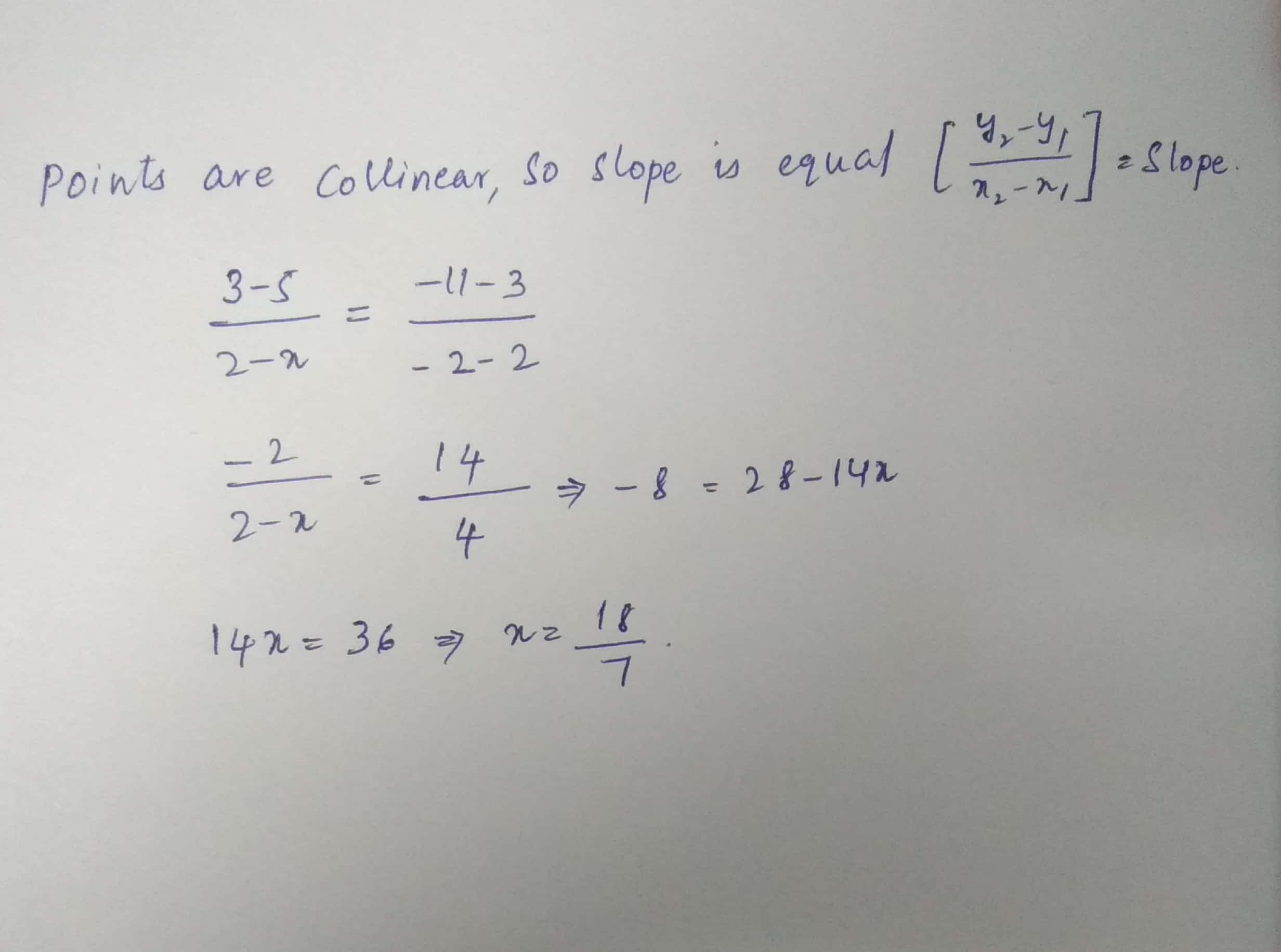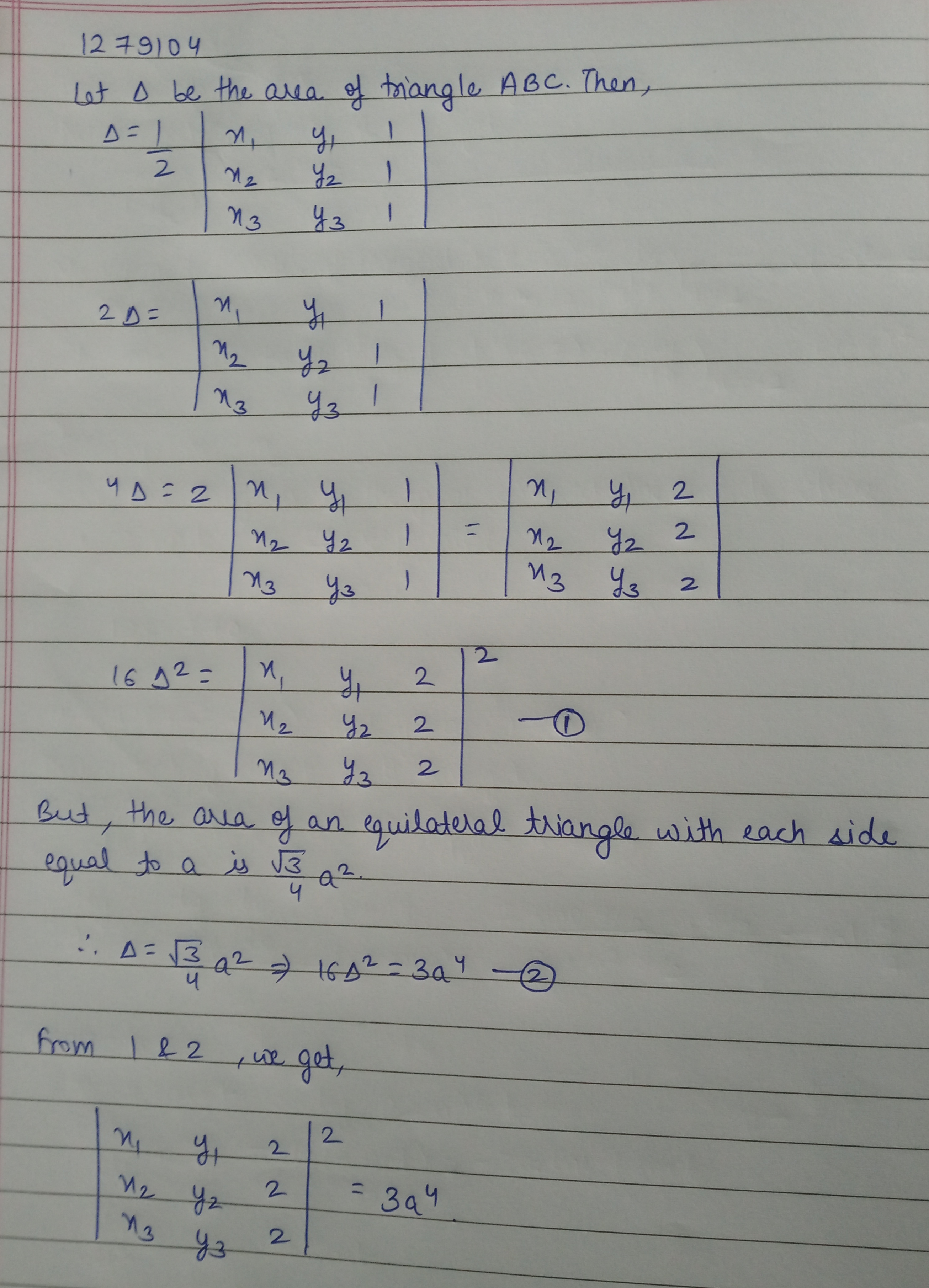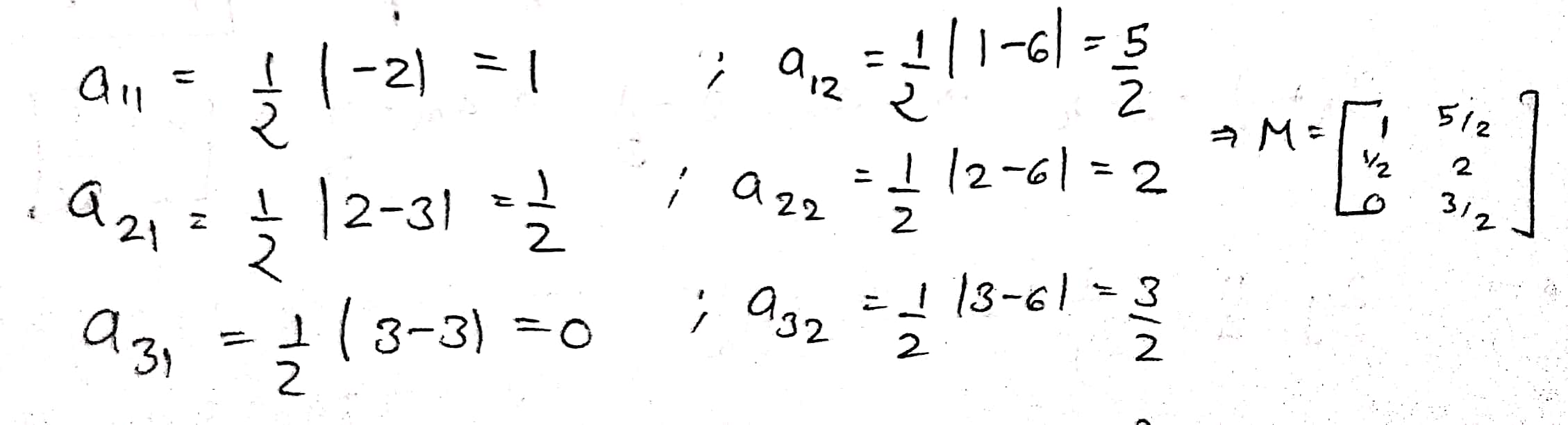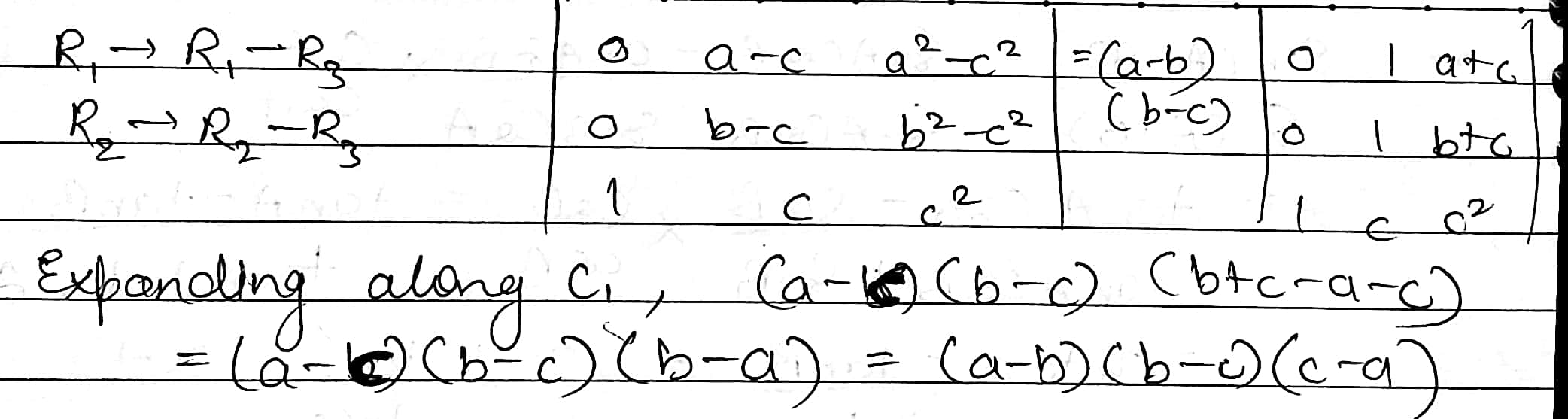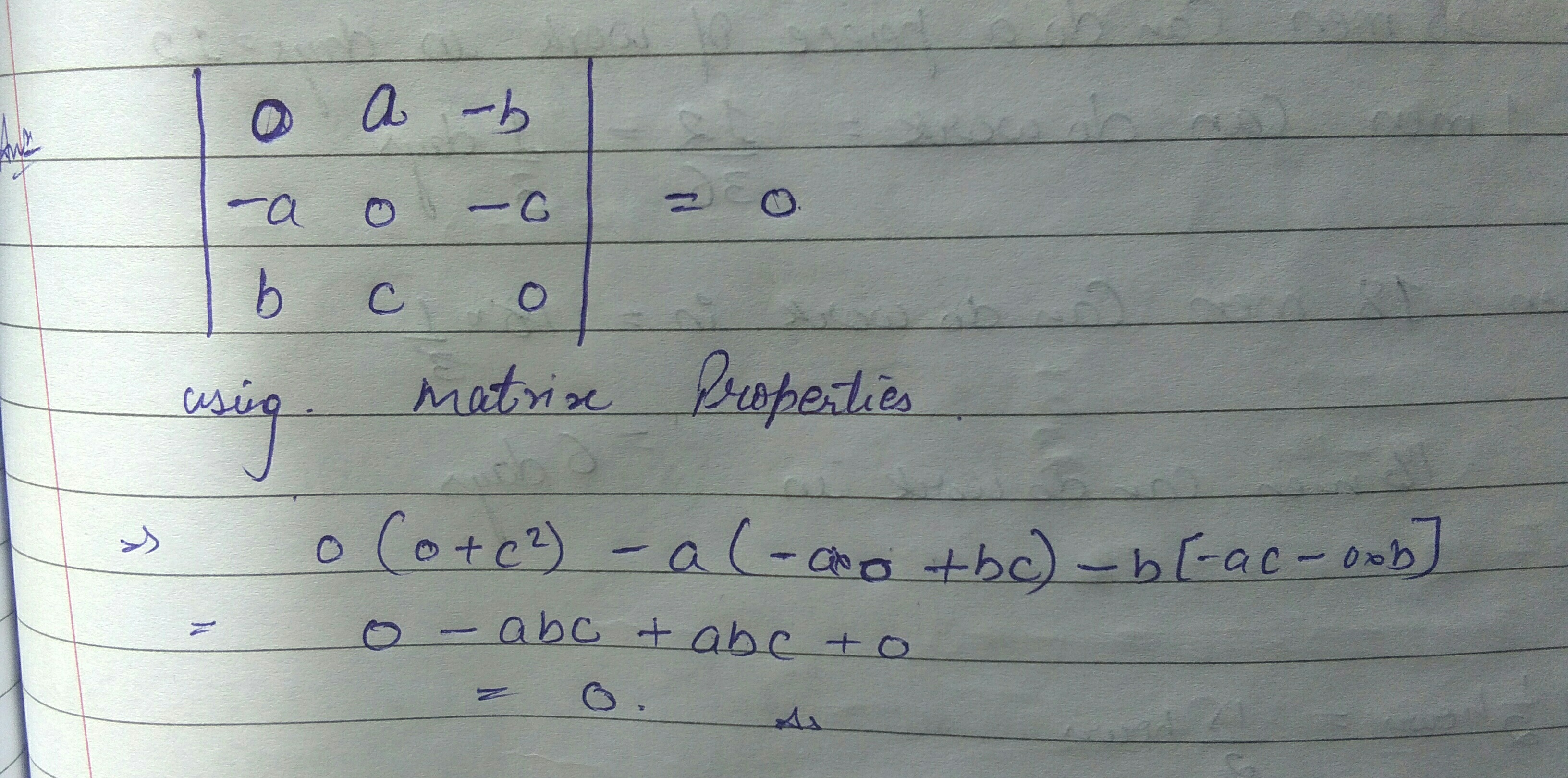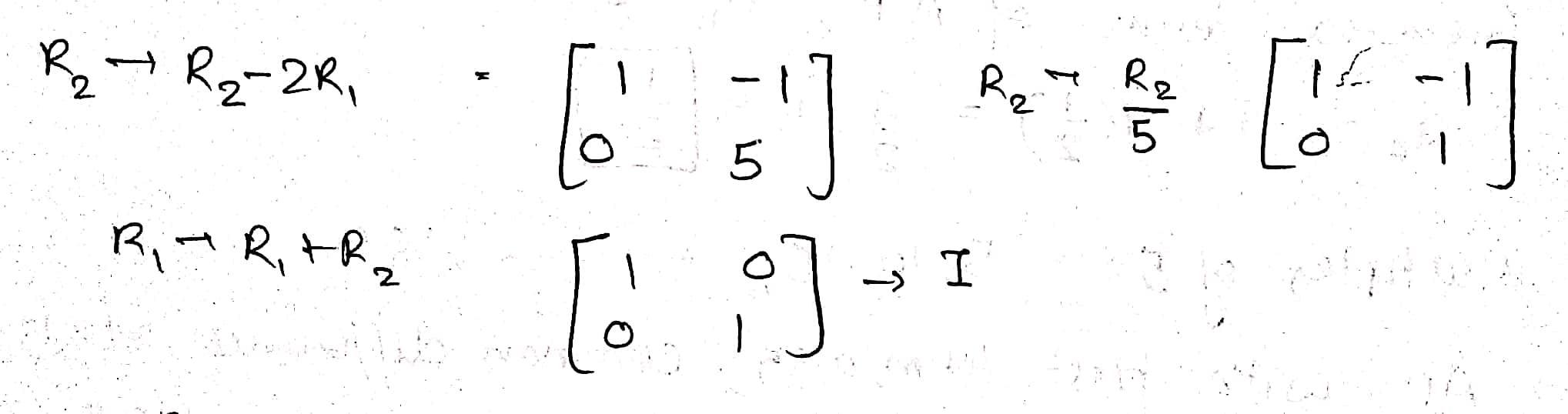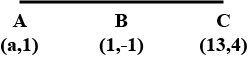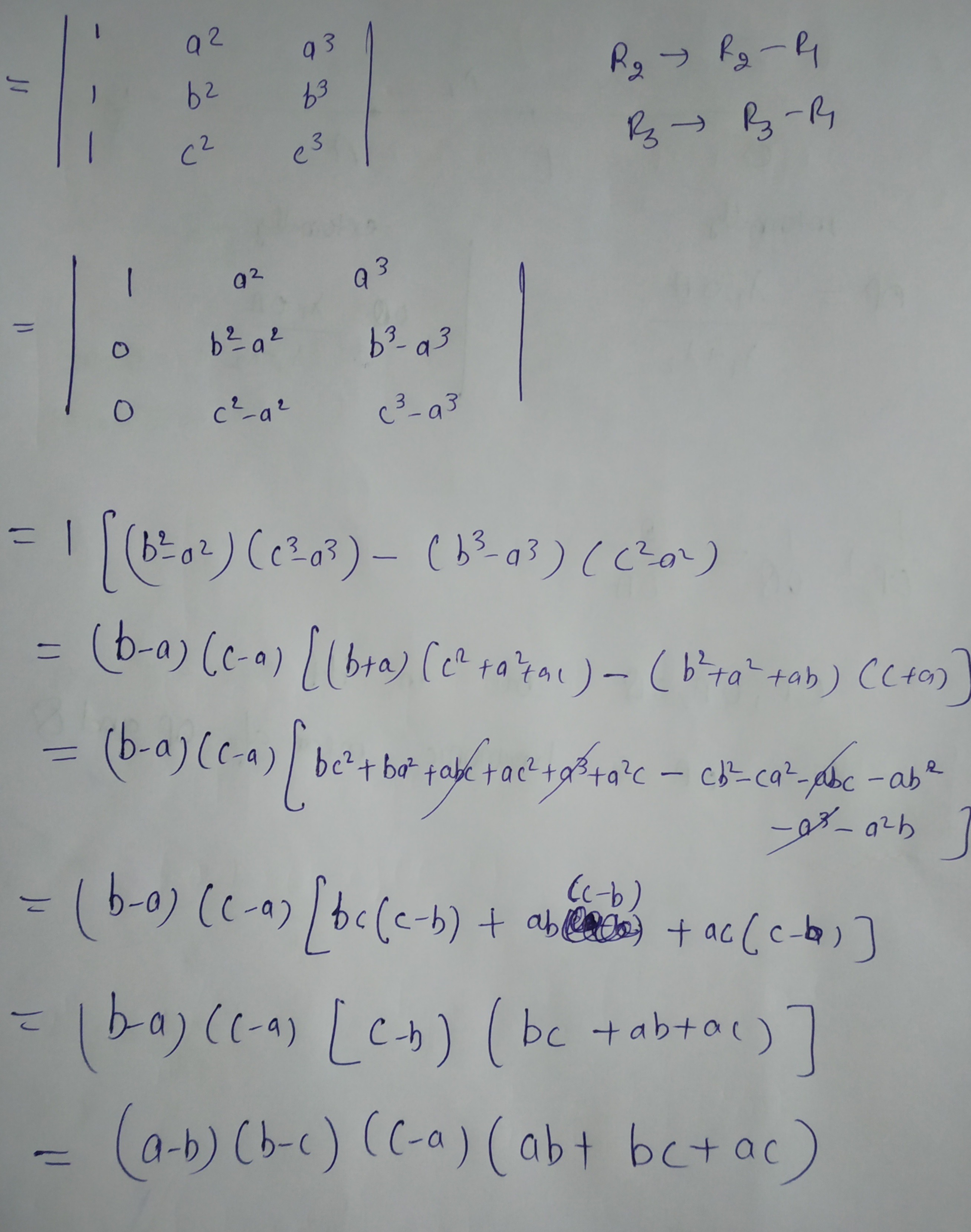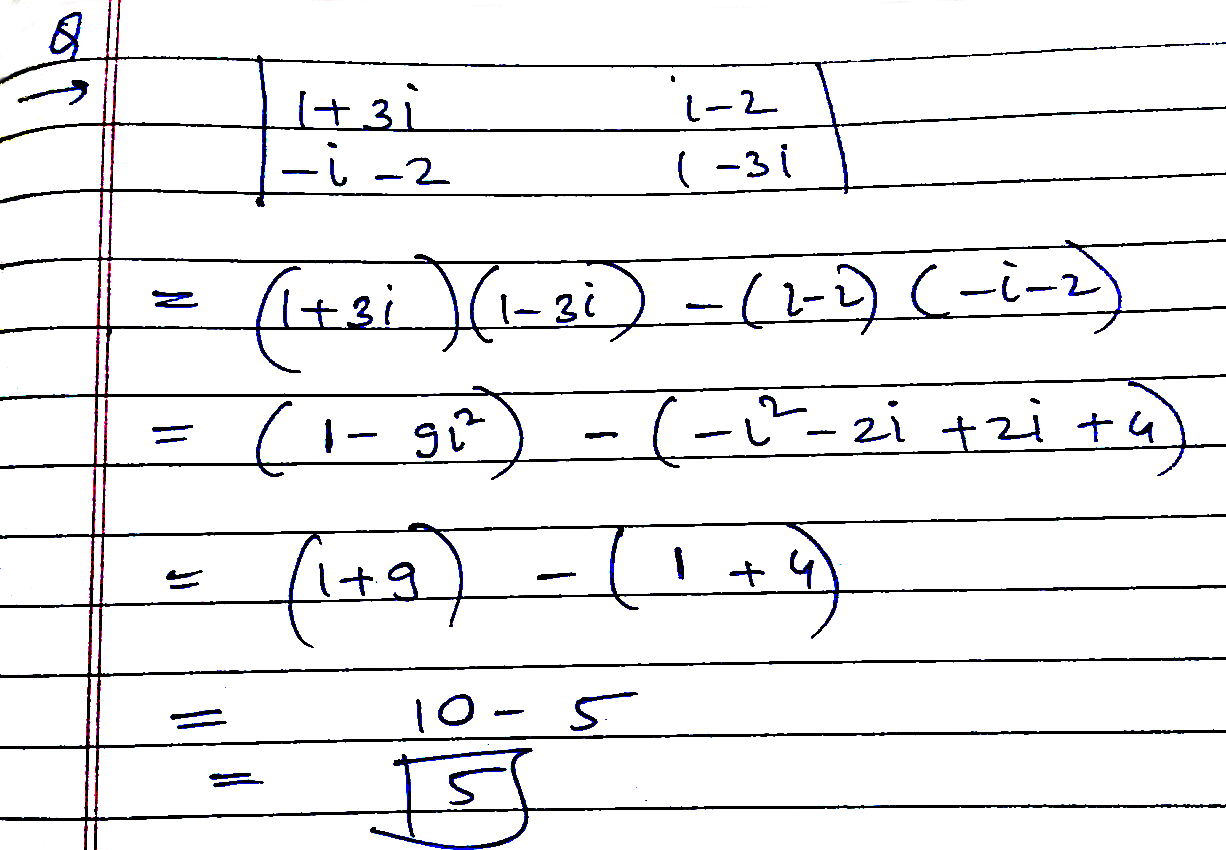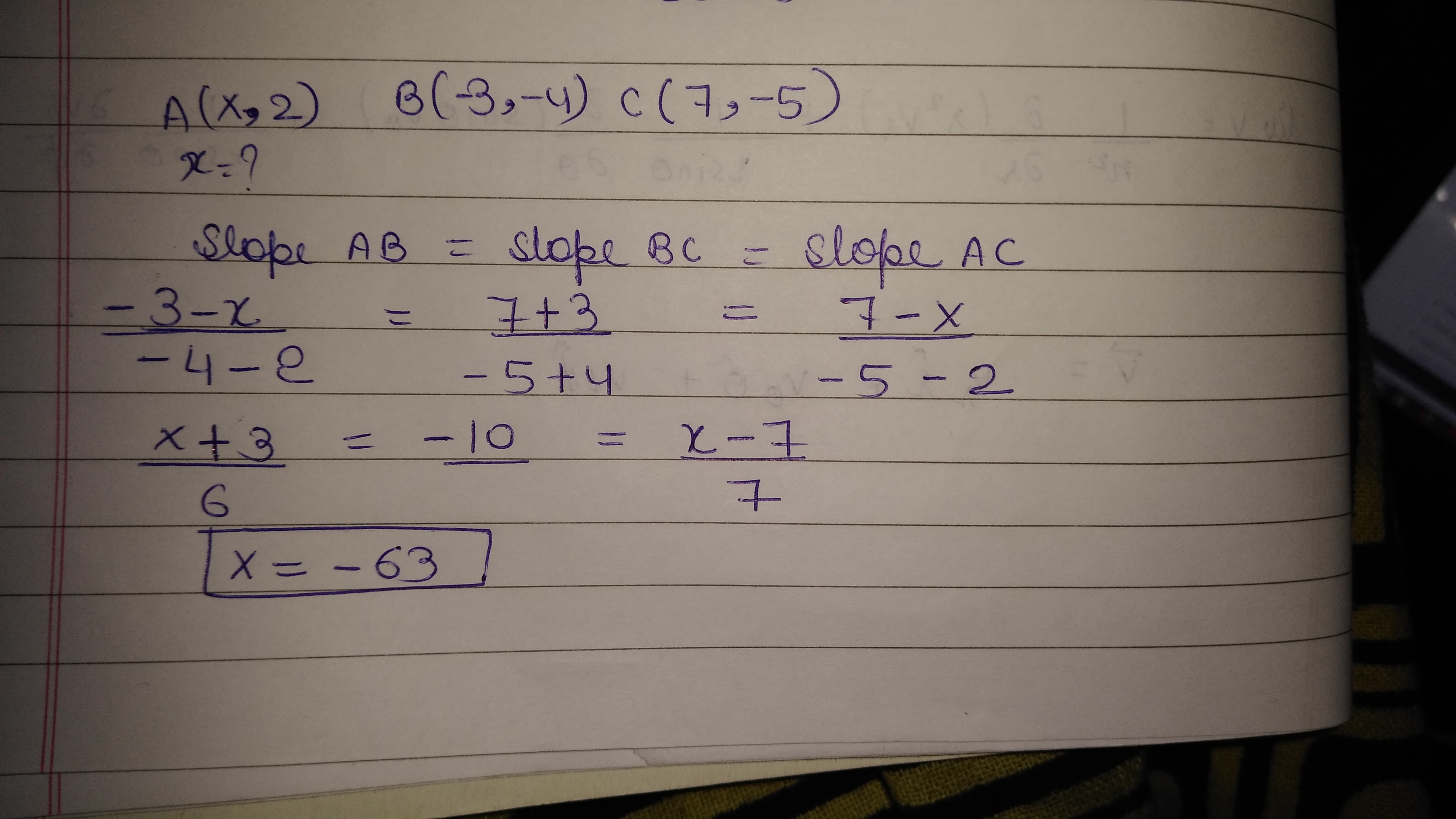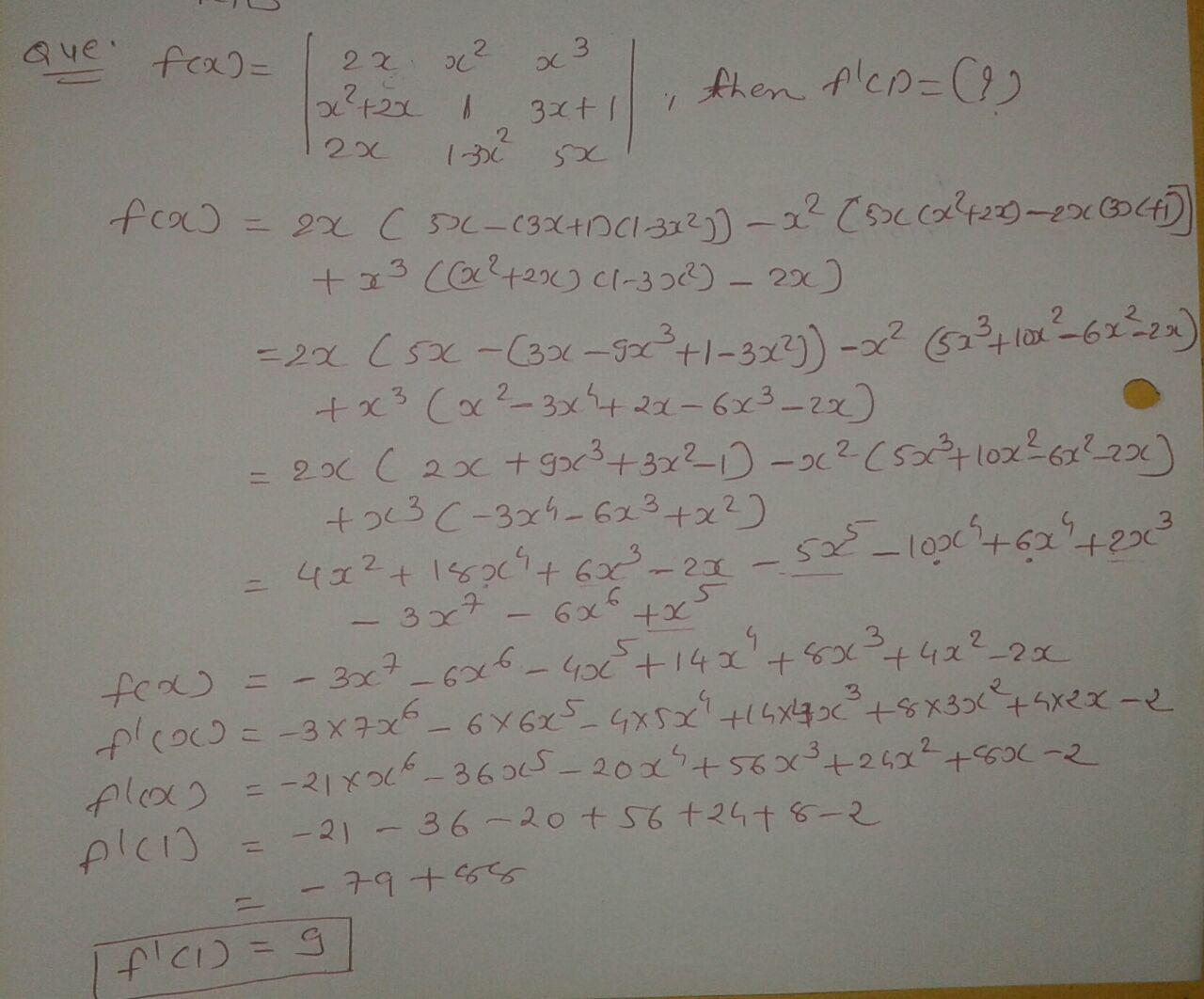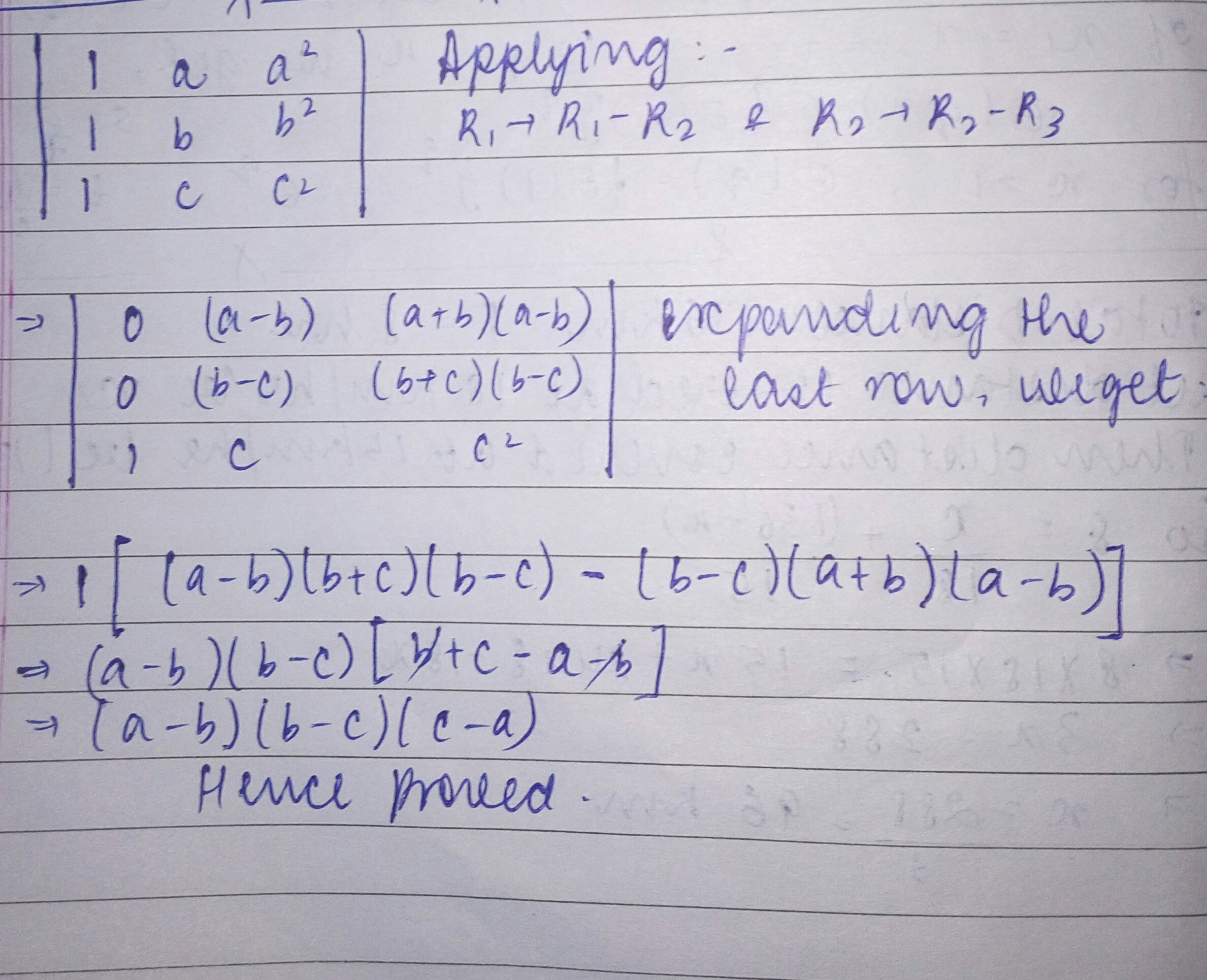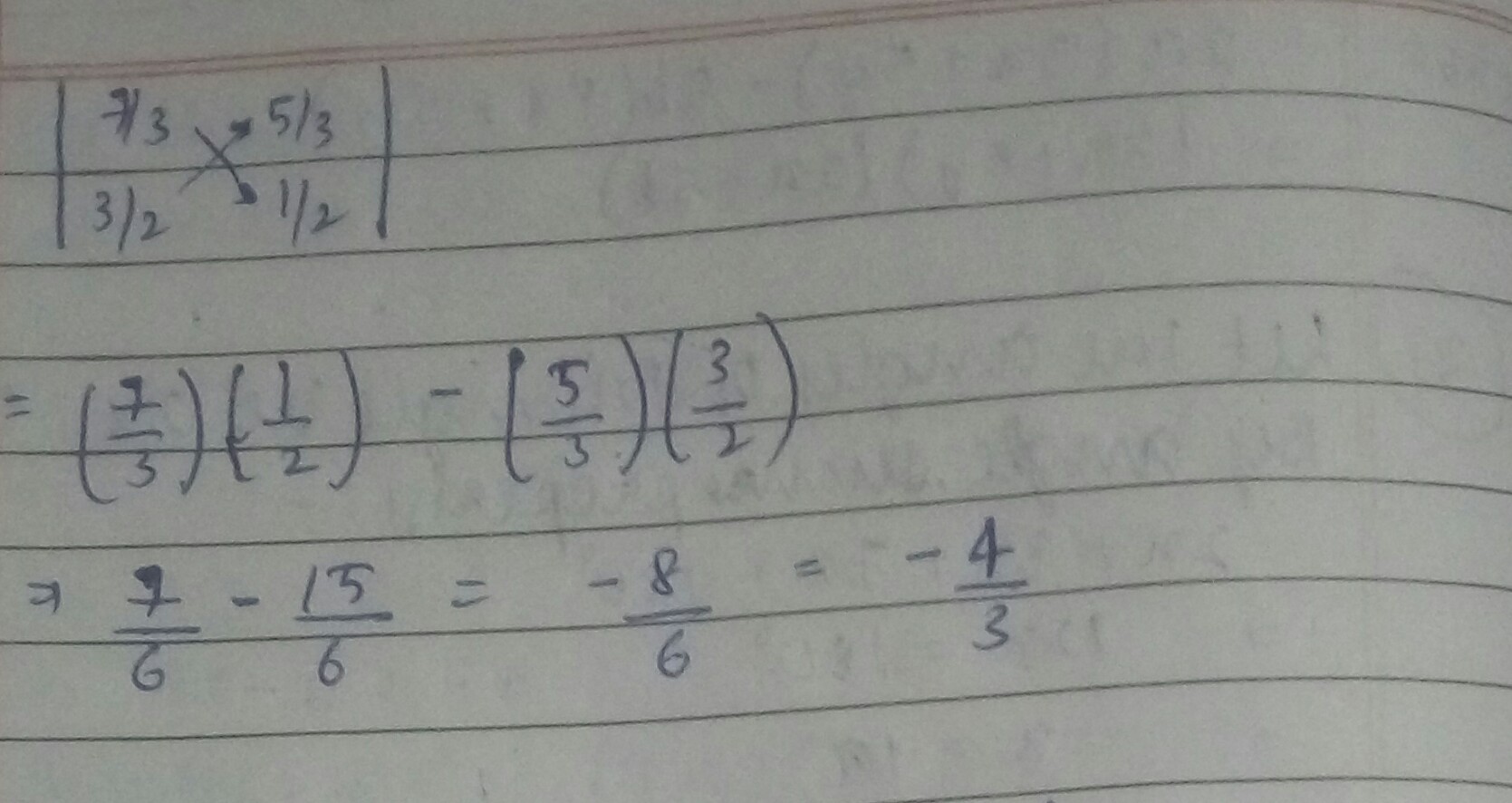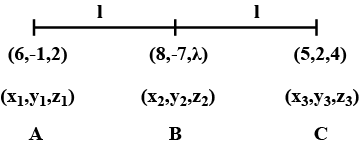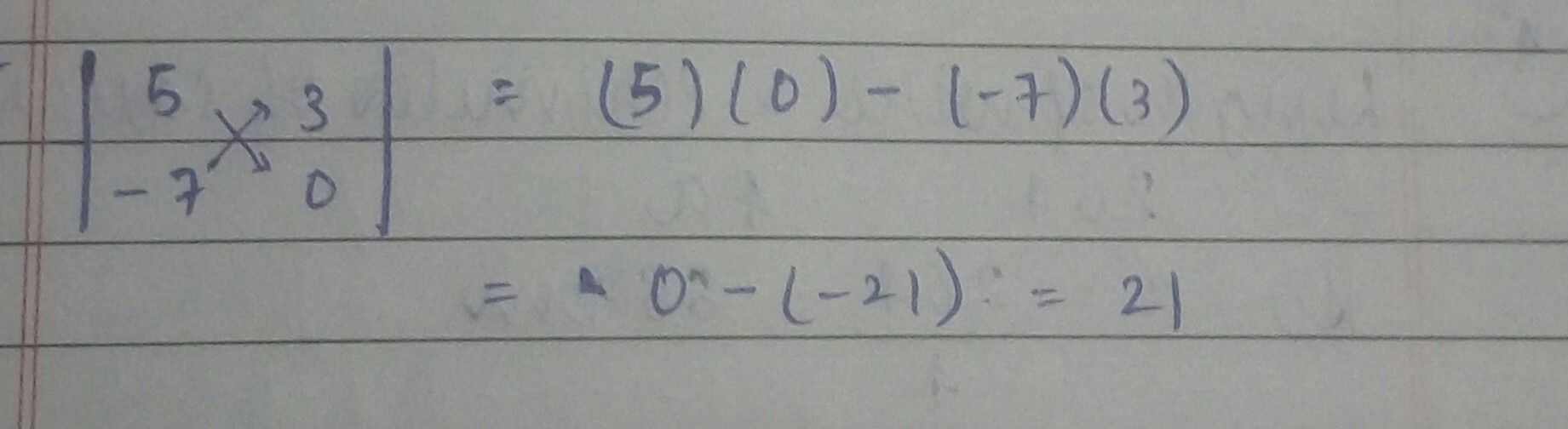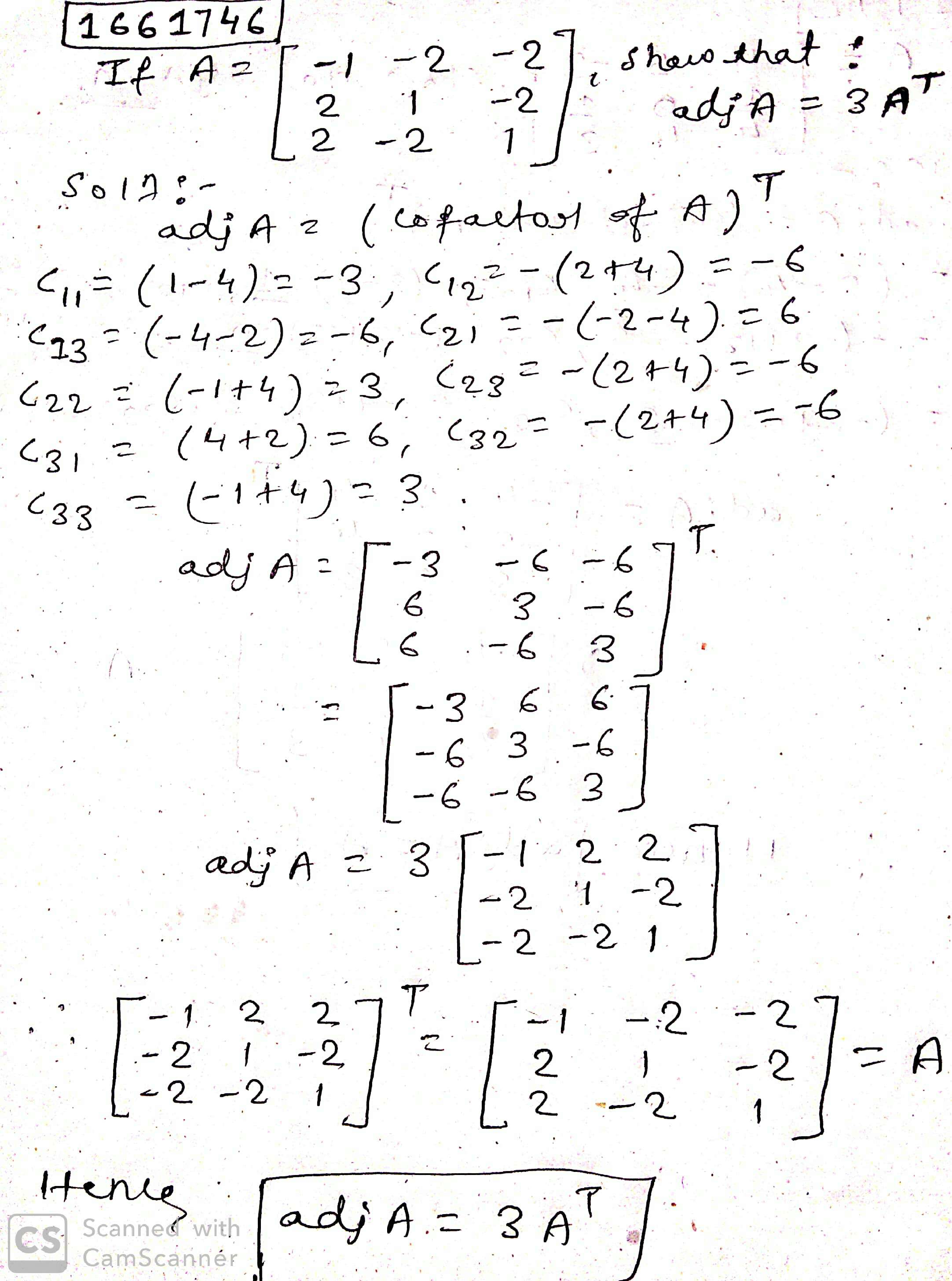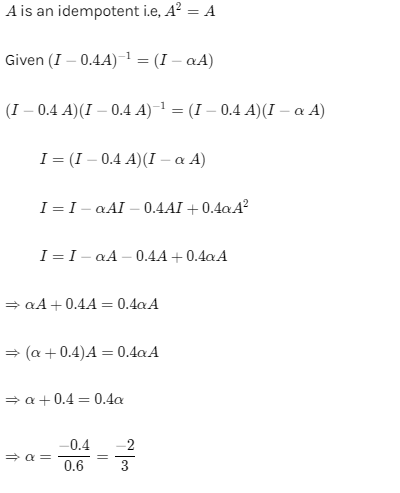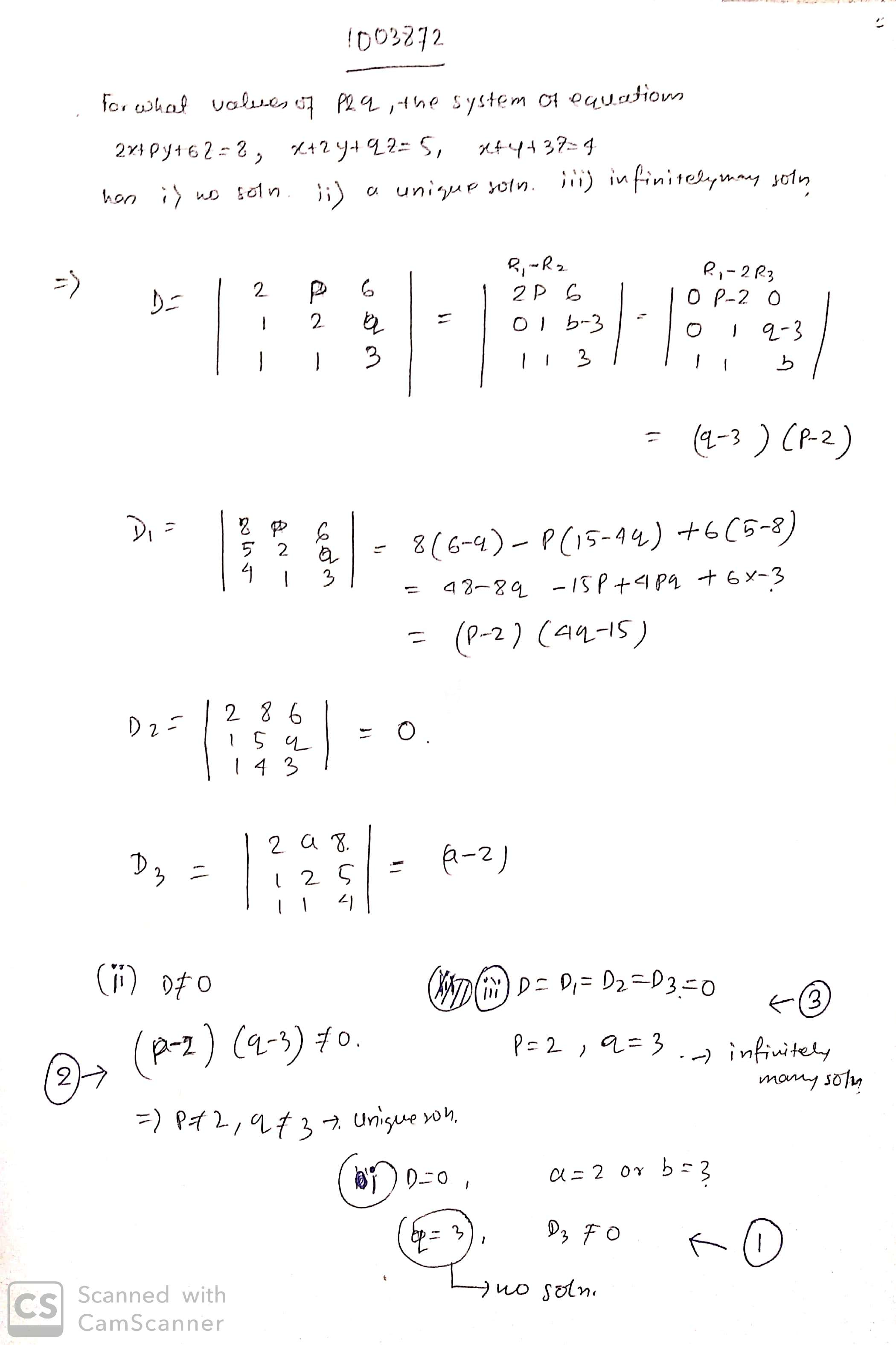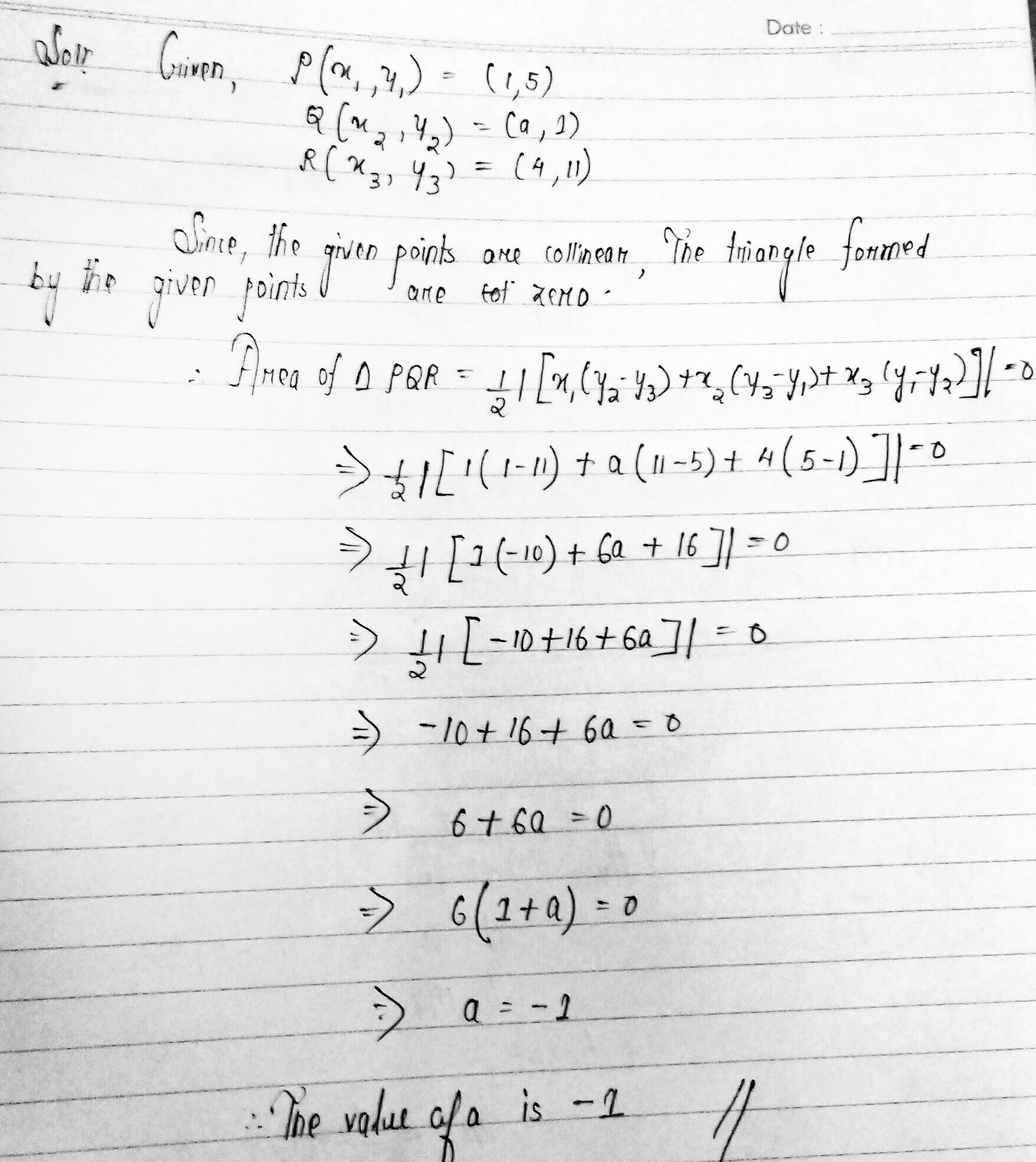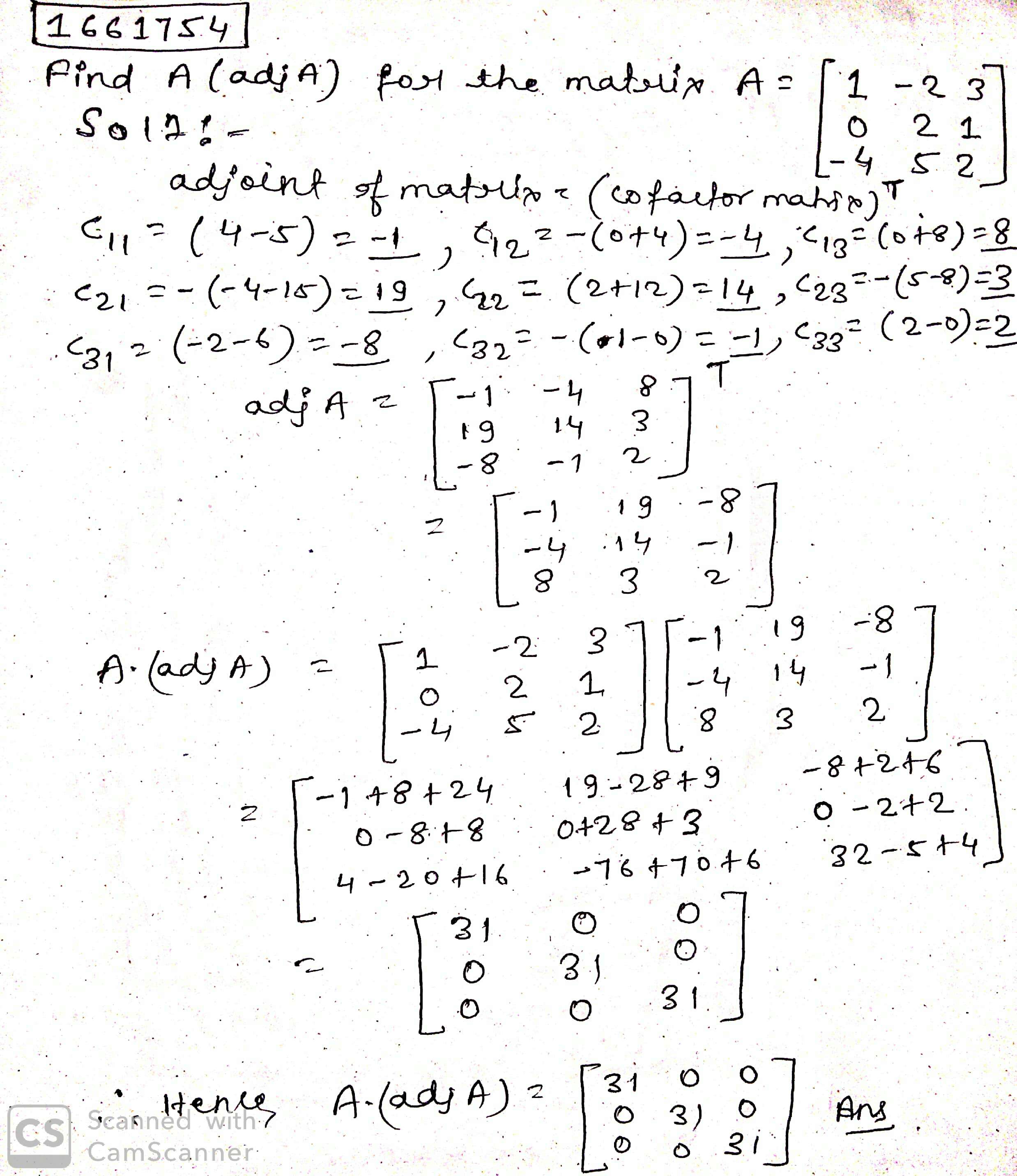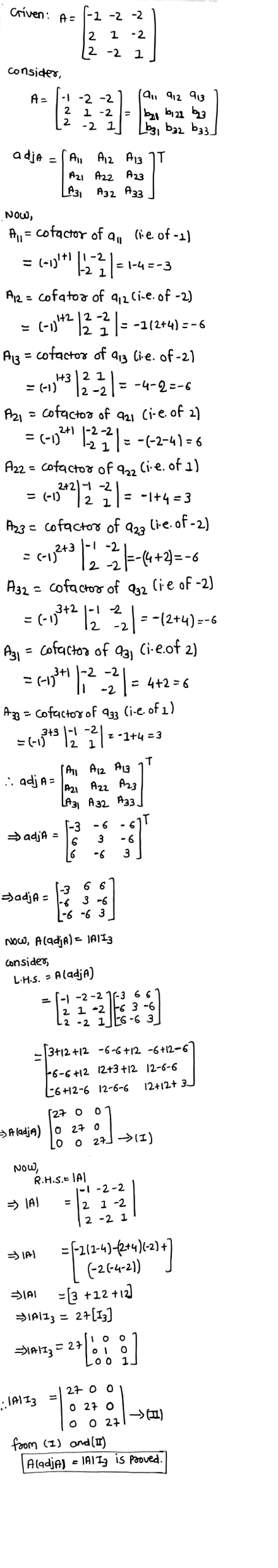Determinants - Class 12 Commerce Maths - Extra Questions
If A is $$2\times 2$$ matrix, $$det A=4$$ then find the product of $$det(3A)$$ and $$det(A^{-1})$$
Write the value of the determinant $$\begin{bmatrix} p & p+1 \\ p-1 & p\end{bmatrix}$$
when $$p=1342$$
Using the properties of determinants, find the value of
$$\begin{vmatrix} 0 & a & -b \\ -a & 0 & -c \\ b & c & 0 \end{vmatrix}$$
Evaluate the determinants
$$\begin{vmatrix} 2 & 4 \\ -5 & -1 \end{vmatrix}$$
If $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 2 & 3 & 4 \\ 5 & -6 & x \end{bmatrix}$$ and $$\det A = 45$$; then find $$x$$.
Find adjoint of matrix $$\ \ \ A=\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 \\ 3 & 4 \end{bmatrix}$$
Show that the points $$A(2,3),B(4,0)$$ and $$C(6,-3)$$ are collinear.
Write the value of $$\triangle = \begin{vmatrix}x+y&y+z&z+x\\z&x&y\\-3&-3&-3\end{vmatrix}$$.
The area of a triangle is zero, then the three points are said to be ______ points.
Find the value of the determinant:
$$\begin{vmatrix}5 & -2\\ -3 & 1\end{vmatrix}$$
If for any $$2 \times 2$$ square matrix A, $$A (adj A) = \begin{bmatrix} 8& 0\\ 0 & 8\end{bmatrix}$$, them write the value of det[A].
Find a value of $$x$$ if $$\begin{vmatrix}x& 2 \\18&x\end{vmatrix} = \begin{vmatrix}6& 2 \\18&6\end{vmatrix}$$
$$\begin{vmatrix} 1 & 1 & 1 \\ a & b & c \\ { a }^{ 2 } & { b }^{ 3 } & { c }^{ 3 } \end{vmatrix}$$
Prove that : = $$(a - b) (b - c) (c - a) (a + b + c).$$
Find the values of $$x$$ for which $$\begin{vmatrix}3&x\\x&1\end{vmatrix}=\begin{vmatrix}3&2\\4&1\end{vmatrix}$$.
Evaluate the following deteminants :
i)$$\begin{vmatrix}
x& -7\\
x &5x+1
\end{vmatrix}$$
ii)$$\begin{vmatrix}
\cos 15^{\circ} & \sin 15^{\circ}\\
\sin 75^{\circ} & \cos 75^{\circ}
