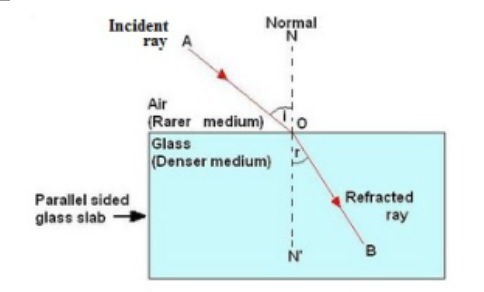
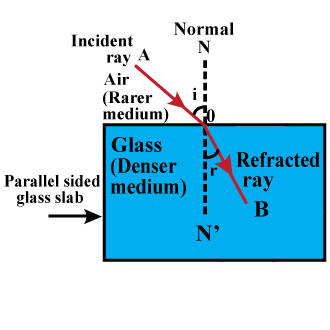
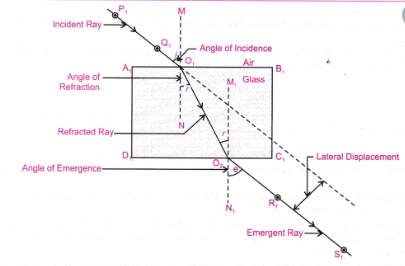
Write laws of refraction of light. Explain the same with the help of ray diagram, when a ray of light passes through a rectangular glass slab.
When a ray of light passes from a rarer to denser medium it bends towards the normal. (True=1 or false=0).
In snells law $$\mu_{1}\sin\theta_{1} = \mu_{2}\sin\theta_{2}$$
Type 1 for true and 0 for flase
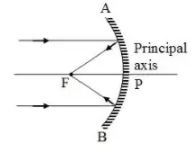
Light rays that are parallel to principal axis of concave mirror get converged at a particular point. It is called principal focus.Type 1 for true and 0 for flase
........ is an imaginary line perpendicular to the surface where the reflection occurs.
...... ray is the ray of light reflected from a surface.
Angle of incidence is the angle between ....... and the .......
State the laws of refraction of light.
When the convex lens acts as a magnifying glass, the object is between the .......... and the optical center of the lens.
State whether the given statement is True or False.
The distance between the principal focus and centre of curvature of a lens is called its radius of curvature.
Match the statements in Column A, with those in Column B.
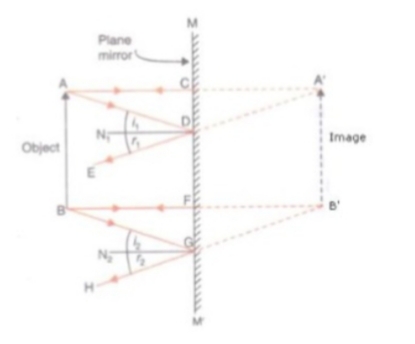
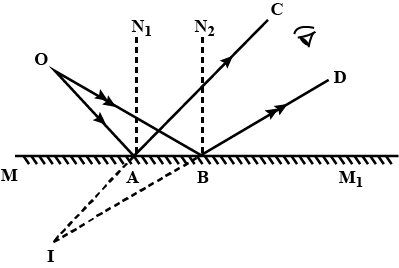
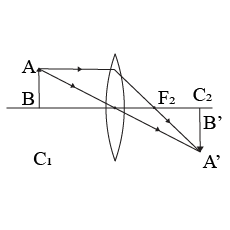
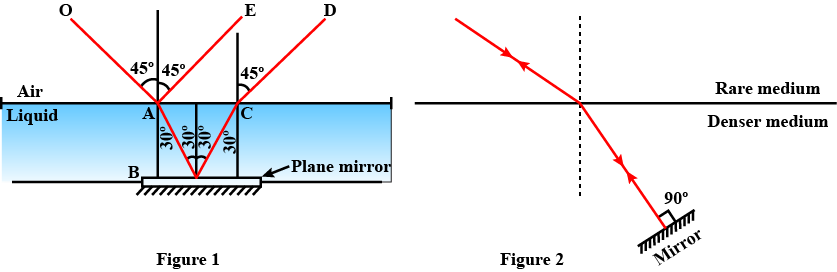
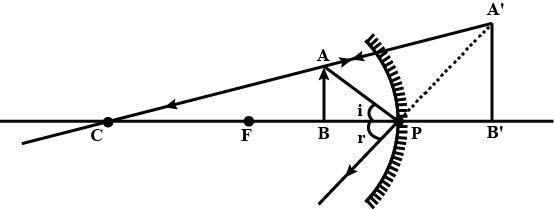
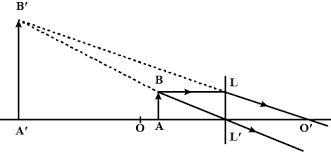
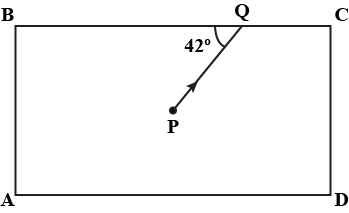
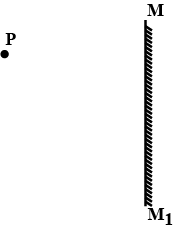
The diagram in a Fig. shows a point object $$P$$ in front of a plane mirror $$MM_1$$.
$$(a)$$ Complete the diagram by taking two rays from the point $$P$$ to show the formation of its image.
$$(b)$$ In the diagram, mark the position of a eye to see the image.
$$(c)$$ Is the image formed real or virtual ? Explain why ?
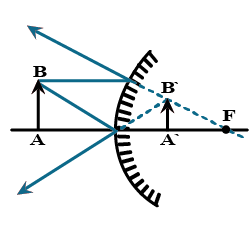
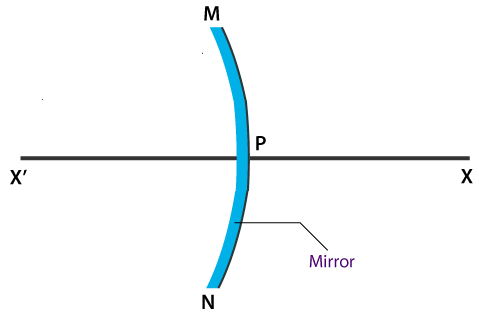
Answer the following:If you are given a part of the hollow spherical glass, how will you convert it into a concave mirror?
List three objects that contain lenses.
For each pair of terms, explain how can you differentiate between them.
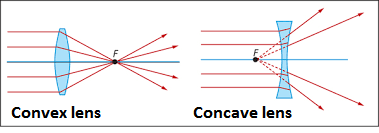
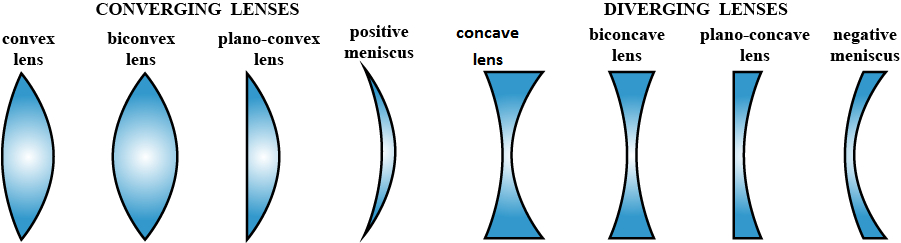
Convex lens and concave lens
A light ray falls on the air glass interface at an angle of $$30^{\circ}$$. What is the angle of refraction for this rays ?
$$(n_{ag}\, =\, \displaystyle \frac {3}{2})$$.
What is the relation between angle of incidence i and angle of refraction r in the glass ?
State Snell's law of refraction of light.
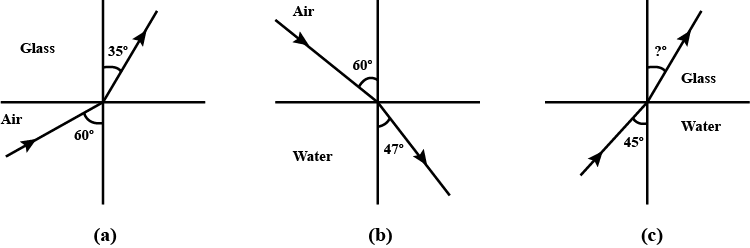
Figures (a) and (b) show the refraction of a ray in air incident at $$60^o$$ with the normal to a glass-air and water-air interface, respectively. Predict the angle of refraction in a glass when the angle of incidence in water is $$45^o$$ with the normal to a water-glass interface [Fig.(c)].
(a) The refractive index of glass is 1.What is the speed of light in glass? (Speed of light in vacuum is $$3.0\times 10^{8} m s^{-1})$$(b) Is the speed of light in glass independent of the colour of light? If not, which of the two colours red and violet travels slower in a glass prism?
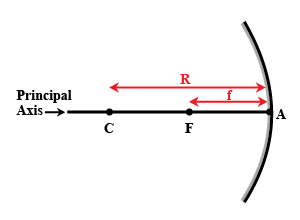
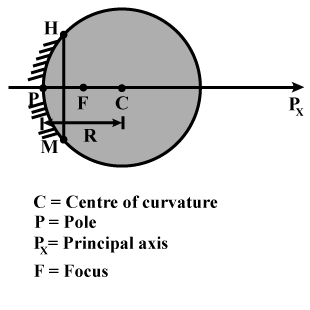
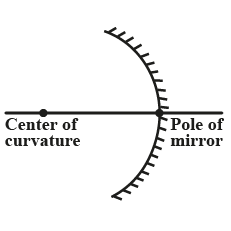
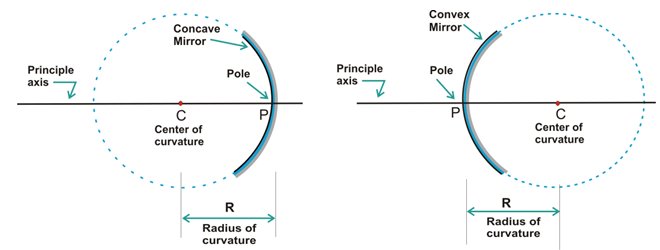
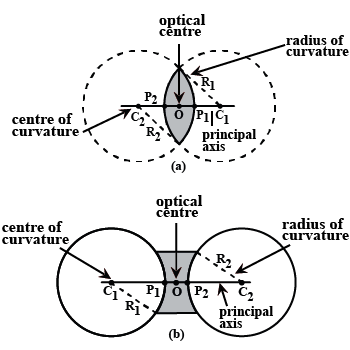
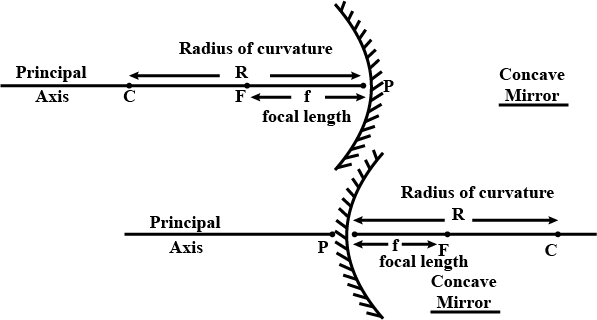
Define radius of curvature.
