Money And Banking - Class 12 Commerce Economics - Extra Questions
How does a central bank act as the lender of the last resort?
What is Repo Rate?
Explain 'Banker to the Government' function of the central bank.
What is meant by Cash Reserve Ratio?
State the treatment of following measures by central bank during excess demand: (i) Bank rate; (ii) Margin requirements; (iii) Open market operation.
Briefly explain the 'change in bank rate policy' as a credit control method adopted by the Central Bank.
What is meant by 'Credit rationing'?
Briefly explain the change in cash reserves of commercial banks.
Mention four functions of a Central Bank.
Explain what is meant by 'Open market operation'.
Discuss briefly about 'Moral suasion'.
How does the fixation of a margin, required on secured loans, affect the flow of credit in India?
Differentiate between SLR and CRR.
Explain the functions of the central bank as a banker to the Government.
State two ways by which a deflationary situation can be controlled by qualitative methods of credit control.
Explain methods of credit control adopted by the 'Central Bank'.
Discuss about the 'Bank Rate'.
What is mean by CRR? Briefly examine its role in credit control.
List two ways in which a Central Bank acts as a 'Banker to the Government'.
Discuss the functions of the central bank as a 'Banker of Banks' and 'Banker to the Government'.
What do you understand by bank rate?
What is meant by 'Cash Reserve Ratio'?
Which bank is called as 'Bankers' Bank'?
Explain the "medium of exchange" function of money.
Explain the Primary and Secondary functions of Money.
Distinguish between the following:
Cash Reserve Ratio and Statutory Liquidity Ratio
Explain the various functions performed by Central Bank.
Give Reasons or Explain the following:
Central Bank acts as a lender of last resort.
Fill in the blanks with appropriate alternatives given in the brackets:
The monetary policy of Central Bank regulates the money supply to realise ___ goals. (Political, social, economic, education)
Fill in the blanks with appropriate alternatives given in the brackets:
The currency notes issued by Central Bank are ___ legal tender.
(Limited, unlimited, restricted, nil)
Give Reasons or Explain the following:
As a banker to the government, the Central Bank transfers government funds.
Fill in the blanks with appropriate alternatives given in the brackets:
Central Bank is the __ of bank credit.
(Creator, manufacturer, controller, supplier)
Define or Explain the following concepts.
Cash Reserve Ratio
Define or Explain the following concepts.
Lender of Last Resort
Define or Explain the following concepts.
Statutory Liquidity Ratio.
Define or Explain the following concepts.
Central Bank as Bank of Note Issue
Define or Explain the following concepts.
Clearing House System.
Give reason or explain:
Central Bank acts as a lender of the last resort.
Give reason or explain:
The Cash Reserve Ratio affects the lending capacity of the banks.
Answer the following questions.
Explain the Data Collection and Publicity function of the Central Bank.
Write Short Notes on:
Qualitative Credit Control methods of the Central Bank.
Give reason or Explain
A Central Bank may take "Direct Action" against the defaulting Commercial Banks.
Give reason or Explain
As a banker to the Government, the Central Bank transfers government funds.
Write Short Notes on:
Cash Reserve Ratio(CRR).
Distinguish between.
Cash Reserve Ratio(CRR) and Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR).
Answer the following questions.
Explain how Central Bank is Banker's Bank?
Write Short Notes on.
Central Bank's measures of regulation of consumer credit.
Answer in detail.
Explain the functions of the Central Bank.
State with reasons whether you agree or disagree with the following statements.
Central Bank works as government bank or Central Bank is called the government's bank.
State with reasons whether you agree or disagree with the following statements.
Central bank does not work as a banker for the government.
State with reasons whether you agree or disagree with the following statements.
A co-operative bank acts as a lender of last resort.
Answer the following questions.
How does a Central Bank transfer funds from one place to another?
State with reasons whether you agree or disagree with the following statements.
Central Bank is the bank of note issue.
State with reasons whether you agree or disagree with the following statements.
Central Bank has control on credit creation.
State with reasons whether you agree or disagree with the following statements.
Issuing currency is the only one function of the Central Bank.
State with reasons whether you agree or disagree with the following statements.
Credit Control is the function of Central Bank of the country.
State with reasons whether you agree or disagree with the following statements.
Central Bank is a profit making institution.
Write Short Notes on.
Types of deposits.
Answer in detail.
Explain in details Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate of Central Bank.
Explain the role of the Reserve Bank of India as the "lender of last resort".
Define multiplier. What is the relation between marginal propensity to consume and multiplier? Calculate the marginal propensity to consume if the value of multiplier is $$4$$.
You have Rs. $$1,000$$ as your pocket money. You can deposit this money in a bank and get RS. $$1,100$$ after a year. However, you have two other choices:
(i) lend this money to your friend who is ready to pay you Rs. $$1,050$$ after an year, or
(ii) keep the money with you as cash in hand.
What is the opportunity cost of keeping the money as cash in hand?
Give reasons or explain:
As a banker for the government, the Central bank transfers government funds.
State with reasons, whether you 'agree' or 'disagree' with the following statement.
Central bank has the sole power of issuing currency notes.
Give reasons or explain the following statement:
Cash reserve ratio (CRR) affects the lending capacity of banks.
Explain with reasons whether you 'agree' or 'disagree' with the following statement:
Central bank is called as the bankers' bank.
Define or explain the concept of 'bank rate'.
Give reasons or explain:
Central Bank is a banker to the government.
Define or explain reverse repo rate
State with reasons, whether the following statement is True or False:
Reserve Bank of India cannot accept deposits from public.
Explain with reasons whether you 'agree' or 'disagree' with the following statement:
Money performs various functions.
Explain with reasons whether you 'agree' or 'disagree' with the following statement:
Bank rate is a quantitative measure of credit control.
