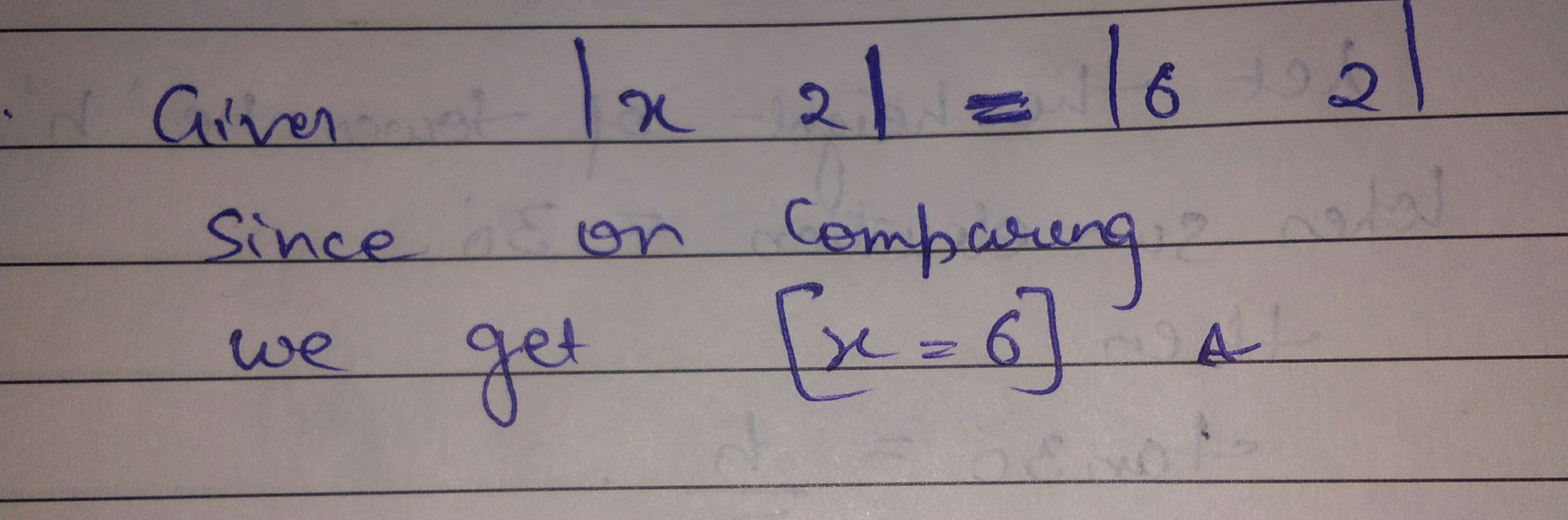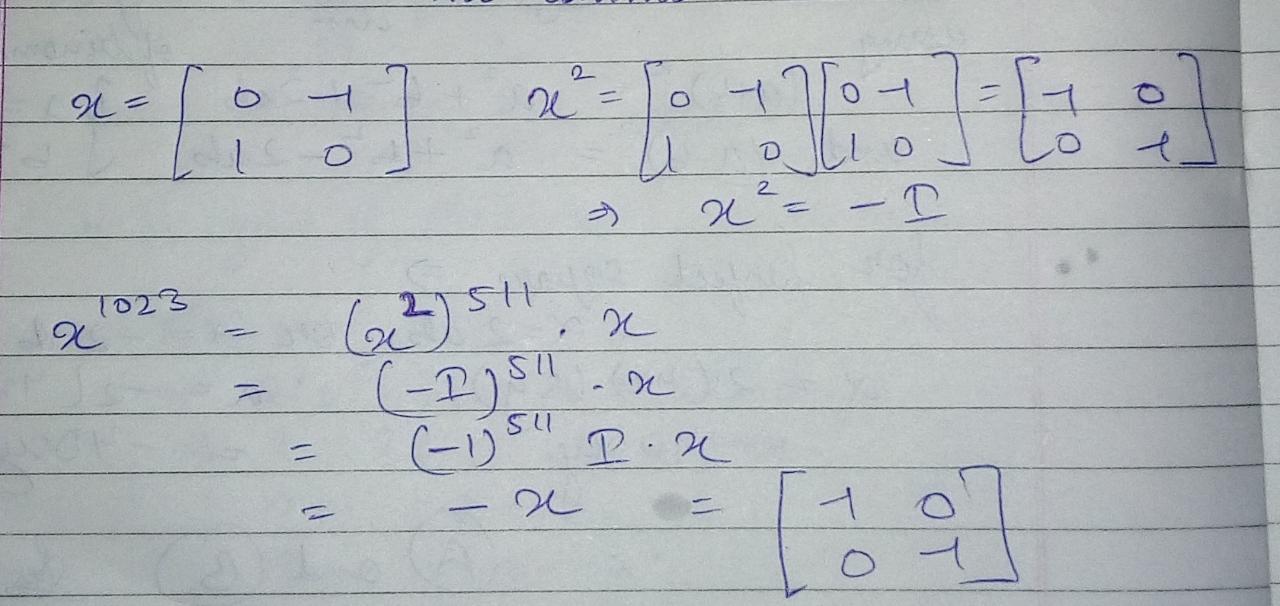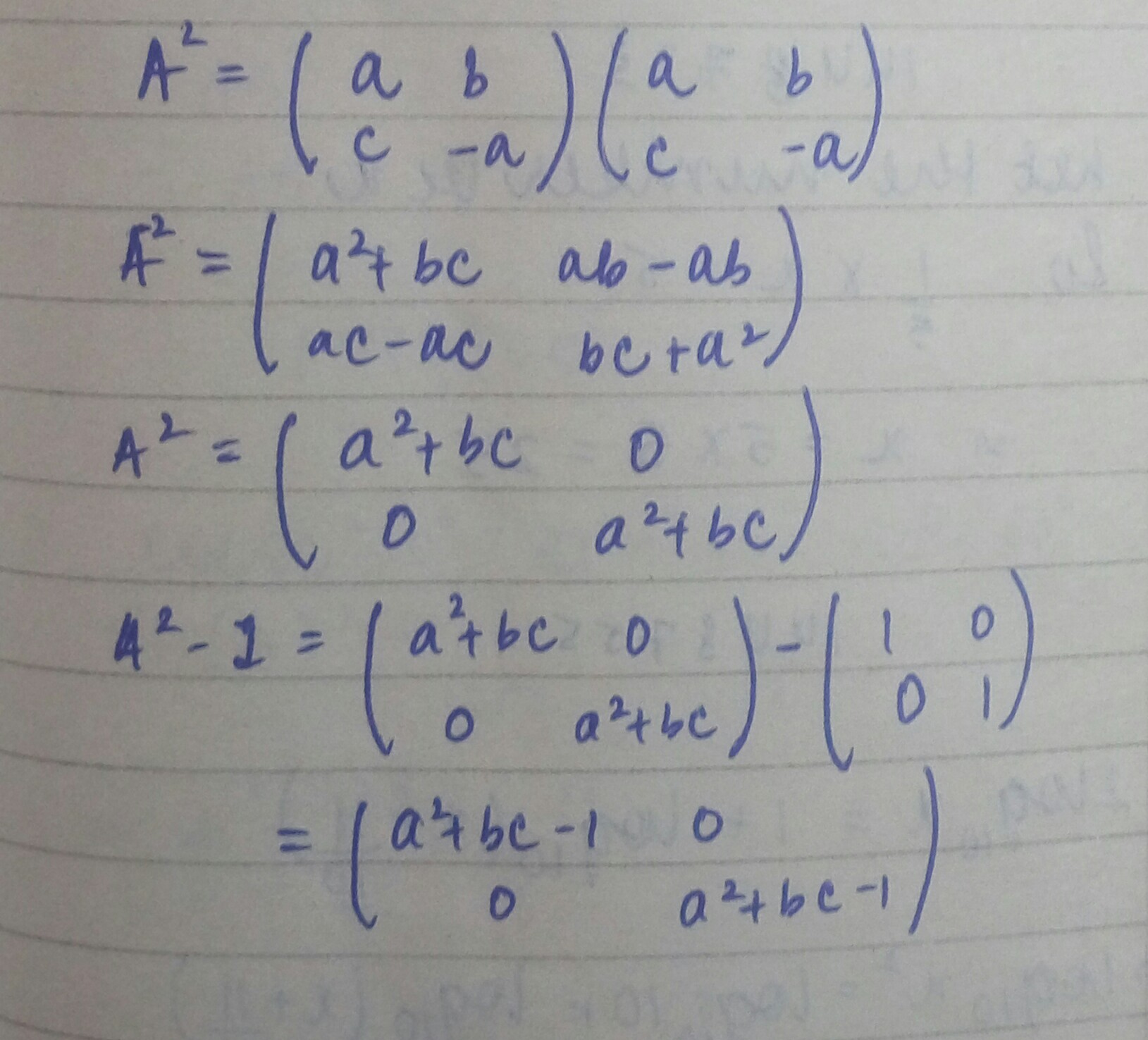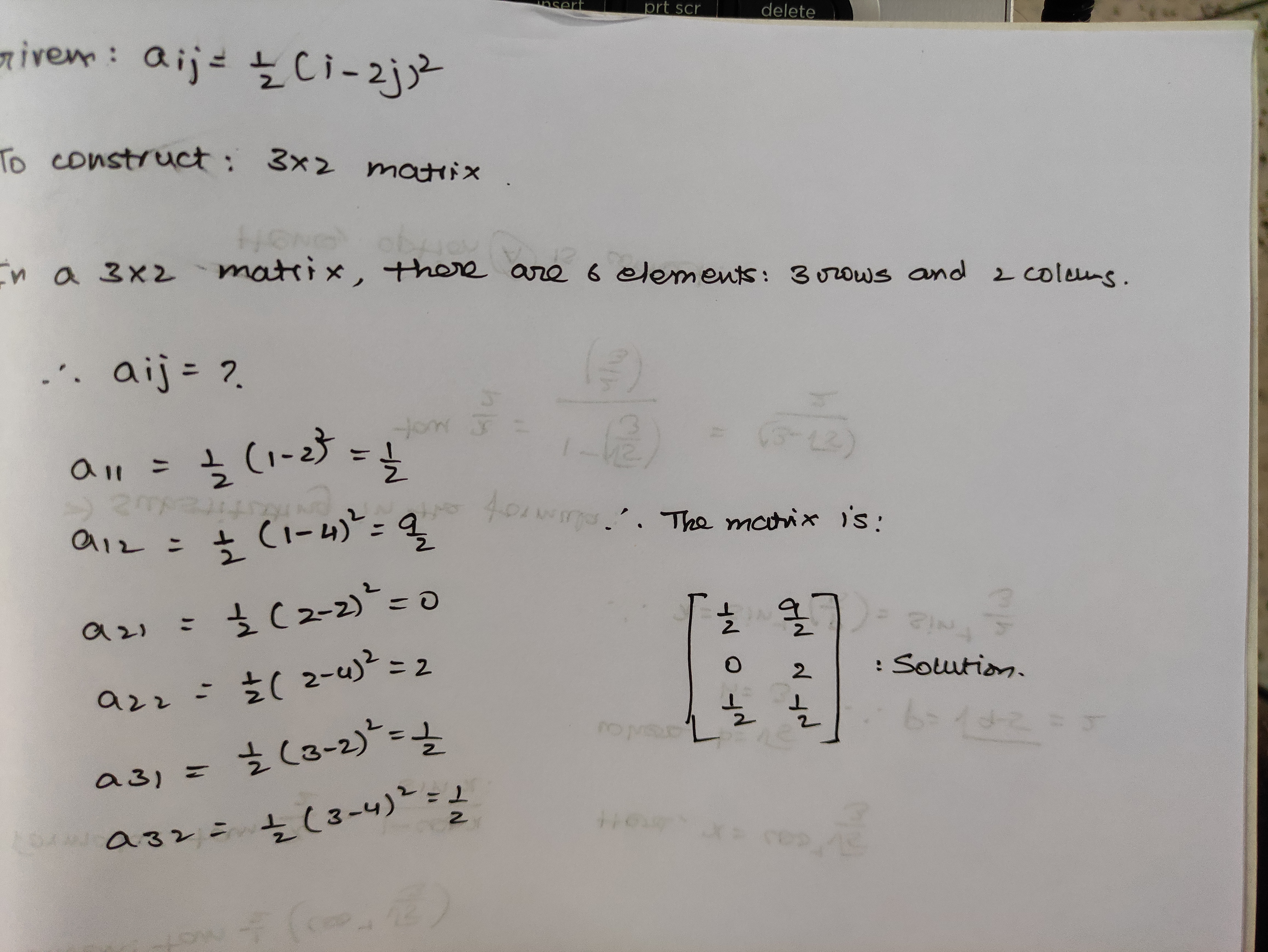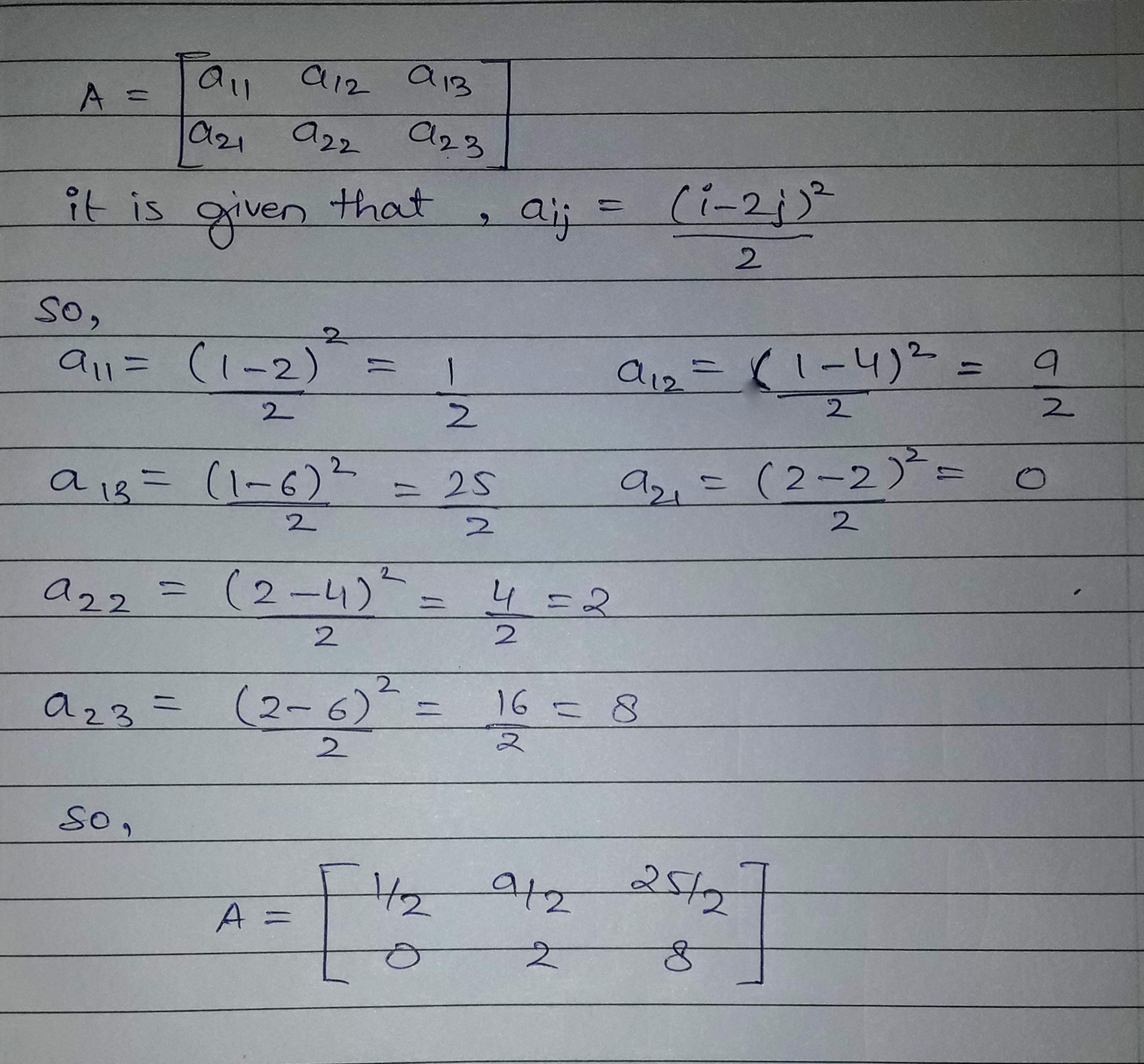