Define Principle focus of a plane mirror.
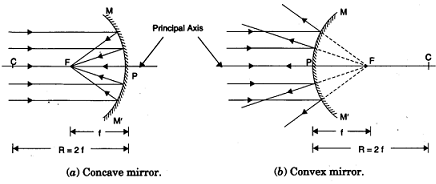
State four points of differences between a Concave mirror and a Convex mirror.
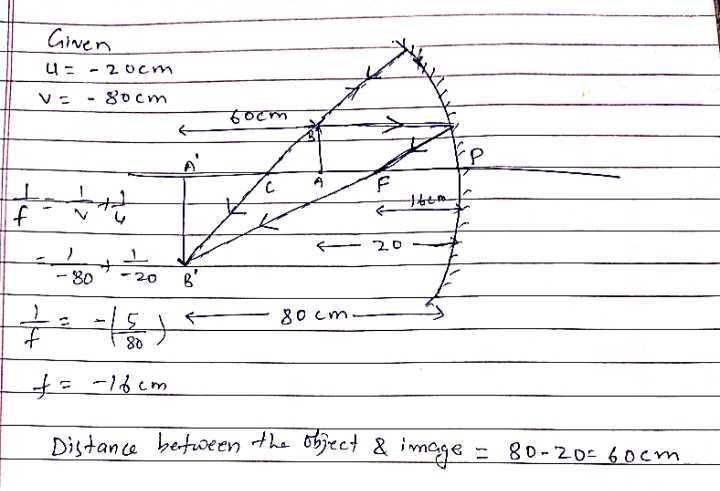
An object $$5.0 cm$$ in length is placed at a distance of $$20 cm$$ in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature $$30 cm$$. Find the position of the image, its nature, and its size.
An object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 15 cm. Find the position and nature of the image.
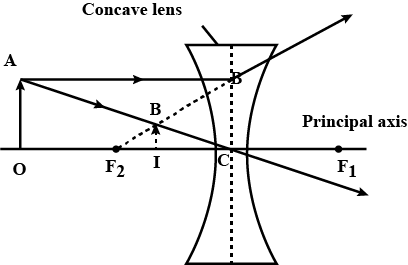
A concave lens of focal length 15cm forms an image 10 cm from the lens . How far is the object placed from the lens? Draw the ray diagram.
An object of size $$7.0 cm$$ is placed at $$27cm$$ in front of a concave mirror of focal length $$18 cm$$. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed so that a sharp focused image can be obtained? Find the size and nature of the image.
Why do stars twinkle?
Explain why the planets do not twinkle.
(a) State the laws of refraction of light. Give an expression to relate the absolute refractive index of a medium with speed of light in vacuum.
(b) The refractive indices of water and glass with respect to air are 4/3 and 3/2 respectively. If the speed of light in glass is $$2 \times 10^8 \,\, ms^{-1}$$, find the speed of light in (i) air, (ii) water.
"A ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab immersed in any medium emerges parallel to itself." Draw labelled ray diagram to justify the statement.
"The magnification produced by a spherical mirror is - $$3$$". List four informations you obtain from this statement about the mirror/image.
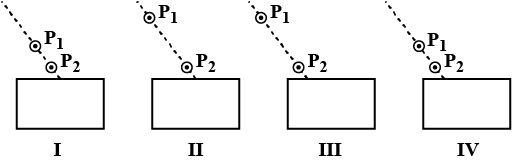
While performing the experiment on tracing the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab, in which of the following experimental setups, students likely to get the best results?
$$P_1$$ and $$P_2$$ are the positions of pins fixed by him :
The absolute refractive index of glass and water are $$3/2$$ and $$4/3$$, respectively. If the speed of light in glass is $$2 \times 10^8$$ m/s, calculate the speed of light in :
(a) vacuum
(b) water
For the same value of angle of incidence, the angles of refraction in three media $$A$$, $$B$$ and $$C$$ are $${15}^{o}$$, $${25}^{o}$$ and $${35}^{o}$$ respectively. In which medium would the velocity of light be minimum?
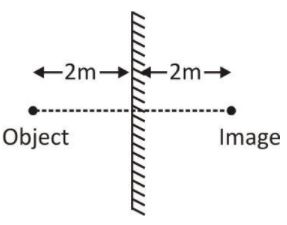
If you take a photograph of your image in a plane mirror, how many meters away should you set your focus if you are $$2$$m in front of the mirror?
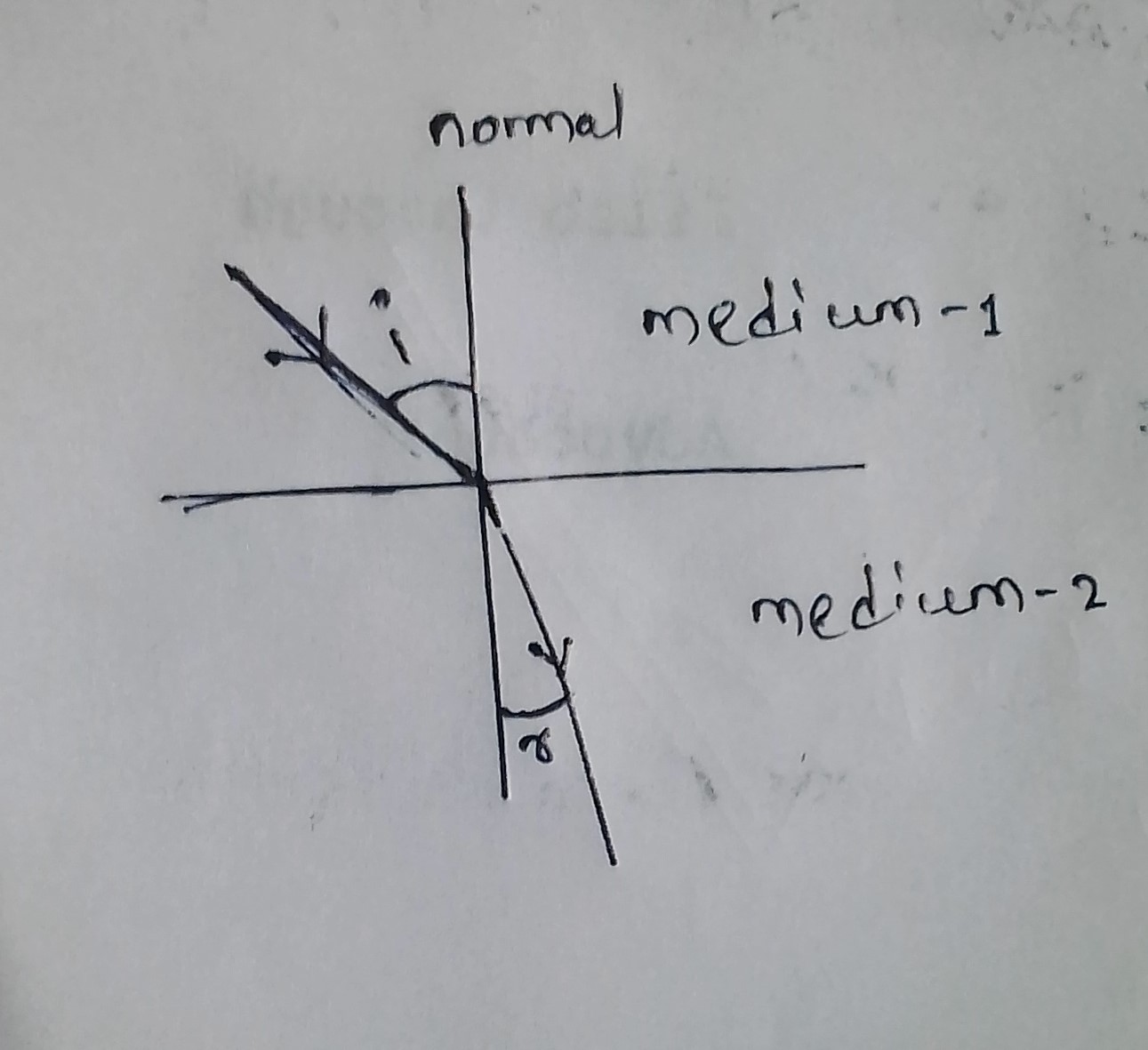
A) State what is meant by the refraction of light. State Snell's law for refraction of light and also express it mathematically.
B) The refractive index of water with respect to air is $$ \frac{4}{3}$$. If the speed of light in air is $$3 \times 10^8$$ m/s, find the speed of light in water.
B) The refractive index of water with respect to air is $$ \frac{4}{3}$$. If the speed of light in air is $$3 \times 10^8$$ m/s, find the speed of light in water.
Fill in the blanks :The centre of curvature of a concave mirror lies in ................... of it.
Fill in the blanks :A ................... lens is thicker in the middle than at its edges.
Fill in the blanks :A light ray travelling obliquely from a denser medium to a rarer medium bends ................... the normal. A light ray bends ................... the normal when it travels obliquely from a rarer to a denser medium.
Fill in the blanks :The reflecting surface of a spherical mirror may be curved ................... or ...................
Fill in the blanks :................... is the surface of the mirrors from which reflection can take place.
Fill in the blanks :When a ray of light enters a glass slab from the air, it bends ..................... the normal.
Fill in the blanks :The distance of the focus from the pole is called the ...................
Fill in the blanks :A spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is curved inwards is called a .................. mirror.
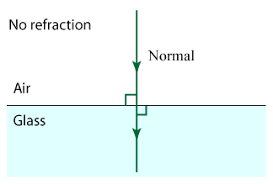
Does a ray of light incident normally on a refracting surface does not suffer any refraction?