\end{vmatrix}$$
If $$3^{n}$$ is a factor of the determinant
$$\left| \begin{matrix} 1 & 1 & 1 \\ _{ }^{ n }{ { C }_{ 1 } } & _{ }^{ n+3 }{ { C }_{ 1 } } & ^{ n+6 }{ { C }_{ 2 } } \\ ^{ n }{ { C }_{ 2 } } & ^{ n+3 }{ { C }_{ 2 } } & ^{ n+6 }{ { C }_{ 2 } } \end{matrix} \right| ,$$
then the maximum value of $$n$$ is $$____$$.
Find the determinant in following case:
$$A=\left [ \begin{array}{c}5\hspace{0.5cm}{20}\\0\hspace{0.5cm}{2}\end{array} \right ]$$
Find if the points (0, 8/3), (1/3) , and (82, 30) are collinear.
Prove the following :
$$\left| \begin{matrix} y+z & z & y \\ z & z+x & x \\ y & x & x+y \end{matrix} \right| =4xyz$$
Prove that the points (a , b), (c , d) and (a - c, b - d) are collinear if ad = bc. Also show that the straight line passing through these points passes through origin.
Show that
$$\begin{vmatrix}
\sin 10^{\circ}& -\cos 10^{\circ}\\
\sin 80^{\circ}&\cos 80^{\circ}
\end{vmatrix}=1$$
Find the value of $$K$$, for which the given points are collinear:
$$\begin{matrix} A \\ \left( 7,-2 \right) \end{matrix}\begin{matrix} B \\ \left( 5,1 \right) \end{matrix}\begin{matrix} C \\ \left( 3,K \right) \end{matrix}$$
In each of the following find the value of $$k$$, for which the points are collinear..
(ii) $$(8, 1), (k, -4), (2, -5)$$
Let $$A=\begin{bmatrix}5&8\\8&13\end{bmatrix}$$ then show that $$A$$ satisfies the equation $$x^2-18x+1=0$$.
In each of the following find the value of $$k$$, for which the points are collinear.(i) $$(7, -2), (5, 1), (3, k)$$
Find the value of $$x$$ if the points $$(x,5),(2,3)$$ and $$(-2,-11)$$ are collinear.
If the minor of three-one element (i.e $$M_{31}$$) in the determinant $$\left| \begin{matrix} 0 & 1 & \sec { \alpha } \\ \tan { \alpha } & -\sec { \alpha } & \tan { \alpha } \\ 1 & 0 & 1 \end{matrix} \right| $$ is $$1$$ then find the value of $$\alpha$$. $$(0 \le \alpha \le \pi)$$
Show that $$\triangle$$ABC is an isosceles triangle, if the determinant$$\begin{vmatrix} 1 & 1 & 1 \\ 1+\cos A & 1+\cos B & 1+\cos C \\ \cos^2A +\cos A & \cos^2B+\cos B & \cos^2C+\cos C\end{vmatrix}=0$$
Using properties of determinants, prove the following$$\begin{vmatrix} 1+a^2-b^2 & 2ab & -2b \\ 2ab & 1-a^2+b^2 & 2a \\ 2b & -2a & 1-a^2-b^2 \end{vmatrix}=(1+a^2+b^2)^3$$.
Solve:$$\begin{vmatrix} 0& -3 &x \\ x+1& 3 &1 \\ 4& 1 & 5\end{vmatrix}$$ =$$0$$
If $$A = \left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
1&{ - 1} \\
{ - 1}&1
\end{array}} \right|$$, then show that $${A^2} = 2A\,\,\& \,\,{A^3} = 4A$$
Find $$\begin{vmatrix}4&6&2\\3&0&9\\7&1&5\end{vmatrix}$$
Show that the point $$P (a,b+c)$$, $$Q(b,c+a)$$ and $$R(c,a+b)$$ are collinear.
