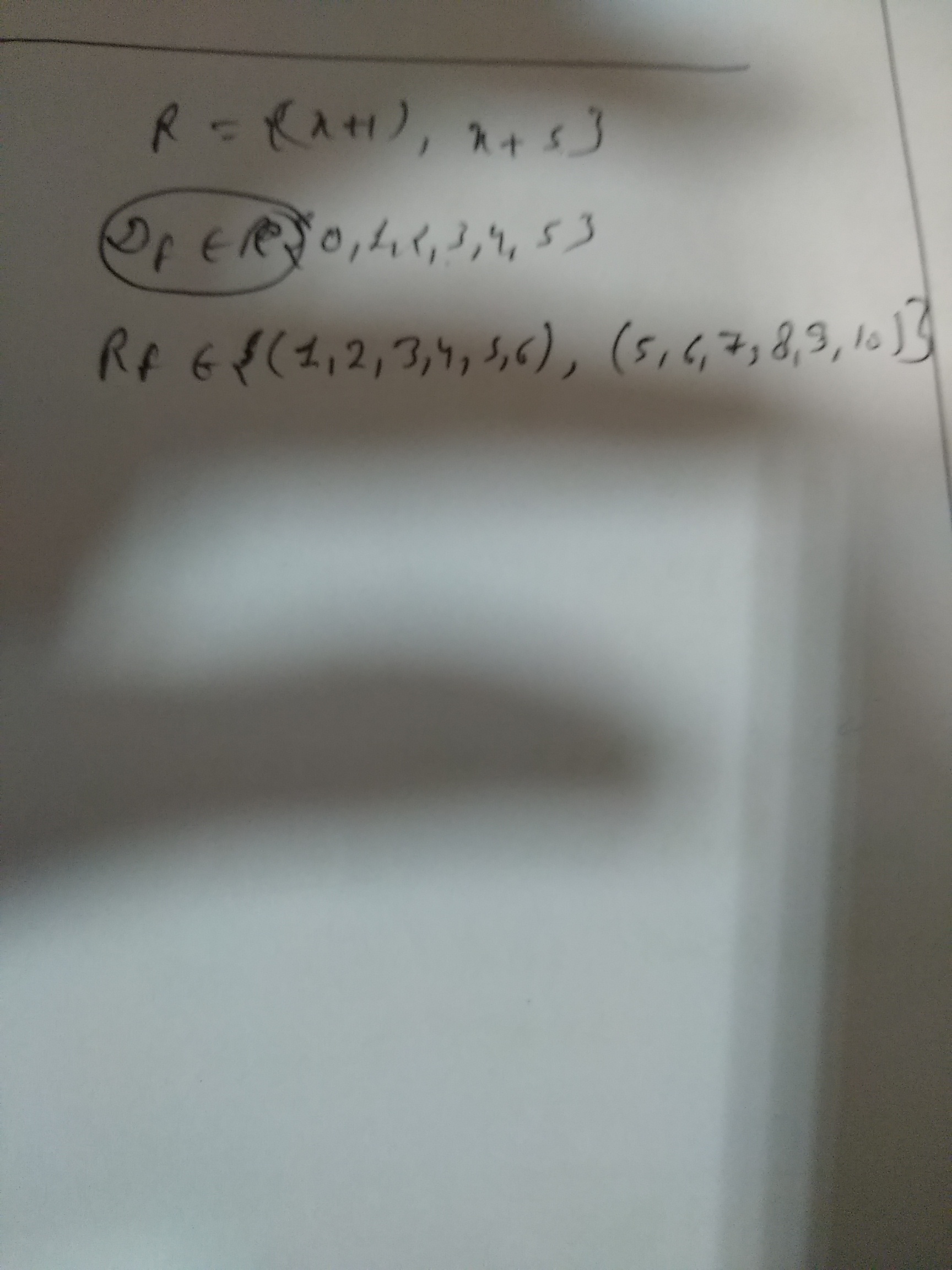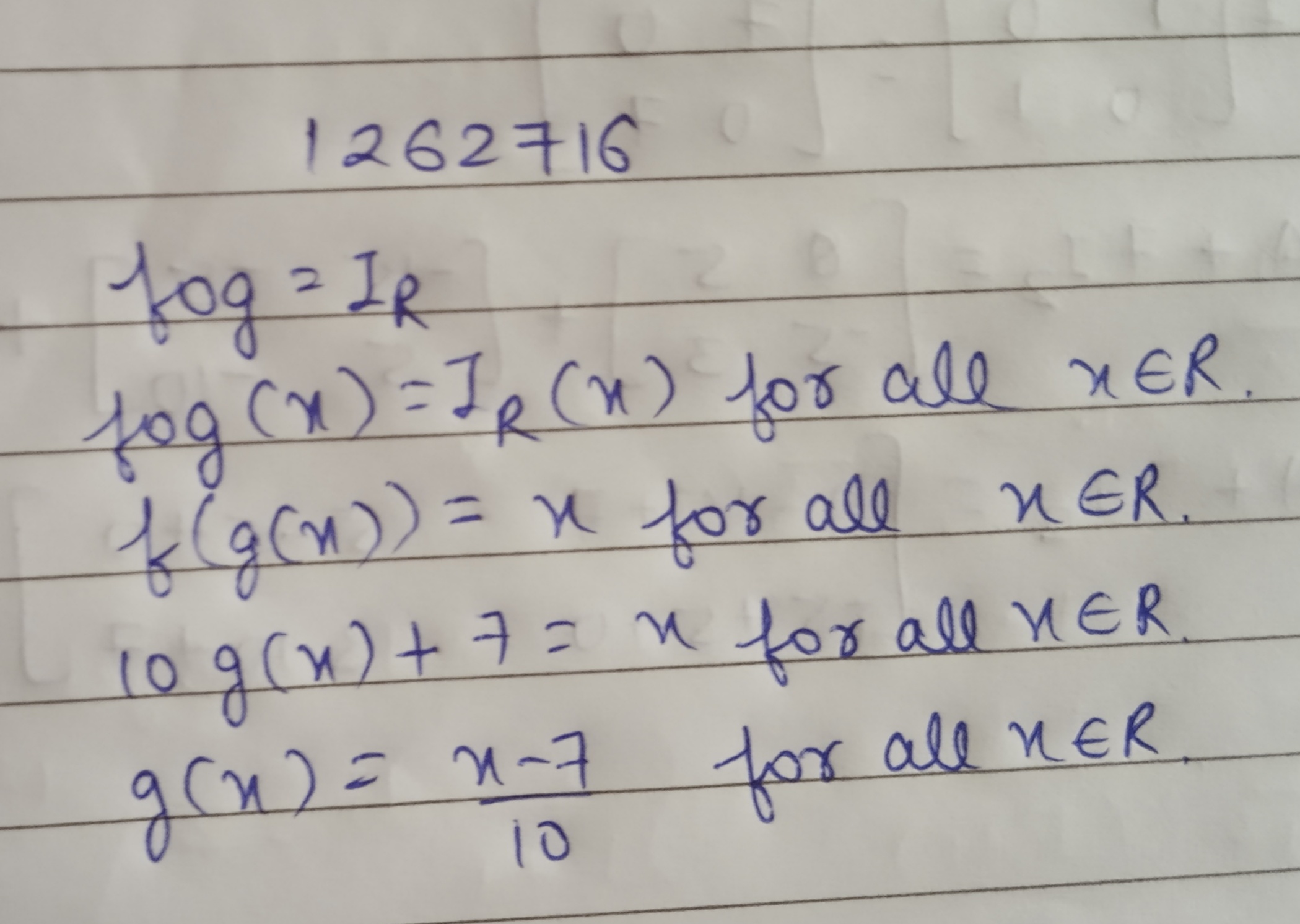