Refractive indices of water and glass are 4/3 and 3/2 respectively. A ray of light travelling in water is incident on the water-glass interface at 30$$^o$$. Calculate the angle of refraction.
A ray of light travels from air into a perspex block of refractive index 1.5 at an angle of incidence of $$45^o$$. Calculate the angle of the refraction of the ray at air-to-perspex boundary and at perspex-to-air boundary.
A lens of focal length $$f$$ produces an image of an object located $$15 \ cm$$ on one side of it at a distance of $$30 \ cm$$ on the other side. If the lens is replaced by another lens of focal length $$\dfrac{f}{2}$$, where would the image form? If the image has to form at the earlier position by what distance should the object be shifted?
A ray of light travels from ethanol into air. If the angle of incidence of the ray at the boundary is 30$$^o$$ and the refractive index of ethanol is 1.36, what is the angle of refraction of the ray as it emerges out of ethanol?
A $$1.2 cm$$ long pin is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex mirror of focal length $$12 cm$$, at a distance of $$8 cm$$ from it. Find the location of the image.
Fill in the blanks with suitable words
The distance between principal focus and the optic centre of a lens is called its ____________.
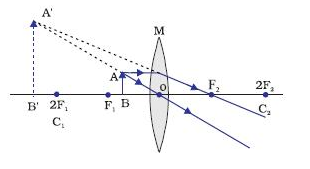
Define the principal focus of a convex lens and that of a concave lens.
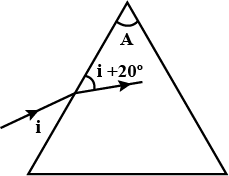
In the diagram given a ray of light incident on a glass prism. Calculate the refractive index of the glass prism.
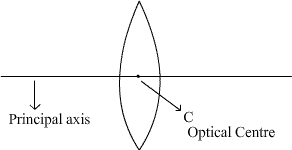
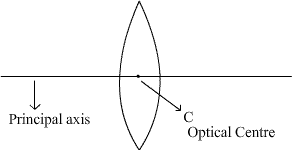
Define principal axis of a lens.
An object is placed at a distance of 50 cm from a concave lens of focal length 20 cm. Find the nature and position of the image.
A ray of light traveling in the air falls on the surface of a rectangular slab of a plastic material whose refractive index is $$1.6$$. If the incident ray makes an angle of $$53^\circ$$ with the normal $$(\sin53^\circ=4/5)$$. Find the angle made by the refracted ray with the normal.
An object is placed 50 cm from a lens produces a virtual image at a distance of 10 cm in front of the lens. Draw a diagram to show the formation of image and calculate the focal length of the lens.
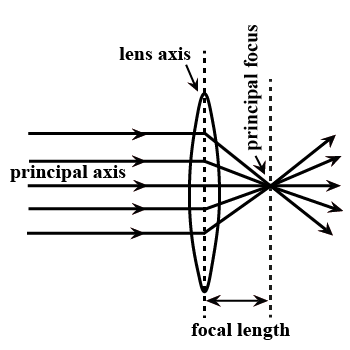
Define focal length of a lens.
What is a real image?
A concave lens of $$20 cm$$ focal length forms an image $$15 cm$$ from the lens. Calculate the object distance.
Fill in the blanks:
The center of the sphere to which a spherical mirror belongs is called ______
A convex lens of focal length $$3 cm$$ forms a real image at $$24 cm$$ from its optic centre. Calculate the distance of the object from the lens.
$$n_{1}\sin i = n_{2} \sin r$$, is called _______ (Newton's, Snell's) law.
The magnifaction produced by a plane mirror is +What does this mean?
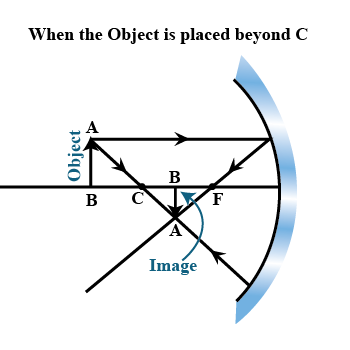
A convex mirror with a radius of curvature of $$3 m$$ is a used as rear view mirror for a vehicle. If a bus is located at $$5 m$$ from this mirror, find the position, nature and size of the image.
Explain the refraction of light through a glass slab with a neat ray diagram.
Fill in the blanks
The geometric centre of the mirror is ______
Fill in the blanks:
The rays which are parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror on reflection, meet at ____
Fill in the blanks:
The distance between pole and centre of curvature is ____
Fill in the blanks:
The distance between pole and focus is ___
Fill in the blanks:
The line which passes through the centre of curvature and pole is ____
You are provided with a printed piece of paper. Using this paper how will you differentiate between a convex lens and a concave lens?
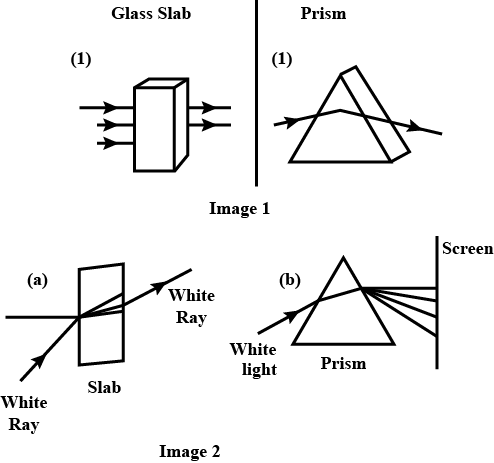
Light passes through a rectangular glass slab and through a triangular glass prism. In what way does the direction of the two emergent beams differ and why?
Define principal focus of the convex lens.
State the laws of refraction.
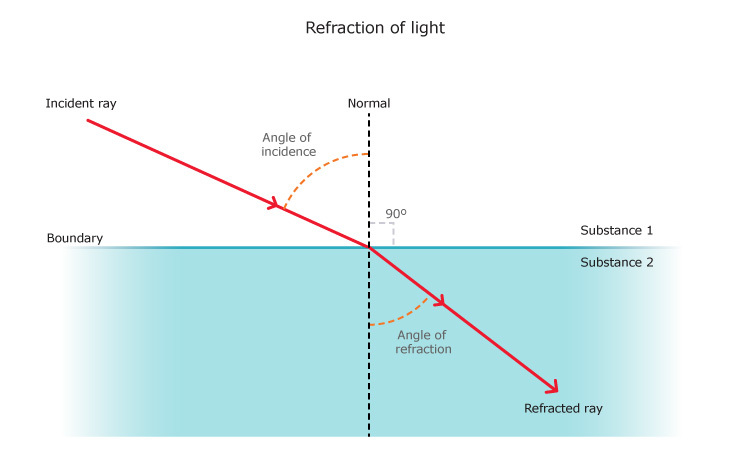
Define refraction and state the laws of refraction.
What is meant by refraction of light? State the laws of refraction.
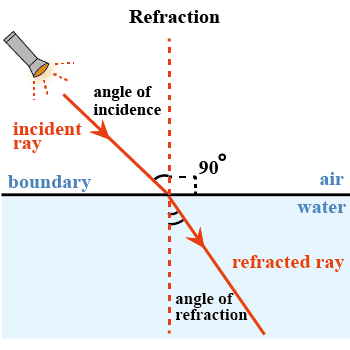
What is refraction of light?
A ray of light enters from air to a medium $$X$$. The speed of light in the medium is $$1.5 \times {10}^{8} {m}/{s}$$ and the speed of light in air is $$3 \times {10}^{8} {m}/{s}$$. Find the Refractive index of the medium $$X$$.
(a) State Snell's law for refraction of light.
(b) A concave mirror forms two times magnified and real image of an object placed at $$15 cm$$ from its pole. Determine the distance of the image from the mirror and the focal length of the mirror.
An object is placed $$25cm$$ from a convex lens whose focal length is $$10cm$$. The image distance is ...............
($$50cm, \ 16.66cm, \ 6.66cm, \ 10cm$$)
Draw a labelled diagram to show the refraction of light when light travels from air into glass and then comes out to reach air.
A 3 cm tall bulb is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a diverging lens having a focal length of 10.5 cm. Determine the distance of the image.
A needle placed at $$30\ cm$$ from the lens forms an image on a screen placed $$60\ cm$$ on the other side of the lens. Identify the type of lens and determine the focal length.
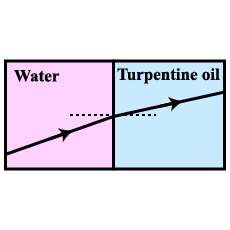
A fruit appears to be bigger in a glass of water due to _________.
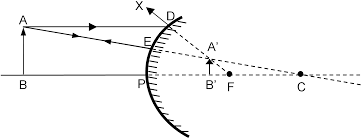
Reena and Vani find a discarded plastic lens lying on the beach. The girls discuss what they learnt in Physics and argue whether the lens is a converging or diverging one. When they look through the lens, they notice that the objects are inverted.
i) If an object 25 cm in front of the lens forms an image 20 cm behind the lens, what is the focal length of the lens?
ii) Is it a converging or diverging lens?
Ranjini makes arrangements for a candle-light dinner and tops it with a dessert of gelatin filled blue berries. If a blueberry that appears at an angle of $$45^o$$ to the normal in air is really located at $$30^o$$ to the normal in gelatin, what is the index of refraction of the gelatin?
The distance from the pole of a spherical mirror to its focus is called _______ of that mirror.
Define refraction.
An object is placed at a distance of $$15 cm$$ from a convex lens of focal length $$20 cm$$. List four characteristics (nature, position, etc.) of the image formed by the lens.
What is refraction? Give its two examples.
At what distance in front of a concave mirror of focal length $$10$$cm, an object be placed so that its real image of size five times that of the object obtain?
What do you mean by 'Reflection of light'? State the laws of reflection.
An air bubble inside water behaves like a ................... lens.
An object is placed at a distance of $$12$$cm from a convex lens of focal length $$8$$cm. Find nature of the image.
What is refraction of light? Draw the diagram of refraction of light in glass slab. Write the laws of refraction.
Why goggles(sun glasses) have zero power even though their surfaces are curved?
Define:
(a) Radius of curvature of spherical mirror
(b) Focal length of spherical mirror.
