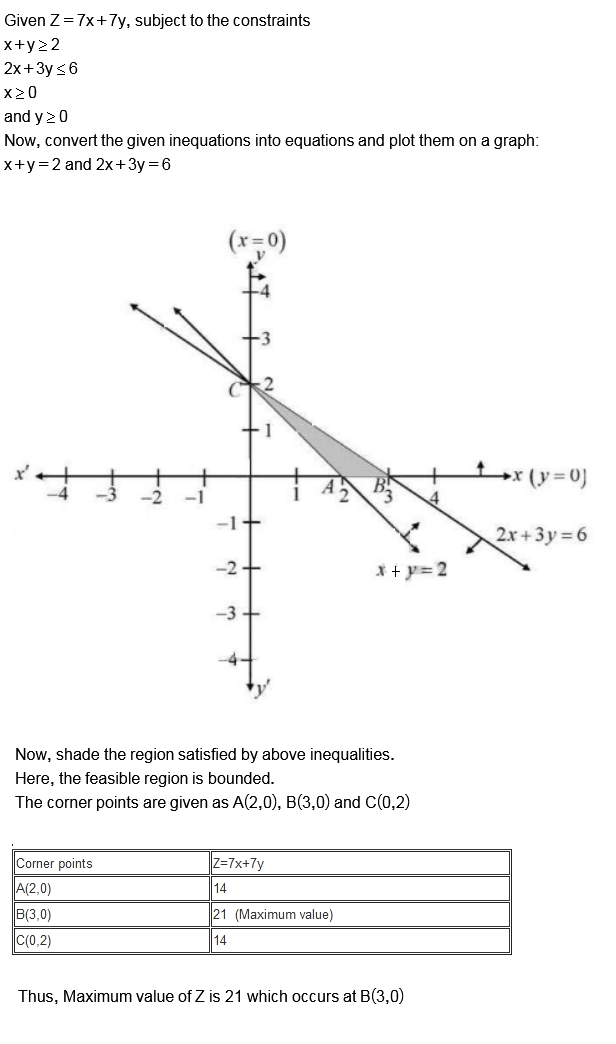
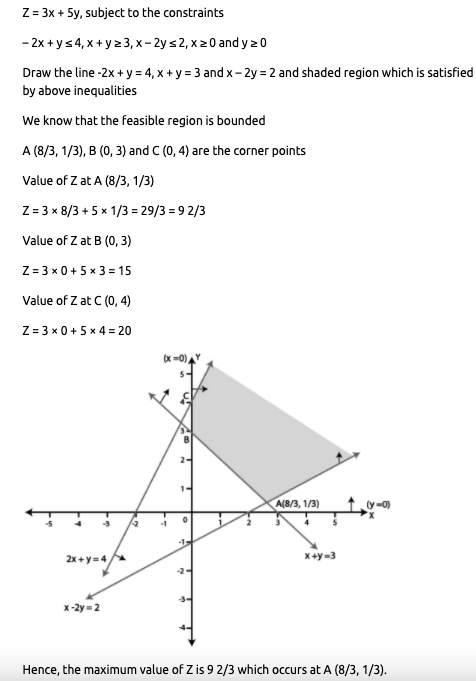
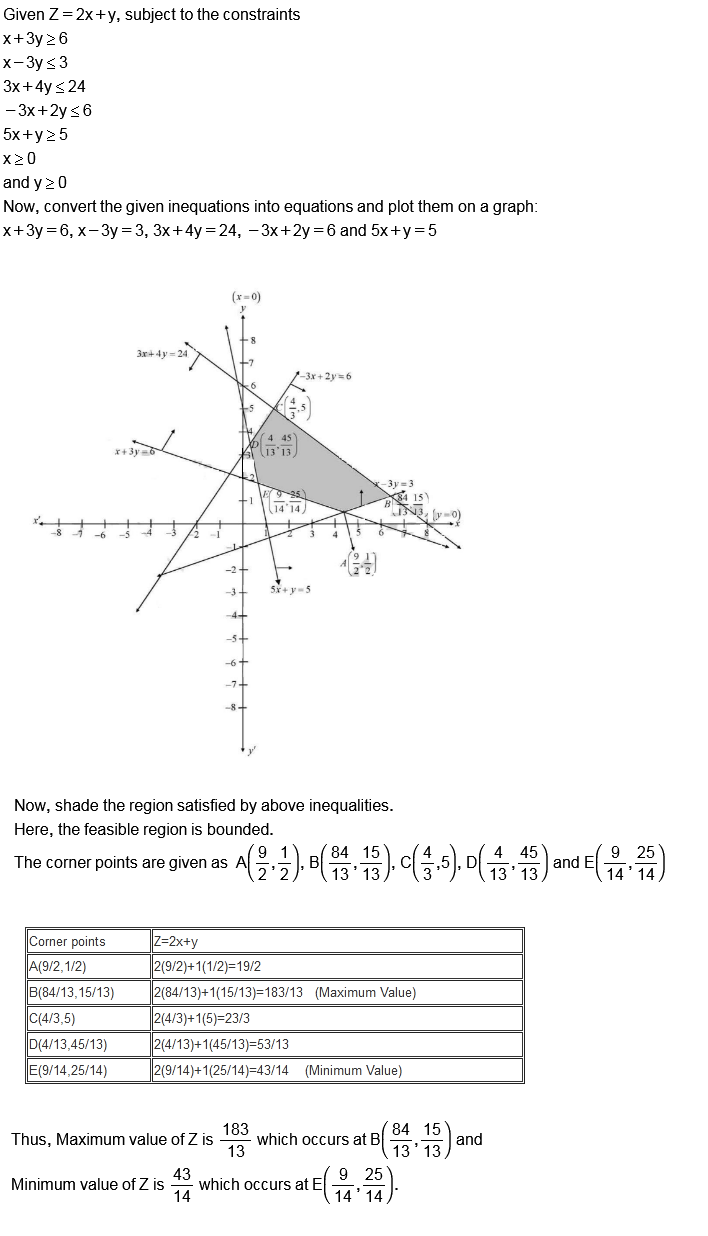
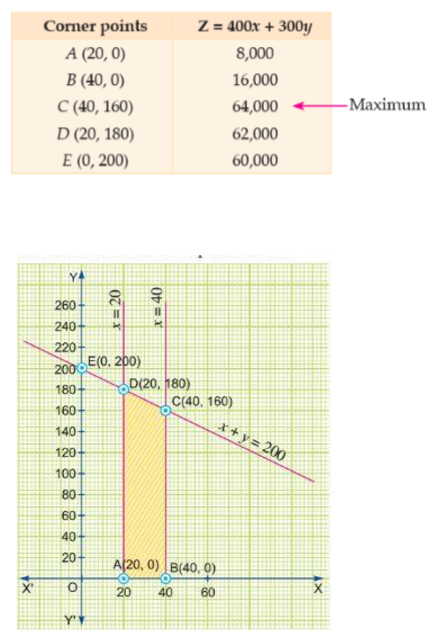
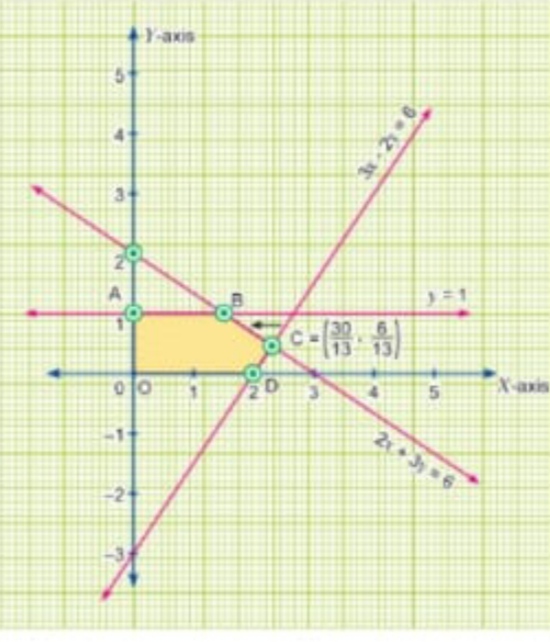
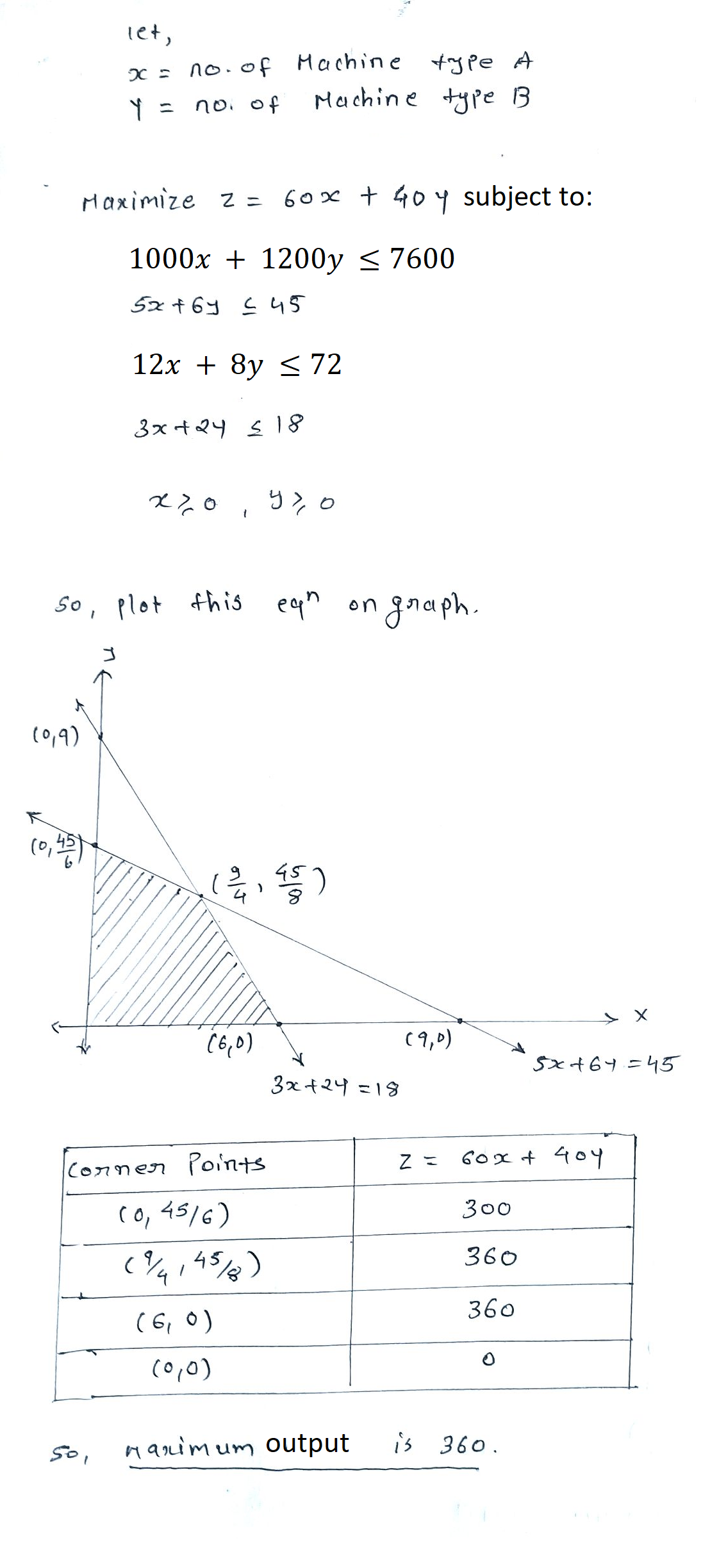
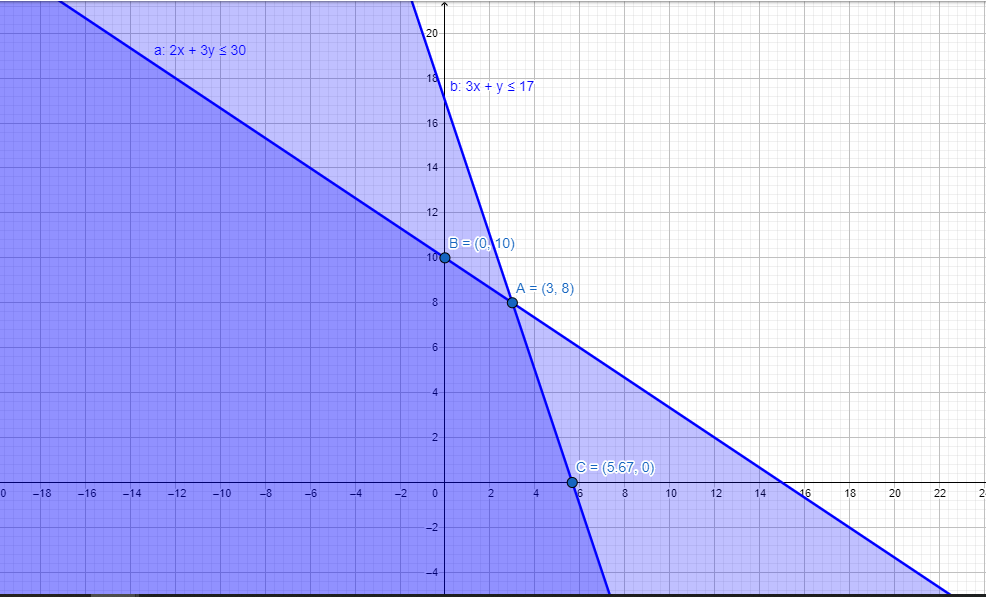
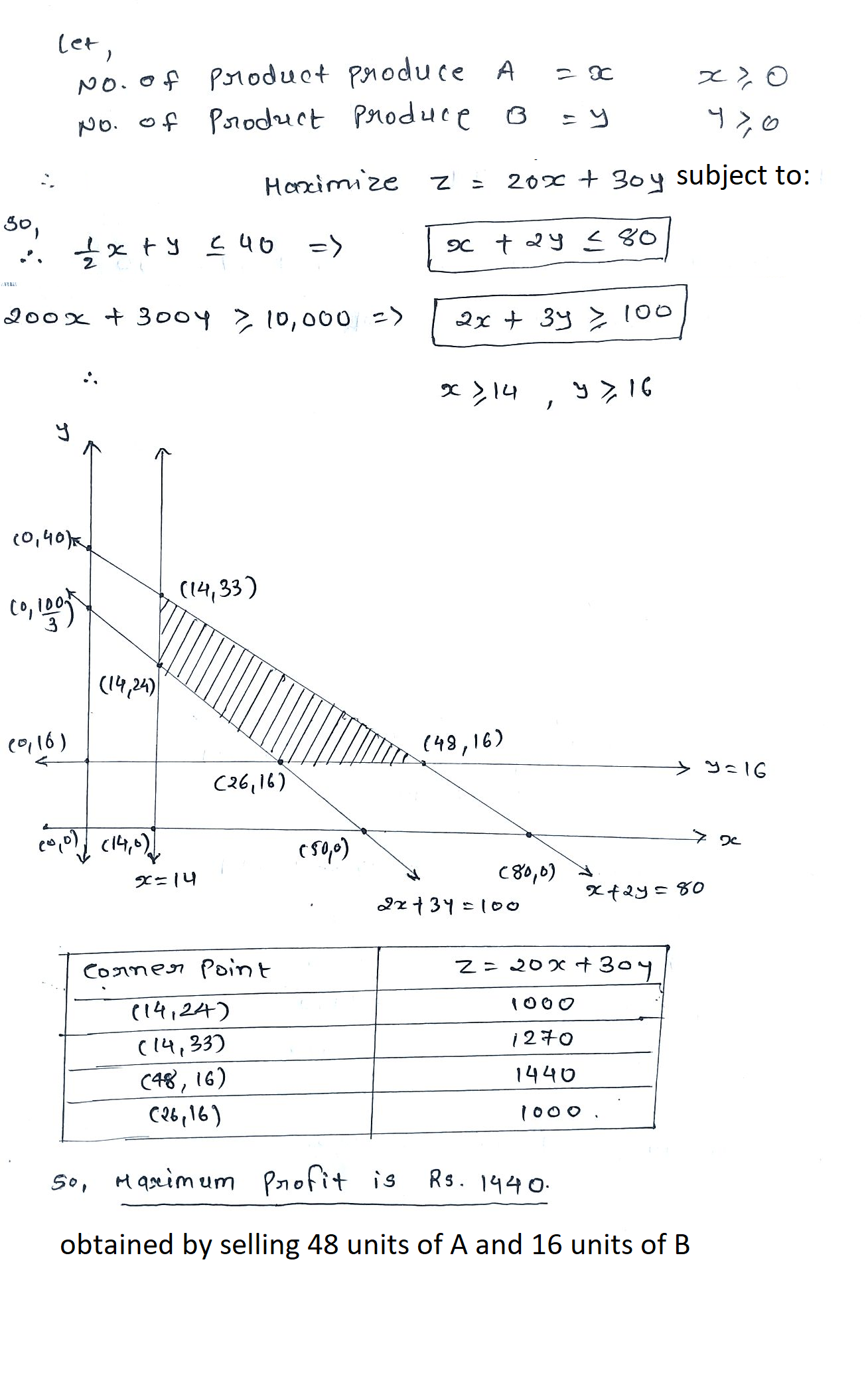
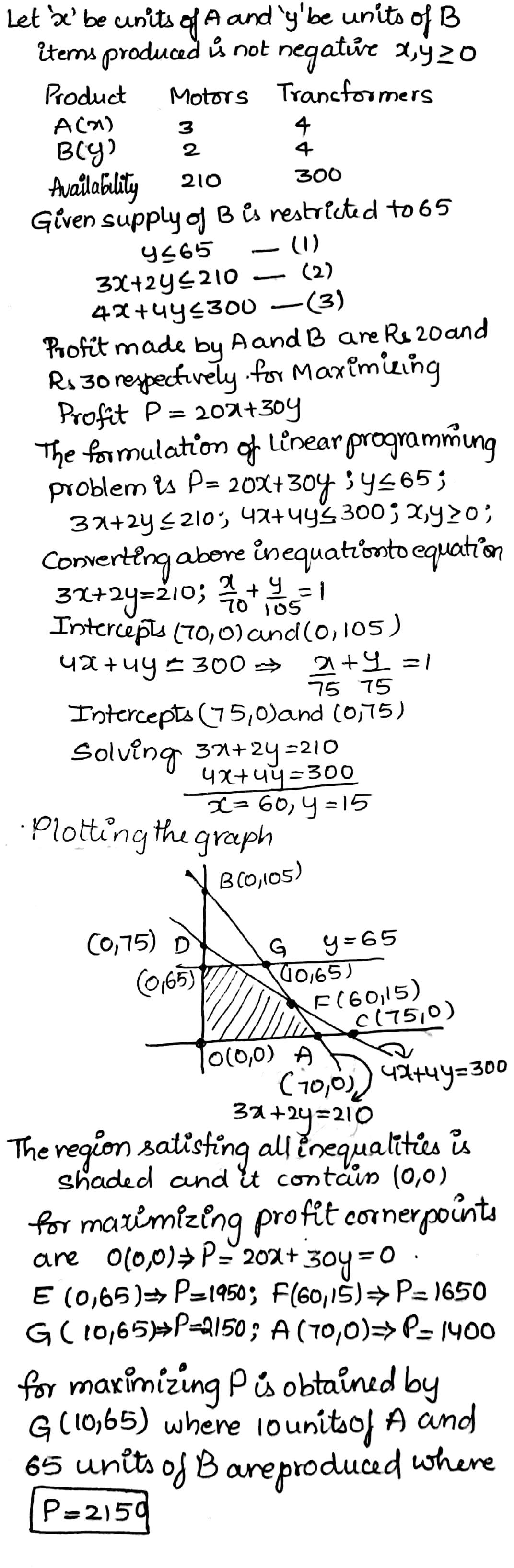
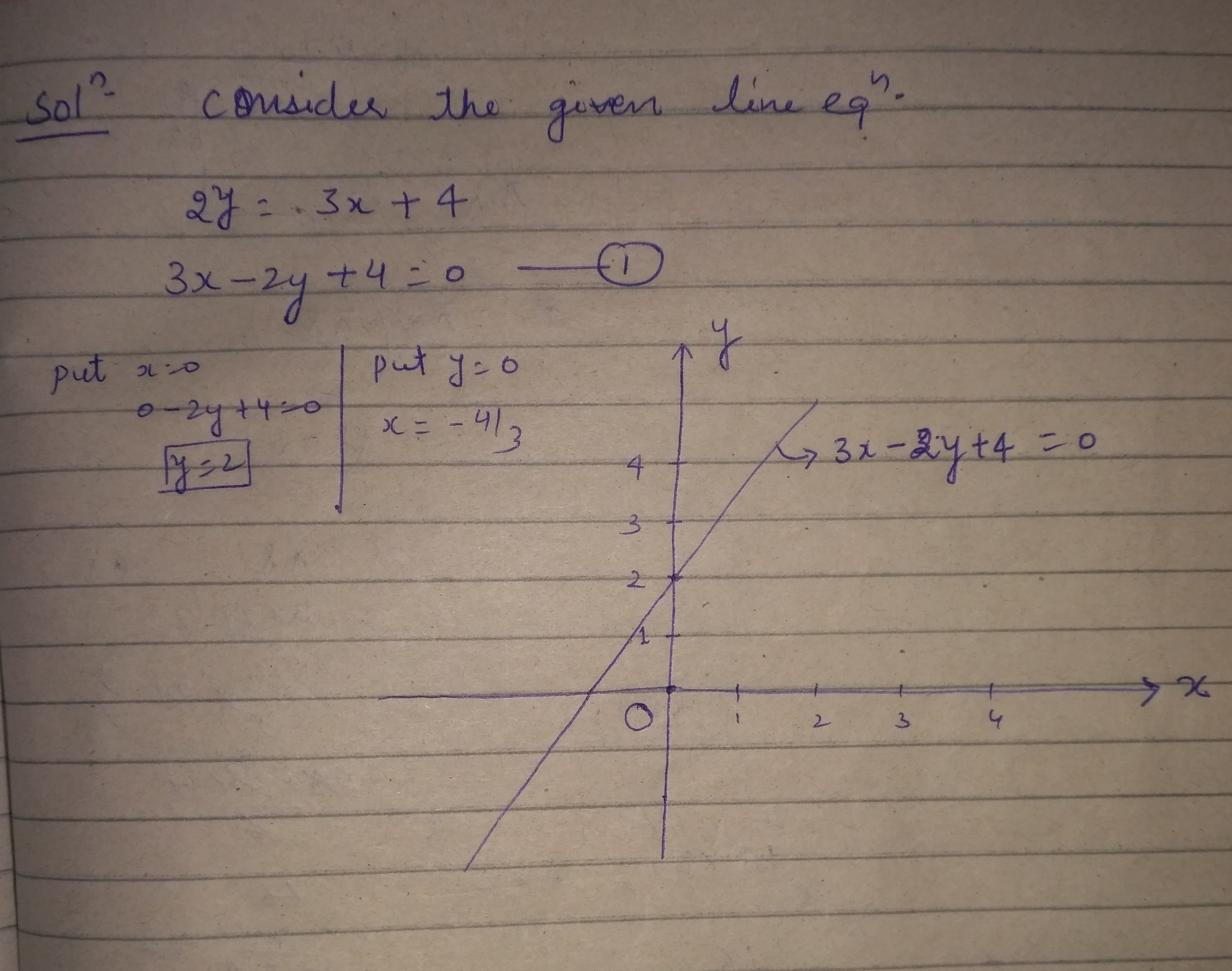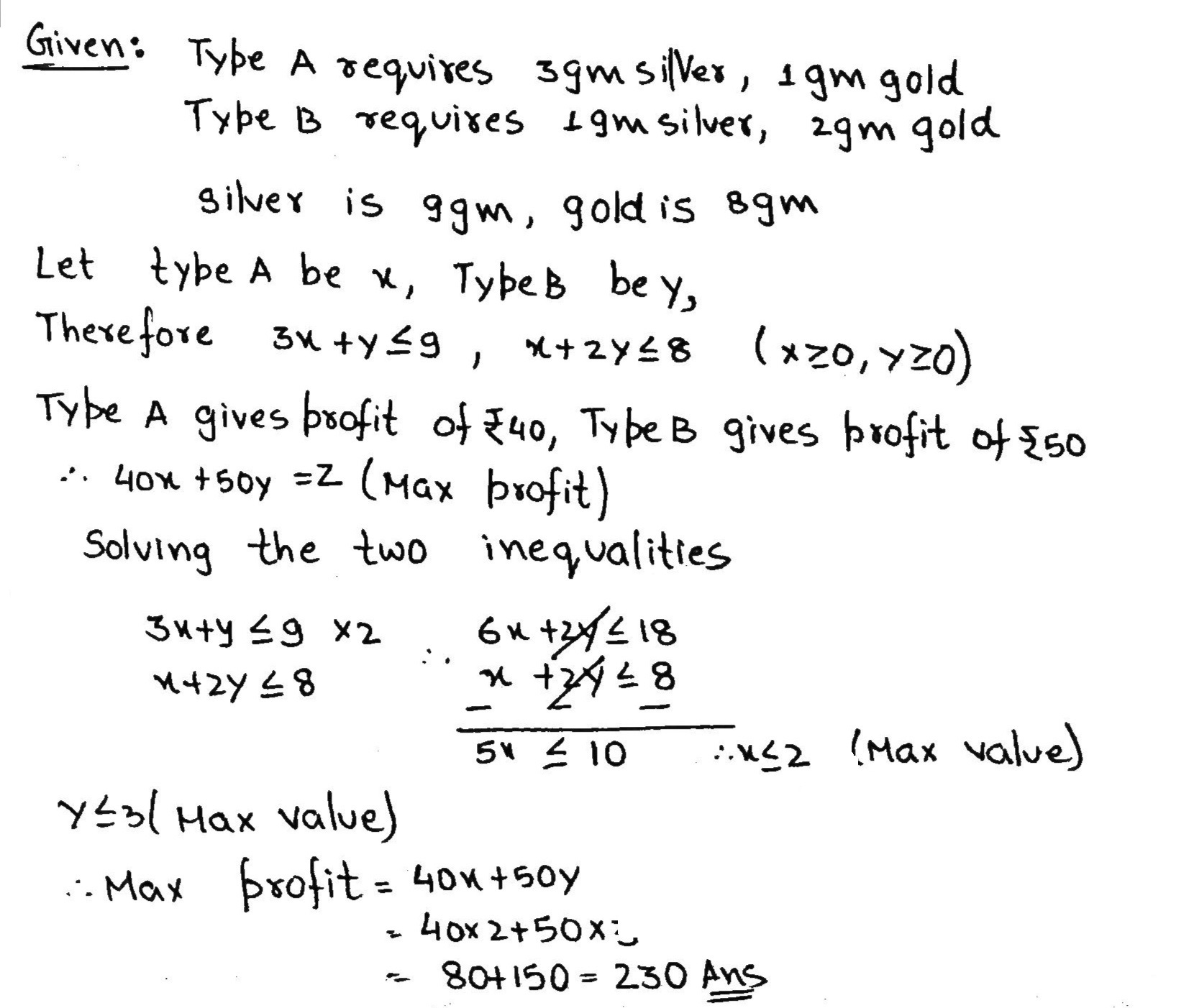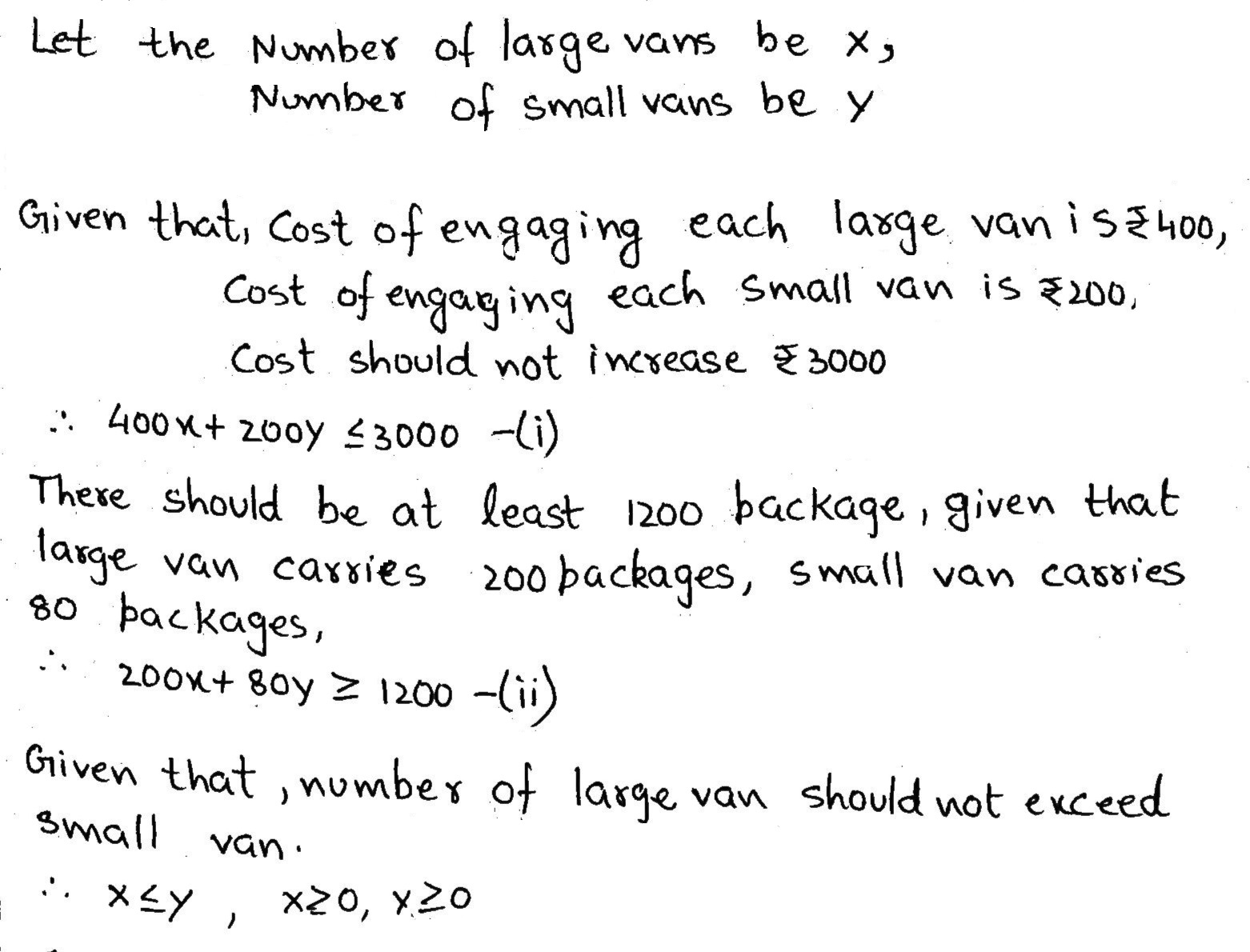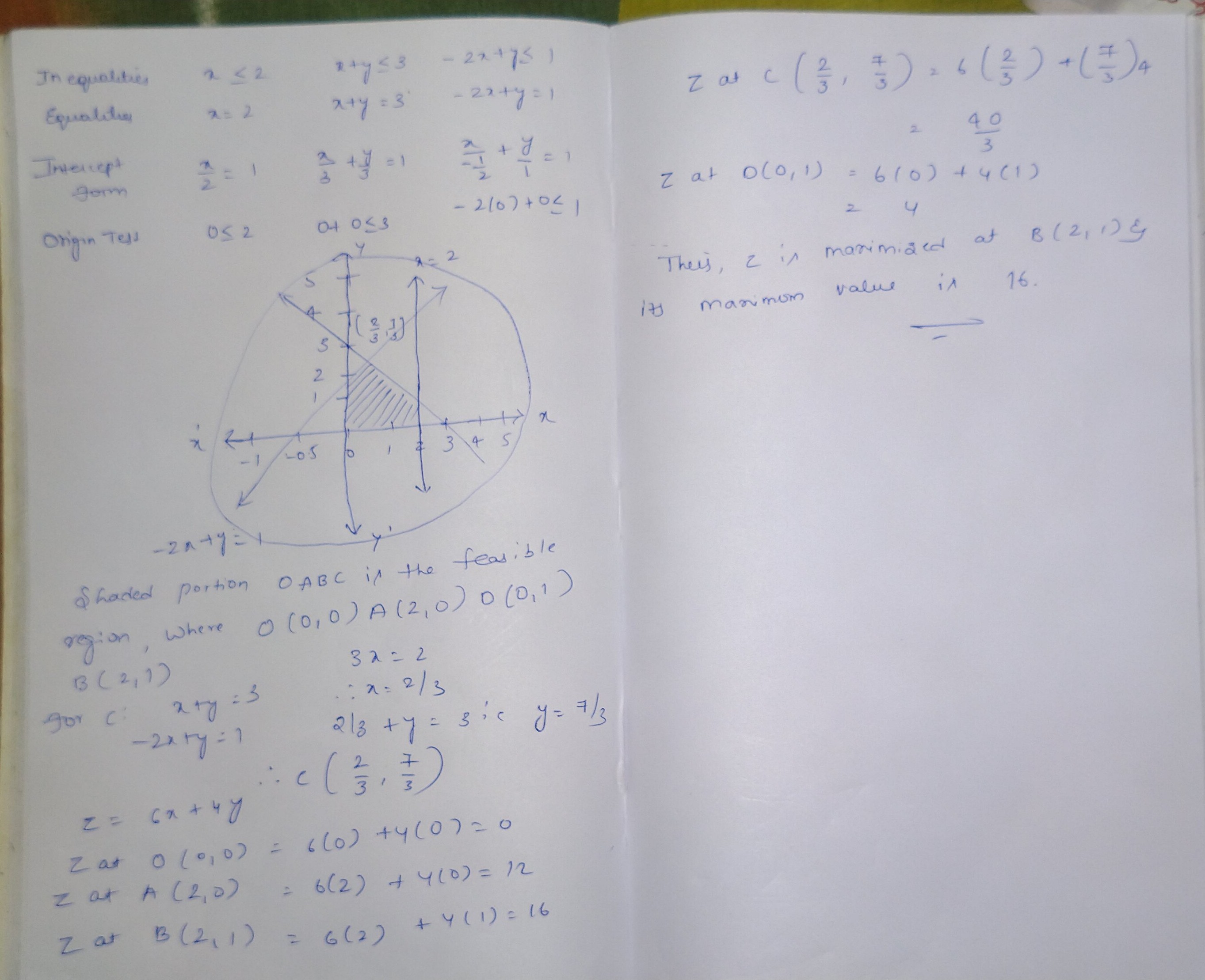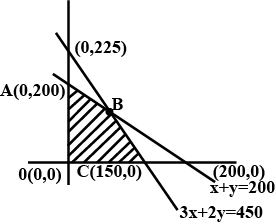Linear Programming - Class 12 Commerce Maths - Extra Questions
Solve the following equation
$$\displaystyle 2\left ( 2x+3 \right )-10\leq 6\left ( x-2 \right )$$
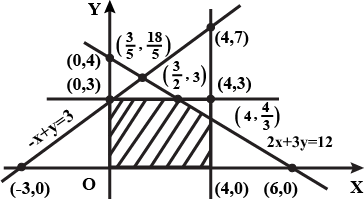
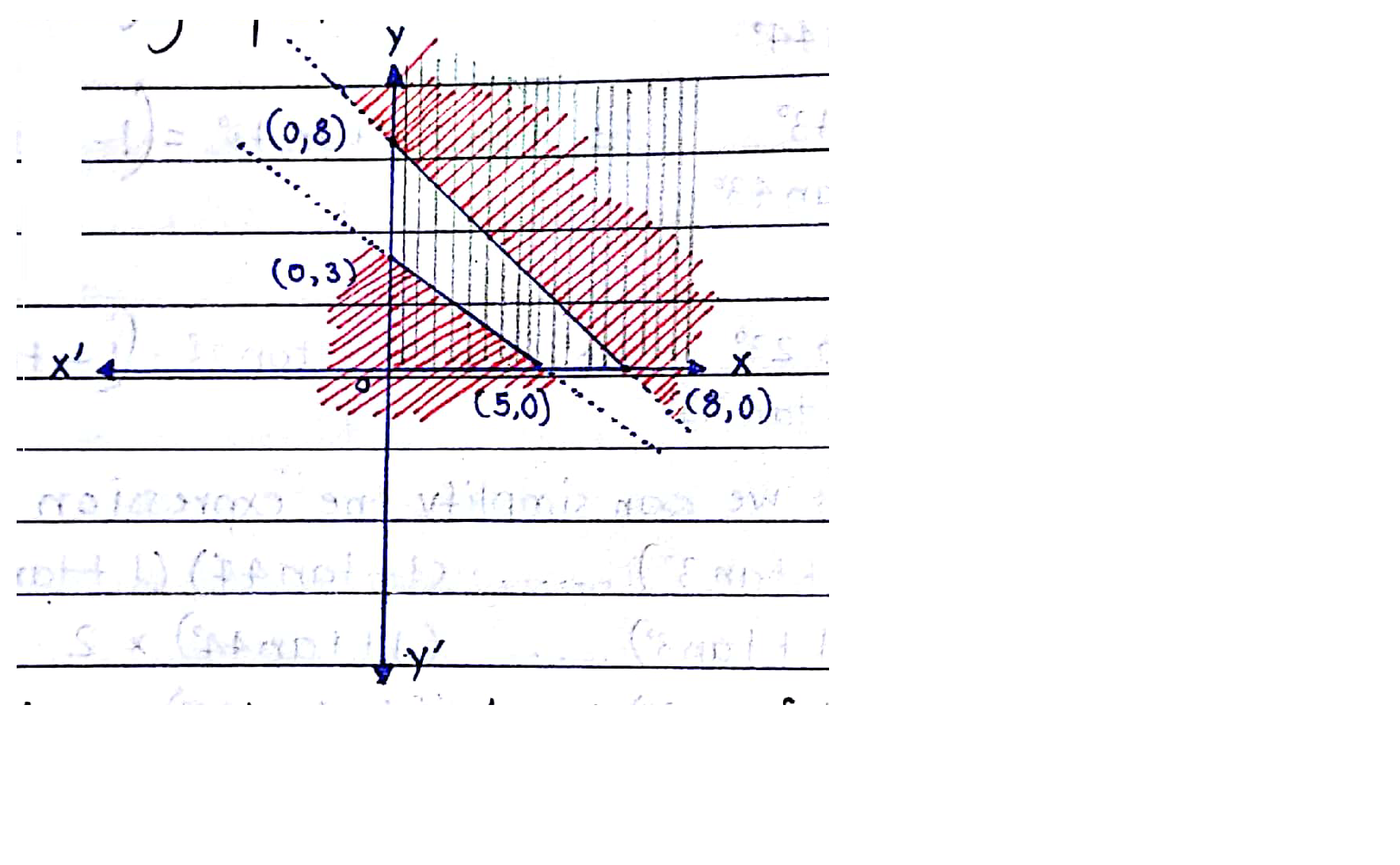
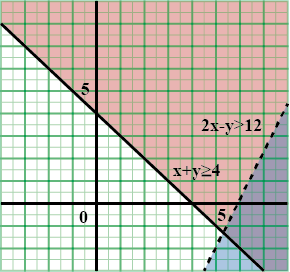
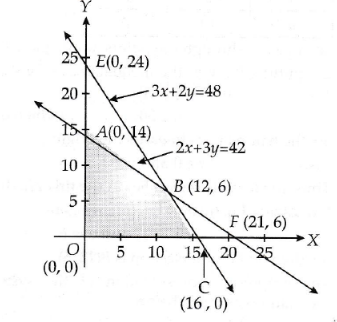
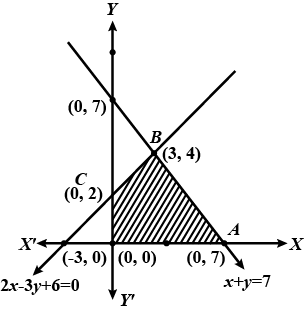
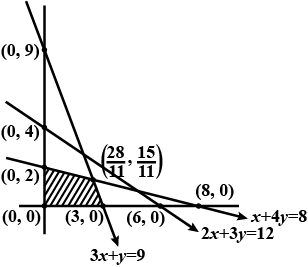
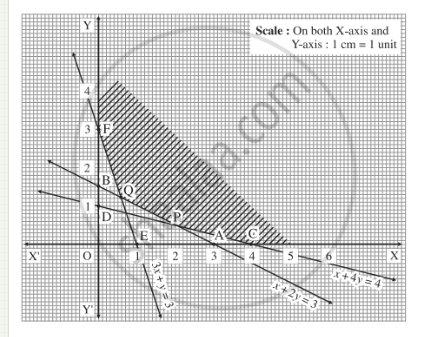
Check, whether the half plane $$3x+6y \geq 0$$ contains $$(1, 1)$$, if so shade the plane containing $$(1, 1)$$.
Shade the following half plane: $$5x+10y-20\geq 0$$.
Check, whether the half plane $$x+y+4 > 0$$ contains the origin. Identify the plane and shade it.
The solution set of constraints of Linear Programming problem is called
What is meant by "Open Convex Region"?
Define: 'Objective function'.
Define feasible region in LPP.
