National Income Accounting - Class 12 Commerce Economics - Extra Questions
Explain the methods of calculating National income.
Explain with the help of an example, the basis of classifying goods into final goods and intermediate goods.
Explain the concept of 'disposable income'.
Which among the following are final goods and which are intermediate goods? Give reasons.
(a) Milk purchased by a tea stall
(b) Bus purchased by a school
(c) Juice purchased by a student from the school canteen.
Explain how the following are treated in estimating National Income:
Wheat grown by a farmer for self-consumption
Discuss the following methods of debt redemption:
Debt conversion
Write explanatory answer.
Explain the output method of measuring national income.
Mention the situation in which following equations will hold true:
(i) National Income $$=$$ Domestic Income
(ii) $$GDP_{FC} > GDP_{MP}$$
(iii) $$NNP_{FC} < NDP_{FC}$$
(iv) $$GDP_{FC} = GDP_{MP}$$
(v) Domestic Income is greater than National Income.
Explain the components of compensation of employees for calculation of National Income by Income method.
Answer briefly each of the following questions.
Explain with the help of an example, the problem of double counting while calculating national income.
From the following data, calculate National Income by Income method and Expenditure method:
| Item | Rs. in crores | |
| (i) | Compensation of employees | 700 |
| (ii) | Government final consumption expenditure | 750 |
| (iii) | Net factor income from abroad | (-) 10 |
| (iv) | Net exports | (-) 15 |
| (v) | Profits | 600 |
| (vi) | Net indirect taxes | 60 |
| (vii) | Mixed income of self-employed | 350 |
| (viii) | Rent | 200 |
| (ix) | Interest | 310 |
| (x) | Private final consumption expenditure | 1100 |
| (xi) | Net domestic capital formation | 385 |
| (xii) | Consumption of fixed capital | 65 |
Write explanatory answer:
Explain the various methods of measuring national income.
Distinguish between 'output method and income method of measuring national income'.
Distinguish between stock and flow. Between net investment and capital which is a stock and which is a flow?
Describe the four major sectors in an economy according to the macroeconomic point of view.
Classify the following as Stock and Flow:
(i) Amount of bank deposits as on 31.03.2017
(ii) Losses
(iii) Production of cement in the year 2017
(iv) Profit
(v) Population of India as on 31st March, 2017
(vi) Number of literate people as on 31.03,2017
(vii) Savings
(viii) National income of a country
(ix) Capital
(x) Number of persons employed during December
(xi) Balance in a bank account
(xii) Raw material in a godown as on 31st Jan, 2018
(xiii) Production
(xiv) Wealth
(xv) Gross domestic product
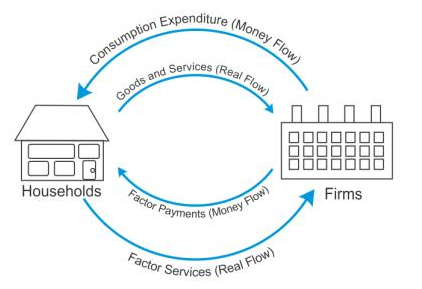
How does real flow consist of factor flow and product flow?
Classify the following as factor income or transfer income:
(i) Unemployment allowances.
(ii) Salary received by Rakesh from a company.
(iii) Financial help to earthquake victims.
(iv) Compensation received from the employer.
(v) Claim received from Insurance company by an injured worker.
(vi) Birthday gift received from a friend.
(vii) Bonus received on Diwali.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
What is meant by intermediate goods?
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Define final goods.
Define capital goods.
Define 'Depreciation'.
What is meant by Net factor income from abroad?
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Out of factor income and transfer income, which one is included in the national income? Give reason.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Can purchase of a new car be categorised as an intermediate good?
What are 'subsidies'?
Give two examples of intermediate goods.
Define flow variable.
Is national income a stock concept or flow concept?
What are stock variables?
Define Gross Investment.
What is meant by the circular flow of income?
Distinguish between Real Flow and Money Flow.