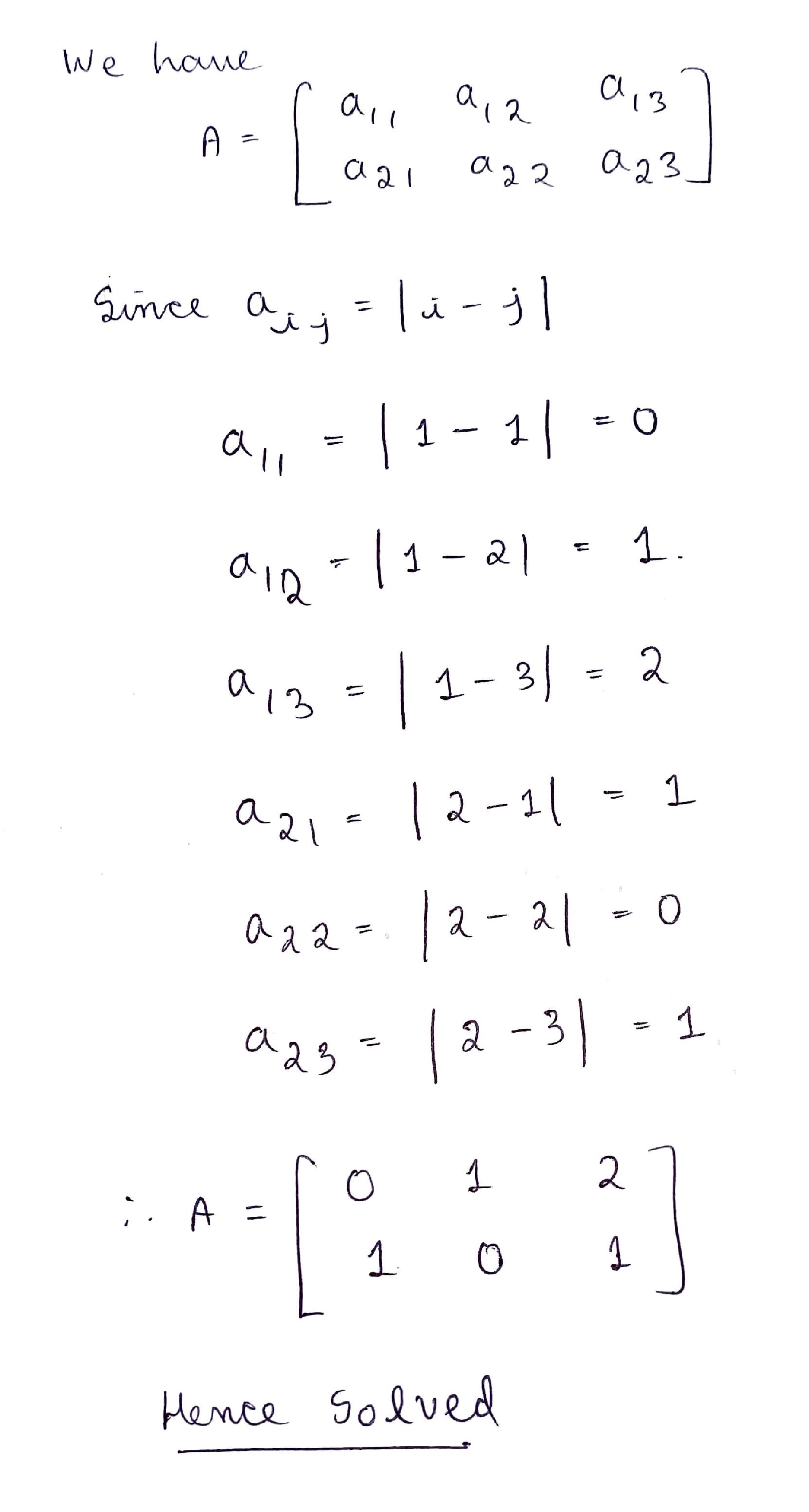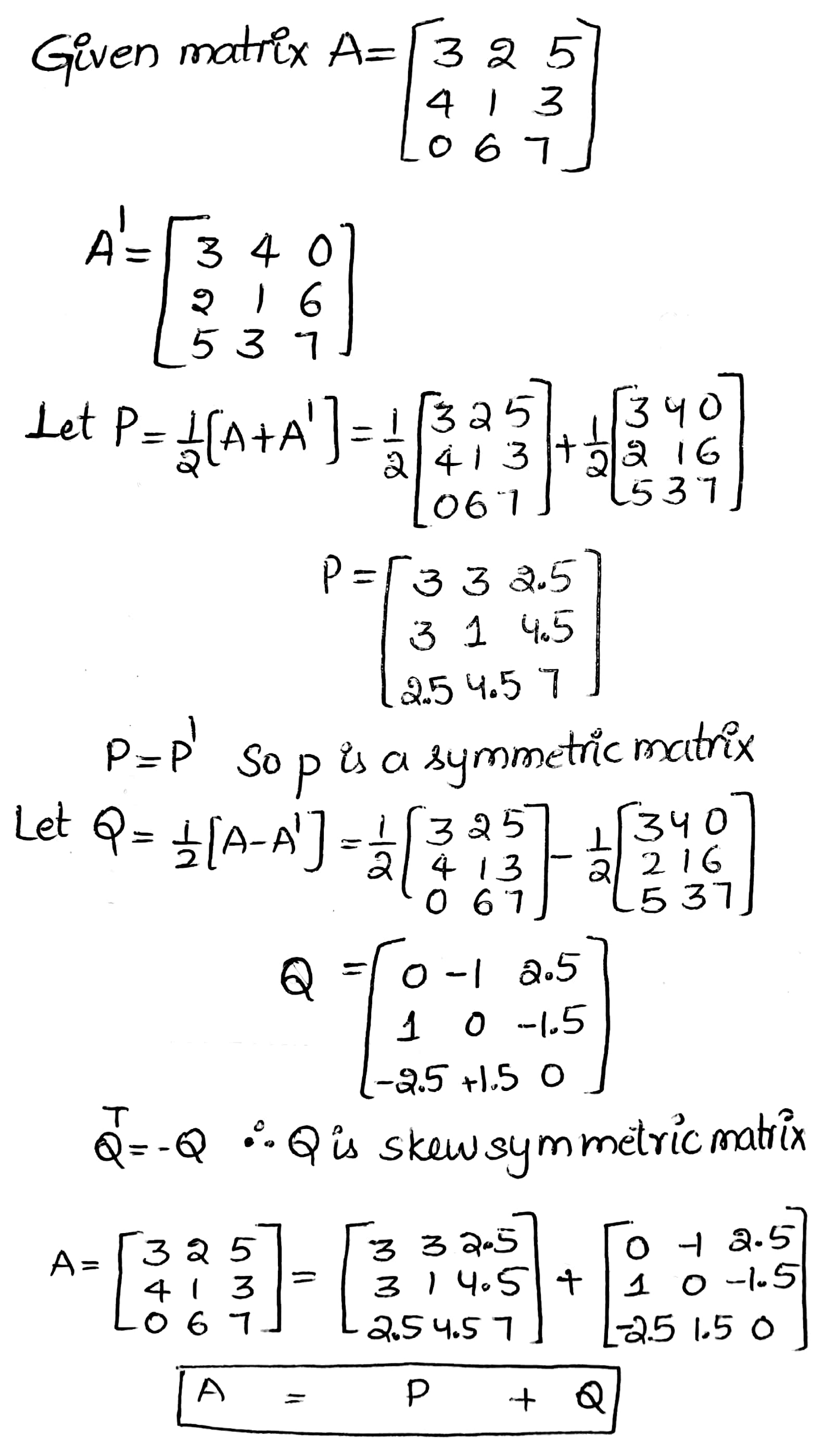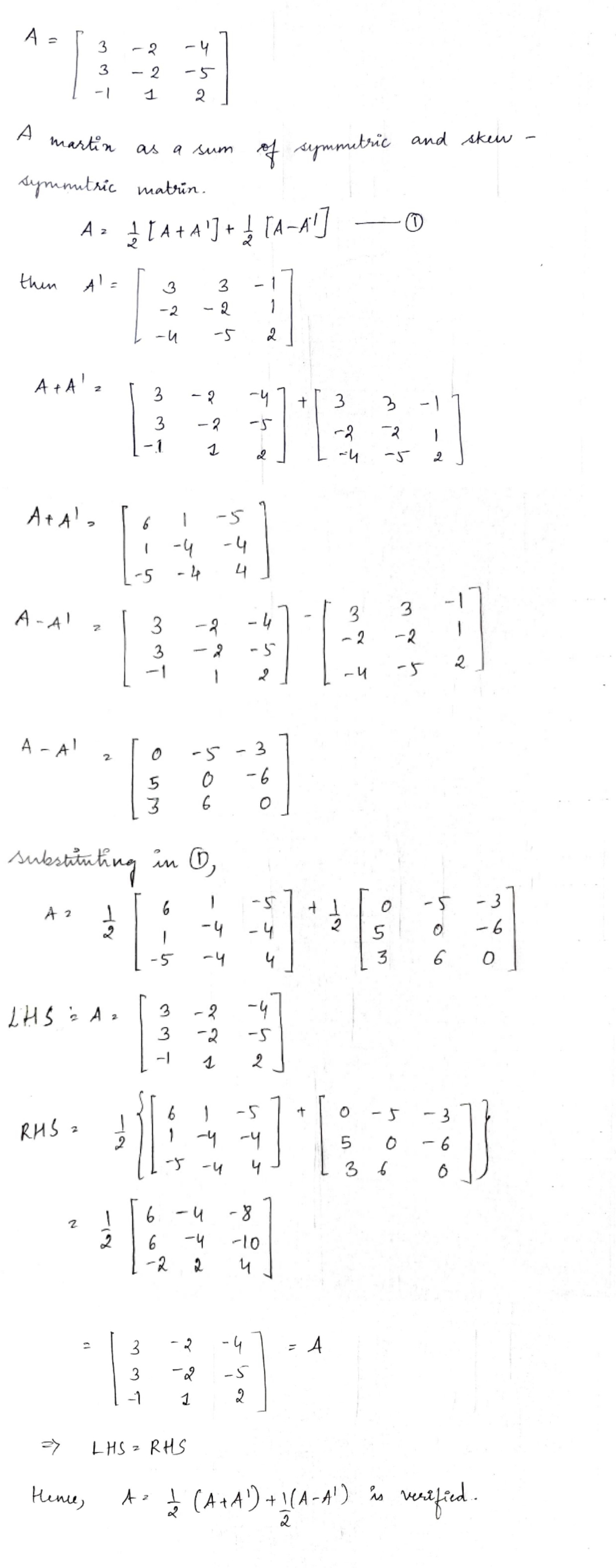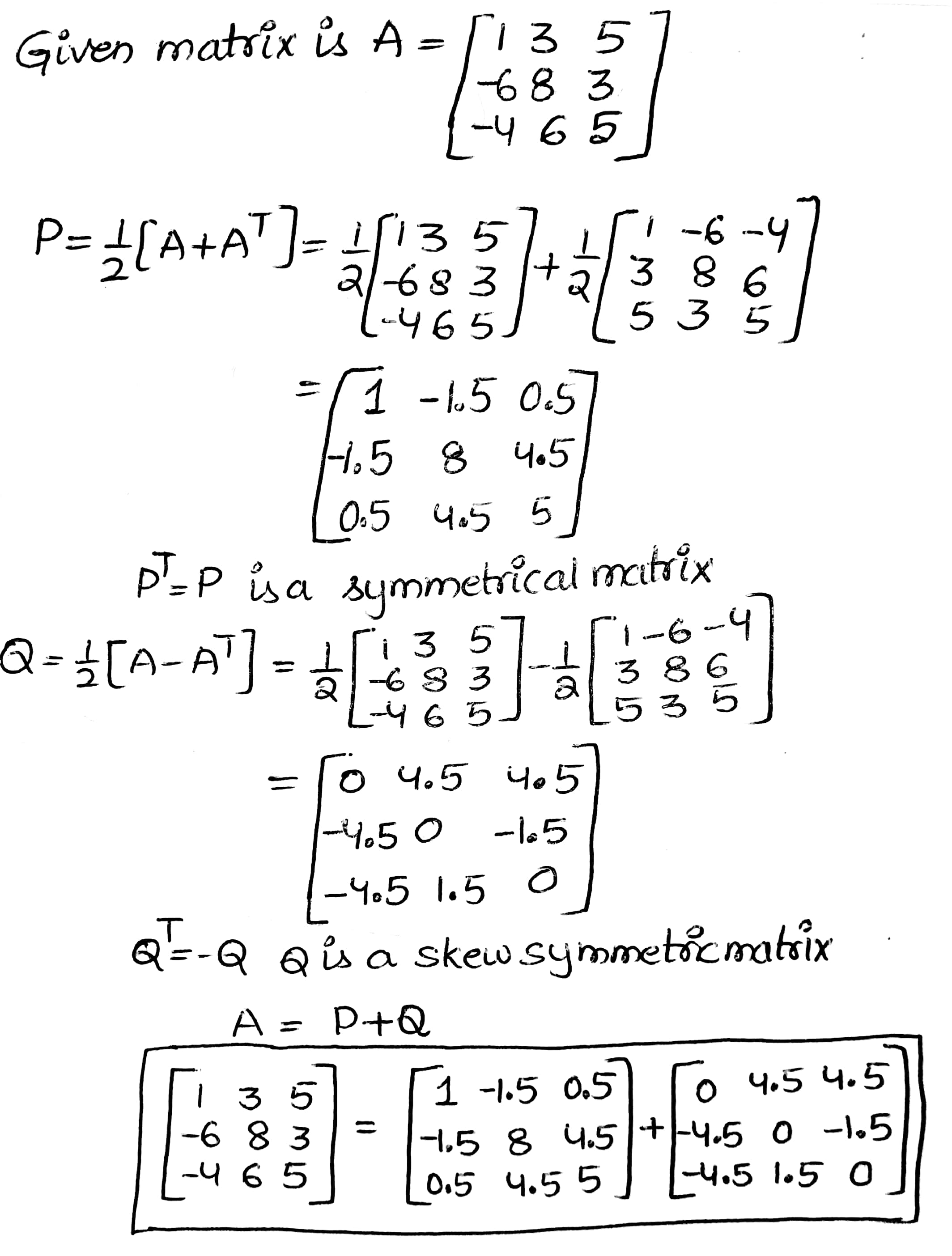Matrices - Class 12 Commerce Applied Mathematics - Extra Questions
Determine whether for given matrices matrix product is defined or not. If the product is defined, state the dimension of the product matrix.
