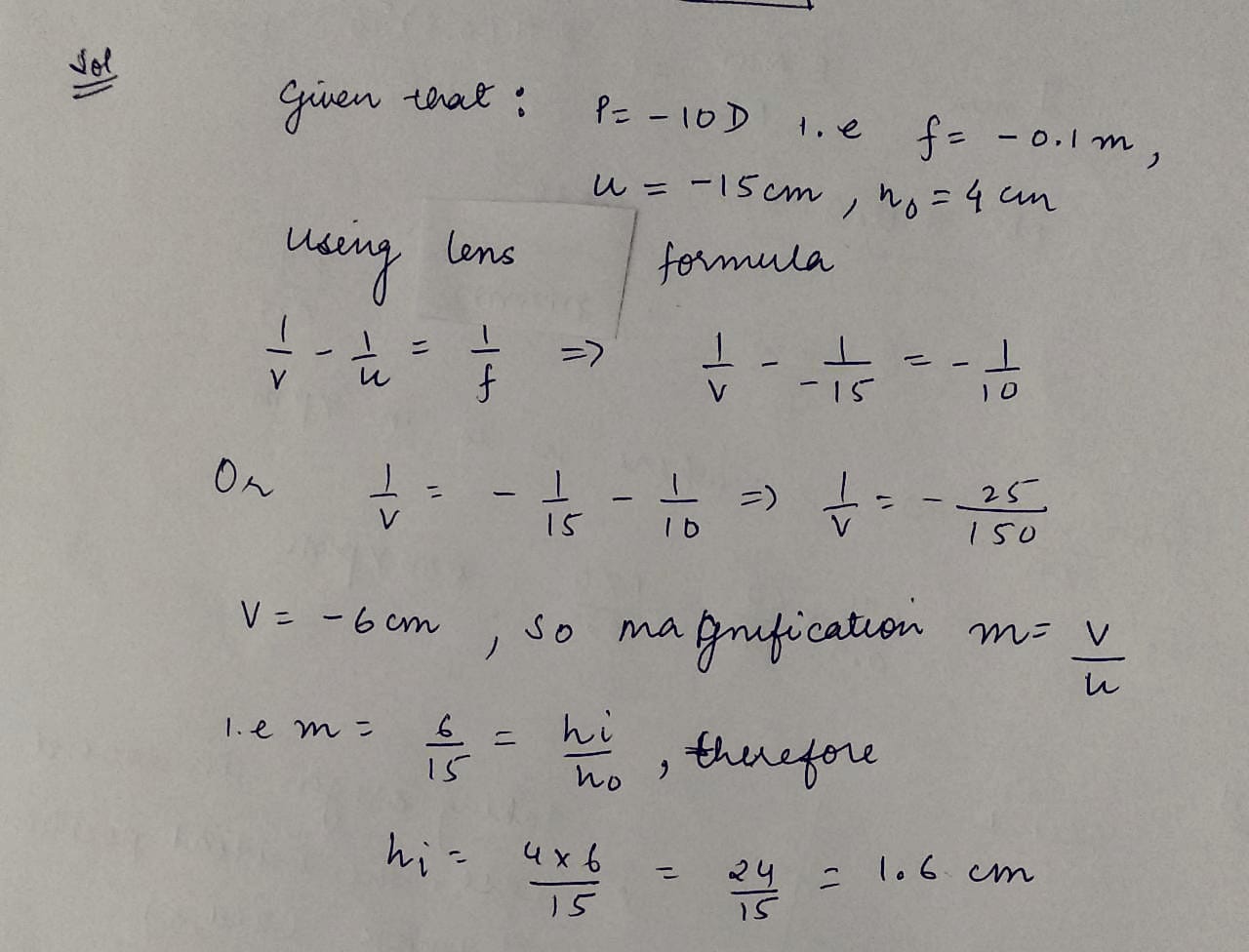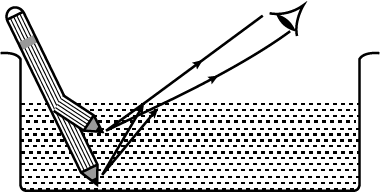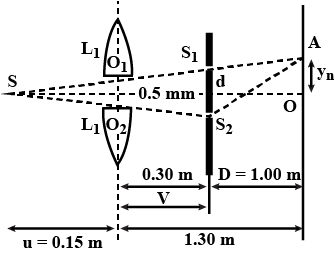Ray Optics And Optical Instruments - Class 12 Engineering Physics - Extra Questions
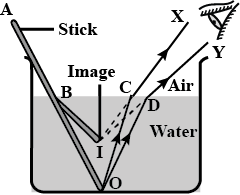
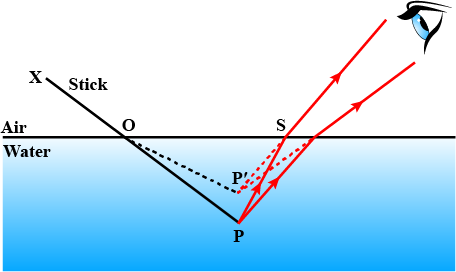
Why does a Stick immersed in water appear bent and short? Explain with the help of a ray diagram.
Match the entries of column I with entries of column II
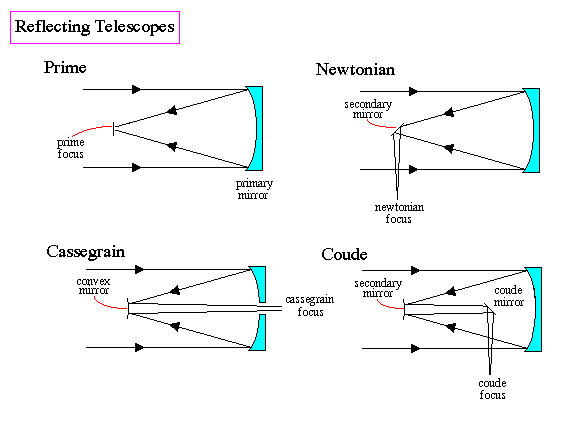
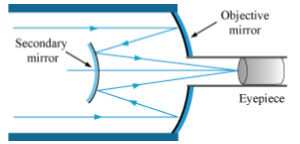
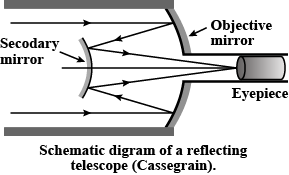
Draw a schematic diagram of a reflecting telescope (Cassegrain). Write its two advantages over a refracting telescope.
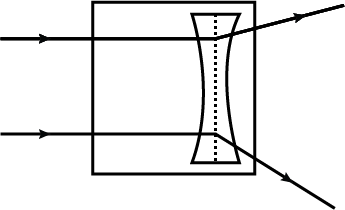
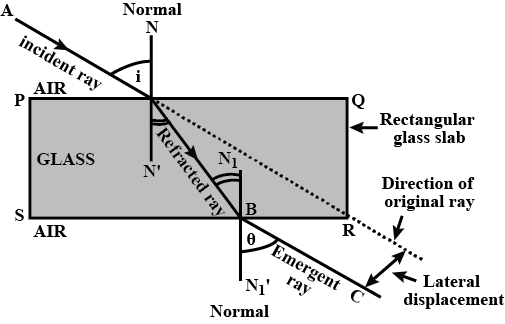
How does the shift depend upon the thickness AD or BC of the block ?
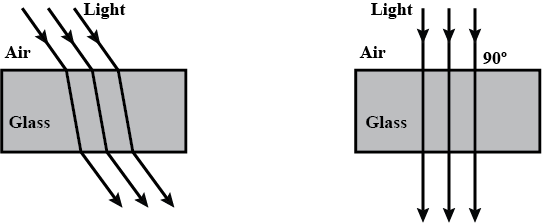
Why does a beam of light bend when it enters glass at an angle ? Why does it not bend if it enters the glass at right angles ?
Draw and complete the following diagrams to show that what happens to the beams of light as they enter the glass block and then leave it :

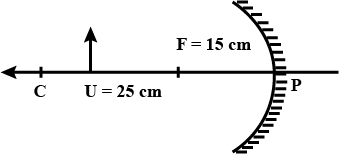
An object is placed at a long distance in front of a convex mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. State the position of its image.
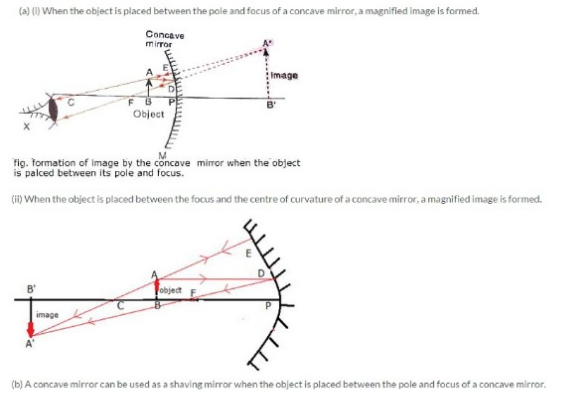
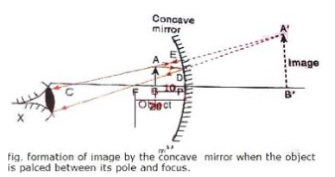
(a) Give two circumstances in which a concave mirror can form a magnified image of an object placed in front of it. Illustrate your answer by drawing labelled ray diagrams for both.
(b) Which one of these circumstances enables a concave mirror to be used as a shaving mirror?