Calculate Indirect Taxes from the following data:
| Particulars | Rs. in crores |
| (i) NDP at FC (ii) Subsidies (iii) Factor income from abroad (iv) Consumption of Fixed Capital (v) Factor income to abroad (vi) GNP at MP | 55,915 1,540 635 1,625 865 58,350 |
Distinguish between factor income and transfer receipt.
Distinguish between stocks and flows. Given an example of each.
Distinguish between:
Final goods and intermediate goods
'Machine purchased is always a final good.' Do you agree with the statement? Give reasons for your answer.
Distinguish between intermediate products and final products. Give examples.
Whether the following items will be included in National Income? Give reasons for your answer.
(i) Payment of electricity bill by a factory.
(ii) Dividend on shares.
(iii) Increase in stock of consumer goods with households.
(iv) Bus fare paid by a passenger.
(v) Gains from sale of shares.
Whether the following items will be included in National Income?
(i) Rent earned by Reliance from its building in USA.
(ii) Gifts from Abroad.
(iii) Retained earnings of resident companies from abroad.
(iv) Expenses of foreign visitors in India.
(v) Gifts to a trust from Japan.
Which of the following expenditures incurred are on intermediate products and which are on final products? You must state reason for your answer:
(i) Purchase of ticket for train journey by an individual.
(ii) Purchase of eatables by a firm.
(iii) Purchase of a car by an employer for office use by his employees.
Distinguish between consumer goods and capital goods. Give examples.
Distinguish between intermediate product and final product. Give suitable examples in support of your answer.
Explain the basis of classifying goods into intermediate and final goods. Give suitable examples.
Which of the following items is part of compensation of employees? Give reasons for your answer.
(i) Entertainment allowance to an employee to entertain business guests.
(ii) Employers' contribution to gratuity fund of the employees.
(iii) Employee's contribution to provident fund.
(iv) Payment of claim of insurance claim by LIC to the injured worker.
(v) Old age pension.
(vi) Medical expenses of a firm on treatment of employee's family.
Manish buys a second hand car from a car broker for Rs. 3,25,The broker receives Rs. 16,500 as commission for his services from Manish. How will this transaction affect the national income of the country? Give reason for your answer.
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
When is value of output equal to value added?
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
What is the value added method of measuring national income?
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
What is meant by mixed income?
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Mention the three methods of measuring national income.
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Income from property, royalty, entrepreneurial income, and interest is Rs. 150, Rs. 100, Rs.75 and Rs.How much is the operating surplus?
Give meaning of 'deficient demand' in macroeconomics.
Due to an increase in Investment, the national income increased by Rs. 10,000 crores. If 20% of additional income is saved, calculate the increase in investment. (Rs. 2,000 crores)
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Under what circumstances, net export is negative?
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Will the commission given to a broker for sale of an old house be included in national income?
Short Answer Type Questions:
Giving reason identify whether the following are final expenditures or intermediate expenditure:
(i) Expenditure on maintenance of an office building.
(ii) Expenditure on improvement of a machine in a factory.
Explain the concept of 'excess demand' in macroeconomics. Also explain the role of 'open market operation' in correcting it.
What is meant by excess demand in Macroeconomics?
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Why do exports form a part of national income?
Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Give one example of "externality" which reduces welfare of the people.
Short Answer Type Questions:
Explain 'mixed income of self-employed' and give an example.
In an economy S = -50 + 0.5 Y is the saving function (where S = saving and Y = national income) and investment expenditure is Rs. 7,Calculate: (I) Equilibrium level of national Income. (II) Consumption expenditure at equilibrium level of national income.
In an economy, marginal propensity to save is 0.How much increase in investment is required so that national income rises by Rs. 400 crores?
An increase in investment in a country leads to increase in national income by Rs. 200 crores. If marginal propensity to consume is 0.75, what is the increase in investment? Calculate.
Explain national income determination through the two alternative approaches. Use diagram.
Explain the methods of calculating National Income
Define the following:
Income from property and entrepreneurship
Define flows.
What do you mean by circular flow of income in a simple economy?
What is the generation phase?
What is the advantage of per capita income ? Mention any one.
NNP at FC is also known as _______________ income.
GNP at MP, _____ , NNP at MP and NNP at FC are four national concepts.
What do you mean by Gross National Product at Factor Cost?