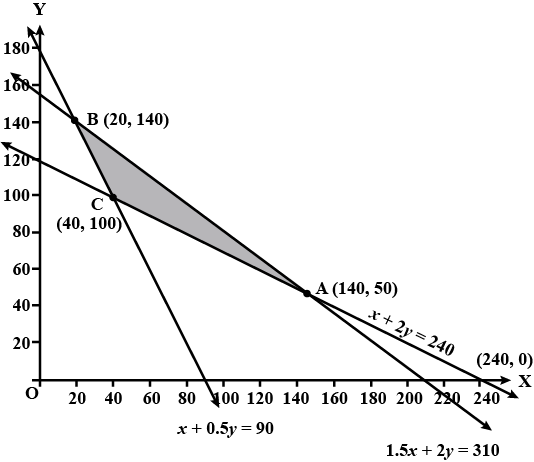
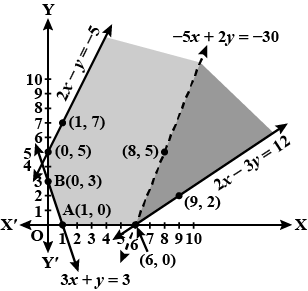
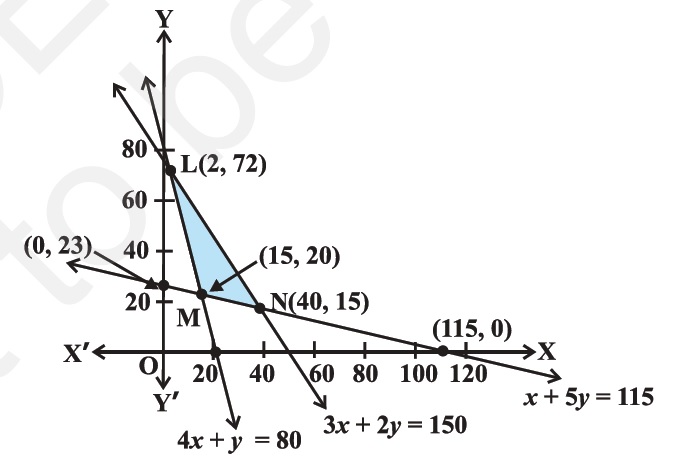
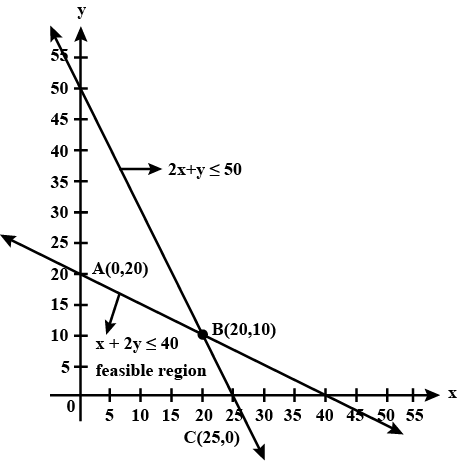
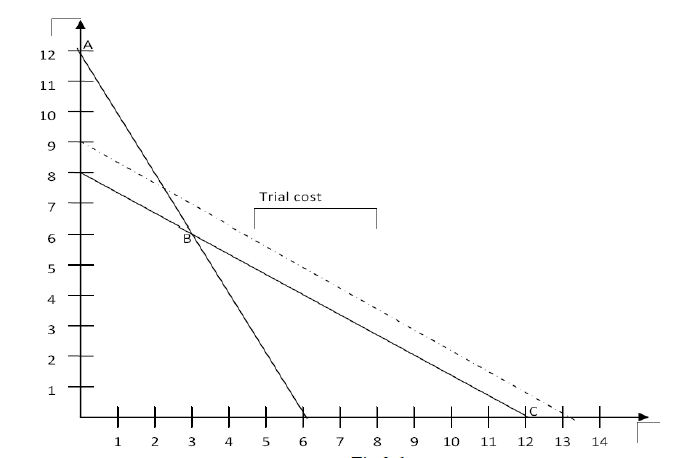
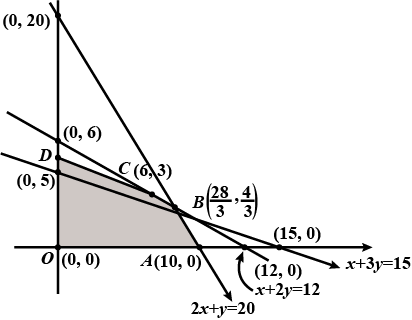
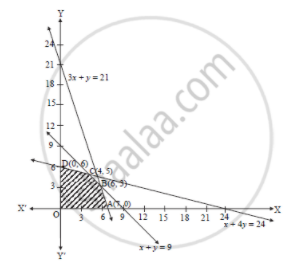
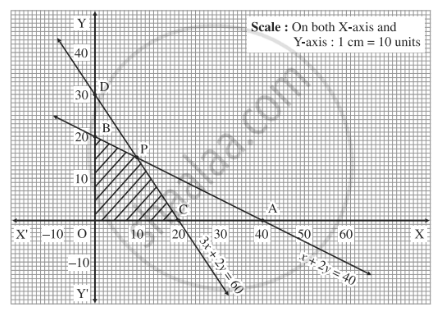
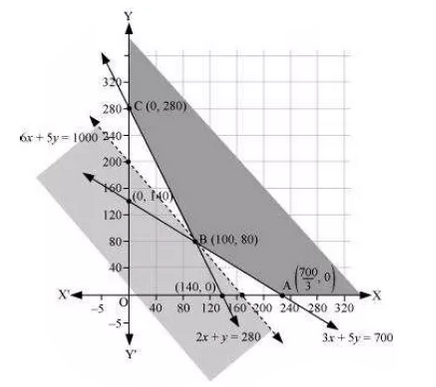
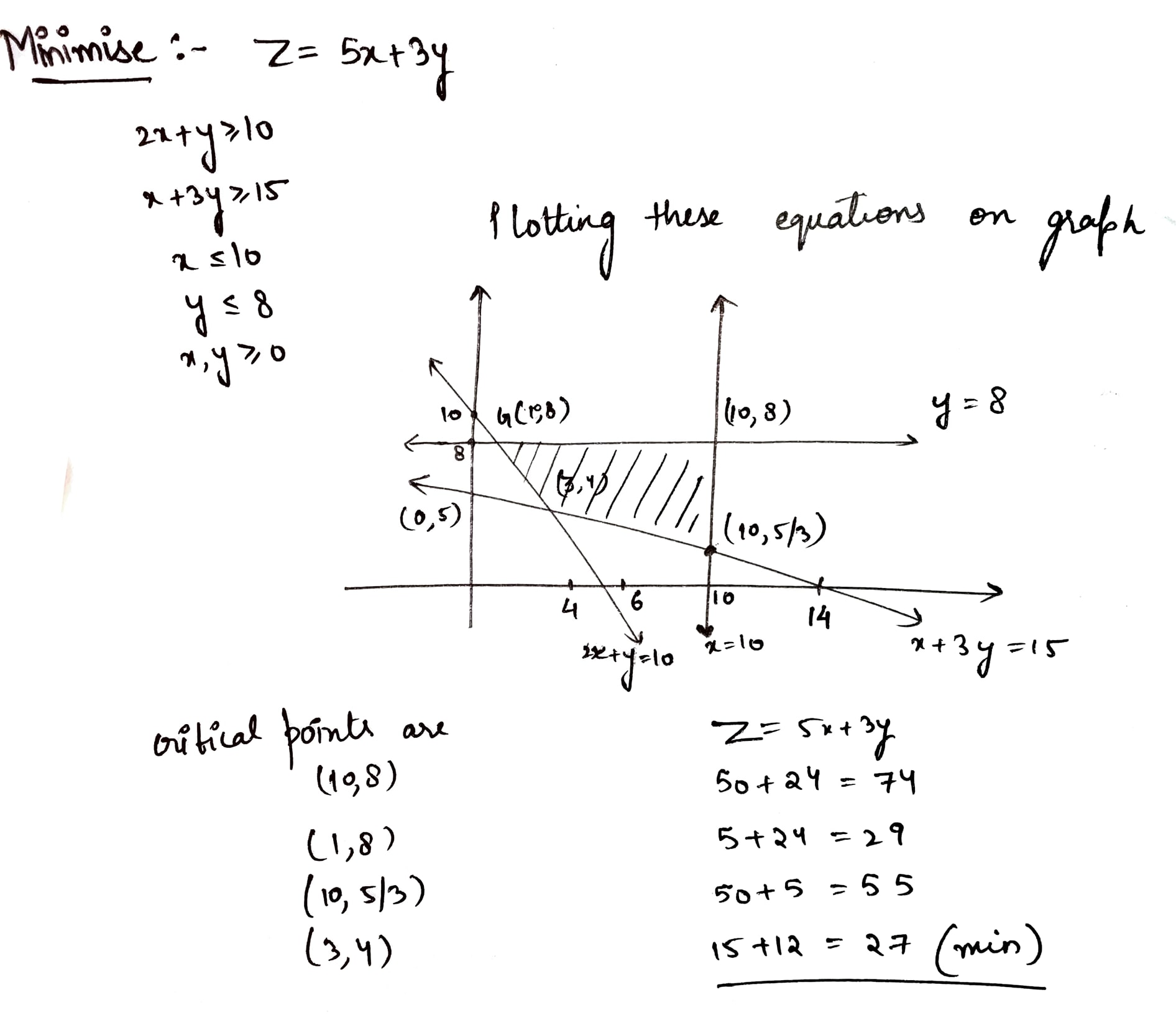
Determine graphically the minimum value of the objective function
$$Z = 50x + 20y ... (1)$$
subject to the constraints:
$$2x y \geq 5 ... (2)$$
$$3x + y \geq 3 ... (3)$$
$$2x -3y \leq 12 ... (4)$$
$$x \geq 0, y \geq 0 ... (5)$$.
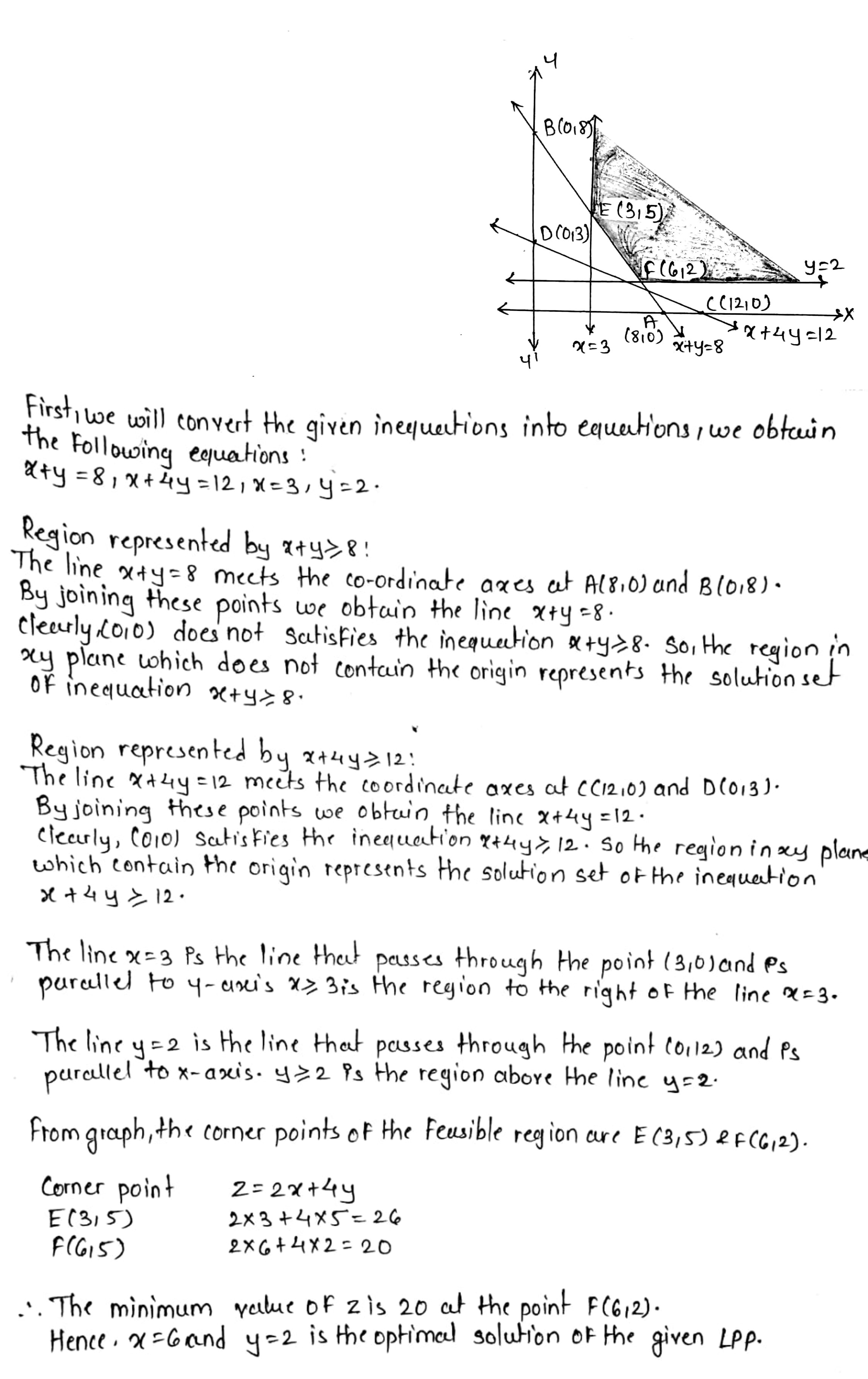
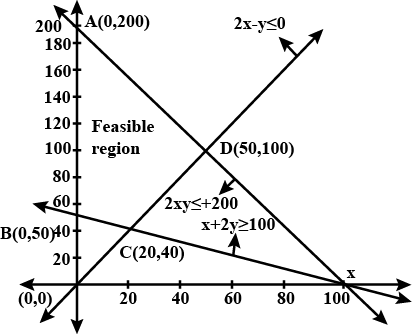
Minimize $$Z = 7x + y$$ subject to
$$5x + y\geq 5, x + y \geq 3, x \geq 0, y\geq 0$$.
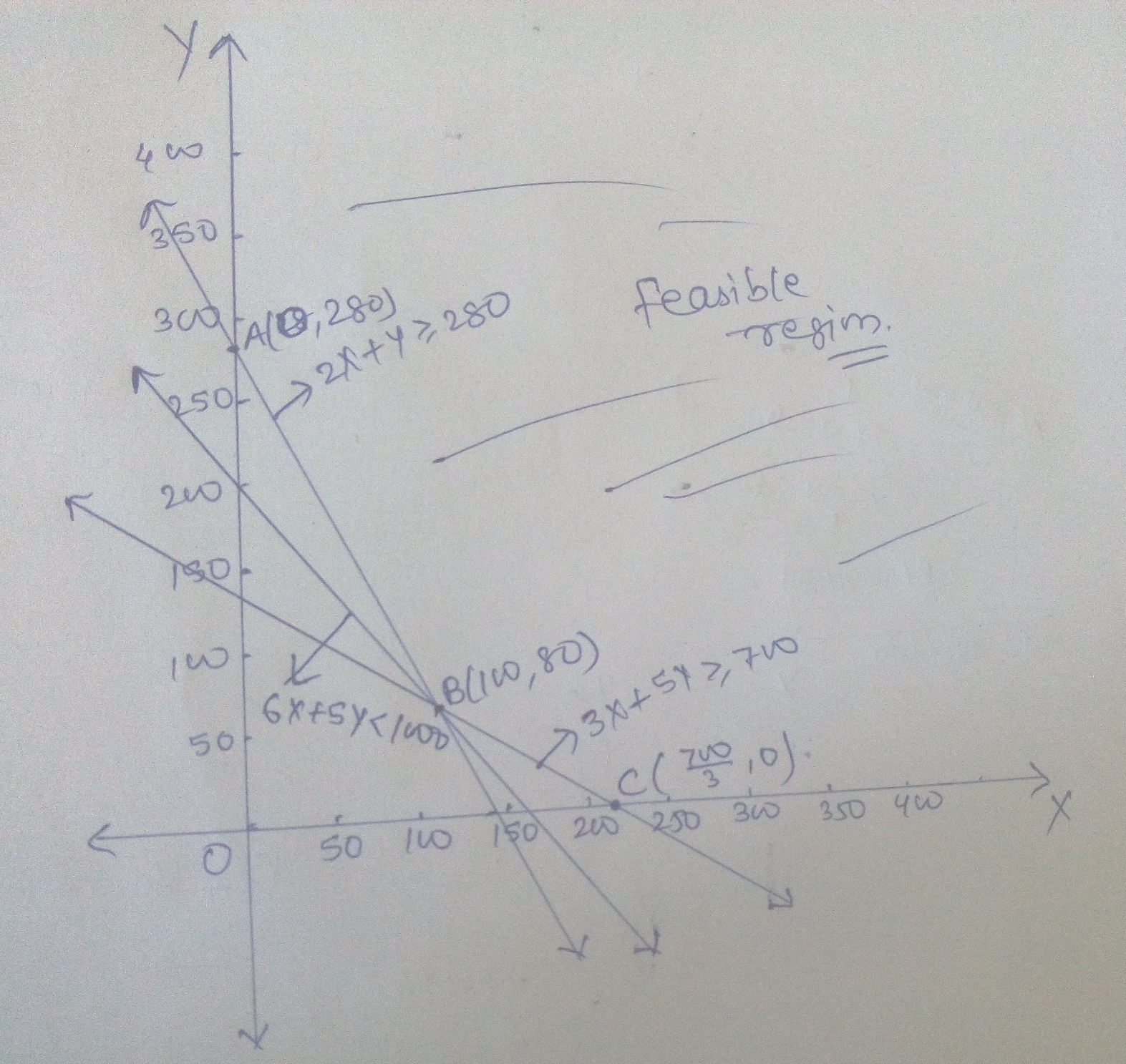
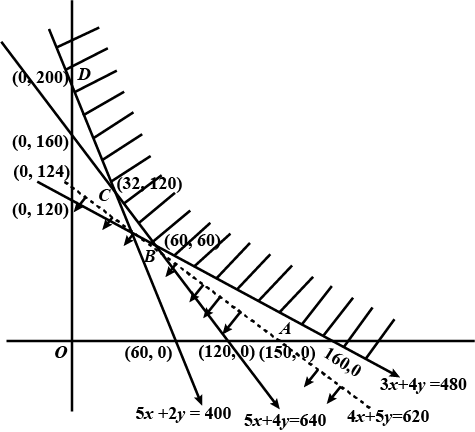
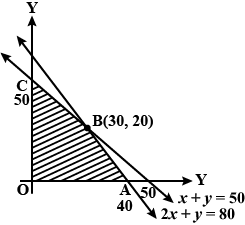
Dietician has to develop a special diet using two foods $$P$$ and $$Q$$. Each packet (containing $$30\ g$$) of food $$P$$ contains $$12$$ units of calcium, $$4$$ units of iron, $$6$$ units of cholesterol and $$6$$ units of vitamin A, while each packet of the same quality of food $$Q$$ contains $$3$$ units of calcium, $$20$$ units of vitamin A. The diet requires atleast $$240$$ units of calcium, atleast $$460$$ units of iron and almost $$300$$ units of cholesterol. How many packets of each food should be used to maximize the amount of vitamin A in the diet? What is the maximum amount of vitamin A?
A factory manufactures two types of screws $$A$$ and $$B$$, each type requiring the use of two machines, an automatic and a hand-operated. It takes $$4$$ minutes on the automatic and $$6$$ minutes on the hand-operated machines to manufacture a packet of screws $$'A'$$ while it takes $$6$$ minutes on the automatic and $$3$$ minutes on the hand-operated machine to manufacture a packet of screws 'B'. Each machine is available for at most $$4$$ hours on any day. The manufacturer can sell a packet of screws $$'A'$$ at a profit of $$70$$ paise and screws $$'B'$$ at a profit of $$Rs. 1$$. Assuming that he can sell all the screws he manufactures, how many packets of each type should the factory owner produce in a day in order to maximize his profit? Formulate the given LLP and solve it graphically and find the maximum profit.
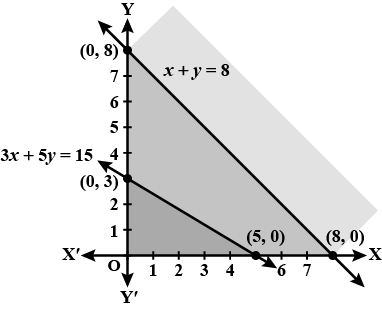
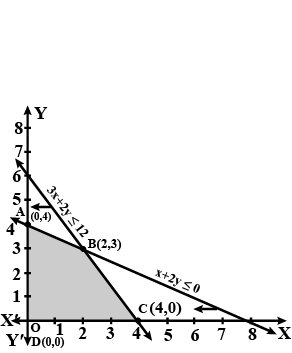
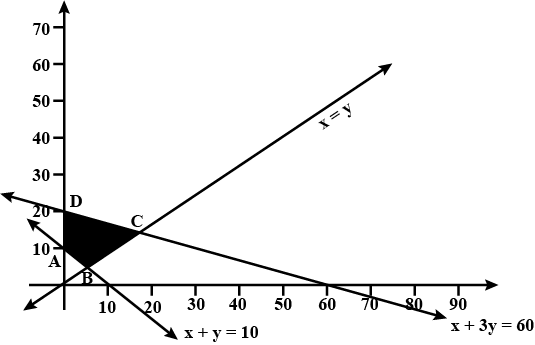
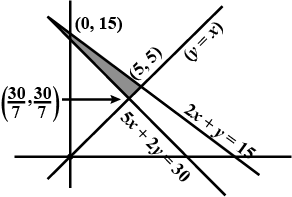
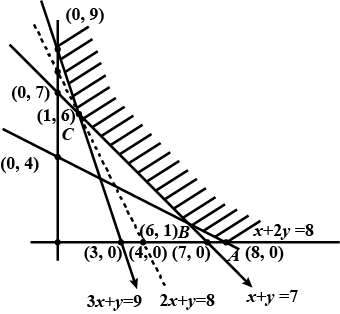
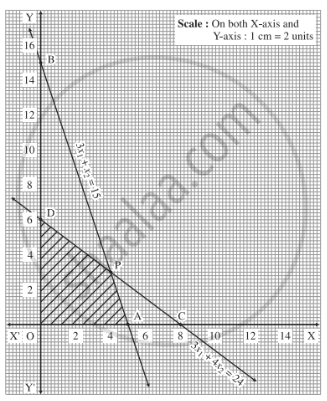
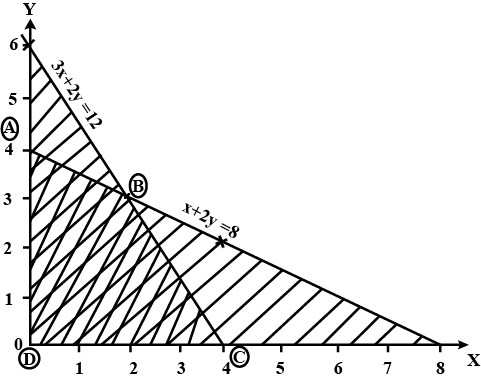
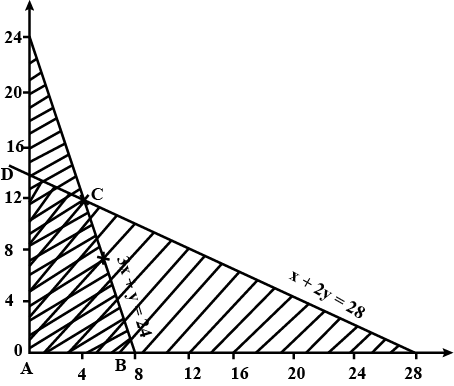
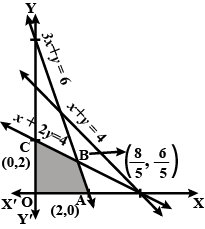
Minimise $$Z = 3x + 2y$$
subject to the constraints:
$$x + y \geq 8 ... (1)$$
$$3x + 5y \leq 15 ... (2)$$
$$x \geq 0, y \geq 0 ... (3)$$.
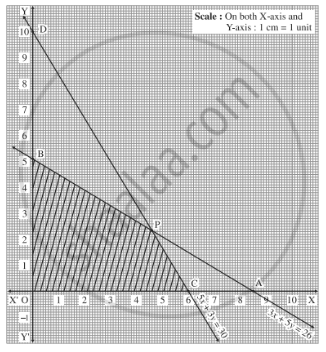
Solve the following inequalities by graphical method:
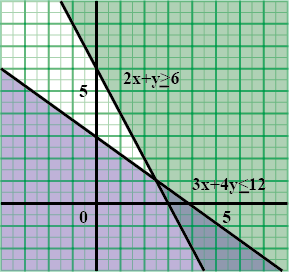
$$2x+y\ge 6,3x+4y\le 12$$
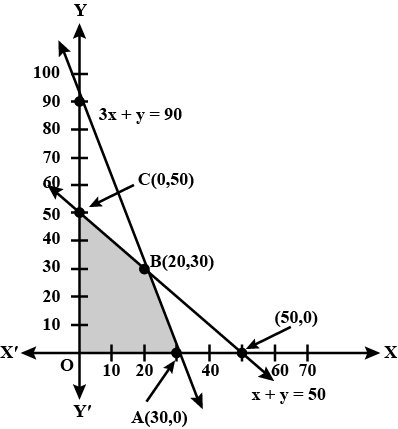
Solve the following linear programming problem graphically:
Maximise $$Z = 4x + y ... (1)$$
subject to the constraints: $$x + y \leq 50 ... (2)$$
$$3x + y\leq 90 ... (3)$$
$$x\geq 0, y\geq 0 ... (4)$$.
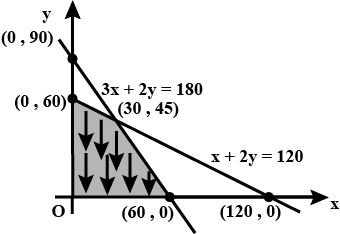
Find graphical solution for the following system of linear inequations:
$$3x + 2y\leq 180; x + 2y \leq 120, x \geq 0, y\geq 0$$
Hence find co-ordinates of corner points of the common region.
(Diet problem) A dietician has to develop a special diet using two foods $$P$$ and $$Q$$. Each packet (containing $$30\ g$$) of food $$P$$ contains $$12$$ units of calcium, $$4$$ units of iron, $$6$$ units of cholesterol and $$6$$ units of vitamin A. Each packet of the same quantity of food $$Q$$ contains $$3$$ units of calcium, $$20$$ units of iron, $$4$$ units of cholesterol and $$3$$ units of vitamin A. The diet requires atleast $$240$$ units of calcium, atleast $$460$$ units of iron and at most $$300$$ units of cholesterol. How many packets of each food should be used to minimise the amount of vitamin A in the diet? What is the minimum amount of vitamin A?
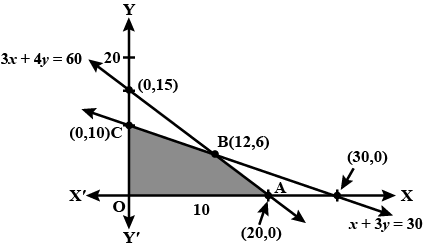
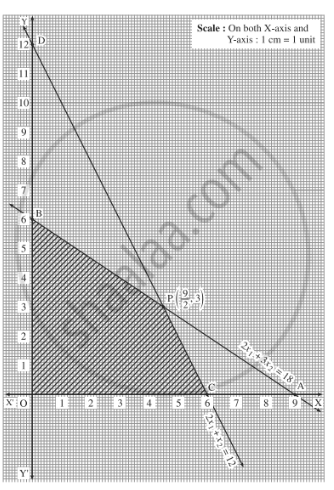
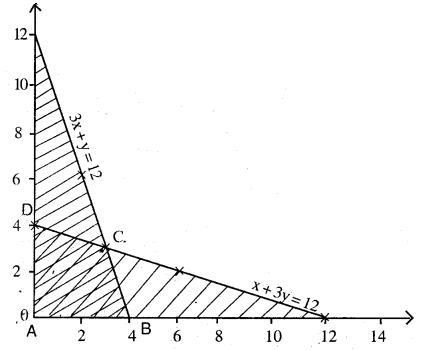
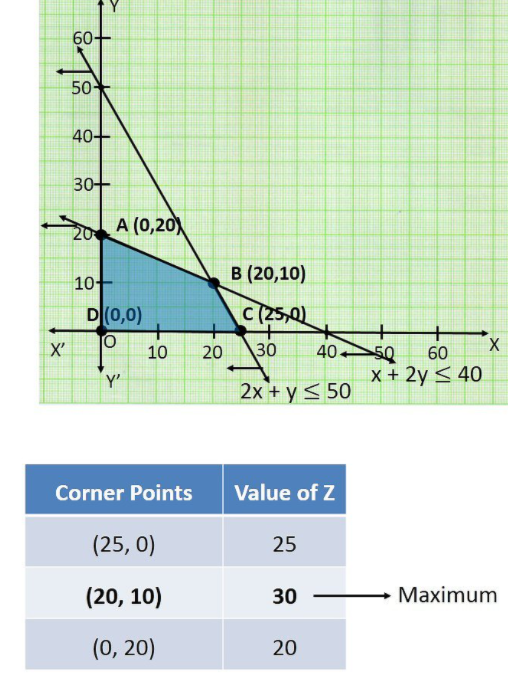
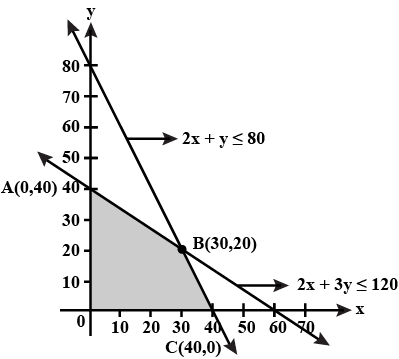
Solve the following Linear Programming Problems graphically:
Maximise $$Z = 3x + 2y$$
subject to $$x + 2y \leq 10, 3x + y \leq 15, x, y \geq 0$$.
Use graphical method
Maximize: $$z=2x+3y$$
Subject to:
$$x+2y\le 40$$
$$6x+5y\le 150$$
$$x\ge 0, y\ge 0$$
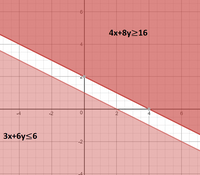
If possible, maximize $$z = x + 4y$$, subject to $$3x + 6y \leq 6, 4x + 8y \geq 16$$ and $$x \geq 0, y \geq 0$$.
A paper mill produces rolls of paper used in making cash registers.Each roll of paper is $$100$$m in length and can be used in widths of $$3,4,6$$ and $$10$$cm.The company's production process results in rolls that are $$24$$cm in width.Thus, the company must cut its $$24$$cm roll to the desired widths.It has six basic cutting alternatives as follows:
| Cutting alternatives | Width of Rolls(cm) $$3$$ | Width of Rolls(cm) $$4$$ | Width of Rolls(cm) $$6$$ | Width of Rolls(cm) $$10$$ | Waste(cm) |
| $$1$$ | $$4$$ | $$3$$ | - | - | - |
| $$2$$ | - | $$3$$ | $$2$$ | - | - |
| $$3$$ | $$1$$ | $$1$$ | $$1$$ | $$1$$ | $$1$$ |
| $$4$$ | - | - | $$2$$ | $$1$$ | $$2$$ |
| $$5$$ | - | $$4$$ | $$1$$ | - | $$2$$ |
| $$6$$ | $$3$$ | $$2$$ | $$1$$ | - | $$1$$ |
| Roll width(cm) | Demand |
| $$2$$ | $$2,000$$ |
| $$4$$ | $$3,600$$ |
| $$6$$ | $$1,600$$ |
| $$10$$ | $$500$$ |
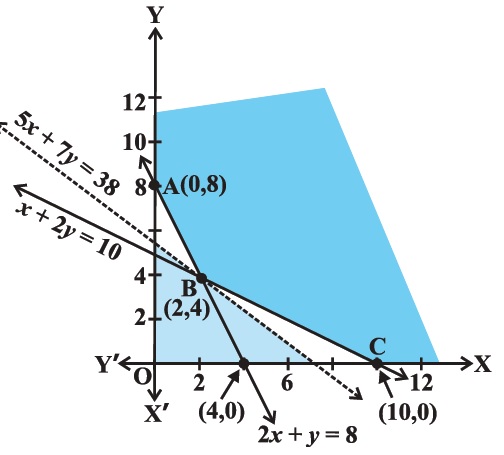
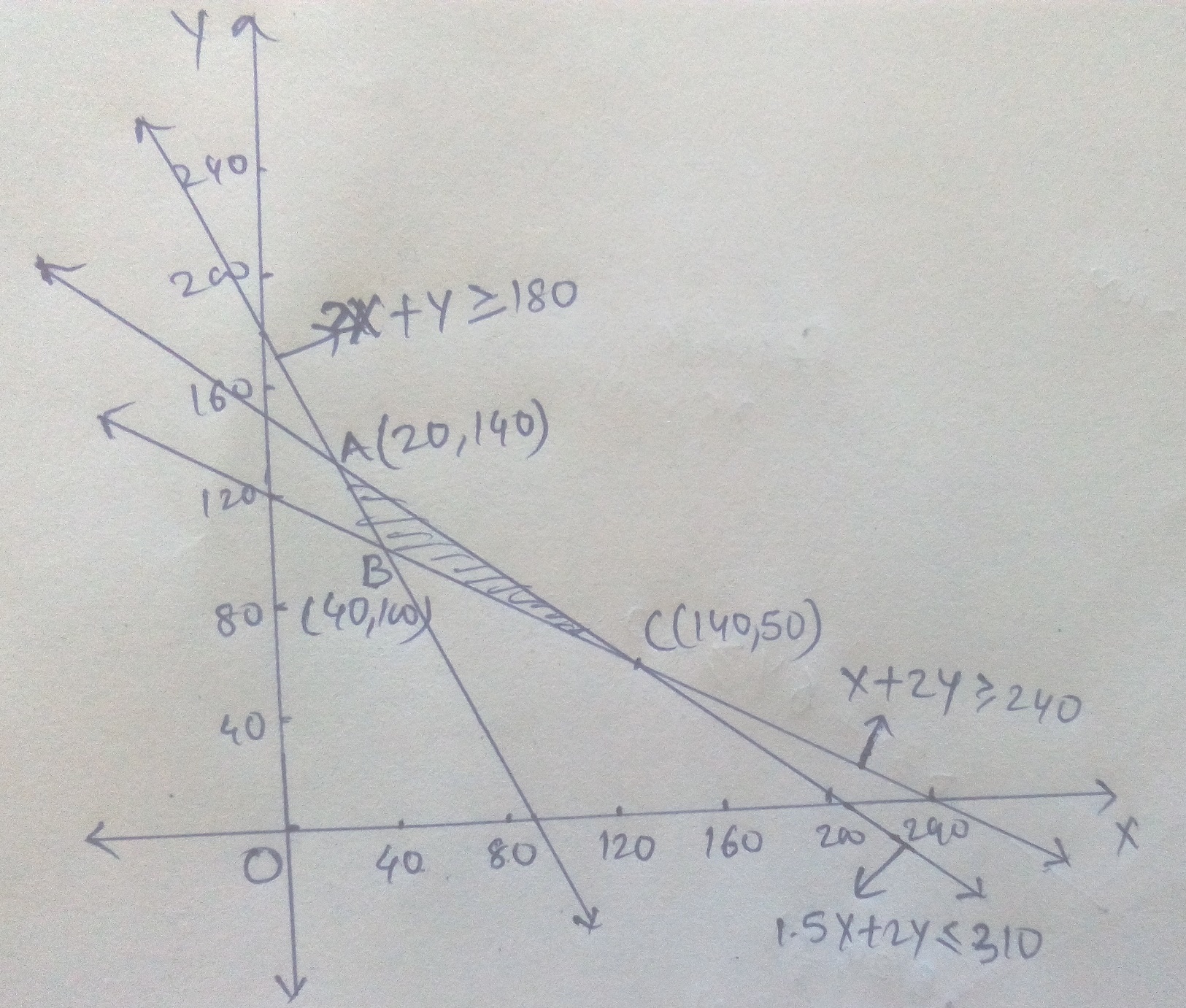
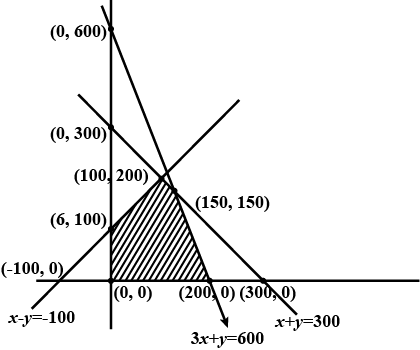
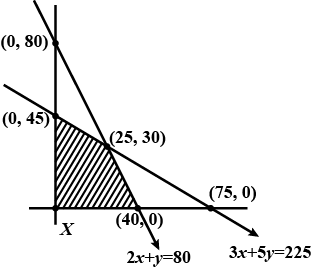
(Diet problem): A dietician wishes to mix two types of foods in such a way that vitamin contents of the mixture contain atleast $$8$$ units of vitamin A and $$10$$ units of vitamin C. Food I contains $$2$$ units/kg of vitamin A and $$1$$ unit/kg of vitamin C. Food II contains $$1$$ unit/kg of vitamin A and $$2$$ units/kg of vitamin C. It costs $$Rs 50$$ per kg to purchase Food I and $$Rs. 70$$ per kg to purchase Food II. Formulate this problem as a linear programming problem to minimise the cost of such a mixture.
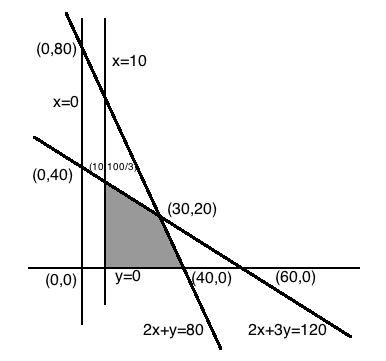
Solve the following linear programming problem using graphical method
Minimize: $$Z=60x+30y$$
Subject to:
$$2x+3y\ge 120$$
$$2x+y\ge 80$$
$$x\ge 0, y\ge 0$$
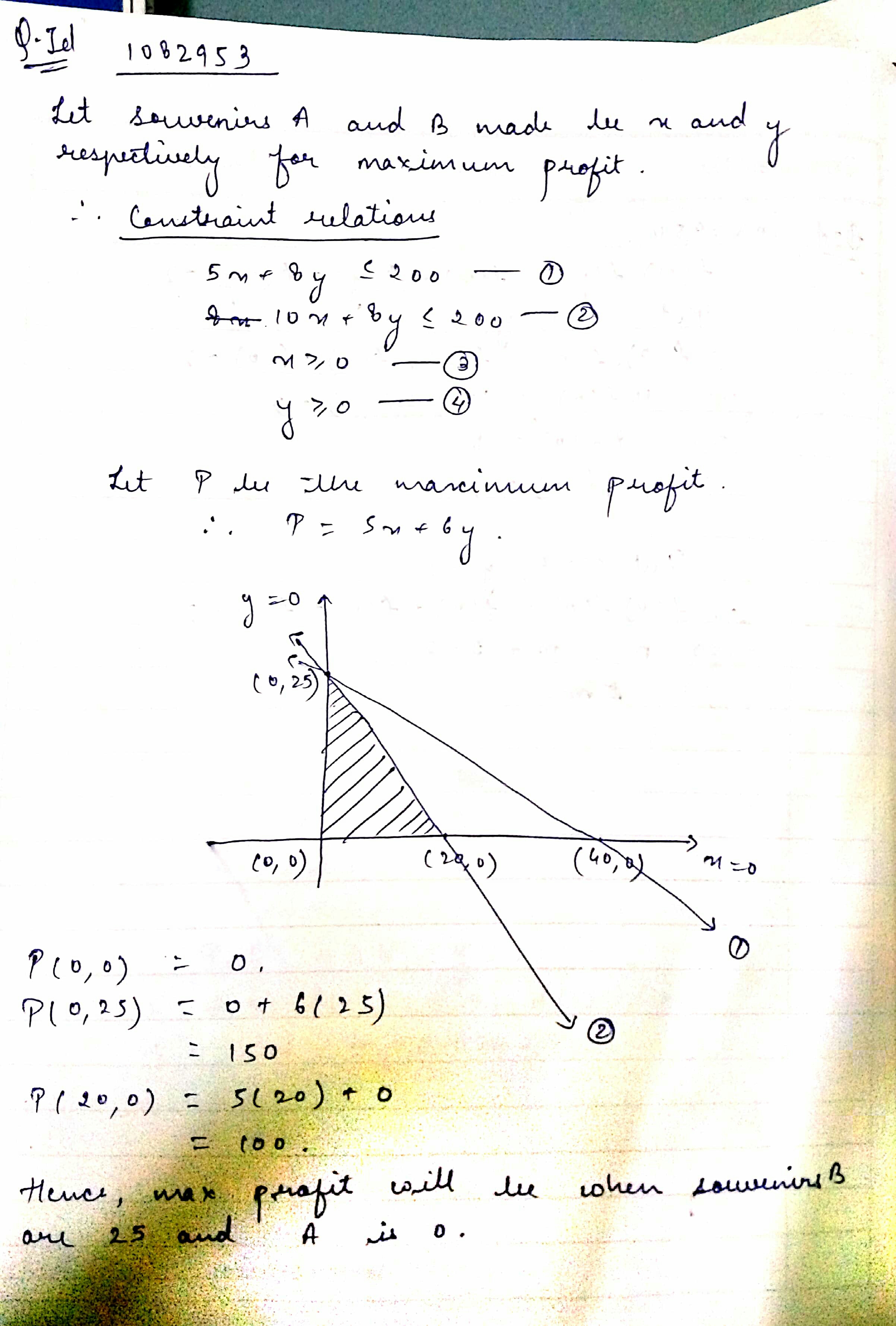
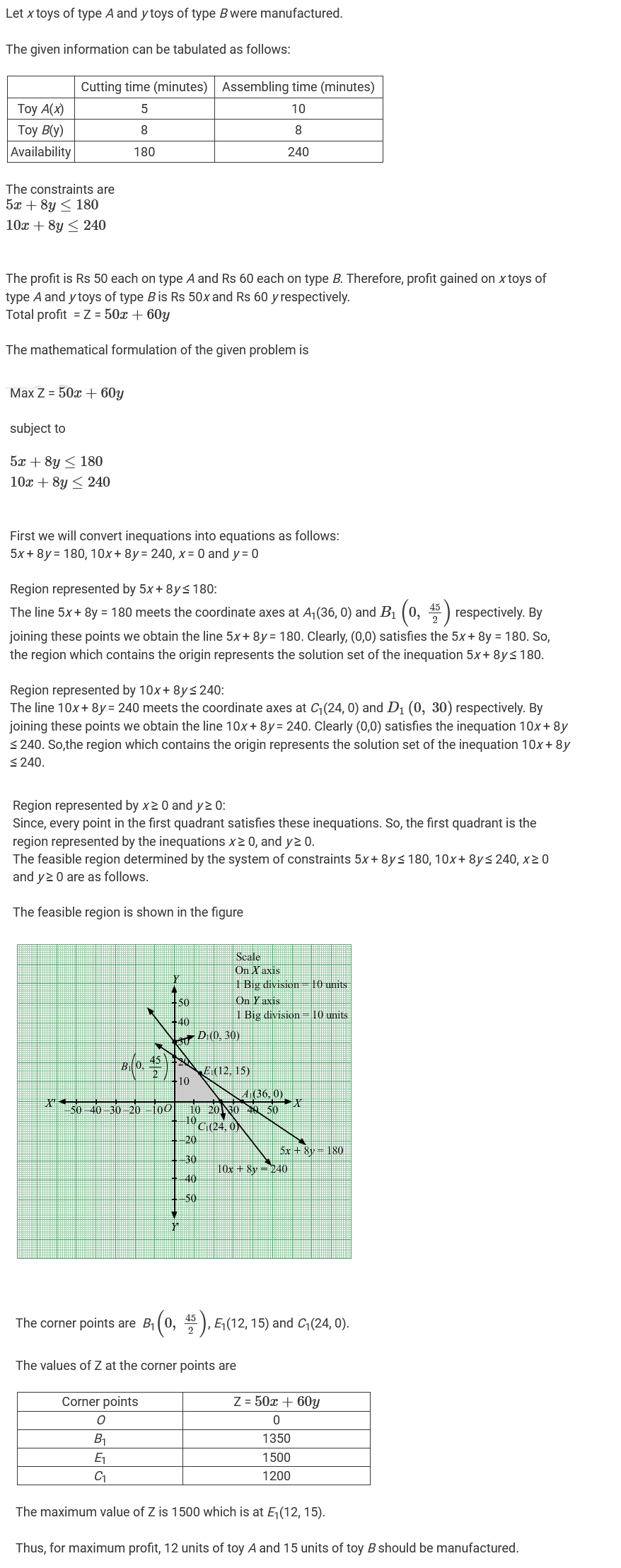
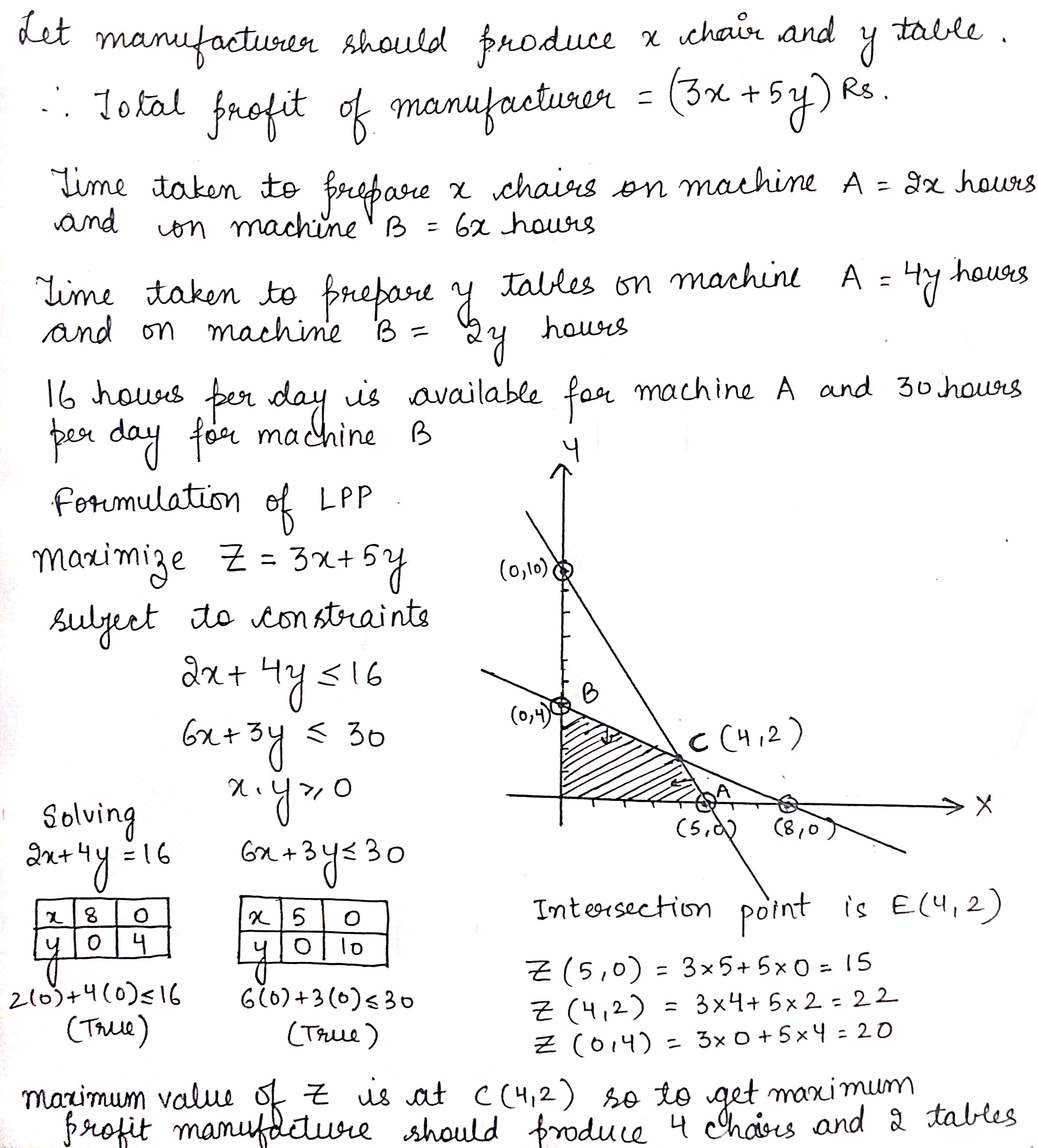
A company manufactures two types of novelty souvenirs made of plywood. Souvenirs of type A requires $$5$$ minutes each for cutting and $$10$$ minutes each for assembling. Souvenirs of type B requires $$8$$ minutes each for cutting and $$8$$ minutes each for assembling. There are $$3$$ hours $$20$$ minutes available for cutting and hours for assembling. The profit is Rs. $$5$$ each for type A and Rs. $$6$$ each for type B souvenirs. How many souvenirs of each type should the company manufacture in order to maximise the profit?