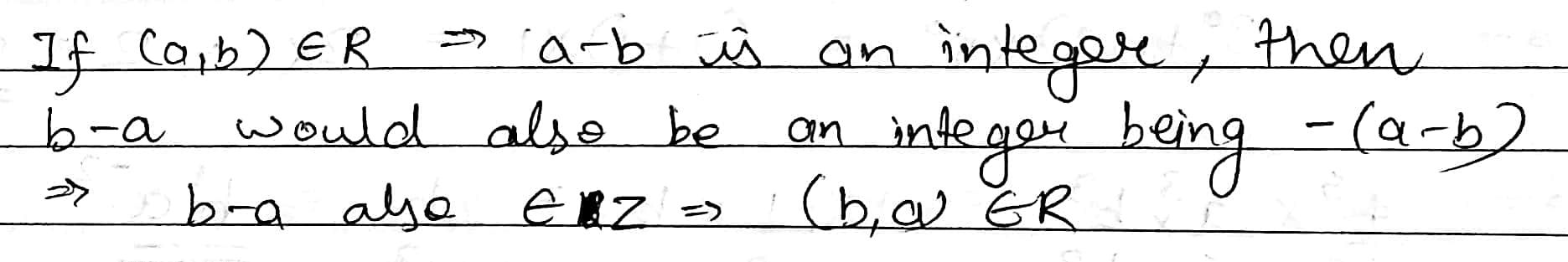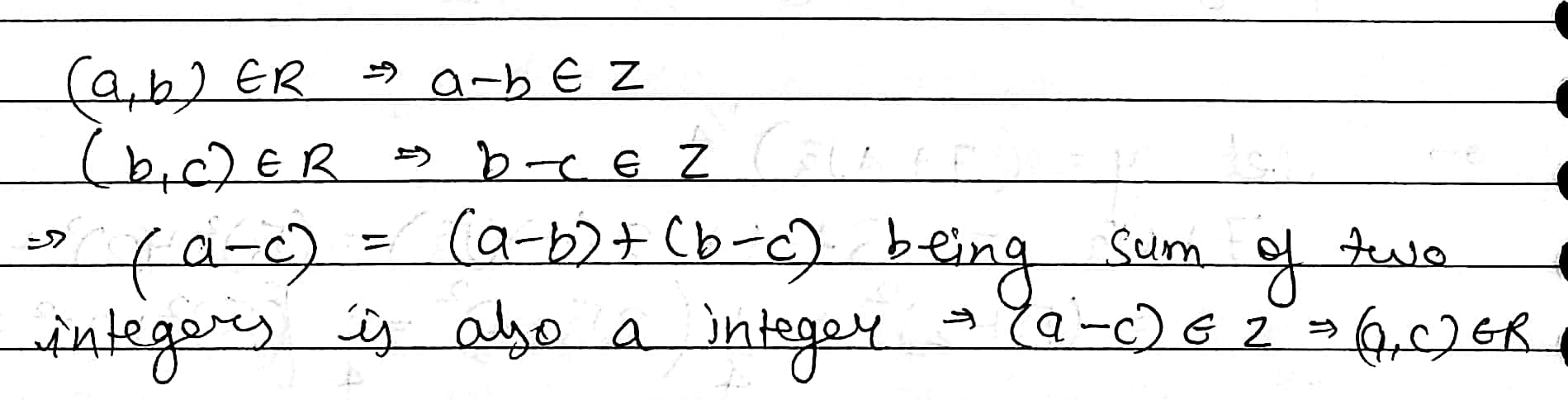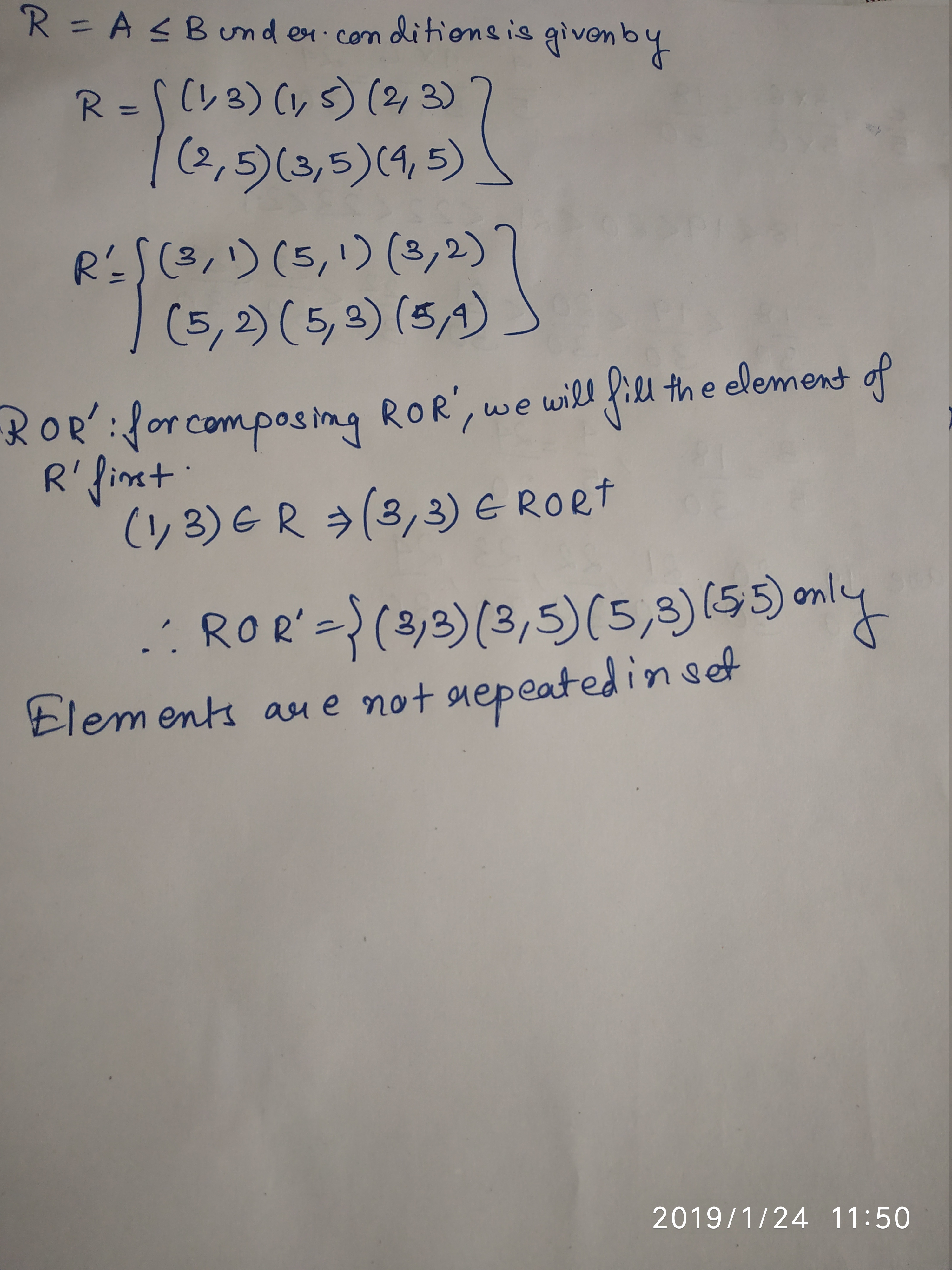