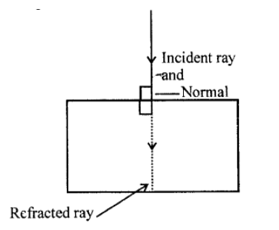
In the given ray diagram write the value of angle of incidence and name of refracted ray.
Write down Snell's law of refraction and explain.
Name the lens that always forms a virtual and erect image.
A ray is incident on a glass slab of refractive index $$\surd{3}$$ from air at an angle of $$30^{o}$$ from the surface. What is the angle of refraction?
Prove that $$n_{12}\times n_{23}\times n_{31} =1$$where $$n_{12}$$ is the refractive index of medium-2 with respect to medium-1, $$n_{23}$$ is the refractive index of medium-3 with respect to medium-2, $$n_{31}$$ is the refractive index of medium-3 with respect to medium-1.
State Snells law.
Calculate the velocity of light in a glass block of refractive index $$1.5$$
(Velocity of light in air $$=3 \times 10^8\ ms^{-1}$$)
Sun rays are incident on a concave mirror parallel to its principal axis. If the image of the sun is formed at 12 cm distance from a pole of the mirror. Find its radius of curvature.
The image distance of an object placed $$10cm$$ in front of a thin lens of focal length $$+5cm$$ ______
Explain Snell's law.
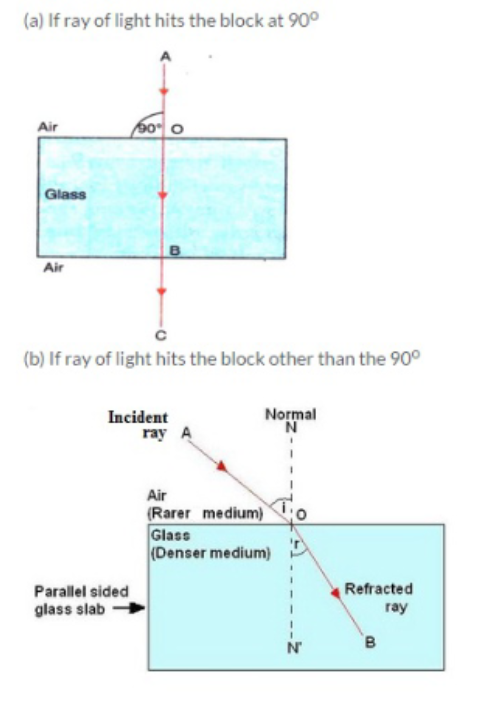
A ray of light strikes the surface of a rectangular glass slab such that the angle of incidence in air is (i) $$ 0^o $$, (ii) $$ 45^o $$. In each ,draw diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass slab and emerges from it.
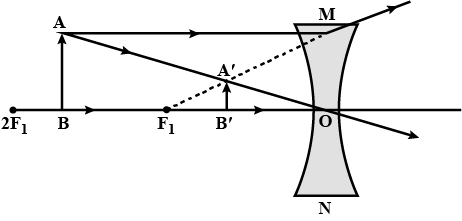
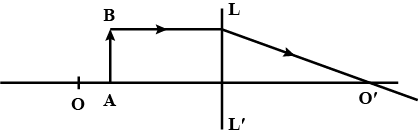
The line $$AB$$ in the ray diagram represents a lens. State whether the lens is convex or concave.

A beam of light passes from air into a substance $$X$$. If the angle of incident be $$72^{o}$$ and the angle of refraction be $$40^{o}$$, calculate the refractive index of substance $$X$$. (Given: $$\sin 72^{o}=0.951$$ and $$\sin 40^{o}=0.642$$)
A concave lens of focal length 15 cm form an image 10 cm from the lens. How far is the object placed from the lens? Draw the ray diagram also.
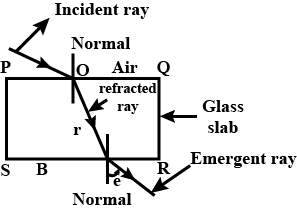
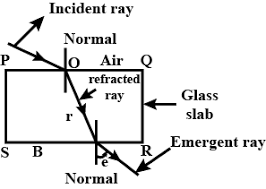
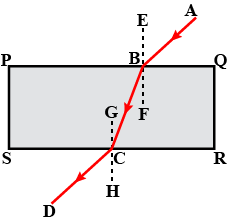
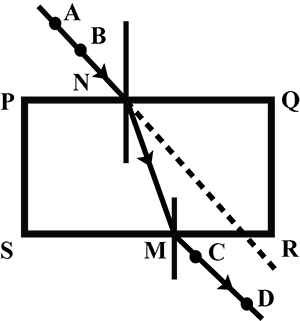
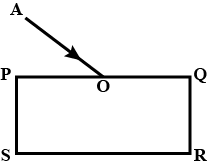
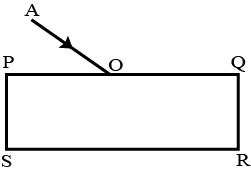
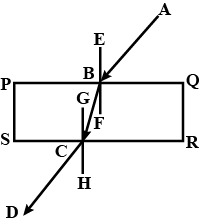
The diagram in Fig. shows a ray of light $$AO$$ falling on a rectangular glass slab $$PQRS$$. Complete the diagram till the ray of light emerges out of the slab. Label on the diagram the incident ray, the refracted ray and the emergent ray.
An object of height of $$2 \ cm$$ is placed in front of a convex lens of focal length of $$20 \ cm$$ at a distance of $$15 \ cm$$ from it. Find the position of the image.
Draw a well labelled diagram to show refraction from a glass slab. Specify the diagram.
An object placed 20 cm in front of a mirror is found to have an image 15 cm (a) in front of it, (b) behind the mirror. Find the focal length of mirror and the kind of mirror in each case.
An object is placed at a distance of $$36\ cm$$ from a diverging mirror of radius $$54\ cm$$. Find the position of the image and focal length?
An object is placed at a distance of $$6\ cm$$ from a convex mirror of focal length $$12\ cm$$. Find the position and nature of the image.
A concave mirror produces $$3$$ times magnified image of an object placed at $$10$$cm from it. Where is the image located?
An object of $$2cm$$ height is placed at a distance of $$16cm$$ from a concave mirror which produces a real image $$-3cm$$ height. What is the focal length & position of the image?
A lens forms the image of an object placed at a distance of 45 cm from it on a screen placed at a distance 90 cm on other side of it. (a) Name the kind of lens.
(b) Find: (i) the focal length of lens, and (ii) the magnification of image.
The line AB in the ray diagram of figure respresents a lens. State whether the lens represented by AB is convex or concave?
A ray of light falls normally on a glass slab. What is the angle of incidence?
Which an object is placed $$20$$cm from a concave mirror, a real image magnified three times is
(a) the focal length of the mirror.
(b) Where must the object be placed to give a virtual image three times the height of the object?
Calculate the focal length of a convex lens which produces a virtual image at a distance of 50 cm of an object placed 20 cm in front of it.
A candle flame $$3 \ cm$$ high is placed at a distance of $$3m$$ from a wall$$.$$ How far from the wall must a concave mirror be placed so that it may form a $$9 \ cm$$ high image of the flame on the same wall$$?$$ Also find the focal length of the mirror$$.$$
When an object is placed $$20\ cm$$ from a concave mirror, a real image magnified $$3$$ times is formed. Find:
Where the object must be placed to give a virtual images three times the height of the object?
A large concave mirror has a radius of curvature of $$1.5\ m$$, A person stands $$10\ m$$ in front of the mirror. Where is the person's image?
An object is kept $$60$$ $$cm$$ from a lens gives a virtual image $$20$$ $$cm$$ in front of lens. What is the focal length of the lens? Is it converging lens or diverging lens?
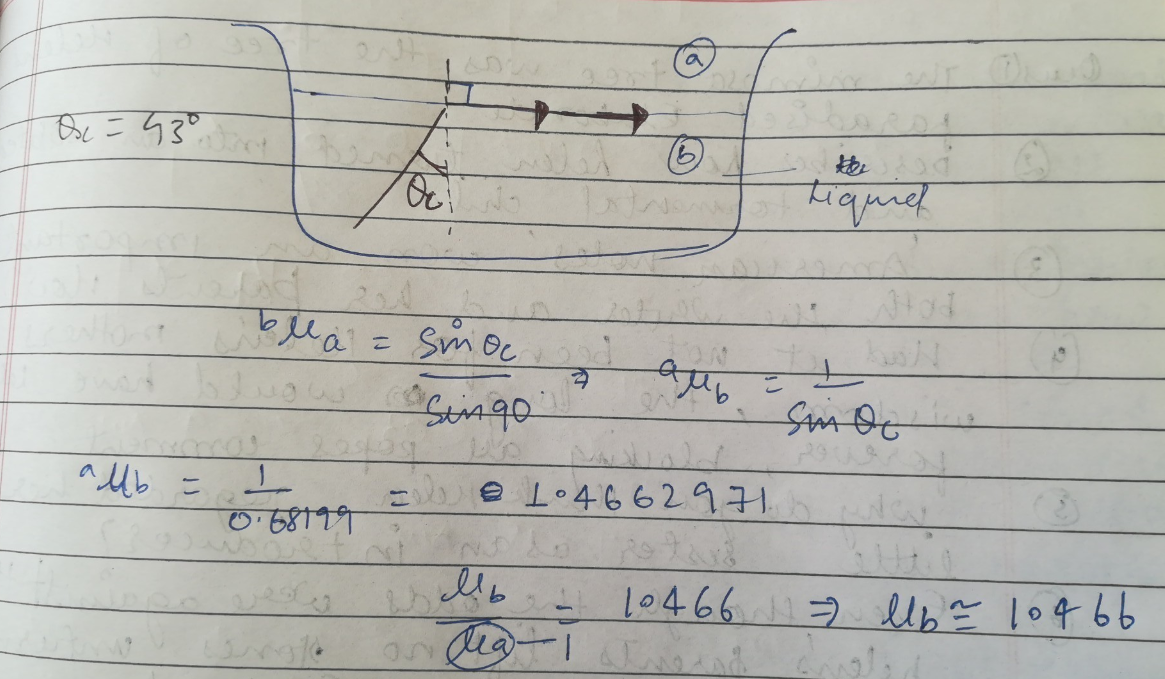
Critical angle of glycerine - air is $$43^\circ$$. Find refractive index of glycerine. $$(\sin 43^\circ = 0.68)$$
A ray of light travelling in air strikes a glass slab of $$30^{o}$$. Calculate the angle of refraction if refractive index of glass is $$1.5$$.