Find the maximum value of $$4x+7y$$ with the conditions $$3x+8y\leq 24, y\leq2, x\geq 0$$ and $$y\geq0$$.
A library has to accommodate two different types of books on a shelf. The books are $$6$$ cm and $$4$$ cm thick and weight $$1 $$ kg and $$1\dfrac{1}{2}$$ kg each respectively. The shelf is $$96$$ cm long and atmost can support a weight of $$21$$ kg. How should the shelf be filled with the books of two types in order to include greatest number of books. Make it a linear programming problem (LPP) .
The taxi fare in a city is as follows: For the first kilometre, the fare is $$Rs 8$$ and for the subsequence distance it is $$Rs 5 per Km$$. Taking the distance covered as $$x Km$$ and total fare as $$Rs y.$$ write linear equation for this information, and draw its graph.
Formulate this problem an LLP and solve it graphically.
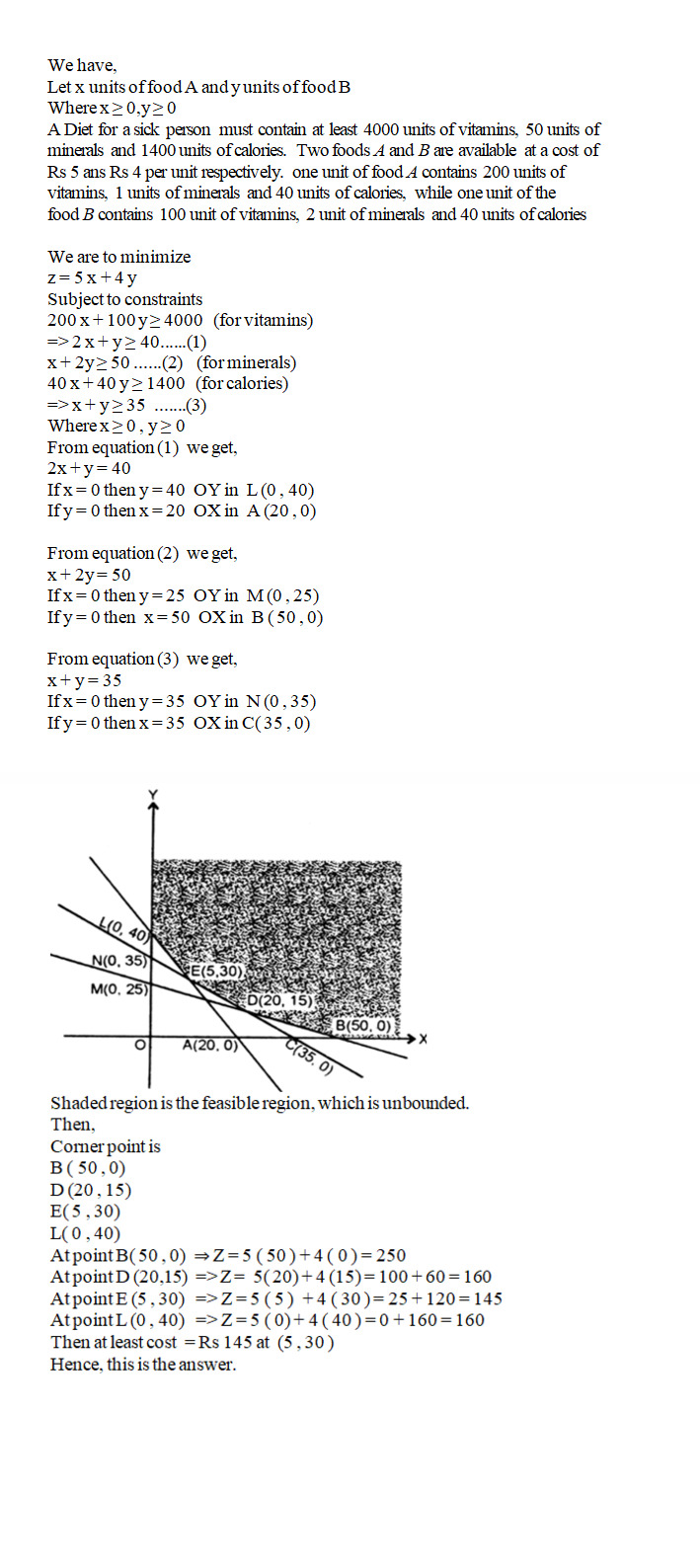
A Diet for a sick person must contain at least $$4000$$ units of vitamins, $$50$$ units of minerals and $$1400$$ units of calories. Two foods $$A$$ and $$B$$ are available at a cost of Rs $$5$$ ans Rs $$4$$ per unit respectively. one unit of food $$A$$ contains $$200$$ units of vitamins, $$1$$ units of minerals and $$40$$ units of calories, while one unit of the food $$B$$ contains $$100$$ unit of vitamins, $$2$$ unit of minerals and $$40$$ units of calories. Find what combination of the foods $$A$$ and $$B$$ should be used to have least cost, but it must satisfy the requirements of the sick person.. form the question as LLP and solve it graphically.
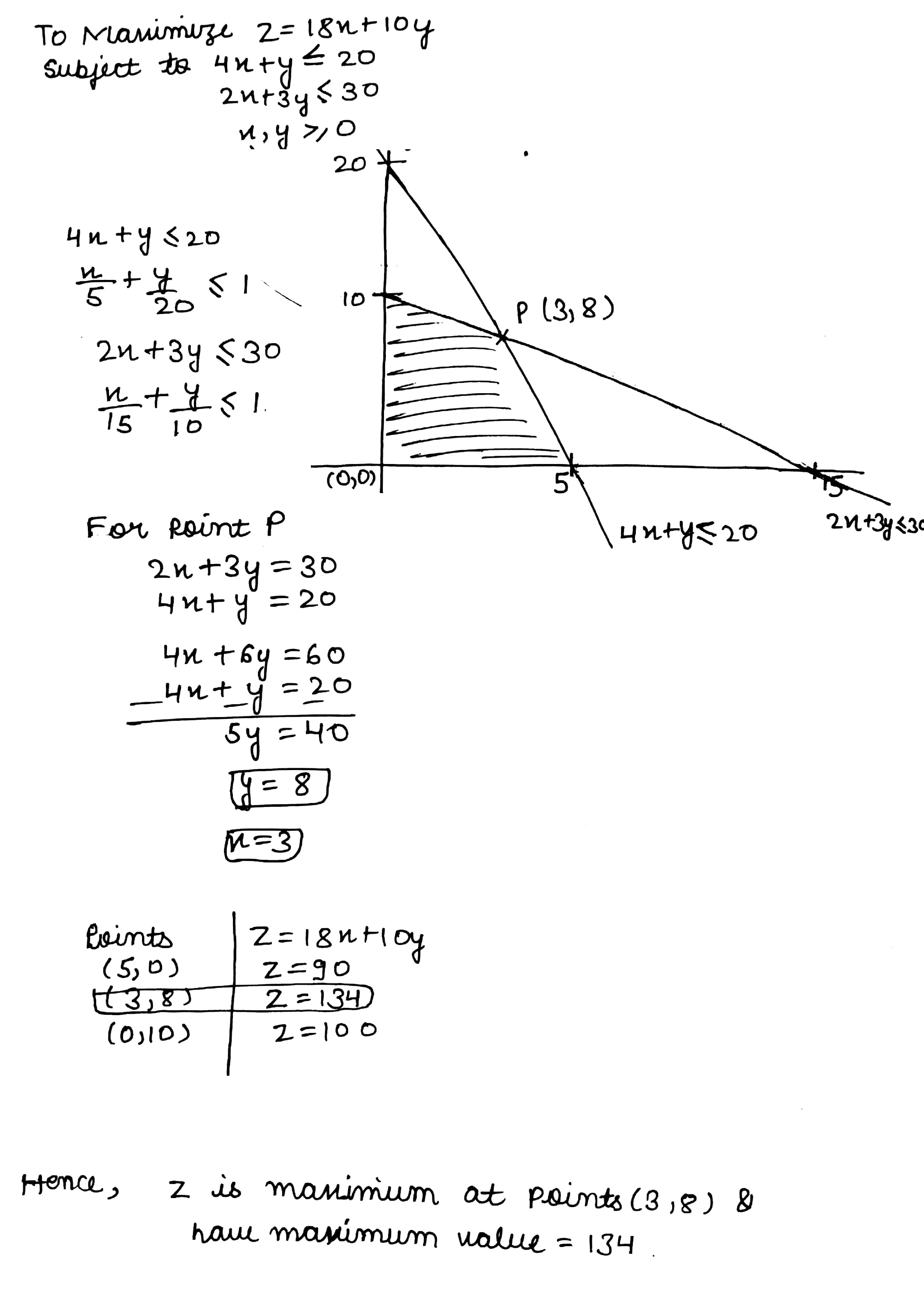
Solve each of the following linear programming problem by graphical method.
Maximize $$Z=18x+10y$$
Subject to $$4x+y\le 20$$
$$2x+3y\le 30$$
$$x,y\ge 0$$
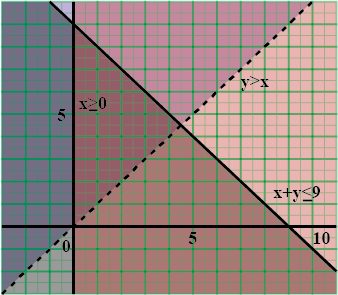
Solve the following systems of inequalities graphically: $$x+y\leq 9, y > x, x\geq
1$$
Solve $$3x+2y\leq 12, x+2y\leq 16, x+y\leq 10, x\geq 0, y\geq 0.$$
Suppose f is the collection of all ordered pairs of real numbers and x=6 is the first element of some ordered pair in f. Suppose the vertical line through x=6 intersects the graph of f twice. Is f a function? Why or why not?
A housewife wishes to mix together two kinds of food, $$X$$ and $$Y$$, in such a way that the mixture contains at least $$10$$ units of vitamin $$A$$, $$12$$ units of vitamin $$B$$ and $$8$$ units of vitamin $$C$$. The vitamin contents of one kg of food is given below :
| Vitamin A | Vitamin B | Vitamin C | |
| Food X | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Food Y | 2 | 2 | 1 |
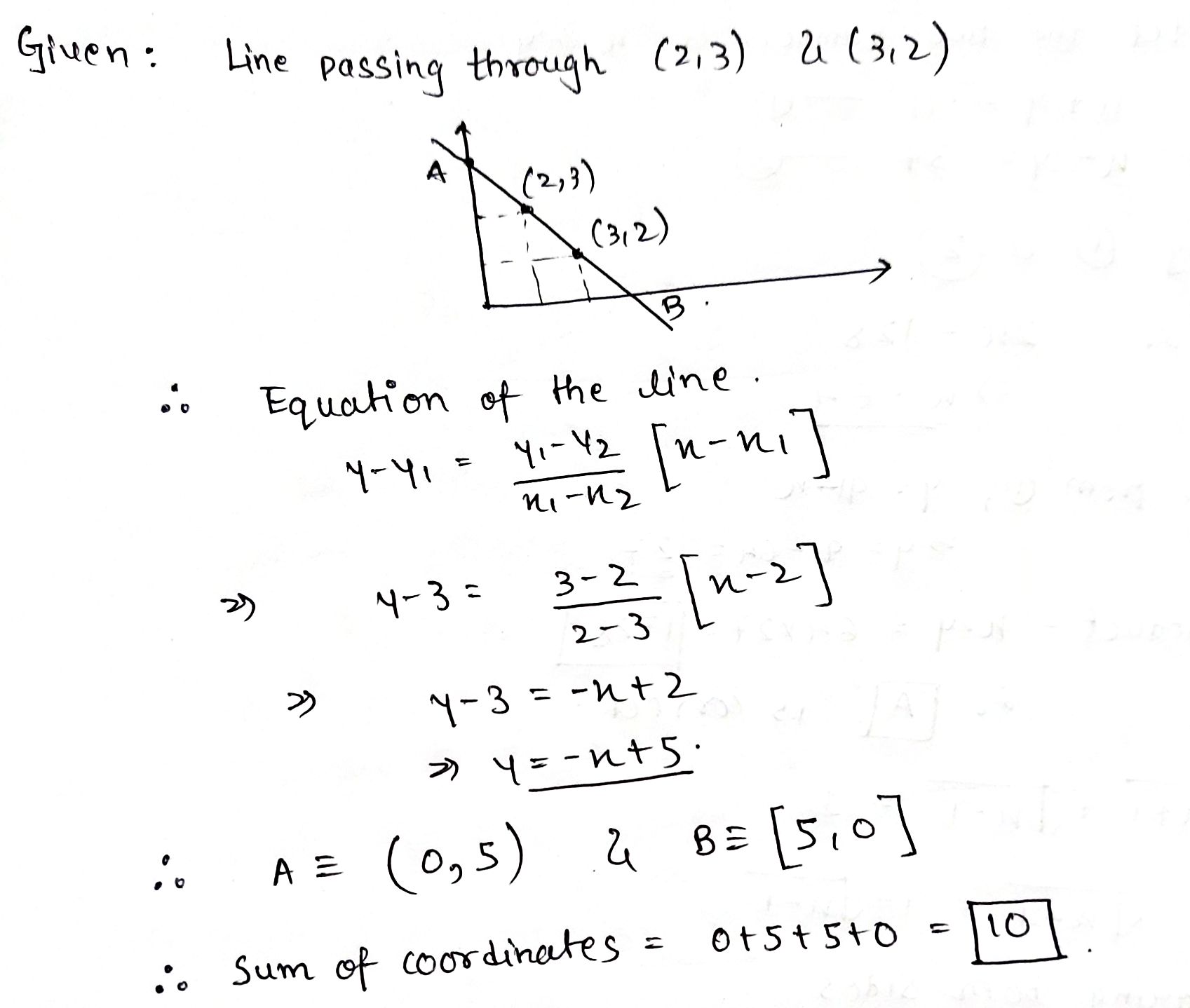
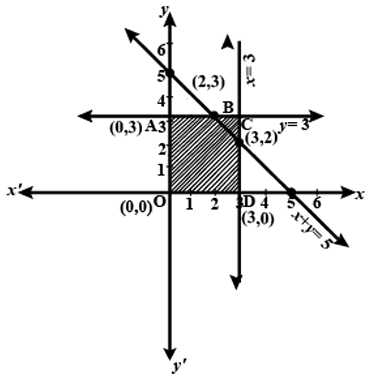
Draw the line passing through(2, 3) and (3,2). Find the sum of coordinates of the points at which this line meets the x-axis and y-axis.
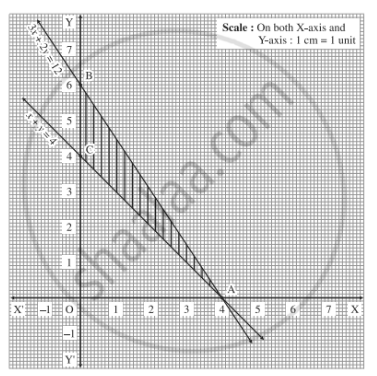
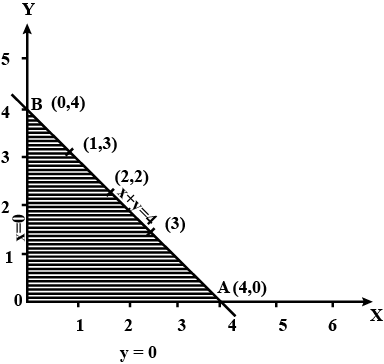
Solve $$4x + 3y > 12$$ graphically
Solve the following inequations $$\displaystyle \frac{2x+4}{x-1}\geq 5$$
Solve & graph the solution set of $$-2 < 2x - 4$$ and $$\displaystyle -2x+5\geq 13,x\: \epsilon \: R$$
A factory makes tennis rackets and cricket bats. A tennis racket takes $$1.5$$ hours of machine time and $$3$$ hours of craftsman's time in its making while a cricket bat takes $$3$$ hour of machine time and $$1$$ hour of craftsman's time. In a day, the factory has the availability of not more than $$42$$ hours of machine time and $$24$$ hours of craftsman's time.
If the profit on a racket and on a bat is Rs.$$20$$ and Rs.$$10$$ respectively, find the maximum profit of the factory when it works at full capacity
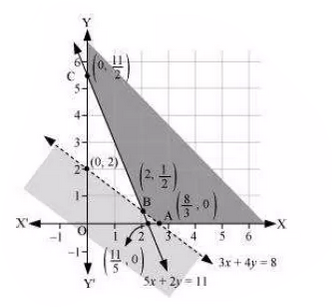
Reshma wishes to mix two types of food $$P$$ and $$Q$$ in such a way that the vitamin contents of the mixture contain at least $$8$$ units of vitamin $$A$$ and $$11$$ units of vitamin $$B$$. Food $$P$$ costs $$Rs.\ 60/kg$$ and Food $$Q$$ costs $$Rs.\ 80/kg$$. Food $$P$$ contains $$3\ units/kg$$ of vitamin $$A$$ and $$5\ units/kg$$ of vitamin $$B$$ while food $$Q$$ contains $$4\ units/kg$$ of vitamin $$A$$ and $$2\ units/kg$$ of vitamin $$B$$. Determine the minimum cost of the mixture.
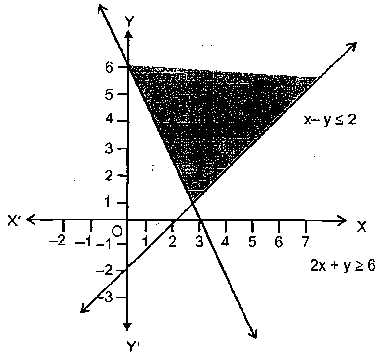
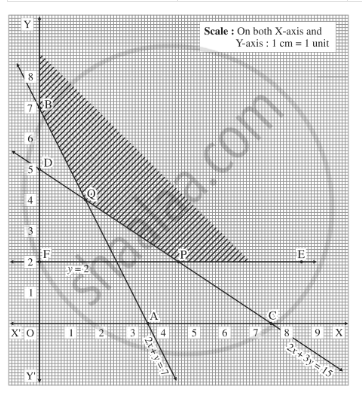
Solve the following system of linear inequality graphically
$$\displaystyle 2x+y\geq 6 $$ ......(1)
$$\displaystyle x-y\leq 2 $$ ......(2)
A diet is to contain at least $$80$$ units of vitamin $$A$$ and $$100$$ units of minerals. Two foods $${F}_{1}$$ and $${F}_{2}$$ are available. Food $${F}_{1}$$ costs Rs.$$4$$ per unit food and $${F}_{2}$$s costs Rs.$$6$$ per unit. One unit of food $${F}_{1}$$ contains $$3$$ units of vitamin $$A$$ and $$4$$ units of minerals. One unit of food $${F}_{2}$$ contains $$6$$ units of vitamin $$A$$ and $$3$$ units of minerals. Formulate this as a linear programming problem. Find the minimum cost for diet that consists of mixture of these two foods and also meets the mineral nutritional requirements?
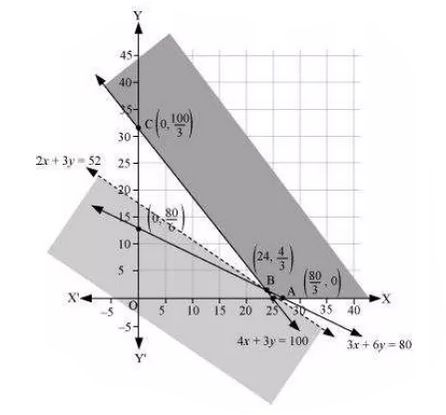
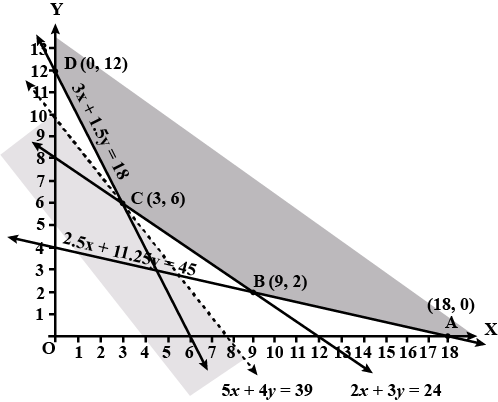
A farmer mixes two brands $$P$$ and $$Q$$ of cattle feed. Brand $$P$$, costing Rs.$$250$$ per bag contains $$3$$ units of nutritional element $$A$$, $$2.5$$ units of element $$B$$ and $$2$$ units of element $$C$$. Brand $$Q$$ costing Rs.$$200$$ per bag contains $$1.5$$ units of nutritional elements $$A$$, $$11.25$$ units of element $$B$$ and $$3$$ units of element $$C$$. The minimum requirements of nutrients $$A, B$$ and $$C$$ are $$18$$ units, $$45$$ units and $$24$$ units respectively. Determine the number of bags of each brand which should be mixed in order to produce a mixture having a minimum cost per bag> What is minimum cost of the mixture per bag?
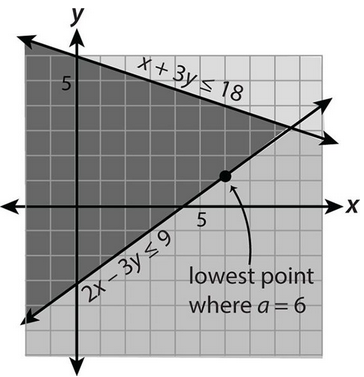
If $$S$$ is the solution region of the inequalities $$\begin{cases} x+3y\le 18 \\ 2x-3y\le 9 \end{cases}$$ and $$(a,b) \in S$$, then the minimum possible value for $$b$$ is
Solve the following systems of inequalities graphically: $$x+y\leq 9, y>x, x\geq 1$$.
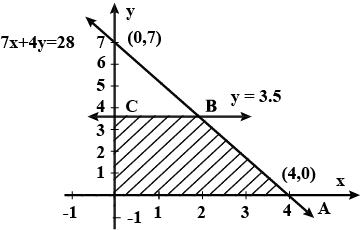
Maximize $$f=4x-y$$, subject to the constraints
$$7x+4y\le 28$$, $$2y\le 7$$, $$x\ge 0$$, $$y\ge 0$$.
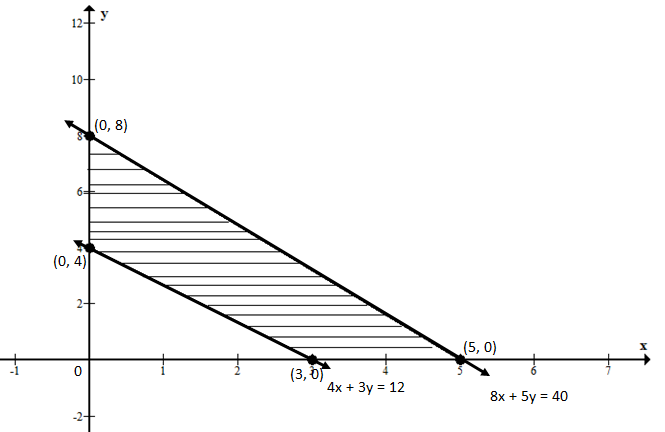
Maximize $$f=3x+y$$ subject to the constraints
$$8x+5y\le 40$$; $$4x+3y\ge 12$$; $$x\ge 0$$ and $$y\ge 0$$.
A firm has the cost function $$C = \dfrac {x^{3}}{3} - 7x^{2} + 111x + 50$$ and demand function $$x = 100 - p$$.
Formulate the total profit function $$P$$ in terms of $$x$$
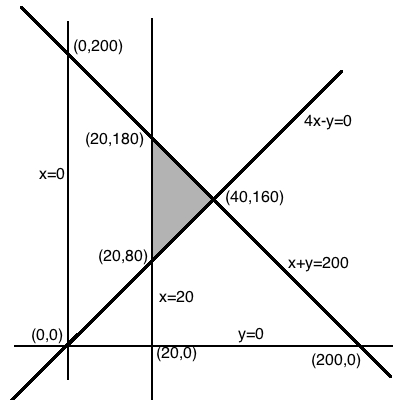
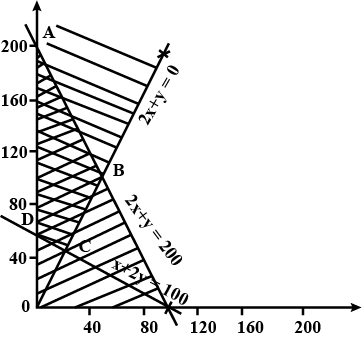
By graphical method solve the following linear programming problem for maximization.
Objective function Z = 1000 x + 600 y
Constraints $$x + y \leq 200$$
$$4x - y \leq 0$$
$$x \geq 20, x \geq 0, y \geq 0$$.
A firm has the cost function $$C = \dfrac {x^{3}}{3} - 7x^{2} + 111x + 50$$ and demand function $$x = 100 - p$$.
Write the total revenue function in terms of $$x$$
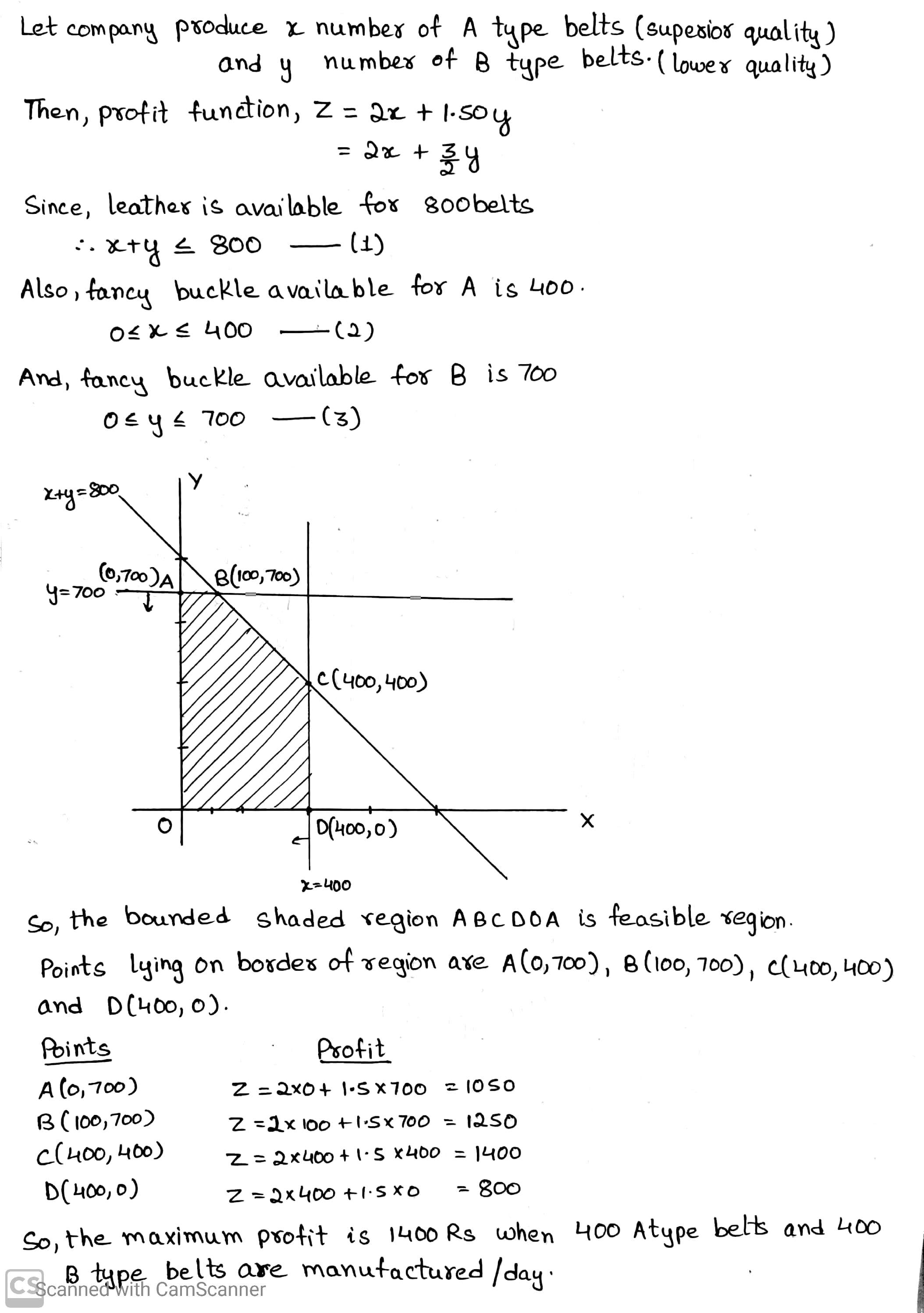
A shopkeeper sells not more than $$30$$ shirts of each colour. Atleast twice as many white ones are sold as green ones. If the profit on each of the white be Rs. $$20$$ and that of green be Rs. $$25$$; then find out how many of each kind be sold to give him a maximum profit. (Graph need not be drawn)
A sweet-shop makes gift packet of sweets by combining two special types of sweets $$A$$ and $$B$$ which weigh $$7\ kg$$. Atleast $$3\ kg$$ of $$A$$ and no more than $$5\ kg$$ of $$B$$ should be used. The shop makes a profit of Rs. $$15$$ on $$A$$ and Rs. $$20$$ on $$B$$ per $$kg$$. Determine the product mix so as to obtain maximum profit.
a) A manufacturing company makes two models $$A$$ and $$B$$ of a product. Each piece of model $$A$$ requires $$9$$ labor hours for fabricating and $$1$$ labor hour for finishing. Each piece of model $$B$$ requires $$12$$ labor hours for finishing and $$3$$ labor hours for finishing. For fabricating and finishing, the maximum labor hours available are: $$180$$ and $$30$$ respectively. The company makes a profit of Rs. $$8000$$ on each piece of model $$A$$ and Rs. $$12000$$ on each piece of model $$B$$. How many pieces of model $$A$$ and model $$B$$ should be manufactured per week to realize a maximum profit? What is the maximum profit per week?
b) Find the value of $$K$$ so that the function $$f (x) = \begin{matrix} \begin{cases}Kx+1, & \text{if }x \le 5 \\ 3x-5, & \text{if }x \le 5\end{cases}\end{matrix}$$ at $$x=5$$ is a continuous function.
Solve the following L.P.P. by graphical method:
Maximise: $$Z = 6x + 4y$$
Subject to $$x\leq 2, x + y \leq 3, -2x + y \leq 1, x \geq 0, y \geq 0$$
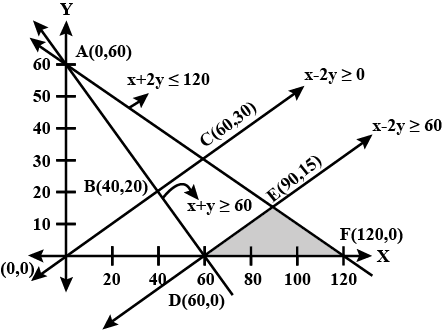
Solve the following linear programming problem graphically:
Maximize $$Z = 7x + 10y$$
subject to the constraints
$$4x + 6y \leq 240$$
$$6x + 3y \leq 240$$
$$x \geq 10$$
$$x \geq 0, y \geq 0$$
Consider the linear inequalities
$$2x+3y\le 6, 2x+y\le 4, x\ge 0, y\ge 0$$
(a) Mark the feasible region.
(b) Maximise the function $$z=4x+5y$$ subject to the given constraints.
Solve graphically the linear inequalities
$$2x+3y\le 7,x+2y\le 4$$
$$x\ge 0,y\ge 0 $$
If $$z=6x+5y$$ is the objective function, find its maximum value.
In a factory, there are two machines $$A$$ and $$B$$ producing toys. They respectively produce $$60$$ and $$80$$ units in one hour. $$A$$ can run a maximum of $$10$$ hours and $$B$$ a maximum of $$7$$ hours a day. The cost of their running per hour respectively amounts to $$2,000$$ and $$2,500$$ rupees. The total duration of working these machines cannot exceed $$12$$ hours a day. If the total cost cannot exceed Rs. $$25,000$$ per day and the total daily production is at least $$800$$ units, then formulate the problem mathematically.
A furniture shop keeper deals only Teak and Rosewood tables which costs Rs. $$25,000$$ and Rs. $$40,000$$ respectively. His shop can contain a maximum of $$250$$ tables. The profit that he gets on these items are respectively Rs. $$4,500$$ and Rs. $$5000$$.
He plans to invest a maximum of Rs. $$70$$ lakhs in his business.
(i) Formulate this problem.
(ii) Write the objective function if he wishes to make maximum profit.
Define feasible region.
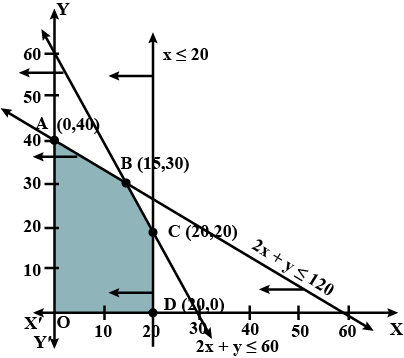
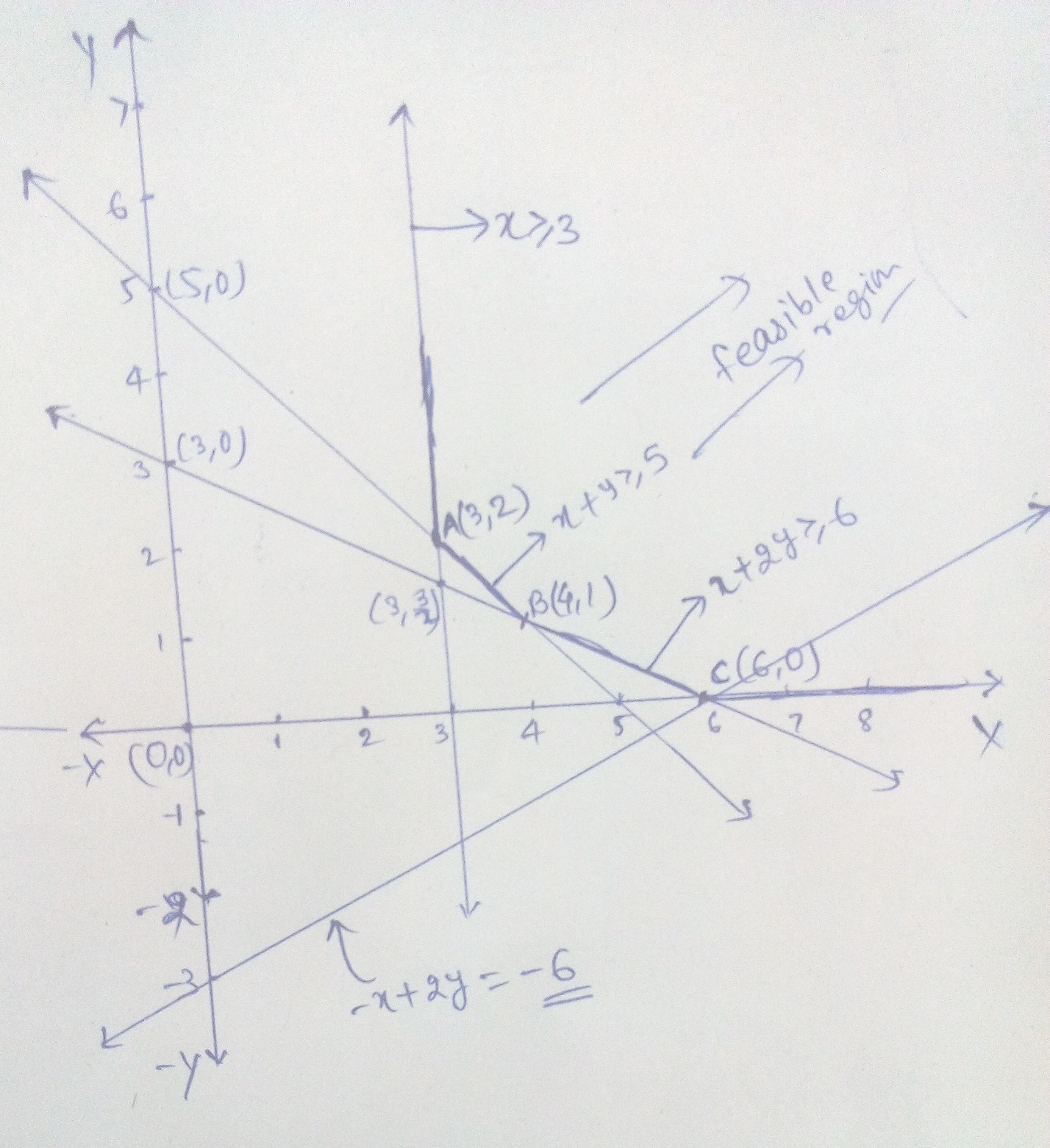
Consider the following L.P.P.
Maximize $$Z=3x+2y$$
Subject to the constraints
$$x+2y\le 10$$
$$3x+y\le 15$$
$$x,y\ge 0$$
(a) Draw its feasible region.
(b) Find the corner points of the feasible region.
(c) Find the maximum value of $$Z$$.
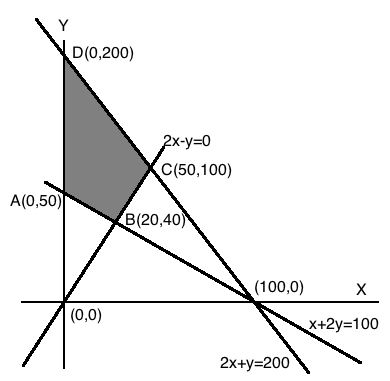
a) Minimize and maximize $$Z=x+2y$$, subject to the constraints
$$x+2y \ge 100$$
$$2x-y \le 0$$
$$2x+y \le 200$$
$$x,y \ge 0$$ by graphical method.
b) Prove that $$\begin{vmatrix}b+c&a&a\\b&c+a&b\\c&c&a+b\end{vmatrix}=4abc$$
By Graphical method solve the following L.P.P under the following constraints.
$$x+y\le 24,2x+y\le 32,x,y\ge 0$$. Find the maximum value of $$z=150x+250y$$
A toy company manufactures two types of doll; a basic version-doll $$A$$ and a deluxe version doll $$B$$. Each doll of type $$B$$ takes twice as long as to produce as one of type $$A$$, and the company would have time to make a maximum of $$2000$$ per day if it produces only the basic version. The supply of plastic is sufficient to produce $$1500$$ dolls per day (both $$A$$ and $$B$$ combined). The deluxe version requires a fancy dress of which there are only $$600$$ per day available. If company makes profit of $$Rs. 3$$ and $$Rs. 5$$ per doll, respectively, on doll $$A$$ and $$B$$; how many each should be produced per day in order to maximize profit.
A farmer has a supply of chemical fertilizer of type $$A$$ which contains $$10\%$$ nitrogen and $$6\%$$ phosphoric acid and of type $$B$$ which contains $$5\%$$ nitrogen and $$10\%$$ phosphoric acid. After soil test, it is found that at least $$7$$ kg of nitrogen and same quantity of phosphoric acid is required for a good crop. The fertilizer of type $$A$$ costs Rs. $$5.00$$ per kg and the type $$B$$ costs Rs. $$8.00$$ per kg. Using Linear programming, find how many kilograms of each type of the fertilizer should be bought to meet the requirement and for the cost to be minimum. Find the feasible region in the graph.
Solve the linear programming problem by graphical method with the following restrictions.
$$3x+5y \leq 5; 5x+2y\leq 10; x\geq 0, y\geq 0$$ and maximize $$Z=5x+3y$$.
Show the solution of the problem of linear programming under the following restrictions by graphical method: $$x+y\leq 4, x \geq 0, y\geq 0$$.
A factory makes tennis rackets and cricket bats. A tennis racket takes $$1.5$$ hours of machine time and $$3$$ hours of craftmans time in its making while a cricket bat takes $$3$$ hour of machine time and $$1$$ hour of craftmans time. In a day, the factory has the availability of not more than $$42$$ hours of machine time and $$24$$ hours of craftsmans time.
(i) What number of rackets and bats must be made if the factory is to work at full capacity?
(ii) If the profit on a racket and on a bat is $$Rs. 20$$ and $$Rs. 10$$ respectively, find the maximum profit of the factory when it works at full capacity.
(Manufacturing problem) A manufacturer has three machines I, II and III installed in his factory. Machines I and II are capable of being operated for at most $$12$$ hours whereas machine III must be operated for atleast $$5$$ hours a day. She produces only two items $$M$$ and $$N$$ each requiring the use of all the three machines.
The number of hours required for producing $$1$$ unit of each of $$M$$ and $$N$$ on the three machines are given in the following table:
| Items | Number of hours required on machines | ||
| I | II | III | |
| $$M$$ | $$1$$ | $$2$$ | $$1$$ |
| $$N$$ | $$2$$ | $$1$$ | $$1.25$$ |
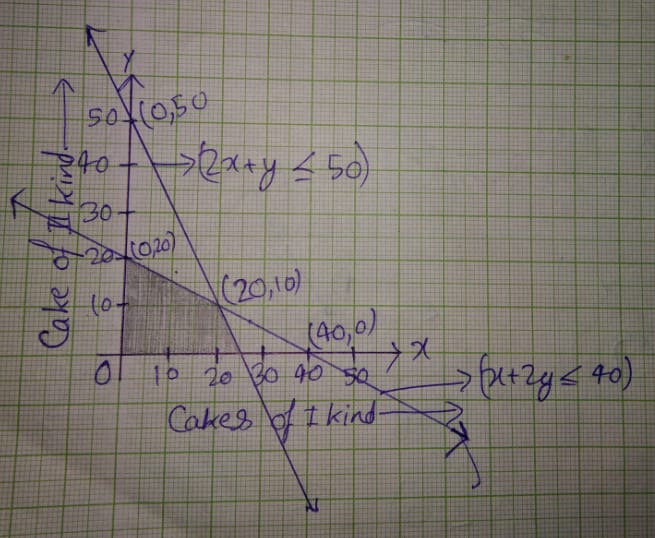
One kind of cake requires $$200g$$ of flour and $$25g$$ of fat, and another kind of cake requires $$100g$$ of flour and $$50g$$ of fat. Find the maximum number of cakes that can be made from $$5kg$$ of flour and $$1\ kg$$ of fat assuming that there is no shortage of the other ingredients used in making the cakes.
(Manufacturing problem) A manufacturing company makes two models $$A$$ and $$B$$ of a product. Each piece of Model $$A$$ requires $$9$$ labour hours for fabricating and $$1$$ labour hour for finishing. Each piece of Model $$B$$ requires $$12$$ labour hours for fabricating and $$3$$ labour hours for finishing. For fabricating and finishing, the maximum labour hours available are $$180$$ and $$30$$ respectively. The company makes a profit of $$Rs. 8000$$ on each piece of model $$A$$ and $$Rs. 12000$$ on each piece of Model $$B$$. How many pieces of Model $$A$$ and Model $$B$$ should be manufactured per week to realise a maximum profit? What is the maximum profit per week?
(Allocation problem) A cooperative society of farmers has $$50$$ hectare of land to grow two crops $$X$$ and $$Y$$. The profit from crops $$X$$ and $$Y$$ per hectare are estimated at $$Rs. 10,500$$ and $$Rs. 9,000$$ respectively. To control weeds, a liquid herbicide has to be used for crops $$X$$ and $$Y$$ at rates of $$20$$ litres and $$10$$ litres per hectare. Further, no more than $$800$$ litres of herbicide should be used in order to protect fish and wildlife using a pond which collects drainage from this land. How much land should be allocated to each crop so as to maximise the total profit of the society?
Solve the following Linear Programming Problems graphically:
Minimise $$Z = -3x + 4y$$
subject to $$x + 2y\leq 8, 3x + 2y \leq 12, x\geq 0, y \geq 0$$.
Solve the following Linear Programming Problems graphically:
Maximise $$Z = 5x + 3y$$
subject to $$3x + 5y\leq 15, 5x + 2y \leq 10, x \geq 0, y \geq 0$$.