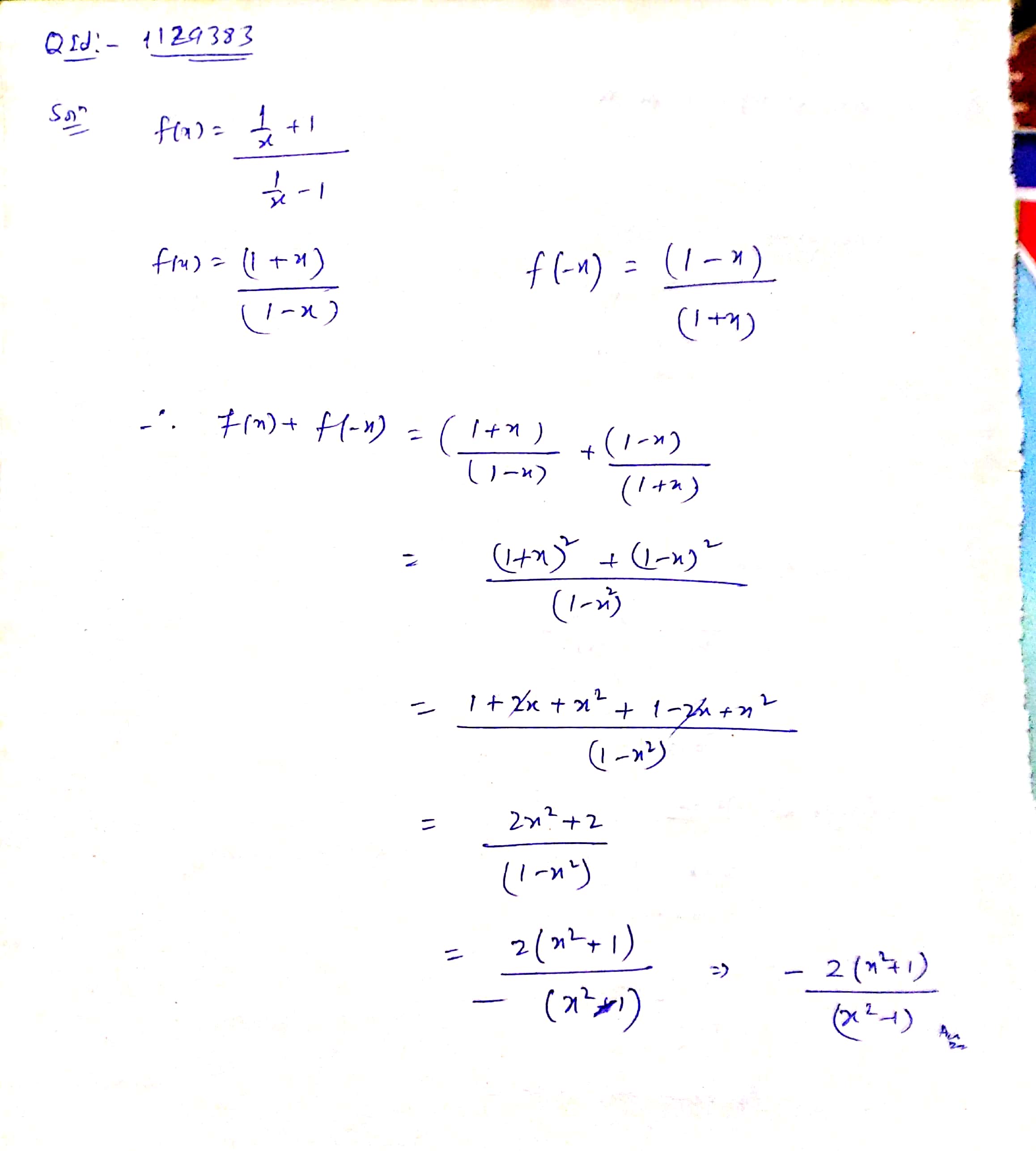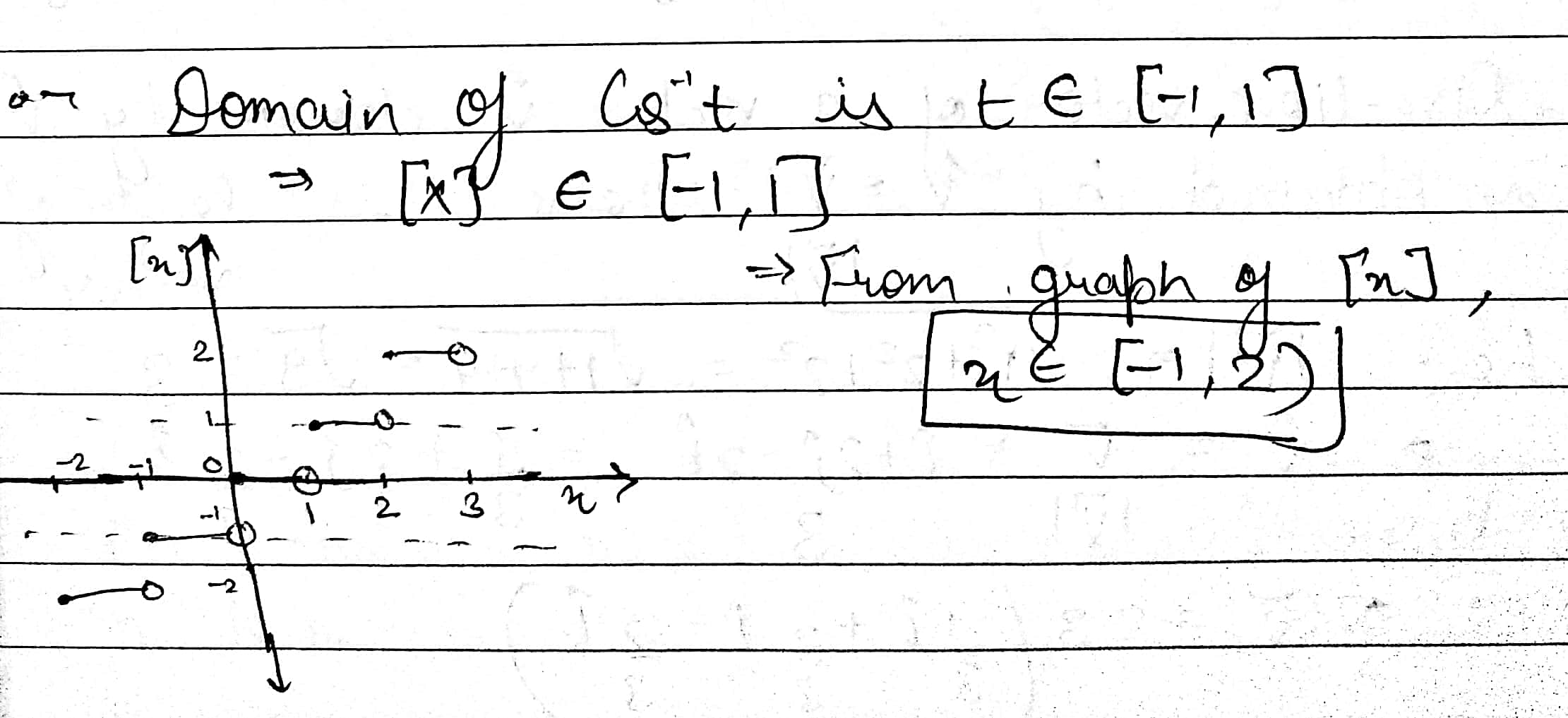