Find the adjoint of $$\begin{vmatrix} 1 & -1 & 2 \\ 3 & 0 & -2 \\ 1 & 0 & 3 \end{vmatrix}$$
Find the value of following determinant.
$$\begin{vmatrix} \dfrac{7}{3} & \dfrac{5}{3}\\ \dfrac{3}{2} & \dfrac{1}{2}\end{vmatrix}$$.
If $$A=\left[ \begin{matrix} 1 & 1 \\ 2 & 1 \end{matrix} \right],$$ find $$|A|$$
If A is a square matrix of order $$3$$ such $$|A|=5$$, then find the value of $$|adjA|$$ ?
If three points $$(x_1 , y_1) , (x_2 , y_2 ) $$ and $$(x_3 , y_3 ) $$ lie on the same line, prove that
$$ \dfrac {y_2 - y_3}{x_2 x_3} + \dfrac {y_3 - y_1}{x_3 x_1}+ \dfrac {y_1 - y_2}{x_1 x_2} = 0$$
Evaluate $$\begin{vmatrix} a & b & c \\ -1 & 1 & -1 \\ 1 & -1 & 1 \end{vmatrix}$$.
Find the values of the following determinants
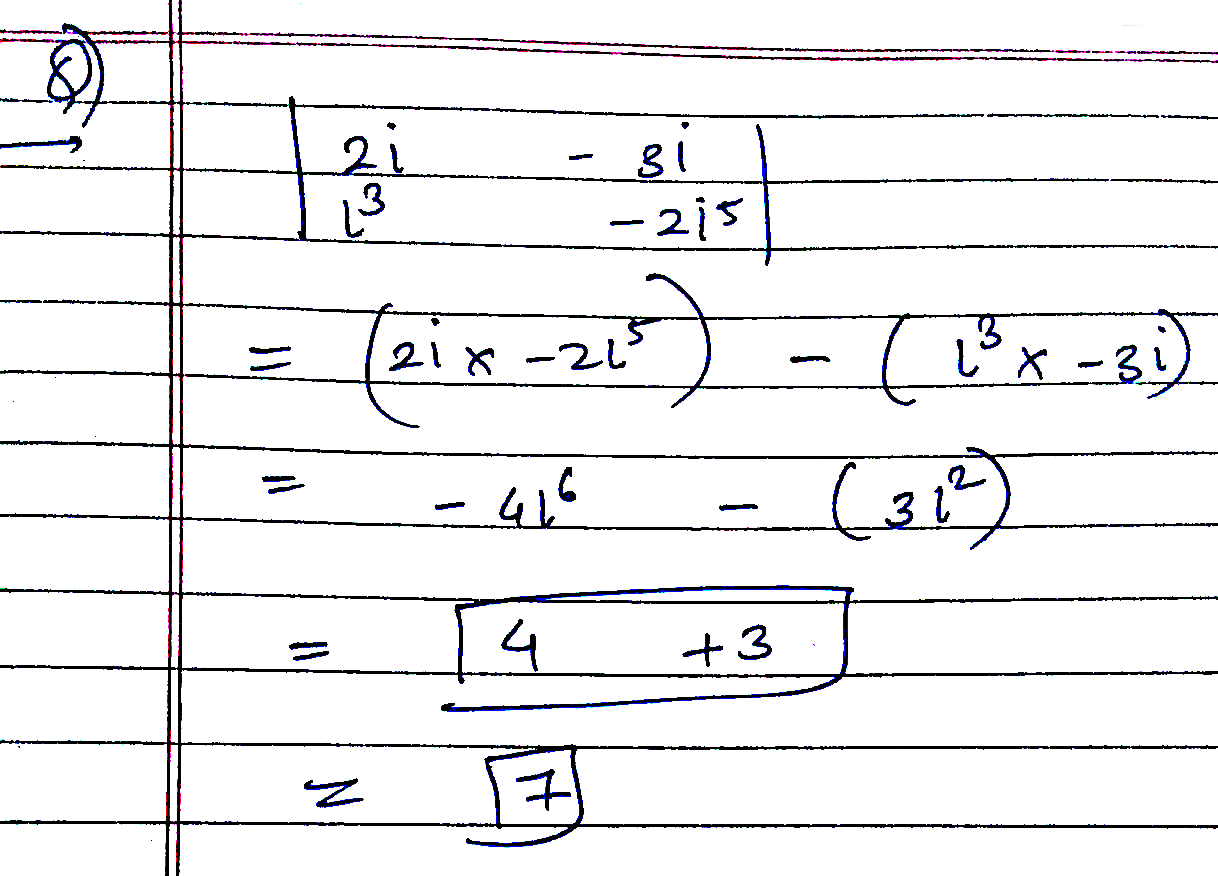
$$\begin{vmatrix} 2i & -3i \\ { i }^{ 3 } & -2{ i }^{ 5 } \end{vmatrix}$$ where $$i=\sqrt{-1}$$.
$$A = \begin{bmatrix} 2&4 \\ 6&8 \end{bmatrix}$$ find det(A)
Compute the following determinant :
$$\begin{vmatrix} { a }^{ 2 } & ab \\ ab & { b }^{ 2 } \end{vmatrix}$$
$$\begin{vmatrix} { a }^{ 2 } & ab \\ ab & { b }^{ 2 } \end{vmatrix}$$
Show that $$\left| \begin{matrix} 1 & 1 & 1 \\ a & b & c \\ { a }^{ 2 } & b^{ 2 } & c^{ 2 } \end{matrix} \right| =(a-b)(b-c)(c-a)$$.
Compute the following determinant :
$$\begin{vmatrix} 3 & 5 \\ -2 & 6 \end{vmatrix}$$
$$\begin{vmatrix} 3 & 5 \\ -2 & 6 \end{vmatrix}$$
Find value of the determinant
$$A = \begin{vmatrix}3 & 2\\ 5 & 7\end{vmatrix} $$
Prove that $$\left| \begin{matrix} 1 & \omega & { \omega }^{ 2 } \\ \omega & { \omega }^{ 2 } & 1 \\ { \omega }^{ 2 } & 1 & { \omega } \end{matrix} \right| =0$$
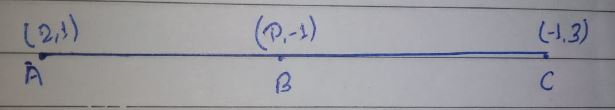
For what value of $$p$$ are the points $$(2,1),(p,-1)$$ and $$(-1,3)$$ collinear.
Using determinants show that points $$A(a,b+c),B(b,c+a)$$ and $$C(c,a+b)$$ are col-linear.
Prove that the adjoint of a symmetric matrix is also a symmetric matrix.
Find deteminant $$\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 2 \end{bmatrix}$$
Prove that: $$2\left| \begin{matrix} 8 & -5 \\ -2 & 6
\end{matrix} \right|=\left| \begin{matrix} 14 & -2 \\ -4 & 6
\end{matrix} \right|$$
In the diagram on a lunar eilpse, if the positions od sun,Earth and moon are shown by $$(-4,6), (k,-2) $$and$$ (5,-6)$$ respectively, then find the value of k.
If the points $$(3,-2), (x,2)$$ and $$(8,8)$$ are collinear find $$10x$$ using determinant.
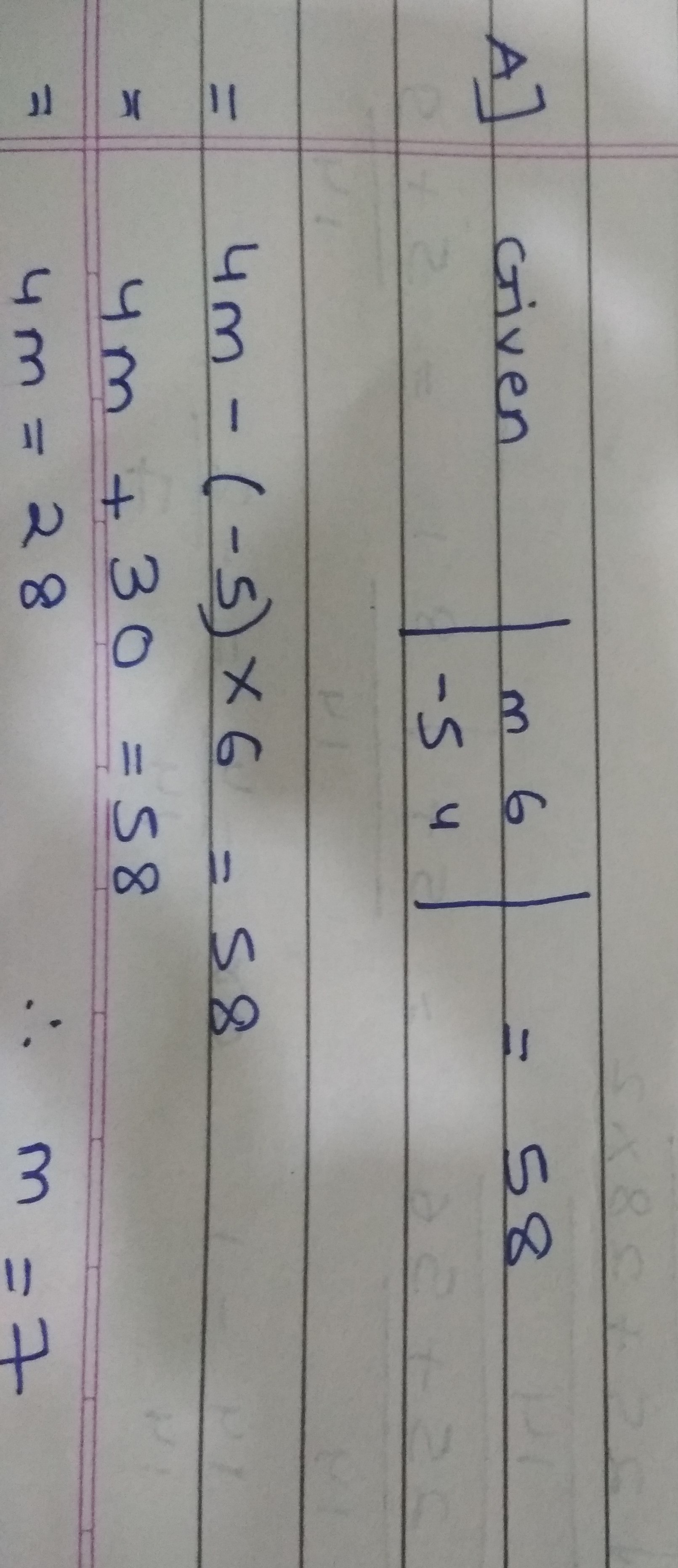
If the value of determinant $$\left| \begin{matrix} m & 6 \\ -5 & 4 \end{matrix} \right| $$ is $$58$$, then find the value of $$m$$.