$$A_{1 \times 3}$$ and $$B_{4 \times 3}$$
Construct a $$2\times 2$$ matrix $$A=[a_{ij}]$$ whose elements are given by $$\dfrac{1}{2}|-3i+j|$$.
If A = $$\begin{bmatrix}2 &3 &1 \\0 & -1 & 5\end{bmatrix}$$ , B =$$ \begin{bmatrix}1 & 2 &-1 \\0 & -1 & 3\end{bmatrix}$$ find 2A - 3B
A = $$\begin{bmatrix}1 & 2 & -3\\ 5 & 0 & 2\\ 1 & -1 & 1 \end{bmatrix}$$ and B = $$\begin{bmatrix}3 & -1 & 2\\ 4 & 2 & 5\\ 2 & 0 & 3 \end{bmatrix}$$
Find the matrix C satisfying the relation A + 2C = B
If $$ A=\begin{pmatrix} 4 & -2 \\ 5 & -9 \end{pmatrix}$$ and $$ B=\begin{pmatrix} 8 & 2 \\ -1 & -3 \end{pmatrix}$$ find $$6A-3B$$
If $$y=\left[ \begin{matrix} 1 & 2 \\ -1 & 5 \end{matrix} \right] $$, find a matrix $$X$$ such that $$2X+Y=\left[ \begin{matrix} 5 & 0 \\ -3 & 3 \end{matrix} \right] $$
Find matrix $$X$$, if $$X+\left[ \begin{matrix} 4 & 6 \\ -3 & 7 \end{matrix} \right] =\left[ \begin{matrix} 3 & -6 \\ 5 & -8 \end{matrix} \right] $$.
Identify the matrix given below:
$$\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 3 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 2 \end{bmatrix}$$
$$A=\begin{bmatrix} 5 & 7 \\ 9 & 4 \end{bmatrix}B=\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 \\ 3 & 5 \end{bmatrix}$$ find $$A-B$$
Construct a $$2\times 2$$ matrix $$A = [a_{ij}]$$, whose element $$a_{ij}$$ is $$a_{ij} = \dfrac {|-3i + j|}{2}$$.
Find x if $$ \left| x\quad 2 \right| $$=$$\left| 6\quad 2 \right| $$.
Find the order of $$AB$$ and $$BA$$ if $$A=\left[a_{ij}\right]_{4 \times 3} , B=\left[b_{ij}\right]_{3 \times 2}$$
Construct a $$2\times 3$$ matrix $$A = [a_{ij}]$$, whose element $$a_{ij}$$ is $$a_{ij} = i + j$$.
If the matrix $$A = \begin{bmatrix}0 & a & -3\\ 2 & 0 & -1\\ b & 1 & 0\end{bmatrix}$$ is skew-symmetric, then find the values of $$'a'$$ and $$'b'$$.
If $$A = [a_{ij}]$$ is a $$2\times 2$$ matrix such that $$a_{ij} = i + 2j$$, then find $$A$$.
If $$A$$ is skew-symmetric and $$n\epsilon N$$, such that $$(A^{n})^{T} = \lambda A^{n}$$, write the value of $$\lambda$$.
Find $$A-B$$$$A=\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 2 & 0 \\ 3 & -4 & 5 \\ 2 & 3 & -7 \end{bmatrix}$$ and $$B=\begin{bmatrix} 3 & 3 & 1 \\ 4 & -5 & 4 \\ 3 & 2 & -4 \end{bmatrix}$$
Find $$A-B$$
$$A=\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 2 & 0 \\ 3 & -4 & 5 \\ 2 & 3 & -7 \end{bmatrix}$$ and $$B=\begin{bmatrix} 3 & 3 & 1 \\ 4 & -5 & 4 \\ 3 & 2 & -4 \end{bmatrix}$$
Show that the elements on the main diagonal of a skew-symmetric matrix are all zero.
Let $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 4 \\ 3 & 2 \end{bmatrix}, B=\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 3 \\ -2 & 5 \end{bmatrix}$$ and $$C=\begin{bmatrix} -2 & 5 \\ 3 & 4 \end{bmatrix}$$. Find:
$$B-4C$$
If $$ A\quad =\quad \left[ \begin{matrix} 2 \\ 5 \end{matrix} \right] ,\quad B\quad =\quad \left[ \begin{matrix} 1 \\ 4 \end{matrix} \right] \quad and\quad C\quad =\quad \left[ \begin{matrix} 6 \\ -2 \end{matrix} \right] $$
$$ A-C $$
Classify the following matrices:
$$\text { (i) }\left[\begin{array}{cc}2 & -1 \\5 & 1\end{array}\right]$$
$$\text { (ii) }\left[\begin{array}{llll}2 & 3 & -7\end{array}\right]$$
$$\text { (iii) }\left[\begin{array}{c}3 \\0 \\-1\end{array}\right]$$
$$\text { (iv) }\left[\begin{array}{cc}2 & -4 \\0 & 0 \\1 & 7\end{array}\right]$$
$$\text { (v) }\left[\begin{array}{rrr}2 & 7 & 8 \\-1 & \sqrt{2} & 0\end{array}\right]$$
$$\text { (vi) }\left[\begin{array}{lll}0 & 0 & 0 \\0 & 0 & 0\end{array}\right]$$
if $$ A = [ 8\ \ -3] $$ and $$ B = [ 4\ \ -5] $$ find
$$ (ii) B- A $$
Construct a $$2 \times 2$$ matrix whose elements a are given by
(i) $$a_{i j}=2 i-j$$
(ii) $$a_{i j}=i . j$$
Let $$ A=\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 4 \\ 3 & 2 \end{bmatrix},B=\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 3 \\ -2 & 5 \end{bmatrix},C=\begin{bmatrix} -2 & 5 \\ 3 & 4 \end{bmatrix} $$
Find the following:
$$ 3A-C $$
Evaluate :
$$ 6 \left[ \begin{matrix} 3 \\ -2 \end{matrix} \right] -2 \left[ \begin{matrix} -8 \\ 1 \end{matrix} \right] $$
Let $$ A=\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 4 \\ 3 & 2 \end{bmatrix},B=\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 3 \\ -2 & 5 \end{bmatrix},C=\begin{bmatrix} -2 & 5 \\ 3 & 4 \end{bmatrix} $$
Find the following:
$$ A-B $$
Given $$ A\quad =\begin{bmatrix} 4 & 1 \\ 2 & 3 \end{bmatrix}\quad and\quad B\quad =\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ -2 & 1 \end{bmatrix} $$ Find
$$ A - B $$
Find the symmetric and skew-symmetric parts of the matrix
$$\quad A = \begin{bmatrix}1 & 2 & 4 \\ 6 & 8 & 1 \\ 3 & 5 & 7 \end{bmatrix}$$
$$\quad A = \begin{bmatrix}1 & 2 & 4 \\ 6 & 8 & 1 \\ 3 & 5 & 7 \end{bmatrix}$$
Write matrix $$A$$ as the sum of a symmetric and a skew symmetric matrix, where
$$\quad A = \begin{pmatrix}4 & 2 & -3 \\ 1 & 3 & -6 \\ -5 & 0 & -7\end{pmatrix}$$
Show any square matrix can be expressed as the sum of two matrices, one symmetric and the other anti-symmetric.