Where should an object be placed from a converging lens of focal length $$15\ cm$$, so as to obtain, a real image of same size as that of the object?
Matching the following:-
What do you mean by refraction of light ? What is the basic cause of refraction ?
The image of an object placed at $$60 \mathrm{cm} $$ in front of a lens is obtained on a screen at a distance of $$120 \mathrm{cm} $$ from it. (i) Find the focal length of the lens. (ii) What would be the height of the image, if the object is $$5 \mathrm{cm} $$ high?
An object is placed a distance of 12 cm in front of concave mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm . (i) find the position of the image formed (ii) List for characteristics of image formed by the mirror.
Fill in the blanks :
The perpendicular to the mirror at the point of incidence is called...............
The image of a candle flame placed at a distance of $$30 \,cm$$ from a mirror is formed on a screen placed in front of the mirror at a distance of $$60 \,cm$$ from its pole. (i)What is the nature of the mirror? Find its focal length. (ii)If the height of the flame is $$2.4 \,cm$$, find the height of its image. (iii)State whether the image formed is erect or inverted.
What are the laws of refraction of light?
Find the focal length of a lens of power $$-2.0D$$. What type of lens is this?
Define principle focus of a convex lens.
A concave lens forms an erect image of $$\dfrac{1}{3}rd$$ size of the object which is placed at a distance 30 cm in front of the lens. Find :
(a) the position of image, and
(b) the focal length of the lens.
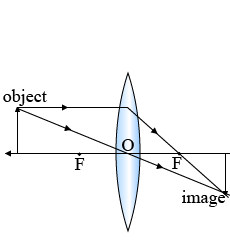
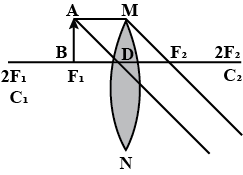
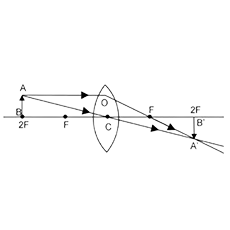
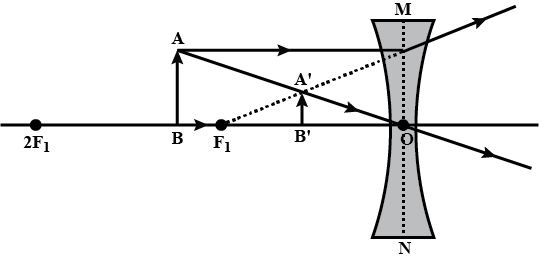
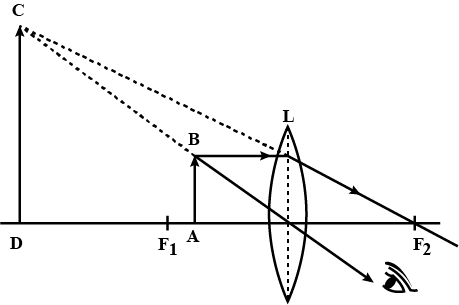
If the object is placed at a principal focus $$F_1$$ of a convex lens, draw the ray diagram for the image formation.
Observe the given figure and answer the following question :
Name the process represented by the figure.

Differentiate between a glass slab and a glass prism. What happens when a narrow beam of (i) a monochromatic light, and (ii) white light passes through (a) glass slab and (b) glass prism?
Observe the given figure and answer the following question :
State the two laws related to the process.

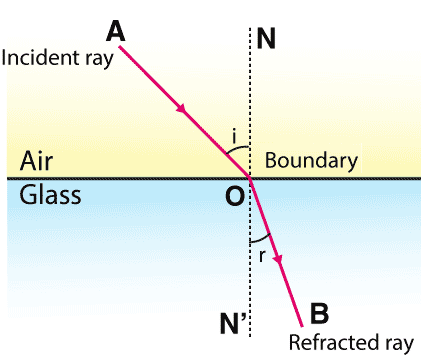
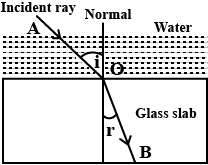
A ray of light passes from air into a block of glass . Does it bend towards the normal or away from it ?
(a) How can you bend light away from the normal?
(b) How must light travel out of a substance if it is not going to be refracted?
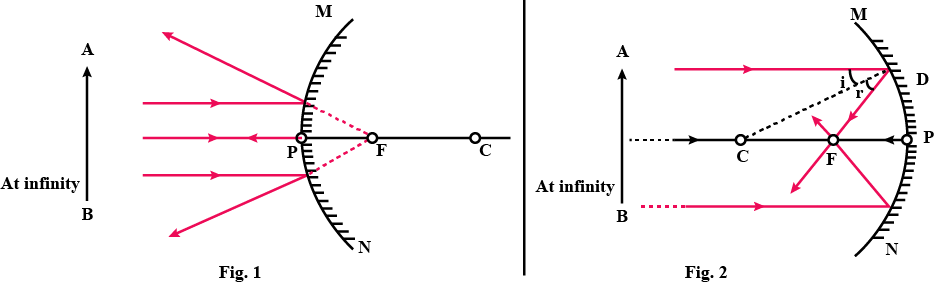
What is meant by the reflection of light ? Define the following terms used in the study of reflection of light by drawing a labelled diagram
(a) Incident ray
(b) Point of Incidence
(c) Normal
(d) Reflected ray
(e) Angle of incidence
(f) Angle of reflection
If the image formed by a convex lens is of the same size as that of the object , what is the position of the image with respect to the lens ?
The lens A produces a magnification of $$-0.6 $$ whereas lens B produces a magnification of $$ + 0.6 $$.
(a) What is the nature of lens A ?
(b) What is the nature of lens B ?
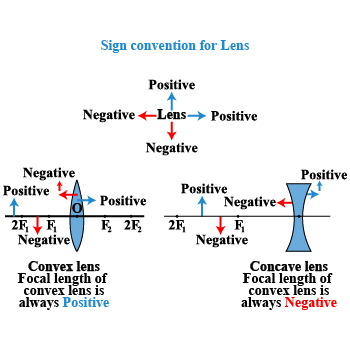
State and explain the New Cartesian Sign Convention for spherical lenses.
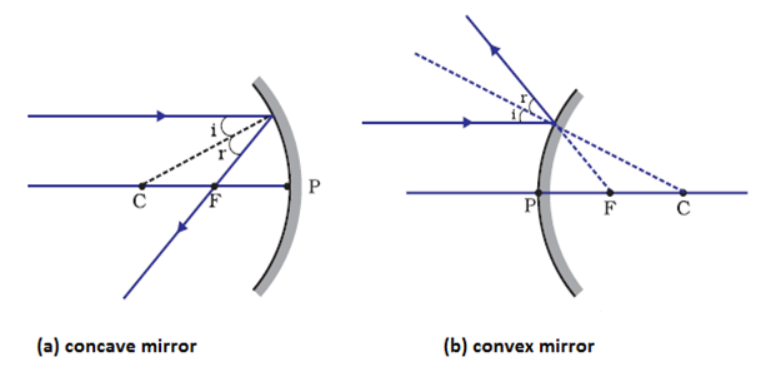
Out of convex mirror and concave mirror, whose focus is situated behind
the mirror?
According to the "New Cartesian Sign Convention" for mirrors, What sign has been given to the focal length of :
(i) a concave mirror?
(ii) a convex mirror?
What is the magnification produced by a plane mirror?
What is the cause of refraction of light?
Name the mirror which can give:
(a) an erect and enlarged image of an object
(b) an erect and diminished image of an object
What sign (+ve or -ve) has been given to the following on the basis of Cartesian Sign Convention?
(a) Height of a real image.
(b) height of a virtual image.
What is the significance of positive sign of magnification?
The speed of yellow light (from a sodium lamp) in a certain liquid is measured to be $$ 1.92 \times 10^{8} \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s} $$. What is the index of refraction of this liquid for the light?
In which direction a ray of light bends when it goes from water to glass?
What is the nature of the image formed by a concave mirror if the magnification product by the mirror is +3
Refractive index of two material mediums X and Y are 1.3 and 1.5 respectively. In which of the two, the light would travel faster?
It was observed that when the distance between an object and a lens decreases, the size of the image increases. What is the nature of this lens? If you keep on decreasing the distance between the object and the lens, will you still able to obtain the image on the screen? Explain.
A concave mirror of focal length $$f$$ produces an image $$n$$ times the size of the object. What would be the object distance for which the image is real?
The image formed by a lens is always virtual, erect and smaller in size for an object kept at different positions in front of it. Identify the nature of the lens.
Under what condition in an arrangement of two plane mirrors, incident ray and reflected ray will always be parallel to each other, whatever may be angle of incidence. Show the same with the help of ray diagram.
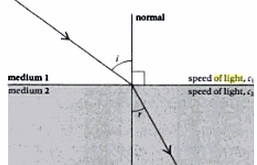
How is the refractive index of a medium related to the speed of light? Obtain an expression for a refractive index of a medium with respect in terms of the speed of light in these two media?
Fill in the blanks:
The inner surface of a steel spoon acts as a ________mirror.
What is a lens?
How are power and focal length of a lens related? You are provided with two lenses of focal length $$20$$ cm and $$40$$ cm respectively. Which lens will you use to obtain more convergent light?
Define the term magnification.
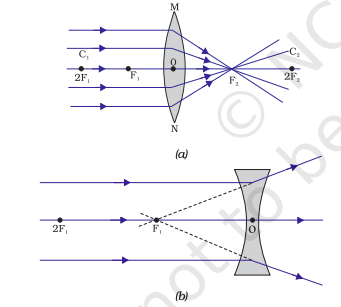
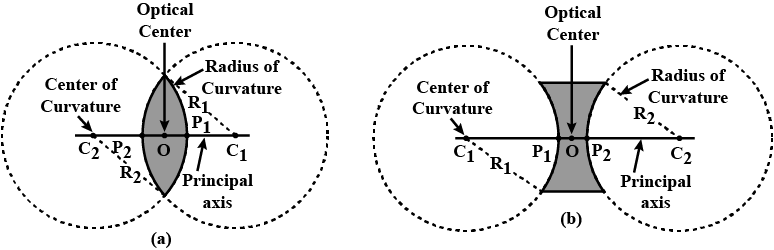
Name the different kinds of lenses. Draw diagrams to illustrate them.