If $$A(x_{1},y_{1}),B(x_{2},y_{2}),C(x_{3},y_{3})$$ are vertices of an equilateral triangle whose each side is equal to a, then prove that $$\begin{vmatrix} x_{1} & y_{1} & 2 \\ x_{2} & y_{2} & 2 \\ x_{3} & y_{3} & 2 \end{vmatrix}=3a^4$$.
Find the value of $$k$$ if det $$\begin{vmatrix} K+3 & 1 & 2 \\ 3 & -2 & 1 \\ -4 & -3 & 3 \end{vmatrix}=0$$
Using the method of slope, show that the following points are collinear : $$( i ) A \left( 4,8\right ) , B \left( 5,12 \right) , C \left( 9,28 \right)$$ $$(ii) A \left( 16 , - 18 \right) , B \left( 3 , - 6 \right) , C \left( - 10,6\right )$$
Show that the points $$P(-2,3,5), Q(1,2,3)$$ and $$R(7,0,-1)$$ are collinear.
Show that the points $$P(-2, 3, 5), Q(1, 2, 3)$$ and $$R(7, 0, -1)$$ are collinear.
Solve:
$$\left[ \begin{matrix} 1 & 4 & 2 \\ 2 & -1 & 4 \\ -3 & 7 & 6 \end{matrix} \right] $$
If $$A= \left[ {\matrix{10 & 0 \cr 4 & 10\cr } } \right]$$, then find $$\left| A \right|$$.
Construct a $$3\times 2$$ matrix whose elements are given by $$a_{1}=\dfrac{1}{2}|i-3j|$$.
Write the value of the determinant $$ \left| \begin{array}{cc}{3} & {-1} \\ {2} & {1}\end{array}\right| $$
$$\left| \begin{matrix} 1 & a & { a }^{ 2 } \\ 1 & b & { b }^{ 2 } \\ 1 & c & { c }^{ 2 } \end{matrix} \right| =(a-b)(b-c)(c-a)$$
Solve:
$$\left| \begin{matrix} 0 & a & -b \\ -a & 0 & -c \\ b & c & 0 \end{matrix} \right| =0$$
Find the value of x for which $$|_{ x }^{ 3 }\quad _{ 1 }^{ x }|=|_{ 8 }^{ 3 }\quad _{ 1 }^{ 2 }|$$.
If the points (-3,6), (-9,a) and (0,15) are collinear, then find a.
Convert $$\begin{bmatrix} 1 & -1 \\ 2 & 3 \end{bmatrix}$$ into an identify matrix by suitable row transformations.
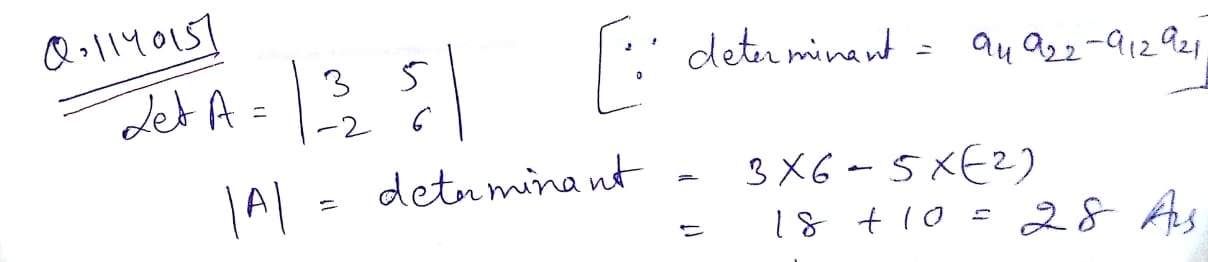
If $$A = \left| \begin{array} { c c } { 2 } & { 3 } \\ { - 1 } & { 2 } \end{array} \right|$$ Find $$A$$.
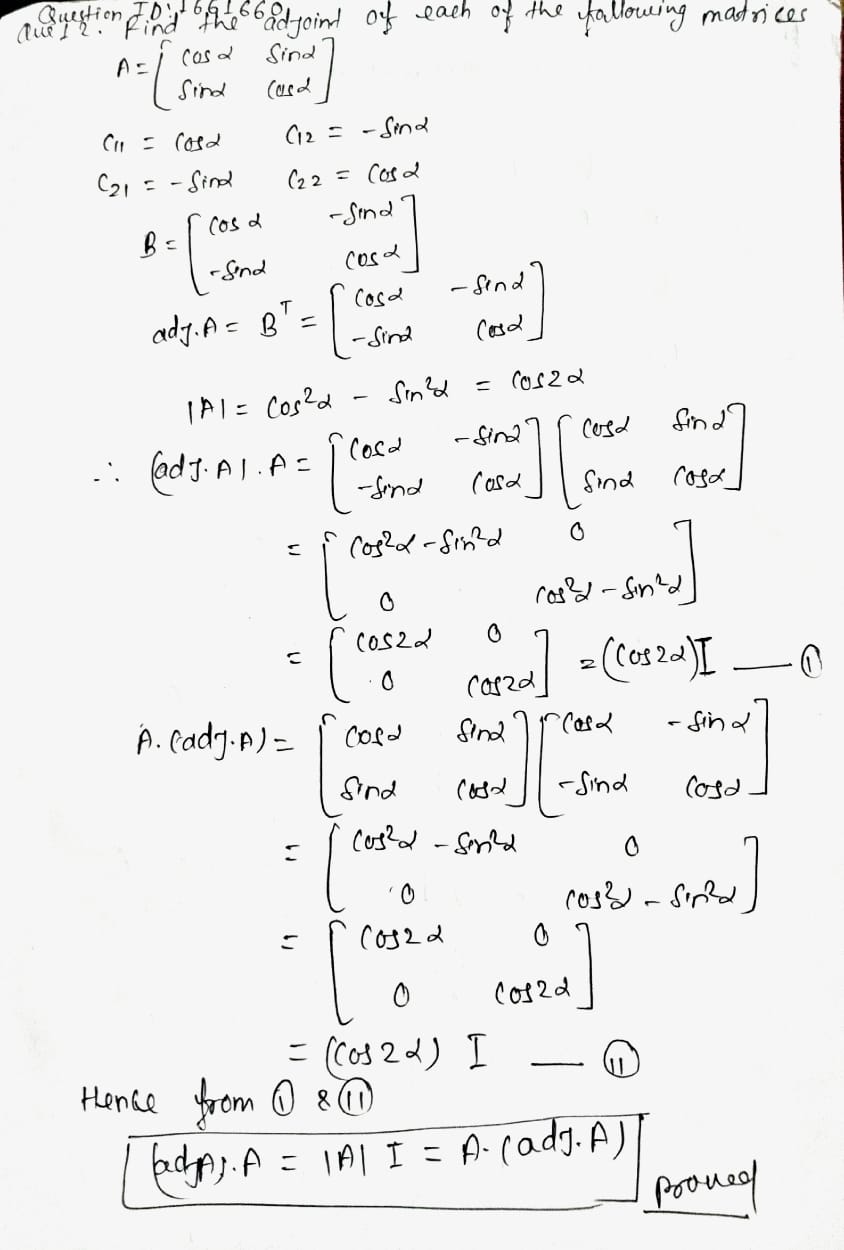
Evaluate $$\Delta = \begin{vmatrix} \cos 2\alpha & \sin 2\alpha \\-\sin 3\alpha & \cos 3\alpha \end{vmatrix}$$
The value of $$\begin{vmatrix} \cos15^{\circ} & \sin15^{\circ} \\ \sin75^{\circ} & \cos75^{\circ} \end{vmatrix}$$ is
Find the value of x, if $$\begin{vmatrix} x+2 & x \\ x-4 & x+3 \end{vmatrix}=\begin{vmatrix} 4 & 2 \\ -2 & 5 \end{vmatrix}$$
Evaluate:$$\begin{vmatrix} \cos30^{\circ} & \sin30^{\circ} \\ \sin105^{\circ} & \cos105^{\circ} \end{vmatrix}$$
Evaluate the determinant :
$$\begin{vmatrix} \cos\theta & -\sin\theta \\ \sin\theta & \cos\theta \end{vmatrix}$$
Find the determinant of the matrix $$A$$
$$A=\begin{bmatrix} -1 & 4 \\ 2 & 3 \end{bmatrix}$$
Show that the points $$A(-7, 4, -2), B(-2, 1, 0)$$ and $$C(3, -2, 2)$$ are collinear.
Find the coordinates of a point $$A$$, where $$AB$$ is diameter of a circle whose centre is $$(2, -3)$$ and $$B$$ is the point $$(1, 4)$$.
Evaluate the following determinants :
$$\begin{vmatrix} \cos15^{\circ} & \sin15^{\circ} \\ \sin75^{\circ} & \cos75^{\circ} \end{vmatrix}$$
Find the values of $$x$$, if $$\begin{vmatrix} 2 & 3 \\ 4 & 5 \end{vmatrix}$$= $$\begin{vmatrix} x & 3 \\ 2x & 5 \end{vmatrix}$$
Are the following pairs of sets equal? Give reasons.
$$A=\{x : x$$ is a letter of the word "WOLF"$$\}$$,
$$B=\{x : x$$ is a letter of the word "FOLLOW"$$\}$$.
The value of the determinant $$\begin{vmatrix} \cos30^{\circ} & \sin60^{\circ} \\ \sin30^{\circ} & \cos60^{\circ} \end{vmatrix}$$ is
Evaluate $$\begin{bmatrix} 14 & 9 \\ -8 & -7 \end{bmatrix}$$.
Find the adjoint of the following matrice:
$$ \begin{bmatrix} a & b \\ c & d \end{bmatrix} $$
The value of the determinant $$\begin{vmatrix} \cos15^{\circ} & \sin15^{\circ} \\ \sin75^{\circ} & \cos75^{\circ} \end{vmatrix}$$ is______
If $${ e }^{ i\theta }=\cos { \theta } +i\sin { \theta } $$, find the value of $$-\begin{vmatrix} 1 & { e }^{ i\pi /3 } & { e }^{ i\pi /4 } \\ { e }^{ -i\pi /3 } & 1 & { e }^{ i2\pi /3 } \\ { e }^{ -i\pi /4 } & { e }^{ -i2\pi /3 } & 1 \end{vmatrix}\quad-{2}^{\frac{1}{2}}$$
Evaluate $$\begin{vmatrix} \cos { \alpha } \cos { \beta } & \cos { \alpha } \sin { \beta } & -\sin { \alpha } \\ -\sin { \beta } & \cos { \beta } & 0 \\ \sin { \alpha } \cos { \beta } & \sin { \alpha } \sin { \beta } & \cos { \alpha } \end{vmatrix}$$
If $$A,B$$ and $$C$$ are the angles of non-right angles triangle $$ABC$$, then find the value of $$\begin{vmatrix} \tan { A } & 1 & 1 \\ 1 & \tan { B } & 1 \\ 1 & 1 & \tan { C } \end{vmatrix}$$
If the value of $$\begin{vmatrix} 1 & 2 & 4 \\ -1 & 3 & 0 \\ 4 & 1 & 0 \end{vmatrix}$$ is $$k$$, then find $$\dfrac{-k}{13}$$.
The absolute value of the determinant $$\begin{vmatrix} -1 & 2 & 1 \\ 3+2\sqrt { 2 } & 2+2\sqrt { 2 } & 1 \\ 3-2\sqrt { 2 } & 2-2\sqrt { 2 } & 1 \end{vmatrix}$$ is $$\displaystyle\frac { k }{ \sqrt { 2 } } $$ then $$k=$$
If $$\begin{vmatrix} x & x+y & x+y+z \\ 2x & 3x+2y & 4x+3y+2z \\ 3x & 6x=3y & 10x+6y+3z \end{vmatrix}=64$$, then the real value of $$x$$ is .........
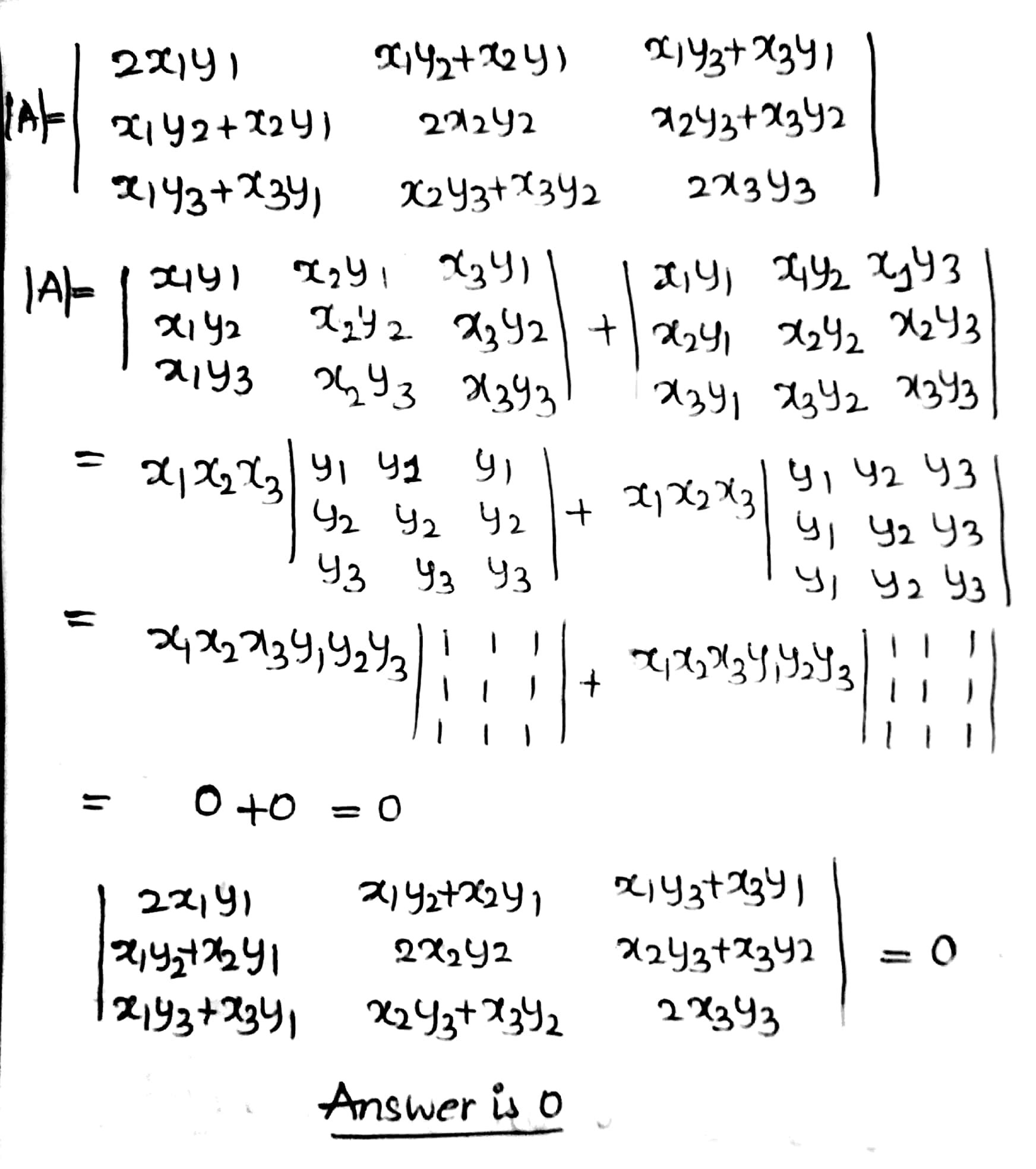
The value of $$\begin{vmatrix} 2{ x }_{ 1 }{ y }_{ 1 } & { x }_{ 1 }{ y }_{ 2 }+{ x }_{ 2 }{ y }_{ 1 } & { x }_{ 1 }{ y }_{ 3 }+{ x }_{ 3 }{ y }_{ 1 } \\ { x }_{ 1 }{ y }_{ 2 }+{ x }_{ 2 }{ y }_{ 1 } & 2{ x }_{ 2 }{ y }_{ 2 } & { x }_{ 2 }{ y }_{ 3 }+{ x }_{ 3 }{ y }_{ 2 } \\ { x }_{ 1 }{ y }_{ 3 }+{ x }_{ 3 }{ y }_{ 1 } & { x }_{ 2 }{ y }_{ 3 }+{ x }_{ 3 }{ y }_{ 2 } & 2{ x }_{ 3 }{ y }_{ 3 } \end{vmatrix}$$ is ........
The constant $$k$$ is such that the following system of equations posses a non-trivial(i.e., not all zero) solution over the set of rationals $$Q$$
$$ x+ky+3z=0,\quad 3x+ky-2z=0\quad 2x+3y-4z=0$$
Then $$\displaystyle \frac{2k}{11}$$ is equal to
If $$A + B + C = \pi$$, then $$\begin{vmatrix} sin (A + B + C)& sin B & cos C\\ - sin B & 0 & tan A\\ cos (A + B) &- tan A &0 \end{vmatrix} = $$ .............
If $$(1,2)$$, $$\displaystyle \left(\frac{1}{2} , 3 \right)$$ and $$(0, k)$$ are collinear points, find the value of $$k$$.
State whether True or False(-1, 8), (9, -2), (3,4) are collinear points.
Let
$$f\left ( x \right )=\begin{vmatrix}
2\cot x & -1 & 0\\
1 & \cot x & -1\\
0 & 1 & 2\cot x
\end{vmatrix}$$
then
Let $$f\left ( \theta \right )=\begin{vmatrix}
\cos ^{2}\theta & \cos \theta \sin \theta & -\sin \theta \\
\cos \theta \sin \theta & \sin ^{2}\theta & \cos \theta \\
\sin \theta & -\cos \theta & 0
\end{vmatrix}$$
find $$f\left ( \pi /3 \right )$$.
$$A_{3 \times 3}$$ is a matrix such that $$|A|=a, \:B = (adj \:A)$$ such that $$|B|= b$$. Find the value of $$\dfrac{(ab^2 + a^2b + 1)S}{25}$$ where $$\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}S=\frac{a}{b}+\frac{a^2}{b^3}+\frac{a^3}{b^5} + \:......... \:up \:to \:\infty $$, and $$a = 3$$.
Find the value of $$x$$ for which the points $$(x, -1), (2,1)$$ and $$(4, 5)$$ are collinear.
Find the values of $$x$$, if
(i)$$\begin{vmatrix} 2 & 4 \\ 5 & 1 \end{vmatrix}=\begin{vmatrix} 2x & 4 \\ 6 & x \end{vmatrix}$$ (ii)$$\begin{vmatrix} 2 & 3 \\ 4 & 5 \end{vmatrix}=\begin{vmatrix} x & 3 \\ 2x & 5 \end{vmatrix}$$
Using the properties of determinants, show that:
(i)$$\begin{vmatrix} a-b-c & 2a & 2a \\ 2b & b-c-a & 2b \\ 2c & 2c & c-a-b \end{vmatrix}=(a+b+{ c) }^{ 2 }$$
(ii)$$\begin{vmatrix} x+y+2z & x & y \\ z & y+z+2x & y \\ z & x & z+x+2y \end{vmatrix}=2(x+y+{ z) }^{ 3 }$$
Using the properties of determinants, show that:
(i)$$\begin{vmatrix} x+4 & 2x & 2x \\ 2x & x+4 & 2x \\ 2x & 2x & x+4 \end{vmatrix}=(5x+4)(4-{ x) }^{ 2 }$$
(ii)$$\begin{vmatrix} y+k & y & y \\ y & y+k & y \\ y & y & y+k \end{vmatrix}={ k }^{ 2 }(3y+k)$$
Find the value of determinant.
(i) $$\begin{vmatrix} \cos\theta & -\sin\theta \\ \sin\theta & \cos\theta \end{vmatrix}$$
(ii) $$\begin{vmatrix} { x }^{ 2 }-x+1 & x-1 \\ x+1 & x+1 \end{vmatrix}$$
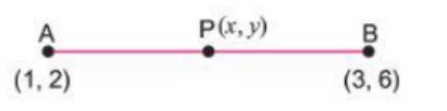
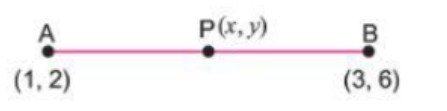
(i) Find equation of line joining $$(1, 2)$$ and $$(3, 6)$$ using determinants
(ii) Find equation of line joining $$(3, 1)$$ and $$(9, 3)$$ using determinants.
Find co-factors of the matrix,$$A=\begin{bmatrix} 1 & -1 & 2 \\ 0 & 2 & -3 \\ 3 & -2 & 4 \end{bmatrix}$$
Write minors and cofactors of the elements of following determinants
(i)$$\begin{vmatrix} 2 & -4 \\ 0 & 3 \end{vmatrix}$$
(ii)$$\begin{vmatrix} a & c \\ b & d \end{vmatrix}$$
Find the Minors and Cofactors of the elements of the following determinants:(i)$$\begin{vmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{vmatrix}$$
(ii)$$\begin{vmatrix} 1 & 0 & 4 \\ 3 & 5 & -2 \\ 0 & 1 & 2 \end{vmatrix}$$
Find the adjoint of matrix $$\ \ \ \ A= \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 & 2 \\ 2 & 3 & 5 \\ 2 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}$$
Find co-factors of the matrix,$$A= \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & \cos\alpha & \sin\alpha \\ 0 & \sin\alpha & -\cos\alpha \end{bmatrix}$$
Using properties of determinants, prove that:
$$\begin{vmatrix} \alpha & { \alpha }^{ 2 } & \beta +\gamma \\ \beta & { \beta }^{ 2 } & \gamma +\alpha \\ \gamma & { \gamma }^{ 2 } & \alpha +\beta \end{vmatrix}$$ $$=(\alpha- \beta)(\beta- \gamma)(\gamma-\alpha)(\alpha +\beta +\gamma )$$
Evaluate $$\begin{vmatrix} \cos\alpha \cos\beta & \cos\alpha \sin\beta & -\sin\alpha \\ -\sin\beta & \cos\beta & 0 \\ \sin\alpha \cos\beta & \sin\alpha \sin\beta & \cos\alpha \end{vmatrix}$$
If true Enter $$'1'$$ else $$'0'.$$$$\begin{vmatrix} x & y & x+y \\ y & x+y & x \\ x+y & x & y \end{vmatrix}=-2(x+y)(x^2+y^2-xy)$$
If true Enter $$'1'$$ else $$'0'.$$
Evaluate $$\begin{vmatrix} 1 & x & y \\ 1 & x+y & y \\ 1 & x & x+y \end{vmatrix}$$
Find cofactors of $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 1 & 3 \\ 4 & -1 & 0 \\ -7 & 2 & 1 \end{bmatrix}$$
If $$A_{ij}$$ is the cofactor of the element $$a_{ij}$$ of the determinant $$\begin{bmatrix}2&-3&5\\6&0&4\\1&5&-7 \end{bmatrix}$$ then write the value of $$a_{32}.A_{32}.$$
If $$\triangle = \begin{vmatrix} 5 & 3 & 8 \\ 2 & 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 2 & 3 \end{vmatrix}$$, white the cofactor of the element $$a_{32}$$.
If $$\Delta = \begin{vmatrix} 5& 3 & 8\\ 2 & 0 & 1\\ 1 & 2 & 3\end{vmatrix}$$, write the cofactor of the element $$a_{32}$$
If $$\Delta = \begin{vmatrix}1 & 2 & 3\\ 2 & 0 & 1\\ 5 & 3 & 8\end{vmatrix}$$, write the minor of the elements $$a_{22}$$
If $$\Delta = \begin{vmatrix} 5 & 3 & 8\\ 2 & 0 &1 \\ 1 & 2 & 3\end{vmatrix}$$, write the minor of the element $$a_{23}.$$
Find the relation between $$x$$ and $$y$$ if the points $$A(x, y), B(-5, 7)$$ and $$C(-4, 5)$$ are collinear.
For how many real values of $$'m'$$ the points $$A (m + 1, 1), B (2m + 1, 3)$$ and $$C (2m + 2, 2m)$$ are collinear.
Show that the adjoint of $$A = \begin{bmatrix}-4 & -3 & -3\\ 1 & 0 & 1\\ 4 & 4 & 3\end{bmatrix}$$ is $$A$$ itself
Find the value of $$ k$$ if $$A (4, 11), B (2, 5), C (6, k) $$ are collinear points.
Find the value of $$a$$ for which the following points $$A (a, 3), B(2, 1)$$ and $$C(5, a)$$ are collinear. Hence find the equation of the line.