Construct a $$3 \times 4$$ matrix, whose elements are given by
(i) $$\displaystyle { a }_{ ij }=\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \left| -3i+j \right| $$
(ii) $$\displaystyle { a }_{ ij }=2i-j$$
Express the following matrices as the sum of a symmetric and a skew symmetric matrix:
(i) $$\displaystyle \begin{bmatrix} 3 & 5 \\ 1 & -1 \end{bmatrix}$$
(ii) $$\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} 6 \\ -2 \\ 2 \end{matrix}\begin{matrix} -2 \\ 3 \\ -1 \end{matrix}\begin{matrix} 2 \\ -1 \\ 3 \end{matrix} \right] $$
(iii) $$\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} 3 \\ -2 \\ -4 \end{matrix}\begin{matrix} 3 \\ -2 \\ -5 \end{matrix}\begin{matrix} -1 \\ 1 \\ 2 \end{matrix} \right] $$
(iv) $$\displaystyle \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 5 \\ -1 & 2 \end{bmatrix}$$
(ii) $$\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} 6 \\ -2 \\ 2 \end{matrix}\begin{matrix} -2 \\ 3 \\ -1 \end{matrix}\begin{matrix} 2 \\ -1 \\ 3 \end{matrix} \right] $$
(iii) $$\displaystyle \left[ \begin{matrix} 3 \\ -2 \\ -4 \end{matrix}\begin{matrix} 3 \\ -2 \\ -5 \end{matrix}\begin{matrix} -1 \\ 1 \\ 2 \end{matrix} \right] $$
(iv) $$\displaystyle \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 5 \\ -1 & 2 \end{bmatrix}$$
Construct a 2 $$\times$$ 2 matrix $$A = [a_{ij}]$$, whose elements are given by $$a_{ij} = |-5i + 2j|$$.
Construct a $$2\times 3$$ matrix $$A=\left[ { a }_{ ij } \right] $$ whose elements are given by $${ a }_{ ij }=\left| 2i-3j \right| $$
Construct a $$2 \times 2$$ matrix $$A = [a_{ij}]$$ whose elements are given by $$a_{ij} = ij$$
A matrix consists of $$30$$ elements. What are the possible orders it can have?
A matrix has 8 elements. What are the possible orders it can have?
The fees structure for one-day admission to a swimming pool is as follows
Daily Admission Fees in Rs.
| Member | Children | Adult |
| Before 2.00 p.m. | 20 | 30 |
| After 2.00 p.m. | 30 | 40 |
| Non - Member | ||
| Before 2.00 p.m. | 25 | 35 |
| After 2.00 p.m. | 40 | 50 |
Construct a $$2 \times 2$$ matrix $$A = [a_{ij}]$$ whose elements are given by $$a_{ij} = 2i - j$$
Write $$A = \begin{bmatrix} 3 & 5 \\ 1 & -1 \end{bmatrix}$$ as the sum of a symmetric and a skew-symmetric matrix.
Prove that any square matrix $$A$$ can be expressed as the sum of two symmetric and skew-symmetric matrices.
Construct a $$2\times 2$$ matrix $$A = [a_{ij}]$$, whose elements are given by $$a_{ij} = \dfrac {i}{j}$$.
ProveIf $$A$$ and $$B$$ are $$n$$ squared skew symmetrics matrices then $$AB$$ is symmetric if and only if $$A$$ and $$B$$ commute.
Solve $$5x - 6y + 4z = 15
7x + 4y - 3z = 19
2x + y + 6z = 46$$.
Prove that:
[ x y z ] $$\begin{bmatrix} a& h & g\\ h & b & f\\ g & f & c \end{bmatrix}$$$$\begin{bmatrix}x\\ y \\ z\end{bmatrix}$$
$$ = [ ax^2 \, + \, by^2 \, + \, cz^2 \, + cfz \, + 2gzx \, + \, 2hxy]$$
If $$A_\alpha \, = \, \begin{bmatrix}cos \, \, n\alpha & \sin \, n\alpha \\ -\sin \, n\alpha &\cos \, \, n\alpha \end{bmatrix}$$ , then the prove following .
$$A_\alpha\,A_\beta \, = \, A_{\alpha + \beta} \, =\,A_\beta A_\alpha $$
If A = $$ \begin{bmatrix} 3 & -4 \\ 1 & -1\end{bmatrix}$$ then $$ A^k \, = \, \begin{bmatrix}1 + 2k & - 4k \\ k & 1 -2k\end{bmatrix}$$
where k is any +ve integer .
If $$X = \left[ \matrix{ 0\;\;-1 \hfill \cr 1\;\; 0 \hfill \cr} \right]$$ then $${X^{1023}} = $$
Express the matrices as the sum of systemmetric & a skew- symmetric matrices $$\begin{bmatrix} 6 & -2 & 2 \\ -2 & 3 & -1 \\ 2 & -1 & 3 \end{bmatrix}$$
Express $$ \begin{bmatrix} 1 & -1 & 1 \\ 2 & 1 & -3 \\ 1 & 1 & 1 \end{bmatrix}$$ as a sum of symmetric and skew symmetric matrices.
If $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 3 \\ 5 & 7 \end{bmatrix},B=\begin{bmatrix} 0 & 4 \\ -1 & 7 \end{bmatrix},C=\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ -1 & 4 \end{bmatrix}$$, find $$AC+{B}^{2}-10C$$
Let $$f(x)=x^2-5x+5$$ then find $$f(A)$$ for $$A=\begin{bmatrix}3&1\\1&2\end{bmatrix}$$.
Find the value of $$\lambda $$, so that the matrix
$$\left[ \begin{gathered} 5 - \lambda \,\,\,\,\,\lambda + 1 \hfill \\ \,\,\,\,2\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,4 \hfill \\ \end{gathered} \right]$$ may be singular.
If $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 3 \\ 4 & 5 \end{bmatrix}$$, show that $$A-{A}^{T}$$ is a skew-symmetric matrix.
If ,$$3\begin{bmatrix} 4 & 2 \\ 1 & 3 \end{bmatrix}-2\begin{bmatrix} -2 & 1 \\ 3 & 2 \end{bmatrix}+\begin{bmatrix} x & -4 \\ 3 & y \end{bmatrix}=0$$ then $$(x,y)=$$
If $$A = \left[ \begin{array} { l l l } { 1 } & { 2 } & { 3 } \\ { 3 } & { 2 } & { 1 } \end{array} \right]$$ and $$B = \left[ \begin{array} { l l l } { 3 } & { 2 } & { 1 } \\ { 1 } & { 2 } & { 3 } \end{array} \right]$$ find$$3 B - 2 A$$
If $$A=\left[ \begin{matrix} a & 2 & 3 \\ b & c & 4 \\ d & e & f \end{matrix} \right]$$ is skew symmetric matrix, then find $$a,b,c,d,e,f$$.
If A and B are two skew symmetric matrices of same order, then AB is symmetric matrix if ___________ .
If $$A$$ is any $$m \times n$$ matrix, then show that$$\left(i\right) \left(1\right) A= A$$$$\left (ii\right) \left( - 1\right ) A = - A$$
If A is a square matrix such that $$A^2=I$$, then find the simplified value of $$(A-I)^3+(A+I)^3-7A$$.
If $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 3 & 5 \\ 7 & -9 \end{bmatrix} $$ and $$B = \begin{bmatrix} 6 & -4 \\ 2 & 3 \end{bmatrix}$$, find $$(4A-3B)$$.