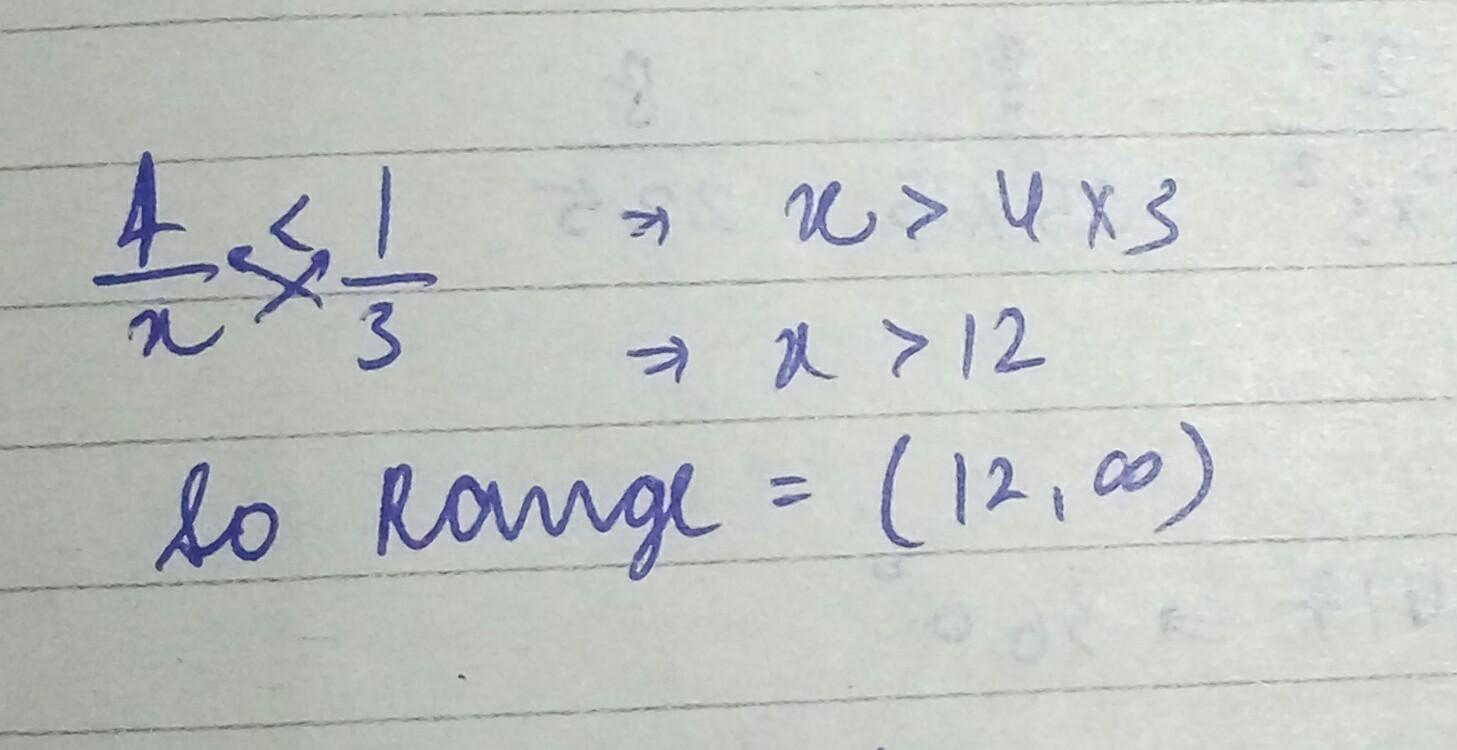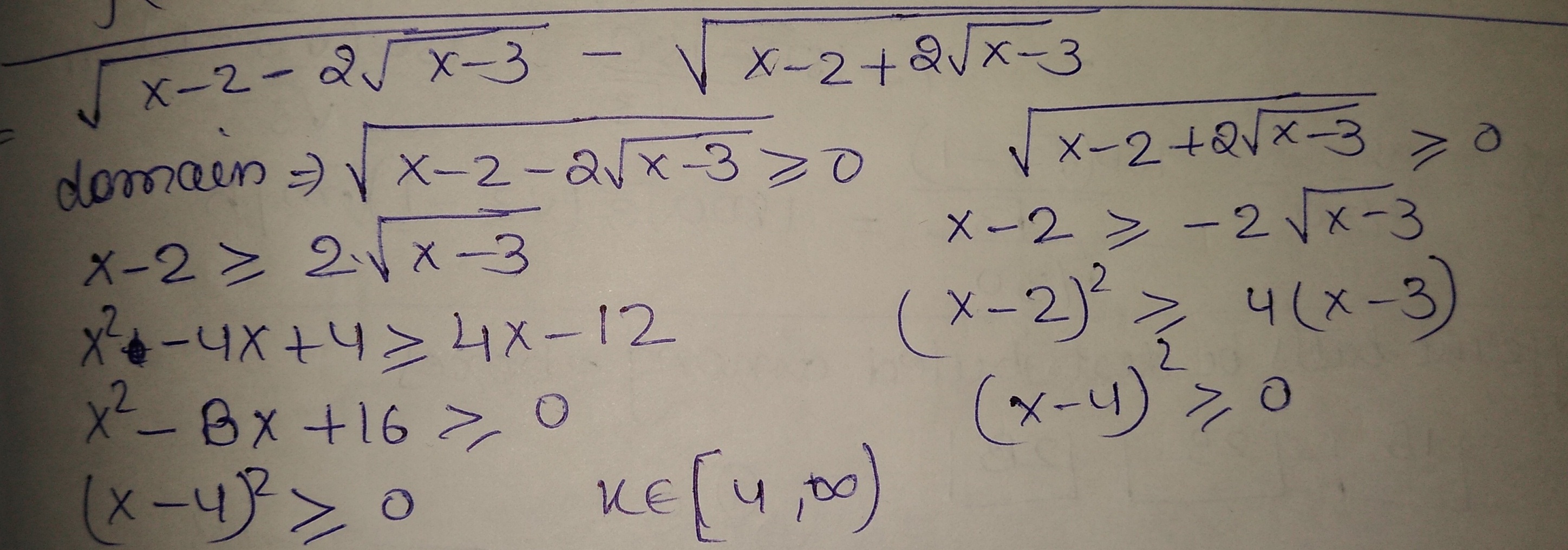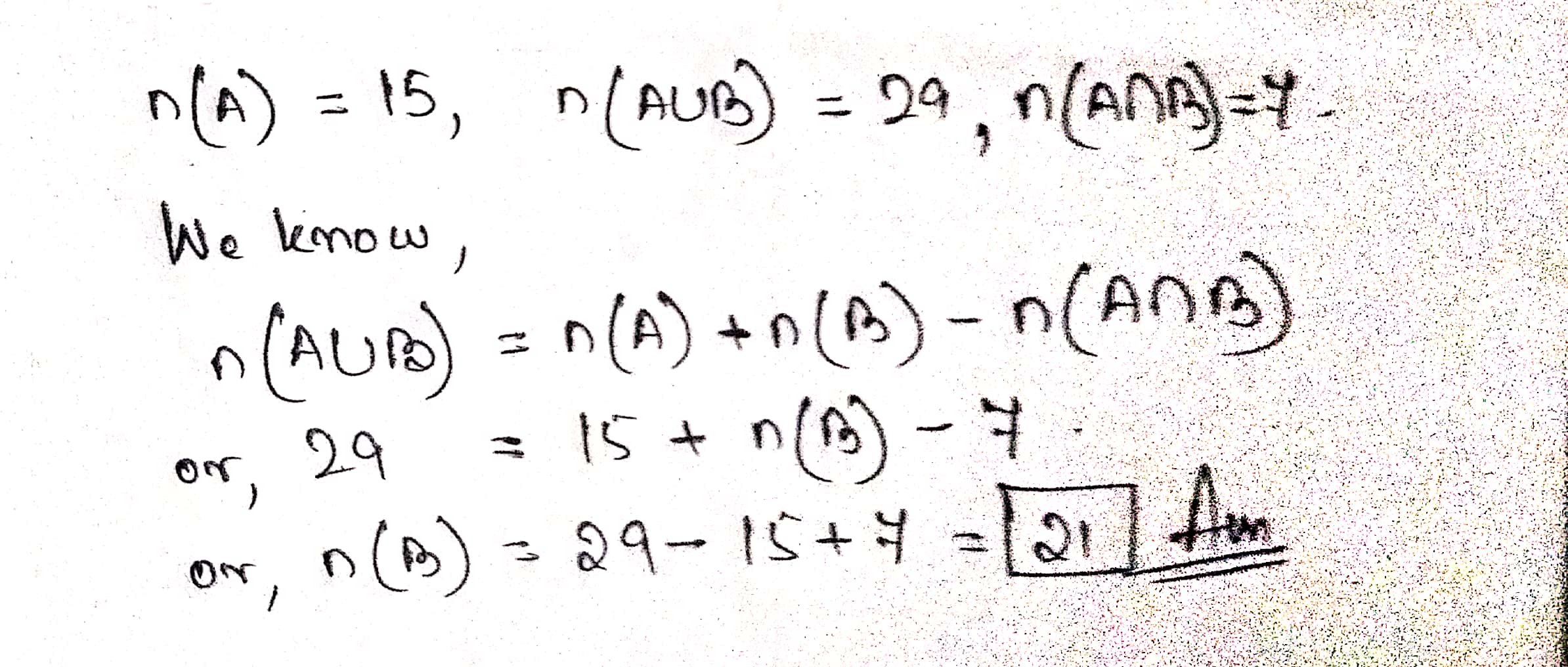