How does phenomenon of lateral inversion occurs
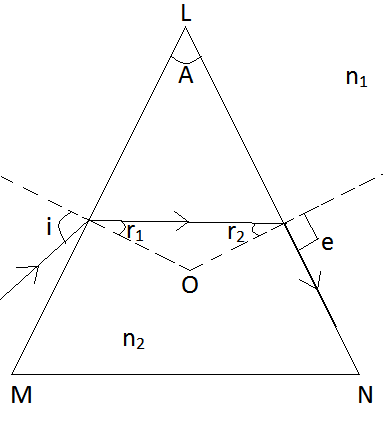
Why does white light split up into different colours while passing through a glass prism
Which is a better reflector- a plane mirror or a right - angled p rism
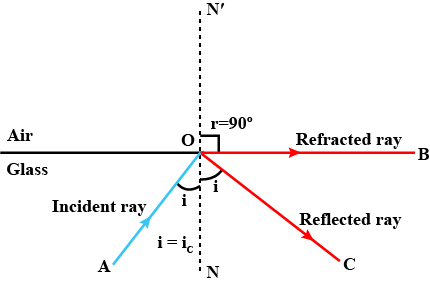
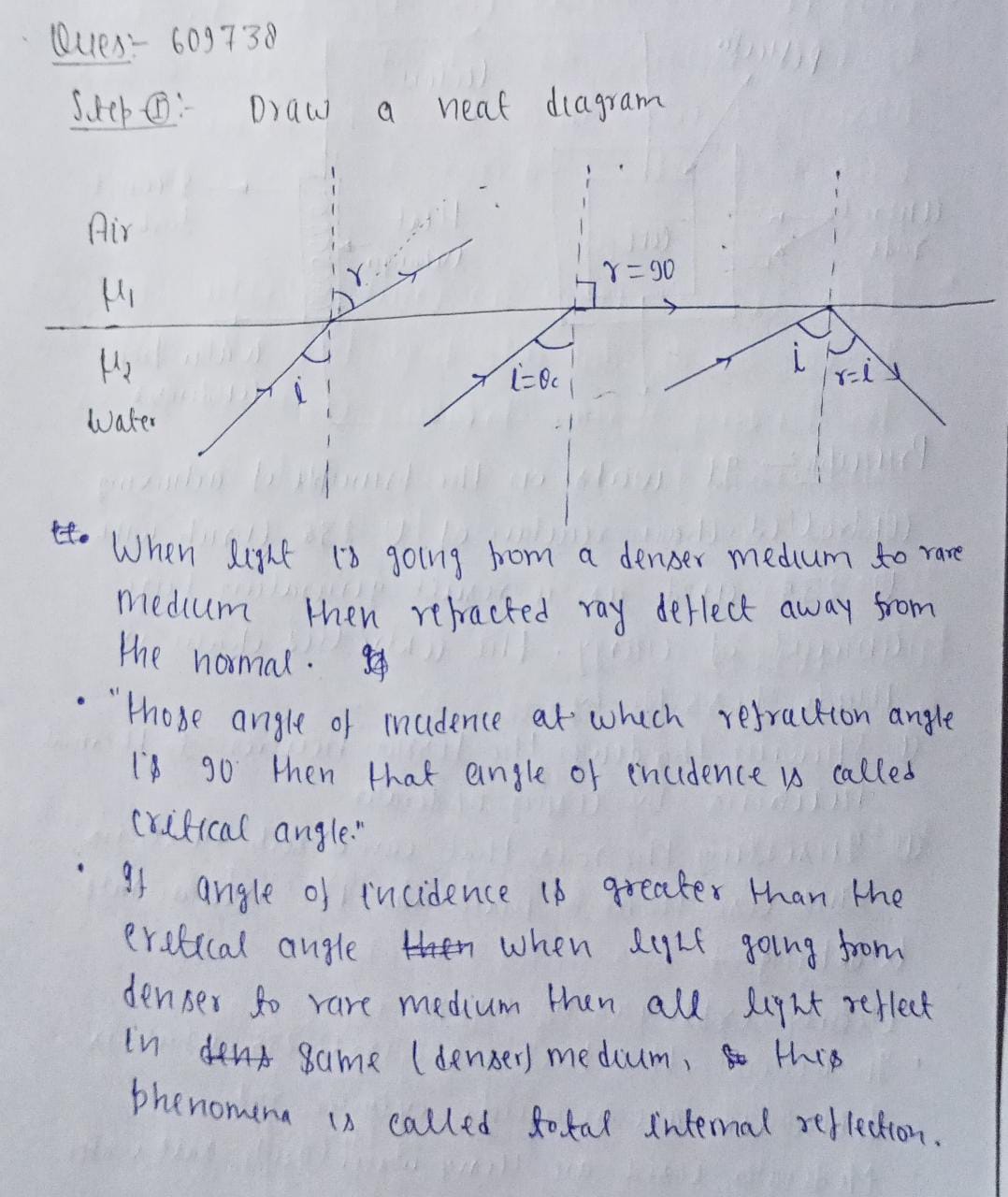
Explain the term critical angle with the aid of a labelled diagram.
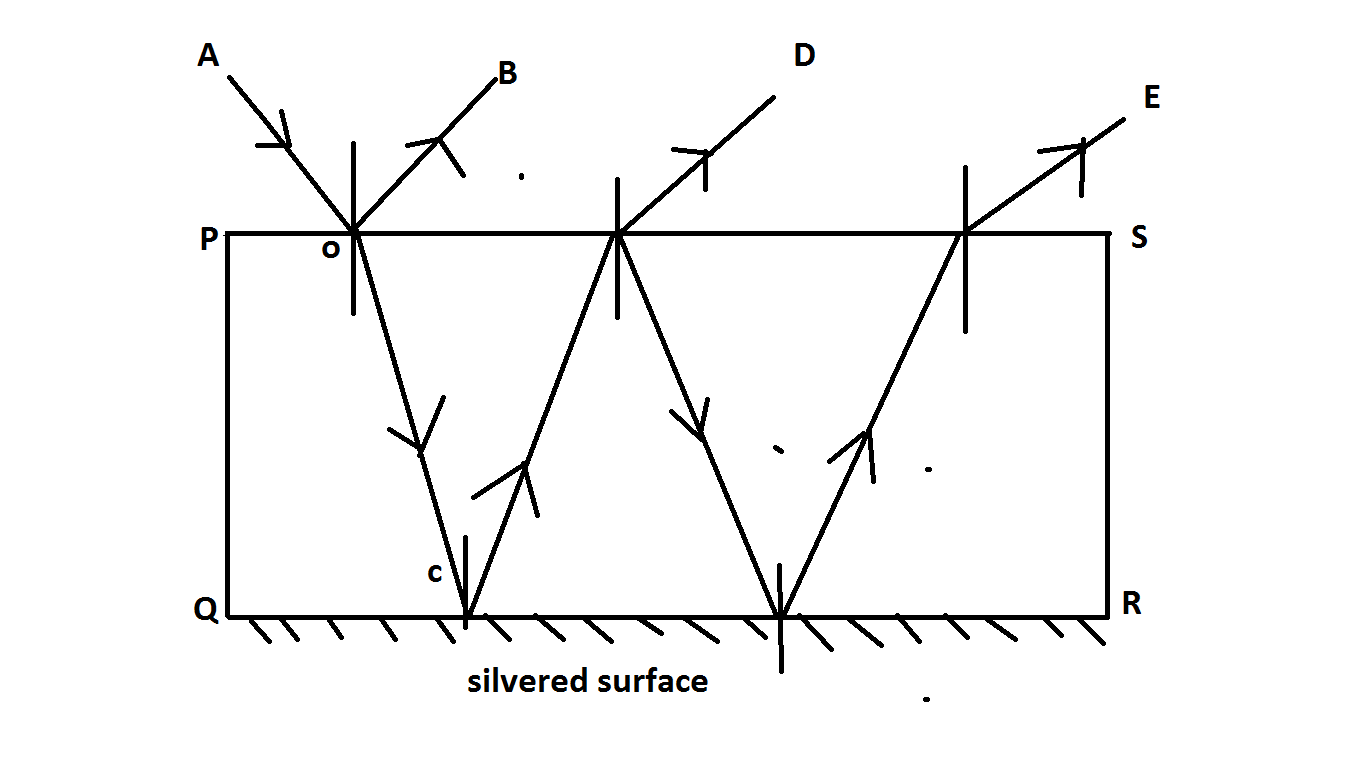
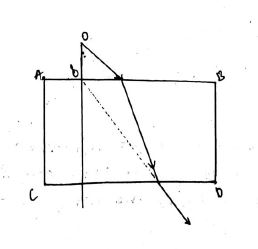
Show at least two rays emerging from the surface PQ after reflection from the surface RS.
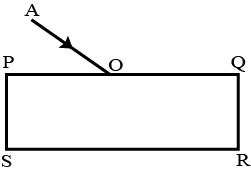
How is the reflection of light ray from a plane mirror different from the refraction of light ray as it enters a block of glass ?