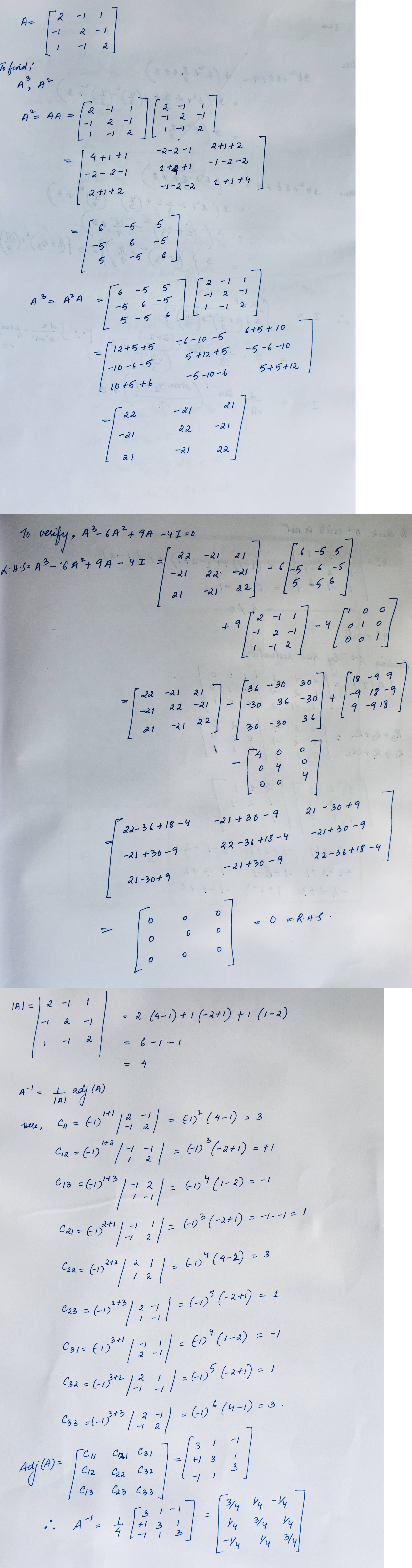
For the matrix $$A=\left[ \begin{matrix} 2 & -1 & 1 \\ -1 & 2 & -1 \\ 1 & -1 & 2 \end{matrix} \right] $$
verify that $$A^{ 3 }-6{ A }^{ 2 }+9A-4I=0$$ Hence find $${ A }^{ -1 }$$
If $$ \Delta _ { r } = \left| \begin{array} { c c c } { r - 1 } & { n } & { 6 } \\ { ( r - 1 ) ^ { 2 } } & { 2 n ^ { 2 } } & { 4 n - 2 } \\ { ( r - 1 ) ^ { 3 } } & { 3 n ^ { 3 } } & { 3 n ^ { 2 } - 3 n } \end{array} \right| .$$ then $$\sum _ { n = 1 } ^ { n } \Delta _ { r }$$ is
Construct a $$2\times 3$$ matrix $$A=\left[{a}_{ij}\right]$$ whose elements are given by $${a}_{ij}=\begin{cases} i-j\,\,\,\,i\ge j \\ i+j\,\,\,\,i<j \end{cases}$$
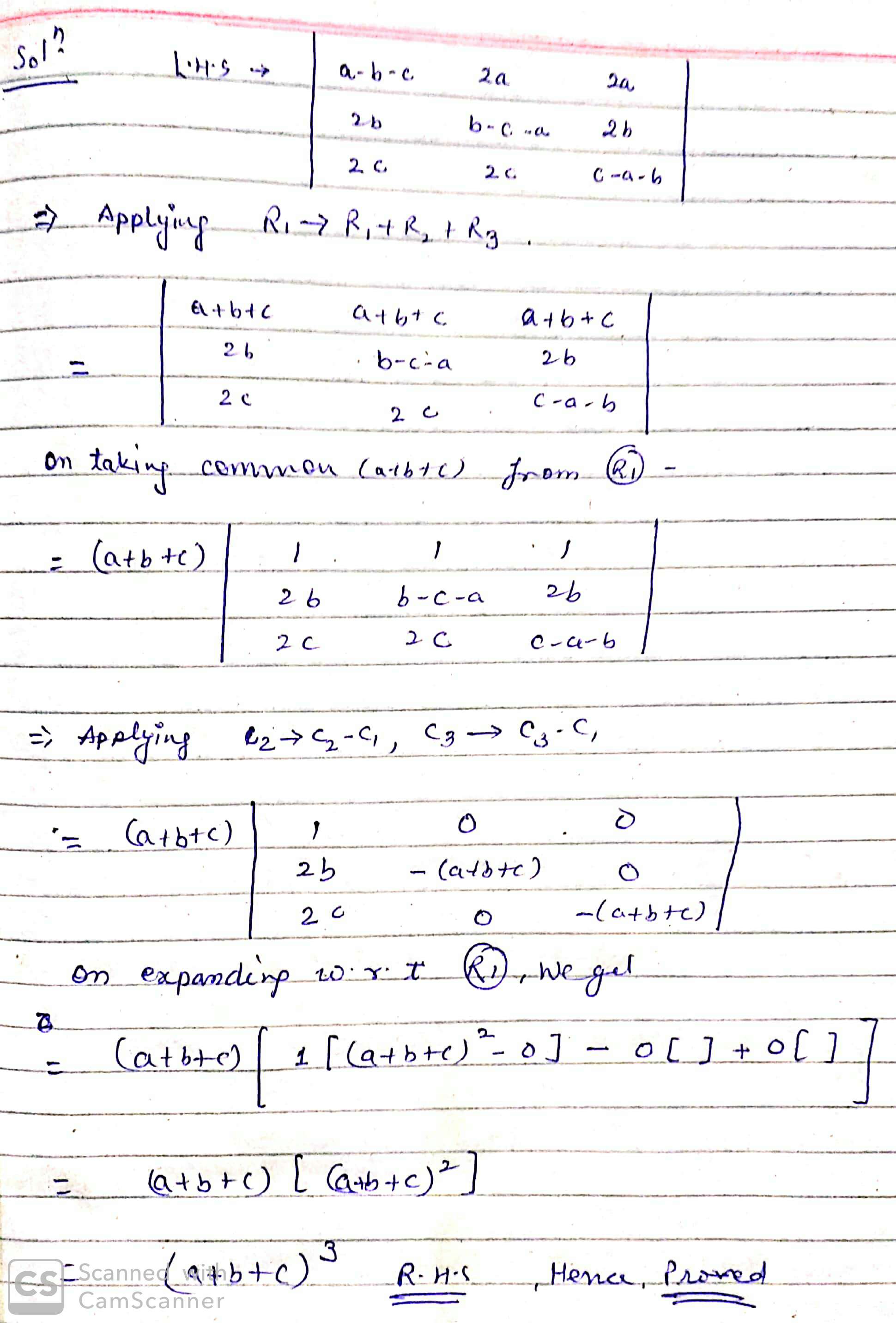
Show that $$\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{a - b - c}&{2a}&{2a}\\{2b}&{b - c - a}&{2b}\\{2c}&{2c}&{c - a - b}\end{array}} \right) = {(a + b + c)^3}$$
Construct a $$2\times 3$$ matrix $$A=\left[{a}_{ij}\right]$$ whose elements are given by $${a}_{ij}=\left[\dfrac{i}{j}\right]$$, where $$\left[.\right]$$ denotes the greatest integer function.
Find the value of a, b, c and d if
$$\left[ \begin{matrix} a+b & 3 \\ a+c & b \end{matrix} \right] =\left[ \begin{matrix} 6 & d \\ -1 & 8 \end{matrix} \right] $$
If A = $$\left( \begin{matrix} a & b \\ c & -a \end{matrix} \right) $$ such that $${ A }^{ 2 }-I$$ then,
If $$A = \left| \begin{matrix} 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \\ p & q & r \end{matrix} \right| $$ and $$I$$ is the identity matrix of order $$3$$, then show that$$A^{ 3 } = pI + qA + rA^{ 2 }$$.
If matrix A = $$[aij] _{3\times2},$$ and $$aij = (3i-2j)^2$$, then find the matrix A.
Express $$A = \begin{bmatrix} 2 & 5 & -1 \\ 3 & 1 & 5 \\ 7 & 6 & 9 \end{bmatrix}$$as sum of symmetric and skew- symmetric matrices.
Express$$\begin{bmatrix} 6 & -4 & 5 \\ 1 & 4 & -2 \\ 7 & 5 & 9 \end{bmatrix}$$ as a sum of a symmetric matrix and a skew-symmetric matrix.
Construct a $$2\times 2$$ matrix $$A = [a_{ij}]$$, whose element $$a_{ij}$$ is $$a_{ij} = \dfrac {|2i - 3j|}{2}$$.
Construct a $$2\times 2$$ matrix $$A = [a_{ij}]$$, whose element $$a_{ij}$$ is $$a_{ij} = \dfrac {(i - 2j)^{2}}{2}$$.
Construct a $$2\times 2$$ matrix $$A = [a_{ij}]$$, whose element $$a_{ij}$$ is $$a_{ij} = \dfrac {(i - j)^{2}}{2}$$.
Construct a $$2\times 2$$ matrix $$A = [a_{ij}]$$ whose elements $$a_{ij}$$ are given by:
$$a_{ij}=\left|{\dfrac{3i-j}{2}}\right|$$
Construct a $$2\times 3$$ matrix $$A = [a_{ij}]$$, whose element $$a_{ij}$$ is $$a_{ij} = 2i - j$$.
Construct a $$2\times 2$$ matrix $$A = [a_{ij}]$$, whose element $$a_{ij}$$ is $$\dfrac {(i +j)^{2}}{2}$$.
Construct a $$2\times 2$$ matrix $$A = [a_{ij}]$$, whose element $$a_{ij}$$ is $$a_{ij} = e^{2ix} \sin xj$$.
Construct a $$2\times 2$$ matrix $$A = [a_{ij}]$$, whose element $$a_{ij}$$ is $$a_{ij} = \dfrac {(2i + j)^{2}}{2}$$.
Construct a $$2\times 2$$ matrix $$A = [a_{ij}]$$, whose element $$a_{ij}$$ is $$a_{ij} = \dfrac {(i + j)^{2}}{2}$$. .
Construct a $$4\times 3$$ matrix $$A =[a_{ij}]$$, whose element $$a_{ij}$$ is $$a_{ij} = 2i + \dfrac {i}{j}$$.
If $$A = \begin{bmatrix}2 & 4\\ 3 & 2\end{bmatrix}, B = \begin{bmatrix} 1& 3\\ -2 & 5\end{bmatrix}$$, then find the value of $$2A - 3B$$.
IF $$B = \begin{bmatrix} 1& 3\\ -2 & 5\end{bmatrix}$$ and $$C = \begin{bmatrix} -2& 5\\ 3 & 4\end{bmatrix}$$, then find the value of $$B - 4C$$.
If $$A = \begin{bmatrix} 3& -4\\ 1 & -1\end{bmatrix}$$, then prove that $$A - A^{T}$$ is a skew-symmetric matrix.
If $$A = \begin{bmatrix}2 & 4\\ 3 & 2\end{bmatrix}$$ and $$B = \begin{bmatrix} -2& 5\\ 3 & 4\end{bmatrix}$$, then find the value of $$3A - B$$.