Solve the following Linear Programming Problems graphically :
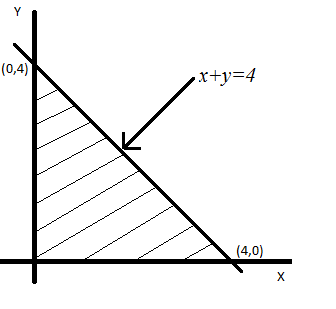
Minimize $$Z = 3x + 5y$$
subject to $$x + y \leq 4, x \geq 0$$ and $$y \ge 0$$
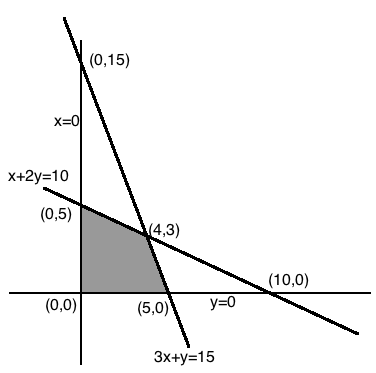
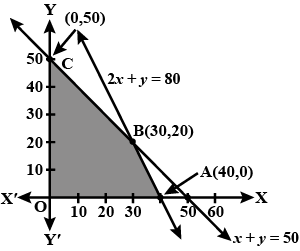
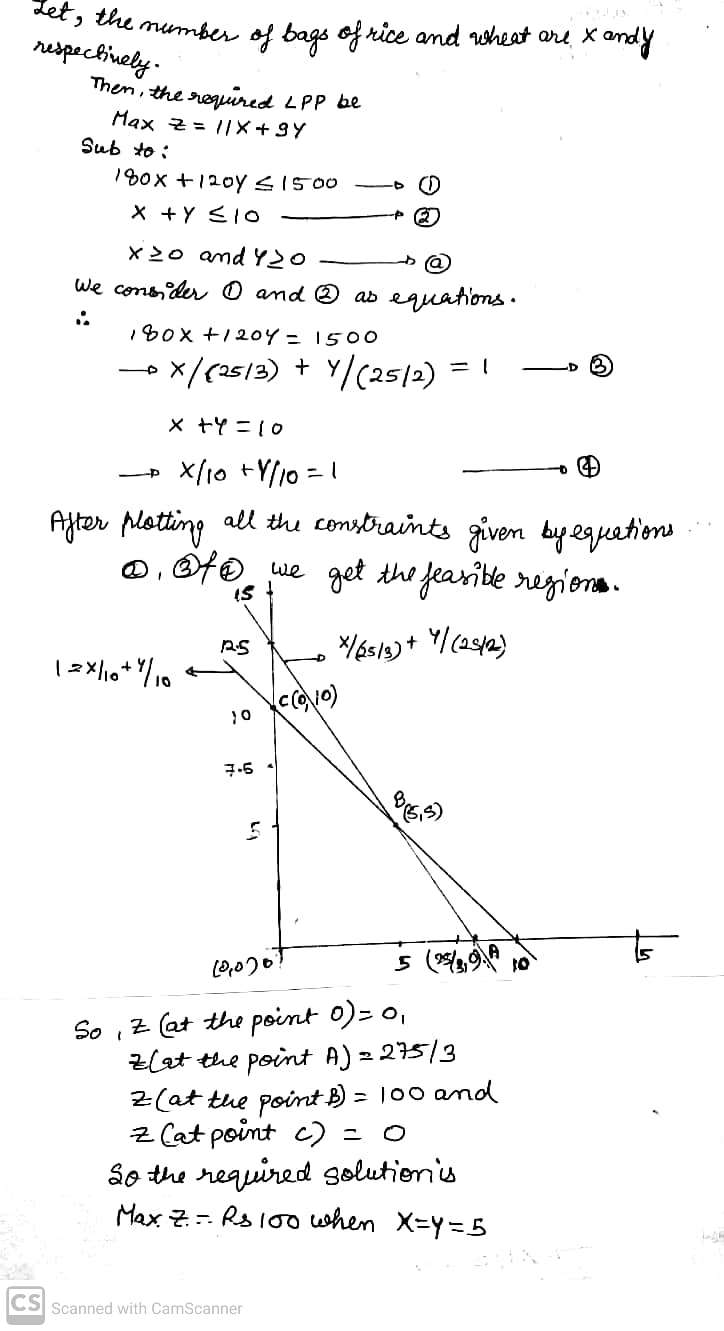
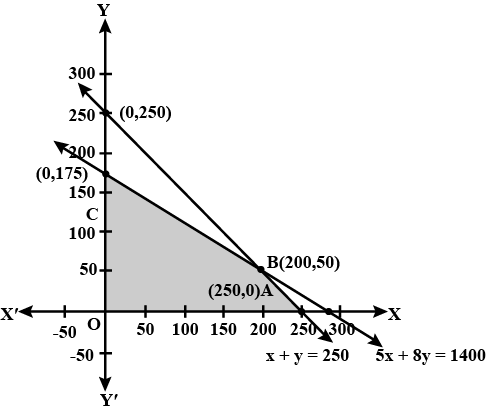
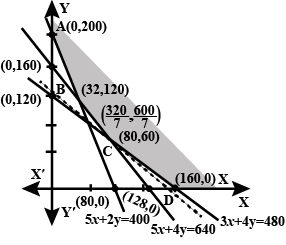
Solve the following linear programming problem graphically :
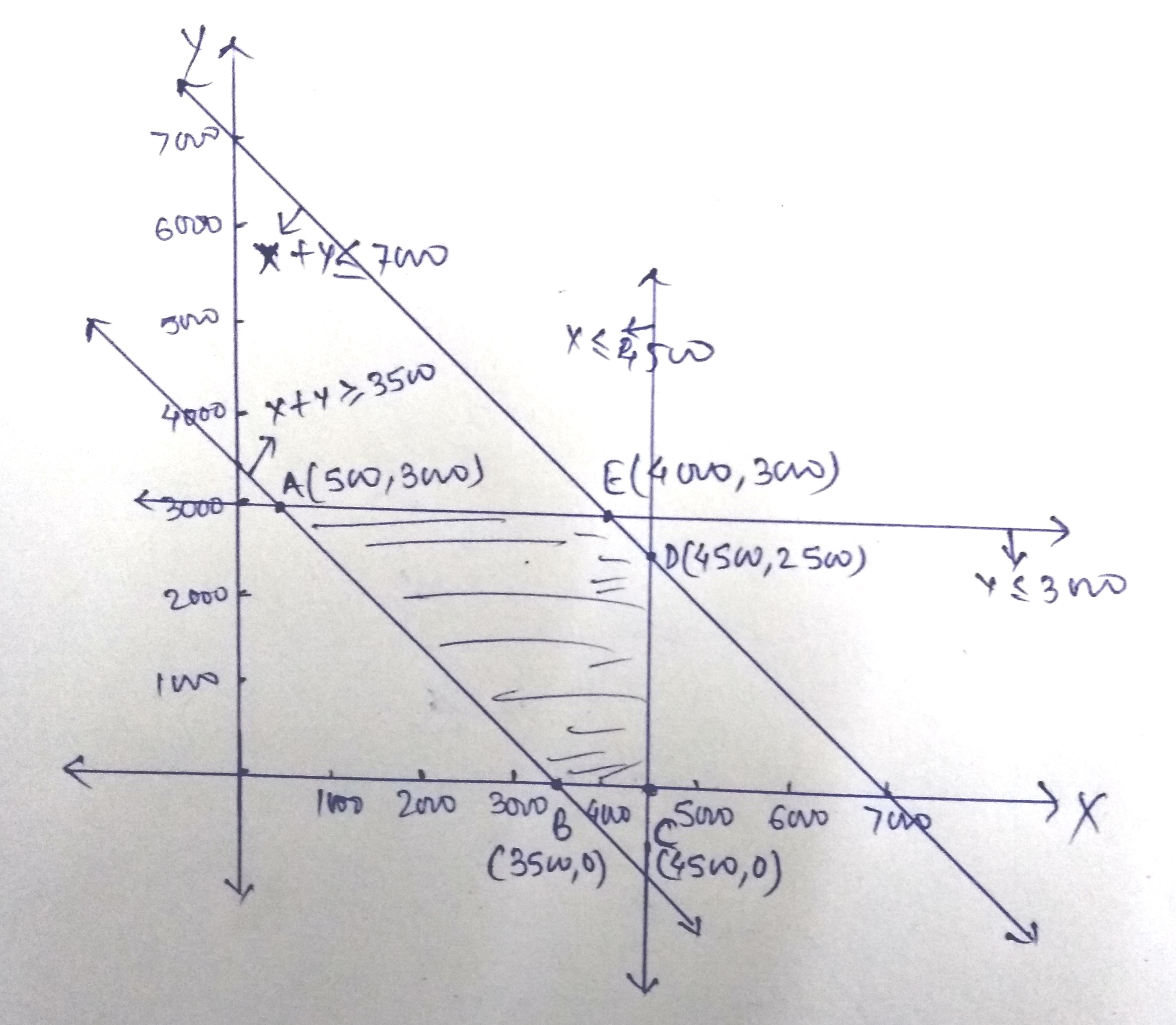
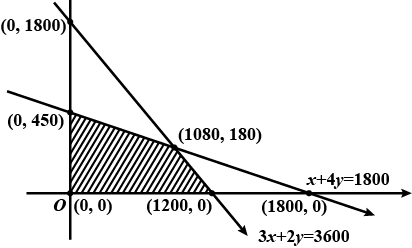
Minimise $$Z = 200 x + 500 y ... (1)$$
subject to the constraints:
$$x + 2y \geq 10 ... (2)$$
$$3x + 4y \leq 24 ... (3)$$
$$x \geq 0, y \geq 0 ... (4)$$.
A manufacturer makes two types of toys $$A$$ and $$B$$. Three machines are needed for this purpose and the time (in minutes) required for each toy on the machines is given below:
| Types of Toys | Machines | Machines | Machines |
| I | II | III | |
| $$A$$ | $$12$$ | $$18$$ | $$6$$ |
| $$B$$ | $$6$$ | $$0$$ | $$9$$ |
Two godowns $$A$$ and $$B$$ have grain capacity of $$100$$ quintals and $$50$$ quintals respectively. They supply to $$3$$ ration shops, $$D, E$$ and $$F$$ whose requirements are $$60, 50$$ and $$40$$ quintals respectively. The cost of transportation per quintal from the godowns to the shops are given in the following table:
| Transportation cost per quintal (in Rs) | ||
| From/ To | $$A$$ | $$B$$ |
| $$D$$ | $$6$$ | $$4$$ |
| $$E$$ | $$3$$ | $$2$$ |
| $$F$$ | $$2.50$$ | $$3$$ |
A manufacturer produces nuts and bolts. It takes $$1$$ hour of work on machine $$A$$ and $$3$$ hours on machine $$B$$ to produce a package of nuts. It takes $$3$$ hours on machine $$A$$ and $$1$$ hour on machine $$B$$ to produce a package of bolts. He earns a profit of $$Rs. 17.50$$ per package on nuts and $$Rs. 7.00$$ per package on bolts. How many packages of each should be produced each day so as to maximise his profit, if he operates his machines for at the most $$12$$ hours a day?
A dietician wishes to mix together two kinds of food $$X$$ and $$Y$$ in such a way that the mixture contains at least $$10$$ units of vitamin A, $$12$$ units of vitamin B and $$8$$ units of vitamin C. The vitamin contents of one kg food is given below:
| Food | Vitamin A | Vitamin B | Vitamin C |
| $$X$$ | $$1$$ | $$2$$ | $$3$$ |
| $$Y$$ | $$2$$ | $$2$$ | $$1$$ |
There are two types of fertilisers $$F_{1}$$ and $$F_{2}\cdot F_{1}$$ consists of $$10$$% nitrogen and $$6$$%phosphoric acid and $$F_{2}$$ consists of $$5$$% nitrogen and $$10$$% phosphoric acid. After testing the soil conditions, a farmer finds that she needs atleast $$14\ kg$$ of nitrogen and $$14\ kg$$ of phosphoric acid for her crop. If $$F_{1}$$ costs $$Rs. 6/kg$$ and $$F_{2}$$ costs $$Rs. 5/kg$$, determine how much of each type of fertiliser should be used so that nutrient requirements are met at a minimum cost. What is the minimum cost?
Use the graphical method to solve each of the following LP problems.
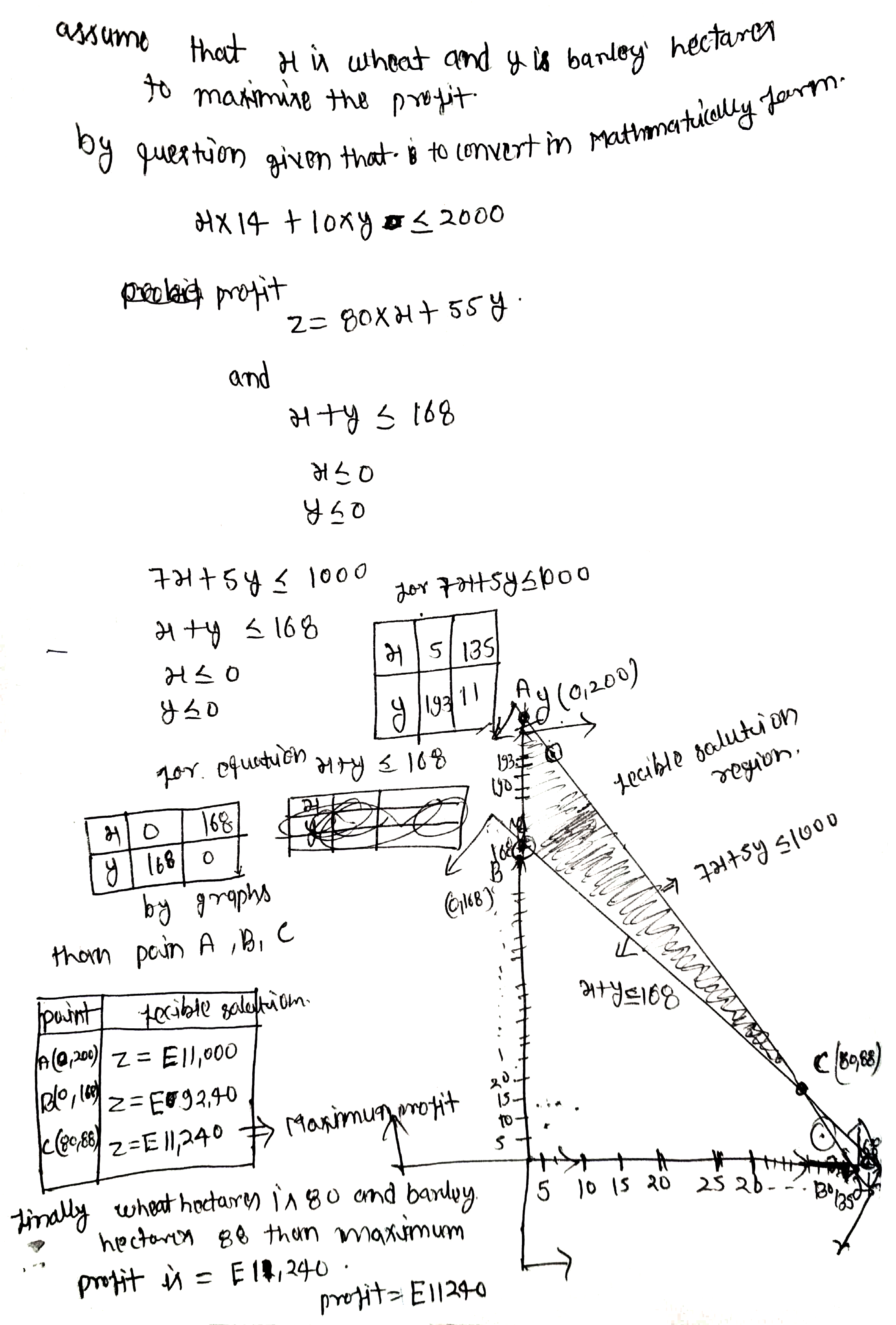
LESCO Engineering produces chairs and tables. Each table takes four hours of labour from the carpentry department and two hours of labour from the finishing department. Each chair requires three hours of carpentry and one hour of finishing. During the current week, $$240$$ hours of carpentry time are available and $$100$$ hours of finishing time. Each table produced gives a profit of $$E70$$ and each chair a profit of $$E50$$. How many chairs and tables should be made in order to maximize profit?
If the grower wants to maximise the amount of nitrogen added to the garden, how many bags of each brand should be added? What is the maximum amount of nitrogen added?
A cottage industry manufactures pedestal lamps and wooden shades, each requiring the use of a grinding/cutting machine and a sprayer. It takes $$2$$ hours on grinding/cutting machine and $$3$$ hours on the sprayer to manufacture a pedestal lamp. It takes $$1$$ hour on the grinding/cutting machine and $$2$$ hours on the sprayer to manufacture a shade. On any day, the sprayer is available for at the most $$20$$ hours and the grinding/cutting machine for at the most $$12$$ hours. The profit from the sale of a lamp is $$Rs. 5$$ and that from a shade is $$Rs. 3$$. Assuming that the manufacturer can sell all the lamps and shades that he produces, how should he schedule his daily production in order to maximise his profit?
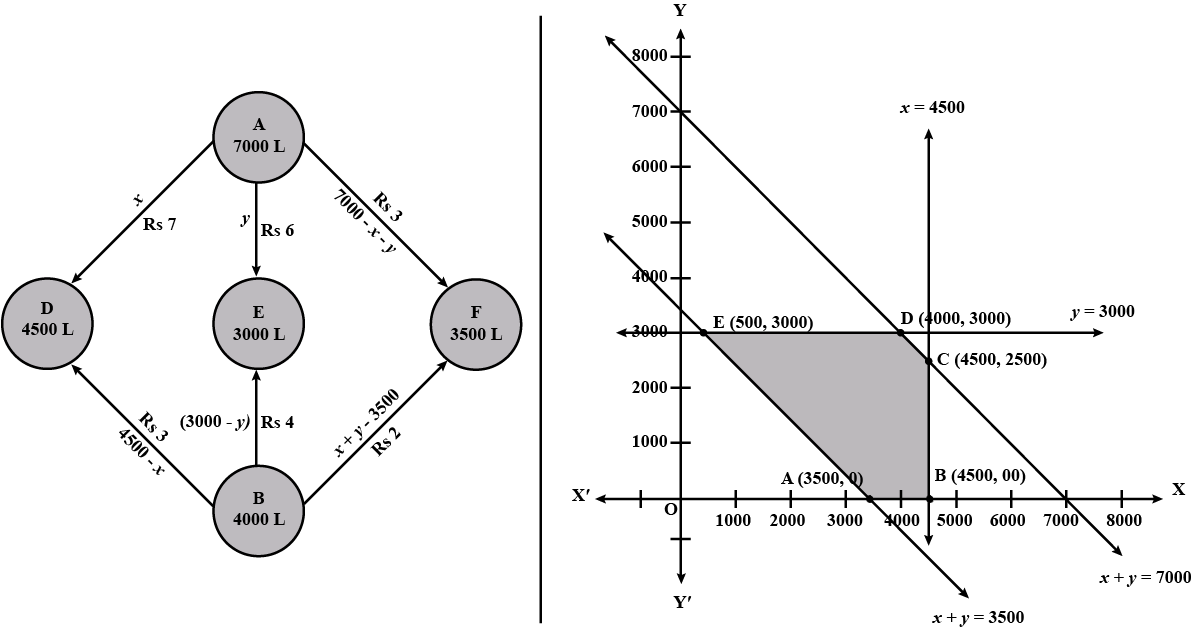
An oil company has two depots $$A$$ and $$B$$ with capacities of $$7000\ L$$ and $$4000\ L$$ respectively. The company is to supply oil to three petrol pumps, $$D, E$$ and $$F$$ whose requirements are $$4500L, 3000L$$ and $$3500L$$ respectively. The distances (in km) between the depots and the petrol pumps is given in the following table:
| Distance in (km.) | ||
| From/ To | $$A$$ | $$B$$ |
| $$D$$ | $$7$$ | $$3$$ |
| $$E$$ | $$6$$ | $$4$$ |
| $$F$$ | $$3$$ | $$2$$ |
What is the minimum cost?
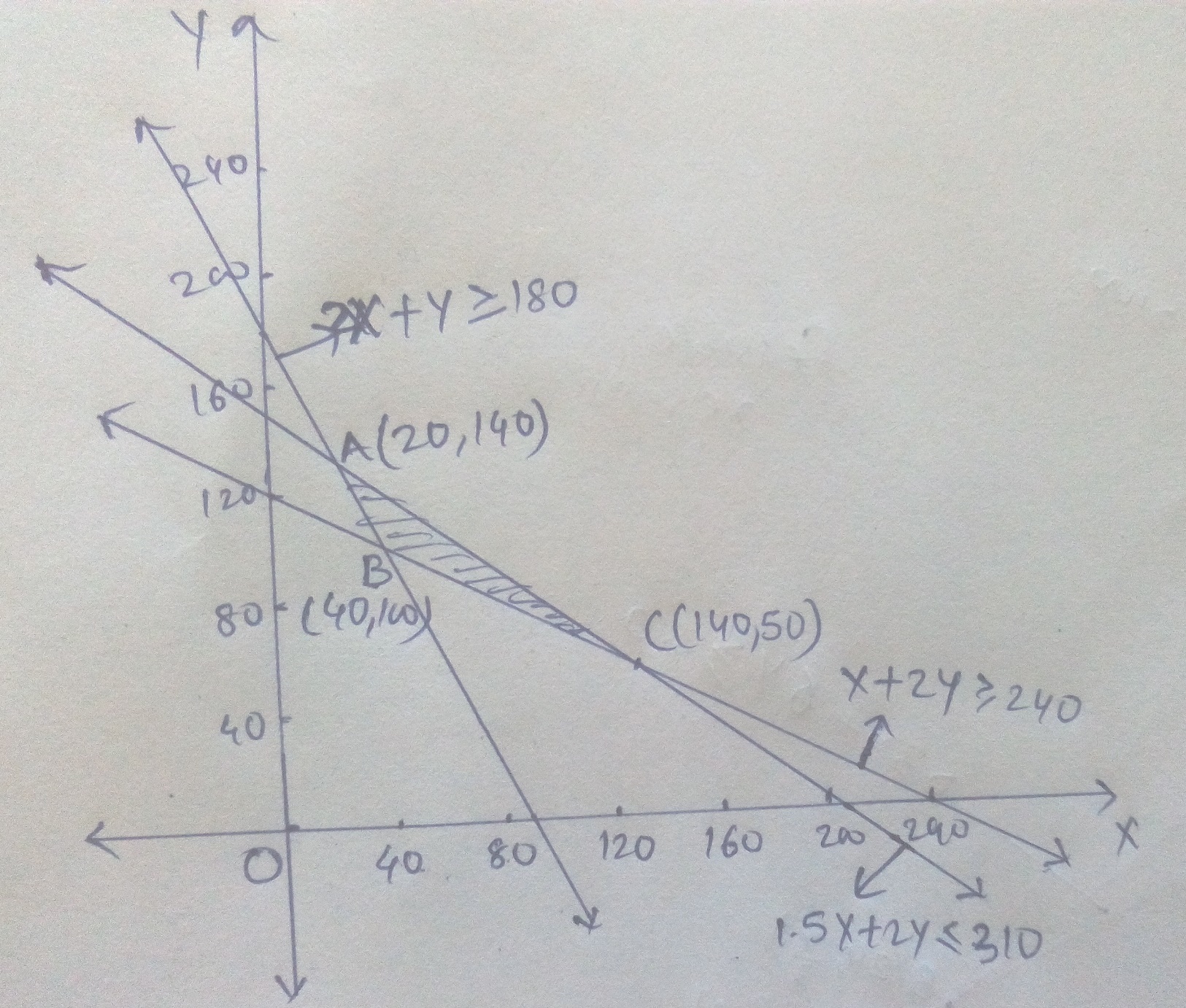
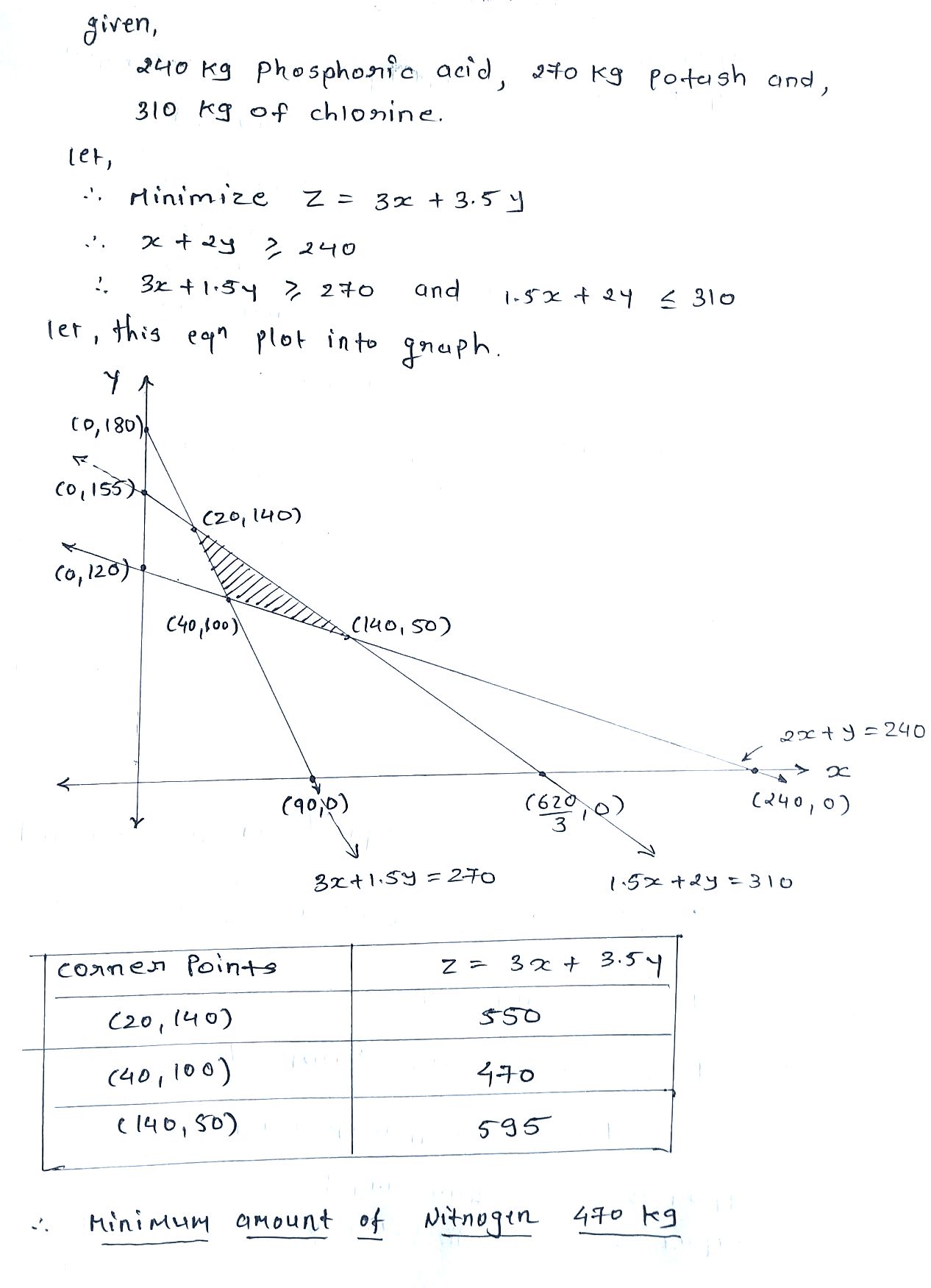
A fruit grower can use two types of fertilizer in his garden, brand $$P$$ and brand $$Q$$.The amounts (in kg) of nitrogen, phosphoric acid, potash, and chlorine in a bag of each brand are given in the table. Tests indicate that the garden needs at least $$240\ kg$$ of phosphoric acid, at least $$270\ kg$$ of potash and at most $$310\ kg$$ of chlorine.
If the grower wants to minimise the amount of nitrogen added to the garden, how many bags of each brand should be used? What is the minimum amount of nitrogen added in the garden?
| Kg per bag | ||
| Brand $$P$$ | Brand $$Q$$ | |
| Nitrogen | $$3$$ | $$3.5$$ |
| Phosphoric acid | $$1$$ | $$2$$ |
| Potash | $$3$$ | $$1.5$$ |
| Chlorine | $$1.5$$ | $$2$$ |
Holiday Mean Turkey Ranch is considering buying two different types of turkey feed. Each feed contains, in varying proportions, some or all of the three nutritional ingredients essential for fattening turkeys. Brand Y feed costs the ranch $$ $0.2$$ per pound. Brand Z costs $$ $.03$$ per pound. The rancher would like to determine the lowest-cost diet that meets the minimum monthly intake requirement for each nutritional ingredient.
The following table contains relevant information about the composition of brand Y and brand Z feeds, as well as the minimum monthly requirement for each nutritional ingredient per turkey.
Composition of Each Pound of Feed
| Ingredient | Brand Y Feed | Brand Z Feed | Minimum Monthly Requirement |
| A | $$5$$ oz | $$10$$ oz | $$90$$ oz |
| B | $$4$$ oz | $$3$$ oz | $$48$$ oz |
| C | $$.5$$ oz | $$0$$ | $$1.5$$ oz |
| Cost/lb | $$ $0.2$$ | $$ $.03$$ |
A farmer plans to mix two types of food to make a mix of low cost feed for the animals in his farm. A bag of food $$A$$ costs $$ $10$$ and contains $$40$$ units of proteins, $$20$$ units of minerals and $$10$$ units of vitamins. A bag of food $$B$$ costs $$ $12$$ contains $$30$$ units of proteins, $$20$$ units of minerals and $$30$$ units of vitamins. How many bags of food $$A$$ and $$B$$ should the consumed by the animals each day in order to meet the minimum daily requirements of $$150$$ units of proteins, $$90$$ units of minerals and $$60$$ units of vitamins at a minimum cost?
A store sells two types of toys, $$A$$ and $$B$$. The store owner pays $$ $8$$ and $$ $14$$ for each one unit of toy $$A$$ and $$B$$ respectively. One unit of toys $$A$$ yields a profit of $$ $2$$ while a unit of toys $$B$$ yields a profit of $$ $2$$. The store owner estimates that no more than $$2000$$ toys will be sold every month and he does not plan to invest more than $$ $20,000$$ in inventory of these toys. How many units each type of toys should be stocked in order to maximize his monthly total profit?
Solve using graphical method:
Maximize: $$Z=4x+5y$$
Subject to:
$$2x+5y\le 25$$
$$6x+5y\le 45$$
$$49$$
$$x\ge 0, y\ge 0$$
Solve the following problem:
Maximize $$Z=-P{x}_{1}+4{x}_{2}$$
Subject to: $$-3{x}_{1}+{x}_{2}\le 6$$
$${x}_{1}+2{x}_{2}\le 4$$
$${x}_{2}\le -3$$
No lower bound constraint for $${x}_{1}$$
Suppose a manufacturer of printed circuits has a stock of $$200$$ resistors, $$120$$ transistors and $$150$$ capacitors and is required to produce two types of circuits.
Type A requires $$20$$ resistors, $$10$$ transistors and $$10$$ capacitors
Type B requires $$10$$ resistors, $$20$$ transistors and $$30$$ capacitors.
If the profit on type $$A$$ circuits is $$E5$$ and that on type $$B$$ circuits is $$E12$$, how many of each circuit should be produced in order to maximize profit?
A company produces two types of tables, $${T}_{1}$$ and $${T}_{2}$$. It takes $$2$$ hours to produce the parts of one unit of $${T}_{1}$$, $$1$$ hour to assemble and $$2$$ hours ot polish. It takes $$4$$ hours to produce the parts of one unit of $${T}_{2}$$, $$2.5$$ hour to assemble and $$1.5$$ hours of polish. Per month, $$7000$$ hours are available for producing the parts, $$4000$$ hours for assembling the parts and $$5500$$ hours for polishing the tables. The profit per unit of $${T}_{1}$$ is $$ $90$$ and per unit of $${T}_{2}$$ is $$ $110$$. How many of each type of tables should be produced in order to maximize the total monthly profit?
Use the graphical method to solve each of the following LP problems.
A factory manufactures two products, each requiring the use of three machines. The first machine can be used at most $$70$$ hours; the second machine at most $$40$$ hours; and the third machine at most $$90$$ hours. The first product requires $$2$$ hours on Machine 1, $$1$$ hour on Machine 2, and $$1$$ hour on Machine 3; the second product requires $$1$$ hour each on machine 1 and 2 and $$3$$ hours on MachineIf the profit in $$E40$$ per unit for the first product and $$E60$$ per unit for the second product, how many units of each product should be manufactured to maximize profit?
Using graphical method
Find the corner points for
$$2x+5y\le 25$$
$$6x+5y\le 45$$
$$x\ge 0,y\ge 0$$
Use graphical method
Minimize: $$z=600x+900y$$
Subject to:
$$40x+60y\ge 480$$
$$30x+15y\ge 180$$
$$x\ge 0,y\ge 0$$
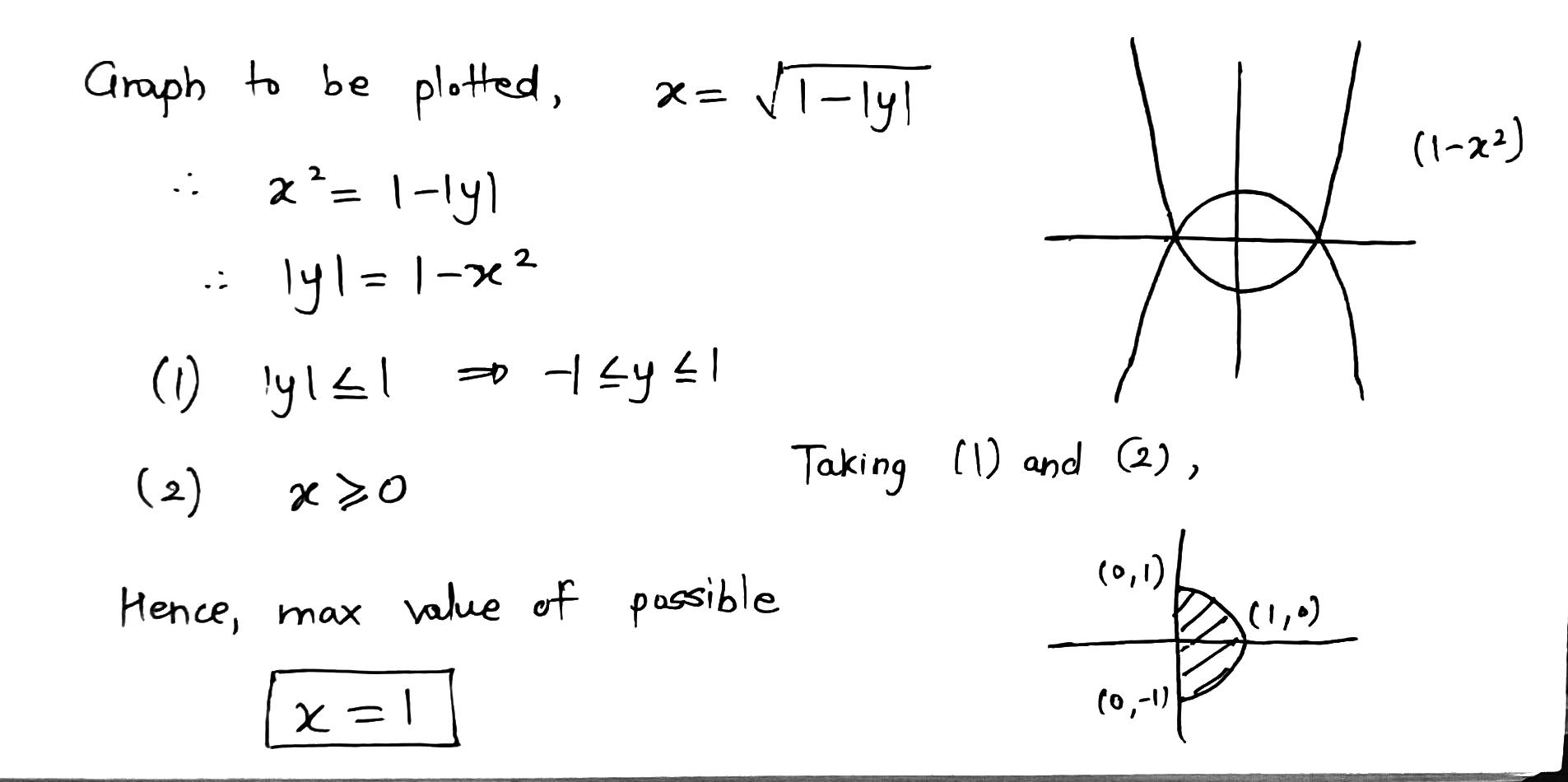
Construct the graphs of the following functions.
$$\displaystyle y \, = \, x \, | x | \, - \, 4x \, - \, 5.$$
Construct the graphs of the following functions.
$$\displaystyle y \, = \, (2x \, + \, 1) \, / \, (x \, - \, 1).$$
Construct the graphs of the following functions.
$$\displaystyle y \, = \, ( |1 \, - \, x \, | \, + \, 2) \, (x \, + \, 1).$$
Construct the graphs of the following functions.
$$\displaystyle y \, = \, | 2x^2 \, - \, 3x \, + \, | x \, - \, 1| \, |.$$
Construct the graphs of the following functions.
$$\displaystyle y \, = \, 1 / | x |.$$
Construct the graphs of the following functions.
$$\displaystyle y \, = \, \frac{| x \, - \, 1 |}{x \, - \, 1} \, (x^2 \, + \, 3).$$
John has $$ $20,000$$ to invest in three funds $${F}_{1},{F}_{2}$$ and $${F}_{3}$$. Fund $${F}_{1}$$ is offers a return of $$2$$% and has a low risk. Fund $${F}_{2}$$ offers a return of $$4$$% and has a medium risk. Fund $${F}_{3}$$ offers a return of $$5$$% but has a high risk. To be the safe side, John invests no more than $$ $3000$$ in $${F}_{3}$$ and at least twice as much as in $${F}_{1}$$ than in $${F}_{2}$$. Assuming that the rates hold till the end of the year, what amounts should he invest in each fund in order to maximize the year end return?
Construct the graphs of the following functions.
$$\displaystyle y \, = \, x (x \, - \, 3)^2.$$
Each month a store owner can spend at most $$ $100,000$$ on PC's laptops. A PC costs the store owner $$ $1000$$ and a laptop costs him $$ $1500$$. Each PC is sold for a profit of $$ $400$$ while laptop is sold for a profit of $$ $700$$. The store owner estimates that at least $$15$$ PC's but no more than $$80$$ are sold each month. He also estimates that the number of laptops sold is at most half the PC's. How many PC's and how many laptops should be sold in order to maximize the profit?
Solve the following maximal assignment problem:
| Branch Manager | Monthly Business (Rs. lakh) | |||
| $$A$$ | $$B$$ | $$C$$ | $$D$$ | |
| $$P$$ | $$11$$ | $$11$$ | $$9$$ | $$9$$ |
| $$Q$$ | $$13$$ | $$16$$ | $$11$$ | $$10$$ |
| $$R$$ | $$12$$ | $$17$$ | $$13$$ | $$8$$ |
| $$S$$ | $$16$$ | $$14$$ | $$16$$ | $$12$$ |
Mr. Anil wants to invest at most $$Rs. 60,000$$ in Fixed Deposit (F.D.) and Public Provident Fund (P.P.F.). He wants to invest at least $$Rs. 20,000$$ in F.D. and at least $$Rs. 15,000$$ in P.P.F. The rate of interest on F.D. is $$8\% p.a.$$ and that on P.P.F. is $$10\% p.a.$$ Formulate the above problem as L.P.P. to determine maximum yearly income.
Minimize and maximize $$Z=600x+400y$$
Subject to the constraints
$$x+2y\le 12$$
$$2x+y\le 12$$
$$4x+5y\le 20$$
$$x\ge 0;y\ge 0$$ by graphical method
Solve the following using graphical method:
Minimize: $$Z = 3x + 5y$$ subject to $$2x+ 3y \geq 12,$$ $$-x+y \leq 3$$, $$x \leq 4, \,\, y \geq 3, \,\, x \geq 0, \,\, y \geq 0$$
Solve the following minimal assignment problem and hence find minimum time where $$'-'$$ indicates that job cannot be assigned to the machine:
| Machines | Processing time in hours | ||||
| $$A$$ | $$B$$ | $$C$$ | $$D$$ | $$E$$ | |
| $$M_{1}$$ | $$9$$ | $$11$$ | $$15$$ | $$10$$ | $$11$$ |
| $$M_{2}$$ | $$12$$ | $$9$$ | - | $$10$$ | $$9$$ |
| $$M_{3}$$ | - | $$11$$ | $$14$$ | $$11$$ | $$7$$ |
| $$M_{4}$$ | $$14$$ | $$8$$ | $$12$$ | $$7$$ | $$8$$ |
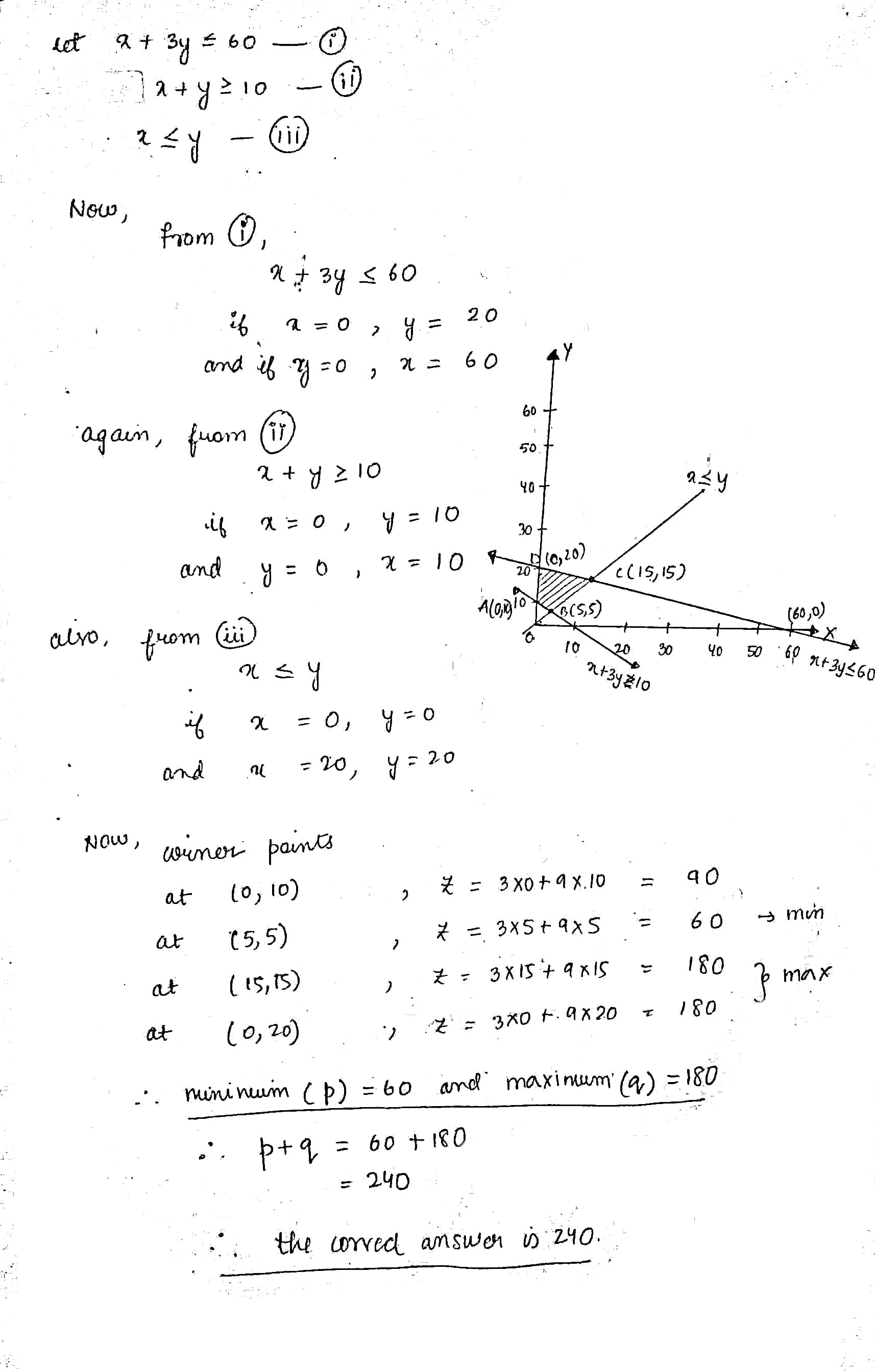
Solve the following problem graphically:
Minimise and Maximise
$$z = 3x + 9y$$
Subject to the constraints:
$$x + 3y \leq 60$$
$$x + y \geq 10$$
$$x \leq y$$
$$x\geq 0, y\geq 0$$.