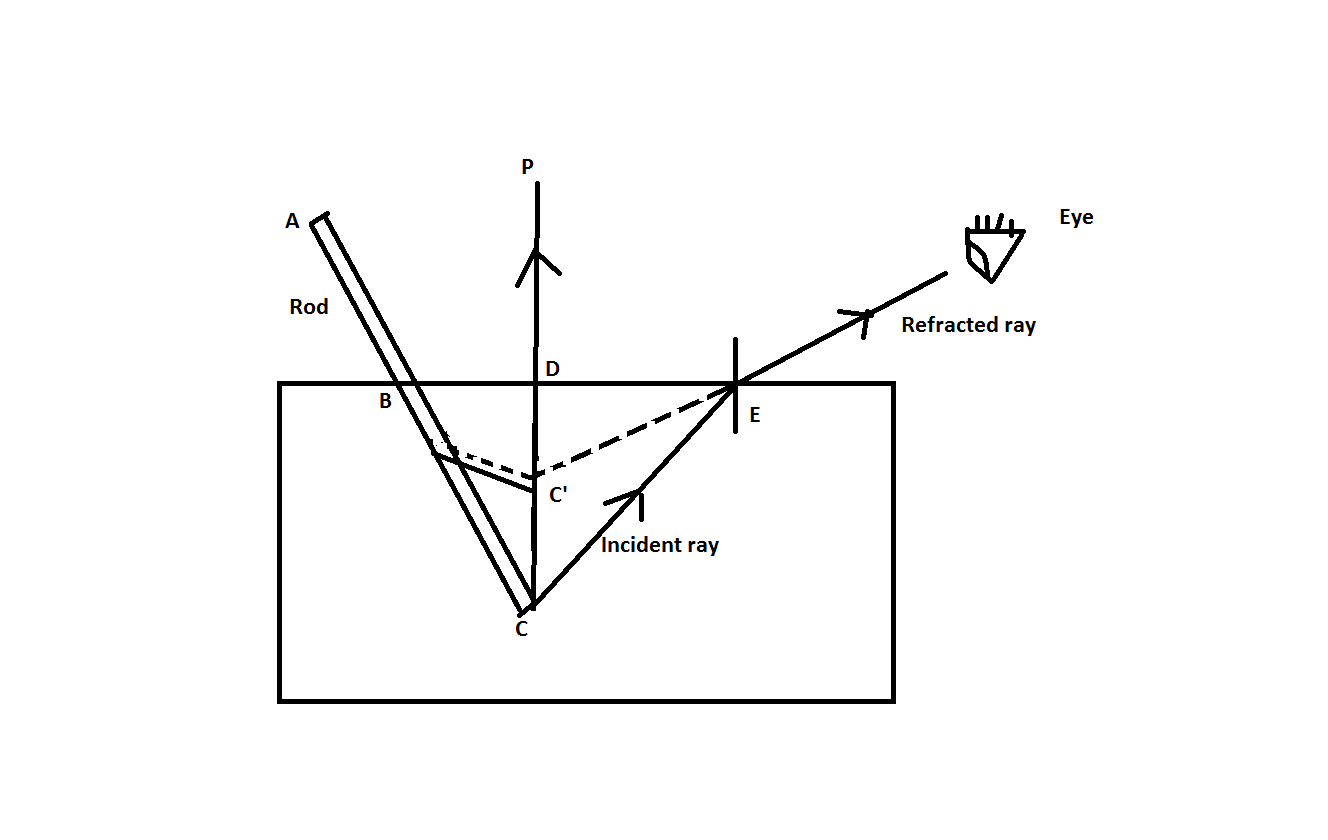
Trace the path of the ray of light through a glass slab, when it passes from water to a glass slab and what will happen to the incident ray ? Draw the ray diagram.
An object is seen first in red light and then in violet light through a simple microscope. In which case is the magnification larger?
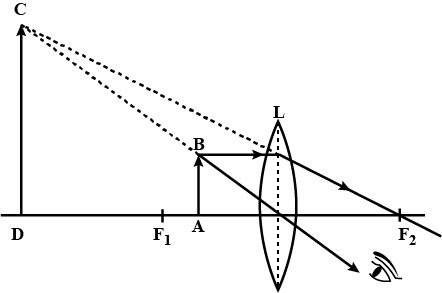
With a neat labelled diagram, explain the formation of image in a simple microscope.
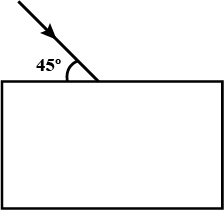
Draw the diagram given below and clearly show the path taken by the emergent ray
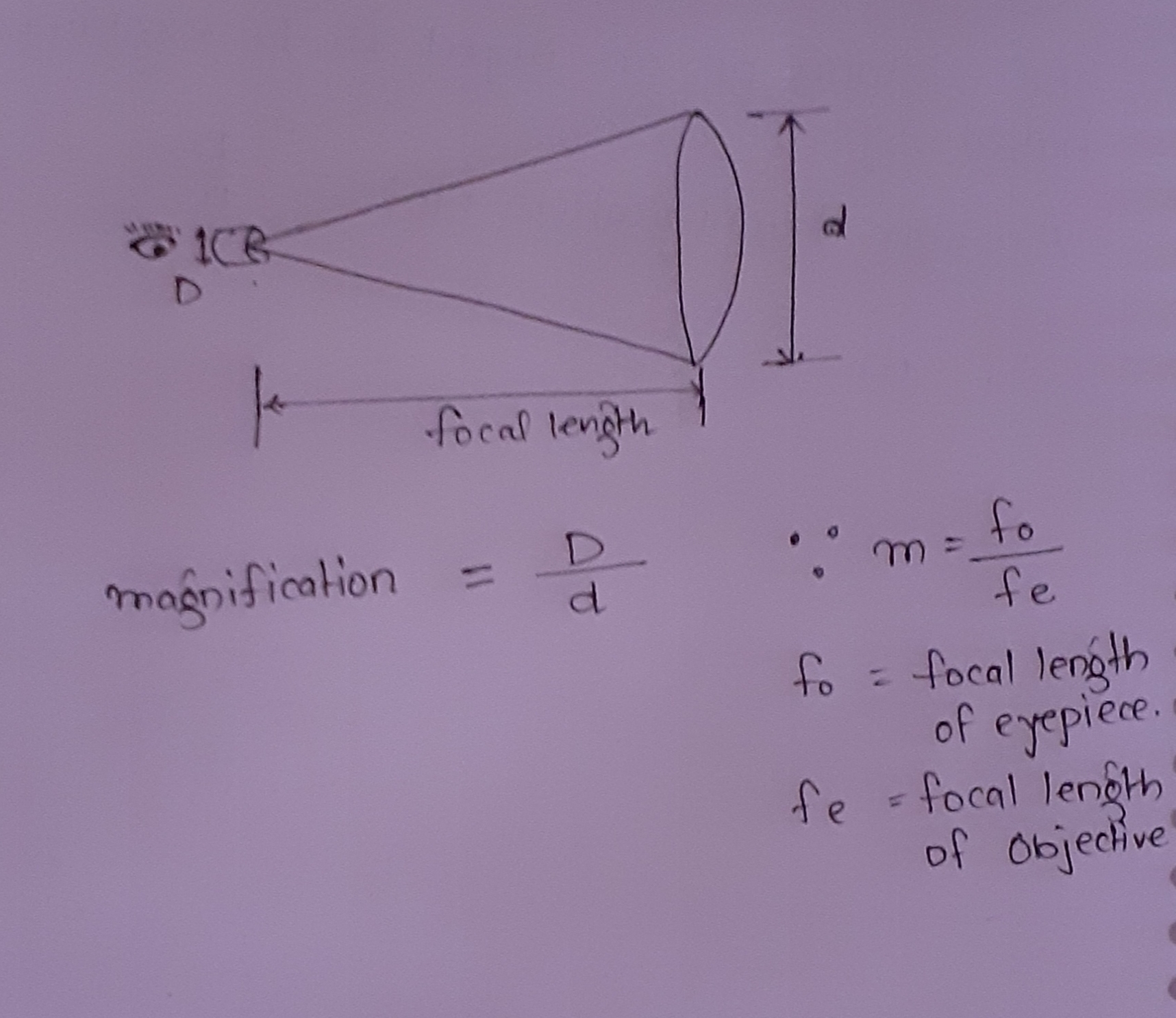
Define magnifying power of a simple microscope. How can it be increased?
Give reason:
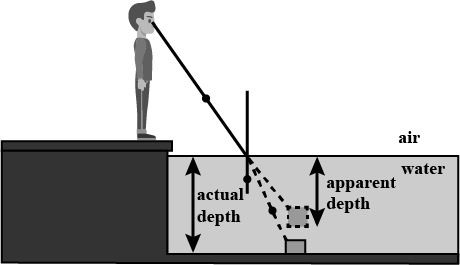
The bottom of water tank appears raised.
What is magnifying glass? State its two uses.
If the magnification of a body of size 1 m is 2, what is the size of the image?
What is refraction? Why pencil appears bent in water?
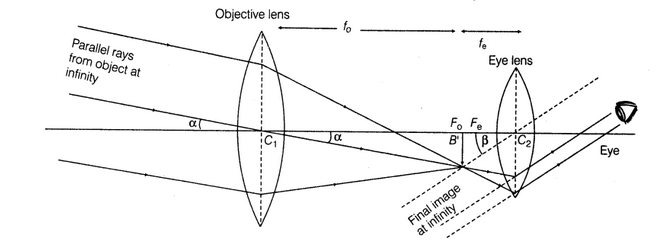
Draw a labelled ray diagram of a reflecting telescope. Mention its two advantages over the refracting telescope.
An optical device used by watch repairers is __________.
Give reasons:A simple microscope is used by watch repairers.
A pencil partly immersed in water in a glass tumbler appears to be bent at the interface of air and water. Name the phenomenon of light responsible for it.
List three optical instruments, and describe what they do ?
Does the source appear to be nearer or farther with respect to surface AB ?

Three convex lenses are available having focal lengths of 4 cm, 40 cm and 4 cm respectively. Which one would you choose as a magnifying glass and why?