Refractive index of diamond with respect to glass is 1.6 and absolute refractive index of glass is $$1.5.$$ Find out the absolute refractive index of diamond.
Explain the following terms:
Incident ray, Reflected ray, Angle of incidence, Angle of reflection, Normal.
A ________ mirror is obtained by silvering the outer surface of a part of a hollow glass sphere.
Show that for a material with refractive index $$\mu \ge \sqrt{2}$$, light incident at any angle shall be guided along a length perpendicular to the incident face.
Define the following terms :
Refracted ray
State the Snell's laws of refraction of light.
The following diagram shows a point object O placed in front of a plane mirror. Take two rays from the point O and show how the image of O is formed and seen by the eye.

Define the term principal axis of a lens.
State the condition when a lens is called an equi- convex or equi-concave
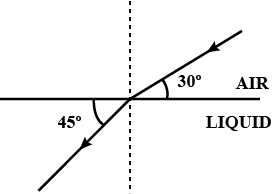
The diagram alongside shows the refraction of a ray of light from air to liquid.
(a) Write the values of (i) angle of incidence, and (ii) angle of refraction.
(b) Use Snell's law to find the refractive index of liquid with respect to air.
Draw a diagram to represent the second focus of a convex lens.
Draw a diagram to represent the second focus of a concave lens .
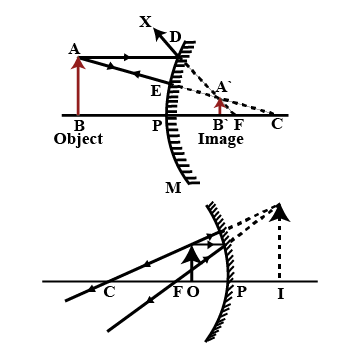
In each case (a) and (b) , draw the reflected rays for the given incident rays and mark focus by the symbol F.
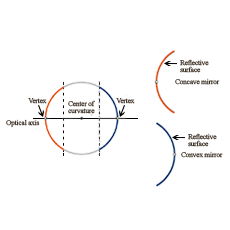
Define the terms pole, principal axis and center of curvature with reference to a spherical mirror.
A lens forms an inverted image of an object.
(a) What kind of lens is this?
(b) What is the nature of the image real or virtual?
Explain the following terms :Reflected ray
Define main focus and optical centre of spherical lens.
What do you understand by the radius of curvature and center of curvature of the spherical lens?
How is the sign (+ Or -) of power of a lens related to its divergent or convergent action?
Write the lens formula.
Define angle of reflection.
Write Snell's Law.
Define reflected ray.
The image formed by a convex mirror is of size one-third the size of object . How are u and v related?
Define reflection of light.
Give the relation between focal length and radius of curvature.
State lens formula and write it mathematically.
Define magnification of the mirror.
Define magnification of lens.
What is lens? How many types of lenses are there?
Define the following term:
Principal axis
Define the following term:
Optical center
What is refraction ? What is the cause of refraction ?
Define the following term:
Focus of a lens.
A glass lens of refractive index 1.5 is kept in a liquid. What must be the refractive index of the liquid so that the lens will disappear.
Define the following term:
Focal length
$$\dfrac{h_i}{h_0}$$ is magnification produced by a spherical mirror. Does it have any relational with the value of $$\dfrac{u}{v}$$?
Observe the given figures and complete the table using New Cartesian Sign Convention.
| Fig | $$h_o$$ | $$h_i$$ | Magnification | Image type | Size |
| i | |||||
| ii | |||||
| ii | |||||
| iv | |||||
| v |

Fill in the blanks:
An image formed by a ............. mirror is always of the same size as that of the object.
Which medium has the highest optical density? Also, which medium has the lowest optical density?Mediums: air, glass, water, diamond, oil.
What is the cause of refraction ?
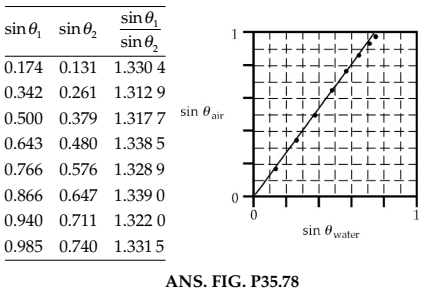
The following table gives the value of refractive indices of a few media.
| $$1$$ | $$2$$ | $$3$$ | $$4$$ | $$5$$ | $$6$$ | |
| Medium | Ice | Water | Kerosene | Flint glass | Ruby | Diamond |
| Refractive Index | $$1.31$$ | $$1.333$$ | $$1.44$$ | $$1.66$$ | $$1.71$$ | $$2.42$$ |
An object is placed at the following distances from a concave mirror of focal length $$15\ cm$$.
(a) $$10\ cm$$
(b) $$20\ cm$$
(c) $$30\ cm$$
(d) $$40\ cm$$
Which position of the object will produce
Virtual Image
A diminished real image
An enlarged real image
An image of same size.
A coin placed at the bottom of a tank appears to be raised when water is poured into it. Explain.
How does light make an object visible ?
For the same angle of incidence $$45^{\circ}$$, the angle of refraction in two transparent media : I and II is $$20^{\circ}$$ and $$30^{\circ}$$ respectively. Out of I and II, which medium is optically denser and why ?
If the refractive index of water with respect to air $$(_a \mu_w) $$ is $$\dfrac{5}{3}$$. Calculate the refractive index of air with respect to water $$(_w\mu_a)$$
Sameer says that he can start a fire by using sun's rays and a concave mirror which is true. Can he do the same if he uses a convex mirror instead of a concave mirror? State whether yes or no.
Complete the table
| No. | angle of incidence | Angle of reflection |
| 1 | $${30}^{o}$$ | (a) ______ |
| 2 | (b) _____ | $${40}^{o}$$ |
| 3 | $${50}^{o}$$ | (c) _____ |
| 4 | $${60}^{o}$$ | (d) _____ |
A shaving mirror of focal length 72 cm is kept in a beauty clinic. A man uses it standing 18 cm away from the mirror. At what distance will the image be formed? Is the image real or virtual? What is the magnification of the image?
A girl was playing with a thin beam of light from her laser torch by directing it from different directions on a convex lens held vertically. She was surprised to see that in a particular direction the beam of light continues to move along the same direction after passing through the lens. State the reason for this observation.
Figure shows a ray of light meeting the glass of the window of a car at an angle of incidence of $$40^\circ.$$(i) Assuming that the refractive index of glass is $$1.5,$$ find the angle of refraction for this ray in the glass.
A lens produces a magnification of -1.5 Is this a converging or diverging lens? If the focal length of the is 20 cm, draw a ray diagram showing the image fromation in this case.
An object is placed at a distance of $$12cm$$ in front of a concave mirror. It forms a real image four times larger than the object. Calculate the distance of the image from the mirror.
(i)An object is placed at a distance of 60 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30cm. Use lens formula to find the distance of the image from the lens. (ii)List characteristics of image formed. (iii)Draw a ray diagram of image formation by concave lens in above case.
The angle of incidence i and refraction r are equal in a transparent slab when the value of i is
A $$6$$ cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length $$15$$ cm. the distance of the object from the lens is $$10$$ cm. Find the position, size and nature of the image formed, using the lens formula.
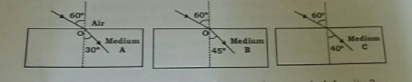
The path of light passing from air to different media A,B and C for a given angle of incidence is shown study the diagram and answer the following question.
Will the light travelling from A to B bend towards or away from the normal?
In an experiment with a rectangular glass slab, a student observed that a ray of light incident at an angle of $$45^\circ$$ with the normal on one face of the slab, after refraction strikes the opposite face of the slab before emerging out into air making an angle of $$30^\circ$$ with the normal. Draw a labeled diagram to show the path of this ray. What value would you assign to the angle of refraction and angle of emergence?
The path of light passing from air to different media A,B and C for a given angle of incidence is shown study the diagram and answer the following question.
Which of the media A,B or C has maximum optical density?
A concave mirror is used for image formation for different positions of an object. What inferences can be drawn about the following when an object is placed at a distance of 10 cm from the pole of a concave mirror of focal length 15 cm?
(a) Position of the image
(b) Size of the image
(c) Nature of the image
Draw a labelled ray diagram to justify your inferences.
A divergent lens of focal length 30 cm forms the image of an object of size 6 cm on the same side as the object at a distance of 15 cm from its optical centre use formula to determine the distance of the object from the lens and the size of the image formed.
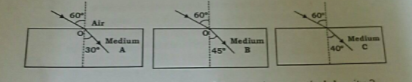
The figure shows refraction of a light ray from a glass slab. Write the value of angles x and y. What is refractive index of slab material ?
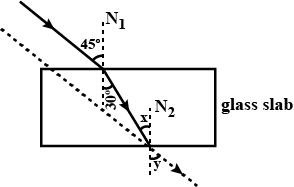
Trace the path of the reflected and refracted rays.
An object of height $$4 \ cm$$ is placed at $$30 \ cm$$ from a concave mirror of focal length $$20 \ cm$$. The position of the image is $$x$$ and the size of the image is $$y$$.
Then what will be the value of $$x+5y$$ ? (Take magnitude only)
The figure given below shows a container C partially filled with water. There is a plane mirror M at the bottom of the container. A light ray AB incidents on the surface of water at angle of incidence $$30^{\circ}$$. Copy and complete the ray diagram. Mark the ray emerging from the water surface. Refractive index of water = $$\displaystyle \frac {4}{3}$$.

A small candle, $$2.5 cm$$ in size is placed at $$27 cm$$ in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature $$36 cm.$$ At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed in order to obtain a sharp image? Describe the nature and size of the image. If the candle is moved closer to the mirror, how would the screen have to be moved?
A $$4.5\ cm$$ needle is placed $$12\ cm$$ away from a convex mirror of focal length $$15\ cm$$. Give the location of the image and the magnification. Describe what happens as the needle is moved farther from the mirror.