Construct the graphs of the following functions.
$$\displaystyle y \, = \, (2 | x | -1) \, / \, (x \, - \, 3).$$
In solving LP problem : minimize $$z = 6x + 10y$$, subject to $$ x \geq 6, y \geq 2, 2x + y \geq 10, x \geq 0, y \geq 0,$$ which constraints are reduntant?
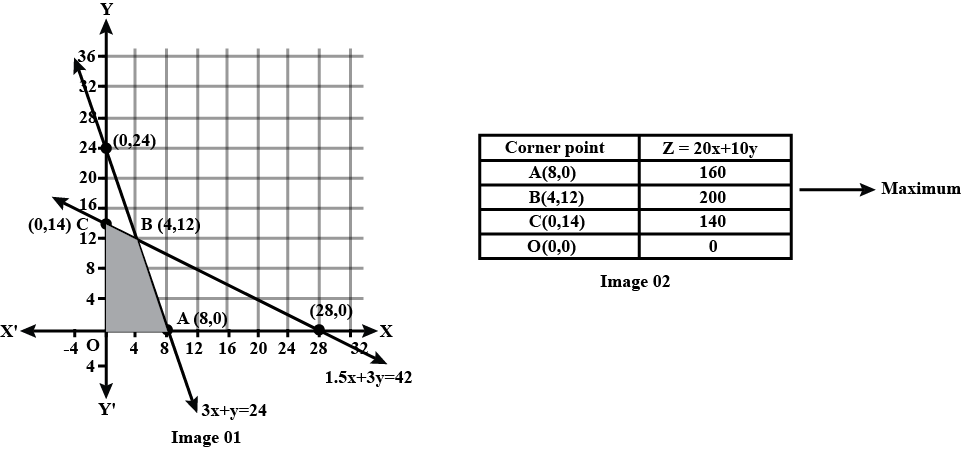
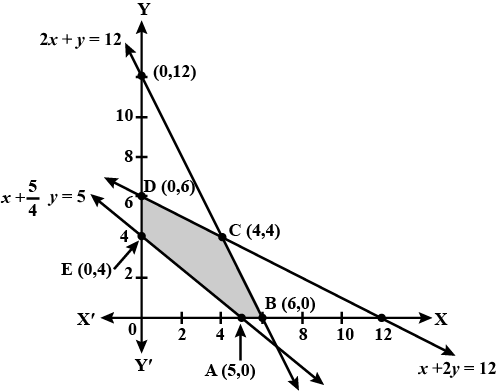
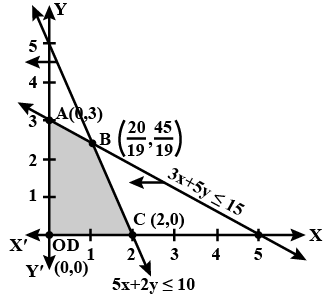
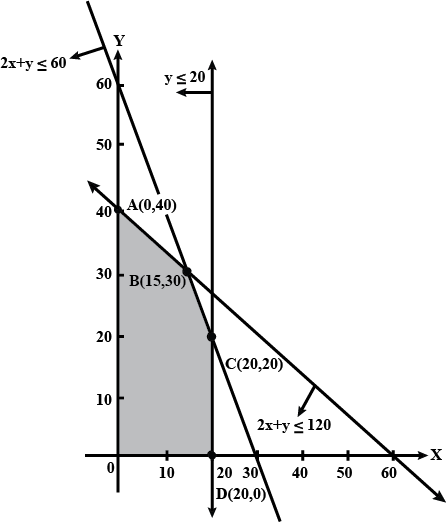
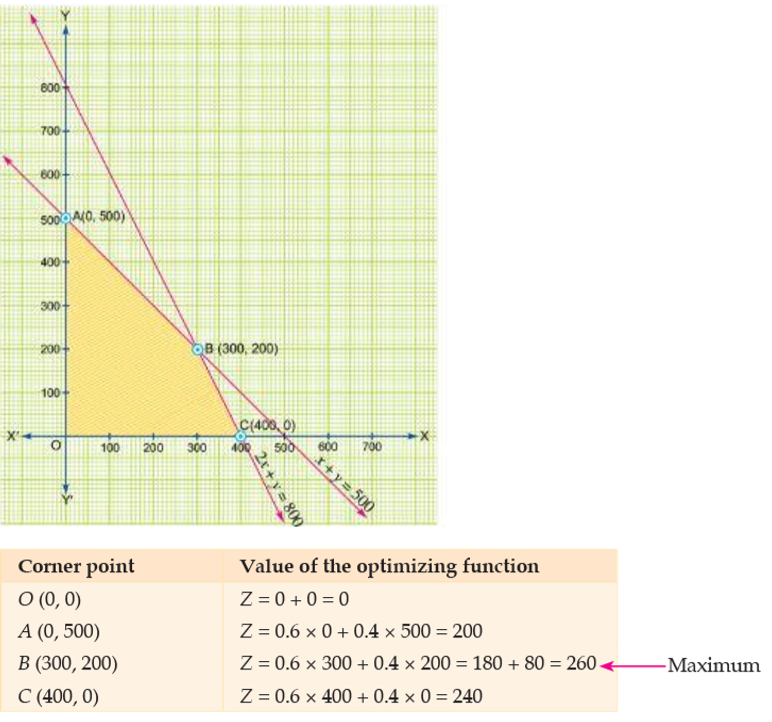
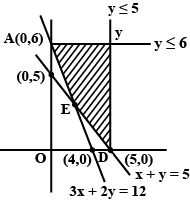
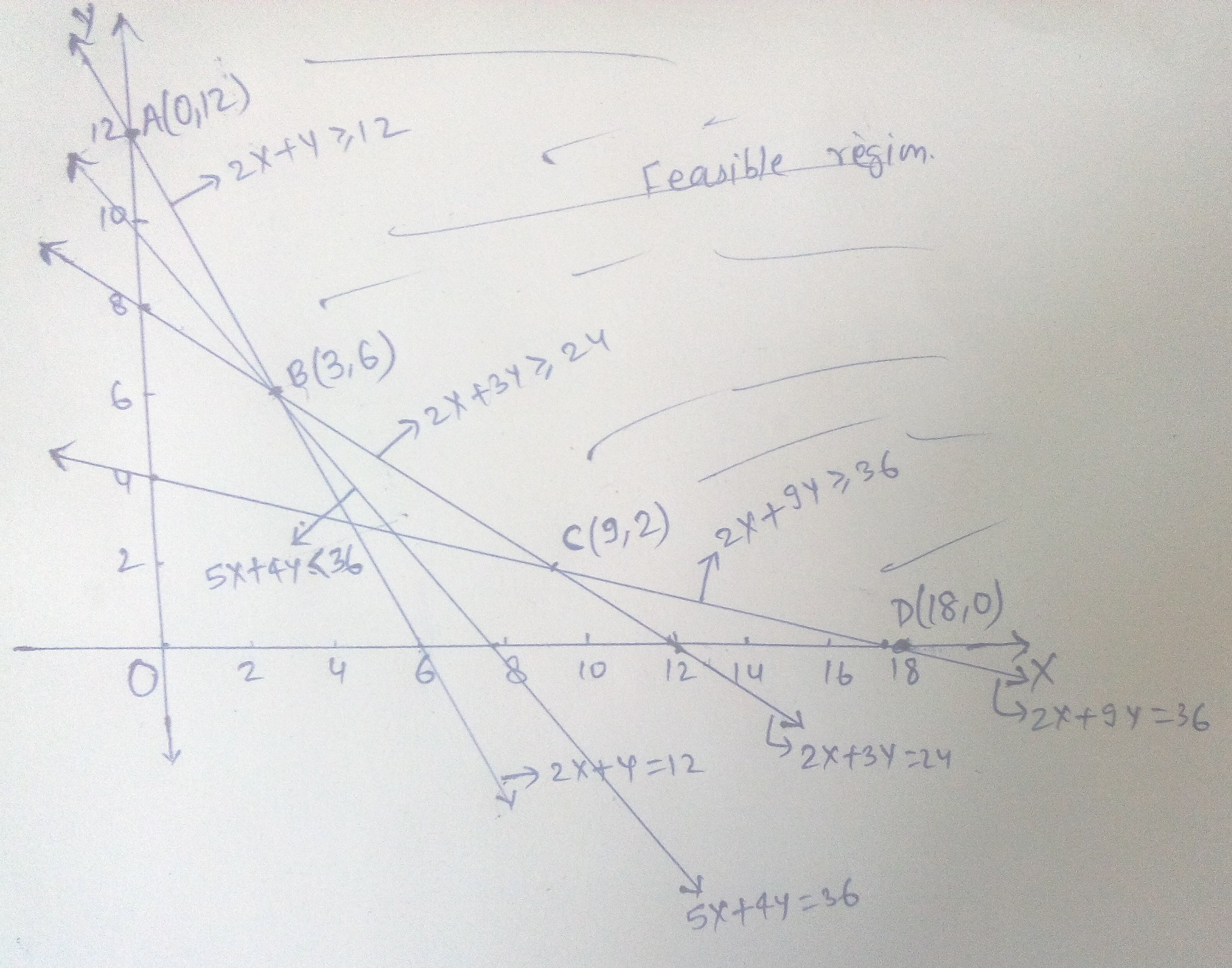
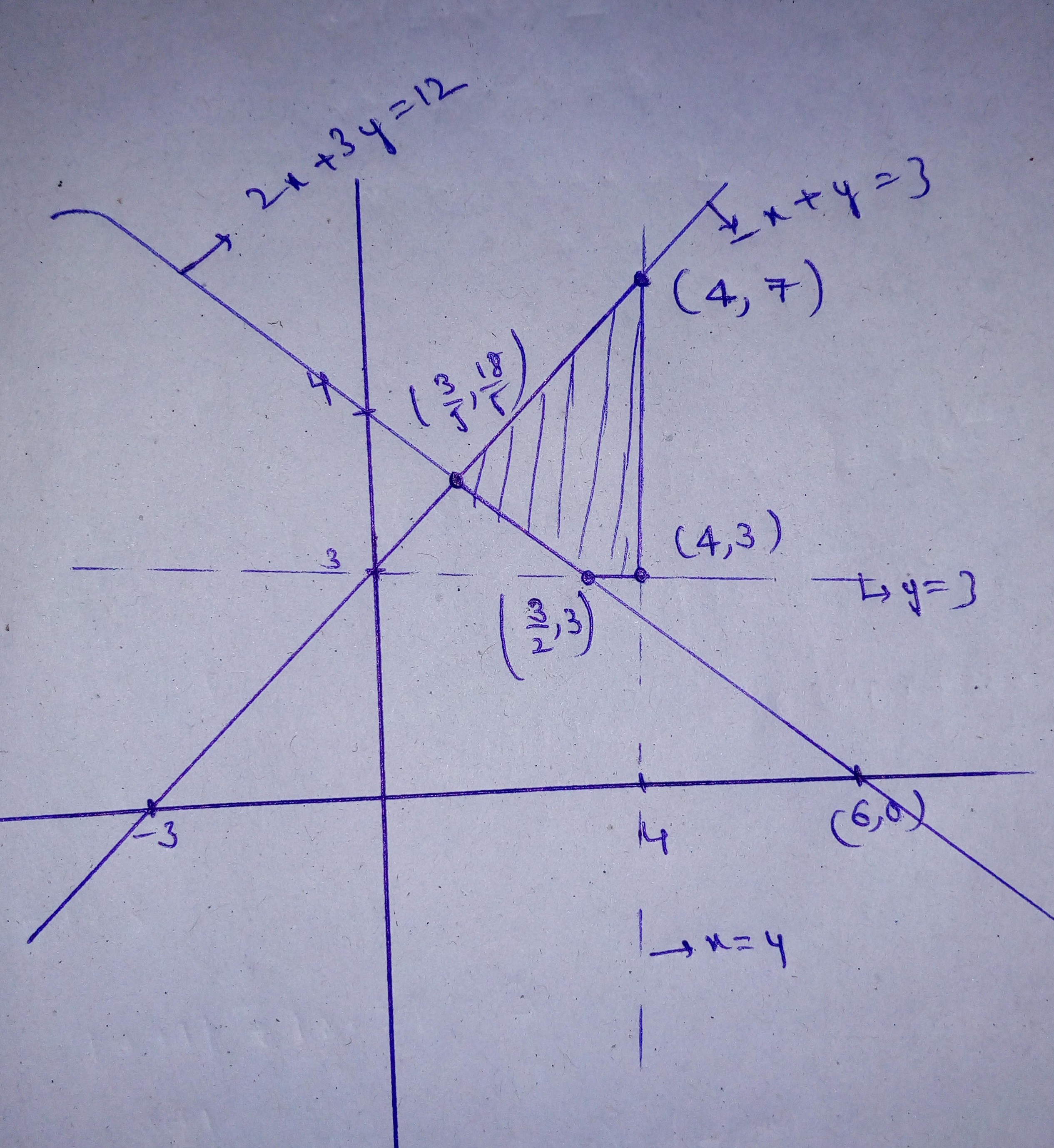
Minimise $$Z= 3x +2y$$
subject to constraints:
$$x+y \geq 8$$
$$3x+ 5y\leq 15$$
$$x\geq 0, y \geq 0$$
A chemical company produces two products,$$X$$ and $$Y$$.Each unit of product $$X$$ requires $$3$$hrs on operation $$I$$ and $$4$$hrs on operation $$II$$,while each unit of product $$Y$$ requires $$4$$hrs on operation $$I$$ and $$5$$hrs on operation$$II$$.
Total available time for operations $$I$$ and $$II$$ is $$20$$hrs and $$26$$ hrs respectively.The production of each unit of product $$Y$$ also results in two units of a by-product $$Z$$ at no extra cost.
Product $$X$$ sells at profit of Rs.$$10$$/unit, while $$Y$$ sells at profit of Rs.$$20$$/unit.By-product $$Z$$ brings a unit profit of Rs.$$6$$ if sold;in case it cannot be sold, the destruction cost is Rs.$$4$$ per unit.Forecasts indicate that not more that $$5$$ units of $$Z$$ can be sold.Formulate the L.P model to determine the quantities of $$X$$ and $$Y$$ to be produced,keeping $$Z$$ in mind, so that the profit earned is maximum.
An aeroplane can carry a maximum of 250 passengers, A profit of Rs. 1500 is made on each executive class ticket and a profit of Rs. 900 is made on each economy class ticket. The airline reserves at least 30 seats for executive class. However at least 4 times as many passengers prefer to travel by economy class than by executive class. Formulate LPP in order to maximize the profit For the airline.
One-fourth of a herd of camels was seen in the forest. Twice the square root of the herd had gone to mountains and the remaining $$15$$ camels were seen on the bank of a river. Find the total number of camels.
A firm produces three products. These products are processed on three different machines. The time required to manufacture one unit of each of the three products and the daily capacity of the three machines are given in the table below:
| Machine | Time per unit (in minutes) of product-$$1$$ | Time per unit (in minutes) of product-$$2$$ | Time per unit (in minutes) of product-$$3$$ | Machine capacity (minutes/day) |
| $${M}_{1}$$ | $$2$$ | $$3$$ | $$2$$ | $$440$$ |
| $${M}_{2}$$ | $$4$$ | - | $$3$$ | $$470$$ |
| $${M}_{2}$$ | $$2$$ | $$5$$ | - | $$430$$ |
A firm produces an alloy having the following specifications:
$$\left(i\right)$$ specific gravity$$\le0.98$$
$$\left(ii\right)$$chromium$$\ge8$$percent
$$\left(iii\right)$$melting point$$\ge{450}^{0}$$C
Raw materials $$A,B$$ and $$C$$ having the properties shown in the table can be used to make the alloy.
| Property | Property of raw material A | Property of raw material B | Property of raw material C |
| Specific gravity | $$0.92$$ | $$0.97$$ | $$1.04$$ |
| Chromium | $$7$$ percent | $$13$$ percent | $$16$$ percent |
| Melting point | $${440}^{0}$$ Celsius | $${490}^{0}$$ Celsius | $${480}^{0}$$ Celsius |
A company has two grades of inspectors,$$I$$ and $$II$$ to undertake quality control inspection.At least $$1,500$$ pieces must be inspected in an $$8-$$hour day.Grade$$I$$ inspector can check $$20$$ pieces in an hour with an accuracy of $$96$$percent.
Grade$$II$$ inspector checks $$14$$ pieces an hour with an accuracy of $$92$$ percent.
Wages of grade $$I$$ inspector are Rs.$$5$$ per hour while those of grade $$II$$ inspector are Rs.$$4$$ per hour. Any error made by an inspector costs Rs.$$3$$ to the company.If there are,in all, $$10$$ grade $$I$$ inspectors and $$15$$ grade $$II$$ inspectors in the company,find the optimal assignment of inspectors that minimizes the daily inspection cost.
A person wants to decide the constituents of a diet which will fulfill his daily requirements of proteins,fats and carbohydrates at the minimum cost.The choice is to be made from four different types of foods.The yields per unit of these foods are given in table below.
| Food Type | Proteins (yield per unit) | Fats (yield per unit) | Carbohydrates (yield per unit) | Cost per unit (in Rupees) |
| $$1$$ | $$3$$ | $$2$$ | $$6$$ | $$45$$ |
| $$2$$ | $$4$$ | $$2$$ | $$4$$ | $$40$$ |
| $$3$$ | $$8$$ | $$7$$ | $$7$$ | $$85$$ |
| $$4$$ | $$6$$ | $$5$$ | $$4$$ | $$65$$ |
| Minimum Requirement | $$800$$ | $$200$$ | $$700$$ |
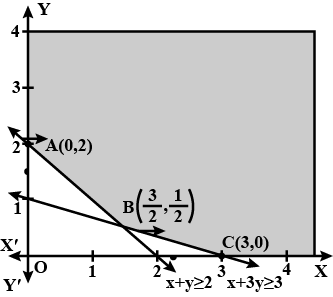
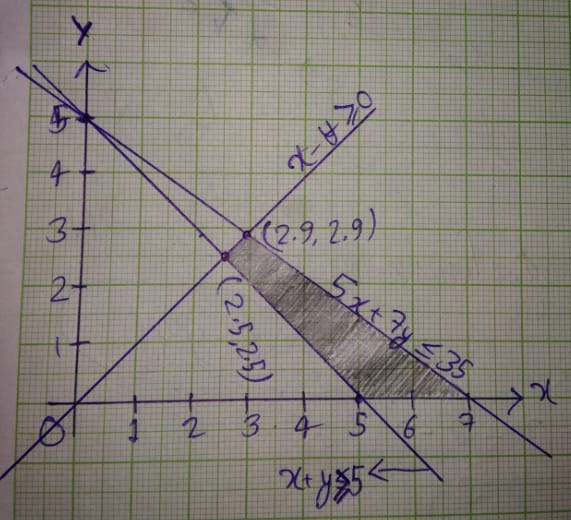
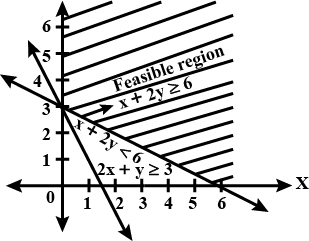
Solve the following system of inequalities graphically $$2x+y\ge 6, 3x+4y\le 12$$
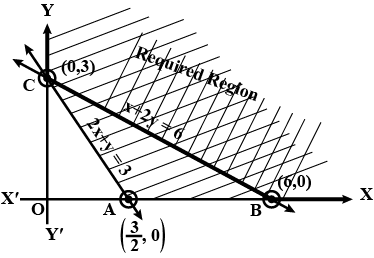
Maximize $$Z=x+2y$$ subject to $$2x+y\ge 3,x+2y\ge 6, x,y\ge 0$$.
Draw the line $$2y=3x+4$$ on the $$xy$$ plane.
Solve the following system of inequalities graphically $$x+y\ge 4, 2x-y> 12$$
Solve the following system of inequalities graphically $$x+y\le 9, y>x, x\ge 0$$
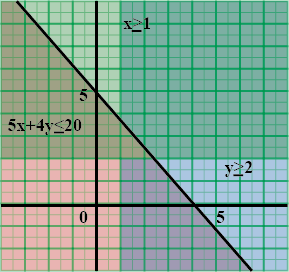
Solve the following system of inequalities graphically $$5x+4y\le 20, x\ge 1, y\ge 2$$
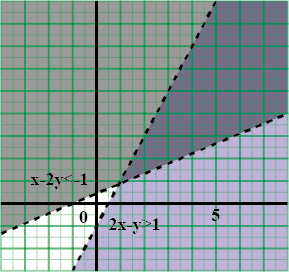
Solve the following system of inequalities graphically $$2x-y>1, x-2y<-1$$
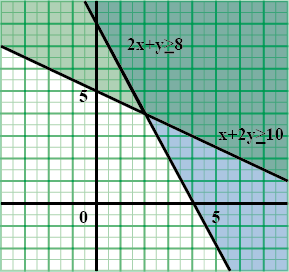
Solve the following system of inequalities graphically $$2x+y\ge 8, x+2y\ge 10$$
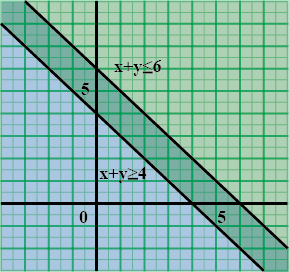
Solve the following system of inequalities graphically $$x+y\le 6, x+y\ge 4$$
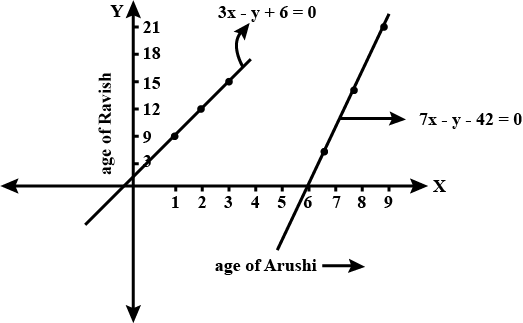
Ravish tells his daughter Aarushi, "Seven years ago, I was seven times as old as you were then. Also, there years from now, I shall be three times as old as you will be. If the present ages of Aarushi and Ravish are x and y years respectively, represent this situation algebraically as well as graphically.
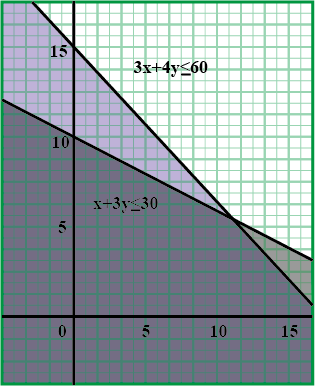
Solve the following system of inequalities graphically $$3x+4y\le 60, x+3y\le 30, x\ge 0, y\ge 0$$
If the point $$(2K-3,K+2)$$ lies on the graph of equation $$2x+3y+15=0$$, find the value of k.
Solve the following Linear programming problems graphically :
Maximize$$z = 3x + 4y$$ subject to the constraints : $$x + y \le 4, \, x \ge 0 , \, y \ge 0$$
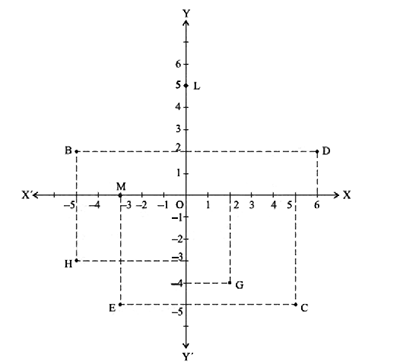
See the given figure and write the following:
$$(i)$$ The coordinates of $$B$$
$$(ii)$$ The coordinates of $$C$$
$$(iii)$$ The point identified by the coordinates $$(-3,-5)$$
$$(iv)$$ The ordinate of the point $$B$$.
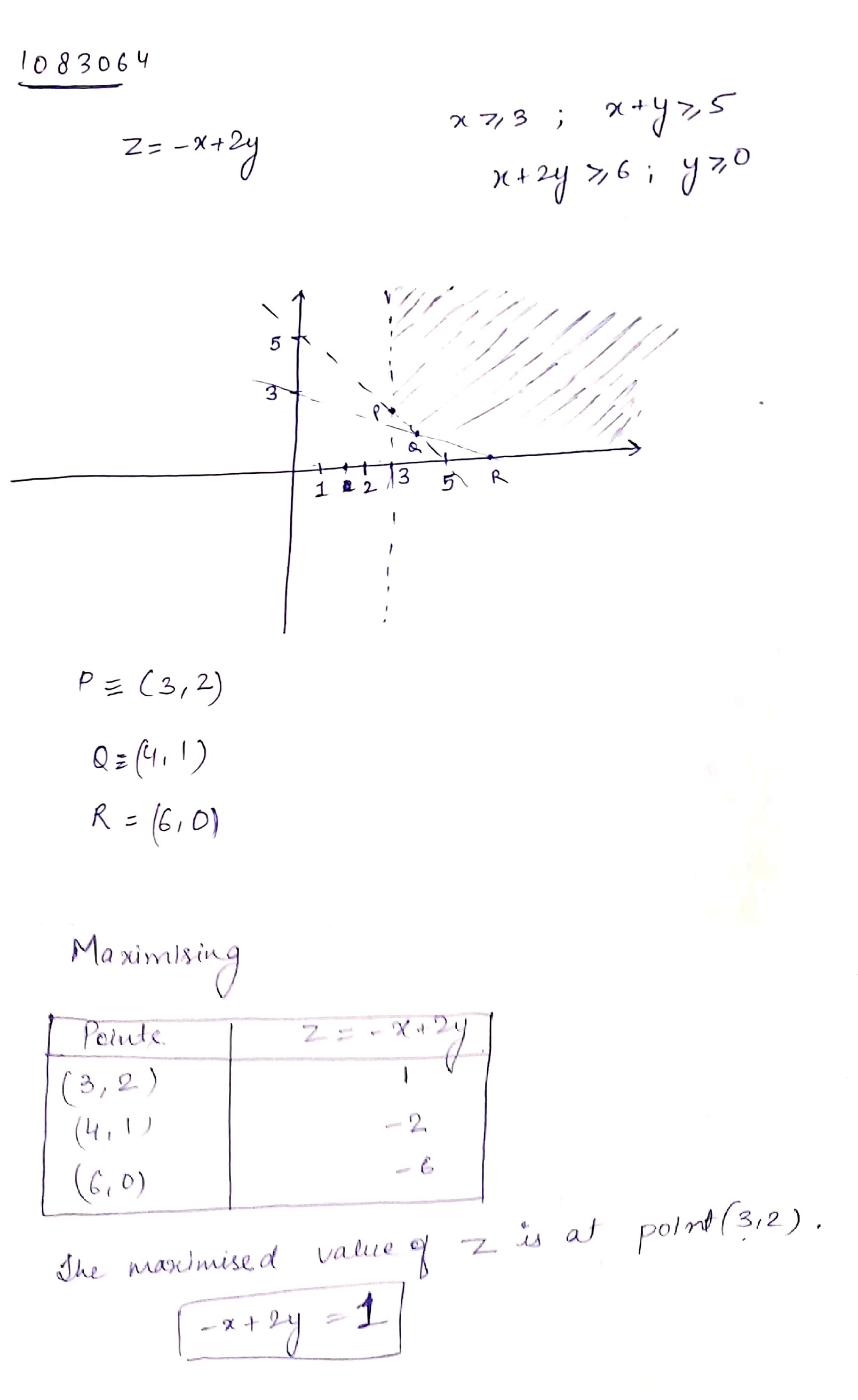
Maximize $$Z=-x+2y$$, subject to the constraints: $$x\geq 3; x+y\geq 5, x+2 y\geq 6, y\geq 0$$.
Solve the following system of inequalities graphically $$2x+y\ge 4, x+y\le 3, 2x-3y\le 6$$
Solve the following Linear Programming problems graphically:
Maximize $$Z = 3x + 4y$$ Subject to the constraints : $$x + y \le 4, \, x \ge 0 , \, y \ge 0$$
Minimize $$Z = -3x + 4 y$$ subject to $$x + 2y \le 8 , \, 3x + 2y \le 12, \, x \ge 0 , \, y \ge 0$$
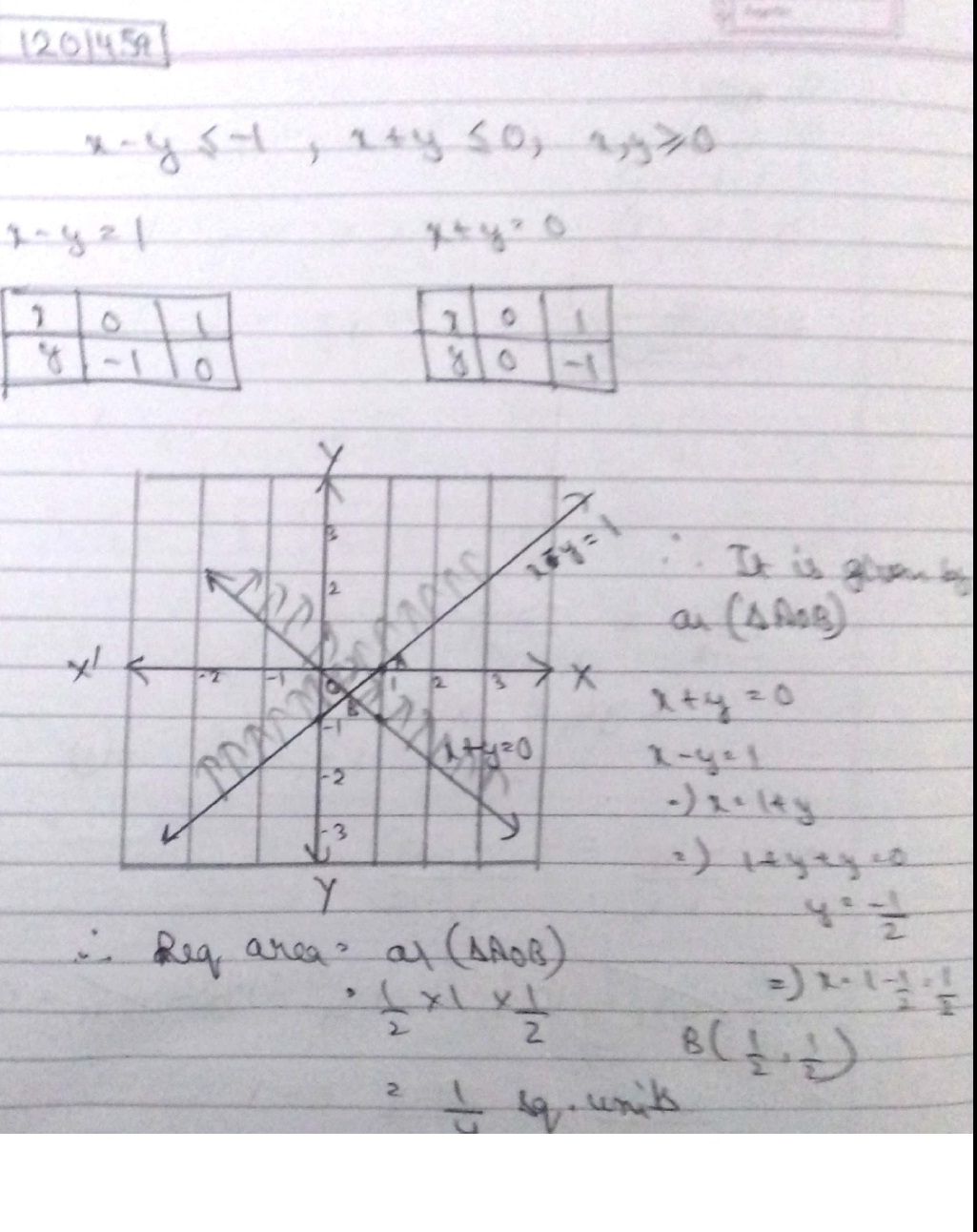
$$x-y\leq -1,x+y\leq 0,x,y\geq0$$
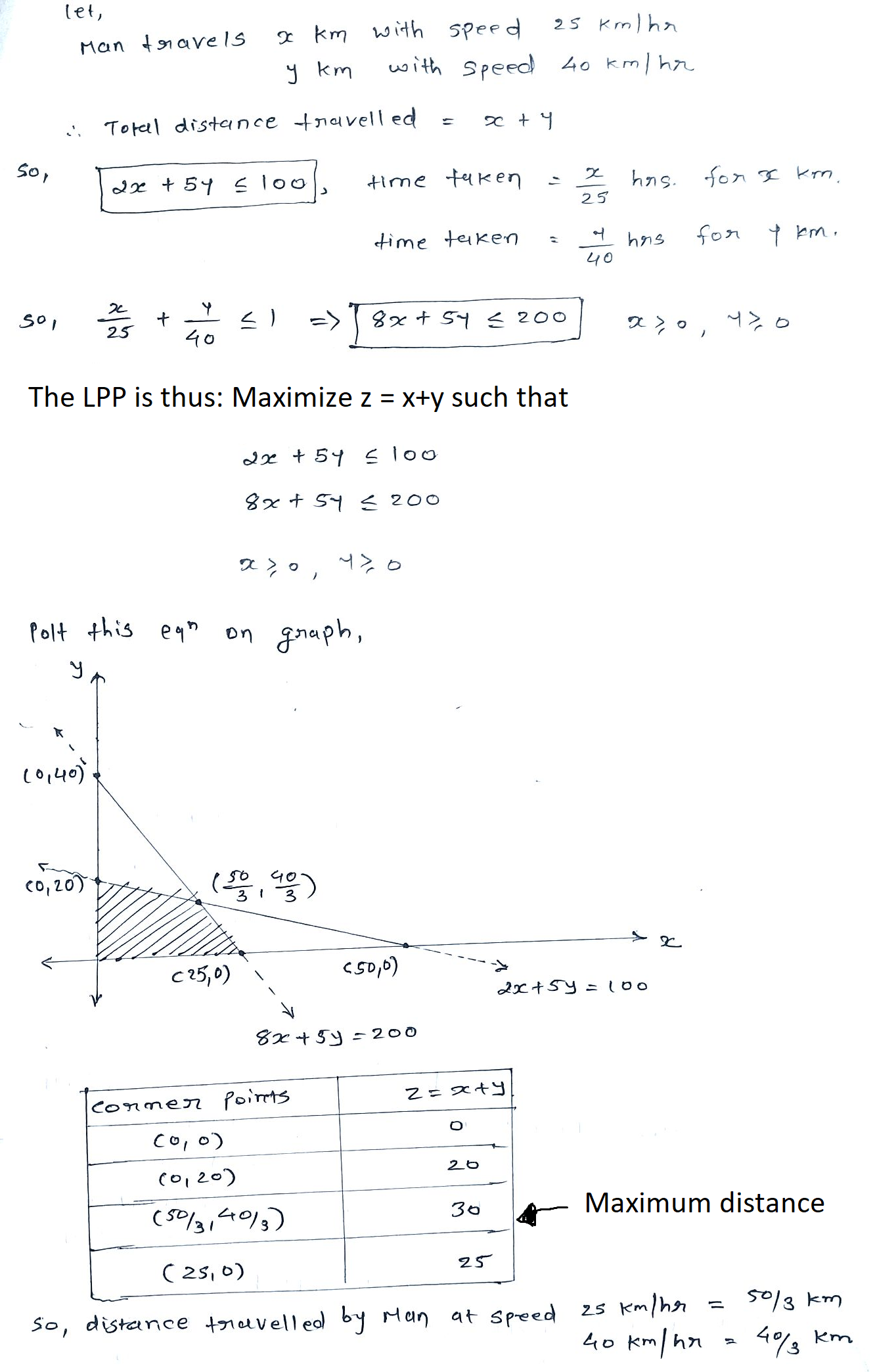
If a $$20$$ year old girl drives her car at $$25\ km/h$$, she has to spend $$Rs\ 4/km$$ on petrol. If she drives her car at $$40km/h$$, the petrol cost increases to $$Rs\ 5\ /km$$. She has $$Rs\ 200$$ to spend on petrol and wishes to find the maximum distance she can travel within one hour. Express the above problem as Linear Programming Problem. Write any one value reflected in the problem.
A store sells two types of toys, A and B. The store owner pays Rs. 8 and Rs. 14 for each unit of toy A and toy B respectively. One unit of toy A yields a profit of Rs. 2 while a unit of toy B yields a profit of Rs.The store owner estimates that no more than 2000 toys will be sold every month and he does not plan to invest more than Rs. 20,000 in inventory of these toys. How many units of each type of toys should be stocked in order to maximize his monthly total profit ?
Find the solution of the following LP problem ''Maximize z=x+ y subject $$x + y \leq 1,-3x+y\geq 3,x\geq 0,y\geq 0''$$ is.............
A firm is engaged in producing two models $${X_{1.}}{X_2}$$ performing only three operations assembling, pianting and testing.The relevant data are as follows.
Total number of hours available each week for assemblling $$600$$ hours, painting $$100$$ hours and testing $$30$$ hours.The firm wishes to determine its weekly products mix so as to maximize revenue formulate I.P.P model for maximize the revenue
There are $$50$$ apples trees in an orchard. Each tree produces $$800$$ apples. For each additional tree planeted in the orchord. The output additional tree drops by $$10$$ apples tree drops by$$10$$ apples. Number of trees that should to the existing orchord for maximising the output of the trees is $$3k$$, then $$k=$$ ?
A producer has $$20$$ and $$10$$ units of labour and capital respectively which he can use to produce two kinds of goods $$X$$ and $$Y$$. To produce one unit of $$X,2$$ units of capital and $$1$$ unit of labour is required. To produce one unit of $$Y,3$$ units of labour and $$1$$ unit of capital is required. Find $$X$$ and $$Y$$ ?
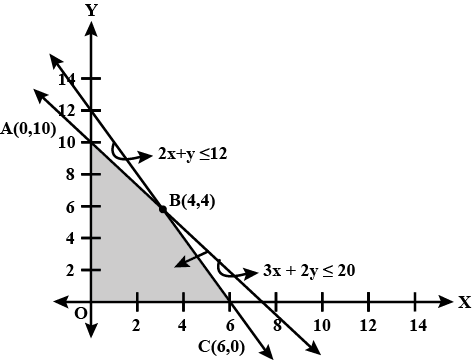
Maximize $$z=3x+5y$$, Subject to $$x+4y \le 24$$, $$3x+y \le 21,x+y \le 9,x \ge 0$$. Also find maximum value of $$z$$.
A small firm makes necklaces and bracelets. The combined number of necklaces and bracelets that it can handle per day is at most $$24$$. A bracelet takes one hour to make and necklace takes $$30$$ minutes. The maximum number of hours available per day is $$16$$. If the profit on a bracelet is Rs. $$300$$/- and on a necklace is Rs. $$100$$/-, How many necklaces and bracelets must be made per day to get the maximum profit? Make it as an LLP and solve graphically.
Maximize z = 2x + 4y subject to the constraints
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, x + y ≥ 1, 3x + 2y <= 6
Maximise ,Z=x+y, subject to $$x-y\leq -1$$, $$-x+y\leq 0$$$$x,y\leq 0$$
A library has to accommodate two different types of books on a shelf. The books are 6cm and 4cm thick and weigh 1kg and 1.5kg respectively. The shelf is 96cm long and at most can support a weight of 21kg. How should the shelf be filled with the books of two types in order to include the greatest number of books? Make it as an LLP and solve it graphically.
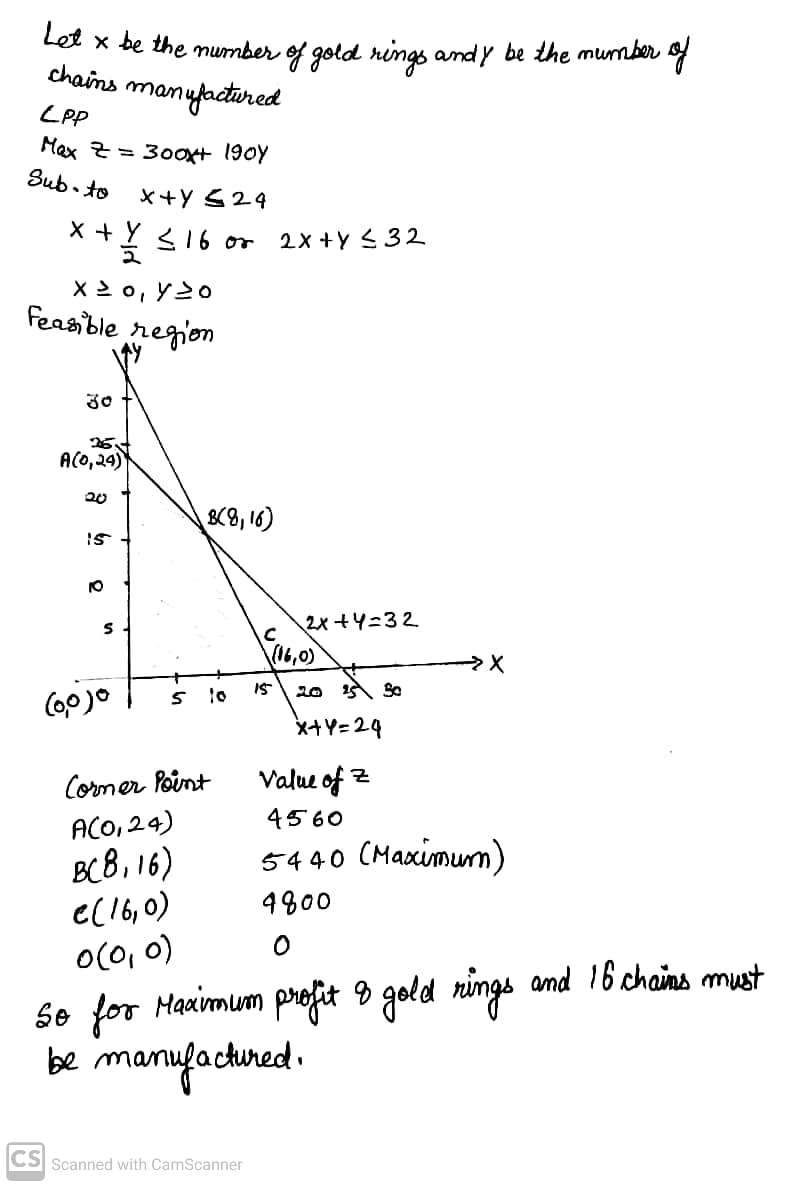
A small firm manufactures gold rings and chains.The total number of rings and chains manufactured per day is almost $$24$$. It takes $$1\ h$$ to make a ring and $$30$$ min to make a chain. The maximum number of hours available per day is $$16$$. If the profit on a ring is $$Rs. 300$$ and that on a chain is $$Rs. 190$$, then find the number of rings and chains that then find the number of rings and chains that should be manufactured per day so as to earn the maximum profit. Make it as an LPP and solve it graphically.
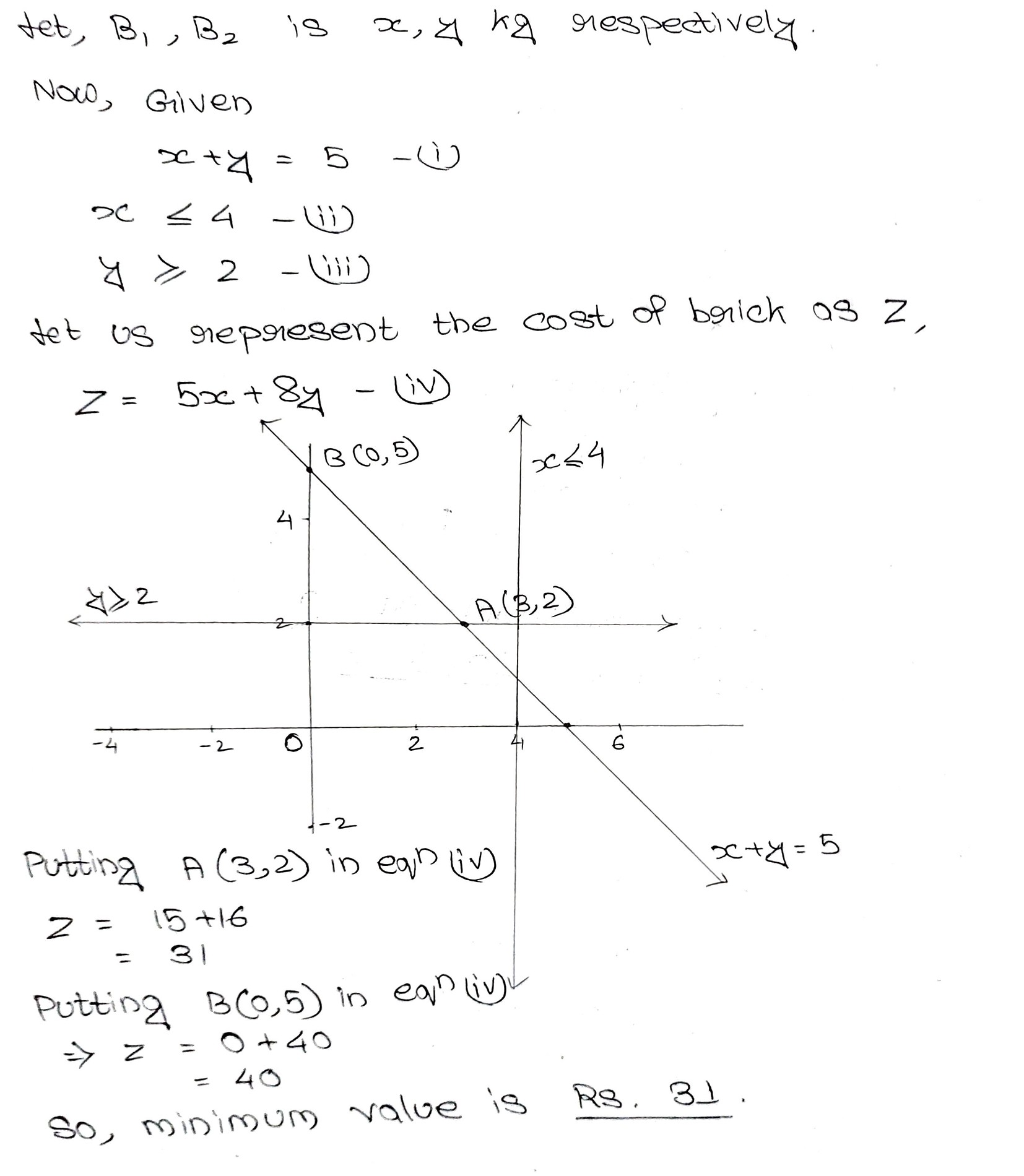
The standard weight of a special purpose brick is $$5\mathrm { kg }$$ and It must contain two basic ingredients $$ B _ { 1 } \text { and } B _ { 2 } , B _ { 1 }$$ costs $$Rs. 5$$ per kg and $$B _ { 2 }$$ costs $$Rs.8$$ per kg, Strength considerations dictate that the brick should contain not more than $$4\mathrm { kg }$$ of $$B _ { 1 }$$ and minimum $$2 \mathrm { kg }$$ of $$\mathrm { B } _ { 2 } .$$ Since the demand for the product is likely to be related to the price of the brick. find the minimum cost of brick satisfying the above conditions, Formulate this situation as an $$LPP$$ and solve it graphically.