What is the distribution phase?
Determine the missing items in GNP at FC = GNP at MP - _________.
What is private income?
NNP at FC = GNP at MP - ___________ - Depreciation.
What is the disposition phase?
What is the formula for calculating private income?
What is personal income?
What is personal disposable income?
What does personal disposable income exclude?
What are the components of compensation of employees under income method?
What is the formula of gross national disposable income?
What is the formula of net national disposable income?
What is gross national disposable income?
What is the compensation of employees under income method?
What are the different formulae to calculate personal disposable income?
What is net national disposable income?
What is royalty?
What excludes from wages and salaries in kind?
What are the components of gross fixed capital formation?
What are the examples of royalty?
State whether construction of a new house is included in national income.
National income is a ___________ (stock /flow) concept.
Calculate Net National Product at Market price from the following data:
| Items | Rupees | |
| 1 | Closing Stock | 10 |
| 2 | Consumption of fixed capital | 40 |
| 3 | Private final consumption expenditure | 600 |
| 4 | Export | 50 |
| 5 | Opening stock | 20 |
| 6 | Government final consumption expenditure | 100 |
| 7 | Imports | 60 |
| 8 | Net domestic fixed capital formation | 80 |
| 9 | Net current tranfer from abroad | -10 |
| 10 | Net factor income from abroad | 30 |
State with valid reason, which of the following statement is true or false:
a. A kind of goods used as intermediary goods can never be final goods.
b. With money as a medium of exchange, only money flows prevail in the economy, not the real flows.
Calculate (a) Domestic Income and (b) Operating Surplus.
Mixed Income = 400
Undistributed Profit = 100
Consumption of fixed capital = 100
Rent and interest = 700
Corporation tax = 600
Dividend = 860
NFIA = 150
Subsidies = 40
Indirect tax = 100
Compensation of employees = 1500
Calculate NNP at MP by (i) Income Method and (ii) Expenditure Method
| Items | Rupees in Cr | |
| 1 | Mixed income by the self-employed | 50 |
| 2 | Indirect tax | 30 |
| 3 | Wages and salaries | 400 |
| 4 | Exports | 15 |
| 5 | Imports | 45 |
| 6 | Operating Surplus | 300 |
| 7 | Profits | 130 |
| 8 | Employers Contribution to social security schemes | 80 |
| 9 | Net capital formation | 150 |
| 10 | Private final consumption expenditure | 500 |
| 11 | Net factor income from abroad | 10 |
| 12 | Govt. final consumption expenditure | 230 |
| 13 | Consumption on fixed capital | 20 |
| 14 | Subsidies | 10 |
Calculate Net National Product at factor cost.
| No. | Items | ( Rs. in Crore) |
| i | Private final consumption expenditure | 8000 |
| ii | Government final consumption expenditure | 1000 |
| iii | Exports | 700 |
| iv | Imports | 120 |
| v | Annual allowance for wear and tear | 60 |
| vi | Fixed business investment | 300 |
| vii | Residential investment | 200 |
| viii | Change in stock | 100 |
| ix | Factor income to abroad | 40 |
| x | Factor income from abroad | 90 |
| xi | Net product taxes | 400 |
| xii | Net productionn taxes | 250 |
From the following data calculate imports:
| SR. No. | Particulars | ( Rs. crores) |
| (i) | Sales | 3500 |
| (ii) | Net fixed capital formation | 150 |
| (iii) | Intermediate Consumption | 1650 |
| (iv) | Consumption of fixed capital | 100 |
| (v) | Exports | 800 |
| (vi) | Change in stock | 250 |
| (vii) | Household Consumption expenditure | 500 |
| (viii) | Expenditure incurred by non-profit institutions serving households. | 50 |
| (ix) | Purchase of goods by the government | 250 |
| (x) | Compensation of employees paid by the government | 200 |
| (xi) | Net indirect taxes | 220 |
| S.NO | Items | Rs. (In Crores) |
| 1 | Wages and salaries | 3065 |
| 2 | Interest | 700 |
| 3 | Compensation of employees in kind | 65 |
| 4 | Rent | 400 |
| 5 | Undistributed profit | 110 |
| 6 | Dividend | 240 |
| 7 | Net Income From Abroad | 110 |
| 8 | Social security contribution by employees | 60 |
| 9 | Direct taxes of firms | 150 |
| 10 | Private consumption | 2000 |
| 11 | Public consumption | 1200 |
| 12 | Gross domestic investment abroad | 1500 |
| 13 | Net investment abroad | 270 |
| 14 | Net indirect taxes | 100 |
| 15 | Depreciation | 80 |
| 16 | Transfer payment | 130 |
| 17 | Direct personal taxes | 75 |
Match the following by choosing the correct set from Column A and Column B:
| Column A | Column B |
| a. Private Consumption Expenditure | i. Market Rate of Interest |
| b. Private Investment Expenditure | ii. Total Expenditure |
| c. Autonomous Investment | iii. Level of personal disposable income |
| d. Aggregate Demand | iv. Construction of Roads |
Give two points of distinguished between private and public goods?