A ray of light falls on three glass slabs of the same material at the same angle of incidence. In which case, is the lateral displacement of the emergent ray of light
(a) maximum
(b) minimum
Draw a ray diagram to illustrate the bending of a stick in water
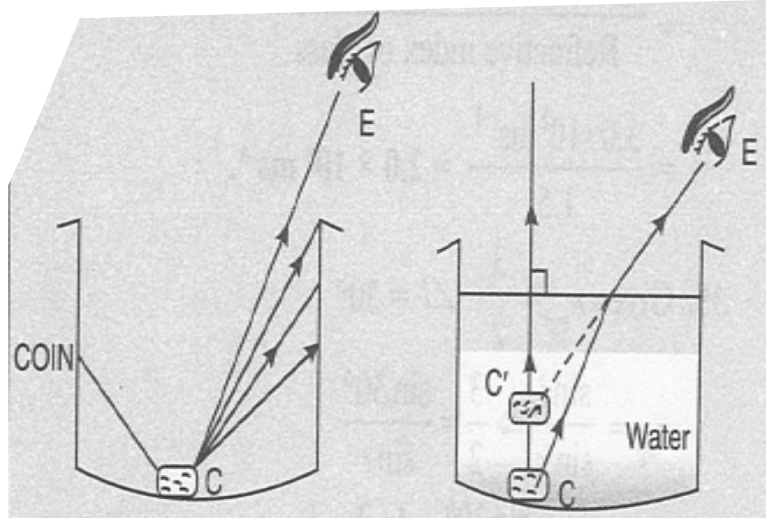
A coin is placed at the bottom of a tin can. Move your eyes until the coin is just out of sight (see diagram). Keep your eyes in this position while someone pours water gradually into the tin can. What would you observe ? Explain your observation.
With the help of a well-labelled diagram show that the apparent depth of an object, such as a coin, in water is less than its real depth.
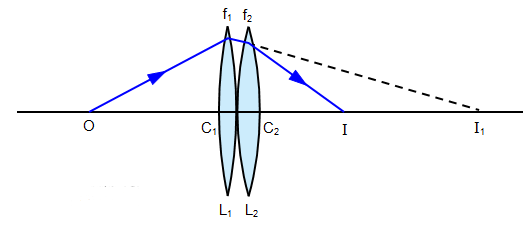
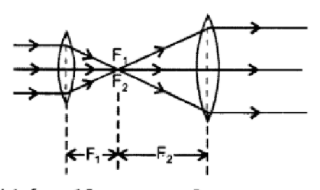
What is the focal length of a convex lens of focal length 30 cm in contact with a concave lens of focal length 20cm? Is the system a converging or a diverging lens? Ignore thickness of the lenses.
A tank is filled with water to a height of 12.5 cm. The apparent depth of a needle lying at the bottom of the tank is measured by a microscope to be 9.4 cm. What is the refractive index of water? If water is replaced by a liquid of refractive index 1.63 up to the same height, by what distance would the microscope have to be moved to focus on the needle again?
A small pin fixed on a table top is viewed from above from a distance of 50 cm. By what distance would the pin appear to be raised if it is viewed from the same point through a 15 cm thick glass slab held parallel to the table? Refractive index of glass $$=$$ 1.Does the answer depend on the location of the slab?
A slab of refractive index $$1.5$$ is placed in water of refractive index $$\dfrac {4}{3}$$. If the apparent shift in the object $$O$$ due to the slab is $$1\ cm$$, the thickness of slab is
A Cassegrain telescope uses two mirrors as shown in above figure. Such a telescope is built with the mirrors $$20\,mm$$ apart. If the radius of curvature of the large mirror is $$220\,mm$$ and the small mirror is $$140\,mm$$, where will the final image of an object at infinity be?
A man with normal near point (25 cm) reads a book with small print using a magnifying glass: a thin convex lens of focal length 5 cm.
(a) What is the closest and the farthest distance at which he should keep the lens from the page so that he can read the book when viewing through the magnifying glass?
(b)
What
is the maximum and the minimum angular magnification (magnifying
power) possible using the above simple microscope?
(b) What is the maximum and the minimum angular magnification (magnifying power) possible using the above simple microscope?
A card sheet divided into squares each of size $$1 \,mm^2$$ is being viewed at a distance of $$9 cm$$ through a magnifying glass (a converging lens of focal length $$9 cm$$) held close to the eye.(a) What is the magnification produced by the lens? How much is the area of each square in the virtual image?(b) What is the angular magnification (magnifying power) of the lens?(c) Is the magnification in (a) equal to the magnifying power in (b)? Explain
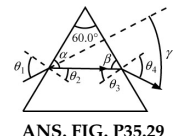
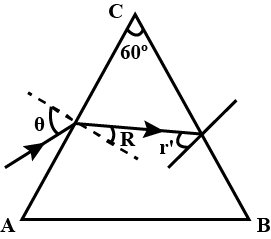
At what angle should a ray of light be incident on the face of a prism of refracting angle $$60^\circ$$ so that it just suffers total internal reflection at the other face? The refractive index of the material of the prism is $$1.524$$.
(i) A screen is placed at a distance of 100 cm from an object. The image of the object is formed on the screen by a convex lens for two different locations of the lens separated by 20 cm. Calculate the focal length of the lens used.
(ii) A converging lens is kept coaxially in contact with a diverging lens - both the lenses being of equal focal length. What is the focal length of the combination?
A magnifying glass is what kind of lens, and where do where should I place the lens relative to the object to see an image larger than the object and right-side-up? ("F" stands for the focal length of the lens.)
A convex lens of focal length 25 m is placed coaxially in contact with a concave lens of focal length 20 cm .Determine the power of the combination. Will the system be converging or diverging in nature?
Draw a labeled ray diagram of a refracting telescope. Define its magnifying power and write the expression for it.
Write two important limitation of a refracting telescope over a reflecting type telescope
A convex lens of focal length $$f_{1}$$ is kept in contact with a concave lens of focal length $$f_{2}$$. Find the focal length of the combination.
Velocity of light in glass is $$2 \times 10^8 ms^{-1}$$ and that in air is $$3 \times 10^8 ms^{-1}$$. By how much would an ink dot appear to be raised, when covered by a glass plate 6.0 cm thick?
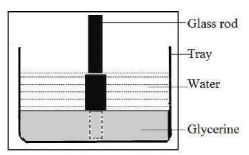
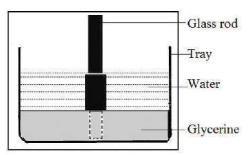
Take a glass vessel and pour some glycerine into it and then pour water up to the brim. Take a quartz glass rod. Keep it in the vessel. Observe the glass rod from the sides of the glass vessel.
What changes do you notice?
Take a glass vessel and pour some glycerine into it and then pour water up to the brim. Take a quartz glass rod. Keep it in the vessel. Observe the glass rod from the sides of the glass vessel.
What could be the reasons for these changes?
At critical angle, the angle of refraction is _______.
Suppose you are inside the water in a swimming pool near an edge. A friend is standing on the edge. Do you find your friend taller or shorter than his usual height? Why?
Define critical angle. Explain total internal reflection using a neat diagram.
Draw a neat (labelled) diagram for the formation of image in a simple microscope.
What is chromatic aberration ? How can it be minimized or eliminated ?
Drive an expression for equivalent focal length of two thin lenses kept in contact.
The focal length of objective lens and eyepiece for a compound microscope are $$0.95$$ and $$5$$ cm and they are placed at $$20$$ cm from each other final image is formed at $$25$$ cm in eyepiece find the magnifying power of the microscope?
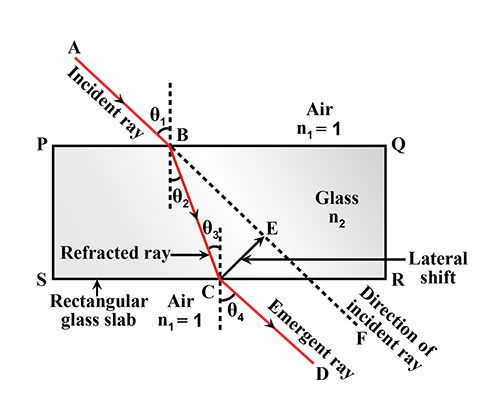
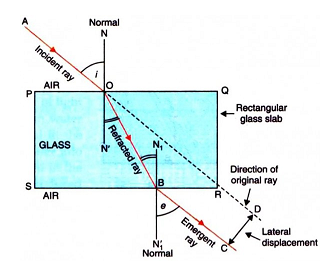
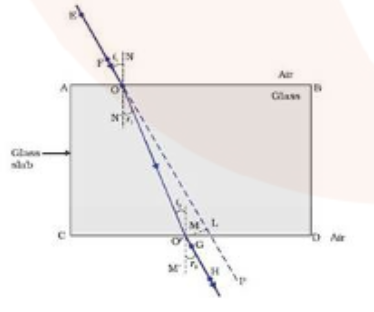
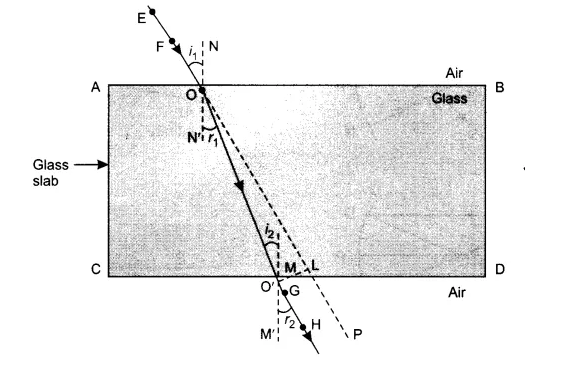
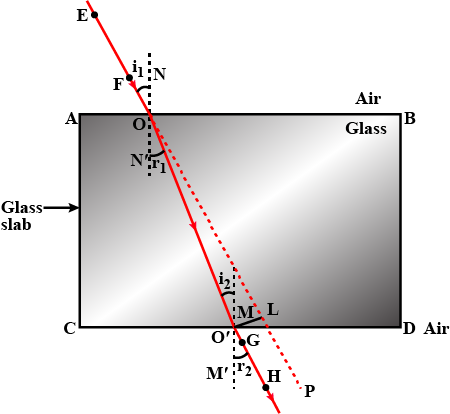
Explain refraction of light and lateral shift using a rectangular glass slab with figure.