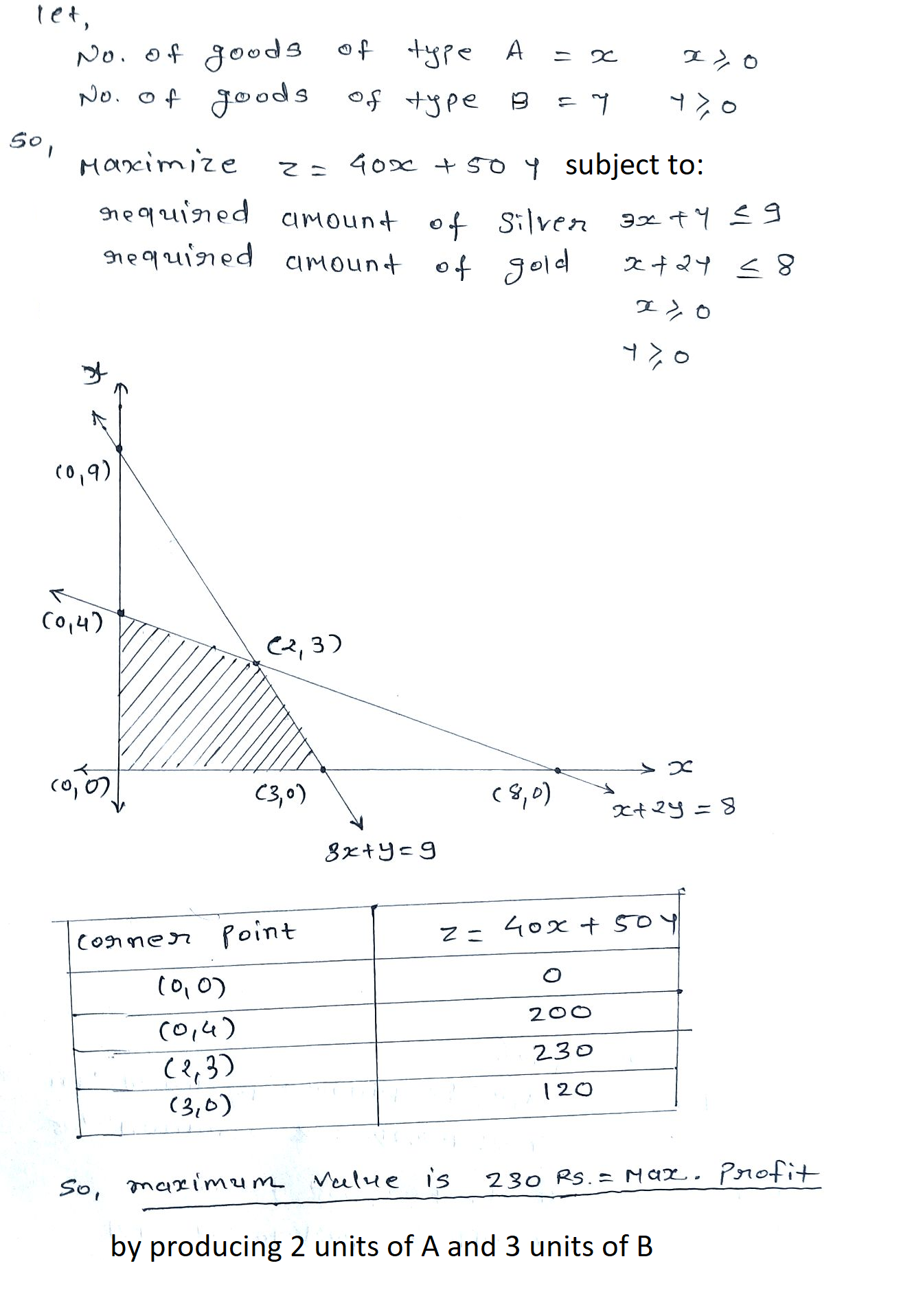
A company produces two types of goods, A and B, that require gold and silver. Each unit of type A requires $$3g$$ of silver and $$1$$g of gold while that of B requires $$1$$g of silver and $$2$$g of gold. The company can use atmost $$9$$g of silver and $$8$$g of gold. If each unit of type A brings a profit of $$40$$ and that of type B $$50$$, find the number of units of each type that the company should produce to maximize the profit. Formulate and solve graphically the LPP and find the maximum profit.
A man has $$Rs. 1500$$ for purchasing wheat and rice. A bag of rice and a bag of wheat cost $$Rs. 180$$ and $$Rs. 120$$ respectively. He has a storage capacity of only $$10$$ bags. He earns a profit of $$Rs. 11$$ and $$Rs. 9$$ per bag of rice and wheat, respectively. Formulate the problem as an $$LPP$$ to find the number of bags of each type he should buy for getting maximum profit and solve it graphically.
Maximize $$Z=12x+24y$$ subject to the constraints $$x+y\ge 5, 5x+7y\le 35, x-y\ge0,x,y\ge0$$ graphically.
A firm has to transport at least 1200 packages daily using large vans which carry 200 packages each and small vans which can take 80 packages each. The cost of engaging each large van is Rs. 400 and each small van is Rs.Not more than Rs. 3000 is to be spent daily on the job and the number of large vans cannot exceed the number of small vans. Formulate this problem as a LPP given that the objective is to minimize cost.
One kind of cake requires $$300gm$$ of flour and $$15gm$$ of fat and another kind of cake requires $$150gm$$ of flour and $$ 30gm$$ of fat. Find the maximum number of cake that can be made from $$ 7.5kg$$ of flour and $$ 600gm$$ of fat . Form a linear programming problem and solve it graphically.
A manufacturer of patent medicines is preparing a production plan on medicines $$A$$ and $$B$$. There are sufficient row material available to make $$20000 $$ bottles of $$A$$ and $$40000$$ bottles of $$B$$, but there are $$45000$$ bottles into which either of the medicines can be put. Further, it takes $$3$$ hours to prepare enough material to fill $$1000$$ bottles of $$A$$, it takes $$1$$ hours to prepare enough material to fill $$1000$$ bottles of $$B$$ and there are $$66$$ hours available for this operation. The profit is Rs. $$8$$ per bottle for $$A$$ and Rs. $$7$$ per bottle for $$B$$. Construct the maximization problem.
Maximize $$z=6x+4y$$, Subject to $$x\leq 2, x+y\leq 3$$, $$-2x+y\leq 1$$, $$x\geq 0$$, $$y\geq 0$$. Also find maximum value of z.
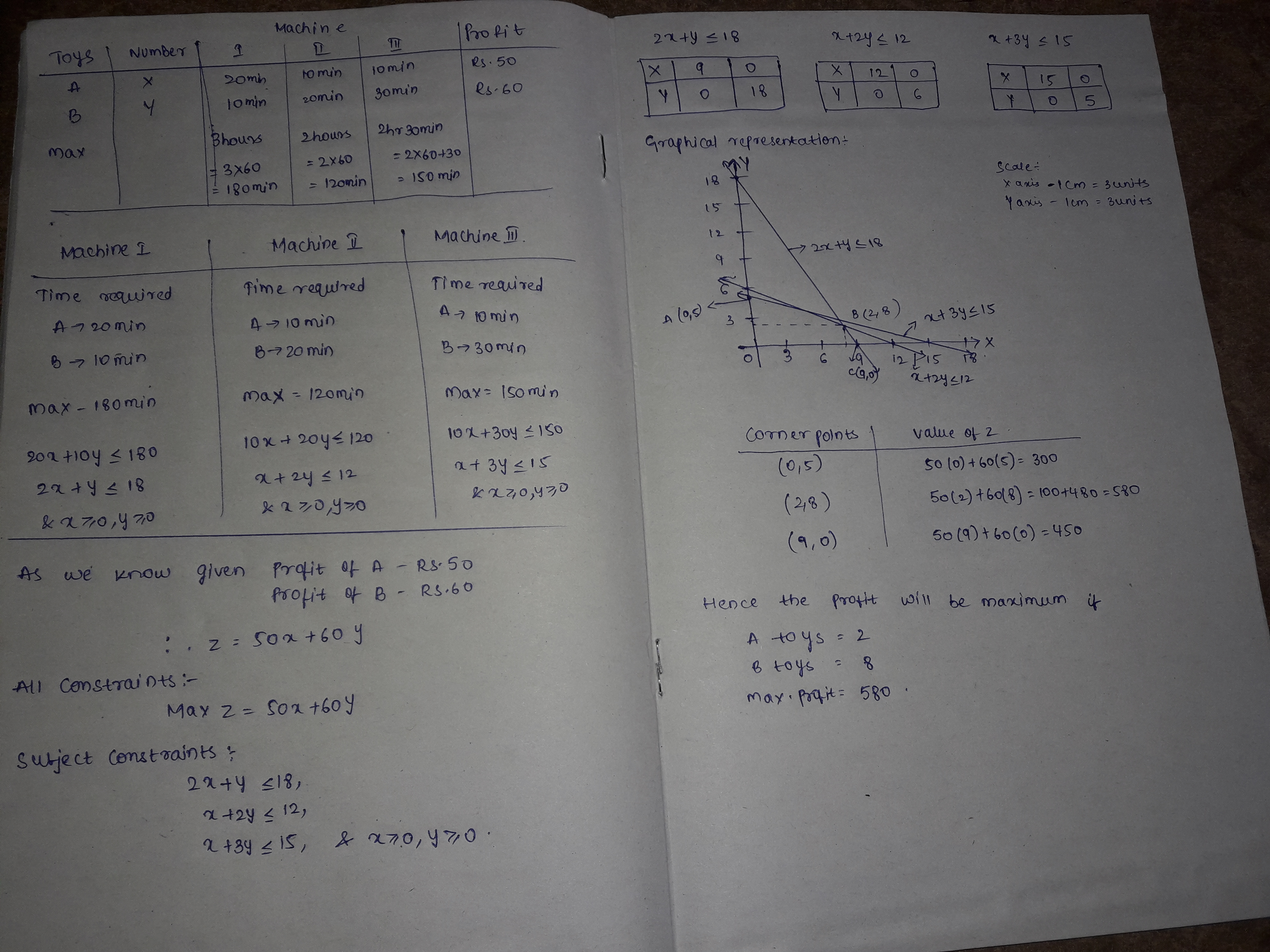
A company manufactures two types of novelty souvenirs made of plywood. Souvenirs of type A require $$5$$ minutes each for cutting and $$10$$ minutes each for assembling. Souvenirs of type $$B$$ require $$8$$ minutes each for cutting and $$ 8$$ minutes each for assembling. There are $$3$$ hours and $$20$$ minutes available for cutting and $$4$$ hours available for assembling. The profit is $$Rs. 5$$ each for type $$A$$ and $$Rs. 6$$ each for type $$B$$ souvenirs. How many souvenirs of each type should the company manufacture in order to maximize profit ? Formulate the above $$LPP$$ and solve it graphically and also find the maximum profit.
If the replacement set is the set of all non-negative integers, find the solution set of the following A) $$x + 1 < 9$$
B) $$3x - 4 \leqslant 20$$
C) $$5 + 2x > 10$$
D) $$10 < x + 5 < 21$$
An automobile manufacturer makes automobiles and trucks in a factory that is divided into two shops. Shop $$A$$, which performs the basic assembly operation, must work $$5$$ man-days on each truck but only $$2$$ man-days on each automobile. Shop $$B$$, which performs finishing operations, must work $$3$$ man-days for each automobile or truck that it produces. Because of men and machine limitation, shop $$A$$ has $$180$$ man-days per week available whole shop $$B$$ has $$135$$ man-days per week. If the manufacturer makes a profit of Rs. $$ 30000$$ on each truck and Rs. $$ 2000$$ on each automobile, how many of each should he produce to maximum his profit? Formulate this as a $$LPP$$.
A small manufacturing firm produces two types of gadgets $$A$$ and $$B$$, which are first processed in the foundry then sent to the machine shop for finishing. The number of man-hours of labour required in each shop for the production of each unit of $$A$$ and $$B$$, and the number of man-hours the firm has available per week are as follows:
| Gadget | Foundry | Machine-shop |
| $$A$$ | $$10$$ | $$5$$ |
| $$B$$ | $$6$$ | $$4$$ |
| Firm's capacity per week | $$1000$$ | $$600$$ |
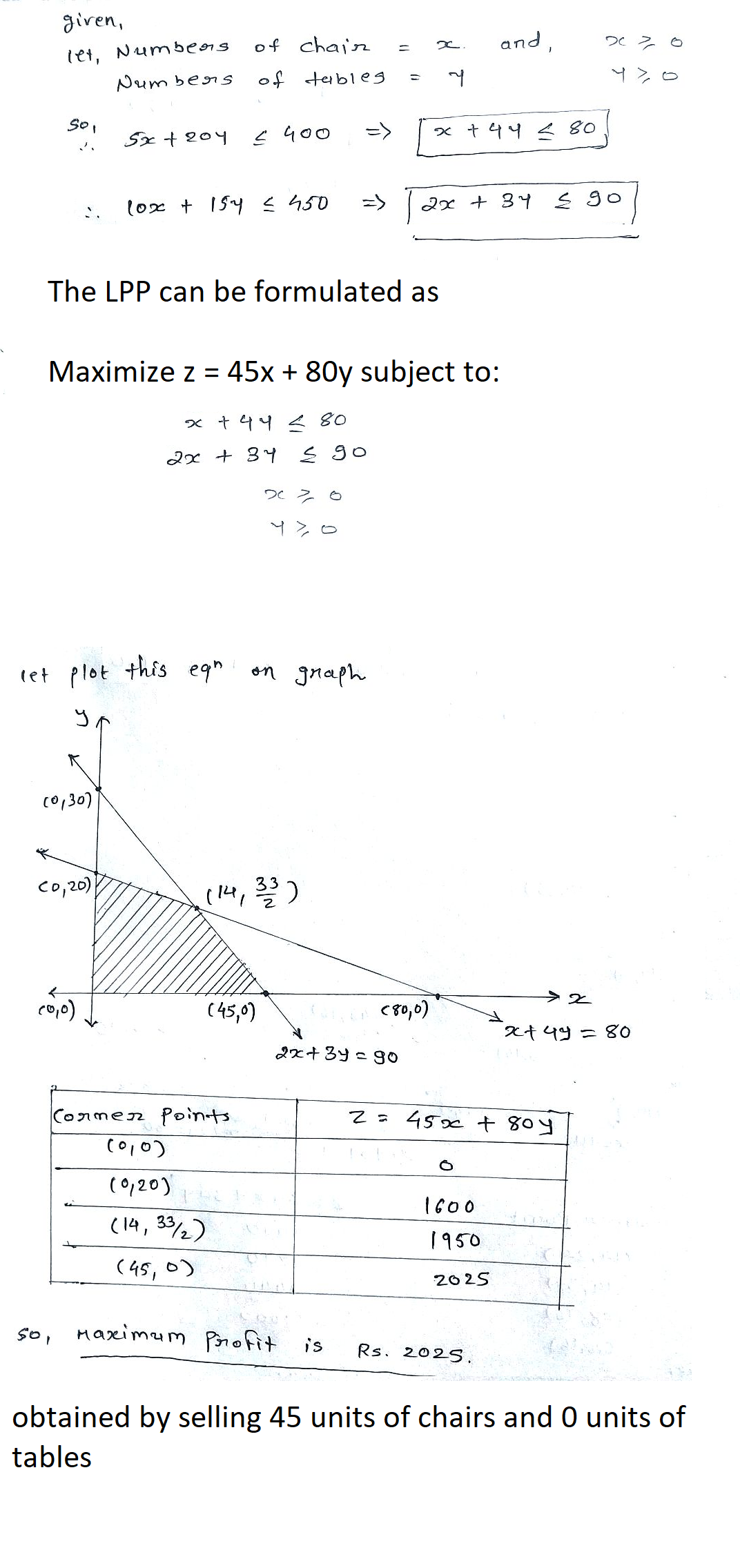
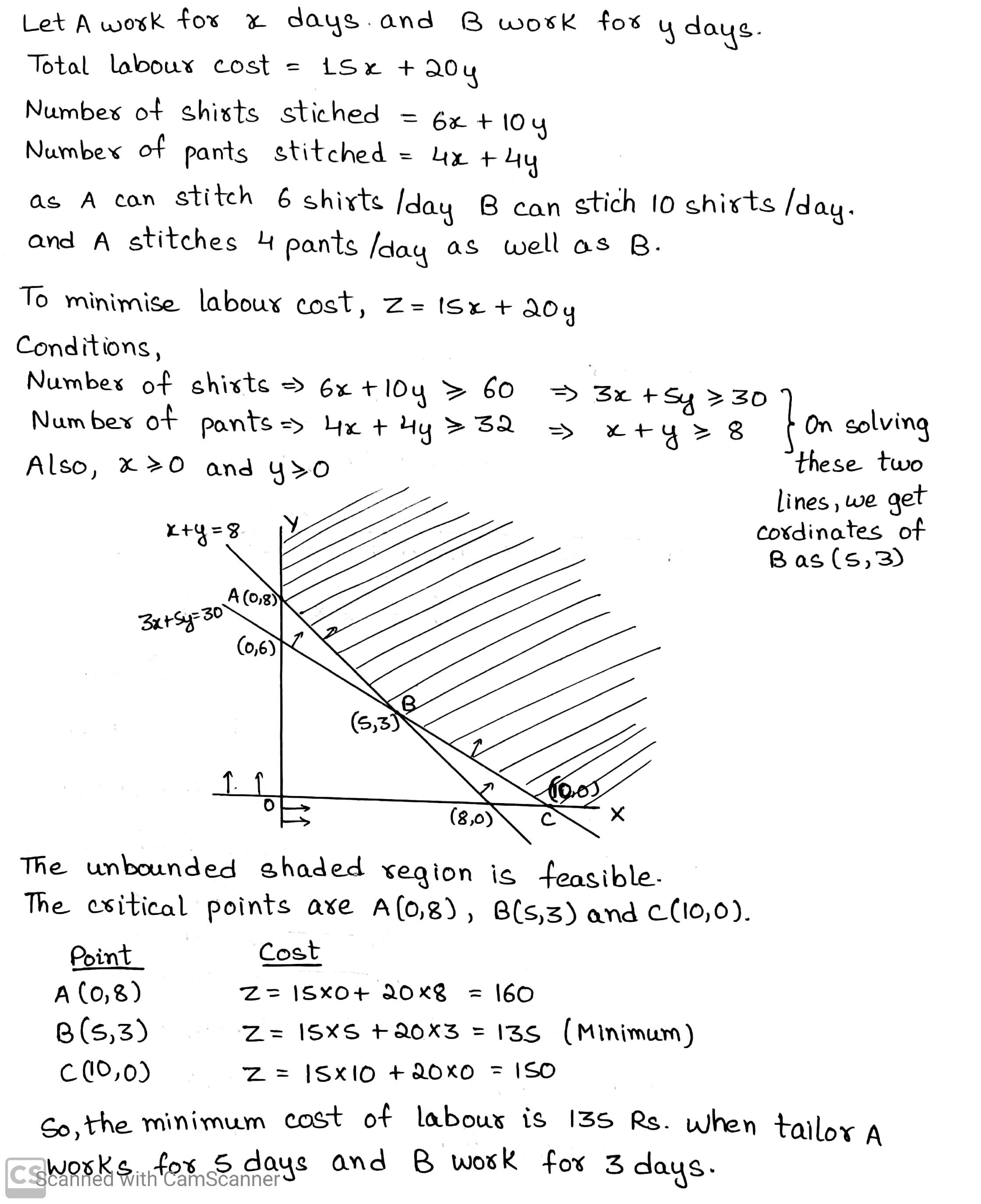
Two tailors $$A$$ and $$B$$ earn Rs. $$ 300$$ and Rs. $$ 400$$ per day respectively. A can stitch $$6$$ shirts and $$4$$ pants per day while $$B$$ can stitch $$10$$ shirts and $$4$$ pants per day. Form a linear programming problem to minimize the labour cost to produce at least $$60$$ shirts and $$32$$ pants.
Vitamin $$A$$ and $$B$$ are found in two different foods $$F_{1}$$ and $$F_{2}$$. One unit of food $$F_{1}$$ contains $$2$$ units of vitamin $$A$$ and $$3$$ units of vitamin $$B$$. One unit of food $$F_{2}$$ contains $$4$$ units of vitamin $$A$$ and $$2$$ units of vitamin $$B$$. One unit of food $$F_{1}$$ and $$F_{2}$$ cost Rs. $$ 50$$ and $$25$$ respectively. The minimum daily requirement for a person of vitamin $$A$$ and $$B$$ is $$40$$ and $$50$$ units respectively. Assuming that any things in excess of daily minimum requirement of vitamin $$A$$ and $$B$$ is not harmful, find out the optimum mixture of food $$F_{1}$$ and $$F_{2}$$ at the minimum cost which meets the daily minimum requirement of vitamin $$A$$ and $$B$$. Formulate this as a $$LPP$$.
Solve each of the following linear programming problem by graphical method.
Minimize $$Z=5x+3y$$
Subject to $$2x+y\ge 10$$
$$x+3y\ge 15$$
$$x\le 10$$
$$y\le 8$$
$$x, y\ge 0$$
Solve each of the following linear programming problem by graphical method.
Minimize $$Z=18x+10y$$
Subject to $$4x+y\le 20$$
$$2x+3y\le 30$$
$$x,y\ge 0$$
Solve each of the following linear programming problem by graphical method.
Maximize $$Z=7x+10y$$
Subject to $$x+y\le 30000$$
$$y\le 12000$$
$$x\ge 6000$$
$$x\ge y$$
$$x, y\ge 0$$
Solve each of the following linear programming problem by graphical method.
Minimize $$Z=2x+4y$$
Subject to $$x+y\ge 8$$
$$x+4y\ge 12$$
$$x\ge 3, y\ge 2$$
A firm has to transport at least $$1200$$ packages daily using large vans which carry $$200$$ packages each and small vans which can take $$80$$ packages each. The cost of engaging each large and the number of large vans is Rs. $$ 400$$ and each small can is Rs. $$ 200$$. Not more than Rs. $$ 3000$$ is to be spent daily on the job and the number of large vans cannot exceed the number of small vans. Formulate this problem as a LPP given that the objective is to minimize cost.
Solve each of the following linear programming problem by graphical method.
Maximize $$Z=15x+10y$$
Subject to $$3x+2y\le 80$$
$$2x+3y\le 70$$
$$x,y\ge 0$$
Solve each of the following linear programming problem by graphical method.
Maximize $$Z=10x+6y$$
Subject to $$3x+y\le 12$$
$$2x+5y\le 34$$
$$x,y\ge 0$$
Solve each of the following linear programming problem by graphical method.
Maximize $$Z=9x+3y$$
Subject to $$2x+3y\le 13$$
$$3x+y\le 5$$
$$x,y\ge 10$$
Solve each of the following linear programming problem by graphical method.
Maximize $$Z=3x+4y$$
Subject to $$2x+2y\le 80$$
$$2x+4y\le 120$$
Solve each of the following linear programming problem by graphical method.
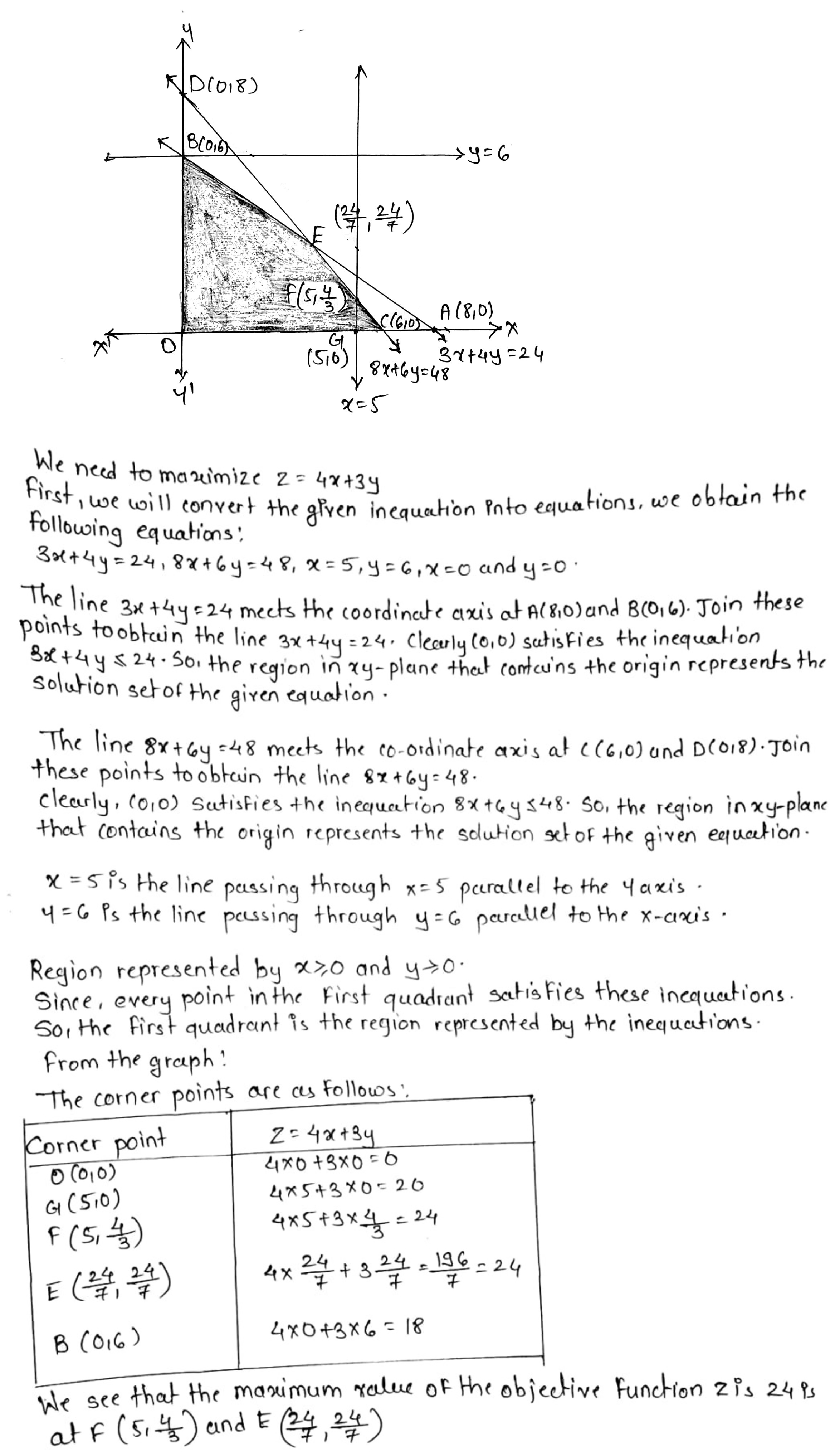
Maximize $$Z=4x+3y$$
Subject to $$3x+4y\le 24$$
$$8x+6y\le 48$$
$$x\le 5$$
$$y\le 6$$
$$x, y\ge 0$$
A diet for a sick person must contain at least $$4000$$ units of vitamins, $$50$$ units of minerals and $$1400$$ of calories. Two foods $$A$$ and $$B$$, are available at a cost of $$Rs. 5$$ and $$Rs. 4$$ per unit respectively. If one unit of $$A$$ contains $$200$$ units of vitamins, 1 unit of minerals and 40 units of calories, while one unit of the food B contains 100 unit of vitamins, 2 unit of minerals and 40 units of calories. Find what combination of foods should be used to have the least cost, but it must satisfy the requirements of the sick person. Form the question as LPP and solve it graphically.
Kellogg is a new cereal formed of a mixture of a mixture of bran and rice that contains at least $$88$$ grams of proteins and at least $$36$$ milligrams of iron. knowing that bran contains $$80$$ grams of protein and $$40$$ milligrams of iron per kilogram, and that rice constant $$100$$ grams of protein and $$30$$ milligrams of iron per kilogram, find the minimum cost of producing this new cereal if bran costs $$Rs. 5$$ per kg and rice costs $$Rs. 4$$ per kg.
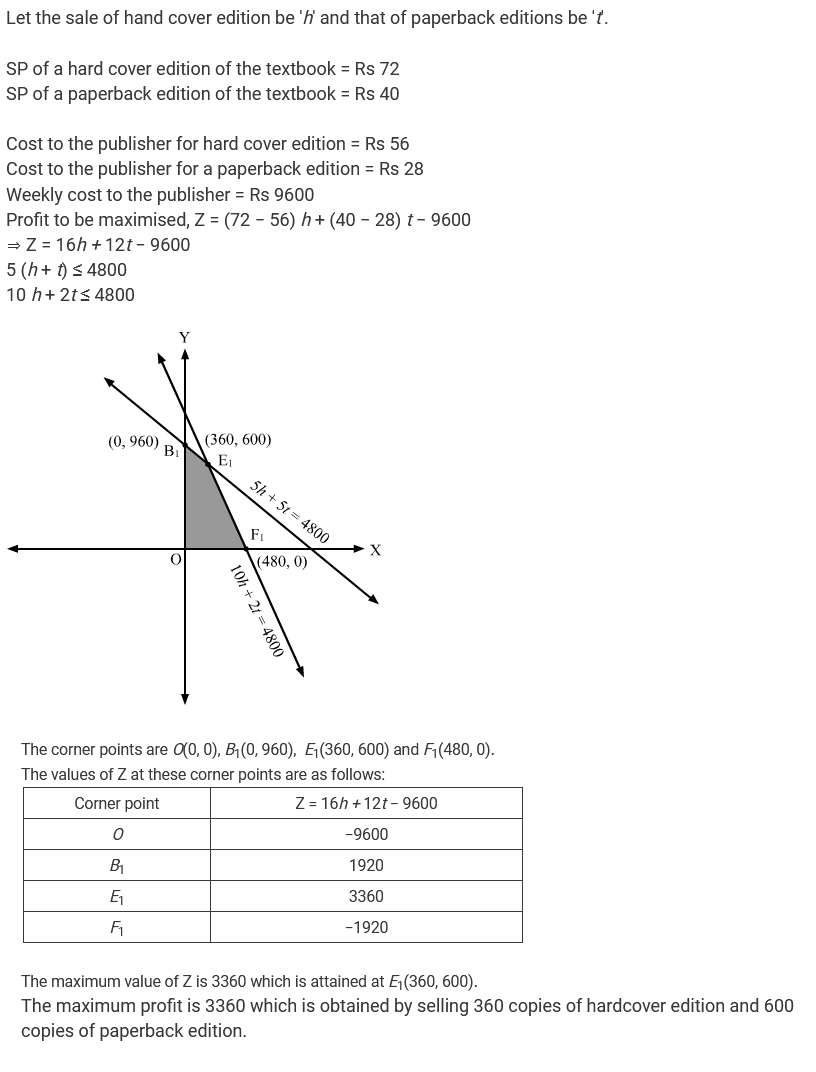
A publisher sells a hard cover edition of a text book for $$Rs. 72$$ and a paperback edition of the same ext for $$Rs. 40$$. Costs to the publisher are $$Rs. 56$$ and $$Rs. 28$$ per book respectively in addition to weekly costs of $$Rs. 9600$$. Both types requires $$5$$ minutes of printing time, although hardcover requires $$10$$ minutes binding time and the paperback requires only $$2$$ minutes. Both the printing the binding operation have $$4,800$$ minutes available each week. How many of each type of book should be produced in order to maximize profit?
A gardener has supply to fertilizer of type I which consists of $$10\%$$ nitrogen and $$6\%$$ phosphoric acid and type II fertilizer which consists of $$5\%$$ nitrogen and $$10\%$$ phosphoric acid. After testing the soil conditions, he finds that he needs at least $$14$$ kg of nitrogen and $$14$$ kg of phosporic acid for his crop. If the type I fertilizer costs $$60$$ paise per kg and type II fertilizer costs $$40$$ paise per kg, determine how many kilogram of each fertilizer should be used so that nutrient requirement are met at a minimum cost. What is the minimum cost?
Anil wants to invest at most $$Rs. 12000$$ in saving certificates and national saving bonds. According to rule, he has to invest at least $$Rs. 2000$$ in saving certificates and at least $$Rs. 4000$$ in National Saving Bonds. If the rate of interest on saving certification is $$8\%$$ per annum and the rate of interest on National Saving Bond is $$10\%$$ per annum, how much money should he invest to earn maximum yearly income? Also find his maximum yearly income.
Solve each of the following linear programming problem by graphical method.
Maximize $$Z=3x+5y$$
Subject to $$x+2y\le 20$$
$$x+y\le 15$$
$$y\le 5$$
$$x,y\ge 0$$
A firm manufactures two types of products $$A$$ and $$B$$ and sells them at a profit of $$Rs. 5$$ per unit of type $$A$$ and $$Rs. 3\ per$$ unit of type $$B$$. Each product is processed on two machines $$M_{1}$$ and $$M_{2}$$. One unit of type $$A$$ requires one minutes of processing time on $$M_{1}$$ and two minutes of processing time on $$M_{2}$$, whereas one unit of type $$B$$ requires one minutes of processing time on $$M_{1}$$ and one minutes on $$M_{2}$$. Machines $$M_{1}$$ and $$M_{2}$$ are respectively available for at most $$5$$ hours and $$6$$ hours in a day. Find out how many units of each type of product should the firm produce a day in order to maximize the profit. Solve the problem graphically.
A company manufactures two types of types of toys $$A$$ and $$B$$. Type $$A$$ requires $$5$$ minutes each for cutting and $$10$$ minutes each for assembling. Type $$B$$ requires $$8$$ minutes each for cutting and $$8 $$ hours minutes each for assembling. There are $$3$$ hours available for cutting and $$4$$ hours available for assembling in a day. The profit is $$Rs. 50$$ each on type $$A$$ and $$Rs. 60$$ each on type $$B$$. How many toys of each type should the company manufacture in a day to maximize the profit?
A dietician mixes together two kinds of food in such a way that the mixture contains at least $$6$$ units of vitamin $$A,7$$ units of vitamin $$B, 11$$ units of vitamin $$C$$ and $$9$$ units of vitamin $$D$$. The vitamin contents of $$1\ kg$$ of food $$X$$ and $$1\ kg$$ of food $$Y$$ are given below:
| Vitamin $$A$$ | Vitamin $$B$$ | Vitamin $$C$$ | Vitamin $$D$$ | |
| Food $$X$$ | $$1$$ | $$1$$ | $$1$$ | $$2$$ |
| Food $$Y$$ | $$2$$ | $$1$$ | $$3$$ | $$1$$ |
A manufacturer produces two types of steel trunks requires $$3$$ hours on machine $$A$$ and $$B$$. For completing, the first types of the trunk requires $$3$$ hours on machine $$A$$ and $$3$$ hours on machine $$B$$. Machine $$A$$ and $$B$$ can work at most for $$18$$ hours and $$15$$ hours per day respectively. He earns a profit if $$Rs. 30$$ and $$Rs. 25$$ per trunk of the first type and the second type respectively. How many trunks of each type must he make each day to make maximum profit?
There are two types of fertilizers $$'A'$$ and $$'B'$$. $$'A'$$ consists of $$12\%$$ nitrogen and $$5\%$$ phosphoric acid whereas $$'B'$$ consists of $$4\%$$ nitrogen and $$5\%$$ phosphoric acid. After testing the soil conditions, farmer finds that he needs at least $$12$$ kg of nitrogen and $$12$$ kg of phosphoric acis for his crops. If $$'A'$$ costs Rs. $$ 10$$ per kg and $$'B'$$ cost Rs. $$8$$ per kg, then graphically determine how much of each type of fertilizers should be used sot hat nutrient requirements are met at a minimum cost.
A factory makes tennis rackets and cricket bats. A tennis racket takes $$1.5$$ hours of machine time and $$3$$ hours of craftsman's time in its making while a cricket bat takes $$3$$ hour of machine time and $$1$$ hour of craftsman's time. In a day, the factory has the availability of not more than $$42$$ hours of machine time and $$24$$ hours of craftsman's time. If the profit on a racket and on a bat is Rs. $$ 20$$ and Rs. $$10$$ respectively, find the maximum profit of the factory when it works a full capacity.
Find the maximum value of $$Z = 7x + 7y$$, subject to the constraints $$x\geq 0, y \geq, x + y \geq 2$$ and $$2x + 3y \leq 6$$.
Solve the following linear programming problem:
Maximise: $$z=150x+250y$$
Subject to: $$4x+y \le 40$$
$$3x+2y\le 60$$
$$x\ge 0$$
$$y\ge 0$$
Show that the solution set of the following linear constraints is empty:
$$x - 2y \geq 0, 2x - y \leq -2, x \geq 0$$ and $$y\geq 0$$.
A company manufactures two articles $$A$$ and $$B$$. There are two department through which these article are processed : (i) assembly and (ii) finishing department. The maximum capacity of the first department is $$60$$ hours a week and that of other department. $$48$$ hours, per week. The product of each unit of article $$A$$ requires $$4$$ hours in assembly and $$2$$ hours in finishing and that of each unit of $$B$$ requires $$2$$ hours in assembly and $$4$$ hours in finishing. If the profit is Rs. $$ 6$$ for each unit $$A$$ and Rs. $$ 8$$ for each unit of $$A$$ and Rs. $$ 8$$ for each unit of $$B$$, find the number of units of $$A$$ and $$B$$ to be produced per week in order to have maximum profit.
A medical company has factories at two places, $$A$$ and $$B$$. From these places, supply is made to each of its three agencies situated at $$P,Q$$ and $$R$$. The monthly requirement of the agencies are respectively $$40, 40$$ and $$50$$ packets of the medicines, while the production capacity of the factories, $$A$$ and $$B$$ are $$60$$ and $$70$$ packets respectively. The transportation cost per packet from the factories to the agencies are given below:
| Transportation cost per packet (in Rs) | ||
| To $$\downarrow$$ \ From $$\to$$ | $$A$$ | $$B$$ |
| $$P$$ | $$5$$ | $$4$$ |
| $$Q$$ | $$4$$ | $$2$$ |
| $$R$$ | $$3$$ | $$5$$ |
Find the linear constraints for which the shaded area in the figure given is the solution set.
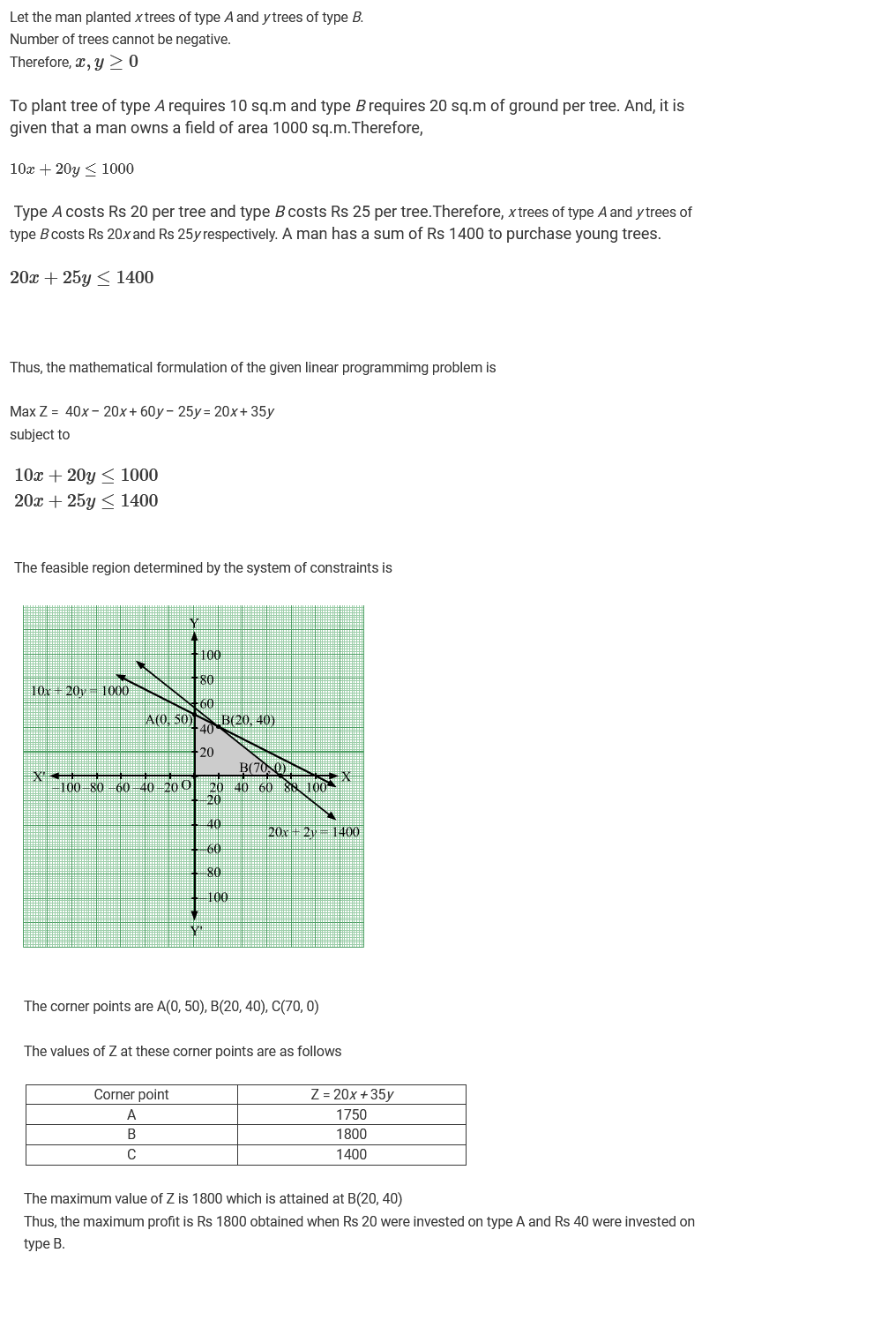
A man owns a field of area $$1000\ m^{2}$$. He wants to plant fruit trees in it. He has a sum of $$Rs. 1400$$ to purchase young trees. He has the choice of two types of trees. Type $$A$$ requires $$10\ m^{2}$$ of ground per tree and costs $$Rs. 20$$ per tree, and type $$B$$ requires $$20\ m^{2}$$ of ground per tree and costs $$Rs. 25$$ per tree. When full grown, a type-$$A$$ tree produces and average of $$20\ kg$$ of fruit which can be sold at a profit of $$Rs. 2$$ per kg and a type -$$B$$ tree produces an average of $$40\ kg$$ of fruit which can be sold at a profit of $$Rs. 1.50$$ per kg. How many of each type should be planted to achieve maximum profit when trees are fully grown? What is the maximum profit?