Find Wages and salaries from the following data:
| Royalty | 50 |
| Rent | 100 |
| Interest | 400 |
| Net Indirect Tax | 70 |
| Net national product at market price | 1700 |
| Profit | 300 |
| Net Factor Income to abroad | (-)20 |
| Consumption of fixed capital | 120 |
| Social security contribution by the employers | 60 |
| Social security Contribution by employees | 40 |
Calculate GNP at mp from the following information-
| Items | (Rs. in crore) | |
| I | Compensation of employees | 4000 |
| II | Rent | 800 |
| III | Profits | 1500 |
| IV | Undistributed profit | 400 |
| V | Mixed-income of the self-employed | 1800 |
| VI | Net imports | 30 |
| VII | Net Investment | 900 |
| VIII | Gross domestic fixed capital formation | 1000 |
| IX | Inventory Investment | 50 |
| X | Interest | 900 |
| XI | Net Indirect tax | 500 |
| XII | Net factor income to abroad | (-80) |
| Component | Expenditure (In thousand) |
| Social Security payments | $250 |
| Depreciation | $47 |
| Private investment | $630 |
| Exports | $260 |
| Imports | $300 |
| Salaries earned by foreigners working in Magnolia | $160 |
| Household consumption | $850 |
| Purchase of raw materials | $270 |
| Government purchases | $900 |
| Capital Income | $290 |
| Salaries earned by Mangolian citizens working abroad | $350 |
Calculate the value of Magnolia's GNP.
Does Magnolia's GDP differ from its GNP? Why?
| S.No | Items | Rs (In crores) |
| 1 | Compensation of employees paid by the Government | 40 |
| 2 | Mixed Income | 50 |
| 3 | Wages and Salaries | 400 |
| 4 | Employers Contribution to SSS | 80 |
| 5 | Operating Surplus | 300 |
| 6 | Indirect Taxes | 30 |
| 7 | Subsidies | 10 |
| 8 | Net Capital formation | 150 |
| 9 | NFIA | 10 |
| 10 | Government Final consumption Expenditure | 230 |
| 11 | Private Final Consumption Expenditure | 500 |
| 12 | Exports | 15 |
| 13 | Imports | 45 |
| 14 | Depreciation | 20 |
| 15 | Profits | 130 |
Calculate the missing values from the following information:
| S. No. | Items | Rs. in lakhs |
| 1. | National Income | 60000 |
| 2. | Goods and services tax | 2000 |
| 3. | Government final consumption expenditure | ? |
| 4. | gross domestic fixed capital formation | 18000 |
| 5. | Subsidies | 1000 |
| 6. | Private final consumption expenditure | 11500 |
| 7. | Wages and salaries | 10000 |
| 8. | Consumption of fixed capital | 700 |
| 9. | Mixed-income of self-employed | ? |
| 10. | Operating surplus | 15000 |
| 11. | Net factor income to abroad | (-)800 |
| 12. | Net imports | (-) 2000 |
| 13. | Opening stock | 1000 |
| S.NO | PARTICULARS | AMOUNTS |
| A | Compensation of employees | 4,000 |
| B | Rent on land | 3,500 |
| C | Dividend | 800 |
| D | Undistributed profit | 500 |
| E | Royalty | 700 |
| F | Change in stock | 900 |
| G | Interest | 5,000 |
| H | Mixed-income of self-employed | 500 |
| I | Consumption of fixed capital | 800 |
| J | Indirect tax | 500 |
| K | Subsidies | 300 |
| L | Net factor income to abroad | -350 |
| M | Employees contribution to social security | 800 |
Calculate Value of output at market price from the following data.