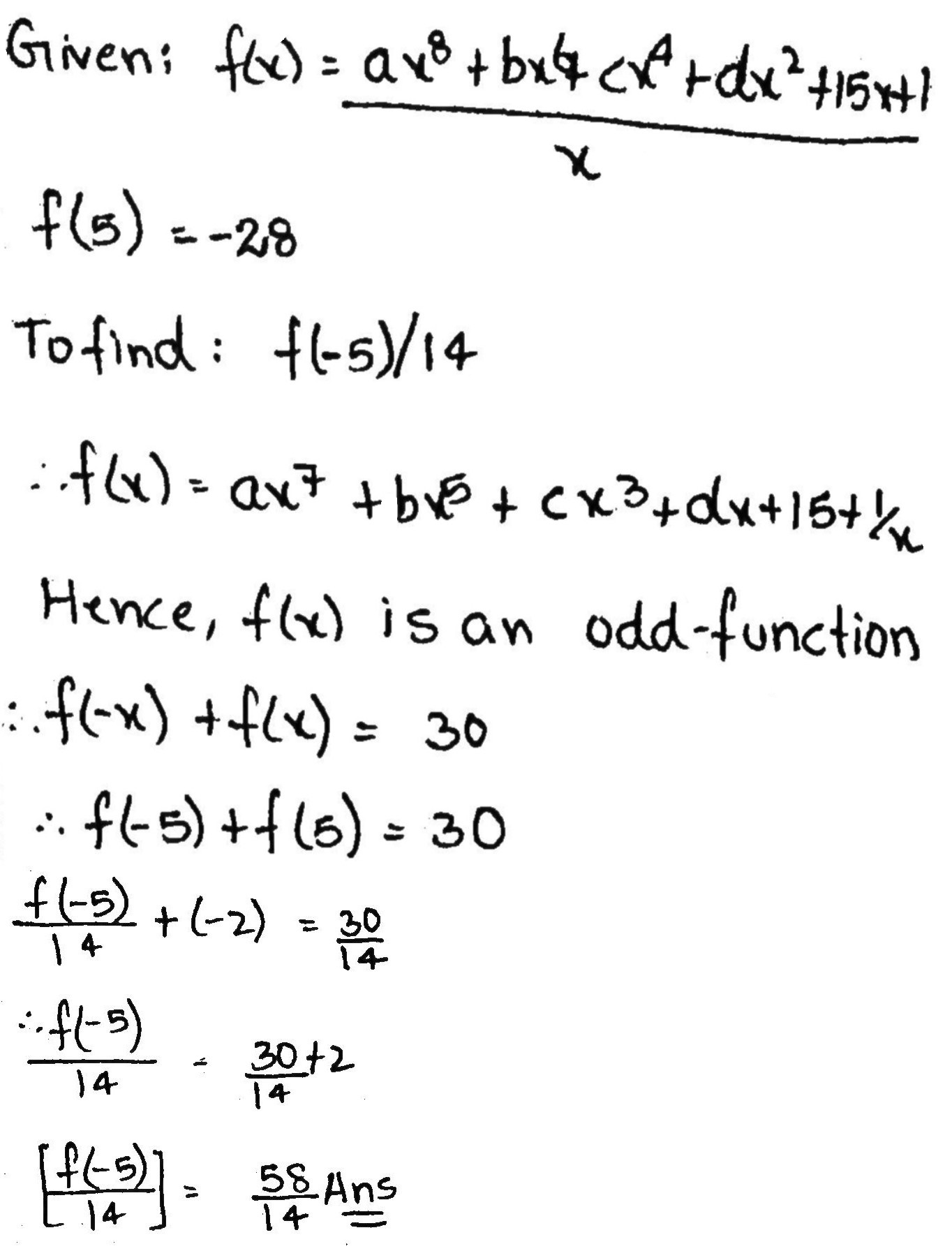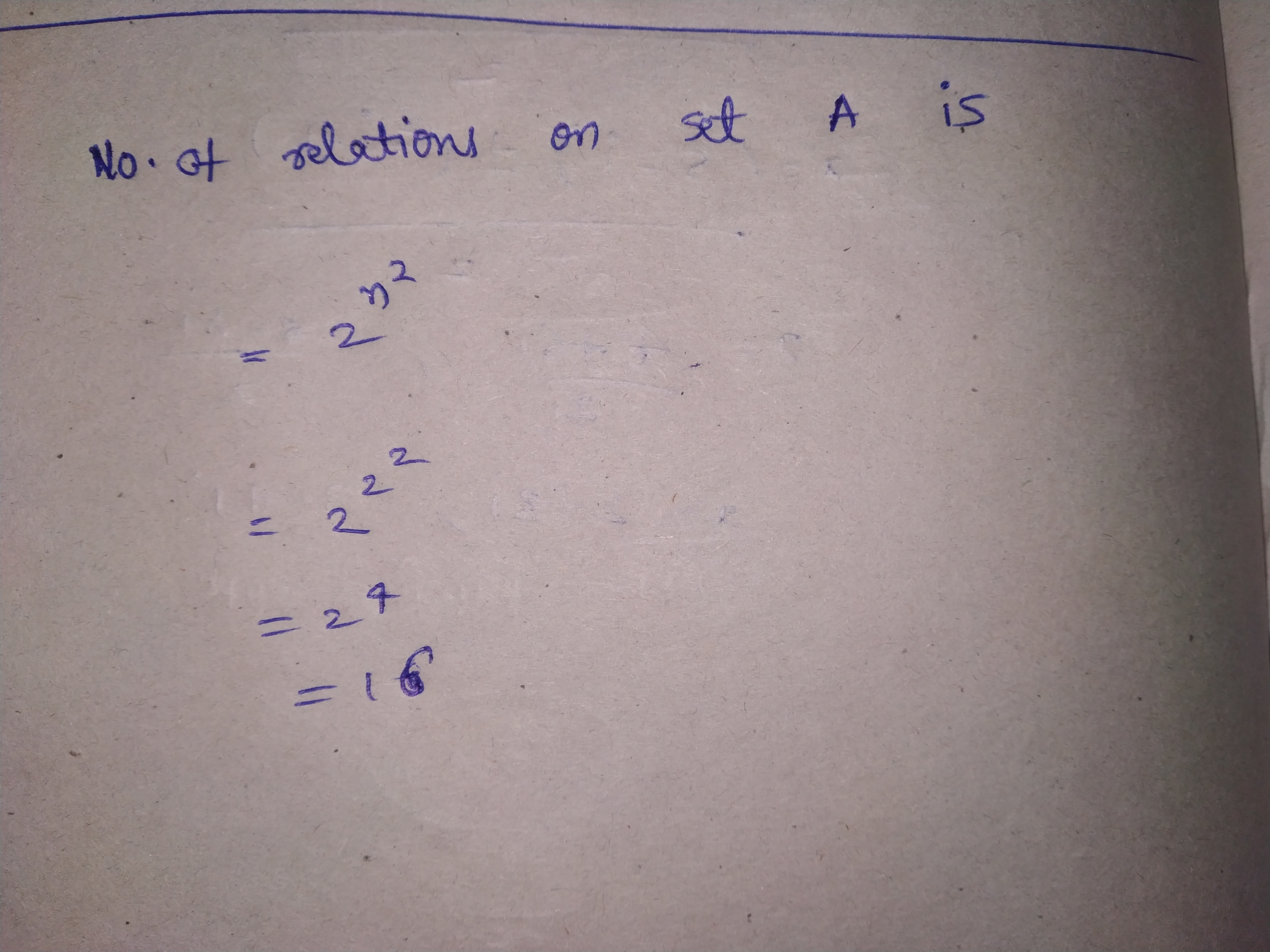