A, B, and C are three collinear points. The coordinates of A and B are (3, 4) and (7, 7) respectively and AC =10 units. Find sum of co-ordinates of C.
Using determinants show that points $$A (a, b + c), B(b, c + a)$$ and $$C (c, a + b)$$ are collinear.
find the value of $$k$$ for which the points $$(k,-1)(2,1)$$ and $$(4,5)$$ are collinear.
Show that the points $$A(-3,3)$$, $$B(0,0)$$, $$C(3,-3)$$ are collinear.
If $$A=\begin{bmatrix}1&2\\3&4\end{bmatrix},$$ find $$|2A|$$.
Find the equation of line joining (1, 2) and (3, 6) using determinants.
Calculate the values of the determinants:
$$\begin{vmatrix}a & h & g\\ h& b & f\\ g & f & c\end{vmatrix}$$.
For what values of $$m$$ will the expression $${y}^{2}+2xy+2x+my-3$$ be capable of resolution into two rational factors?
Calculate the values of the determinants:
$$\begin{vmatrix}1 & 1 & 1\\ 1& 1 + x & 1\\ 1 & 1 & 1 + y\end{vmatrix}$$.
Calculate the values of the determinants:
$$\begin{vmatrix}1 & z & -y\\ -z& 1 & x\\ y & -x & 1\end{vmatrix}$$.
Solve for $$\lambda$$ if $$\begin{vmatrix} a^2+\lambda & ab & ac\\ ab & b^2+\lambda & bc\\ ac & bc & c^2+\lambda\end{vmatrix}=0$$.
Calculate the values of the determinants:
$$\begin{vmatrix}b + c & a & a\\ b& c + a & b\\ c & c & a + b\end{vmatrix}$$.
Prove that $$\begin{vmatrix} 1+a & 1 & 1\\ 1& 1+b & 1\\ 1& 1& 1+c\end{vmatrix} =abc\displaystyle (1+\frac{1}{a}+\frac{1}{b}+\frac{1}{c})$$.
Find the area of $$\triangle PQR$$ whose vertices are $$P(2,1),Q(3,4)$$ and $$R(5,2)$$.
Find the equation of the line joining $$A(1,3)$$ and $$B(0,0)$$ using determine and find $$k$$ of $$D(k,0)$$ is a point such that area of $$\triangle$$ $$ABD$$ is $$3$$ sq. units.
If points $$\left( a,0 \right) ,\left( 0,b \right) $$ and $$\left( x,y \right) $$ are collinear, prove that $$\cfrac { x }{ a } +\cfrac { y }{ b } =1$$.
If the points $$A(-2, 1), B(a, b)$$ and $$C(4, -1)$$ are collinear and $$a-b=1$$, find the values of $$a$$ and $$b$$.
Find the ratio in which the line segment joining the points $$P(x, 2)$$ divides the line segment joining the points $$A (12, 5)$$ and $$B(4,-3)$$. Also find the value of $$x$$.
Evaluate :
$$\begin{vmatrix}
2& 3 & -5\\
7 &1 & -2\\
-3 & 4 &1
\end{vmatrix}$$
If three points $$\left( { x }_{ 1 },{ y }_{ 1 } \right) ,\left( { x }_{ 2 },{ y }_{ 2 } \right) ,\left( { x }_{ 3 },{ y }_{ 3 } \right) $$ lie on the same line, prove that
$$\cfrac { { y }_{ 2 }-{ y }_{ 3 } }{ { x }_{ 2 }{ x }_{ 3 } } +\cfrac { { y }_{ 3 }-{ y }_{ 1 } }{ { x }_{ 3 }{ x }_{ 1 } } +\cfrac { { y }_{ 1 }-{ y }_{ 2 } }{ { x }_{ 1 }{ x }_{ 2 } } =0$$
Show that the following set of points are collinear.
$$(2,5), (4,6)$$ and $$(8,8)$$
If $$a\ne b\ne c$$, prove that the points $$\left( a,{ a }^{ 2 } \right) ,\left( b,{ b }^{ 2 } \right) ,\left( c,{ c }^{ 2 } \right) $$ can never be collinear.
Find the value of $$k$$ if points $$(k,3),(6,-2)$$ and $$(-3,4)$$ are collinear.
For what value of $$a$$ the point $$(a,1),(1,-1)$$ and $$(11,4)$$ are collinear?
Evaluate :
$$\Delta=\begin{vmatrix}
\cos \alpha \cos \beta& \cos \alpha \sin \beta & -\sin \alpha\\
-\sin \beta &\cos \beta & 0\\
\sin \alpha \cos \beta & \sin \alpha \sin \beta &\cos \alpha
\end{vmatrix}$$
Prove that the points $$\left( ab, \right) ,\left( { a }_{ 1 },{ b }_{ 1 } \right) $$ and $$\left( a-{ a }_{ 1 },b-{ b }_{ 2 } \right) $$ are collinear if $$a{ b }_{ 1 }={ a }_{ 1 }b$$
Prove that the points $$(a,0),(0,b)$$ and $$(1,1)$$ are collinear if $$ \left (
\cfrac { 1 }{ a } +\cfrac { 1 }{ b } =1 \right )$$
Prove that the points $$(2,3), (-4,-6)$$ and $$1,3/2)$$ do not form a triangle.
Find the value of $$\lambda$$ if the following equations are consistent
$$x + y - 3 = 0$$
$$(1 + \lambda) x + (2 + \lambda) y - 8 = 0$$
$$ x - (1 + \lambda) y + (2 + \lambda) = 0$$
Find cofactors of the elements of the matrix $$A = \begin{bmatrix} -1 & 2 \\ -3 & 4 \end{bmatrix}$$
Find the value of $$k$$, if the points $$A(8,1),B(3,-4)$$ and $$C(2,k)$$ are collinear.
If the points $$A(-1,-4),B(b,c)$$ and $$C(5,-1)$$ are collinear and $$2b+c=4$$, find the values of $$b$$ and $$c$$.
Find the value(s) of $$k$$ for which the points $$(3k-1,k-2),(k,k-7)$$ and $$(k-1,-k-2)$$ are collinear.
Find the value of $$k$$, if the points $$A(7,-2),B(5,1)$$ and $$C(3,2k)$$ are collinear.
Let $$a > 0,\ d > 0.$$ Find the value of the determinant
$$\left| \begin{matrix} \dfrac { 1 }{ a } & \dfrac { 1 }{ a\left( a+d \right) } & \dfrac { 1 }{ \left( a+d \right) \left( a+2d \right) } \\ \dfrac { 1 }{ \left( a+d \right) } & \dfrac { 1 }{ \left( a+d \right) \left( a+2d \right) } & \dfrac { 1 }{ \left( a+2d \right) \left( a+3d \right) } \\ \dfrac { 1 }{ \left( a+2d \right) } & \dfrac { 1 }{ \left( a+2d \right) \left( a+3d \right) } & \dfrac { 1 }{ \left( a+3d \right) \left( a+4d \right) } \end{matrix} \right| $$
Prove the following :
$$\left| \begin{matrix} ax & by & cz \\ { x }^{ 2 } & { y }^{ 2 } & { z }^{ 2 } \\ 1 & 1 & 1 \end{matrix} \right| =\left| \begin{matrix} a & b & c \\ x & y & z \\ yz & zx & xy \end{matrix} \right| $$
Without expanding prove that the determinant $$
\left |
\begin{array}{111}
sinA & CosA & sin(A+\theta) \\
sin B & cos B & sin(B+\theta) \\
sin C & CosC & sin (c+\theta) \\
\end {array}
\right |
$$ =0
A, B , C are the points (a, p), (b,q) and (c,r) respectively such that a, b, c are in A. P. and p, q ,r in G.P. If the points are collinear then prove that p = q = r
If $$x,y,z \in R$$ then find Determinant$$\left( {\matrix{
{{{({2^x} + {2^{ - x}})}^2}} & {{{({2^x} - {2^{ - x}})}^2}} & 1 \cr
{{{({3^x} + {3^{ - x}})}^2}} & {{{({3^x} - {3^{ - x}})}^2}} & 1 \cr
{{{({4^x} + {4^{ - x}})}^2}} & {{{({4^x} - {4^{ - x}})}^2}} & 1 \cr
} } \right)$$
{{{({2^x} + {2^{ - x}})}^2}} & {{{({2^x} - {2^{ - x}})}^2}} & 1 \cr
{{{({3^x} + {3^{ - x}})}^2}} & {{{({3^x} - {3^{ - x}})}^2}} & 1 \cr
{{{({4^x} + {4^{ - x}})}^2}} & {{{({4^x} - {4^{ - x}})}^2}} & 1 \cr
} } \right)$$
If A = diag (a, b, c) = $$\begin{bmatrix}
a & 0 & 0 \\[0.3em]
0 & b & 0 \\[0.3em]
0 & 0 & c
\end{bmatrix}$$ such that $$abc \neq 0$$
then $$A^{-1} = diag (\frac{1}{a}, \frac{1}{b}, \frac{1}{c}) = \begin{bmatrix}
\frac{1}{a} & 0 & 0 \\[0.3em]
0 & \frac{1}{b} & 0 \\[0.3em]
0 & 0 & \frac{1}{c}
\end{bmatrix}$$
If where r = 1,2,3 be the co-ordinates of the points A, B, C respectively, then prove the following:
The equation of internal bisector of angel A is
$$b \, \begin{vmatrix} x & y & 1\\ x_1 & y_1 & 1\\ x_2 & y_2 & 1 \end{vmatrix} \, + \, c \, \begin{vmatrix} x & y & 1\\ x_1 & y_1 & 1\\ x_3 & y_3 & 1 \end{vmatrix} \, = \, 0$$
where b = AC and c = AB.
If $$A$$ is a matrix of order $$3 \times 3$$ then find $$\left| adj\ A \right|$$ where $$\left| A \right| =2$$
Find $$a$$ if $$\begin{vmatrix} i & -2i & -1\\ 3i & i^{3} & -2\\ 1& -3 & -i\end{vmatrix}$$ = $$ai$$, where $$i =\sqrt{-1}$$
Find the non-zero roots of the equation,
$$\Delta = \begin{vmatrix} a & b & ax + b \\ b & c & bx + c \\ ax + b & bx + c & c\end{vmatrix} = 0$$
Solve: $$\begin{vmatrix} 3x+4 & x+2 & 2x+3 \\ 4x+5 & 2x+3 & 3x+4 \\ 10x+17 & 3x+5 & 5x+8 \end{vmatrix}=0$$. The value of the determinant at $$x=-1$$is:
By using properties of determinants prove that $$\begin{vmatrix} (y+z)^{2}&xy& zx\\ xy&(x+z)^{2} & yz\\ xz & yz & (x+y)^{2}\end{vmatrix}$$ is divisible by $$(x+ y + z)^{n}$$. Find $$n$$ .
Find $$n$$ if: $$\begin{vmatrix} 1+a^{ 2 }-b^{ 2 } & 2ab & -2b \\ 2ab & 1-a^{ 2 }+b^{ 2 } & 2a \\ 2b & -2a & 1-a^2-b^2 \end{vmatrix} = (1 + a^2 + b^2)^n$$
$$\begin{vmatrix} 1+a & 1 & 1 \\ 1 & 1+b & 1 \\ 1 & 1 & 1+c \end{vmatrix}=abc\left(1+ \dfrac { 1 }{ a } +\dfrac { 1 }{ b } +\dfrac { 1 }{ c } \right) $$
Evaluate:
$$\begin {vmatrix} x^{2} -x +1 & x-1\\ x+1 & x+1\end{vmatrix}$$
Prove that $$\begin{vmatrix} \left( \beta +\gamma -\alpha -\delta \right) ^{ 4 } & \left( \beta +\gamma -\alpha -\delta \right) ^{ 2 } & 1 \\ \left( \gamma +\alpha -\beta -\delta \right) ^{ 4 } & \left( \gamma +\alpha -\beta -\delta \right) ^{ 2 } & 1 \\ \left( \alpha +\beta -\gamma -\delta \right) ^{ 4 } & \left( \alpha +\beta -\gamma -\delta \right) ^{ 2 } & 1 \end{vmatrix}=-64\left( \alpha -\beta \right) \left( \alpha -\gamma \right) \left( \alpha -\delta \right) \left( \beta -\gamma \right) \left( \beta -\delta \right) \left( \gamma -\delta \right)$$
Minor $$m_{33}$$ of the determinant $$\begin{vmatrix} 2 & 3 & 5 \\ 2 & -1 & 8 \\ 1 & 2 & 4 \end{vmatrix}$$ is
Prove $$\begin{vmatrix} x+4 & 2x & 2x\\ 2x & x+4 & 2x \\ 2x & 2x & x+4\end{vmatrix}=(5x+4)(4-x)^2$$.
Find the adjoint of matrix $$A =\begin{bmatrix}2&0&1\\3&1&2\\-1&1&2\end{bmatrix}$$
Find the adjoint of $${ \left( \dfrac { { 7 }^{ -4 } }{ { 4 }^{ -2 } } \right) }^{ \dfrac { 1 }{ 4 } }\begin{bmatrix} 1 & -1 & 2 \\ 3 & 0 & -2 \\ 1 & 0 & 3 \end{bmatrix}$$
If $$x, y, z$$ are non-zero real numbers and $$\begin{vmatrix} 1+x & 1 & 1 \\ 1+y & 1+2y & 1 \\ 1+z & 1+z & 1+3z \end{vmatrix}=0$$ then $$-\left( \dfrac { 1 }{ x } +\dfrac { 1 }{ y } +\dfrac { 1 }{ z } \right)$$ is equal to________
Find $$x$$ if $$\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 2 & 3 & 4 \\ 5 & -6 & x \end{bmatrix}=45$$
Find the adjoint of $$\begin{bmatrix} 1 & -1 & 2 \\ 3 & 0 & -2 \\ 1 & 0 & 3 \end{bmatrix}$$
Prove that $$\begin{vmatrix}ax & by & cz\\x^{2}& y^{2}& z^{2}\\ 1&1&1 \end{vmatrix} = \begin{vmatrix}a&b&c\\x&y&z\\yz&xz&xy \end{vmatrix}$$
Solve for $$x$$:$$\begin{vmatrix}1&5&2\\2&6&4\\3&7&x\end{vmatrix}=0$$
Prove that $$\triangle =\begin{vmatrix} a & b & a\alpha +b \\ b & c & b\alpha +c \\ a\alpha +b & b\alpha +c & 0 \end{vmatrix}=0$$ if a,b,c are in G.P.
Show that:$$\left| \begin{matrix} 1 & { a }^{ 2 } & { a }^{ 3 } \\ 1 & { b }^{ 2 } & { b }^{ 3 } \\ 1 & { c }^{ 2 } & { c }^{ 3 } \end{matrix} \right| =(a-b)(b-c)(c-a)(ab+bc+ca)$$
show that $$\left| \begin{matrix} 1 & a & { a }^{ 2 } \\ 1 & b & b^{ 2 } \\ 1 & c & c^{ 2 } \end{matrix} \right| =\left( a-b \right) \left( b-c \right) \left( c-a \right)$$
Find the solution set of $$\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}x&5&9\\{16}&{3x\, + \,8}&{36}\\3&1&7\end{array}} \right|\, = \,0$$.
Solve:$$\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}1&1&1\\1&{1 + \sin \theta }&1\\{1 + \cos \theta }&1&1\end{array}} \right|$$
Solve:
$$\begin{vmatrix} 1 & 1 & 2 \\ 1 & -2 & 3 \\ 1 & (x+1) & x \end{vmatrix}=0$$
Find the area of quadrilateral ABCD, the co ordinates of whose vertices are $$A(-3,2), B(5,4), C(7,-6), D(-5,-4)$$
Prove that, $$\left| \begin{matrix} x+\lambda & 2x & 2x \\ 2x & x+\lambda & 2x \\ 2x & 2x & x+\lambda \end{matrix} \right| =(5x+\lambda)( \lambda -x)^{2}$$.
Show that $$\begin{vmatrix} b+c & c+a & a+b \\ a+b & b+c & c+a \\ a & b & c \end{vmatrix} = a^3 + b^3 +c^3 - 3abc$$
If $$a \ne p, b \ne q$$ and $$c \neq r$$ $$\begin{vmatrix} p & b & c \\ a & q & c \\ a & b & r \end{vmatrix}= 0$$ then, find the value of :-
$$\dfrac{p}{p-a} + \dfrac{q}{q-b} + \dfrac{r}{r-c} = ?$$
Find the value of following determinant.
$$\begin{vmatrix} -1 & 7\\ 2 & 4\end{vmatrix}$$.
Find the value of the following determinant.
$$\begin{vmatrix} 2i & -3i \\ { i }^{ 3 } & -2{ i }^{ 3 } \end{vmatrix}$$, where $$i=\sqrt {-1}$$.
If $$f\left( x \right) = a + bx + c{x^2}$$ and $$\alpha ,\beta ,\gamma $$ are the roots of the equation $${x^3} = 1$$, then $$\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}a & b & c\\b & c & a\\c & a & b\end{array}} \right|$$ is equal to
If $$A$$ is a skew-symmetric matrix of order $$3$$ then find $$\left| A \right|$$
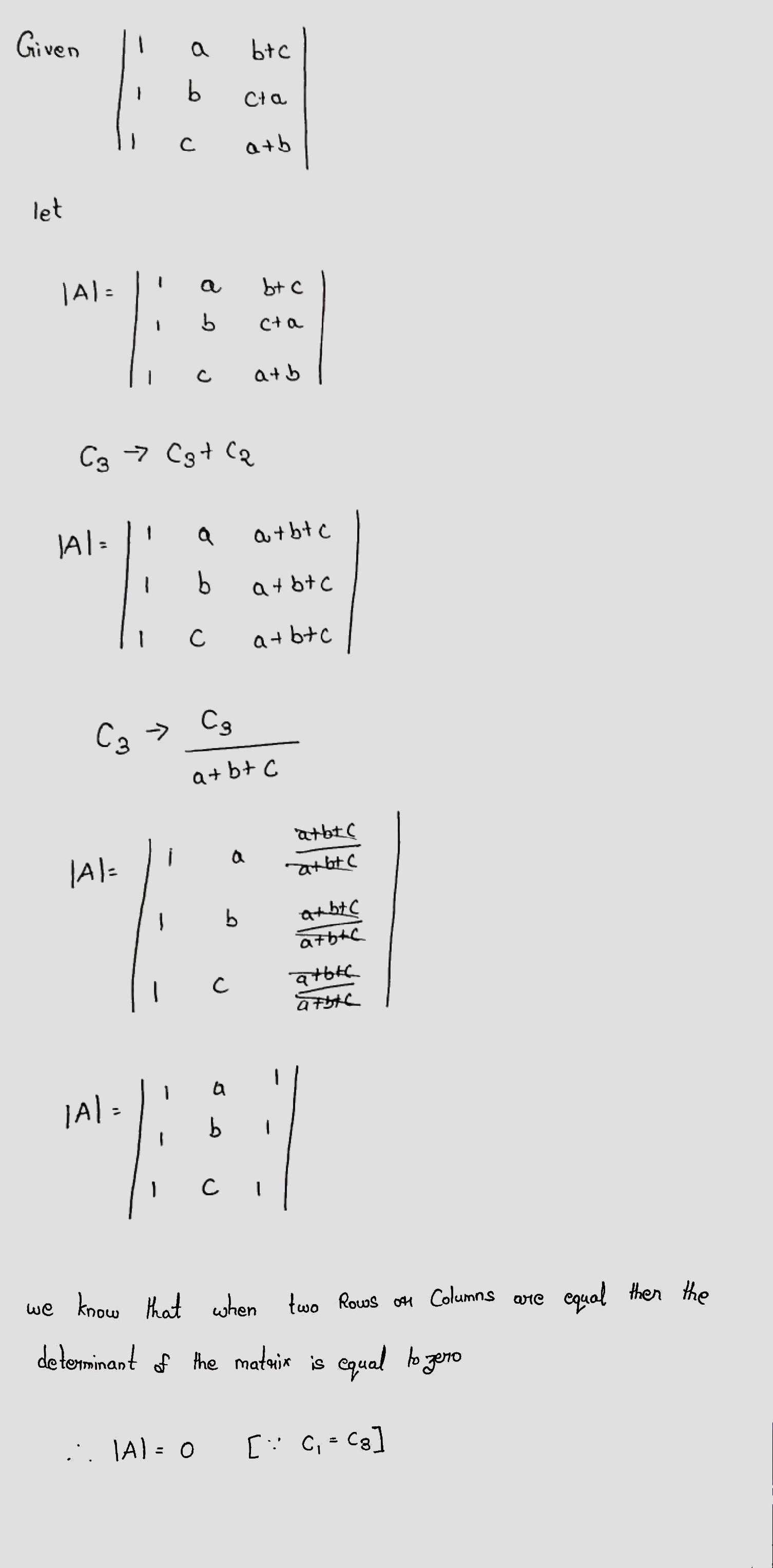
Evaluate $$\left| \begin{matrix} 1 & a & b+c \\ 1 & b & c+a \\ 1 & c & a+b \end{matrix} \right|$$ without direct expansion.
Find the value of the determinant: $$\begin{vmatrix} \sqrt{2} & 2\sqrt{3}\\ 3\sqrt{2} & \sqrt{3}\end{vmatrix}$$.
$$\begin{vmatrix}1 & 2 & 3\\ 0 & 2 & 4\\ 0 & 0 & 5\end{vmatrix}$$.
If $$\vec { a } =\tilde { i } +\tilde { j } +\tilde { k } ,\vec { b } =\tilde { i } -\tilde { j } +\tilde { k } ,\vec { c } =\tilde { i } +2\tilde { j } -\tilde { k } $$, then the value of $$\left| \begin{matrix} \overrightarrow { a } .\overrightarrow { a } & \overrightarrow { a } .\overrightarrow { b } & \overrightarrow { a } .\overrightarrow { c } \\ \overrightarrow { b } .\overrightarrow { a } & \overrightarrow { b } .\overrightarrow { b } & \overrightarrow { b } .\overrightarrow { c } \\ \overrightarrow { c } .\overrightarrow { a } & \overrightarrow { c } .\overrightarrow { b } & \overrightarrow { c } .\overrightarrow { c } \end{matrix} \right| =$$
Prove that $$\left| \begin{matrix} a-b-c & 2a & 2a \\ 2b & b-c-a & 2b \\ 2c & 2c & c-a-b \end{matrix} \right| =(a+b+c)^3$$
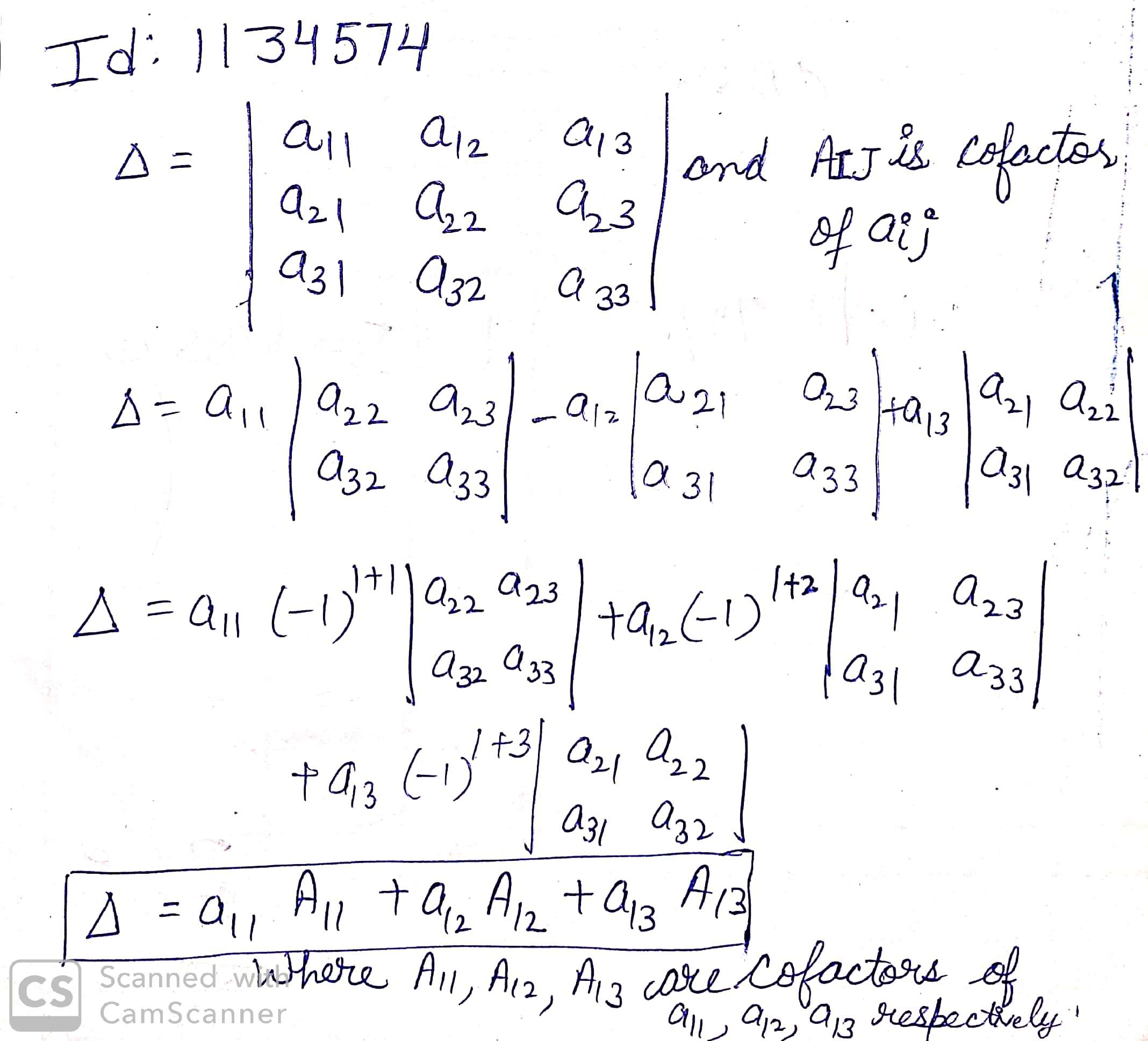
If $$\Delta=\left| \begin{matrix} { a }_{ 11 } & { a }_{ 12 } & { a }_{ 13 } \\ { a }_{ 21 } & { a }_{ 22 } & { a }_{ 23 } \\ { a }_{ 31 } & { a }_{ 32 } & { a }_{ 33 } \end{matrix} \right| $$ and $$A_{IJ}$$ is cofactors of $$a_{ij}$$ then the value of $$\Delta$$ is given by
$$\left| \begin{matrix} 1 & w & { w }^{ 2 } \\ w & { w }^{ 2 } & 1 \\ { w }^{ 2 } & w & 1 \end{matrix} \right| $$ Where w is a complex cube root of unity.