a) Subsidies = 40
b) Intermediate Consumption = 200
c) Compensation of employees = 400
d) Depreciation = 50
e) Royalty = 5
f) Interest = 25
g) Indirect Taxes = 100
h) Rent = 10
i) Profits = 60
j) Net change in stocks = 20
Define circular flow of income.
Give meaning of durable goods and perishable goods.
| S.NO | PARTICULARS | RS. IN CRORES |
| i | Transfer payments by government | 7 |
| ii | Government final consumption expenditure | 50 |
| iii | Net imports | -10 |
| iv | Net domestic fixed capital formation | 60 |
| v | Private final consumption expenditure | 300 |
| vi | Net factor income from abroad | 5 |
| vii | Depreciation | 12 |
| viii | Closing stock | 8 |
| ix | Opening stock | 8 |
| x | Direct tax | 60 |
| xi | Net indirect taxes | 5 |
| S.NO | Items | Rs. (In Crores) |
| 1 | Wages and salaries | 3065 |
| 2 | Interest | 700 |
| 3 | Compensation of employees in kind | 65 |
| 4 | Rent | 400 |
| 5 | Undistributed profit | 110 |
| 6 | Dividend | 240 |
| 7 | Net Income From Abroad | 110 |
| 8 | Social security contribution by employees | 60 |
| 9 | Direct taxes of firms | 150 |
| 10 | Private consumption | 2000 |
| 11 | Public consumption | 1200 |
| 12 | Gross domestic investment abroad | 1500 |
| 13 | Net investment abroad | 270 |
| 14 | Net indirect taxes | 100 |
| 15 | Depreciation | 80 |
| 16 | Transfer payment | 130 |
| 17 | Direct personal taxes | 75 |
| S.no | Items | Rs (In crores) |
| 1 | Private final consumption expenditure | 85 |
| 2 | Net domestic fixed capital formation | 25 |
| 3 | Consumption of fixed capital | 02 |
| 4 | Closing stock | 10 |
| 5 | Opening stock | 05 |
| 6 | Govt final consumption expenditure | 10 |
| 7 | Net exports | -5 |
| 8 | Wages & Salaries | 80 |
| 9 | Contribution of employers towards SSS | 10 |
| 10 | Operating surplus | 20 |
| 11 | NFIA | -5 |
| 12 | NIT | 10 |
Identify and explain the concepts: Anand made ice cream, paneer and curd form milk.
Identify and explain the concepts from the given illustration: Mr. Prasad purchased Air Conditioner for his house in the summer season.
Explain the precautions that should be taken while estimating national income by expenditure method.
Find national income and private income:
| Sr.No | Particle | Rs Crores |
| i. | Wages and Salaries | $$1,000$$ |
| ii. | Net current transfers to abroad | $$20$$ |
| iii. | Net factor income paid to abroad | $$10$$ |
| iv. | Profit | $$400$$ |
| v | National Debt Interest | $$120$$ |
| vi. | Social Security contributions by employers | $$100$$ |
| vii. | Current transfers from government | $$60$$ |
| viii. | National Income accruing to government | $$150$$ |
| ix. | Rent | $$200$$ |
| x. | Interest | $$300$$ |
| xi. | Royalty | $$50$$ |
What is the difference between National Income and domestic Income?
What is 'excess demand' in macroeconomics? Show the same in a diagram. Explain the role of 'open market operations' in reducing it.