Define money supply and explain its components.
Give the meaning of:
(i) Barter Exchange;
(ii) Money;
(iii) Money Supply.
What are demand deposits?
What is transaction demand for money? How is it related to the value of transactions over a specified period of time?
What is a 'legal tender'? What is 'fiat money?
State whether money supply is a stock variable or flow variable.
State the two components of money supply.
OR
State the components of money supply.
Long Answer Type Questions:
What is meant by 'money supply' ? Discuss, in brief, the various constituents of money supply.
Explain the concepts of:
(i) Currency and coins with public;
(ii) Demand deposits held by commercial banks.
What will be the effect of a rise in the bank rate on money supply?
How does central bank control credit creation by commercial banks through open market operations? Explain.
Mention any one factor affecting credit creation by banks.
Explain Central Bank's function as currency authority.
Explain 'bank of issue' function of central bank.
Explain the function of a Central Bank as a banker to the government.
State the main functions of a Central Bank.
Explain the lender of last resort' function of the Central Bank.
What is the meaning of open market operations?
Explain any two methods of credit control used by central bank.
Define cash reserve ratio and statutory liquidity ratio. How can they be used to control the situation of excess money supply?
Explain the 'banker's banks' and 'supervisor' function of the central bank.
What is bank rate policy? How does it work as a method of credit control?
Explain the "varying reserve requirements" method of credit control by the central bank.
Explain the role of statutory liquidity ratio in increasing money supply.
Explain the 'currency authority' function of central bank.
Explain the role of Reverse Repo Rate in controlling credit creation.
Explain the following functions of the central bank: (i) Bank of issue (ii) Banker's bank.
Explain the distinction between 'Statutory Liquidity Ratio' and 'Cash Reserve Ratio'.
How can a central bank control excess demand in an economy by making changes in the legal reserve requirements?
How does a central bank influence credit creation by commercial banks through 'open market operations'? Explain.
Explain any two functions of central bank.
State two measures by which a central bank can attempt to reduce the inflationary gap.
Briefly discuss the following functions of central bank: (i) Currency Authority; (ii) Banker to the Government; (ill) Banker's Bank and Supervisor.
Explain the role of bank rate and open market operations for controlling the situation of deficient demand.
Discuss how the central bank plays the role of 'controller of credit' in an economy?
What is meant by Repo Rate? How does the Central Bank use this measure to control inflationary conditions in an economy?
Currency is issued by the central bank, yet we say that commercial banks create money. Explain. How is this money creation by commercial banks likely to affect the national income? Explain.
Explain the role of the following in correcting 'deficient demand' in an economy: (i) Open market operations. (ii) Bank rate.
Calculate MPC and Multiplier (k) from the following data:
| Income | 100 | 200 | 300 |
| Consumption | 80 | 160 | 250 |
Calculate the value of multiplier if the entire increase in income is saved.
Explain the role of the following in correcting 'excess demand' in an economy: (i) Bank rate. (ii) Open market operations.
Would you advocate expansion or contraction of money supply during excess demand?
Calculate the value of multiplier, if the marginal propensity to save is 0.25.
Explain how controlling money supply is helpful in reducing excess demand.
If consumption function for an economy Is given as: C = 120 + 0.9 Y, then what is the value of multiplier?
Assuming that 'increase' in investment is Rs. 900 crore and marginal propensity to consume is 0.6, explain the working of multiplier.
Discuss the changes that will take place in the economy when planned saving is less than planned investment.
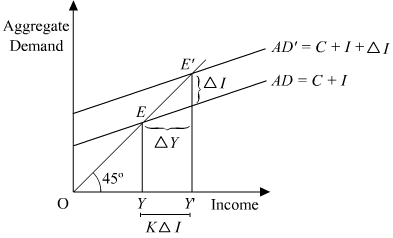
Discuss the concept of multiplier with the help of a diagram.
Explain how open market operations are helpful in controlling credit creation.
Define the term 'multiplier. How do we measure it?
State the relationship between multiplier and MPC.
What can be the maximum value of multiplier?
If marginal propensity to save is 0.1, calculate value of multiplier.
Briefly explain venture capital.
The central bank acts as _____________ to both central and state government.
Money supply refers to total volume of money held by ____________ at a particular point of time in an economy.
How does the Central Bank work as a fiscal agent to the Government?
Briefly explain the quantitative credit control policy of the central bank.
How does a Central Bank act as a custodian of foreign exchange reserve?
Explain any three methods of qualitative credit control.
What is meant by Monetary policy? Explain the following :
1) Bank rate policy
2) Open market operations.
1) Bank rate policy
2) Open market operations.
How does the Central Bank act as a fiscal agent to the Government?
Explain the function of Central Bank as a "Banker to the Government".
State five differences between the Central Bank and a Commercial Bank.
Explain the 'bankers' bank" function of the central bank.
Distinguish between 'quantitative and qualitative measures of credit control'.
Class 12 Commerce Economics Extra Questions
- Comparative Development Experiences Of India And Its Neighbours Extra Questions
- Determination Of Income And Employment Extra Questions
- Employment: Growth,Informalisation And Other Issues Extra Questions
- Environment And Sustainable Development Extra Questions
- Government Budget And The Economy Extra Questions
- Human Capital Formation In India Extra Questions
- Indian Economy (1950-1990) Extra Questions
- Infrastructure Extra Questions
- Introduction To Macroeconomics Extra Questions
- Liberalization,Privatisation And Globalisation: An Appraisal Extra Questions
- Money And Banking Extra Questions
- National Income Accounting Extra Questions
- Open Economy Macroeconomics Extra Questions
- Poverty Extra Questions
- Rural Development Extra Questions