Find the value of $$k$$ if points $$\left (k,3\right),\left (6,-2\right)\ and \left (-3,4\right)$$ are collinear.
Find the value of $$\begin{vmatrix} 53 & 106 & 159 \\ 52 & 65 & 91 \\ 102 & 153 & 221 \end{vmatrix}$$
Solve $$ \left| \begin{matrix} x & -4 & -4 \\ 3 & 2 & 1 \\ -2 & 4 & 1 \end{matrix} \right|$$ =0
Find the value of K if the point A $$(2,3)$$ ,B$$ (4,K) $$and C$$( 6,-3)$$ are collinear?
Find the values of the following determinants
$$\begin{vmatrix} 1+3i & i-2 \\ { -i-2 } & 1-3{ i } \end{vmatrix}$$
where $$i=\sqrt{-1}$$.
If $$\left| \begin{matrix} a & b & a\alpha +b \\ b & c & b\alpha +c \\ a\alpha +b & b\alpha +c & 0 \end{matrix} \right| =0$$. Prove that $$a,b,c$$ are in G.P. or $$\alpha$$ is a root of $$ax^{2}+2bx+c=0$$
Without expanding , find the value of $$\begin{vmatrix} a+b & 2a+b & 3a+b \\ 2a+b & 3a+b & 4a+b \\ 4a+b & 5a+b & 6a+b \end{vmatrix}$$
Find the roots of equation $$\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}1 & 4 & {20}\\1 & { - 2} & 5\\1 & {2x} & {5{x^2}}\end{array}} \right| = 0$$.
Solve
$$\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}1&1&{ - 1}\\6&4&{ - 5}\\{ - 4}&{ - 2}&3\end{array}} \right|$$
Verify whether the points $$(1,5)$$,$$(2,3)$$,and$$(-2,-1)$$ are collinear or not.
Solve $$D = \left| \begin{array} { c c c } { 1 } & { - 2 } & { 1 } \\ { 2 } & { 1 } & { - 1 } \\ { 1 } & { 3 } & { 1 } \end{array} \right]$$
$$\left| \begin{matrix} 0 \\ -a \\ b \end{matrix}\begin{matrix} a \\ 0 \\ c \end{matrix}\begin{matrix} -b \\ -c \\ 0 \end{matrix} \right| =0$$
Prove that points $$(2,-2),(-3,8),(-1,4)$$ are collinear.
If the points $$A\ (x,2),B\ (-3,-4),C\ (7,-5)$$ are collinear, then find the value of $$x$$.
Evaluate :
$$\left| { \begin{array} { *{ 20 }{ c } }3 & { -1 } & { -2 } \\ 0 & 0 & { -1 } \\ 3 & { -5 } & 0 \end{array} } \right| $$
Find minor & cofactors of elements '6', '5', '0' & '4' of the determinant $$\begin{vmatrix} 2 & 1 & 3 \\ 6 & 5 & 7 \\ 3 & 0 & 4 \end{vmatrix}$$
Solve:$$\left| \begin{matrix} 1 & xy & xy(x+y) \\ 1 & yz & yz(y+z) \\ 1 & zx & zx(2+x) \end{matrix} \right| $$
$$\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}2&1&1\\1&{ - 2}&{ - 3}\\3&2&4\end{array}} \right| = ?$$
Find $$x$$ if:$$\left| \begin{matrix} 2 & 1 & x+1 \\ -1 & 3 & -4 \\ 0 & -5 & 3 \end{matrix} \right| $$ $$= 1$$
Show that:
$$\left| \begin{array} { c c c } { a ^ { 2 } } & { b ^ { 2 } } & { c ^ { 2 } } \\ { a } & { b } & { c } \\ { 1 } & { 1 } & { 1 } \end{array} \right| = - ( a - b ) ( b - c ) ( c - a )$$
If $$\Delta=\begin{vmatrix} 1 & \sin{\theta} & 1\\ -\sin{\theta} & 1 & \sin{\theta} \\ -1 & -\sin{\theta} & 1 \end{vmatrix}$$ then prove that $$2\le \Delta\le 4$$
Expand:$$\begin{vmatrix} 3 & 2 & 5\\ 9 & -1 & 4 \\ 2 & 3 & -5 \end{vmatrix}$$
Expand:$$\begin{vmatrix} 1 & 2 & 3\\ 4 & 6 & 2 \\ 5 & 9 & 4 \end{vmatrix}$$
Prove that
$$\begin{vmatrix} bc & a & { a }^{ 2 } \\ ca & b & { b }^{ 2 } \\ ab & c & { c }^{ 2 } \end{vmatrix}=\begin{vmatrix} 1 & { a }^{ 2 } & { a }^{ 3 } \\ 1 & { b }^{ 2 } & { b }^{ 3 } \\ 1 & { c }^{ 2 } & { c }^{ 3 } \end{vmatrix}$$
Find the value of k so that point colinear(7,-2)(5,1)(3,k).
Solve
$$\left| \begin{matrix} 4 \\ 3 \end{matrix}\begin{matrix} x+1 \\ x \end{matrix} \right| =5$$
If for any 2 x 2 square matrix A, A(adj A) = $$\left[ \begin{array}{l}8\,\,0\\0\,\,8\end{array} \right]$$,then write the value of $$\left| A \right|$$ .
Find the value of the determinant $$\begin{vmatrix} -1 & 2 & 1\\ 3+2\sqrt{2} & 2+2\sqrt{2} & 1 \\ 3-2\sqrt{2} & 2-2\sqrt{2} & 1 \end{vmatrix}$$
Show that $$\begin{vmatrix} a & \quad a+b & \quad a+b+c\quad \\ 2a & 3a+2b & 4a+3b+2c \\ 3a\quad & 6a+3b & 10a+6b+3c \end{vmatrix}={ a }^{ 3 }$$
Prove that $$\begin{vmatrix} {a}^{2}+1 & ab & ac\\ ab & {b}^{2}+1 & bc \\ ac & bc & {c}^{2}+1 \end{vmatrix}=1+{a}^{2}+{b}^{2}+{c}^{2}$$
Solve for $$x$$$$\begin{vmatrix} 4x & 6x+2 & 8x+1\\ 6x+2 & 9x+3 & 12x \\ 8x+1 & 12x & 16x+2 \end{vmatrix}=0$$
Given that matrix $$A=\left[ \begin{matrix} x & 3 & 2 \\ 1 & y & 4 \\ 2 & 2 & z \end{matrix} \right]$$. If $$xyz=2013$$ and $$8x+4y+3z=2012$$ then A(adj A) is equal to
If $$f(x)=\left| \begin{matrix} 2x & { x }^{ 2 } & { x }^{ 3 } \\ { x }^{ 2 }+2x & 1 & 3x+1 \\ 2x & 1-3{ x }^{ 2 } & 5x \end{matrix} \right| $$, then find $$f'(1)$$
Show that the points $$A(1,2,7),\ B(2,6,3)$$ and $$C(3,10,-1)$$ are collinear.
$$(k,k ), (2,3)$$ and $$(4,-1)$$ are collimear. So find the value of $$k$$.
Solve the matrix
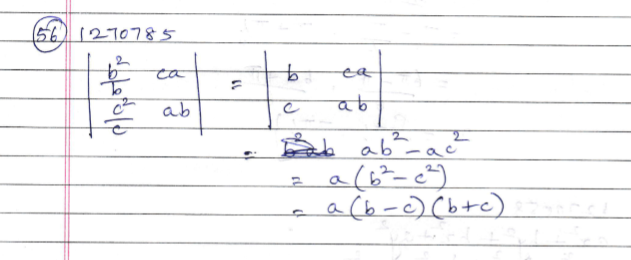
$$\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{\frac{1}{b}{b^2}} & {ca}\\{\frac{1}{c}{c^2}} & {ab}\end{array}} \right|$$
Prove that point $$(1,1),(-2,7)$$ and $$(3,-3)$$ are collinear.
If the points ( a,0),(0,b)and (3,2) are col linear, prove that $$\dfrac { 2 }{ b } +\dfrac { 3 }{ a } =1$$
Evaluate $$\left| \begin{matrix} x & x^{ 2 } & x^{ 2 } \\ y & y^{ 2 } & y^{ 2 } \\ z & z^{ 2 } & z^{ 3 } \end{matrix} \right| $$
Prove that.$$\left| \begin{matrix} 1 & a & a^{2} \\ 1 & b & b^{2} \\ 1 & c & c^{2} \end{matrix} \right| (a-b)(b-c)(c-a)$$
Prove that :
$$\begin{vmatrix} 0 & a & -b \\ -a & 0 & -c \\ b & c & 0 \end{vmatrix}=0$$.
Find the value of the following determinants.
$$\begin{vmatrix} \dfrac { 7 }{ 3 } & \dfrac { 5 }{ 3 } \\ \dfrac { 3 }{ 2 } & \dfrac { 1 }{ 2 } \end{vmatrix}$$
Given $$\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 1 \\ -3 & 4 \end{bmatrix} X=\begin{bmatrix} 7 \\ 6 \end{bmatrix}$$. Write :
the order of the matrix $$X$$
the matrix $$X$$.
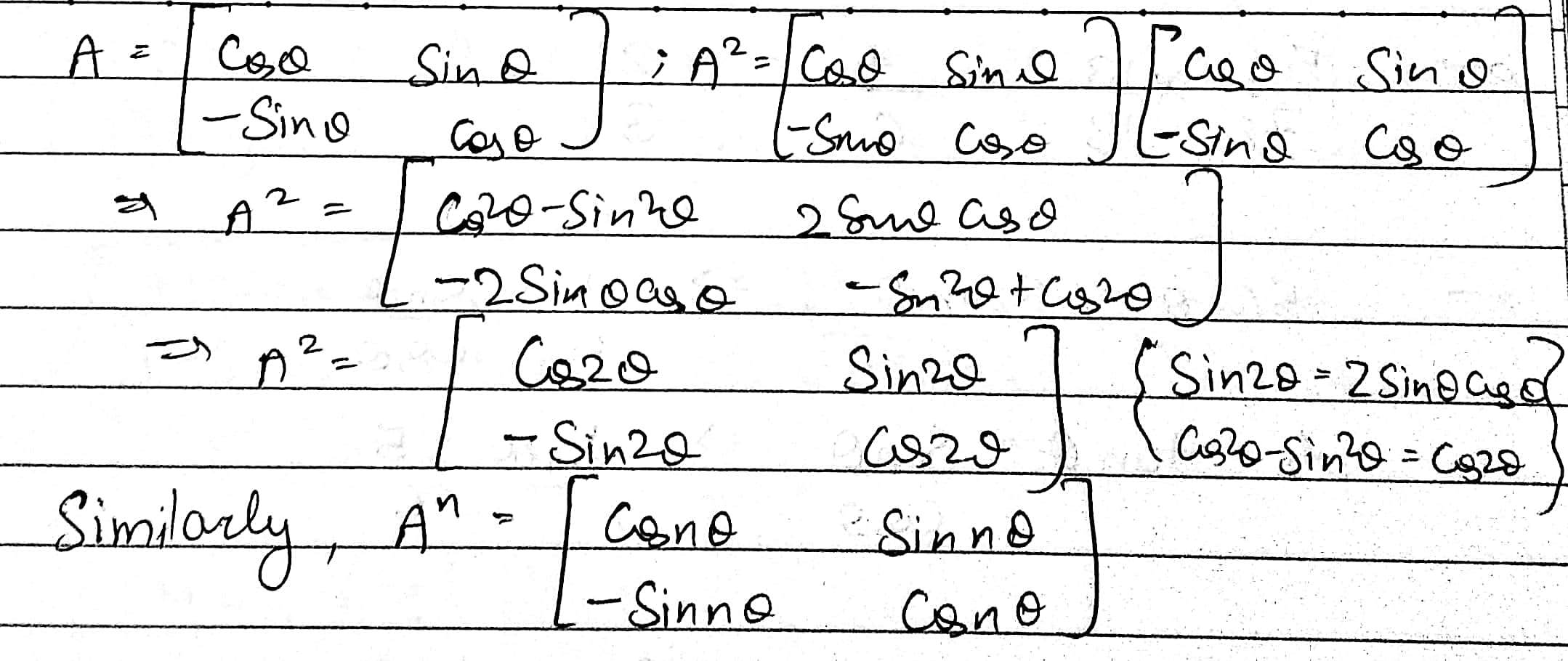
If $$A=\begin{bmatrix} \cos { \theta } & \sin { \theta } \\ -\sin { \theta } & \cos { \theta } \end{bmatrix}$$ the $$A^{n}=$$
Find the value of $$\lambda$$ for which the points $$(6,-1,2),(8,-7,\lambda)$$ and $$(5,2,4)$$ are collinear.
Find the value of the following determinants.
$$\begin{vmatrix} -1 & 7 \\ 2 & 4 \end{vmatrix}$$
Find the value of the following determinants.
$$\begin{vmatrix} 5 & 3 \\ -7 & 0 \end{vmatrix}$$
If $$A=[aij]$$ is a matrix of order 2x2 such that $$|A|=15$$ and cij represents the co factor of aij then find $${ a }_{ 21 }{ c }_{ 21 }+{ a }_{ 22 }{ c }_{ 22 }$$.
A square matrix $$\mathrm { B }$$ of order $$3 ,$$ has $$| B | = 7 ,$$ find $$| B$$ adjB $$|$$
A. square matrix $$A$$ of order $$3 ,$$ has $$| A | = 5 ,$$ find $$| A$$ adja|
Find equation of line joining (1,2) and (3,6) using determinants.
Prove that $$\begin {vmatrix} a^2 & bc & ac + c^2 \\ a^2 + ab & b^2 & ac \\ ab & b^2 + bc & c^2 \end {vmatrix}$$ = 4$$a^2b^2c^2$$
Prove that $$\begin{vmatrix} a & a & a \\ a & b & b \\ a & b & c \end{vmatrix}=a(b-c)(a-b)$$, Hence find the value of $$\begin{vmatrix} 3 & 3 & 3 \\ 3 & 5 & 5 \\ 3 & 5 & 7 \end{vmatrix}.$$
A point $$P\left(2,-1\right)$$ is equidistant from points $$\left(a,7\right)$$ and $$\left(-3,a\right)$$. Find $$a$$.
Prove that : $$\begin {vmatrix} a & c & a + c \\ a + b & b & a \\ b & b + c & c \end {vmatrix}$$ = $$4abc$$
Prove that:
$$\begin{vmatrix} a+b+2c & a & b \\ c & b+c+2a & b \\ c & a & c+a+2b \end{vmatrix}=2{ \left( a+b+c \right) }^{ 3 }$$
Fill in the blanks with correct number
$$\left| \begin{matrix} 3 \\ 4 \end{matrix}\begin{matrix} 2 \\ 5 \end{matrix} \right| =3\times \Box -\Box \times 4=\Box -8=\Box $$
Using properties of determinant solve :-
$$\left| \begin{matrix} 1 & a & { a }^{ 2 }-bc \\ 1 & b & { b }^{ 2 }-ac \\ 1 & c & { c }^{ 2 }-ab \end{matrix} \right| =$$
Find the values of x, if
$$\begin{vmatrix} 2x & 5 \\ 8 & x \end{vmatrix}=\begin{vmatrix} 6 & 5 \\ 8 & 3 \end{vmatrix}$$
Prove that $$\left| \begin{matrix} cos\theta & cos\phi \\ sin\theta & sin\phi \end{matrix} \right| =-sin\left( \theta -\phi \right) $$
Find the cofactors of the elements of the following matrices :
(i) $$\begin{bmatrix} -1 & 2 \\ -3 & 4 \end{bmatrix}$$
(ii) $$\left[ \begin{matrix} 1 & -1 & 2 \\ -2 & 3 & 5 \\ -2 & 0 & -1 \end{matrix} \right] $$
Find the minor of $$\begin{bmatrix} 2 & 7 & 3 \\ -4 & 3 & -1 \\ 0 & -3 & 7 \end{bmatrix}$$.
Prove that $$\left| \begin{matrix} \sin\alpha & \cos\alpha & \cos(a+\delta ) \\ \sin\beta & \cos\beta & cos(\beta +\delta ) \\ \sin\gamma & \cos\gamma & \cos(\gamma +\delta ) \end{matrix} \right| =0.$$
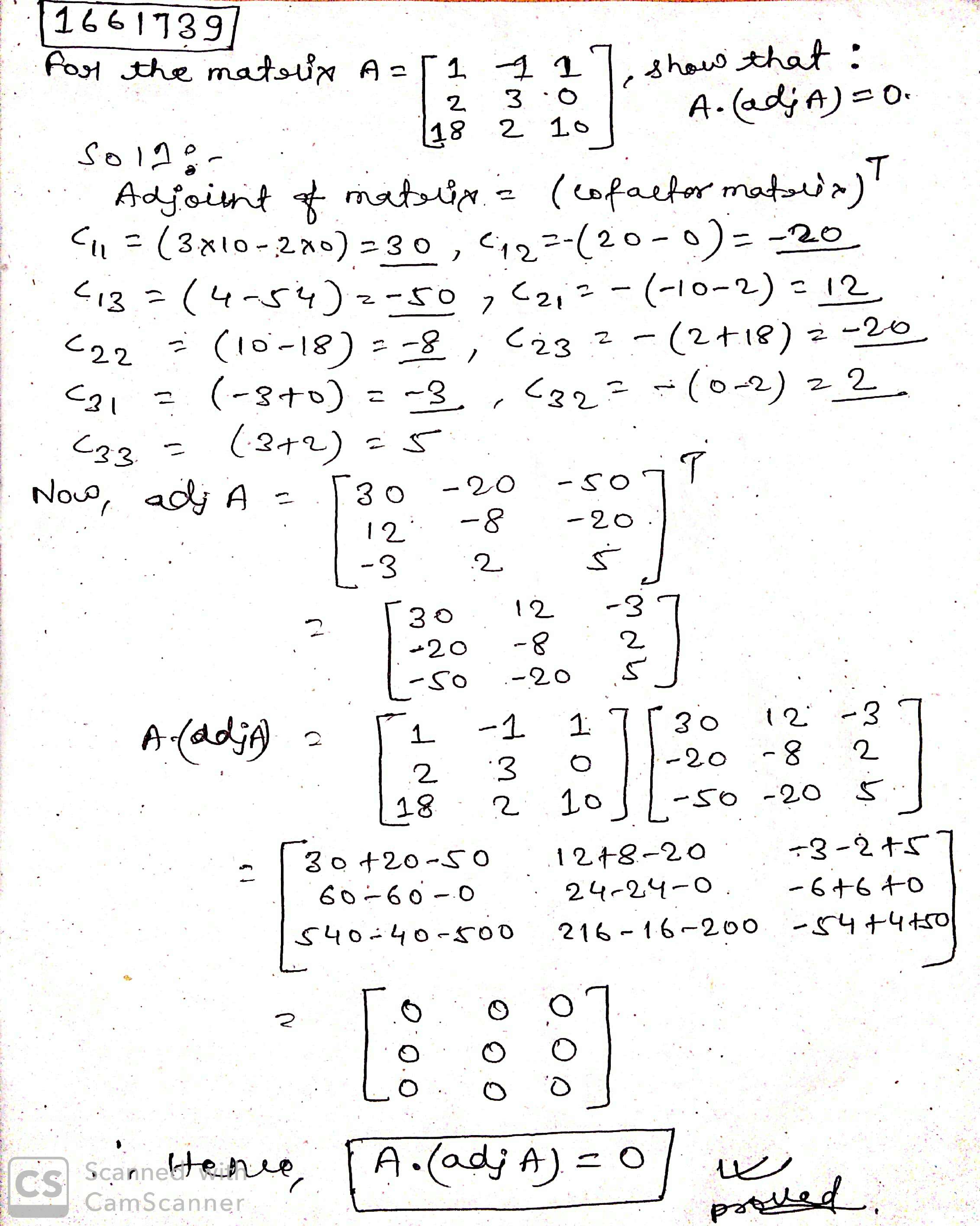
For the matrix $$ A = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & -1 & 1 \\ 2 & 3 & 0 \\ 18 & 2 & 10 \end{bmatrix}$$, show that $$A (adj A) = 0 $$.
Find the values of x, if $$\begin{vmatrix} 3 & x \\ x & 1 \end{vmatrix}$$= $$\begin{vmatrix} 3 & 2 \\ 4 & 1 \end{vmatrix}$$
Solve:$$ \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 5 & -2 \\ 3x & 2 & 4 \\ 5 & -1 & 0 \end{bmatrix}=0$$
Solve:
$$ \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 5 & -2 \\ 3x & 2 & 4 \\ 5 & -1 & 0 \end{bmatrix}=0$$
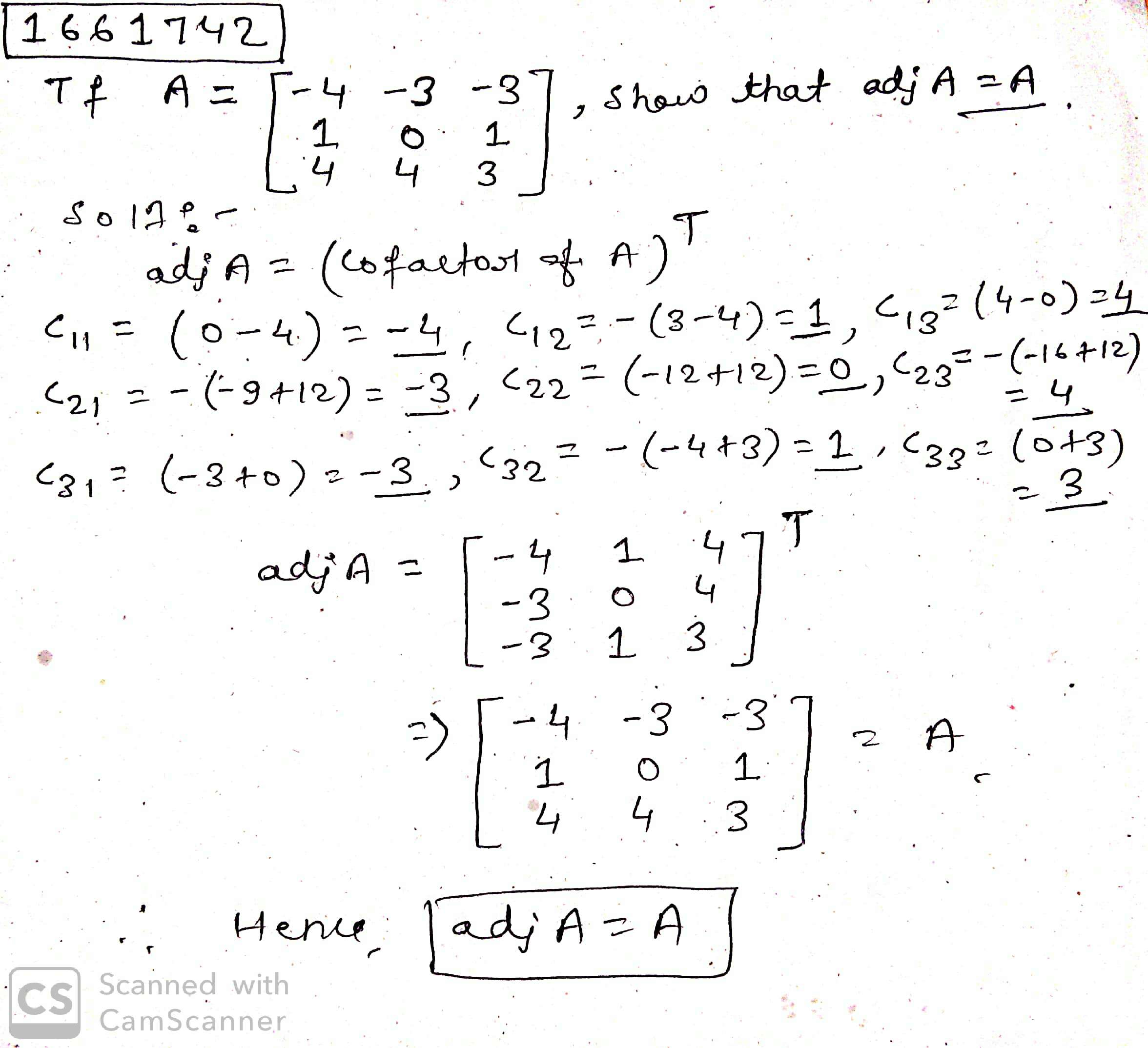
If $$ A = \begin{bmatrix} -4 & -3 & -3 \\ 1 & 0 & 1 \\ 4 & 4 & 3 \end{bmatrix}$$, show that adj $$ A = A $$.