Draw a ray diagram showing the formation of image by a reflecting telescope.
A converging lens of focal length $$40$$cm is kept in contact with a diverging lens of focal length $$30$$cm. Find the focal length of the combination.
How is the refractive index of a material related to real and apparent depth?
The image of an object form at the distance of distinct vision from the lens of a simple microscope of focal length $$2.5cm$$. It magnifying power is ____.
An object is placed $$20\ cm$$ in front of a block of glass $$10\ cm$$ thick and its farther surface is silvered. The image is formed $$23.2\ cm$$ behind the silvered face. Determine the refractive index of the glass.
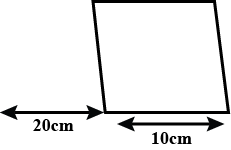
Three lenses of power $$+1.5\ D$$ and $$-0.5\ D$$ are kept in contact on their principal axis. What is the effective power of the combination?
Why must both the $$f_0$$ and the $$f_e$$ of a compound microscope have short focal length?
A vessel contains water up to a height of $$20\ cm$$ and above it an oil up to another $$20\ cm$$. The refractive indices of the water and the oil are $$1.33$$ and $$1.30$$ respectively. Find the apparent depth of the vessel when viewed from above.
A ray of light of wavelength 5400 A suffers refraction from air to glass. Taking $$a_{\mu}g$$ as 3/2, find the wavelength of light in glass.
Derive $$\frac { 1 }{ f } =\frac { 1 }{ v } +\frac { 1 }{ u } $$ formula for spherical mirror.
A narrow beam of light is incident at $$53^{\circ}$$ angle made with normal on a glass plate of refractive index $$1.6$$. If the thickness of the plate is $$20\;mm$$. Calculate the shift of the beam.
A convex lens of focal length $$f_1$$ is kept in contact with a concave lens of focal length $$f_2$$. Find the focal length of the combination.
A postage stamp kept below a rectangular glass slab of refractive index $$1.5$$ when viewed vertically above it, appears to be raised by $$7.0 mm$$. Calculate the thickness of the glass slab.
An object is placed in front of a glass slab $$(\mu = 1.5)$$ of thickness $$6 \,cm$$ at a distance $$28 \,cm$$ from it. Other face of glass slab is silvered. Find the position of final image of object.
A simple microscope is rate 5 X for a normal relaxed eye. What will be its magnifying power for a relaxed farsighted eye whose near point is 40?
A candle flame 3 cm high is placed at a distance of 3 m from a wall.how far from the wall must a concave mirror be placed so that it may form 9 cm high image of the flame on the same wall? Also find the focal length of the mirror.
What is the lateral displacement when a ray of light falls normally on a glass slab?
Does the magnifying power of a microscope depend on the colour of the light used? Justify your answer.
Define critical angle. Prove that the refractive index of the denser medium is reciprocal of the sine of the critical angle .
What is this distance between the lens and the screen called ?
A particle executes a simple harmonic motion of amplitude $$1.0 cm$$ along the principal axis of convex lens of focal length $$12 cm$$. The mean position of oscillation is at $$20 cm$$ from the lens. Find the amplitude of oscillation of the image of the particle.
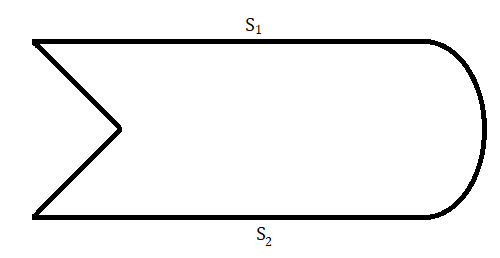
If the glass slab is of the following shape , and the experiment is performed as above , will the effects be same ? Here $$S_{ 1 }$$ and $$S_{ 2 }$$ are slab surfaces parallel to each other.
Define critical angle and polarising angle what is the relation between the two angles ?
An object of height 4 cm is placed at a distance of 15 cm infront of a concave lens of power -10D. Find the size of the image.
When an object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror its image is formed at 10 cm in front of the mirror. Calculate the focal length of the mirror.
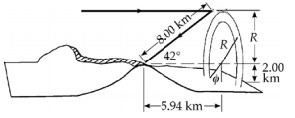
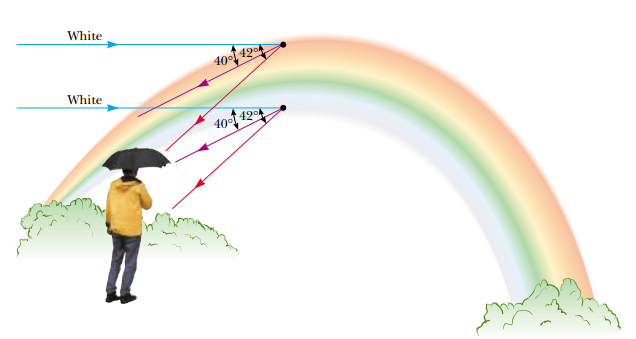
A mountaineer on a peak observes a rainbow in a valley, caused by water droplets in the sir $$ 8\ km $$ away. The valley is $$2\ km$$ below the mountain peak and is entirely flat. What fraction of the complete circular arc of the rainbow is visible to him?
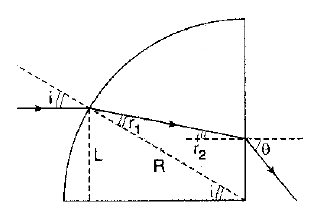
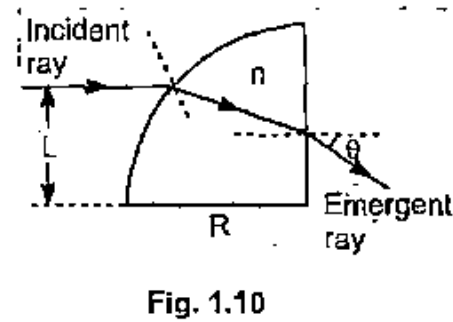
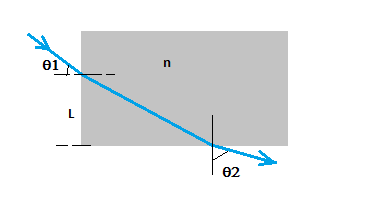
A material having an index of refraction $$ n $$ is surrounded by a vacuum and is in the shape of a quarter circle of radius $$ R $$. Alight parallel to the base of the material is incident from the left at a distance of $$ L $$ above the base and emerges out of the material at the angle $$ \theta $$. Determine an expression for $$ \theta $$.
An object is placed 15cm from (a) a converging mirror, and (b) a diverging mirror, of radius of curvature 20cm. (c) Calculate the image position and magnification in case.
Two narrow parallel slits separated by $$0.850\ mm$$ are illuminated by $$600\ nm$$ light, and the viewing screen is $$2.80\ m$$ away from the slits. (a) What is the phase difference between the two interfering waves on a screen at a point $$2.50\ mm$$ from the central bright fringe? (b) What is the ratio of the intensity at this point to the intensity at the centre of a bright fringe?
The main focal, length of the objective of a microscope is $$ f_{obj} = 3 \,mm $$ and of the eyepiece $$ f_{eye} = 5 \,cm. $$ An object is at a distance of $$ a= 3.1 \, mm $$ from the objective. Find the magnification of the microscope for a normal eye.
A simple microscope has a magnifying power of $$3.0$$ when the image is formed at the near point $$(25 cm)$$ of a normal eye. What will be its magnifying power if the image is formed at infinity?
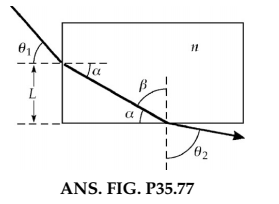
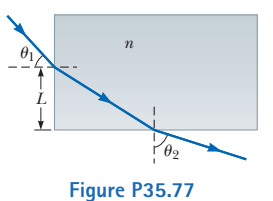
A light ray enters a rectangular glass slab at angle $$ \theta_1 = 45^{\circ} $$ and emerges at an angle $$ \theta_2 = 76^{\circ} $$, as shown in the figure. (a) Determine the refractive index of refraction for the slab. (b) If the light ray enters the plastic at a point $$ L = 50\, cm $$ from the bottom edge, how long does it take the light ray to travel through the slab?
The objective is taken out of a telescope adjusted to infinity and replaced by a diaphragm with a diameter $$ D.$$ A screen shows a real image of the diaphragm having a diameter $$ d $$ at a certain distance from the eyepiece. What was the magnification of the telescope?
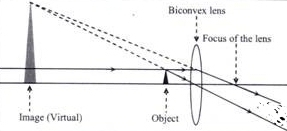
Where should an object be placed in order to use a convex lens as a magnifying glass ?
Give three examples of material that refract light rays . What happens to the speed of light rays when they enter these materials ?
What name is given to the ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction ?
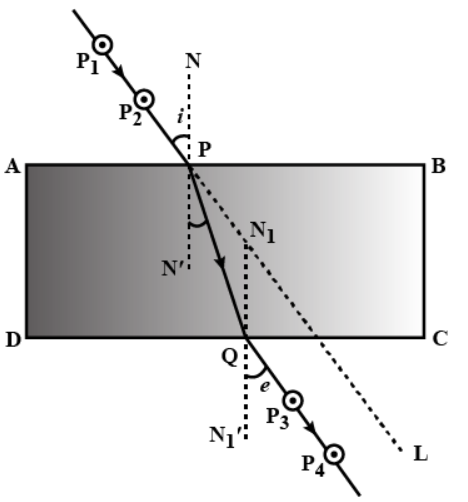
(a) With the help of a diagram , show that how when light falls obliquely on the side of a rectangular glass slab, the emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray .