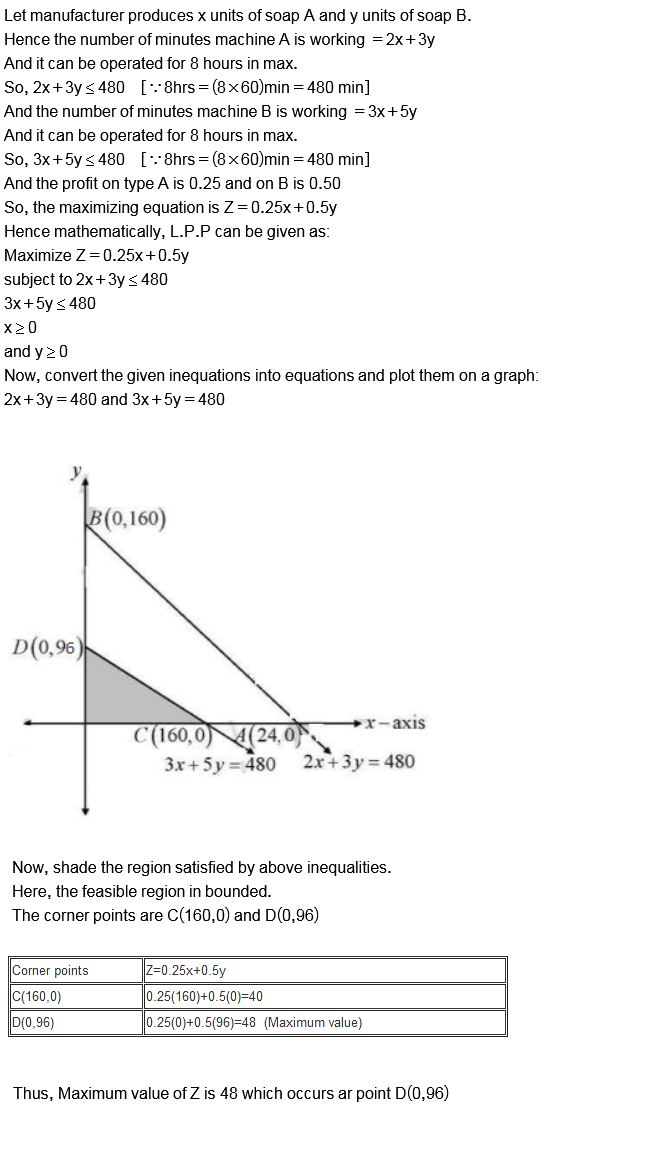
A manufacturer produces two types of soap bars using two machines, $$A$$ and $$B$$. $$A$$ is operated for $$2$$ minutes and $$B$$ for $$3$$ minutes to manufacture the first type, while it takes $$3$$ minutes on machine $$A$$ and $$5$$ minutes on machine $$B$$ to manufacture the second type. Each machine can be operated at the most for $$8$$ hours per day. The two types of soap bars are sold at a profit of $$Rs. 0.25$$ and $$Rs. 0.50$$ each. Assuming that the manufacturer can sell all the soap bars he can manufacture, how many bars of soap of each type should be manufactured per day so as to maximize his profit?
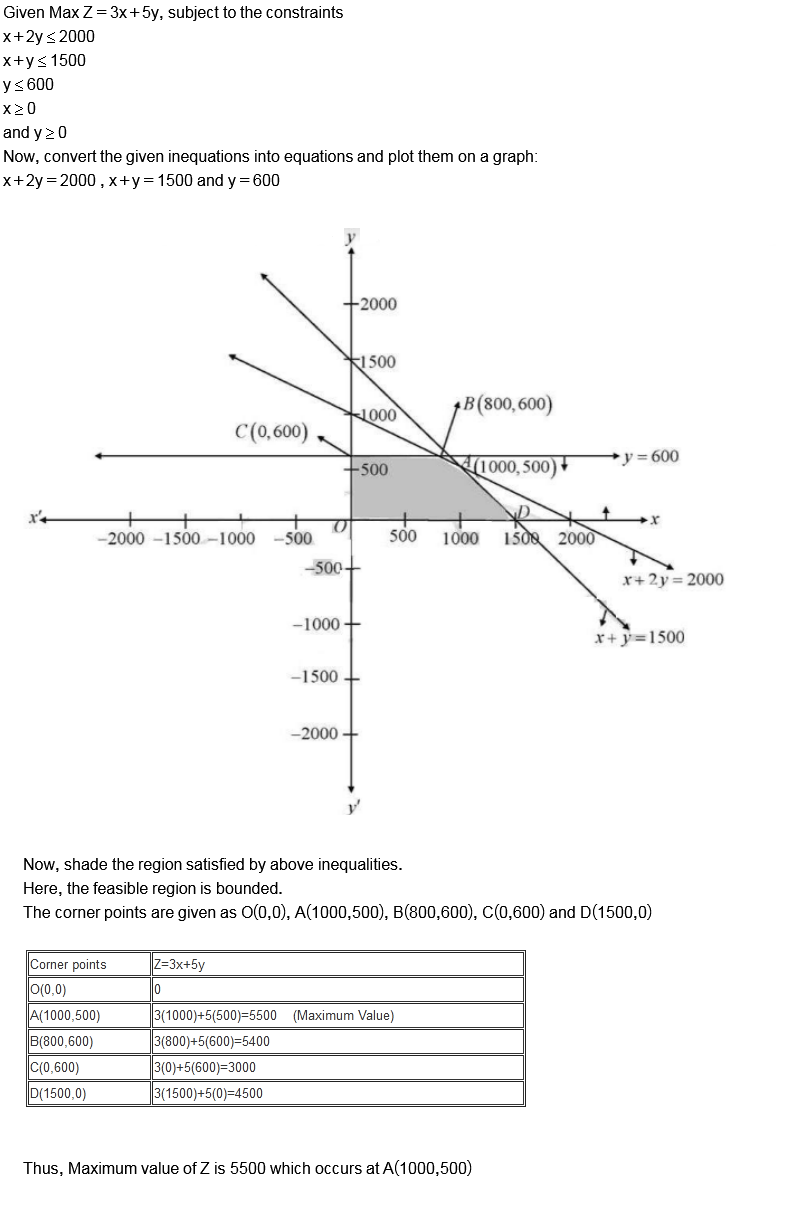
Maximize $$Z = 3x + 5y$$, subject to the constraints $$x + 2y \leq 2000, x + y \leq 1500, y \leq 600, x \geq 0$$ and $$y\geq 0$$.
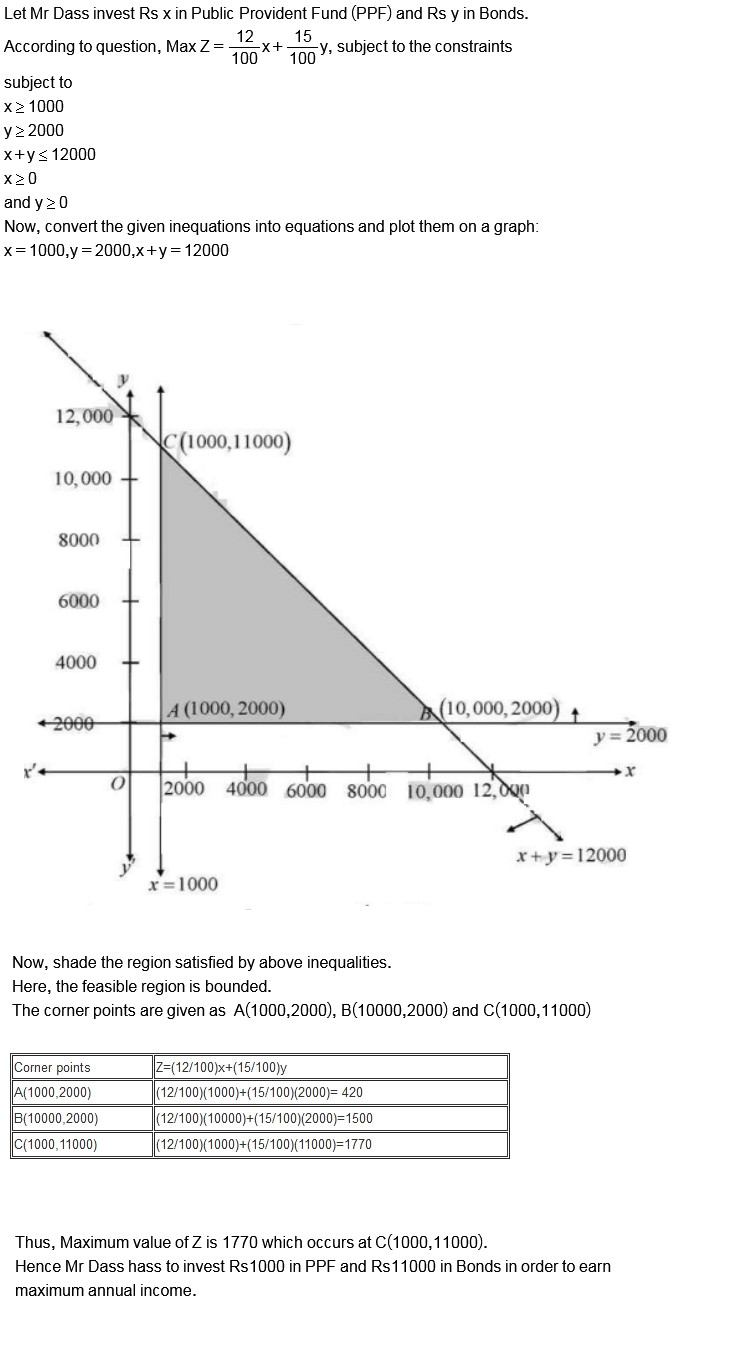
Mr Dass wants to invest $$Rs. 12000$$ in Public Provident Fund (PPF) and in National bonds. He has to invest at least $$Rs. 1000$$ in PPF and at least $$Rs. 2000$$ in bonds. If the rate of interest on PPF is $$12\%$$ per annum and that on bonds is $$15\%$$ per annum, how should he invest the money to earn maximum annual income? Also find maximum annual income.
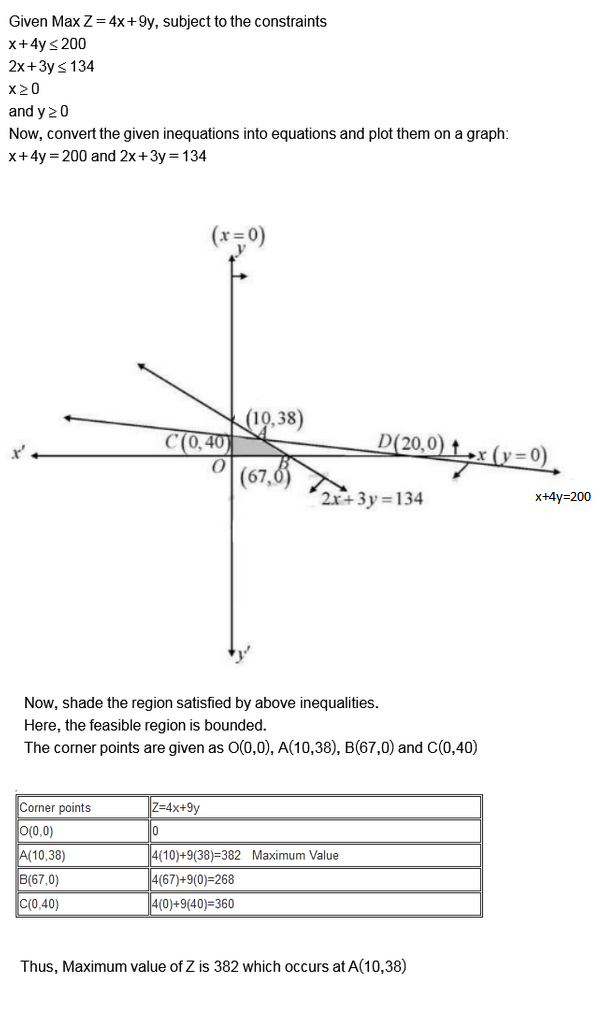
Maximize $$Z = 4x + 9y$$, subject to the constraints $$x\geq 0, y \geq 0, x + 4y \leq 200, 2x + 3y \leq 134$$.
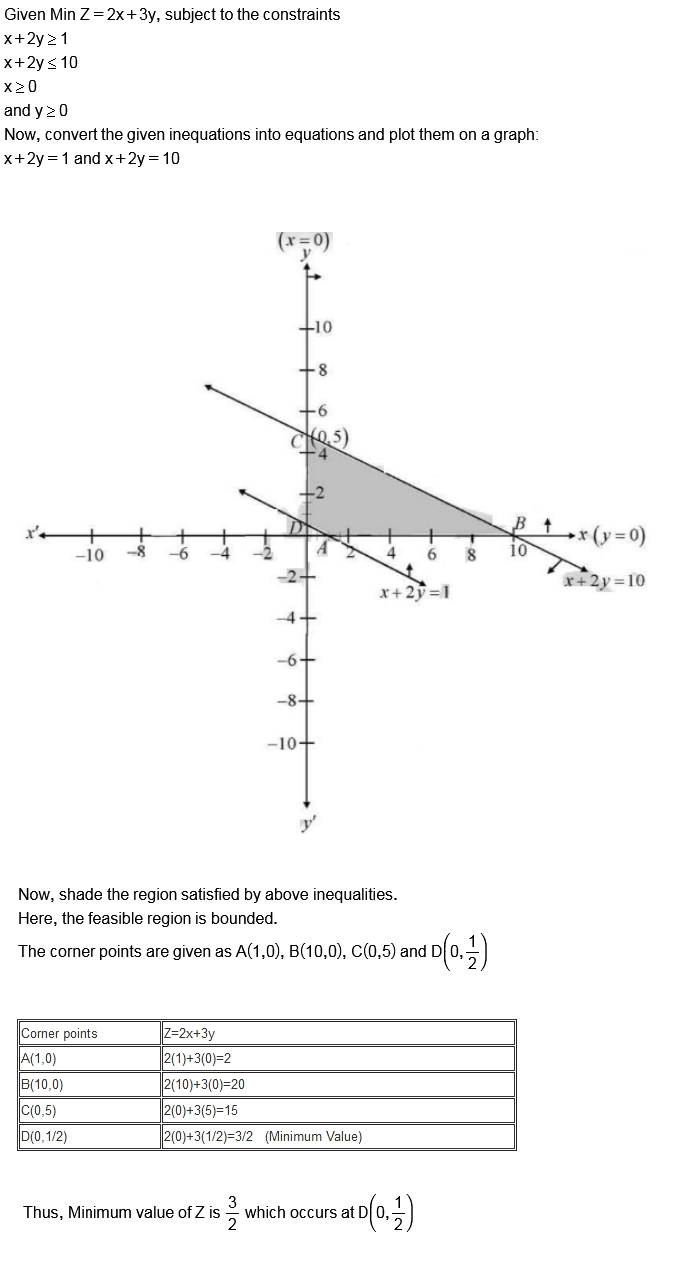
Minimize $$Z = 2x + 3y$$, subject to the constraints $$x \geq 0, y \geq 0, x + 2y \geq 1$$ and $$x + 2y \leq 10$$.
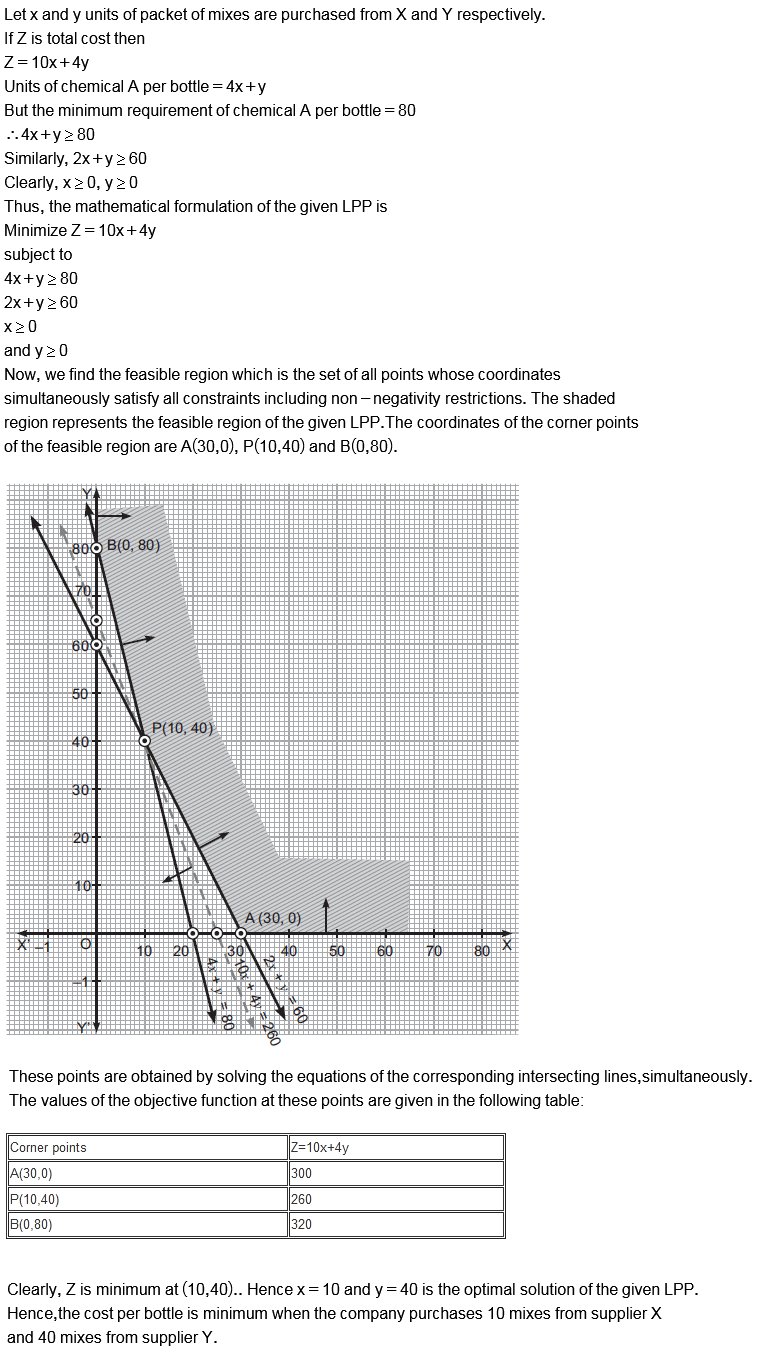
A company producing soft drinks has a contract which requires a minimum of $$80$$ units of chemical $$A$$ and $$60$$ units of chemical $$B$$ to go in each bottle of the drink. The chemicals are available in a prepared mix from two different suppliers. Supplier $$X$$ has a mix of $$4$$ units of $$A$$ and $$2$$ units of $$B$$ that costs $$Rs. 10$$, and the supplier $$Y$$ has a mix of $$1$$ unit of $$A$$ and $$1$$ unit of $$B$$ that costs $$Rs. 4$$. How many mixes from $$X$$ and $$Y$$ should the company purchase to honour the contract requirement and yet minimize the cost?
A firm manufactures two types of products, $$A$$ and $$B$$, and sells them at a profit of $$Rs. 2$$ on type $$A$$ and $$Rs. 2$$ on type $$B$$. Each product is processed on two machines, $$M_{1}$$ and $$M_{2}$$. Type $$A$$ requires one minute of processing time on $$M_{1}$$ and two minutes on $$M_{2}$$. Type $$B$$ requires one minute on $$M_{1}$$ and one minute on $$M_{2}$$ is available for at most $$10$$ hours a day.
Find how many producs of each type the firm should produce each day in order to get maximum profit.
Find the minimum value of $$Z = 3x + 5y$$, subject to the constraints $$-2x + y \leq 4, x + y \geq 3, x - 2y \leq 2, x \geq 0$$ and $$y\geq 0$$.
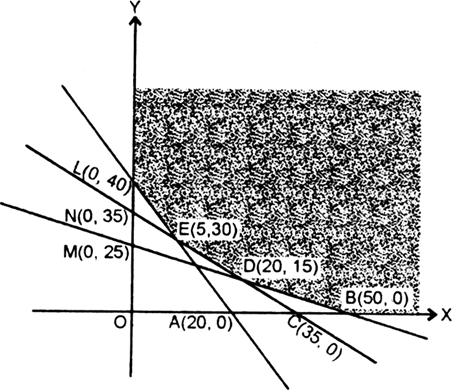
Find the maximum and minimum values of $$Z = 2x + y$$. subject to the constraints
$$x + 3y \geq 6, x - 3y \leq 3, 3x + 4y \leq 24, -3x + 2y \leq 6, 5x + y \geq 5, x \geq 0$$ and $$y \geq 0$$.
An aeroplane can carry a maximum of $$200$$ passengers. A profit of $$500 \ Rs.$$ is made on each executive class ticket out of which $$20 \%$$ will go to the welfare fund of the employees. Similarly a profit of $$400 \ Rs.$$ is made on each economy ticket out of which $$25 \%$$ will go for the improvement of facilities provided to economy class passengers. In both cases, the remaining profit goes to the airline's fund. The airline reserves at least 20 seats for executive class. However, at least four times as many passengers prefer to travel by economy class than by the executive class. Determine, how many tickets of each type must be sold in order to maximise the net profit of the airline. Make the above as an LPP and solve graphically.
A brick manufacturer has two depots, $$P$$ and $$Q$$, with stocks of $$30000$$ and $$20000$$ bricks respectively. He receives order from three buildings $$A, B, C$$ for $$15000, 20000$$ and $$15000$$ bricks respectively. The cost of transporting $$1000$$ bricks to the buildings from the depots are given below.
| Cost of transportation (in Rs. per $$1000$$ bricks) | |||
| From To | A | B | C |
| $$P$$ | $$40$$ | $$20$$ | $$30$$ |
| $$Q$$ | $$20$$ | $$60$$ | $$40$$ |
Maximise $$ z = 8x + 9y $$ subject to the constraints given below :
$$ 2x + 3y \leq 6; 3x - 2y \leq 6; y \leq 1; x\geq 0; y \geq 0$$
A manufacturer has $$640$$ litres of a $$8\%$$ solution of boric acid. How many litres of a $$2\%$$ boric acid solution be added to it so that the boric acid content in the resulting mixture will be more than $$4\%$$ but less than $$6\%$$?
A company manufactures cassettes. Its cost and revenue functions are $$C(x)=26000+30x$$ and $$R(x)=43x$$ respectively, where $$x$$ is the number of cassettes produced and sold in a week. How many cassettes must be sold by the company to realise some profit?
How many litres of water will have to be added to $$600$$ litres of the $$45\%$$ solution of acid so that the resulting mixture will contain more than $$25\%$$, but less than $$30\%$$ acid content?
The water acidity in a pool is considered normal when the average $$pH$$ reading of three daily measurements between $$8.2$$ and $$8.5$$. If the first two $$pH$$ readings are $$8.48$$ and $$8.35$$, find the range of the $$pH$$ values for the third reading that will result in the acidity level being normal.
A village has 500 hectare of land to grow two types of plants, $$X$$ and $$Y$$. The contributions of total amount of oxygen produced by plant $$X$$ and plant $$Y$$ are $$60 \%$$ and $$40 \%$$ per hectare respectively. To control weeds, a liquid herbicide has to be used for $$X$$ and $$Y$$ at rates of $$20$$ litres and $$10$$ litres per hectare, respectively. Further no more than $$8000$$ litres of herbicides should be used in order to protect aquatic animals in a pond which collects drainage from this land. How much land should be allocated to each crop so as to maximise the total production of oxygen?
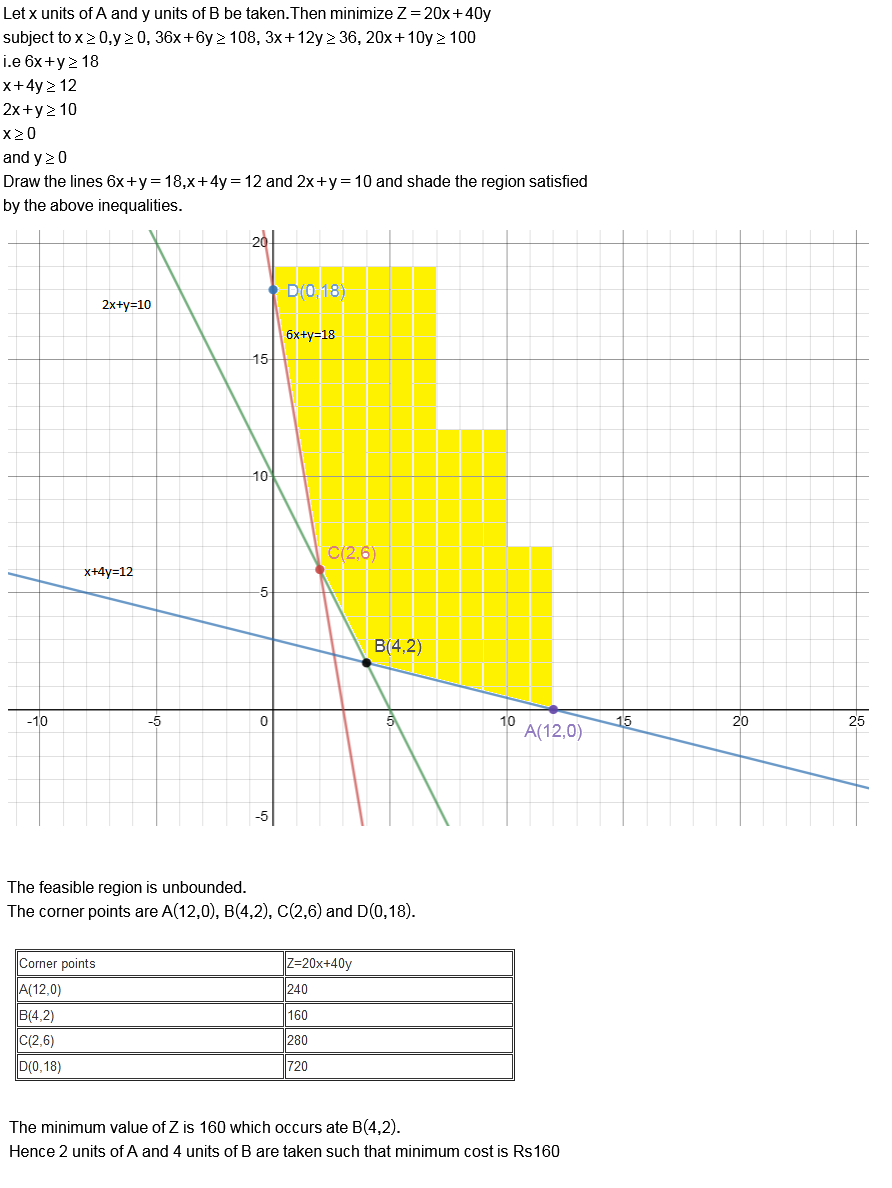
A firm is engaged in breeding pigs. The pigs are fed on various products grown on the farm. They need certain nutrients, names as $$X, Y, Z$$. The pigs are fed on two products, $$A$$ and $$B$$. One unit of product $$A$$ contains $$36$$ units of $$X, 3$$ units of $$Y$$ and $$20$$ units of $$Z$$, while one unit of product $$B$$ contains $$6$$ units of $$X, 12$$ units of $$Y$$ and $$10$$ units of $$Z$$. The minimum requirements of $$X, Y, Z$$ are $$108\ units, 36\ units$$ and $$100\ units$$. respectively. Product $$A$$ costs $$Rs. 20$$ per unit and product $$B$$ costs $$Rs. 40$$ per unit. How many uits of each product must be taken to minimize the cost? Also, find the minimum cost.
Determine the maximum value of $$Z = 3x + 4y $$ if the feasible region (shaded) for a LPP is shown in Fig.
The feasible region for a LPP is shown in Fig. 12.Find the minimum value of $$Z = 11x + 7y$$.
Feasible region (shaded) for a LPP is shown in Fig., Maximise $$Z = 5x + 7y$$.
Maximise $$Z = 3x + 4y$$, subject to the constraints : $$x + y \leq 1, x \geq 0, y \geq 0$$.
Minimise $$Z = 13x - 15y$$ subject to the constraints :
$$x + y \leq 7, 2x - 3y + 6 \geq 0, x \geq 0, y \geq 0$$.
Maximise the function $$Z = 11x + 7y$$, subject to the constraints:
$$x \leq 3, y \leq 2, x \geq 0, y \geq 0$$
The feasible region for a LPP is shown in Fig. Evaluate $$Z = 4x + y$$ at each of the corner points of this region. Find the minimum value of Z, if it exists.
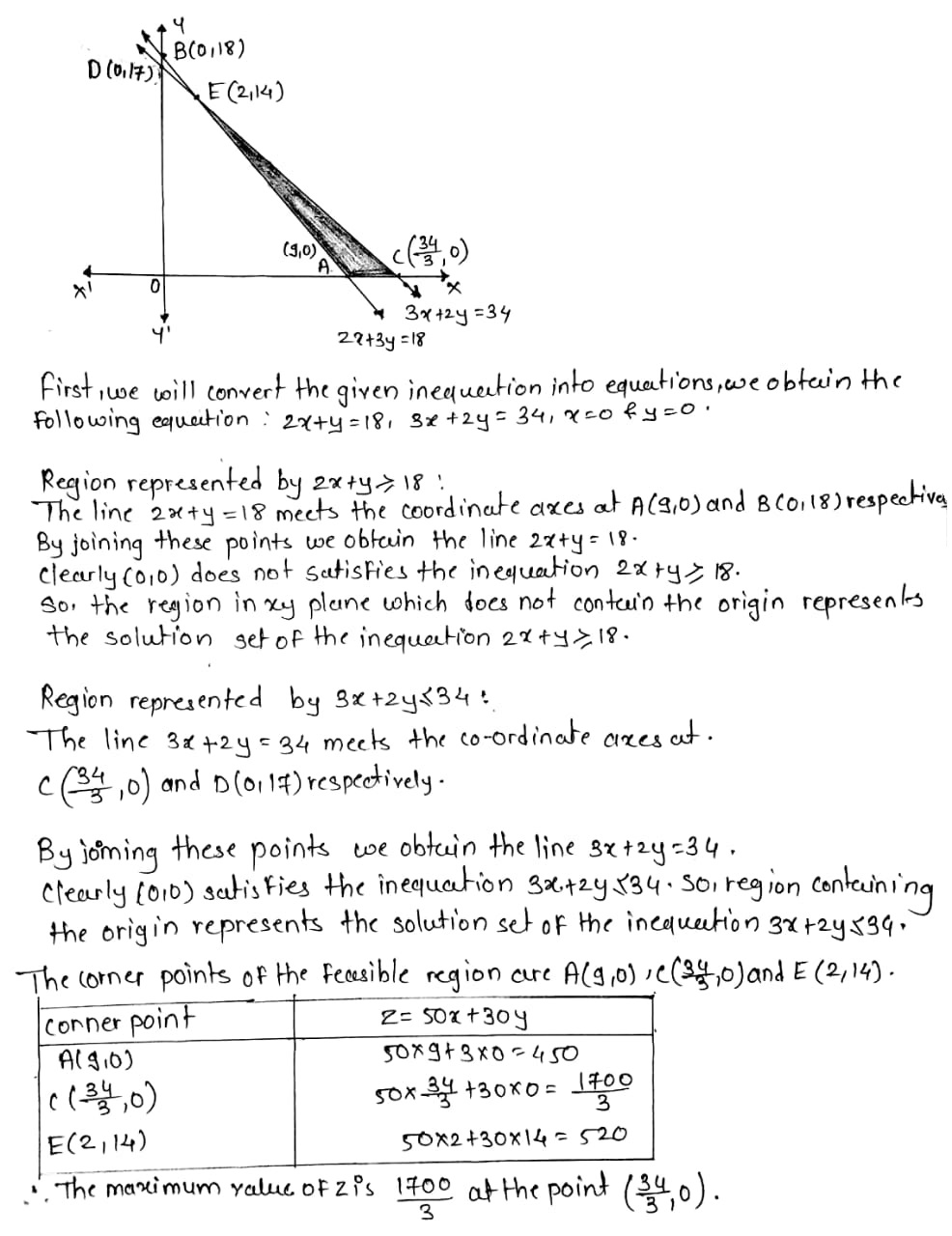
A manufacturer of electronic circuits has a stock of 200 resistors, 120 transistors and 150 capacitors and is required to produce two types of circuits A and B. Type A requires 20 resistors, 10 transistors and 10 capacitors. Type B requires 10 resistors, 20 transistors and 30 capacitors. If the profit on type A circuit is Rs. 50 and that on type B circuit is Rs. 60, formulate this problem as a LPP so that the manufacturer can maximise his profit.
Determine the maximum value of $$Z = 11x + 7y$$ subject to the constraints : $$2x + y \leq 6, x \leq 2, x \geq 0, y \geq 0$$.
In Fig., the feasible region (shaded) for a LPP is shown. Determine the maximum and minimum value of $$Z = x + 2y$$.
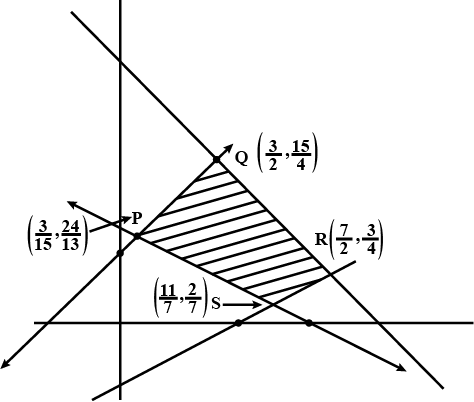
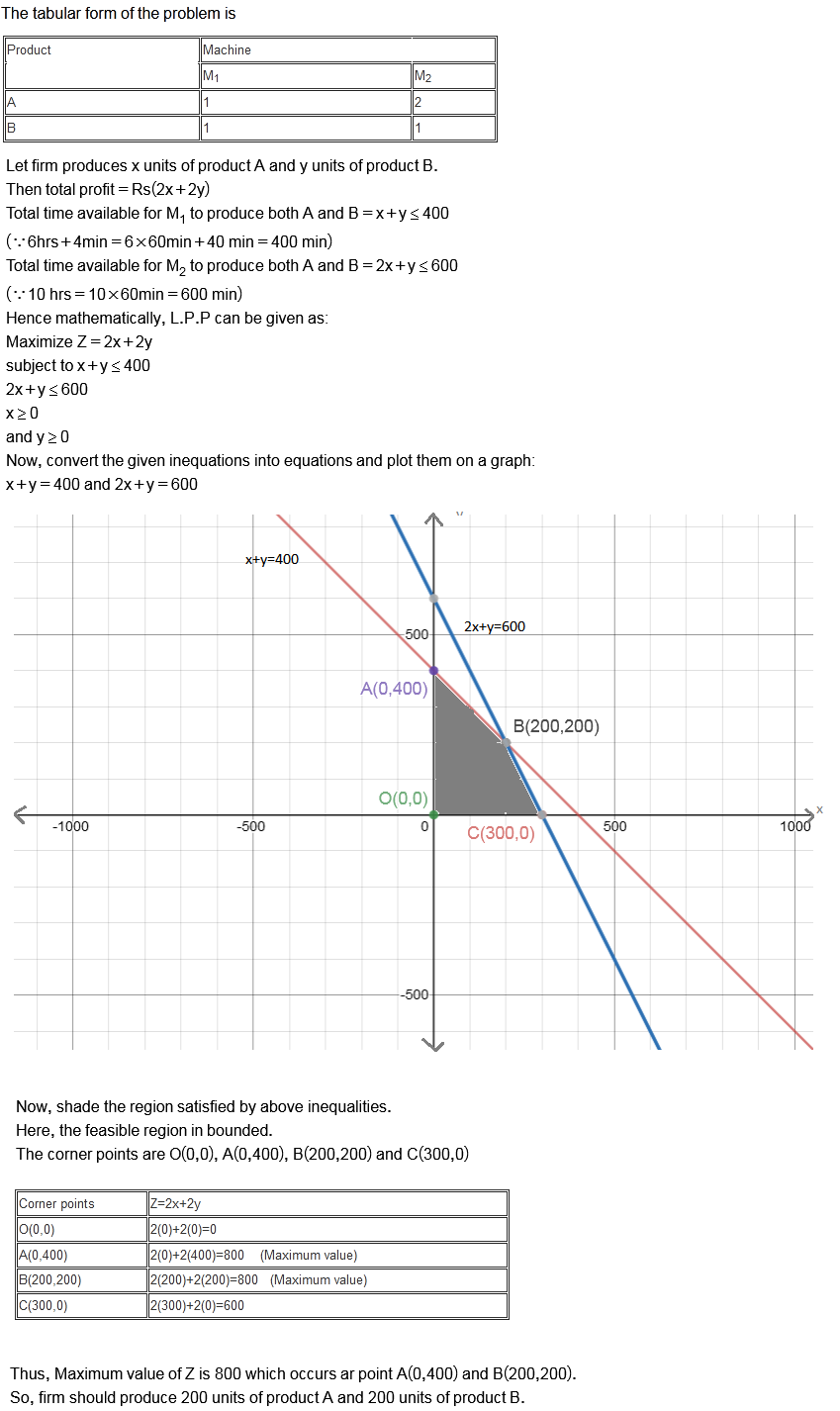
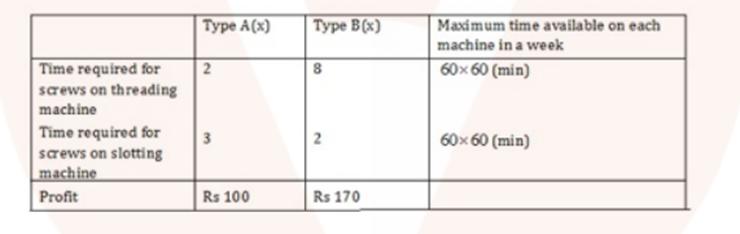
A company manufactures two types of screw A and B. All the screws have to pass through a threading machine and a slotting machine. A box type A screws requires 2 minutes on the threading machine and 3 minutes on the slotting machine. A box of type B screws requires 8 minutes of threading on the threading machine and 2 minutes on the slotting machine. In a week, each machine is available for 60 hours.
On selling these screws, the company gets a profit of Rs 100 per box on type A screws and Rs 170 per box on type B screws.
Formulate this problem as a LPP given that the objective is to maximise profit.
Fill in the blank.If the feasible region for a LPP is _______, then the optimal value of the objective function Z = ax + by may or may not exist.
Fill in the blank.In a LPP, the objective function is always _________ .
A man rides his motorcycle at the speed of 50 km/hour. He has to spend Rs 2 per km on petrol. If he rides it at a faster speed of 80 km/hour, the pertrol cost increases to Rs 3 per km. He has at most Rs 120 to spend on petrol one hour time. He wishes to find the maximum distance that he can travel.
Express this problem as a linear programming problem.
A company manufactures two types of sweaters: type A and type B. It costs Rs 360 to make a type A sweater and Rs 120 to make a type B sweater. The company can make at most 300 sweaters and spend at most Rs 72000 a day. The number of sweaters of type B cannot exceed the number of sweaters of type A by more thanThe company makes a profit of Rs 200 for each sweater of type A and Rs 120 for every sweater of type B. Formulate this problem as a LPP to maximise the profit of the company.
Fill in the blank.A corner point of a feasible region is a point in the region which is the _________ of two boundary lines.
Refer to ExerciseHow many of circuits of Type A and Type B, should be produced by the manufacturer so as to maximise his profit? Determine the maximum profit.
Fill in the blank.A feasible region of a system of linear inequalities is said to be ________ if it can be enclosed within a circle.
Fill in the blank.In a LPP if the objective function Z = ax + by has the same maximum value on two corner points of the feasible region, then every point on the line segment joining these two points give the same ________ value.
Fill in the blank.The feasible region for an LPP is always a _________ polygon.
Refer to ExerciseWhat will be the minimum cost?
A company makes 3 model of calculators : A, B and C at factory I and factory II. The company has ordered for at least 6400 calculators of model A, 4000 calculators of model B and 4800 calculators of model C. At factory I, 50 calculators of model A, 50 calculators of model B and 30 calculators of model C are made every day; at Factory II, 40 calculators of model A, 20 calculators of model B and 40 calculators of model C are made everyday. It costs Rs 12000 and Rs 15000 each day to operate factory I and II, respectively. Find the number of days each factory should operate to minimise the operating costs and still meet the demand.
Refer to ExerciseHow many sweaters of each type should the company make in a day to get a maximum profit? What is the maximum profit?
| Tablets | Iron | Calcium | Vitamin |
| X Y | 6 2 | 3 3 | 2 4 |
The person needs at least 18 milligram of iron, 21 milligram of calcium and 16 milligram of vitamins. The price of each tablet of X and Y is Rs 2 and Re 1 respectively. How many tablets of each should the person take in order to satisfy the above requirement at the minimum cost?
In a cattle breeding firm, it is prescribed that the food ration from one animal must contain 14.22 and 1 units of nutrients A, B, and C respectively. Two different kinds of fodder are available. Each unit of these two contains the following amounts of these three nutrients:
Fodder$$\rightarrow$$
| Nutrient | Fodder 1 | Fodder 2 |
| Nutrients A | 2 | 1 |
| Nutrients B | 2 | 1 |
| Nutrients C | 1 | 1 |
A manufacturing firm produces two types of gadgets A and B, which are first processed in the foundry and then sent to the machine shop for finishing. The number of man-hours of labour required in each shop for production of A and B and the number of man-hours available for the firm is as follows:
| Gadgets | Foundry | Machine shop |
| A | 10 | 5 |
| b | 6 | 4 |
| TIme available (Hour) | 60 | 35 |
Refer to ExerciseSolve the linear programming problem and determine the maximum profit to the manufacturer.
Refer to ExerciseDetermine the maximum distance that the man can travel.
A manufacturer produces two models of bikes- model X and model Y. Model X takes a 6 man-hours to make per unit, while model Y takes 10 man-hours per unit. There is a total of 450 man-hour available per week. Handling ans marketing costs are Rs 2000 and Rs 1000 per unit for models X and Y respectively. The total funds available for these purpose are Rs 80,000 per week. Profits per unit for models X and Y are Rs 1000 and Rs 500, respectively. How many bikes of each model should the manufacturer produce so as to yield a maximum profit? Find the maximum profit.
Maximise Z = x + y subject to $$x + 4y \leq 8, 2x + 3y \leq 12, 3x + y \leq 9, x \geq 0, y \geq 0$$.
Maximise and minimise Z = 3x - 4y, subject to
$$x - 2y \leq 0$$
$$-3x + y \leq 4$$
$$x -y \leq 6$$
$$x, y \geq 0$$
Solve the following LPP by graphical method:
Maximize $$z = 7x + 11y,$$ subject to $$3x + 5y \leq 26, 5x +3y \leq 30, x \geq 0, y \geq 0 $$
Solve then following LPP graphically:
Maximize : Z = 10x + 25y
Subjec to : $$x \leq 3, y \leq 3, x + y \leq 5, x \geq 0, y \geq 0.$$
If john drives a car at a speed of 60 km/hour, he has to spend $$\square$$ 5 per km on petrol. If he drives at a faster speed of 90 km/hour, the cost of petrol increases $$\square$$ 8 per km. he has $$\square$$ 600 to spend on petrol and wishes to travel the maximum distance within an hour. Formulate the above problem as LPP.
A manufacturer produces bulbs and tubes. Each of these must be processed through two machines $$M_{1}$$ and $$M_{2}$$. A package of build requires 1 hour of work on machine $$M_{1}$$ and 3 hours on machine $$M_{2}$$. A package of tubes requires 2 hours on machine $$M_{1}$$ and 4 hours on machine $$M_{2}$$. He earns a profit of $$\square$$13.5 per package of bulbs and $$\square$$ 55 per package of tubes. Formulate the LPP to maximize the profit, if he operates the machine $$M_{1}$$, for almost 10 hours a day and machine $$M_{2}$$ for almost 12 hours a day.
Solve the following LPP by graphical method:
Maximize $$z = 4x + 6y,$$ subject to $$3x + 2y \leq 12, x + y \geq 4, x, y \geq 0.$$
Solve the following LPP by graphical nethod:
Maximmize : $$z = 3x + 5y$$
Subject to : $$x + 4y \leq 24$$
$$3x + y \leq 21$$
$$x + 7 \leq 9$$
$$x \geq 0, y \geq 0.$$
A company manufactures two types of fertilizers $$F_{1}$$ and $$F_{2}$$. Each type of fertilizers requires two types of raw materials A and B. The number of unit of A and B required to manufacture one unit of fertilizer $$F_{1}$$ and $$F_{2}$$ and availability of the raw materials A and B per day are given in the table below:
Fertilizers$$\rightarrow$$
| Raw material | $$F_{1}$$ | $$F_{2}$$ | Availability |
| A | 2 | 3 | 40 |
| B | 1 | 4 | 70 |
The company makes concrete bricks made up of cement and sand. The weight of a concrete brick has to be at least 5 kg. Cement costs $$\square$$20 per kg and sand costs of $$\square$$6 per kg. Strength consideration dictates that a concrete brick should contain minimum 4 kg of cement and not more than 2 kg of sand. Form the LPP for the cost to be minimum.