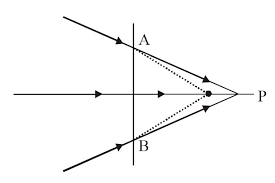
A beam of light converges at a point P. Now a lens is placed in the path of the convergent beam $$12$$ cm from P. At what point does the beam converge if the lens is (a) a convex lens of focal length $$20$$ cm, and (b) a concave lens of focal length $$16$$ cm?
A person stands straight infront of a convex mirror at a distance of 30 m away from it. He sees his erect image whose height is $$\dfrac{1}{6}$$th of his real height. Find the focal length of the convex mirror.
A light ray is incident on air-liquid interface at $$45^{\circ}$$ and is refracted at $$30^{\circ}$$. What is the refractive index of the liquid? For what angle of incidence will the angle between reflected ray and refracted ray be $$90^{\circ}$$?
Explain the refraction of light through a glass-slab with neat ray diagram.
S.No. | Object-Distance u(cm) | Image-Distance v(cm) |
| 1. | -100 | +25 |
| 2. | -60 | +30 |
| 3. | -40 | +40 |
| 4. | -30 | +60 |
| 5. | -25 | +100 |
| 6. | -15 | +120 |
What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give reason to justify your answer.
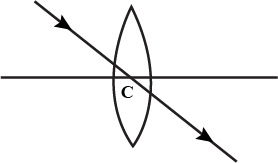
The ray passing through the _____ of the lens is not deviated.
Optical CentreFocus
An object is placed at $$30cm$$ from a convex lens and its real image is formed at $$20cm$$ away from the lens. Calculate the focal length of convex lens. Draw ray diagram also.
Convex lens and concave lens are placed at a separation of 5cm each of f=10 cm . If an object is placed at a distance of 30 cm infront of convex lens . Find the position and nature of the final image formed
Find the position of the object which when raised in front of convex mirror of focal length $$20cm $$ produces virtual image which is half size of the object.
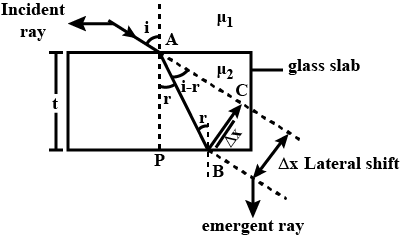
Width of a slab is $$6\ cm$$ whose $$\mu = \dfrac {3}{2}$$. If its rear surface is silvered and object is placed at a distance $$28\ cm$$ from the front face. Calculate the final position of the image from the silvered surface.
A concave mirror produces a real image of half the size of an object placed at 60 cm infront of it. Where should the object be placed to obtain a virtual image of double the size of the object?
If the angle of incidence and angle of emergence of a light ray falling on a glass slab are $$i$$ and $$e$$ respectively, prove that , $$ i = e $$
A converging mirror forms a real image of height $$4 cm$$ of an object of height $$1cm$$ placed $$20 cm $$ away from the mirror. Calculate the image distance. What is the focal length of the mirror.
A concave mirror forms a real image of an object placed in front of it at a distance $$30cm$$, of size three times the size of object. Find (a) the focal length of mirror (b) position of image
Calculate distance of an object from height $$'h'$$ of a concave mirror of focal length $$ = 10 $$ so as to obtain real image of magnification.
$$ m = -2 ,v = 2u $$
An object of height $$3\ cm$$ is placed at a distance of $$15\ cm$$ infront of a concave mirror of radius of curvature $$10\ cm$$. Calculate the height of image and distance of image?
Light is incident from glass $$(\mu=1.50)$$ to water $$(\mu=1.33)$$. Find the range of the angle of deviation for which there are two angles of incidence.
"During refraction of light through the glass slab, incident ray and emergent ray are parallel to each other." Explain.
State $$1^{st} $$ and $$2^{nd} $$ law of refraction.
The refractive indices of water for red and violet colours are $$1.325$$ and $$1.334$$ respectively. Find the difference between the velocities of rays for these two colours in water. $$(c=3\times 10^{8}m/s)$$
Does an air bubble inside water behave like a lens? If so, what type of lens is it? Explain?
What would be the path of refracting ray and emergent ray, if a ray of light is incident on a rectangular glass slab?
A ray of light passes from medium $$A$$ to $$B$$ and bends towards the normal. Comment on refractive index of $$A$$ and $$B$$.
Light in air is incident at an angle of $$45^o$$ on the surface of glass plate having refractive index $$1.526$$ through what angle is light deviated upon refraction at top of surface.
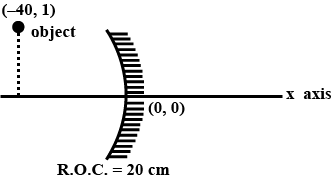
Figure shown a spherical concave mirror with its pole at (0,0) and principal axis along x axis. There is a point object at (-40 cm, 1cm), find the position of image.
An illuminated object lies at a distance $$1.0m$$ from a screen. A convex lens is used to form the image of object on a screen placed at distance $$75cm$$ from the lens.Find :(i) the focal length of lens and (ii)The magnification.
Calculate the angle of incidence of the light ray incident on a surface of a plastic slab of refractive index $$\sqrt 3$$, if the angle of refraction is $$30^o$$.(Use: $$sin\ 30^o=\dfrac{1}{2}$$ and $$sin\ 60^o = \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$$)
A convex lens has focal length 20 cm. Calculate at what distance from the lens should the object be placed so that it forms an image at 40 cm on the other side of the lens. State the nature of the image formed.
State the laws of refraction. What is the meaning of "the refractive index of crown glass is $$1.52$$"?
A person looks into a spherical mirror. The size of image of his face is twice the actual size of his face. If the face is at a distance 20 cm then find the nature of radius of curvature of the mirror.
An object placed on a meter scale at $$8\ cm$$ mark, was focused on a white screen placed at $$92\ cm$$ using a converging lens placed on the scale at $$50\ cm$$ mark.
Find the focal length of the converging lens.
An object placed $$45cm$$ from a lens forms an image on a screen placed $$90cm$$ on other side of the lens Identify the type of the lens and find its focal length
A converging mirror form $$3$$ times magnified and virtual image when the object is at $$8cm$$. Find the position of the image and focal length.?
At what distance from a concave mirror of focal length $$10\ cm$$ should an object $$2\ cm$$ long be placed in order to get erect image $$6\ cm$$ tall?
An object is $$24cm$$ away from a concave mirror and its image is $$16cm$$ from the mirror. Find the focal length and radius of curvature of the mirror, and the magnification of the image.
Write snell's law.
A dentist uses a small mirror that gives a magnification of $$4$$ when it is held $$0.60$$ cm from a tooth. Find the radius of curvature of the mirror.
The distance between two points sources of light is $$24\ cm$$. Where should a converging lens with a focal length of $$f = 9\ cm$$ be placed between them to obtain the images of both sources at the same point?
A beam of light composed of red and green ray is incident obliquely at a point on the face of rectangular glass slab. When coming out on the opposite parallel face, the red and green ray emerge from
What is snell's law?
The R.I of ice and glass are 1.31 and 1.5 respectively. Find the R.I of ice w.r.t. glass.
A $$2.0\; cm$$ tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length $$10\;cm$$. The distance of the object from from the lens is $$15\;cm$$ find the nature,position, and size of the image also find its magnification.
A ray of light is incident on a glass plate making an angle of $${ 60 }^{ \circ }$$ with the normal at the point of incidence. If the reflected and refracted rays are prependicular, find the refractive index (R.I.) of glass.
What is the meaning of refraction.
Complete the refracted ray in the flowing ray diagram.
If an object is placed $$25 cm$$ in front of the converging lens forms an image $$20 cm$$ behind the lens, then what is the focal length of the lens ?
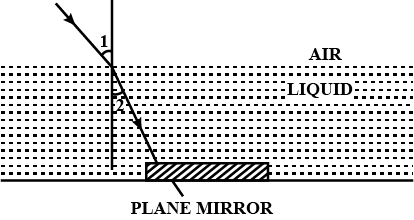
A ray of red light enters a liquid from air, as shown in figure . The angle $$1$$ is $$45 ^ { \circ }$$ and $$2$$ is $$30 ^ { \circ }$$.
(a) Find the refractive index of liquid.
(b) Show in the diagram the path of the ray after it strikes the mirror and re-enters in air. Mark in the diagram the angles wherever necessary.
(c) Redraw the diagram if plane mirror becomes normal to the refracted ray inside the liquid. State the principle used.
A beam of light travelling in a rectangular glass slab emerges into air . Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path .
A ray of light travelling in air is incident on a parallel-sided glass slab (or rectangular glass slab) . Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path in glass .
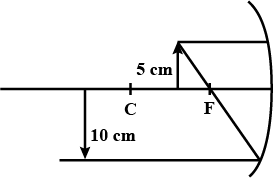
A concave mirror forms an image of $$20 cm$$ high object on a screen placed $$5.0 m$$ away from the mirror. The height of the image is $$50 cm$$. Find the focal length of the mirror and the distance between the mirror and the object.
An object is kept at a distance of 5 cm in front of a convex mirror of focal length 10 cm. Calculate the position and magnification of the image and state its nature.
How does the light have to enter the glass:
(a) to produce a large amount of bending?
(b) for no refraction to happen?
Giving reasons, state the 'signs' ( positive or negative) which can be given to the following:
(a) object distance (u) for a concave mirror or convex mirror.
(b) image distance (v) for a concave mirror.
(c) image distance (v) for a convex mirror.
An object 20 cm from a spherical mirror gives rise to a virtual image 15 cm behind the mirror. Determine the magnification of the image and the type of mirror used.
When a light ray passes from air into glass, what happens to its speed? Draw a diagram to show which way the ray of light
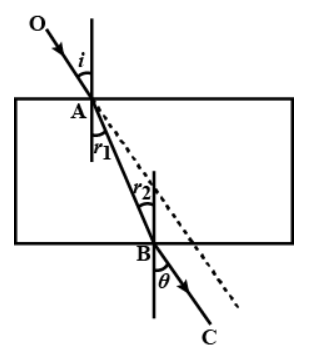
A ray of light traveling in air is incident on a rectangular glass block and emerges out into the air from the opposite face. Draw a labeled ray diagram to show the complete path of this ray of light. Mark the two points where the refraction of light takes place. What can you say about the final direction of ray of light?
Define Snell's law of refraction . A ray of light is incident on a glass slab at an angle of incidence of $$ 60^{\circ} $$ . If the angle of refraction be $$ 32.7^{\circ} $$ ,calculate the refractive index of glass .