(b) Show the lateral displacement of the ray on the diagram .
(c) State two factors on which the lateral displacement of the emergent ray depends.
Fill in the following blanks with suitable words :
(a) Parallel rays of light are refracted by a convex lens to a point called the ______
(b) The image in a convex lens depends upon the distance of the ____ from the lens.
Where is the object placed in reference to the principal focus of a magnifying glass, so as to see its enlarged image? Where is the image obtained?
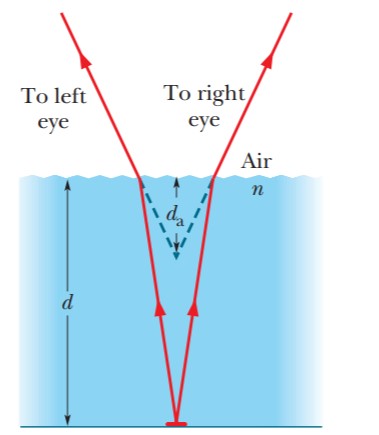
You look down at a coin that
lies at the bottom of a pool of liquid
of depth $$d$$ and index of refraction n. Because you view with
two eyes, which intercept different
rays of light from the coin, you perceive the coin to be where
extensions of the intercepted rays
cross, at depth $$d_a$$ instead of $$d$$.
Assuming that the intercepted rays
in Figure are close to a vertical axis through the coin, show that $$d_a = d/n$$. (Hint: Use the small-angle
approximation $$\sin \theta \approx \tan \theta \approx \theta$$.)
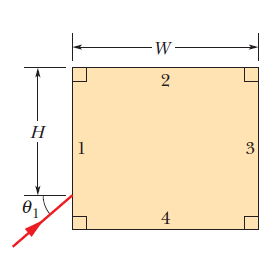
In above figure, a light ray in air is incident at angle $$\theta_{1}$$ on a block of transparent plastic with an index of refraction of $$1.56$$. The dimensions indicated are $$H=2.00cm$$ and $$W=3.00cm$$. The light passes through the block to one of its sides and there undergoes reflection (inside the block) and possibly refraction (out into the air). This is the point of first reflection. The reflected light then passes through the block to another of its sidesa point of second reflection. If $$\theta_{1}=40^{0}$$, on which side is the point of (a) first reflection and (b) second reflection? If there is refraction at the point of (c) first reflection and (d) second reflection, give the angle of refraction; if not, answer none. If $$\theta_{1}=70^{0}$$, on which side is the point of (e) first reflection and (f) second reflection? If there is refraction at the point of (g) first reflection and (h) second reflection, give the angle of refraction; if not, answer none.
Draw a ray diagram showing the path of rays of light when enters with oblique incidence (i) from air into water,. (ii) from water into air
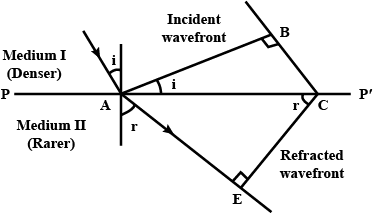
Use Huygens' Principle to show how a plane wave front propagates from a denser to rarer medium. Hence, verify Snell's law of refraction.
Fill in the blanks :
When a ray of light travels from water to air , it bends _______ the normal.
How is the refractive index of a medium related to the real and apparent depths of an object in that medium?
The ray diagrams given below show the paths of a ray of light travelling from a medium M into different media 1,2 and 3.
(a) In which of three media 1,2 or 3 in descending order of (i) faster, (ii) slower than in medium M

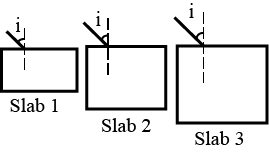
In the following figures, one lens is placed inside each box. State the nature of the lens. Complete the ray diagrams
Draw a neat labelled ray diagram to show the formation of image by a magnifying glass. State three characteristics of the image.
Where should be an object placed in front of convex lens so as to use it as a magnifier?
A student puts his pencil into an empty trough and observes the pencil from the position as indicated in the figure above.
(i) What change will be observed in the appearance of the pencil when water is poured into the trough?
(ii) Name the phenomenon which accounts for the above started observation.
(iii) Complete the diagram showing how the student's eye sees the pencil through
water.

Define lateral displacement.
Draw a ray diagram to show the appearance of a stick partially immersed in water. Explain your answer.
Solve the following example.
An object of height 7 cm is kept at a distance of 25 cm in front of a concave mirror. The focal length of the mirror is 15 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be kept so as to get a clear image? what will be the size and nature of the image?
Where is the telescope used? Discuss it with your friends and teachers.
Which lens has magnification less than $$1 ?$$
Now, look in the glass from the top. What can you see?
What type of lens is used in simple microscope ?
How does the pencil appear, when it is kept in glass full of water?
Light of wavelength 700 nm is incident on the face of a fused quartz prism $$ (n=1.458 $$ at 700 nm) at an incidence angle of $$ 75.0^{\circ}. $$ The apex angle of the prism is $$ 60.0^{\circ}. $$ Calculate the angle of incidence at the second surface.
An object is placed in front of a concave mirror 20 cm away from it. If its focal length is 40 cm, locate the position of image and its nature.
An object of 5 cm is kept in front of a convex mirror having radius of curvature 30 cm at a distance of 10 cm. Calculate the position, size, and feature of object.
Light passes from air into flint glass at a nonzero angle of incidence. Is it possible for the component of its velocity perpendicular to the interface to remain constant? Explain your answer.
Yellow light of wavelength $$ 589 \mathrm{nm} $$ is used to view an object under a microscope. The objective lens diameter is $$ 9.00 \mathrm{mm} $$.
Suppose water fills the space between the object and the objective. What effect does this change have on the resolving power when $$ 589-\mathrm{nm} $$ light is used?
In given Figure shows a pencil partially immersed in a cup of water. Why does the pencil appear to be bent?

A ray of light, incident obliquely on a face of a rectangular glass slab placed in air, emerges from the opposite face parallel to the incident ray.
State two factors on which the lateral displacement of the emergent ray depends.
List the sign conventions that are followed in case of refraction of light through spherical lenses. Draw a diagram and apply these conventions in determining the nature and focal length of a spherical lens which forms three times magnified real image of an object placed $$16\ cm$$ from the lens.
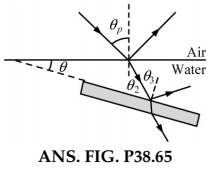
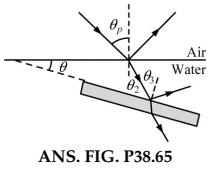
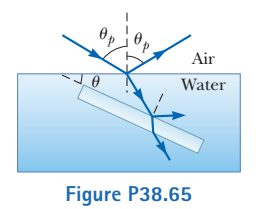
Light in air (assume $$ n=1 $$ ) strikes the surface of a liquid of index of refraction $$ n_{\ell} $$ at the polarizing angle. The part of the beam refracted into the liquid strikes a submerged slab of material with refractive index $$ n $$ as shown in Figure $$ \mathrm{P} 38.$$ The light reflected from the upper surface of the slab is completely polarized. Find the angle $$ \theta $$ between the water surface and the surface of the slab as a function of $$ n $$ and $$ n_{\ell} $$
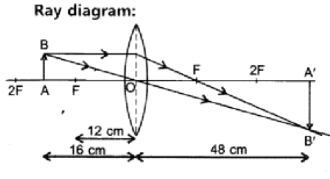
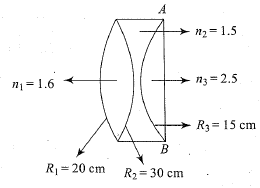
The image of a candle flame placed at a distance of $$45\ cm$$ from a spherical lens is formed on a screen placed at a distance of $$90\ cm$$ from the lens. Identify the type of lens and calculate its focal length. If the height of the flame is $$2\ cm$$, find the height of its image.
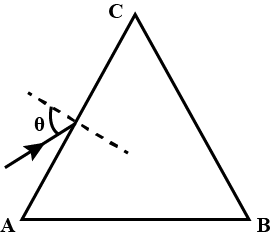
Light is incident on a prism with an equilateral triangular cross-section, making an angle of $$\theta$$ w.r.t the normal as shown in the figure. The index of refraction of the prism is $$\displaystyle \frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}$$. If the angle $$\theta$$ starts at $$60^{\circ}$$ and is gradually made smaller until no light exist from side BC, the final value of $$\theta$$ in degrees is
The distance of the object from the lens is 1/x. Find out the value of x?
For a prism of refracting angle A and refractive indexAssume rays are incident at all angles of incidence $$0^o \leq i \leq 90^o$$. Ignore partial reflection
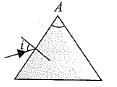
As shown in the figure, light is incident normally on one face of the prism. A liquid of refractive index $$\mu$$ is placed on the horizontal face $$AC$$. The refractive index of prism is $$3/2$$. If total internal reflection taken place on face $$AC$$, $$\mu$$ should be less than $$\dfrac {I\sqrt {3}}{4}$$, where $$I$$ is an integer. Find the value of $$I$$.