A doctor has prescribed two different units of food A and B to form a weekly diet for a sick person. The minimum requirements of fat, carbohydrates and proteins are 18, 24, 14 units respectively. One unit of food A has 4 units of fat, 14 units of carbohydrates and 8 units of protein. One unit of food B has 6 units of fat, 12 units of carbohydrates and 8 units of protein. The price of food A is $$\square$$ 4.5 per unit and that of food B is $$\square$$ 3.5 per unit. Form the LPP, so that the sick person's diet meets the requirements at a minimum cost.
A printing company prints two types of magazines A and B. The company earns $$\square$$ 10 and $$\square$$ 15 in magazines A and B per copy. These are processed on three machines I, II, III. Magazine A requires 2 hours on Machine I, 5 hours on Machine II, and 2 hours on Machine III. Magazine B requires 3 hours on Machine I, 2 hours on Machine II, and 6 hours on Machine III. Machines I, II, III are available for 36,50, and 60 hours per week respectively. Formulate the LPP to determine weekly production of magazines A and B, so that the total profit is maximum.
Solve the following LPP:
Maximize $$z = 4x_{1} + 3x_{2}$$ subject to
$$3x_{1} + x_{2} \leq 15, 3x_{1} + 4x_{2} \leq 24, x_{1} \geq 0, x_{2} \geq 0.$$
Solve then following LPP graphical method:
Maximize : Z = 7x + y
Subject to : $$5x +y \geq 5, x + y \geq 3, x \geq 0, y \geq 0.$$
Solve the following LPP:
Maximize $$z = 5x_{1} + 6x_{2}$$ subject to $$2x_{1} + 3x_{2} \leq 18, 2x_{1} + x_{2} \leq 12, x_{1} \geq 0, x_{2} \geq 0.$$
Solve the following LPP by graphical method:
Mininize z = 8x + 10y,
Subject to $$2x + y \geq 7, 2x + 3y \geq 15, y \geq 2, x \geq 0, y \geq 0.$$
Solve then following LPP graphical method:
Maximize : z = 6x + 21y
Subject to : $$x + 2y \geq 3, x + 4y \geq 4, 3x + y \geq 3, x \geq 0, y \geq 0.$$
Solve the following problem graphically:
Minimize $$Z = -3x + 4y$$ subject to $$x + 2y \leq 8; 3x + 2y \leq 12; x \geq 0, y \geq 0.$$
Solve the following problem graphically:
Maximize $$Z = 3x + 4y$$ subject to the constraints : $$x + y \leq 4, x \geq 0, y \geq 0.$$
Show that the minimum of Z occurs at more than two points
Minimise and Maximise $$Z = x + 2y$$
subject to $$x + 2y \geq 100, 2x - y \leq 0, 2x + y \leq 200; x, y \geq 0.$$
Show that the minimum of Z occurs at more than two points
Maximise $$Z = x + y,$$
subject to $$x - y \leq -1, -x + y \leq 0, x, y \geq 0.$$
A factory makes tennis rackets and cricket bats. A tennis racket takes $$1.5$$ hours of machine time and $$3$$ hours of craftman's time in its making while a cricket bat takes $$3$$ hour of machine time and $$1$$ hour of craftman's time. In a day, the factory has the availability of not more than $$42$$ hours of machine time and $$24$$ hours of craftman's time.
(i) What number of rackets and bats must be made if the factory is to work at full capacity ?
(ii) If the profit on a racket and on a bat is $$Rs.20$$ and $$Rs.10$$ respectively, find the maximum profit of the factory when it works at full capacity.
A manufacturer produces nuts and bolts. It takes $$1$$ hour of work on machine A and $$3$$ hours on machine B to, produce a package of nuts. It takes $$3$$ hours on machine A and $$1$$ hour on machine B to produce a package of bolts. He earns a profit of ? $$17.50$$ per package on nuts and ? $$7.00$$ per package on bolts. How many packages of each should be produced each day his machines for at the most $$12$$ hours a day ?
Solve the following LPP:
Maximize z = 60x + 50 y subject to
$$x + 2y \leq 40, 3x + 2y \leq 60, x \geq 0, y \geq 0.$$
Show that the minimum of Z occurs at more than two points
Maximise $$Z = -x + 2y,$$ subject to the constraints:
$$x \geq 3, x + y \geq 5, x + 2y \geq 6, y \geq 0$$
Solve the following problem graphically:
Minimum $$Z = 3x + 5y$$ such that $$x + 3y \leq 3, x + y \geq 2, x, y \geq 0.$$
One kind of cake requires $$200\,g$$ of flour and $$25\,g$$ of fat, and another kind of cake requires $$100\,g$$ of flour and $$50\,g$$ of fat. Find the maximum number of cakes which can be made from $$5 \,kg$$ of flour and $$1 \,kg$$ of fat assuming that there is no shortage of the other ingredients used in making the cakes.
Minimize $$Z = - 50x + 20y$$
Subject to the constraints
$$2x - y \geq -5$$
$$3x + y \geq 3$$
$$2x- 3y \leq 12$$
and $$x \geq 0, y \geq 0$$
Minimize $$Z = -3x + Ay$$
subject to the constraints $$x + 2y \leq 8$$
$$3x + 2y \leq 12$$
and $$x \geq 0, y \geq 0$$
Find graphically, the maximum value of $$z = 2x + 5y$$, subject to constraints given below :
$$2x + 4y \leq 8 $$
$$3x + y \leq 6 $$
$$x + y \leq 4 $$
$$x \geq 0 , y \geq 0 $$
One kind of cake required $$300 \,g$$ of flour and $$15\,g$$ of fat, another kind requires $$150 \,gm$$ of flour and $$30 \,gm$$ of fat. Find the maximum number of cakes which can be made from $$7.5 \,kg$$ of flour and $$600\,gm$$ of fat.
The marks obtained by a student of class XI in first and second terminal examination are 62 and 48, respectively. Find the minimum marks he should get in the annual examination to have an average of at least 60 marks.
Minimize $$Z = x + 2y$$
Subject to the constraints
$$2x + y \geq 3$$
$$x + 2y \geq 6$$
and $$x \geq 0,\,y \geq 0$$
Maximize $$Z = x + y$$
Subject to the constraints
$$x - y \leq -1$$
$$-x + y \leq 0$$
and $$x \leq 0,y \leq 0$$
Maximize
$$Z = -x + 2y$$
Subject to the constraints
$$x \geq 3$$
$$x + y \geq 5$$
$$x + 2y \geq 6$$ and
$$x \geq 0,y \geq 0$$
Two tailors, A and B, earn < 300 and < 400 per day respectively. A can stitch 6 shirts and 4 pairs of trousers while B can stitch 10 shirts and4 pairs of trousers per day. To find how many days should each of them work and if it is desired to produce at least 60 shirts and 32 pairs of trousers at a minimum labor cost, formulate this as an LPP.
A fruit grower can use two types of fertilizer in his garden, brand $$P$$ and brand $$Q$$. The amounts (in kg) if nitrogen, phosphoric acid, potash and chlorine in a bag of each brand are given in the table. Tests indicate that the garden needs at least $$240$$kg of phosphoric acid at least $$270$$kg of potash and at most $$310$$ kg of chlorine.
If the grower wants to minimize the amount of nitrogen added to the garden, how many bags of each brand should be used? What is the minimum amount of nitrogen added in the garden?
| kg per bag |
| Brand $$P$$ | Brand $$Q$$ | |
| Nitrogen | $$3$$ | $$3.5$$ |
| Phosphoric acid | $$1$$ | $$2$$ |
| Potash | $$3$$ | $$1.5$$ |
| Chlorine | $$1.5$$ | $$2$$ |
There are two types of fertilizers $${F}_{1}$$ and $${F}_{2}$$. $${F}_{1}$$ consists of $$10$$% nitrogen and $$6$$% phosphoric acid and $${F}_{2}$$ consists of $$5$$% nitrogen and $$10$$% phosphoric acid. After testing the soil conditions, a farmer finds that she needs at least $$14$$kg of nitrogen and $$14$$kg of phosphoric acid for her crop. If $${F}_{1}$$ cost Rs.$$6$$/kg and $${F}_{2}$$ costs Rs.$$5$$/kg, determine how much of each type of fertilizer should be used so that nutrient requirements are met at a minimum cost. What is the minimum cost?
A dietician wishes to mix together two kinds of food $$X$$ and $$Y$$ in such a way that the mixture contains at least $$10$$ units of vitamin $$A$$, $$12$$ units of vitamin $$B$$ and $$8$$ units of vitamin $$C$$. The vitamin content of one kg of food is given below:
| Food | Vitamin A | Vitamin B | Vitamin C |
| $$X$$ | $$1$$ | $$2$$ | $$3$$ |
| $$Y$$ | $$2$$ | $$2$$ | $$1$$ |
A fruit grower can use two types of fertilizer in his garden, brand $$P$$ and brand $$Q$$. The amounts (in kg) if nitrogen, phosphoric acid, potash and chlorine in a bag of each brand are given in the table. Tests indicate that the garden needs at least $$240$$kg of phosphoric acid at least $$270$$kg of potash and at most $$310$$ kg of chlorine.
If the grower wants to maximize the amount of nitrogen added to the garden, how many bags of each brand should be added? What is the maximum amount of nitrogen added?
| kg per bag |
| Brand $$P$$ | Brand $$Q$$ | |
| Nitrogen | $$3$$ | $$3.5$$ |
| Phosphoric acid | $$1$$ | $$2$$ |
| Potash | $$3$$ | $$1.5$$ |
| Chlorine | $$1.5$$ | $$2$$ |
A merchant plans to sell two types of personal computers, a desktop model and a portable model that will cost Rs 25000 and Rs 40000 respectively. He estimates that the total monthly demand of computers will not exceed 250 units. Determine the number of units of each type of computers which the merchant would stock to get maximum profit if he does not want to invest more than Rs 70 lakhs and if his profit on the desktop model is Rs 4500 and on portable model is Rs 5000.
A manufacturer makes two types of toys $$A$$ and $$B$$. Three machines are needed for this purpose and the time (in minutes) required for each toy on the machines is given below
| Type of toys | Machine $$I$$ | Machine $$II$$ | Machine $$III$$ |
| $$A$$ | $$12$$ | $$18$$ | $$6$$ |
| $$B$$ | $$6$$ | $$0$$ | $$9$$ |
The graph of 3x + 2y = 6 meets the x-axis at point P and the y-axis at point Q. Use the graphical method,then the co-ordinates of points P and Q are P = (2, 0) and Q = (0, 3)
If true then enter $$1$$ and if false then enter $$0$$
An oil company has two depots $$A$$ and $$B$$ with capacities of $$7000L$$ and $$4000L$$ respectively. The company is to supply oil to three petrol pumps $$D, E$$ and $$F$$ whose requirements are $$4500L, 3000L$$ and $$3500L$$ respectively. The distance (in km) between the depots and the petrol pumps is given in the following table:
| Distance (in km) |
| From/To | $$A$$ | $$B$$ |
| $$D$$ | $$7$$ | $$3$$ |
| $$E$$ | $$6$$ | $$4$$ |
| $$F$$ | $$3$$ | $$2$$ |
A manufacturing company makes two types of teaching aids A and B of Mathematics for class XII. Each type of A requires $$9$$ labour hours of fabricating and $$1$$ labour hour for finishing. Each type of B requires $$12$$ labour hours for fabricating and $$3$$ labour hours for finishing. For fabricating and finishing, the maximum labour hours available per week are $$180$$ and $$30$$ respectively. The company makes a profit of $$80$$ on each piece of type A and $$120$$ on each piece of type B. How many pieces of type A and type B should be manufactured per week to get a maximum profit? Make it as an LPP and solve graphically. What is the maximum profit per week?
You need to buy some filing cabinets. You know that Cabinet $$X$$ costs $$ $10$$ per unit, requires six square feet of floor space, and holds eight cubic feet of files. Cabinet $$Y$$ costs $$ $20$$ per unit, requires eight square feet of floor space, and holds twelve cubic feet of files. You have been given $$ $140$$ for this purchase, though you don't have to spend that much. The office has room for no more than $$72$$ square feet of cabinets. How many of which model should you buy, in order to maximise storage volume. Write the maximum storage volume in the provided box.
A dietician wishes to mix two types of foods in such away that the vitamin contents of the mixture contains at least $$8$$ units of vitamin A and $$10$$ units of vitamin C. Food I contains $$2$$ units/kg of vitamin A and $$1$$ unit/kg of vitamin C while Food II contains $$1$$ unit/kg of vitamin A and $$2$$ units/kg of vitamin $$1$$ unit/kg of vitamin C. It costs $$Rs. 5$$ per kg to purchase food I and $$Rs. 7$$ per kg to purchase Food II. Determine the maximum cost of such a mixture. Formulate the above as a LPP and solve it graphically.
A toy company manufactures two types of dolls, $$A$$ and $$B$$. Market tests and available resources have indicated that the combined production level should not exceed $$1200$$ dolls per week and the demand for dolls of type $$B$$ is at most half of that for dolls of type $$A$$. Further, the production level of dolls of type $$A$$ can exceed three times the production of dolls of other type by at most $$600$$ units. If the company makes profit of $$Rs.\ 12$$ and $$Rs.\ 16$$ per doll respectively on dolls $$A$$ and $$B$$, how many of each should be produced weekly in order to maximize the profit?
A cooperative society of farmers has $$50$$ hectares of land to grow two crops A and B. The profits from crops A and B per hectare are estimated as Rs $$10,500$$ and Rs $$9,000$$ respectively. To control weeds, a liquid herbicide has to be used for crops A and B at the rate of $$20$$ litres and $$10$$ litres per hectare, respectively. Further not more than $$800$$ litres of herbicide should be used in order to protect fish and wildlife using a pond which collects drainage from this land. Keeping in mind that the protection of fish and other wildlife is more important than earning profit, how much land should be allocated to each crop so as to maximize the total profit? Form an LPP from the above and solve it graphically. Do you agree with the message that the protection of wildlife is utmost necessary to preserve the balance in environment?
A cooperative society of farmers has 50 hectares of land to grow two crops A and B. The profits from crops A and B per heclare are estimated as Rs 10,500 and Rs 9,000 respectively. To control weeds, a liquid herbicide has to be used for crops A and B at the rate of 20 litres and 10 litres per hectare, respectively. Further not more than 800 litres of herbicide should be used in order to protect fish and wildlife using a pond which collects drainage from this land. Keeping in mind that the protection of fish other wildlife is more important than earning profit, how much land should be allocated to each crop so as to maximize the total profit?
From an LPP from the above and solve it graphically. Do you agree with the massage that the protection of wildlife is utmost necessary to preserve the balance in environment?
A manufacturing company makes two types of teaching aids $$A$$ and $$B$$ of Mathematics for Class XII. Each type of $$A$$ requires $$9$$ labour hours of fabricating and $$1$$ labour hour for finishing. Each type of $$B$$ requires $$12$$ labour hours for fabricating and 3 labour hours for finishing, the maximum labour hours available per week are $$180$$ and $$30$$ respectively. The company makes a profit of $$Rs. 80$$ on each piece of type $$A$$ and $$Rs. 120$$ on each piece of type $$B$$. How many pieces of type $$B$$ should be manufactured per week to get a maximum profit? Make it as an LPP and solve graphically. What is the maximum profit per week?
A dietician wishes to mix two kinds of food $$X$$ and $$Y$$ in such a way that the mixture contains at least $$10$$ units of vitamin $$A, 12$$ units of vitamin $$B$$ and $$8$$ units of vitamin $$C$$. The vitamin contains of per kg food is given below.
| Food | Vitamin $$A$$ | Vitamin $$B$$ | Vitamin $$C$$ |
| $$X$$ | $$1$$ unit | $$2$$ units | $$3$$ units |
| $$Y$$ | $$2$$ units | $$2$$ units | $$1$$ unit |
A dealer in rual area wishes to purchase a number of sewing machines. He has only $$Rs\ 5,760$$ to invest and has space for at most $$20$$ items for storage. An electronic sewing machine costs him $$Rs\ 360$$ and a manually operated sewing machine $$Rs\ 240$$. He can sell an electronic sewing machine at a profit of $$Rs\ 22$$ and a manually operated sewing machine at a profit of $$Rs\ 18$$. Assuming that he can sell all the items that he can buy how should he invest his money in order to maximize his profit? Formulate this problem mathematically and then solve it.
A company manufactures three kinds of calculators : A, B and C in its two factories I and II, The company has got an order for manufacturing at least $$6400$$ calculators of kind A, $$4000$$ of kind B and $$4800$$ of kind C. The daily output of factory I is of $$50$$ calculators of kind A, $$50$$ calculators of kind B, and $$30$$ calculators of kind C. The daily output of factory II is of $$40$$ calculators of kind A, $$20$$ of kind B and $$40$$ of kind C. The cost per day to run factory I is Rs. $$12,000$$ and of factory II is Rs. $$15,000$$.
How many days do the two factories have to be in operation to produce the order with the minimum cost? Formulate this problem as an LPP and solve it graphically.
A company manufactures two types of products $$A$$ and $$B$$. Each unit of $$A$$ requires $$3$$ grams of nickel and $$1$$ gram of chromium, while each unit of $$B$$ requires $$1$$ gram of nickel and $$2$$ grams of chromium. The firm can produce $$9$$ grams of nickel and $$8$$ grams of chromium. The profit is Rs. $$40$$ on each unit of product of type $$A$$ and Rs. $$50$$ on each unit of type $$B$$. How many units of each type should the company manufacture so as to earn maximum profit? Use linear programming to find the solution
Find graphically, the maximum value of $$z=2x+5y$$, subject to constraints given below:
$$2x+4y\le 8$$
$$3x+y\le 6$$
$$x+y\le 4$$
$$x\ge 0, y \le 0.6$$
Minimize: $$Z=6x+4y$$
Subject to : $$3x+2y \ge 12$$,
$$x+y\ge 5$$,
$$0\le x\le 5$$,
$$0\le y\le 6$$
A mill owner buys two types of machines $$A$$ and $$B$$ for his mill. Machine $$A$$ occupies $$1,000$$ sqm of area and requires $$12$$ men to operate it; while machine $$B$$ occupies $$1,200$$ sqm of area and requires $$8$$ men to operate it. The owner has $$7,600$$ sqm of area available and $$72$$ men to operate the machines. If machine $$A$$ produces $$50$$ units and machine $$B$$ produces $$40$$ units daily, how many machines of each type should he buy to maximize the daily output? Use Linear Programming to find the solution.
Solve the following L.P.P. graphically
Maximize: $$z = 10x + 25y$$
Subject to: $$x\leq 3 y\leq 3, x + y \leq 5, x \geq 0, y \geq 0$$
Two tailors P and Q eart Rs. 150 and Rs. 200 per day respectively. P can stitch 6 shirts and 4 trousers a day, while Q can stitch 10 shirts and 4 trousers per day. How many days should each work to produce at least 60 shirts and 32 trousers at minimum labour cost?
A diet of a sick person must contains at least $$48$$ units of vitamin $$A$$ and $$64$$ units of vitamin $$B$$. Two foods $$F_1$$ and $$F_2$$ are available. Food $$F_1$$ costs Rs. $$6$$ per unit and Food $$F_2$$ costs Rs. $$10$$ per unit. One unit of food $$F_1$$ contains $$6$$ units of vitamin $$A$$ and $$7$$ units of vitamin $$B$$. One unit of food $$F_2$$ contains $$8$$ units of vitamin $$A$$ and $$12$$ units of vitamin $$B$$. Find the minimum cost for the diet that consists of mixture of these two foods and also meeting the minimum nutritional requirements.
Solve the following linear programming problem graphically:
Maximize: $$Z=60x+40y$$
subject to the constraints:$$x+2y\le 12$$; $$2x+y\le 12$$
$$x+\cfrac{5}{4}y\ge 5;x\ge 0, y\ge 0$$.
$$x+\cfrac{5}{4}y\ge 5;x\ge 0, y\ge 0$$.
A company manufactures two types of toys $$A$$ and $$B$$. A toy of type $$A$$ requires $$5$$ minutes for cutting and $$10$$ minutes for assembling. A toy of type $$B$$ requires $$8$$ minutes for cutting and $$8$$ minutes for assembling. There are $$3$$ hours available for cutting and $$4$$ hours available for assembling the toy in a day. The profit is $$Rs. 50$$ each on a toy of type $$A$$ and $$Rs. 60$$ each on a toy of type $$B$$. How many toys of each type should the company manufacture in a day to maximize the profit? Use linear programming to find the solution
Solve the following linear programming problem by graphical method:
Maximize $$Z = 3x + 2y$$
subject to the in constraints
$$x + 2y \leq 10, 3x + y \leq 15, x, y\geq 0$$
An aeroplane can carry a maximum load of $$200$$ passengers. Baggage allowed to the first class ticket holder is $$30$$ kg and for the economy class ticket holder is $$20$$ kg. Maximum capacity of the aeroplane to carry the baggage is $$4500$$ kg. The profit on each first class ticket is Rs.$$500$$ and on each economy class ticket is Rs.$$300$$. Formulate the problem, as L.P.P to maximize the profit.
Show that the minimum of $$Z$$ occurs at more than two points.
Minimise and Maximise $$Z = x + 2y$$
subject to $$x + 2y \geq 100, 2x - y \leq 0, 2x + y \leq 200; x, y \geq 0$$.
Solve the following Linear Programming Problems graphically:
Minimise $$Z = x + 2y$$
subject to $$2x + y \geq 3, x + 2y \geq 6, x, y \geq 0$$.
A factory manufactures two types of screws, $$A$$ and $$B$$. Each type of screw requires the use of two machines, an automatic and a hand-operated. It takes $$4$$ minutes on the automatic and $$6$$ minutes on hand-operated machines to manufacture a package of screws $$A$$, while it takes $$6$$ minutes on automatic and $$3$$ minutes on the hand-operated machines to manufacture a package of screws $$B$$. Each machine is available for at the most $$4$$ hours on any day. The manufacturer can sell a package of screws $$A$$ at a profit of $$Rs. 7$$ and screws $$B$$ at a profit of $$Rs. 10$$. Assuming that he can sell all the screws he manufactures, how many packages of each type should the factory owner produce in a day in order to maximize his profit? Determine the maximum profit.
Reshma wishes to mix two types of food $$P$$ and $$Q$$ in such a way that the vitamin contents of the mixture contain at least $$8\ units$$ of vitamin $$A$$ and $$11\ units$$ of vitamin $$B$$. Food $$P$$ costs $$Rs.\ 60/kg$$ and Food $$Q$$ costs $$Rs.\ 80/kg$$. Food $$P$$ contains $$3\ units/kg$$ of Vitamin $$A$$ and $$5\ units / kg$$ of Vitamin $$B$$ while food $$Q$$ contains $$4\ units/kg$$ of Vitamin $$A$$ and $$2\ units/kg$$ of vitamin $$B$$. Determine the minimum cost of the mixture.
Show that the maximum of $$Z$$ occurs at more than two points.
Minimise and Maximise $$Z = 5x + 10y$$ subject to $$x + 2y \leq 120, x + y \geq 60, x - 2y \geq 60, x - 2y \geq 0, x, y\geq 0$$.
Show that the maximum of $$Z$$ occurs at more than two points.
Maximise $$Z = -x + 2y$$, subject to the constraints:
$$x\geq 3, x + y \geq 5, x + 2y \geq 6, y \geq 0$$.
A manufacturing company makes two types of teaching aids A and B of Mathematics for Class X. Each type of A requires $$9$$ labour hours for fabricating and $$1$$ labour hour for finishing. Each type of B requires $$12$$ labour hours for fabricating and $$3$$ labour hours for finishing. For fabricating and finishing, the maximum labour hours available per week are $$180$$ and $$30$$ respectively. The company makes a profit of Rs. $$80$$ on each piece of type A and Rs. $$120$$ on each piece of type B. How many pieces of type A and type B should be manufactured per week to get a maximum profit? Formulate this as Linear Programming Problem and solve it. Identify the feasible region from the rough sketch.
A company manufactures two types of novelty souvenirs made of plywood. Souvenirs of type $$A$$ require $$5$$ minutes each for cutting and $$10$$ minutes each for assembling. Souvenirs of type $$B$$ require $$8$$ minutes each for cutting and $$8$$ minutes each for assembling. There are $$3$$ hours $$20$$ minutes available for cutting and $$4$$ hours for assembling. The profit is $$Rs. 5$$ each for type $$A$$ and $$Rs. 6$$ each for type $$B$$ souvenirs. How many souvenirs of each type should the company manufacture in order to maximize the profit?
Determine graphically the minimum value of the objective function.
$$Z = -50x + 20y$$
Subject to constraints
$$2x - y \geq -5$$
$$3x + y \geq 3$$
$$2x - 3y \leq 12$$
$$x \geq 0, y \geq 0$$.
Use the graphical method to solve each of the following LP problems.
A wheat and barley farmer has $$168$$ hectare of ploughed land, and a capital of $$E2000$$. It costs $$E14$$ to sow hectare wheat ad $$E10$$ to sow one hectare of barley. Suppose that his profit is $$E80$$ per hectare of wheat and $$E55$$ per hectare of barley. Find the optimal number of hectares of wheat and barley that must be ploughed in order to maximise profit? What is the maximum profit?
Solve the following minimal assignment problem and hence find the minimum value:
| I | II | III | IV | |
| A | 2 | 10 | 9 | 7 |
| B | 13 | 2 | 12 | 2 |
| C | 3 | 4 | 6 | 1 |
| D | 4 | 15 | 4 | 9 |
An aeroplane can carry a maximum of $$200$$ passengers. A profit of $$Rs. 1000$$ is made on each executive class ticket and a profit of $$Rs. 600$$ is made on each economy class ticket. The airline reserves at least $$20$$ seats for executive class. However, at least $$4$$ times as many passengers prefer to travel by economy class than by the executive class. Determine how many tickets of each type must be sold in order to maximise the profit for the airline. What is the maximum profit?
A merchant plans to sell two types of personal computers - a desktop model and a portable model that will cost $$Rs. 25000$$ and $$Rs. 40000$$ respectively. He estimates that the total monthly demand of computers will not exceed $$250$$ units. Determine the number of units of each type of computers which the merchant should stock to get maximum profit if he does not want to invest more than $$Rs. 70$$ lakhs and if his profit on the desktop model is $$Rs. 4500$$ and on portable model is $$Rs. 5000$$.
Construct the graphs of the following functions.
$$\displaystyle y \, = \, (x \, + \, 3) \, / \, (x \, - \, 1).$$
Construct the graphs of the following functions.
$$\displaystyle x \, = \, \sqrt{1 \, - \, | y |}.$$The maximum possible value of x is:
A toy company manufactures two types of dolls, $$A$$ and $$B$$. Market tests and available resources have indicated that the combined production level should not exceed $$1200$$ dolls per week and the demand for dolls of type $$B$$ is at most half of that for dolls of type $$A$$. Further, the production level of dolls of type $$A$$ can exceed three times the production of dolls of other types by at most $$600$$ units. If the company makes a profit of $$Rs. 12$$ and $$Rs. 16$$ per doll respectively on dolls $$A$$ and $$B$$, how many of each should be produced weekly in order to maximize the profit?
A diet is to contain at least $$80$$ units of vitamin A and $$100$$ units of minerals. Two foods $$F_{1}$$ and $$F_{2}$$ are available. Food $$F_{1}$$ costs $$Rs. 4$$ per unit food and $$F_{2}$$ costs $$Rs. 6$$ per unit. One unit of food $$F_{1}$$ contains $$3$$ units of vitamin A and $$4$$ units of minerals. One unit of food $$F_{2}$$ contains $$6$$ units of vitamin A and $$3$$ units of minerals. Formulate this as a linear programming problem. Find the minimum cost for a diet that consists of a mixture of these two foods and also meets the minimal nutritional requirements.
A farmer mixes two brands $$P$$ and $$Q$$ of cattle feed. Brand $$P$$, costing $$Rs. 250$$ per bag, contains $$3$$ units of nutritional element $$A, 2.5$$ units of element $$B$$ and $$2$$ units of element $$C$$. Brand $$Q$$ costing $$Rs. 200$$ per bag contains $$1.5$$ units of nutritional element $$A, 11.25$$ units of element $$B$$, and $$3$$ units of element $$C$$. The minimum requirements of nutrients $$A, B$$ and $$C$$ are $$18\ units, 45\ units$$ and $$24\ units$$ respectively. Determine the number of bags of each brand which should be mixed in order to produce a mixture having a minimum cost per bag? What is the minimum cost of the mixture per bag?
An company manufactures two electrical products: air conditioners and large fans. The assembly process for each is similar in that both require a certain amount of wiring and drilling. Each air conditioner takes $$3$$ hours of wiring and $$2$$ hours of drilling. Each of fan must go through $$2$$ hours of wiring and $$1$$ hour of drilling. During the next production period, $$240$$ hours of wiring time are available and up to $$140$$ hours of drilling time may be used. Each air conditioner sold yields a profit of $$E25$$. Each fan assembled may be sold for a profit of $$E15$$. Formulate and solve this linear programming mix situation to find the best combination of air conditioners and fans that yields the highest profit.
Solve graphically:
$$x+2y\le 10;x+y\ge 1;x-y\le 0;\le 0$$
A small firm manufactures necklaces and bracelets. The total number of necklaces and bracelets that it can handle per day is at most $$24$$. It takes one hour to make a bracelet and a half an hour to make a necklace. The maximum number of hours available per day is $$16$$. If the profit on a necklace is $$Rs\100$$ and that on a bracelet is $$Rs\ 300$$. Formulate on L.P.P. for finding how many of each should be produced daily to maximize the profit? It is being given that at least one of each must be produced.
An advertising company wishes to plan its advertising strategy in three different media-television,radio and magazines.The purpose of advertising is to reach as large a number of potential customers as possible.Following data have been obtained from market survey:
| Strategies | Television | Radio | Magazine-I | Magazine-II |
| Cost of an advertising company | Rs.$$30,000$$ | Rs.$$20,000$$ | Rs.$$15,000$$ | Rs.$$10,000$$ |
| No.of potential customers reached per unit | $$2,00,000$$ | $$6,00,000$$ | $$1,50,000$$ | $$1,00,000$$ |
| No.of female customers reached per unit | $$1,50,000$$ | $$4,00,000$$ | $$70,000$$ | $$50,000$$ |
$$\left(i\right)$$at least $$1$$ million exposures take place among female customers.
$$\left(ii\right)$$advertising on magazines be limited to Rs.$$1,50,000$$
$$\left(iii\right)$$at least $$3$$ advertising units be bought on magazine $$I$$ and $$2$$ units on magazine $$II$$
$$\left(iv\right)$$the number of advertising units on television and radio should each be between $$5$$ and $$10.$$
Formulate an L.P model for the problem.
Solve the following system of inequalities graphically$$x\ge 3, y\ge 2$$
David wants to invest at most $$Rs.\ 12,000$$ in bonds $$A$$ and $$B$$. According to the rule, he has to invest at least $$Rs.\ 2,000$$ in Bond $$A$$ and at least $$Rs.\ 4,000$$ in Bond $$B$$. If the rates of interest on Bonds $$A$$ and $$B$$ respectively are $$8\%$$ and $$10\%$$ perannum, formulate the problem as L.P.P. and solve it graphically for maximum interest. Also determine the maximum interest received in a year.
Find the number of integer solutions of $${x}_{1}+{x}_{2}+{x}_{3}+{x}_{4}=20$$ where $${x}_{1}\ge -5, {x}_{2}\ge 3, {x}_{3}\ge 0, {x}_{4}\ge 1$$
The following table gives production yields per hutone whest of 100 farms of a village
| Production Yield | 50-55 | 55-60 | 60-65 | 65-70 | 70-75 | 75-80 |
| Number of Farms | 2 | 8 | 12 | 24 | 38 | 46 |
Change the distribution to a more then type distribution and draw its vgive.
To solve the following L.P.P.
Minimize $$z=30x+20y$$
Subject to the constraint, $$x+y\leq 8$$, $$x+2y \geq 4$$, $$6x+7y\geq 12$$, $$x\geq 0; y\geq 0$$.
Solve the following L.P.P. graphically .Minimize $$Z=3x+5y$$ .SSubject to constraints$$2x+3y \ge 12$$$$-x+y\le3$$
$$x\le 4$$
$$y\ge 3$$
Minimize and maximize z=3x+9y subject to the constraints
$$x+3y\le 60$$
$$10\le x+y$$
$$x\le y$$
$$0\le x,y$$
by the graphical method. Minimum and maximum values are p and q then p+q =
A manufacturer makes two types of toys $$A$$ and $$B$$. Three machine are need for this purpose and the time (In minutes) required for each toy on the machines is given below
| Types of toys | $$I$$ | $$II$$ | $$III$$ |
| $$A$$ | $$20$$ | $$10$$ | $$10$$ |
| $$B$$ | $$10$$ | $$20$$ | $$30$$ |
Formulate the above problem as a LPP and solve it graphically to maximize profit.
Solve each of the following linear programming problem by graphical method.
Maximize $$Z=50x+30y$$
Subject to $$2x+y\le 18$$
$$3x+2y\le 34$$
$$x,y\ge 0$$
A manufactures can produce two products, $$A$$ and $$B$$, during a given time period. Each of these products requires four different manufacturing operation: grinding, turning, assembling and testing. The manufacturing requirements in hours per unit of products $$A$$ and $$B$$ are given below.
| $$A$$ | $$B$$ | |
| Grinding | $$1$$ | $$2$$ |
| Turning | $$3$$ | $$1$$ |
| Assembling | $$6$$ | $$3$$ |
| Testing | $$5$$ | $$4$$ |
Solve each of the following linear programming problem by graphical method.
Minimize $$Z=5x+3y$$
Subject to $$2x+y\ge 10$$
$$x+3y\ge 15$$
$$x\le 10$$
$$y\le 8$$
$$x, y\ge 0$$
A company produces two types of goods, $$A$$ and $$B$$ that require gold and silver. Each unit of type $$A$$ requires $$3$$ gm of silver and $$1$$ gm of gold while that of type $$B$$ requires $$1$$ gm of silver and $$2$$ gm of gold. The company can produce $$9$$ gm of silver and $$8$$ gm of gold. If each unit of type $$A$$ brings a profit of Rs. $$ 40$$ and that of type $$B$$ Rs. $$ 50$$, find the number of units of each type that the company should produce to maximize the profit. What is the maximum profit?
A furniture manufacturing company plans to make two products: chairs and tables. From its available resources which consists of $$400$$ square feet of teak wood and $$450$$ man hours. It is known that to make a chair requires $$5$$ square feet of wood and $$10$$ man-hours and yields a profit of Rs. $$ 45$$, while each table uses $$20$$ square feet of word and $$15$$ man-hours and yields a profit of Rs. $$ 80$$. How many items of each product should be produced by the company so that the profit is maximum?
Two tailors, $$A$$ and $$B$$ earn $$Rs\ 15$$ and $$Rs\ 20$$ per day respectively. A can stitch $$6$$ shirts and $$4$$ pants while $$b$$ can stitch $$10$$ shirts and $$4$$ pants per day. How many days shall each work if it is desired to produce (at least) $$60$$ shirts and $$32$$ pants at a minimum labour cost?
A manufacturer makes two types $$A$$ and $$B$$ of tea-cups.Three machines are needed for the manufacturer and the time in minutes required for each cup on the machines is given below:
| Machines | |||
| $$I$$ | $$II$$ | $$III$$ | |
| $$A$$ | $$12$$ | $$18$$ | $$6$$ |
| $$B$$ | $$6$$ | $$0$$ | $$9$$ |
A fruit grower can use two types of fertilizer in his garden, brand $$P$$ and $$Q$$. The amounts (in kg) of nitrogen, phosphoric acid, potash, and chlorine in a bag of each brand are given as at least $$240$$ kg of phosphoric acid, $$270$$ kg of potash and at most $$310$$ kg of chlorine.
| $$kg$$ per bag | ||
| Brand $$P$$ | Brand $$Q$$ | |
| Nitrogen | $$3$$ | $$3.5$$ |
| Phosphoric acid | $$1$$ | $$2$$ |
| Potash | $$3$$ | $$1.5$$ |
| Chlorine | $$1.5$$ | $$2$$ |
A manufacturer of Furniture make two products : chairs and tables. Processing of these products is done on two machine $$A$$ and $$B$$. A chair requires $$2$$ hr on machine $$A$$ and $$6$$ hrs on machine $$B$$. A table requires $$4$$ hrs on machines $$A$$ and $$2$$ hrs on machine $$B$$. There are $$16$$ hrs of time per day available on machine $$A$$ and $$30$$ hrs on machine $$B$$. Profit gained by the manufacturer from a chair and a table is Rs. $$ 3$$ and Rs. $$ 5$$ respectively. Find with the help of graph what should be the daily production of each of the two products so as to maximize his profit.
A company produces two types of leather belts, say type $$A$$ and $$B$$. Belt $$A$$ is a superior quality and belt $$B$$ is of a lower quality. Profits on each type of belt are Rs. $$ 2$$ and Rs. $$ 1.50$$ per belt, respectively. Each belt of type $$B$$, the company could produce $$1000$$ belts per day. But the supply of leather is sufficient only for $$800$$ belts per day (both $$A$$ and $$B$$ combined). Belt $$A$$ requires a fancy buckle and only $$400$$ fancy buckles are available for this per day. For belt of type $$B$$, only $$700$$ buckles are available per day. How should the company manufacture the two types of belts in order to have a maximum overall profit?
If a young man drives his scooter at a speed of $$25$$ km/hr, he to spend Rs. $$ 2\ \text{per km}$$ on petrol. If he drives the scooter at a speed of $$40$$ km/hour, it produces air pollution and increases his expenditure on petrol to Rs. $$ 5\ \text{per km}$$. He has a maximum of Rs. $$ 100$$ to spend on petrol and travel a maximum distance in one hour time with less polution. Express this problem as an LPP and solve it graphically. What value do you find here?
A factory owner purchase two types of machines, $$A$$ and $$B$$ for his factory. The requirements and limitations for the machines are as follows:
| Area occupied by the machine | Labour force for each machine | Daily output in units | |
| Machine $$A$$ | $$1000.sq.\ m$$ | $$12\ men$$ | $$60$$ |
| Machine $$B$$ | $$1200\ sq.\ m$$ | $$8\ men$$ | $$40$$ |
A factory uses three different resources for the manufacture of two different products $$20$$ units of the resources $$A, 12$$ units of $$B$$ and $$16$$ units of $$C$$ being available. $$1$$ unit of the first produce requires $$2,2$$ and $$4$$ units of the respective resources and $$1$$ unit of the second product requires $$4,2$$ and $$0$$ units of respective resources. It is known that the first product gives a profit of $$2$$ monetary units per unit and the second $$3$$. Formulate the linear programming problem. How many units of each product should be manufactured for maximizing the profit? Solve it graphically.
A man owns a field of area $$1000$$ sq.m. He wants to plant fruit trees in it. He has a sum of Rs. $$1400$$ to purchase young trees. He has the choice of two years. Type $$A$$ requires $$10$$ sq.m of ground per tree and costs Rs. $$ 20$$ per tree and type $$B$$ requires $$20$$ sq.m of ground per tree and costs Rs. $$ 25$$ per tree. When fully grown type $$A$$ produces an average of $$20$$ kg of fruit which can be sold at a profit of Rs. $$ 2.00$$ per kg and type $$B$$ produces an average $$40$$ kg of fruit which can be sold at a profit of Rs. $$ 1.50$$ per kg. How many of each type should be planted to achieve maximum profit when when the trees are fully grown? What is the maximum profit?
A producer has $$30$$ and $$17$$ units of labour and capital respectively which he can use to produce two type of goods $$X$$ and $$Y$$. To produce one unit of $$X, 2$$ units of labour and $$3$$ units of capital are required. Similarly $$3$$ units of labour and $$1$$ unit of capital is required to produce one unit of $$Y$$. If $$X$$ and $$Y$$ are priced at Rs. $$ 100$$ and Rs. $$ 120$$ per unit respectively, how should be producer use his resources to maximize the total revenue? Solve the problem graphically.
A manufacture consider that men and women worker are equally efficient and so he pays them at the same rate. He has $$30$$ and $$17$$ units of workers (male and female) and capital respectively, which he uses to produces two types of goods $$A$$ and $$B$$. To produce one unit of $$A, 2$$ workers and $$3$$ units of capital are required while $$3$$ workers and $$1$$ unit of capital is required to produce one unit of $$B$$. If $$A$$ and $$B$$ are priced at Rs. $$100$$ and Rs. $$120$$ per unit respectively, how should he use his resource to maximize the total revenue? From the above as an LPP and solve graphically. Do you agree with this total view of the manufacturer that men and women workers are equally efficient and so should be paid at the same rate?
A furniture dealer deals in only two items: tables and chairs. He has RS $$30000$$ to invest and a space to store at most $$60$$ pieces. A table costs him RS $$1500$$ and a chair RS $$300.$$ Formulate the data in the of inequatins and draw a graph representing the solution of these inequations.
A manufacturer makes two products $$A$$ and $$B$$. Product $$A$$ sells at Rs. $$ 200$$ each and takes $$\dfrac {1}{2}$$ hour to make. Product $$B$$ sells at Rs. $$ 300$$ each and takes $$1$$ hour to make. There is a permanent order for $$14$$ of product $$A$$ and $$16$$ of product $$B$$. A working week consists of $$40$$ hours of production and weekly turnover must not be less than Rs. $$ 10000$$. If the profit on each of product $$A$$ is Rs. $$ 20$$ and on product $$B$$ is Rs. $$ 30$$, then how many of each should be produced so that the profits is maximum. Also, find the maximum profit.
A firm manufactures two products $$A$$ and $$B$$. Each product is processed on two machines $$M_{1}$$ and $$M_{2}$$. Product A requires $$4$$ minutes of processing time on $$M_{1}$$ and $$8$$ min. on $$M_{2}$$; product $$B$$ requires $$4$$ minutes on $$M_{1}$$ and $$4$$ min. on $$M_{2}$$. The machine $$M_{1}$$ is available for not more than $$8$$ hrs $$20$$ min. while machine $$M_{2}$$ is available for $$10$$ hrs during any working day. The products $$A$$ and $$B$$ are sold at a profit of Rs. $$ 3$$ and Rs. $$ 4$$ respectively.
Formulate the problem as a linear programming problem and find how many product of each type should be produced by the firm each day in order to get maximum profit.
A firm manufacturing two types of electric items, $$A$$ and $$B$$ can make a profit of Rs. $$ 20$$ per unit of $$A$$ and Rs. $$ 30$$ per unit of $$B$$. Each unit of $$A$$ requires $$3$$ motors and $$4$$ transformers and each unit of $$B$$ requires $$2$$ motors and $$4$$ transformers. The total supply of these per month is restricted to $$210$$ motors and $$300$$ transformers. Type $$B$$ is an export model requiring a voltage stabilizer which has a supply restricted to $$65$$ units per month. Formulate the linear programming problem for maximum profit and solve ir graphically.
A chemical company produces two compounds $$A$$ and $$B$$. The following table gives the units of ingredients, $$C$$ and $$D$$ per $$kg$$ of compounds $$A$$ and $$B$$ as well as minimum requirement of $$C$$ and $$D$$ and costs per kg of $$A$$ and $$B$$. Find the quantities of $$A$$ and $$B$$ which would give a supply of $$C$$ and $$D$$ at a minimum cost.
| Compounds | Minimum requirement | ||
| $$A$$ | $$B$$ | ||
| Ingredient $$C$$ | $$1$$ | $$2$$ | $$80$$ |
| Ingredient $$D$$ | $$3$$ | $$1$$ | $$75$$ |
| Cost (in $$Rs$$) $$per\ kg$$ | $$4$$ | $$6$$ |
Two godowns, $$A$$ and $$B$$ grain storage capacity of $$100$$ quintals and $$50$$ quintals respectively. They supply to $$3$$ ration shops, $$D, E$$ and $$F$$ whose requirement are $$60,50$$ and $$40$$ quintals respectively. The cost transportation per quintal from the godowns to the shops are given in the following table:
| Transportation cost per quintal (in Rs) | ||
| To $$\downarrow$$ \ From $$\to$$ | $$A$$ | $$B$$ |
| $$D$$ | $$6.00$$ | $$4.00$$ |
| $$E$$ | $$3.00$$ | $$2.00$$ |
| $$F$$ | $$2.50$$ | $$3.00$$ |
To receive grade $$A$$ in a course one must obtain an average of $$90$$ marks or more in five papers, each of $$100$$ marks. If Tanvy scored $$89, 93, 95$$ and $$91$$ marks in first four papers, find the minimum marks that she must score in the last paper to get grade $$A$$ in the course.
Class 12 Commerce Maths Extra Questions
- Application Of Derivatives Extra Questions
- Application Of Integrals Extra Questions
- Continuity And Differentiability Extra Questions
- Determinants Extra Questions
- Differential Equations Extra Questions
- Integrals Extra Questions
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions Extra Questions
- Linear Programming Extra Questions
- Matrices Extra Questions
- Probability Extra Questions
- Relations And Functions Extra Questions
- Three Dimensional Geometry Extra Questions
- Vector Algebra Extra Questions