(Give $$ {\text{sin}}\,60^{\circ} = 0.866 , $$ and $$ {\text{sin}}\,32.7^{\circ} = 540 $$ ) .
When a ray of light passes from air into glass , is the angle of refraction greater than or less than the angle of incidence ?
Draw a labeled ray diagram to show how a ray of light passes through a parallel-sided glass block :
(a) if it hits the glass block at $$ 90^{\circ} $$ (that is perpendicular to the glass block)
(b) if it hits the glass block at an angle other than $$ 90^{\circ} $$ (that is, obliquely to the glass block).
Write the formula for a lens connecting image distance $$ (v) $$ , object $$ (u) $$ and the focal length $$ (f) $$ . How does the lens formula differ from the mirror formula ?
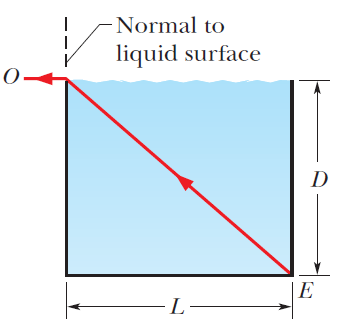
When the rectangular metal tank in above figure, is filled to the top with an unknown liquid, observer $$O$$, with eyes level with the top of the tank, can just see corner $$E$$. A ray that refracts toward $$O$$ at the top surface of the liquid is shown. If $$D=85.0 cm$$ and $$L=1.10 m$$, what is the index of refraction of the liquid?
With the help of a ray diagram, state the meaning of refraction of light. State Snell's law of refraction of light and also express it mathematically.
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays of lights which are so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from the mirror. Choose these two rays and state the path of these ray after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the nature and position of the image of an object placed at a distance of $$15 cm$$ from a concave mirror of focal length $$10 cm$$.
The linear magnification produced by a spherical mirror is $$+3$$. Analyse this value ans state the (i) type of mirror and (ii) position of the object with respect to the pole of the mirror. Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case.
Sudha finds out that the sharp image of the window pane of her science laboratory is foamed a distance of $$15$$ cm from the lens. She now tries to focus the building visible to her outside the window intend of the window pane without dusturbing the kens, in which direction will she move the screen to obtain a sharp image of the building? What is the approximate focal length of this lens?
A $$5\ cm$$ tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length $$18\ cm$$ at a distance of $$12\ cm$$ from it. Use lens formula to determine the position, size and nature to the image formed.
A convergent lens has a focal length of $$15\ cm$$. At what distance should an object from the optical centre of the lens be placed so that its real image is formed at $$30\ cm$$ on the other side of the lens?
Light in vacuum is incident on the surface of a glass slab. In the vacuum the beam makes an angle of $$32^{0}$$ with the normal to the surface, while in the glass it makes an angle of $$21^{0}$$ with the normal. What is the index of refraction of the glass? (Given : $$\sin 32^{\circ}= 0.53, \sin 21^{\circ} = 0.36, \mu_{vacuum} = 1)$$
How can you distinguish between a plane mirror, a concave mirror and a convex mirror without touching them?
A student want to project the image of a candle flame on a screen $$80 cm$$ in front of a mirror by keeping the candle flame at a distance of $$20 cm $$ from its pole.
Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case and mark the distance between the object and its image.
Observe the figure given as Figure 15.1 carefully.
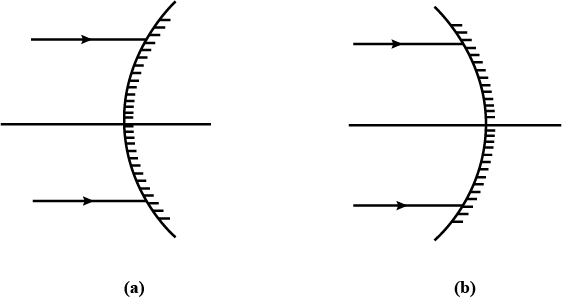
The given figures show the path of light through lenses of two different types, represented by rectangular boxes A and B. What is the nature of lenses A and B?

Size of image of an object by a mirror having a focal length of $$20 \mathrm{cm}$$ is observed to be reduced to $$1 / 3$$ rd of its size. At what distance the object has been placed from the mirror? What is the nature of the image and the mirror?
The optical properties of a medium are governed by the relative permittivity ($$\epsilon_{p}$$ ) and relative permeability ($$\mu_{r}$$). The refractive index is defined as $$\sqrt{\epsilon_{p} \mu_{r}} = \mu$$. For ordinary material $$\epsilon_{r} > 0$$ and $$\mu_{r} > 0$$ and the positive sign is taken for the square root. In 1964, a Russian scientist V. Veselago postulated the existence of material with $$\epsilon_{r} < 0$$ and $$\mu_{r} < 0$$. Since then such $$meta\ materials$$ have been produced in the laboratories and their optical properties studied. For such materials $$\mu =\sqrt{\mu_{r}\epsilon_{r}}$$. As light enters a medium of such refractive index the phases travel away from the direction of propagation. Prove that Snell's law holds for such a medium.
What is the focal length of the convex lens?
The image of a candle flame formed by a lens is obtained on a screen placed on the other side of the lens. If the image is three times the size of the flame and the distance between lens and image is $$80 \mathrm{cm},$$ at what distance should the candle be placed from the lens? What is the nature of the image at a distance of $$80 \mathrm{cm}$$ and the lens?
If the image formed by a lens for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always virtual, erect and diminished, state the type of the lens. Draw a ray diagram in support of your answer. If the numerical value of focal length of such a lens is 20 cm, find its power in new Cartesian sign conventions.
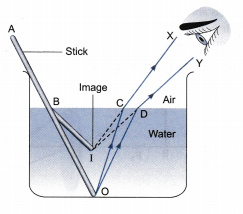
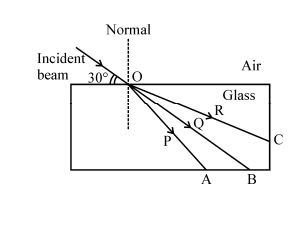
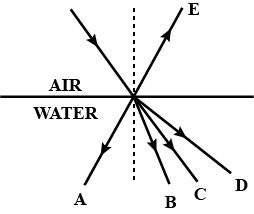
In above figure a ray of light from air suffers partial reflection at the boundary of water. which of the ray $$A,B,C,D$$ and $$E$$ is the correct(i) refracted ray(ii) partially reflected ray?
Explain optical centre of a lens with the help of proper diagram(s)
A light ray on passing from a transparent medium 1 to another transparent medium 2 (i) speeds up (ii) slows down. In each case, state whether the refractive index of medium 2 is equal to, less than or greater than the refractive index of medium 1.
Draw a diagram showing the refraction of light from water to glass. Label on it the incident ray, the angle of incidence (i), and the angle of refraction (r).
An object is placed on the axis of a lens. An image is formed by refraction in the lens. For all positions of the object on the axis of the lens, the positions of the image are always between the lens and the object. (a) name the lens. (b) Draw a ray diagram to show it. (c) State three characteristics of the image.
A ray of light incident at a point on the principal axis of a convex lens passes undeviated through the lens.
(a) What special name is given to this point on the principal axis ?
(b) Draw a labelled diagram to support your answer in part (a)
A lens forms an erect, magnified and virtual image of an object.
(a) Name the type of lens.
(b) Where is the object placed in relation to the lens?
(c) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image.
(d) Name the device which uses this principle.
Draw a figure explaining various terms related to a lens.
Study the diagram given
(a) Name the lens LL'
(b) What are the points O and O' called?
(c) Complete the diagram to form the image of the object AB.
(d) State the three characteristics of the image.
(e) Name a device in which this action of lens is used.
The given below figure shows an object OA and its image IB formed by a lens.
(a) Name the lens and show it in the diagram
(b) Draw suitable rays to locate the lens and its focus
(c) State three characteristics of the image.
Focal length of a concave mirror is 30 cm. If object is at a distance of 40 cm then find the image distance. Find the magnification as well.
Find the magnification by a convex lens of focal length 10 cm if erect image of object is formed at minimum distance of clear vision.
Refractive index of kerosene oil is 1.44 and that of water is $$ 1.33 . $$ A ray of light enters from kerosene oil to water. Where would light ray bend and why?
What is meant by magnification ? Write its expression . What is its sign for the (a) real and (b) virtual,image ?
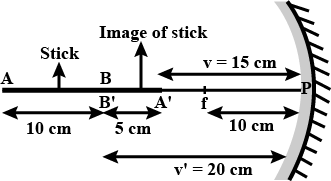
A $$10\ cm$$ long stick is kept in front of a concave mirror having a focal length of $$10\ cm$$ in such a way that the end of the stick closest to the pole is at a distance of $$20\ cm$$. What will be the length of the image?
A ray of light is incident on a glass plate at $$50^\circ.$$ If angle of refraction is $$30^\circ,$$ then find out refractive index of glass.
Find the refractive index of water with respect to air.
Why is pencil immersed under water appears to be bent ?
For the given figure, describe the light ray and the different angles.
What is called the absolute refractive index of a medium? Obtain the general form of Snell's law in terms of refractive indices of two media?
Do the experiments of refraction, which you know, with your friends. Discuss it and note down.
Fig $$h_i$$ $$h_o$$ Magnification Erect, virtual / inverted, real
$$m = \dfrac{h_i}{h_o}$$ Size is same as that of the object /
magnified / diminidhed Fig 1
Fig 2
Fig 3
Fig 4
Fig 5 Negative
Negative
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Positive
Negative
Negative
Positive
Positive
Positive
Inverted, real
Inverted, real
Direct, virtual
Direct, virtual
Direct, virtual
dimished
Size same as object
bigger than object
smaller than object
smaller than object
From the above table, find out which mirror always gives an erect and diminished image and write it down.
| Fig | $$h_i$$ | $$h_o$$ | Magnification | Erect, virtual / inverted, real $$m = \dfrac{h_i}{h_o}$$ | Size is same as that of the object / magnified / diminidhed |
| Fig 1 Fig 2 Fig 3 Fig 4 Fig 5 | Negative Negative Positive Positive Positive | Positive Positive Positive Positive Positive | Negative Negative Positive Positive Positive | Inverted, real Inverted, real Direct, virtual Direct, virtual Direct, virtual | dimished Size same as object bigger than object smaller than object smaller than object |