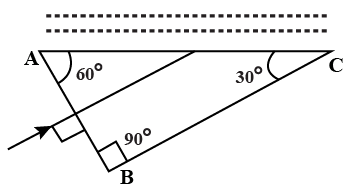
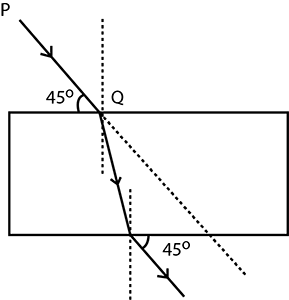
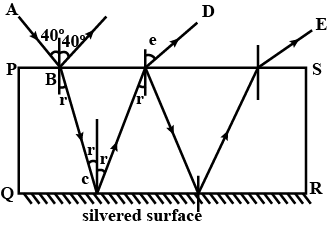
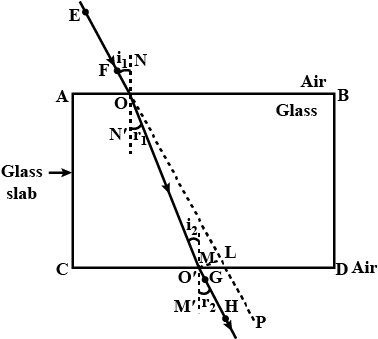
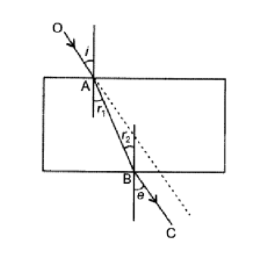
The figure given below shows a solid glass block of refractive index $$1.5$$. The lower surface of the block is silvered and behaves as a reflecting mirror. A white light ray $$AB$$ incidents on the glass block at an angle of incidence $$40^{\circ}$$. Copy the diagram and trace the path of reflected and refracted rays from the upper and lower surface of the block.
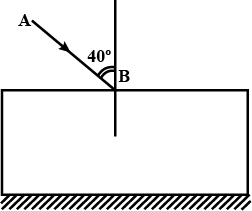
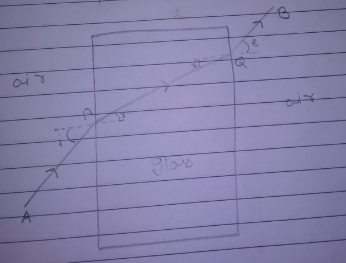
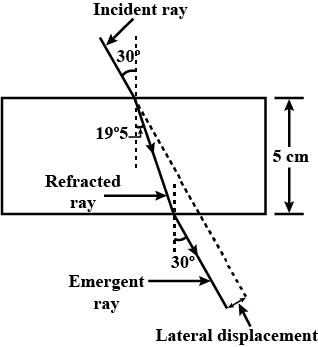
A ray of light strikes a glass slab 5 cm thick, making an angle of incidence equal to $$30^{\circ}$$. Construct the ray diagram showing showing the emergent ray and the refracted ray through the glass block. The refractive index of glass is 1.Also, measure the lateral displacement of the ray. Take $$\sin 19.5^{\circ}\, =\, 1/3$$.
A card sheet divided into squares each of size $$1 \,mm^2$$ is being viewed at a distance of $$9\, cm$$ through a magnifying glass (a converging lens of focal length $$9\, cm$$) held close to the eye.In order to view the squares distinctly with the maximum possible magnifying power.(a) What is the magnification produced by the lens? How much is the area of each square in the virtual image?(b) What is the angular magnification (magnifying power) of the lens?(c) Is the magnification in (a) equal to the magnifying power in (b)?Explain:
A card sheet divided into squares each of size $$1 \,mm^2$$ is being viewed at a distance of $$9 cm$$ through a magnifying glass (a converging lens of focal length $$9 cm$$) held close to the eye and the magnifying glass if the virtual image of each square is to have an area of $$6.25 mm^{2}$$. Would you be able to see the squares distinctly with your eyes very close to the magnifier?
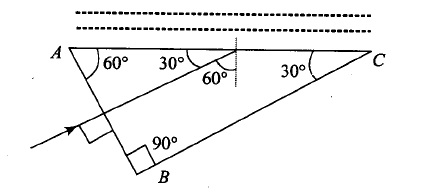
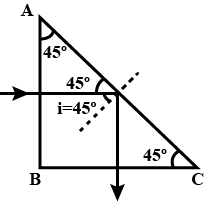
A ray of light passes through a right angled prism as shown in figure. State the angles of incidence at the faces $$AC$$ and $$BC$$.
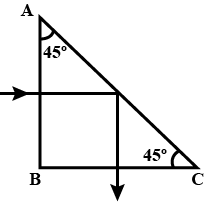
A ray of light strikes a glass slab of thickness $$t$$
(a) Prove that the ray is deflected laterally by distance
$$t \sin \theta \left[ 1-\sqrt {\dfrac {1-\sin^{2} \theta}{n^{2}-\sin^{2}\theta}}\right]$$
(b) Prove that for a small angle of incident the lateral shift $$y$$ is given by $$y=t \theta \left( 1-\dfrac {1}{n}\right)$$
When $$n$$ is the refractive index of glass with respect to air
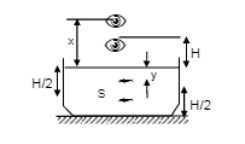
Consider the situation in figure. The bottom of the pot is a reflecting plane mirror, $$S$$ is a small fish, and $$T$$ is a human eye. Refractive index of water is $$\mu$$.
A) At what distance(s) from itself will the fish see the image(s) of the eye?
B) At what distance(s) from itself will the eye see the images(s) of the fish?

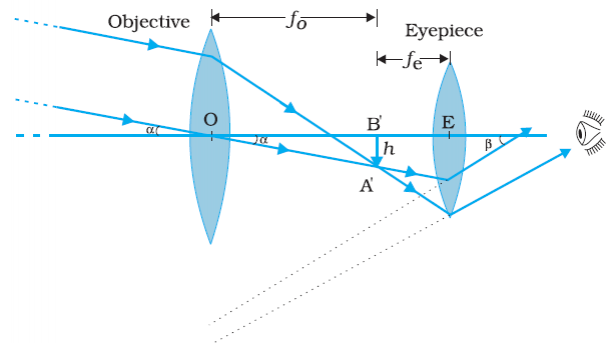
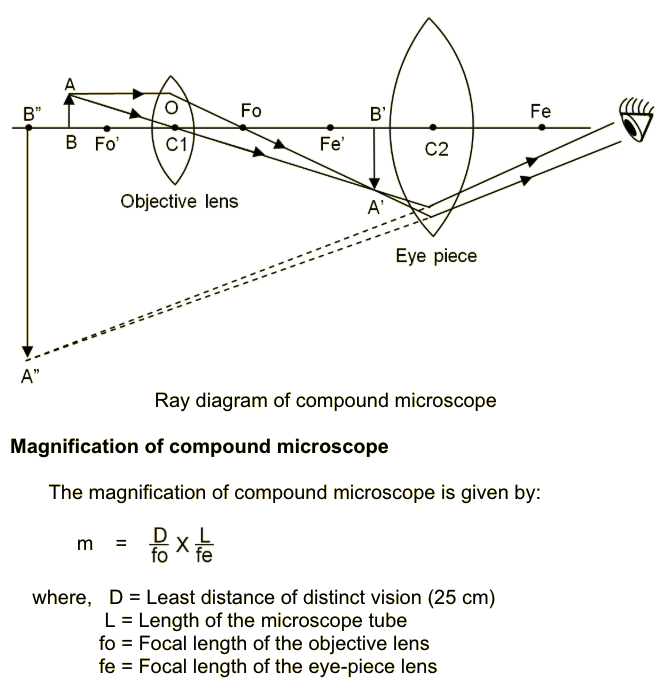
With the help of ray diagram, describe the construction, working of a compound microscope when the final image is formed at least distance of distinct vision $$(D = 25 \,cm)$$. Derive an expression fords magnifying power (m).
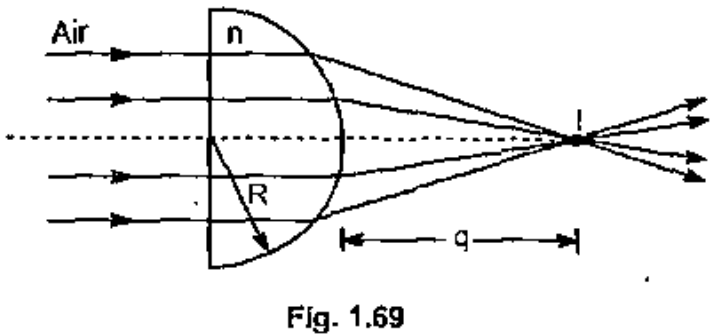
A parallel beam of light enters a glass hemisphere perpendicular to the flat face, as shown in Fig. 1.69. The radius is $$ R = 6.00 \,cm $$ and the index of refraction is $$ n = 1.560 $$. Determine the point at which the beam is focussed. (Assume paraxial rays).
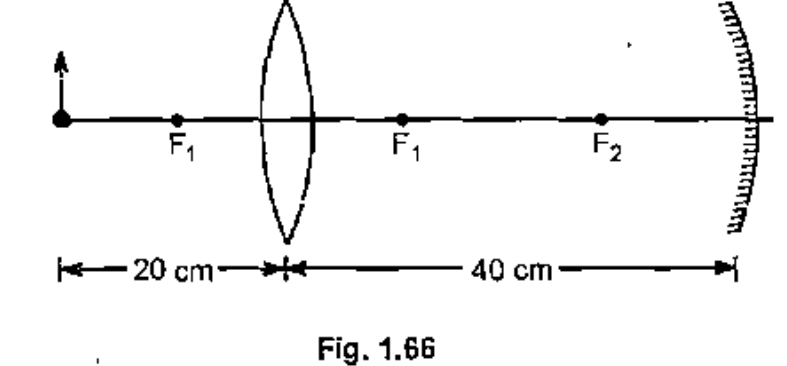
A biconvex lens $$ (f_1 = 10.0\,cm) $$ is placed $$ 40.0 \,cm $$ infront of a concave mirror $$ (f_2 = 7.50 \,cm) $$ as shown in Fig. 1.An object $$ 2.00 \,cm $$ high is placed $$ 20.0 \,cm $$ to the left of the lens. Using the lens and mirror equations and a ray diagram, find the locations of three images : (a) the image formed by the lens as rays travel to the right, (b) the image formed after the rays reflect from the mirror, and (c) the final image after the leftward travelling rays once again pass through the lens. Complete the ray diagram and characterize each image and object.