Construct a $$4\times 3$$ matrix $$A =[a_{ij}]$$, whose element $$a_{ij}$$ is $$a_{ij} = \dfrac {i - j}{i + j}$$.
Express the matrix $$A = \begin{bmatrix} 4& 2 &-1 \\ 3 & 5 & 7\\ 1 & -2 & 1\end{bmatrix}$$ as the sum of symmetric and a skew-symmetric matrix.
Write matrix $$A$$ satisfying $$A + \begin{bmatrix} 2& 3\\ -1 & 4\end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix}3 & -6\\ -3 & 8\end{bmatrix}$$.
Express the square matrix $$A$$ as the sum of a symmetric and a skew-symmetric matrix.
If $$A = [a_{ij}]$$ is a skew-symmetric matrix, then write a value of $$\displaystyle \sum_{i} \displaystyle \sum_{j} a_{ij}$$.
If $$A$$ and $$B$$ are symmetric matrices of the same order, write whether $$AB - BA$$ is symmetric or skew-symmetric or neither of the two.
If $$\begin{bmatrix} 9& -1 & 4\\ -2 & 1 & 3\end{bmatrix} = A + \begin{bmatrix} 1& 2 & -1\\ 0 &4 &9 \end{bmatrix}$$, then find matrix $$A$$.
For what value of $$x$$, is the matrix $$A = \begin{bmatrix}0 & 1 & -2\\ -1 & 0 & 3\\ x & -3 & 0\end{bmatrix}$$ a skew-symmetric matrix?
Construct a $$2\times 2$$ matrix $$A = [a_{ij}]$$, whose elements $$a_{ij}$$ are given by $$a_{ij} = \left\{\begin{matrix}\dfrac {|-3i + j|}{2}, & \ \text{if}\ i\neq j\\ (i + j)^{2}, & \ \text{if}\ i = j\end{matrix}\right.$$
If $$A = \begin{bmatrix}-1 & 1 & -1\\ 3 & -3 & 3\\ 5 & 5 & 5\end{bmatrix}$$ and $$B = \begin{bmatrix}0 & 4 & 3\\ 1 & -3 & -3\\ -1 & 4 & 4\end{bmatrix}$$, then find $$A^{2} - B^{2}$$.
If $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 3 & 1 & 2 \\ 1 & 2 & -3 \end{bmatrix}$$ and $$B=\begin{bmatrix} -2 & 0 & 4 \\ 5 & -3 & 2 \end{bmatrix}$$, find $$(2A-B)$$.
Let $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 4 \\ 3 & 2 \end{bmatrix}, B=\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 3 \\ -2 & 5 \end{bmatrix}$$ and $$C=\begin{bmatrix} -2 & 5 \\ 3 & 4 \end{bmatrix}$$. Find:
$$A-2B+3C$$
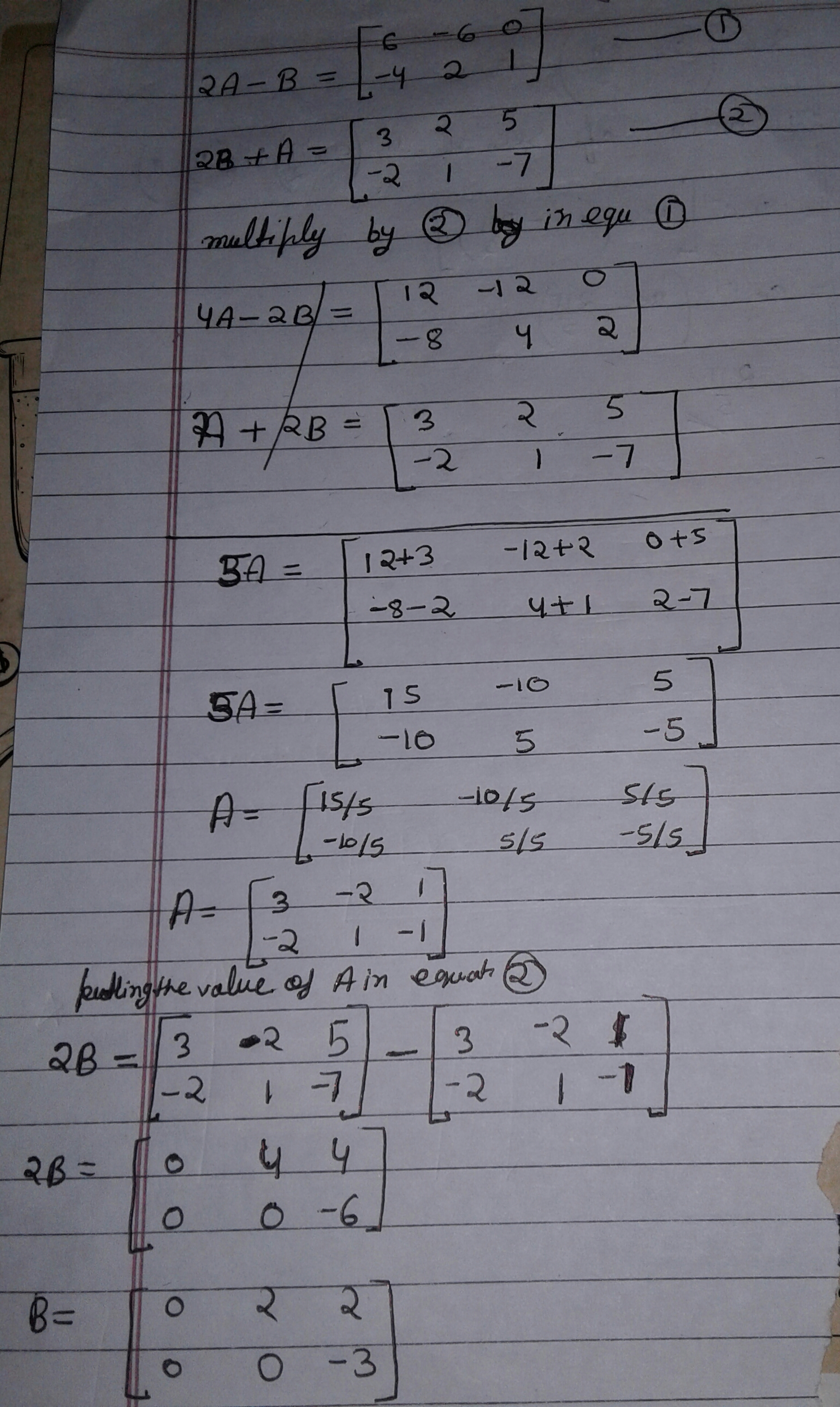
Find matrices $$A$$ and $$B$$, if
$$2A-B=\begin{bmatrix} 6 & -6 & 0 \\ -4 & 2 & 1 \end{bmatrix}$$ and $$2B+A=\begin{bmatrix} 3 & 2 & 5 \\ -2 & 1 & -7 \end{bmatrix}$$.
Express the matrix $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 3 & 2 & 5 \\ 4 & 1 & 3 \\ 0 & 6 & 7 \end{bmatrix}$$ as sum of two matrices such that one is symmetric and the other is skew-symmetric.
If $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & -2 \\ 3 & -1 & 0 \\ -2 & 1 & 1 \end{bmatrix},B=\begin{bmatrix} 0 & 5 & -4 \\ -2 & 1 & 3 \\ -1 & 0 & 2 \end{bmatrix}$$ and $$C=\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 5 & 2 \\ -1 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & -1 & 1 \end{bmatrix}$$ verify that $$A(B-C)=(AB-AC)$$.
Construct a $$2\times 3$$ matrix whose elements are given by
$$a_{ij}=\dfrac{1}{2}|-3i+j|$$.
Construct a $$3\times 2$$ matrix whose elements are given by $$a_{ij}=(2i -j)$$
Construct a $$3\times 2$$ matrix whose elements are given by
$$a_{ij}=\dfrac{1}{2}(i-2j)^2$$.
Construct a $$3\times 4$$ matrix whose elements are given by $$a_{ij}=\dfrac {1}{2}|-3i+j\ |$$.
Construct a $$4\times 3$$ matrix whose elements are given by $$a_{ij}=\dfrac {i}{j}$$.
Construct a $$2\times 3$$ matrix whose elements are $$a_{ij}=\dfrac {(i-2j)^2}{2}$$.
Construct a $$2\times 2$$ matrix whose elements are $$a_{ij}=\dfrac {(i+2j)^2}{2}$$.
Express the matrix $$A$$ as the sum of a symmetric and a skew symmetric matrix, where
$$A= \begin{bmatrix} 2 & 4 & -6 \\ 7 & 3 & 5 \\ 1 & -2 & 4 \end{bmatrix}$$
Prove that every square matrix can be uniquely expressed as the sum of a symmetric matrix and skew-symmetric matrix.
Construct $$a_{2 \times 2}$$ matrix, where $$a_v=\dfrac{(i-2j)^2}{2}$$
Construct a $$3 \times 2$$ matrix whose elements are given by $$a_v=e^{ix}.\sin \ jx$$.
Construct $$a_{2 \times 2}$$ matrix, where $$a_v=|-2i+3j|$$
Sum of two skew symmetric matrices is always ______ matrix.
If the matrix $$\begin{bmatrix} 0 & a & 3 \\ 2 & b & -1 \\ c & 1 & 0 \end{bmatrix}$$ is a skew symmetric matrix, then find the values of $$a,\ b$$ and $$c$$.