Given the following data, find the value of 'Operating Surplus' and 'Net Exports'.
| S.No. | Particulars | Amount in crores |
| 1. | Net factor income from abroad | 300 |
| 2. | Gross domestic capital formation | 1,300 |
| 3. | Mixed income of self employed | 400 |
| 4. | Private final consumption expenditure | 1,000 |
| 5. | Net indirect taxes | 150 |
| 6. | Operating Surplus | ? |
| 7. | Net Exports | ? |
| 8. | Wages and salary | 3,000 |
| 9. | Government final consumption expenditure | 1,500 |
| 10. | Consumption of fixed capital | 100 |
| 11. | Profit | 300 |
| 12. | National Income | 4,600 |
Write four limitations in estimating the national income of India.
Write short notes.
CSO
| S.No | Items | Rs (In crores) |
| 1 | Wages and salaries | 500 |
| 2 | Government final consumption expenditure | 120 |
| 3 | Royalty | 20 |
| 4 | Interest | 40 |
| 5 | Households final consumption expenditure | 600 |
| 6 | Change in stocks | 10 |
| 7 | Indirect taxes | 100 |
| 8 | Rent | 50 |
| 9 | Final consumption expenditure of private non-profit institution serving households | 30 |
| 10 | Net domestic fixed capital formation | 60 |
| 11 | Profit after tax | 100 |
| 12 | Corporation tax | 20 |
| 13 | Net exports | -20 |
| 14 | Subsidies | 30 |
| 15 | Net factor income from abroad | -5 |
| S.No | Items | Rs (in crores) |
| 1 | Value of output of a primary sector | 10,000 |
| 2 | Value of output of other sectors | 4,000 |
| 3 | Raw materials used by the primary sector | 5,000 |
| 4 | Raw materials used by other sectors | 3,000 |
| 5 | Factor income received from abroad | 100 |
| 6 | Factor income paid to abroad | 150 |
| 7 | Depreciation | 550 |
| 8 | NIT | 800 |
| 9 | Mixed income | 2,000 |
| 10 | Wages and salaries | 1,000 |
| 11 | Rent | 400 |
| 12 | Social security contribution by employers | 700 |
| 13 | Dividend | 100 |
| 14 | Corporation tax | 50 |
| 15 | Corporate savings | 100 |
| 16 | Interest | 300 |
Write short notes
Main concepts of national income
Calculate National income by Expenditure Method.
- Final Consumption Expenditure Private Sector = 350
- Government Sector = 100
- Mixed income of self-employed = 35
- Gross domestic fixed capital formation = 70
- Opening stock = 15
- Compensation of employees = 250
- Closing stock = 25
- Imports = 20
- Rent = 75
- Consumption of fixed capital = 10
- Net indirect taxes = 25
- Interest = 25
- Net factor income from abroad = -5
- Exports = 10
- Profit = 100.
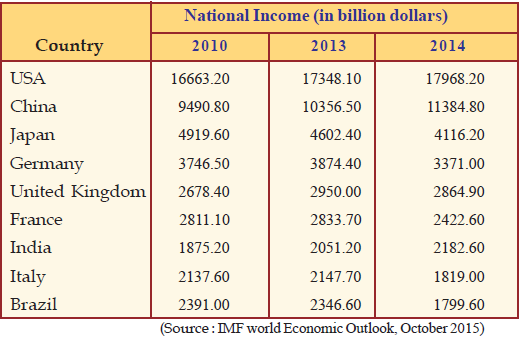
The above table shows the national incomes of a few countries during three years.
Find out the countries which have the highest and the lowest national income in 2014.
Compared to 2013, which countries have achieved economic growth in 2014?
Compared to 2013, which countries have failed in achieving economic growth in 2014?
Class 12 Commerce Economics Extra Questions
- Comparative Development Experiences Of India And Its Neighbours Extra Questions
- Determination Of Income And Employment Extra Questions
- Employment: Growth,Informalisation And Other Issues Extra Questions
- Environment And Sustainable Development Extra Questions
- Government Budget And The Economy Extra Questions
- Human Capital Formation In India Extra Questions
- Indian Economy (1950-1990) Extra Questions
- Infrastructure Extra Questions
- Introduction To Macroeconomics Extra Questions
- Liberalization,Privatisation And Globalisation: An Appraisal Extra Questions
- Money And Banking Extra Questions
- National Income Accounting Extra Questions
- Open Economy Macroeconomics Extra Questions
- Poverty Extra Questions
- Rural Development Extra Questions