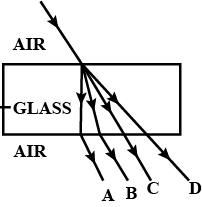
In the above figure, name the ray which represents the correct path of light while emerging out through a glass block.
The mixture a pure liquid and a solution in a long vertical column (ie., horizontal dimensions<< vertical dimensions) produces diffusion of solute particles and hence a refractive index gradient along the vertical dimension. A ray of light entering the column at right angles to the vertical is deviated from its original path. Find the deviation in traveling a horizontal distance $$d<< h$$, the height of the column
Write laws of refraction. Explain the same with the help of ray diagram, when a ray of light passes through a rectangular glass slab.
A ray of light is incident normally on a plane glass slab. What will be (i) the angle of refraction and (ii) the angle of deviation for the ray?
What do you understand by refraction? Write the laws of refraction. Explain refraction through a glass slab.
Why does a light ray incident on a rectangular glass slab immersed in any medium emerges parallel to itself? Explain using a diagram.
(i) Drive the mirror formula. What is the corresponding formula for a thin lens?
(ii) Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation by a concave mirror when the object is kept between its focus and the pole. Use this diagram, drive the magnification formula for the image formed.
What will be the angle of refraction for side $$RS$$?
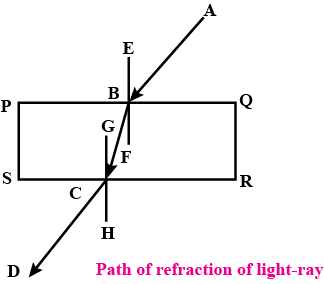
With the necessary figure, explain the refraction of light through a rectangular glass slab.
What happens if light falls on a glass slab making $$ 90^{\circ} $$ at its surface?
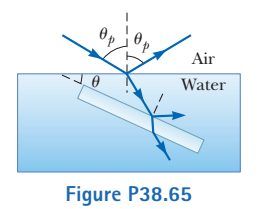
Light in air strikes a water surface at the polarizing angle. The part of the beam refracted into the water strikes a submerged slab of material with refractive index $$ n=1.62 $$ as shown in Figure $$ \mathrm{P} 38.$$ The light reflected from the upper surface of the slab is completely polarized. Find the angle $$ \theta $$ between the water surface and the surface of the slab.
A beam of light both reflects and refracts at the surface between air and glass as shown in this Figure. If the refractive index of the glass is $$ n_{g}, $$ find the angle of incidence $$ \theta_{1} $$ in the air that would result in the reflected ray and the refracted ray being perpendicular to each other.
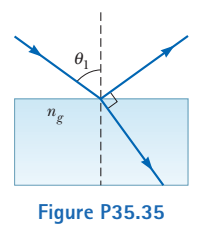
A light ray enters a rectangular block of plastic at an angle $$ \theta_{1}=45.0^{\circ} $$ and emerges at an angle $$ \theta_{2}=76.0^{\circ} $$ as shown in this Figure.
Determine the index of refraction of the plastic.
Draw a neat diagram showing Refraction of light through a rectangular glass slab
A train fo plane light waves propagates in the medium where the phase velocity $$v$$ is a linear function of wavelength: $$v = a + b\lambda$$, where $$a$$ and $$b $$are some positive constants. Demonstrate that in such a medium the shape of an arbitrary train of light waves is restored after the time interval $$\tau = 1/b$$.
A light beam containing red and violet wavelengths is incident on a slab of quartz at an angle of incidence of $$ 50.0^{\circ}. $$ The index of refraction of quartz is 1.455 at $$ 600 \mathrm{nm} $$ (red light), and its index of refraction is 1.468 at $$ 410 \mathrm{nm} $$ (violet light). Find the dispersion of the slab, which is defined as the difference in the angles of refraction for the two wavelengths.
Light passes from air into flint glass at a nonzero angle of incidence. What If? Can the component of velocity parallel to the interface remain constant during refraction? Explain your answer.
A beam of natural light intensity $$I_{0}$$ falls on a system of two crossed Nicol prism between which a tube filled with a certain solution is placed in a longitudinal magnetic field of strength $$H$$. The length of the tube is $$l$$, the coefficient of linear absorption of solution is $$x$$, and the Verdict constant is $$V$$. Find the intensity of the light transmitted through that system.
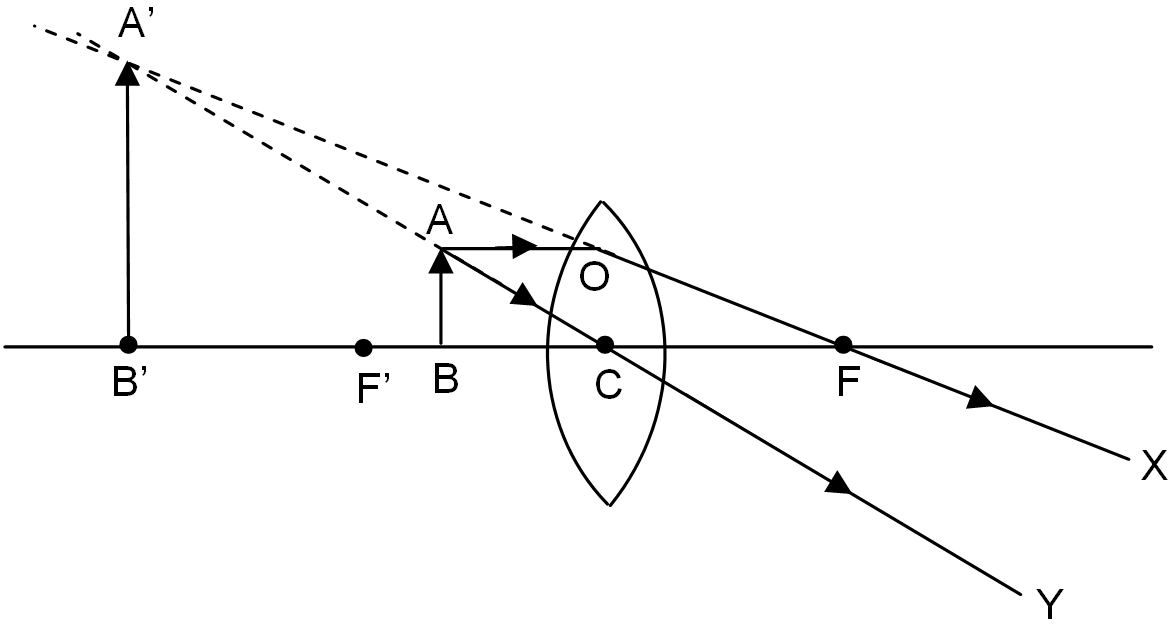
(a)With the help of a ray diagram explain why a concave lens diverges the rays of a parallel beam of light.
(b) A $$2.0\ cm$$ tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave lens of focal length $$15\ cm$$. At what distance from the lens, should the object be placed so that it forms an image $$10\ cm$$ from the lens? Also find the nature and the size of image formed.
In figure $$S$$ is a monochromatic pint source emitting light of wavelength $$\lambda = 500nm$$. A thin lens of circular shape and focal length $$0.01m$$ is cut into identical halves $$L_1$$ and $$L_2$$ by a plane passing through a diameter. The two halves are placed symmetrically about the central axis $$SO$$ with a gap of $$0.5mm$$. The distance along the axis from $$S$$ to $$L_1$$ and $$L_2$$ is $$0.15m$$, while that from $$L_1$$ and $$L_2$$ to $$O$$ is $$1.30m$$. The screen at $$O$$ is normal to $$SO$$.
(i) If the third intensity maximum occurs at point $$A$$ on the screen, find the distance $$OA$$.

In an experiment with a rectangular glass slab, a student observed that a ray of light incident at an angle of $$55^{\circ}$$ with the normal on one face of the slab, after refraction strikes the opposite face of the slab before emerging out into air making an angle of $$40^{\circ} $$ with the normal. Draw a labelled diagram to show the path of this ray. What value would you assign to the angle of refraction and angle of emergence?
A ray of light, incident obliquely on a face of a rectangular glass slab placed in air, emerges from the opposite face parallel to the incident ray. Draw labelled diagram to show it. State two factors on which the lateral displacement of the emergent ray depends.
Perform an experiment to demonstrate that light bends from its path, when it falls obliquely on the surface of a glass slab. Also show that angle of incidence is about equal to the emergent angle.
Class 12 Engineering Physics Extra Questions
- Alternating Current Extra Questions
- Atoms Extra Questions
- Current Electricity Extra Questions
- Dual Nature Of Radiation And Matter Extra Questions
- Electric Charges And Fields Extra Questions
- Electromagnetic Induction Extra Questions
- Electromagnetic Waves Extra Questions
- Electrostatic Potential And Capacitance Extra Questions
- Magnetism And Matter Extra Questions
- Moving Charges And Magnetism Extra Questions
- Nuclei Extra Questions
- Ray Optics And Optical Instruments Extra Questions
- Semiconductor Electronics: Materials,Devices And Simple Circuits Extra Questions
- Wave Optics Extra Questions