Construct a matrix $$A=[a_{i}]_{2\times 2}$$ whose elements $$a_{ij}$$ are given by $$a_{ij}=e^{2ix}\sin jx$$
Express the matrix $$\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 3 & 1 \\ 1 & -1 & 2 \\ 4 & 1 & 2 \end{bmatrix}$$ as the sum of a symmetric and a skew-symmetric matrix.
Show with the usual notation that for any matrix
$$A = [a_{ij}]_{3 \times 3} $$ is $$ a_{11} A_{21} + a_{12} A_{22} + a_{13} A_{23} = 0 $$
Show with the usual notation that for any matrix
$$A = [a_{ij}]_{3 \times 3} $$ is $$ a_{11} A_{11} + a_{12} A_{12} + a_{13} A_{13} = |A| $$
Construct a $$ 3 \times 4 $$ matrix, whose elements are given by:
(i) $$ a_{ij}=\frac{1}{2} \left| -3i+j \right| $$
(ii) $$ a_{ij}=2i-j $$
If $$ A= \left[ \begin{matrix} \frac { 2 }{ 3 } & 1 & \frac { 5 }{ 3 } \\ \frac { 1 }{ 3 } & \frac { 2 }{ 3 } & \frac { 4 }{ 3 } \\ \frac { 7 }{ 3 } & 2 & \frac { 2 }{ 3 } \end{matrix} \right] and\quad B=\left[ \begin{matrix} \frac { 2 }{ 5 } & \frac { 3 }{ 5 } & 1 \\ \frac { 1 }{ 5 } & \frac { 2 }{ 5 } & \frac { 4 }{ 5 } \\ \frac { 7 }{ 5 } & \frac { 6 }{ 5 } & \frac { 2 }{ 5 } \end{matrix} \right] ,then $$
compute $$ 3A-5B $$
Express matrix $$A$$ as the sum of symmetric and skew symmetric matrices, where $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 6 & 2 \\ 5 & 4 \end{bmatrix}$$.
Construct a matrix $$B=[b_{ij}]$$ of the order $$2\times 3$$, whose elements are $$b_{ij}=(i+2j)^2 /2$$.
$$ A = \left[ \begin{matrix} 6 & 8 & 7 \\ 4 & 2 & 3 \\ 9 & 7 & 1 \end{matrix} \right] $$ is the sum of symmentric and skew symmentric matrix , find B
Explain the following matrices as the sum of symmetric and a skew symmetric matrix :
$$ \begin{bmatrix} 3\quad & 5 \\ 1 & -1 \end{bmatrix} $$
Explain the following matrices s the sum of symmetric and a skew symmetric matrix :
$$ \left[ \begin{matrix} 3 & 3 & -1 \\ -2 & -2 & 1 \\ -4 & -5 & 2 \end{matrix} \right] $$
Construct a matrix of order $$3\times 3, B=[b_{ij}]$$, whose elements are $$b_{ij}=(i)\ (j)$$.
Explain the following matrices s the sum of symmetric and a skew symmetric matrix :
$$ \left[ \begin{matrix} 6 & -2 & 2 \\ -2 & 3 & -1 \\ 2 & -1 & 3 \end{matrix} \right] $$
Construct a $$2 \times 2$$ matrix $$A=\left[a_{ij}\right] $$, where elements are given by:
$$ a_{ij} = \dfrac {\left(i+2i\right)^{2}}{2i}$$
Construct a $$2 \times 2$$ matrix $$A=\left[a_{ij}\right] $$, where elements are given by:
$$a_{ij} =2i-3j$$
Fill in the blanks :
A square matrix $$A$$ is said to be skew -symmetric, if ________.
If $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}$$ and $$B=\begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 \\ -1 & 0 \end{bmatrix}$$, then find the matrix from of the following $$(aA+bB) \ (aA-bB)$$.
Construct a $$2 \times 2$$ matrix $$A=\left[a_{ij}\right] $$, where elements are given by:
$$ a_{ij} = \dfrac{2i-j}{3i+j}$$
The rates for the entrance tickets at a water theme park are listed below:
| Week Days rates (Rs.) | Week End rates (Rs.) | |
| Adult | 400 | 500 |
| Children | 200 | 250 |
| Senior Citizen | 300 | 400 |
There are 6 Higher Secondary Schools, 8 High Schools and 13 Primary Schools in a town. Represent these data in the form of $$3 \times 1$$ and $$1 \times 3$$ matrices.
Construct a $$3 \times 2$$ matrix $$ A = [a_{ij}]$$ whose elements are given by $$a_{ij} = \dfrac{i}{j}$$
Prove that $$A= \bigl(\begin{smallmatrix} 5& 2\\ 7 & 3\end{smallmatrix}\bigr)$$ and $$B = \bigl(\begin{smallmatrix} 3& -2 \\ -7 & 5\end{smallmatrix}\bigr)$$ are inverses to each other under matrix multiplication.
Construct a $$2\times 3$$ matrix $$A=\left[{a}_{ij}\right]$$ whose elements are given by $${a}_{ij}=\left(\dfrac{3i+4j}{2}\right)$$, where $$\left(.\right)$$ denotes the least integer function.
If $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 0 & {-1} \\ 4 & {-3} \end{bmatrix}$$, $$B=\begin{bmatrix} {-5} \\ 6 \end{bmatrix}$$ and $$3A \times M = 2B$$
find matrix $$M.$$
If A be any $$m \, \times \, n$$ matrix and both AB and BA are defined prove that B should be $$m \, \times \, n$$ matrix
If A = $$\begin{bmatrix} 2& 3& 4\\ 1& 2& 3\\ -1& 1& 2\end{bmatrix}$$, B = $$\begin{bmatrix} 1& 3& 0\\ -1& 2& 1\\ 0& 0& 2\end{bmatrix}$$
Show that AB $$\neq$$ BA.
If A = $$\begin{bmatrix} 1& 2\\ 3& 0\\ 4& 1\end{bmatrix}$$ and B = $$\begin{bmatrix} 0& 1& 0\\ 0& 2& 1\\ 2& 3& 1\end{bmatrix}$$ find BA. Can we find AB also?
Show that product of two given matrices can be a zero matrix without either of the matrices begins a zero matrix.
Find the values of $$x, y, a$$ and $$b$$ if $$\begin{bmatrix} 3x+4y & 2 & x-2y \\ a+b & 2a-b & -1 \end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 2 & 4 \\ 5 & -5 & -1 \end{bmatrix}$$.
For any square matrix $$A$$ with real numbers,
$$A + A ^ { \prime }$$ is a symmetric and
$$A - A ^ { \prime }$$ is a skew-symmetric
If $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 8 & 0 \\ 4 & -2 \\ 3 & 6 \end{bmatrix}\ and \ B=\begin{bmatrix} 2 & -2 \\ 4 & 2 \\ -5 & 1 \end{bmatrix}$$, then find the matrix $$X$$, such that $$2A+3X=5B$$.
Construct a $$2\times 3$$ matrix $$A=\left[{a}_{ij}\right]$$ whose elements are given by $${a}_{ij}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left|2i-3j\right|$$
Express the matrix $$\left[ \begin{array} { c c c } { 1 } & { - 2 } & { 3 } \\ { 3 } & { 4 } & { 5 } \\ { 5 } & { 7 } & { 9 } \end{array} \right]$$ as the sum of a symmetric and a skew-symmetric matrix.
Construct a $$ 2 \times 3 $$ matrix whose elements are given by $$ {a}_{ij} =|i-j| $$
If $$A=\left[ \begin{matrix} 1 & 2 \\ 3 & 4 \end{matrix} \right] ,B\left[ \begin{matrix} 3 & 8 \\ 7 & 2 \end{matrix} \right] \quad $$ and $$2x+A=B$$ then find $$x$$
Construct a $$2\times 3$$ matrix $$A=\left[{a}_{ij}\right]$$ whose elements are given by $${a}_{ij}=\left\{\dfrac{2\,i}{3\,j}\right\}$$, where $$\left\{.\right\}$$ denotes the fractional part function.
If $$A=\left[ \begin{matrix} 3 & 2 & 0 \\ 1 & 4 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 5 \end{matrix} \right]$$.Show that $${A}^{2}-7A+10=0$$
Let $$A = \begin{bmatrix} 3 & 2 & 5 \\ 4 & 1 & 3 \\ 0 & 6 & 7 \end{bmatrix}$$ , express A as a sum of two matrices such that one is symmetric & other is skew symmetric.
Express the following matrix as the sum of a symmetric and skew symmetric matrix, & verify your result.
$$\begin{bmatrix} 3 &-2 & -4 \\ 3 & -2 & -5 \\ -1 & 1 & 2 \end{bmatrix}$$
Express the following matrix as the sum of a symmetric and a skew- symmetric matrix.
$$ \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 3 & 5 \\ -6 & 8 & 3 \\ -4 & 6 & 5 \end{bmatrix}$$
Let $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 \\ -1 & 3 \end{bmatrix},B=\begin{bmatrix} 4 & 0 \\ 1 & 5 \end{bmatrix},C=\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 0 \\ 1 & -2 \end{bmatrix},a=4,b=-2,$$ then show that:
$$(a+b)B=aB+bB$$
Class 12 Commerce Applied Mathematics Extra Questions
- Application Of Derivatives Extra Questions
- Applications Of Integrals Extra Questions
- Definite Integrals Extra Questions
- Determinants Extra Questions
- Differential Equations Extra Questions
- Indefinite Integrals Extra Questions
- Linear Equations Extra Questions
- Matrices Extra Questions
- Probability Distribution And Its Mean And Variance Extra Questions
- Quantification And Numerical Applications Extra Questions
- Standard Probability Distributions Extra Questions