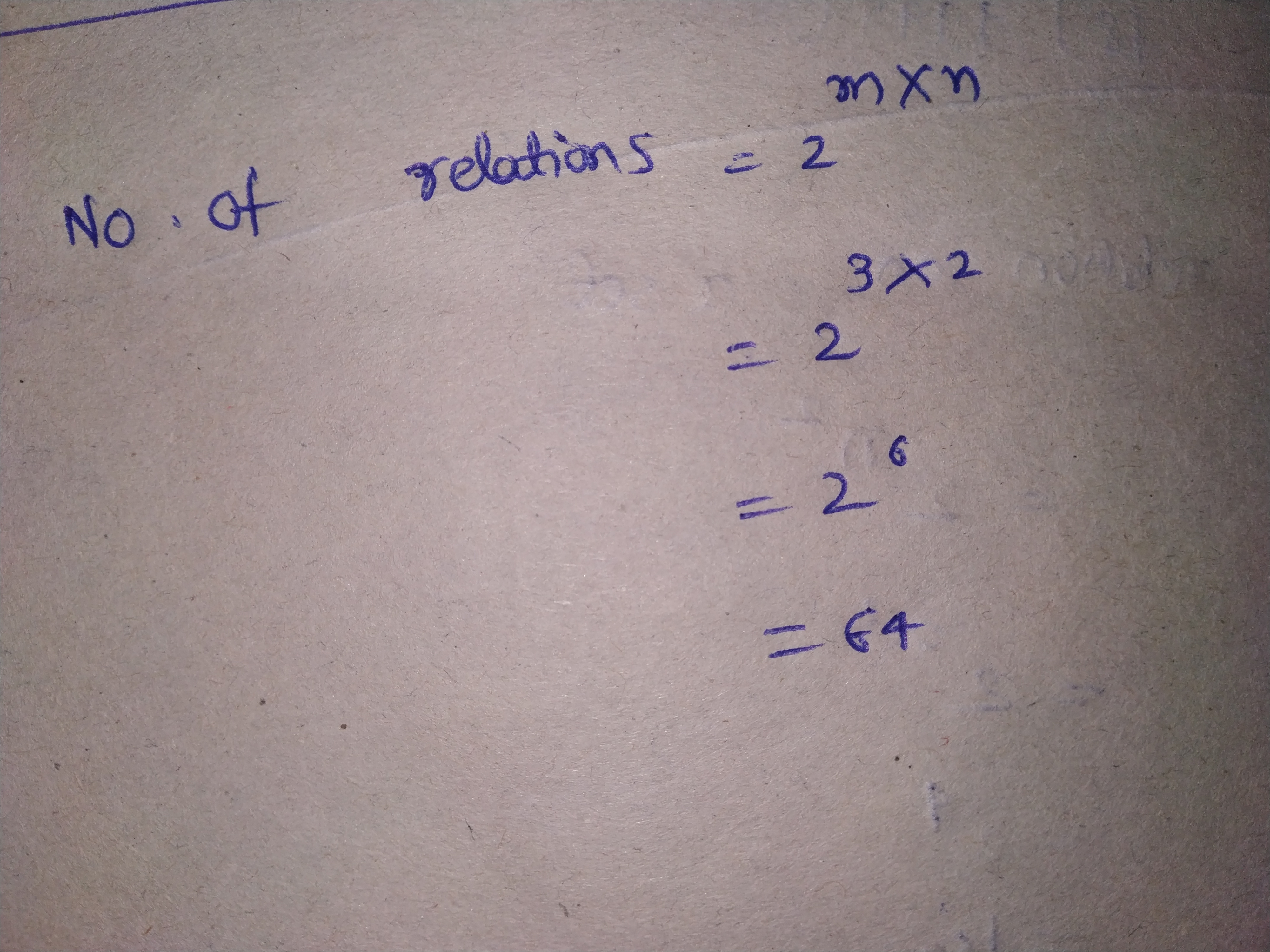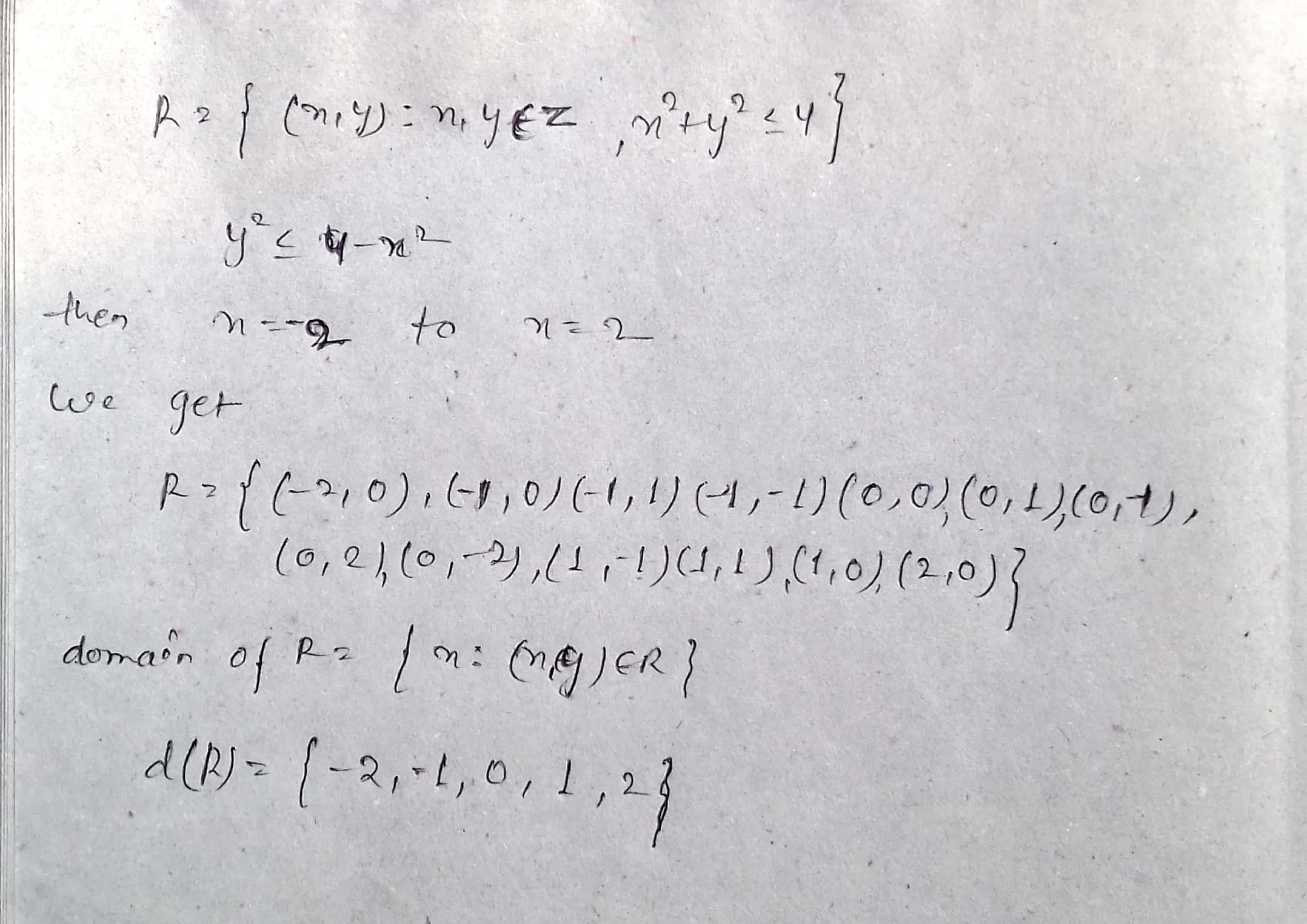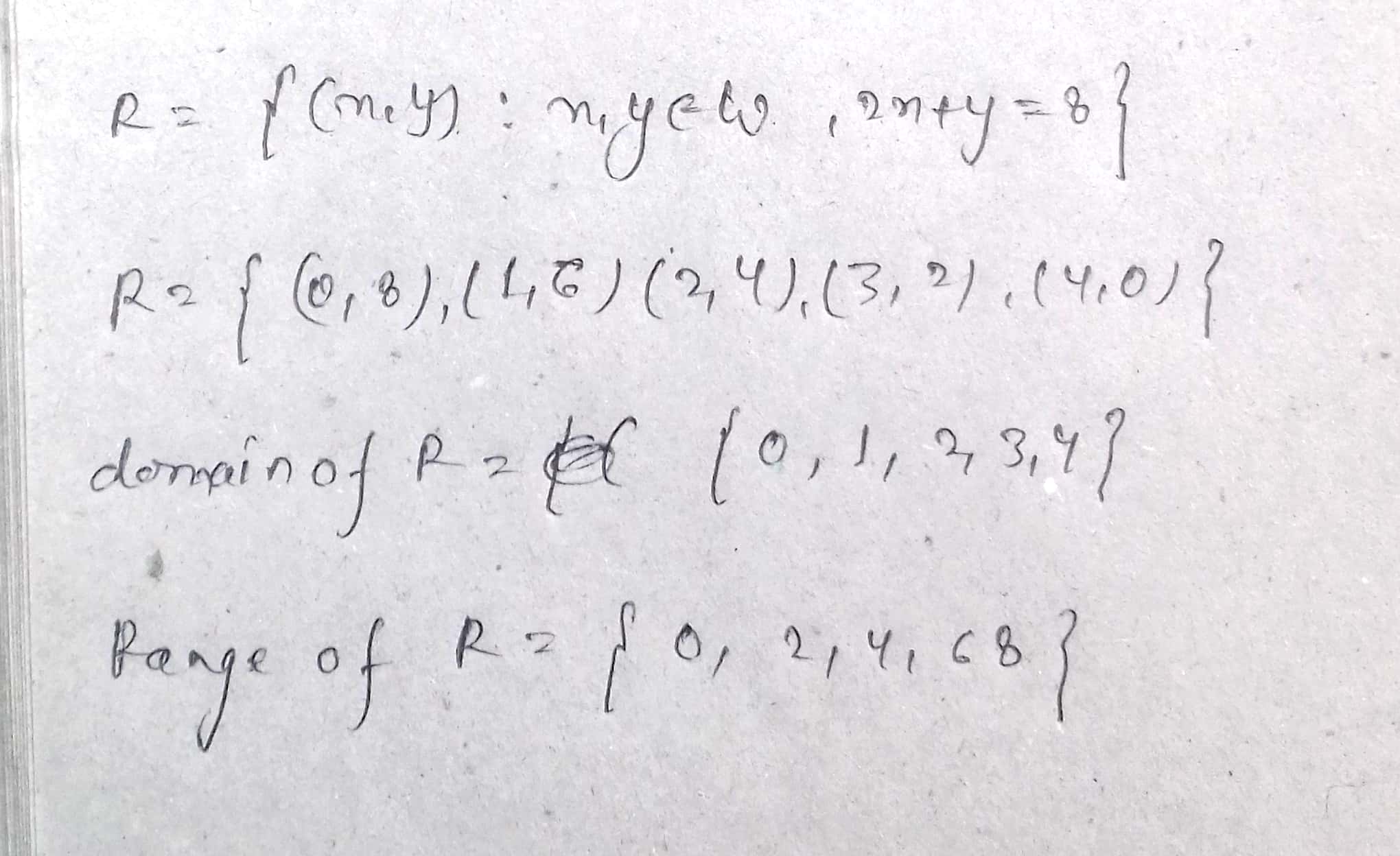