Find the values of x, if
$$\begin{vmatrix} 4 & x+1 \\ x+2 & 2 \end{vmatrix}$$= $$\begin{vmatrix} 4 & 4 \\ 5 & 2 \end{vmatrix}$$
Find the adjoint of the following matrice:
$$ \begin{bmatrix} \cos\,\alpha & \sin\,\alpha \\ \sin\,\alpha & \cos\,\alpha \end{bmatrix} $$
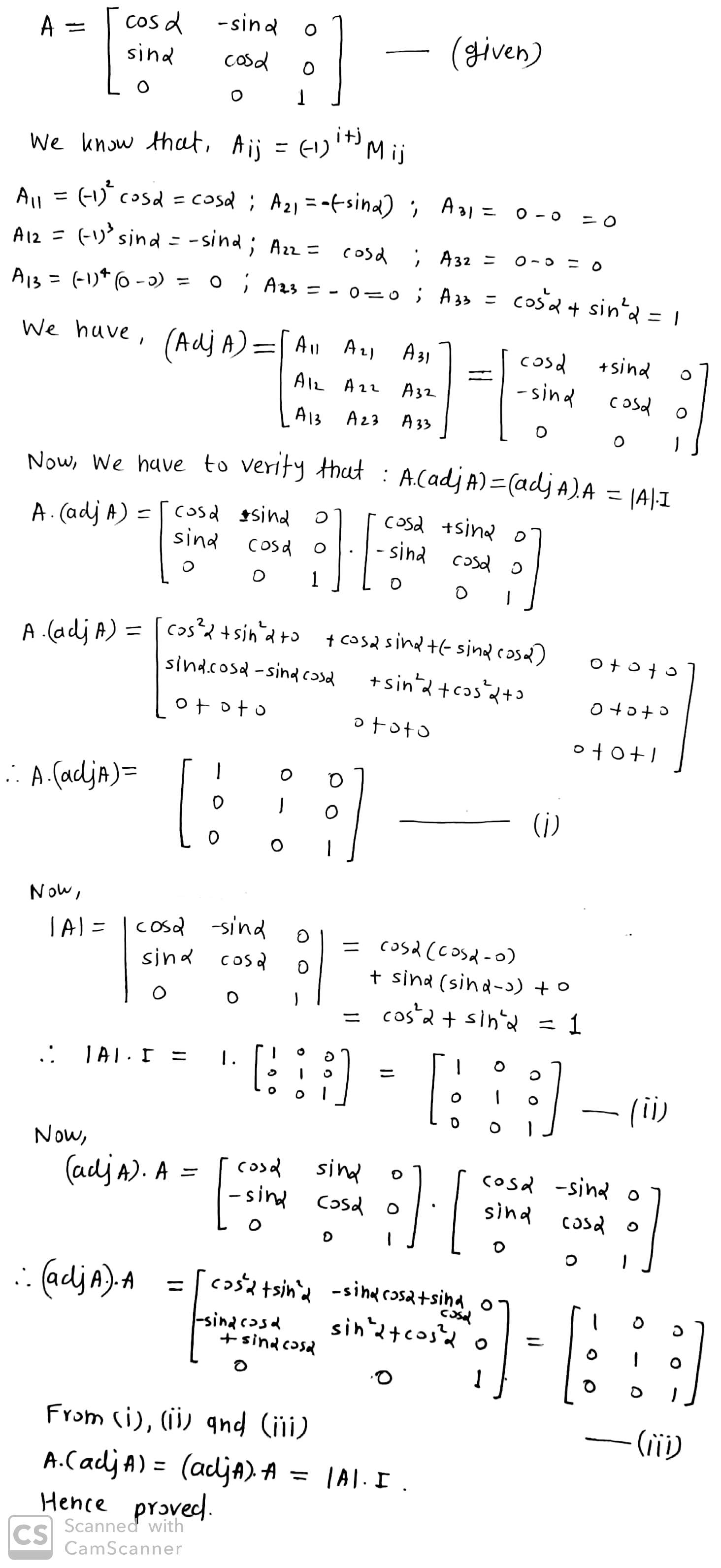
Verify that $$ (adj A ) A = |A| I = A (adj A) $$ for the above matrice.
If $$ A = \begin{bmatrix} -1 & -2 & -2 \\ 2 & 1 & -2 \\ 2 & -2 & 1 \end{bmatrix}$$,show that adj $$ A = 3A^{T}. $$
Solve:$$ \begin{vmatrix} x+2 & 1 \\ -1 & x\end{vmatrix}=0$$
If $$A$$ is a square matrix of order $$n$$, prove that $$\left | A\: adj \: A \right |= \left | A \right |^{n}$$.
Find the values of x, if
$$\begin{vmatrix} 2x & 5 \\ 8 & x \end{vmatrix}=\begin{vmatrix} 6 & 5 \\ 8 & 3 \end{vmatrix}$$
Evaluate the following determinant :
$$ \begin{vmatrix} 1 & -3 & 2 \\ 4 & -1 & 2 \\ 3 & 5 & 2 \end{vmatrix}$$
Evaluate the following determinant : $$ =\begin{vmatrix} 67 & 19 & 21 \\ 39 & 13 & 14 \\ 81 & 24 & 26 \end{vmatrix}$$
Find the integral value of x, if $$\begin{vmatrix} x^{2} & x & 1\\ 0 & 2 & 1 \\ 3 & 1 & 4 \end{vmatrix}= 28$$
Evaluate the following determinant :
$$ \begin{vmatrix} 1 & 3 & 5 \\ 2 & 6 & 10 \\ 31 & 11 & 38 \end{vmatrix}$$
Evaluate the following :
$$ \begin{vmatrix} x+\lambda & x & x \\ x & x+\lambda & x \\ x & x & x+\lambda \end{vmatrix}$$
Evaluate the following :$$ \begin{vmatrix} x+\lambda & x & x \\ x & x+\lambda & x \\ x & x & x+\lambda \end{vmatrix}$$
Evaluate the following determinant :
$$ \begin{vmatrix} a & h & g \\ h & b & f \\ g & f & c \end{vmatrix}$$
If a,b,c are real numbers such that $$\begin{vmatrix} b+c & c+a & a+b \\ c+a & a+b & b+c \\ a+b & b+c & c+a \end{vmatrix}= 0$$, then show that either $$a+b+c=0$$ or, $$a=b=c$$.
Evaluate the following :
$$ \begin{vmatrix} 1 & a & bc \\ 1 & b & ca \\ 1 & c & ab \end{vmatrix}$$
Evaluate the following determinant :
$$\begin{vmatrix} 15 & 11 & 7 \\ 11 & 17 & 14 \\ 10 & 16 & 13 \end{vmatrix}$$
Evaluate the following determinant :
Find the adjoint of the given matrix and verify in each case that $$A \cdot (adj A) = (adj A)\cdot A = |A| \cdot I$$.
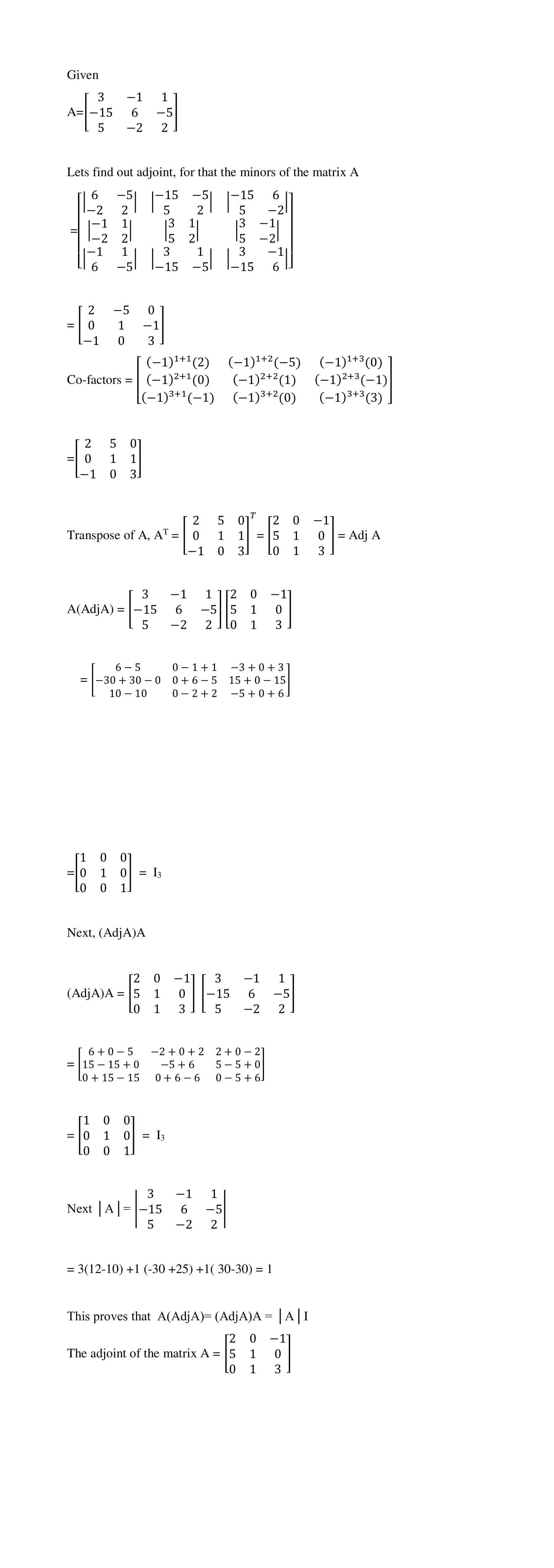
$$\begin{bmatrix} 3& -1 & 1\\ -15 & 6 & -5 \\ 5 & -2 & 2\end{bmatrix}$$
If $$a, b, c$$ are $$p^{th}, q^{th}$$ and $$r^{th}$$ terms respectively of a G.P, then prove that
$$\begin{vmatrix}\log a& p & 1 \\ \log b& q & 1\\ \log c &r & 1 \end{vmatrix} =0$$
Find the cofactors of all the elements of $$\begin{bmatrix}1&-2 \\ 4 & 3 \end{bmatrix}$$
Find the adjoint of the given matrix and verify in each case that $$A \cdot (adj A) = (adj A)\cdot A = |A| \cdot I$$.
$$\begin{bmatrix} 0& 1 & 2\\ 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 3 & 1 & 1\end{bmatrix}$$
Find the adjoint of the given matrix and verify in each case that $$A \cdot (adj A) = (adj A)\cdot A = |A| \cdot I$$.
$$\begin{bmatrix} 2& 3\\ 5 & 9\end{bmatrix}$$
Find the adjoint of the given matrix and verify in each case that $$A \cdot (adj A) = (adj A)\cdot A = |A| \cdot I$$.
$$\begin{bmatrix} \cos \alpha& \sin \alpha\\ \sin \alpha & \cos \alpha\end{bmatrix}$$
Find the adjoint of the given matrix and verify in each case that $$A \cdot (adj A) = (adj A)\cdot A = |A| \cdot I$$.
$$\begin{bmatrix} 9& 7 & 3\\ 5 & -1 & 4 \\ 6 & 8 & 2\end{bmatrix}$$
If $$A$$ and $$B$$ are square matrices each of order $$3$$ and $$|A|= 5, \, |B| = 3$$, then the value of $$|3AB|$$ is ______
Find the adjoint of the given matrix and verify in each case that $$A \cdot (adj A) = (adj A)\cdot A = |A| \cdot I$$.
$$\begin{bmatrix} 1& -1 & 2\\ 3 & 1 & -2 \\ 1 & 0 & 3\end{bmatrix}$$
Find the adjoint of the given matrix and verify in each case that $$A \cdot (adj A) = (adj A)\cdot A = |A| \cdot I$$.
$$\begin{bmatrix} 3& -5\\ -1 & 2\end{bmatrix}$$
Let $$A$$ be a square matrix of order $$3$$, write the value of $$|2A|$$, where $$|A|=4$$.
Evaluate $$\begin{vmatrix} \sqrt { 6 } & \sqrt { 5 } \\ \sqrt { 20 } & \sqrt { 24 } \end{vmatrix}$$.
If $$A=\begin{vmatrix} 3 & 4 \\ 1 & 2 \end{vmatrix}$$, find the value of $$3|A|$$.
Find the adjoint of the given matrix and verify in each case that $$A \cdot (adj A) = (adj A)\cdot A = |A| \cdot I$$.
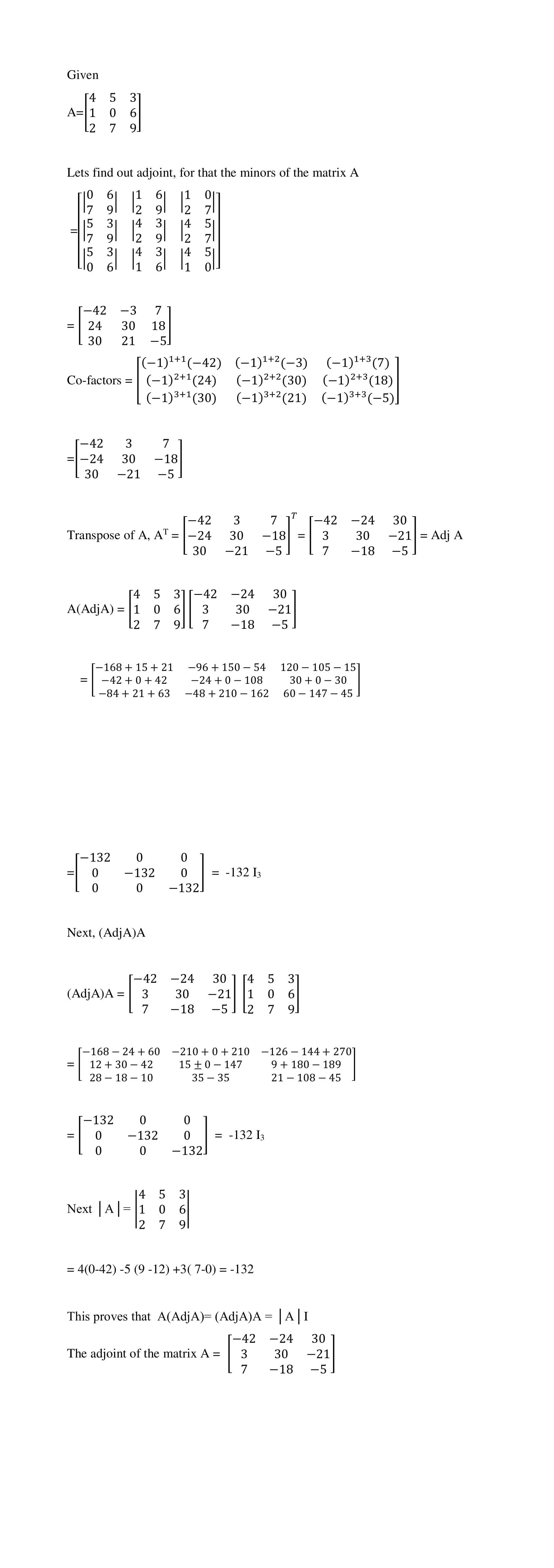
$$\begin{bmatrix} 4& 5 & 3\\ 1 & 0 & 6 \\ 2 & 7 & 9\end{bmatrix}$$
If $$A$$ is a $$2\times 2$$ matrix such that $$|A|\neq 0$$ and $$|A|=5$$, write the value of $$|4A|$$.
If $$A$$ is a $$3\times 3$$ matrix such that $$|A|\neq 0$$ and $$|3A|=k|A|$$, then write the value of $$k$$.
Evaluate $$\begin{vmatrix} \sin { { 60 }^{ o } } & \cos { { 60 }^{ o } } \\ -\sin { { 30 }^{ o } } & \cos { { 30 }^{ o } } \end{vmatrix}$$.
Find the adjoint of the given matrix and verify in each case that $$A \cdot (adj A) = (adj A)\cdot A = |A| \cdot I$$.
$$\begin{bmatrix} \cos \alpha& -\sin \alpha & 0\\ \sin \alpha & \cos \alpha & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1\end{bmatrix}$$
Evaluate $$\begin{vmatrix} 2\cos { \theta } & -2\sin { \theta } \\ \sin { \theta } & \cos { \theta } \end{vmatrix}$$.
Evaluate $$\begin{vmatrix} \cos { \alpha } & -\sin { \alpha } \\ \sin { \alpha } & \cos { \alpha } \end{vmatrix}$$.
Evaluate $$\begin{vmatrix} \cos { { 65 }^{ o } } & \sin { { 65 }^{ o } } \\ \sin { 25^{ o } } & \cos { 25^{ o } } \end{vmatrix}$$.
Evaluate $$\begin{vmatrix} \cos { { 15 }^{ o } } & \sin { { 15 }^{ o } } \\ \sin { 75^{ o } } & \cos { 75^{ o } } \end{vmatrix}$$.
Evaluate $$\begin{bmatrix} \sqrt { 3 } & \sqrt { 5 } \\ -\sqrt { 5 } & 3\sqrt { 3 } \end{bmatrix}$$.
Prove that the three straight lines whose equations are
$$15x - 18y + 1 = 0, 12x + 10y -3 = 0$$, and $$6x + 66y - 11 = 0$$
all meet in a point.
Show also that the third line bisects the angle between the other two.
Prove that the following sets of three lines meet in a point.
$$2x - 3y = 7, 3x - 4y = 13$$, and $$8x - 11y = 33$$.
If $$\begin{vmatrix} { \left( \beta +\gamma -\alpha -\delta \right) }^{ 4 } & { \left( \beta +\gamma -\alpha -\delta \right) }^{ 2 } & 1 \\ { \left( \gamma +\alpha -\beta -\delta \right) }^{ 4 } & { \left( \gamma +\alpha -\beta -\delta \right) }^{ 2 } & 1 \\ { \left( \alpha +\beta -\gamma -\delta \right) }^{ 4 } & { \left( \alpha +\beta -\gamma -\delta \right) }^{ 2 } & 1 \end{vmatrix}=k\left( \alpha -\beta \right) \left( \alpha -\gamma \right) \left( \alpha -\delta \right) \left( \beta -\gamma \right) \left( \beta -\delta \right) \left( \gamma -\delta \right) \quad $$then the value of $${(k)}^{1/2}$$ is
Given $$A=\begin{vmatrix} a & b & 2c \\ d & e & 2f \\ l & m & 2n \end{vmatrix};B=\begin{vmatrix} f & 2d & e \\ 2n & 4l & 2m \\ c & 2a & b \end{vmatrix}$$, then the value of $$\dfrac{B}{A}$$ is ________.
Find the minor of the element of second row and third column ( $$a 23$$ ) in the following determinant:
$$\left|\begin{array}{ccc}2 & -3 & 5 \\ 6 & 0 & 4 \\ 1 & 5 & -7\end{array}\right|$$
If $$A$$ is an invertible metrix of order $$3$$ and $$|A| = 5$$, then find $$|adj \ A|$$.
If $$\Delta=\left|\begin{array}{lll}5 & 3 & 8 \\2 & 0 & 1 \\1 & 2 & 3\end{array}\right| \text { , then write the minor of the element } a_{23}$$
What positive value of $$x$$ makes the following pair of determinants equal?
$$\left|\begin{array}{cc}2 x & 3 \\ 5 & x\end{array}\right|,\left|\begin{array}{cc}16 & 3 \\ 5 & 2\end{array}\right|$$
Find the cofactor of $$a_{12}$$ in the following:
$$\left|\begin{array}{ccc}1 & -3 & 5 \\ 6 & 0 & 4 \\ 1 & 5 & -7\end{array}\right|$$
$$\begin{aligned}& \\&\text { Evaluate: }\left|\begin{array}{ll}\cos 15^{\circ} & \sin 15^{\circ} \\\sin 75^{\circ} & \cos 75^{\circ}\end{array}\right|\end{aligned}$$
If $$A$$ is idempotent matrix satisfying $$ ( I - 0.4 A)^{-1} = I - \alpha A $$ where $$I$$ is the unit matrix of the same order as that of $$A$$ then find the value of $$ | 9 \alpha | $$.
Find the equation of line joining (1,2) and (3,6) using determinants.
Find the value of $$\left|\begin{array}{cccc}\sin A & -\sin B \\\cos A & \cos B\end{array}\right|$$ $$\text { where } A=53^{\circ}, B=37^{\circ}$$
If $$A = \begin{bmatrix}
\alpha & 0 & 0 \\
0 & \alpha & 0 \\
0 & 0 & \alpha
\end{bmatrix}$$, find the value of $$|adj \ A|$$.
If $$ \Delta= \left| \begin{matrix} 0 & b-a & c-a \\ a-b & 0 & c-b \\ a-c & b-c & 0 \end{matrix} \right| $$ then show that $$ \Delta $$ is equal to zero.
Write the adjoint of the following matrix:
$$\Big[\begin{matrix}
2 & -1 \\
4 & 3
\end{matrix}\Big]$$
If $$\left|\begin{array}{ll}x & x \\1 & x\end{array}\right|=\left|\begin{array}{ll}3 & 4 \\1 & 2\end{array}\right|$$ , then write the positive value of $$x$$
Find the equation of the line joining $$A(1,3)$$ and $$B(0,0)$$ using determinants and find $$k$$ if $$D(k, 0)$$ is a point such that the area of $$\Delta A B D$$ is 3 sq units.
The determinant $$ \Delta = \left| \begin{matrix} \sqrt {23} + \sqrt {3} & \sqrt {5} & \sqrt {5} \\ \sqrt {15} + \sqrt {46} & 5 & \sqrt {10} \\ 3 +\sqrt {115} & \sqrt {15} & 5 \end{matrix} \right| $$ is equal to ...............
Show that if the determinant $$ \Delta = \left| \begin{matrix} 3 & -2 & sin\quad 3\quad \theta \\ -7 & 8& cos \quad 2 \theta \\ -11 & 14 & 2 \end{matrix} \right| = 0 $$ then $$ Sin \theta = 0 $$ or $$ \frac {1}{2} $$
Write the value of $$\left|\begin{array}{cc}\sin 20^{\circ} & -\cos 20^{\circ} \\ \sin 70^{\circ} & \cos 70^{\circ}\end{array}\right|$$
Evaluate :
$$ \left| \begin{matrix} y+z & z & y \\ z & z+x & x \\ y & x & x+y \end{matrix} \right| =\quad 4xyz $$
If $$ A$$ is a matrix or order $$ 3 \times 3 $$ then number of minors in determinant of $$ A $$ are__________
Fill in the blank.If $$ A $$ is matrix of order $$ 3 \times 3 $$ then $$ |3A| $$ is equal to_________
If $$ x+y+z = 0 $$ prove that $$ \left| \begin{matrix} xa & yb & zc \\ yc & za & xb \\ zb & xc & ya \end{matrix} \right| \quad =\quad xyz\quad \left| \begin{matrix} a & b & c \\ c & a & b \\ b & c & a \end{matrix} \right| $$
Evaluate :
$$ \left| \begin{matrix} 3x & -x+y & -x+z \\ x-y & 3y & z-y \\ x-z & y-z & 3z \end{matrix} \right| $$
If $$ A +B +C = 0 $$ then prove that $$ \left| \begin{matrix} 1 & cos\quad C & cos\quad B \\ cos\quad C & 1 & cos\quad A \\ cos\quad B\quad & cos\quad A\quad & 1 \end{matrix} \right| =0 $$
If $$ Cos 2 \theta = 0$$ then $$ \left| \begin{matrix} 0 & cos \theta &sin \theta \\ cos \theta & sin \theta & 0 \\ sin \theta & 0 & cos \theta \end{matrix} \right|^2 = $$_________
If $$ a+ b +c \neq 0 $$ and $$ \left| \begin{matrix} a & b & c \\ b & c & a \\ c & a & b \end{matrix} \right| = 0 $$ then prove that $$ a = b = c $$.
Find the value of the following determinant
$$\begin{vmatrix} 5 & {-2}\\{-3} & 1\end{vmatrix}$$.
Find the value of the following determinant
$$\begin{vmatrix} 3 & {-1}\\{1} & 4 \end{vmatrix}$$.