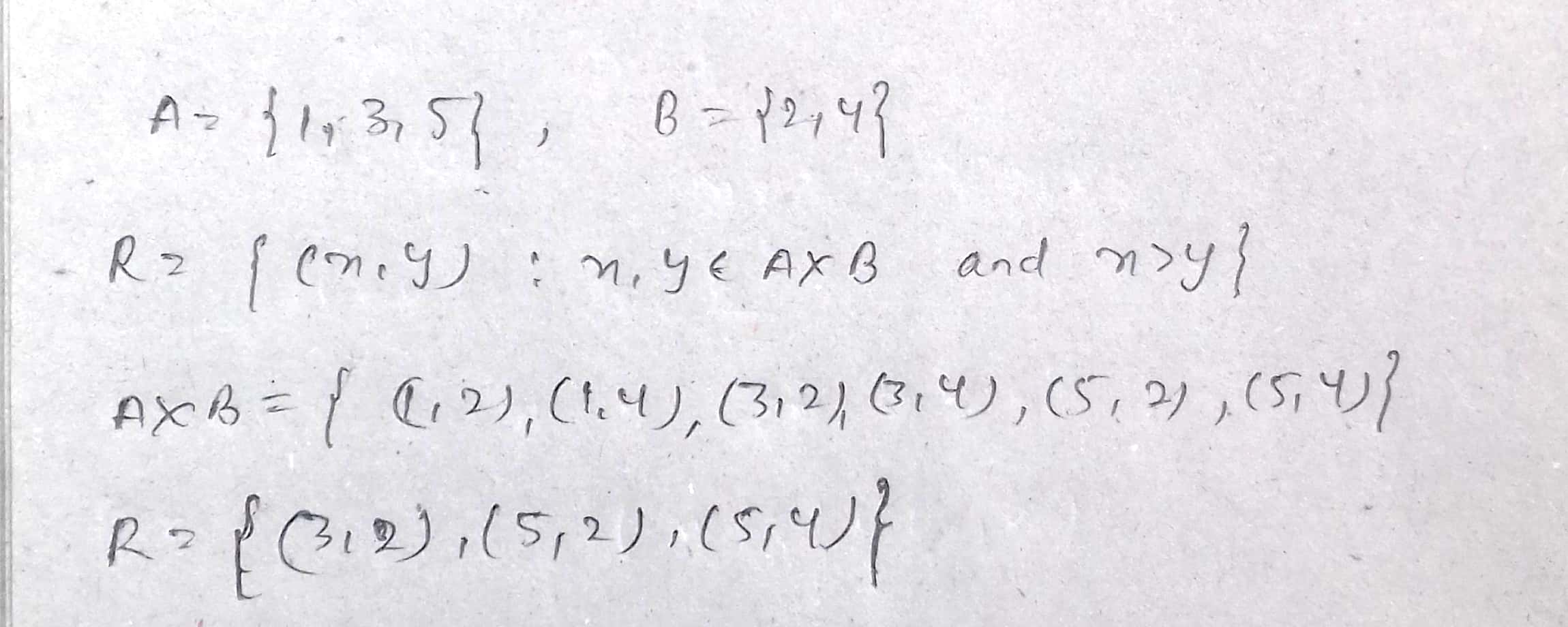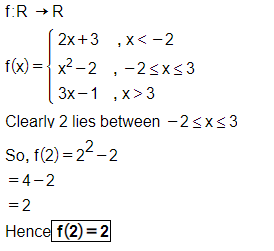