Find the adjoint of the matrix $$A = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2\\ 3 & -5\end{bmatrix}$$ and verify the result $$A(adj \,A) = (adj \,A) = A |A| \cdot I$$.
Find the adjoint of the following matrix.
$$ \begin{bmatrix} 1& -1 & 2 \\ -2 & 3 & 5 \\ -2 & 0 & -1 \end{bmatrix} $$
The sum if the products of element of any row with the co-factors of corresponding elements is equal to __________
Find the adjoint of the following matrix.
$$ \begin{bmatrix} 2 & -3 \\ 3 & 5 \end{bmatrix} $$
Evaluate the determinations:
$$\begin{vmatrix} \cos { \theta } & -\sin { \theta } \\ \sin { \theta } & \cos { \theta } \end{vmatrix}$$
If $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 & -2 \\ 2 & 1 & -3 \\ 5 & 4 & -9 \end{bmatrix}$$ find $$\left| A \right| $$
Find the values of determinant.
$$\begin{vmatrix} -1&7 \\ 2&4 \end{vmatrix} $$
Evaluate the determinations:
$$\begin{vmatrix} 2 & 4 \\ -5 & -1 \end{vmatrix}$$
If $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 \\ 4 & 2 \end{bmatrix}$$, then show that $$\left| 2A \right| =4\left| A \right| $$
Find the values of following determinant.
$$\begin{vmatrix} 5&3 \\ -7&0 \end{vmatrix} $$
Evaluate the determinations:
$$\begin{vmatrix} { x }^{ 2 }-x+1 & x-1 \\ x+1 & x+1 \end{vmatrix}$$
there are n points in a plane of which m points are collinear. how many triangles will be formed by joining three points?
If matrix $$A=\begin{bmatrix} 1 & -1 & 2 \\ 3 & 0 & -2 \\ 1 & 0 & 3 \end{bmatrix}$$ then find $$adj.A$$ also prove that $$A(adj A)= |A| I_3= (adj A)A$$
Find the minors of elements of second row of determinant $$\begin{vmatrix} 2 & 3 & 4\\ 3 & 6 & 5\\ 1 & 8 & 9 \end{vmatrix}$$.
If $$A$$ be a square matrix of order $$3\times 3$$ then find $$\left| kA \right| $$
$$\left| KA \right| ={ k }^{ n }\left| A \right| $$ when $$n$$ is the order
For which value of k, det $$\begin{vmatrix} k & 2\\
4 & -3 \end{vmatrix}$$ will be zero?
Evaluate
$$\begin{vmatrix} \sin { 30 } & \cos { 30 } \\ -\sin { 60 } & \cos { 60 } \end{vmatrix}$$
Find adjoint of matrix :
$$\begin{vmatrix} 1 & -1 & 2 \\ 2 & 3 & 5 \\ -2 & 0 & 1 \end{vmatrix}$$
$$A = \begin{bmatrix}1 & \tan x\\ -\tan x & 1\end{bmatrix}$$ and $$f(x)$$ is defined as $$f(x) = det. (A^T A^{-1})$$ then find the value of $$\underset{\text{n times}}{\underbrace{f(f(f(f.......f(x))))}}$$ is $$(n \geq 2)$$.
If A is a square matrix of order 3, then find $$|(A - A^T)^{2011}|$$.
Match the statements in Column I with statements in column II
Prove that $$\begin{vmatrix}
bc & bc'+b'c & b'c'\\
ca & ca'+c'a & c'a'\\
ab & ab'+a'b & a'b'
\end{vmatrix}=(ab'-a'b)(bc-b'c)(ca'-c'a)$$
Let
$$\Delta _{1}=\begin{vmatrix}
1 & \cos \alpha & \cos \beta \\
\cos \alpha & 1 & \cos \gamma \\
\cos \beta & \cos \gamma & 1
\end{vmatrix}$$
and $$\Delta _{2}=\begin{vmatrix}
0 & \cos \alpha & \cos \beta \\
\cos \alpha & 0 & \cos \gamma \\
\cos \beta & \cos \gamma & 0
\end{vmatrix}$$ .
If $$\Delta _{1}=\Delta _{2}$$, find $$\sin ^{2}\alpha +\sin ^{2}\beta +\sin ^{2}\gamma $$
$$\Delta _{1}=\begin{vmatrix}
1 & \cos \alpha & \cos \beta \\
\cos \alpha & 1 & \cos \gamma \\
\cos \beta & \cos \gamma & 1
\end{vmatrix}$$
and $$\Delta _{2}=\begin{vmatrix}
0 & \cos \alpha & \cos \beta \\
\cos \alpha & 0 & \cos \gamma \\
\cos \beta & \cos \gamma & 0
\end{vmatrix}$$ .
If $$\Delta _{1}=\Delta _{2}$$, find $$\sin ^{2}\alpha +\sin ^{2}\beta +\sin ^{2}\gamma $$
Prove that $$\begin{vmatrix}
bc-a^2 & ca-b^2 & ab-c^2\\
-bc+ca+ab & bc-ca+ab & bc+ca-ab\\
(a+b)(a+c) & (b+c)(b+a) & (c+a)(c+b)
\end{vmatrix}=3.(b-c)(c-a)(a-b)(a+b+c)(ab+bc+ca)$$
bc-a^2 & ca-b^2 & ab-c^2\\
-bc+ca+ab & bc-ca+ab & bc+ca-ab\\
(a+b)(a+c) & (b+c)(b+a) & (c+a)(c+b)
\end{vmatrix}=3.(b-c)(c-a)(a-b)(a+b+c)(ab+bc+ca)$$
If $$ax_1^2+by_1^2+cz_1^2=ax_2^2+by_2^2+cz_2^2=ax_3^2+by_3^2+cz_3^2=d$$ and $$ax_2x_3+by_2y_3+cz_2z_3=ax_3x_1+by_3y_1+cz_3z_1=ax_1x_2+by_1y_2+cz_1z_2=f$$, then prove that $$\begin{vmatrix}
x_1 & y_1 & z_1\\
x_2 & y_2 & z_2\\
x_3 & y_3 & z_3
\end{vmatrix}=(d-f)\left [\frac {d+2f}{abc}\right ]^{1/2}(a, b, c\neq 0)$$
Are the three points $$A(2,3),B(5,6)$$ and $$C(0,2)$$ collinear?
Find the maximum value of $$\begin{vmatrix} 1& 1 & 1\\ 1 & 1 +\sin \theta & 1\\ 1 & 1 & 1 + \cos \theta\end{vmatrix}$$
If $$a^2+b^2+c^2=1$$ then is the value of the determinant $$\begin{vmatrix}
a^2+(b^2+c^2)cos\theta & ba(1-cos\theta) & ca(1-cos\theta)\\
ab(1-cos\theta) & b^2(c^2+a^2)cos\theta & cb(1-cos\theta)\\ ac(1-cos\theta)
& bc(1-cos\theta) & c^2+(a^2+b^2)cos\theta
\end{vmatrix}$$ independent of a,b,c?
If yes enter 1 else enter 0.
A line of slope 2 passes through the point A(1,3).
a) Check whether B(3,7) is a point on this line.
b) Write down the equation of this line.
c) Find the coordinates of a point C on the line such that BC = 2AB.
If $$\begin{vmatrix}x+1&x-1\\x-3&x+2\end{vmatrix}=\begin{vmatrix}4&-1\\1&3\end{vmatrix}$$, then write the value of $$x$$.
Find determinent$$\left( {\matrix{
7 & 1 & { - 6} \cr
{ - 6} & { - 4} & {13} \cr
2 & 5 & { - 8} \cr
} } \right)$$
7 & 1 & { - 6} \cr
{ - 6} & { - 4} & {13} \cr
2 & 5 & { - 8} \cr
} } \right)$$
Find the value of the determinant:$$\begin{vmatrix}\cos(\theta+\phi)&-\sin (\theta+\phi)&\cos 2\phi\\ \sin \theta& \cos \theta &\sin \phi\\ -\cos \theta &\sin \theta &\cos \phi\end{vmatrix}$$
For what values of p and q, the system of equations
$$2x + py + 6z = 8,
x + 2y + qz = 5,
x + y + 3z = 4$$
has (i) no solution (ii) a unique solution (iii) infinitely many solutions.
Solve:
$$\begin{vmatrix} 1+\sin ^2 \theta & \cos ^2\theta & 4\sin 4\theta \\ \sin ^2 \theta &1+\cos ^2 \theta & 4\sin 4\theta \\ \sin ^2 \theta & \cos ^2 \theta & 1+4\sin 4\theta \end{vmatrix}$$ $$=0$$; where, $$0<\theta <\large{\cfrac{\pi}{2}}$$.
The straight lines $$\displaystyle \imath_1, \imath_2 \, and \, \imath_3$$ are parallel and lie in the same plane. A total of m points are taken on the line $$\displaystyle \imath_1,$$ n points on $$\displaystyle \imath_2$$, and k points on $$\displaystyle \imath_3$$. How many triangles are there whose vertices are at these points?
Write minors and cofactors of the elements of the following determinants:
$$(i) \begin{vmatrix} 2 & -4 \\ 0 & 3 \end{vmatrix}$$
$$(ii) \begin{vmatrix} a & c \\ b & d \end{vmatrix}$$
$$(iii) \begin{vmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1\end{vmatrix}$$
$$(iv) \begin{vmatrix} 1 & 0 & 4 \\ 3 & 5 & -1 \\ 0 & 1 & 2 \end{vmatrix}$$
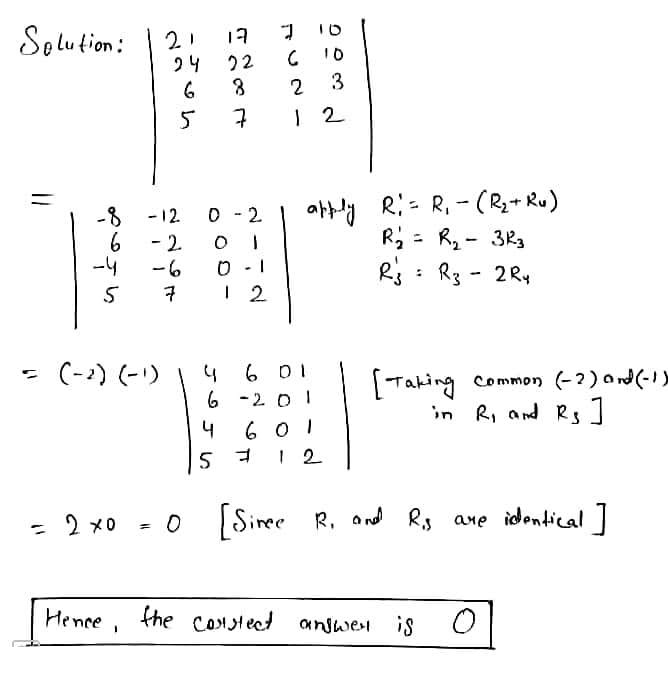
Evaluate the determinants:$$
\left |
\begin{array}{111}
21 & 17 & 7 & 10 \\
24 & 22 & 6 & 10 \\
6 & 8 & 2 & 3 \\
5 & 7 & 1 & 2 \\
\end {array}
\right |
$$
$$ax + by + cz = k$$
$$a^2x + b^2y + c^2z = k^2$$
$$a^3x + b^3y + c^3z = k^3$$
Solve by Crammer's rule
Using properties of determinants, find the value of $$n$$ in the following.
$$
\left |
\begin{array}{111}
3x & -x+y & -x+z \\
x-y & 3y & z-y \\
x-z & y-z & 3z \\
\end {array}
\right |
$$ =$$ n( x+y + z)(xy + yz + zx)$$
The value of determinant $$\begin{vmatrix} 2 & 7 & 65\\ 3 & 8 & 75 \\ 5 & 9 & 86\end{vmatrix} equals $$.
$$\left| \begin{matrix} { a }^{ 2 }+1 & ab & ac \\ ab & { b }^{ 2 }+1 & bc \\ ca & cb & { c }^{ 2 }+1 \end{matrix} \right| =1+{ a }^{ 2 }+{ b }^{ 2 }+{ c }^{ 2 }$$
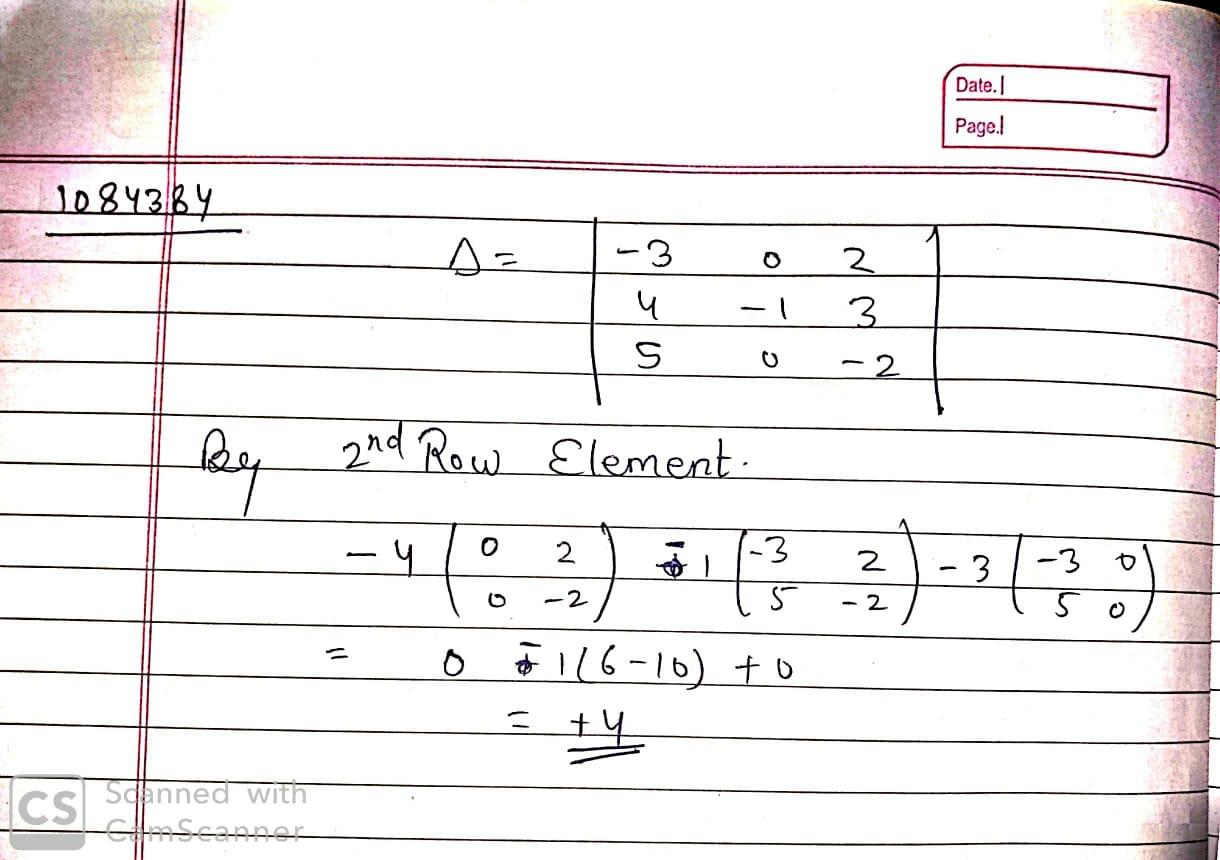
Using cofactor elements of $$2$$nd row, find the value of determinant, $$\Delta =\begin{vmatrix} -3 & 0 & 2\\ 4 & -1 & 3\\ 5 & 0 & -2\end{vmatrix}$$.
Show that the points are collinear $$(-5, 1) (5, 5) (10, 7)$$
Find the value of determinant $$\begin{vmatrix} 5 & -3 \\ -7 & -4 \end{vmatrix}$$
Find the relation between $$x $$ and $$y$$, if the points $$x,y $$ i.e $$(1,2)$$ and $$(7,0)$$ are collinears.
If $$A =\begin{bmatrix} 1 & -1 & 2 \\ 3 & 0 & -2 \\ 1 & 0 & 3 \end{bmatrix}$$, then verify that $$A(adjA)=(adjA)A= I \left| A \right|$$.
Find the value of $$a$$ if the points $$P ( 1,5 ) , Q ( a , 1 )$$ and $$R ( 4,11 )$$ are collinear .
Find the largest value of a third order determinant whose elements are $$1$$ or $$-1$$
Find the cofactor matrix of the determinant $$\begin{vmatrix} 1 & 2 & 3\\ -4 & 3 & 6 \\ 2 & -7 & 9 \end{vmatrix}$$
If the points $$(x_{1},\ y_{1}),\ (x_{2},\ y_{2})$$ and $$(x_{3},\ y_{3})$$ are collinear, show that $$\displaystyle \sum { \left( \frac { { y }_{ 1 }-{ y }_{ 2 } }{ { x }_{ 1 }{ x }_{ 2 } } \right) } =0$$, i.e
$$\dfrac {y_{1}-y_{2}}{x_{1}x_{2}}+\dfrac {y_{2}-y_{3}}{x_{2}x_{3}}+\dfrac {y_{3}-y_{1}}{x_{3}x_{1}}=0$$
If $$A = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}1 & { - 2} & 3\\4 & 0 & { - 1}\\{ - 3} & 1 & 5\end{array}} \right]$$, then $${\left( {adj\,A} \right)}$$ is equal to
Find the largest value of a third order determinant whose elements are $$0$$ or $$1$$
$$adj (adj A) = |A|^{n - 2} A$$
Prove that $$\begin{vmatrix} { yz-x }^{ 2 } & { zx-y }^{ 2 } & xy-z^{ 2 } \\ { zx-y }^{ 2 } & { xy }-z^{ 2 } & { yz-x }^{ 2 } \\ { xy-z }^{ 2 } & { yz-x }^{ 2 } & { zx-y }^{ 2 } \end{vmatrix}$$ is divisible by $$(x+y+z)$$ and hence find the quotient
If $$A=\begin{pmatrix} 2 & 3 & 4 \\ 0 & -2 & 1 \\ 3 & -1 & 2 \end{pmatrix},B=\begin{pmatrix} 2 & 0 & -3 \\ 4 & 0 & -1 \\ 3 & 4 & 5 \end{pmatrix}$$ and $$C=\begin{pmatrix} 5 & 6 & 7 \\ -1 & 2 & 3 \\ 4 & -5 & 4 \end{pmatrix}$$ Prove that $$A(BC)$$ and $$(AB)C$$.
Using properties of determinant, prove that $$\begin{vmatrix} b+c & a-b & a \\ c+a & b-c & b \\ a+b & c-a & c \end{vmatrix}=3abc-{ a }^{ 3 }-{ b }^{ 3 }-{ c }^{ 3 }$$
Compute the adjoint of the following matrice:
$$ \begin{bmatrix} 2 & -1 & 3 \\ 4 & 2 & 5 \\ 0 & 4 & -1 \end{bmatrix}$$
Verify that $$ (adj A)A = |A|I = A(adj A) $$ for the above matrice.
Compute the adjoint of the following matrice:
$$ \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 & 2 \\ 2 & 1 & 2 \\ 2 & 2 & 1 \end{bmatrix}$$
Verify that $$ (adj A)A = |A|I = A(adj A) $$ for the above matrice.
Compute the adjoint of the following matrice:
$$ \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 & 5 \\ 2 & 3 & 1 \\ -1 & 1 & 1 \end{bmatrix}$$
Verify that $$ (adj A)A = |A|I = A(adj A) $$ for the above matrice.
Find the adjoint of the following matrice:
$$ \begin{bmatrix} -3 & 5 \\ 2 & 4 \end{bmatrix} $$
Verify that $$ (adj A ) A = |A| I = A (adj A) $$ for the above matrice.
Find the adjoint of the following matrice:
$$ \begin{bmatrix} 1 & \tan\,\alpha /2 \\ -\tan\,\alpha /2 & 1 \end{bmatrix} $$
Verify that $$ (adj A ) A = |A| I = A (adj A) $$ for the above matrice.
Verify that $$ (adj A ) A = |A| I = A (adj A) $$ for the above matrice.
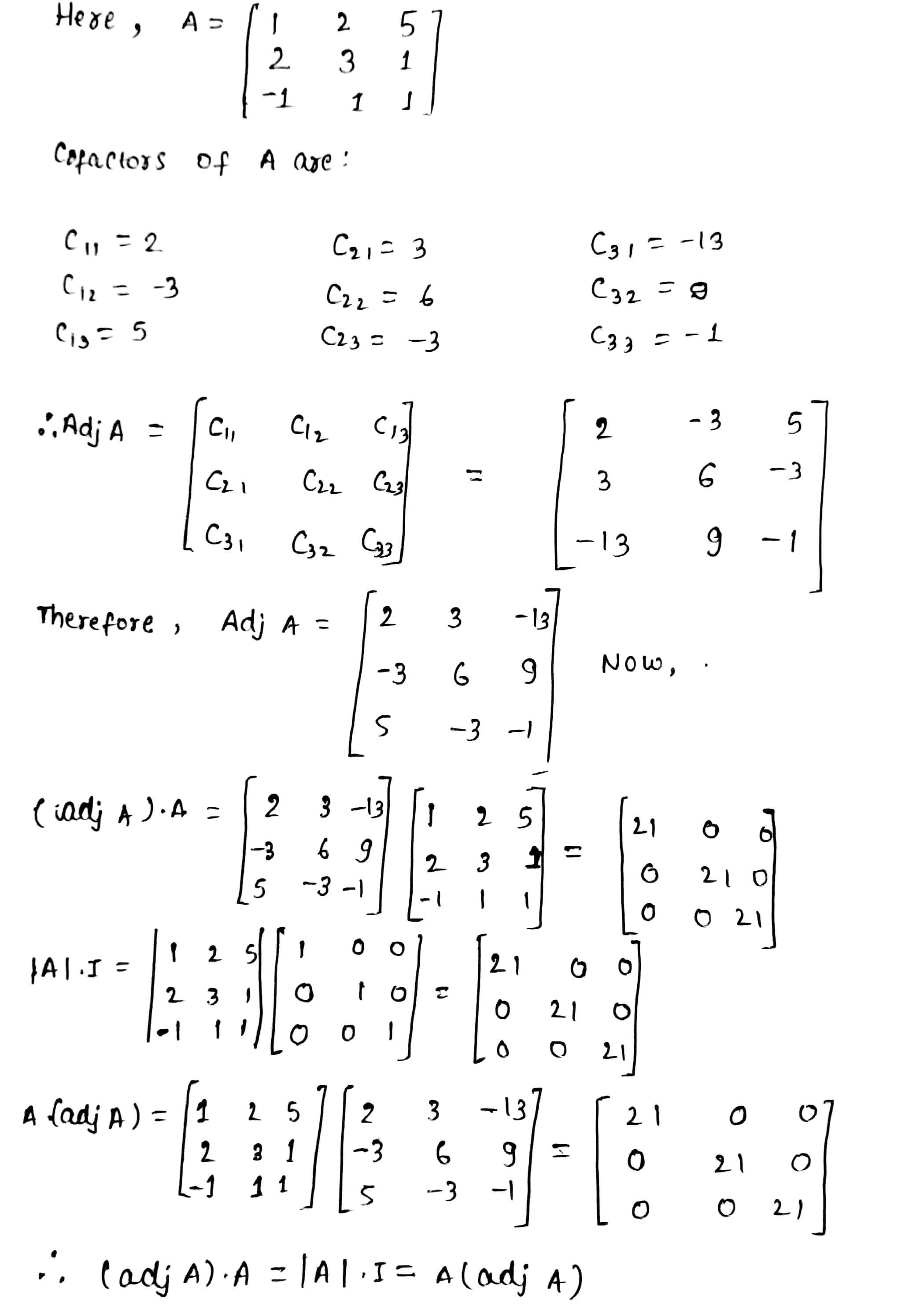
Find A (adj A) for the matrix $$ A = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & -2 & 3 \\ 0 & 2 & 1 \\ -4 & 5 & 2 \end{bmatrix}$$.
Find the adjoint of the matrix $$A= \begin{bmatrix} -1 & -2 & -2 \\ 2 & 1 & -2 \\ 2 & -2 & 1 \end{bmatrix}$$ and hence show that $$A(adj\: A)= \left | A \right |I_{3}$$.
Compute the adjoint of the following matrice:
$$ \begin{bmatrix} 2 & 0 & -1 \\ 5 & 1 & 0 \\ 1 & 1 & 3 \end{bmatrix}$$
Verify that $$ (adj A)A = |A|I = A(adj A) $$ for the above matrice.
$$ \left| \begin{matrix} 0 & xyz & x-z \\ y-x & 0 & y-z \\ z-x & z-y & 0 \end{matrix} \right| $$=_________
Class 12 Commerce Maths Extra Questions
- Application Of Derivatives Extra Questions
- Application Of Integrals Extra Questions
- Continuity And Differentiability Extra Questions
- Determinants Extra Questions
- Differential Equations Extra Questions
- Integrals Extra Questions
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions Extra Questions
- Linear Programming Extra Questions
- Matrices Extra Questions
- Probability Extra Questions
- Relations And Functions Extra Questions
- Three Dimensional Geometry Extra Questions
- Vector Algebra Extra Questions