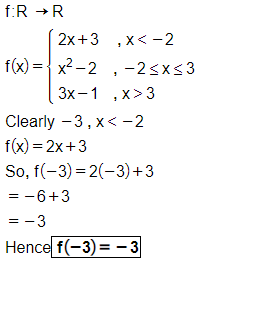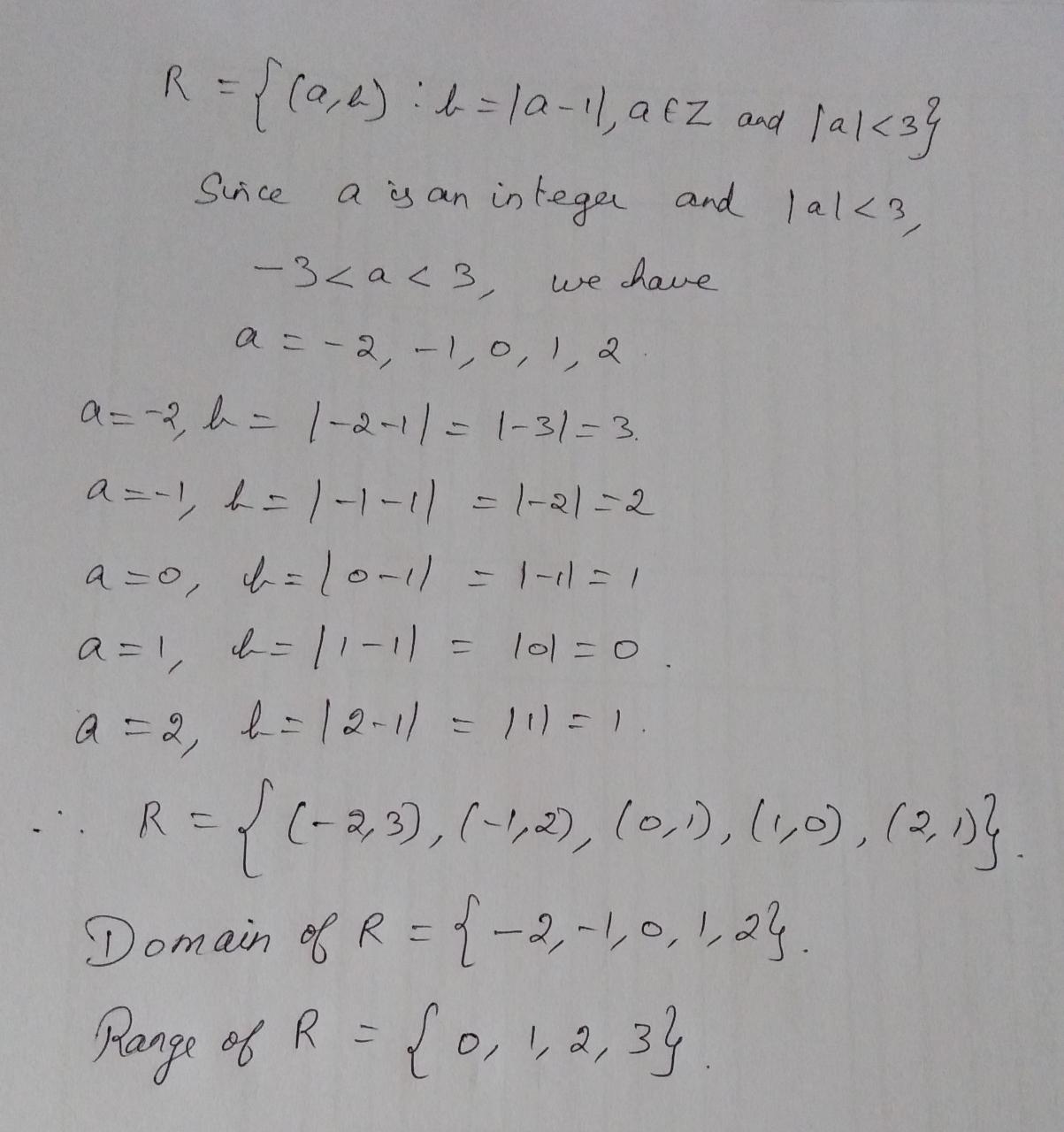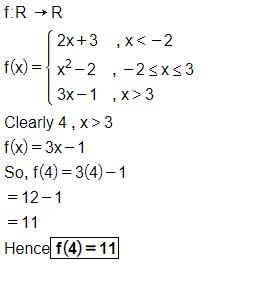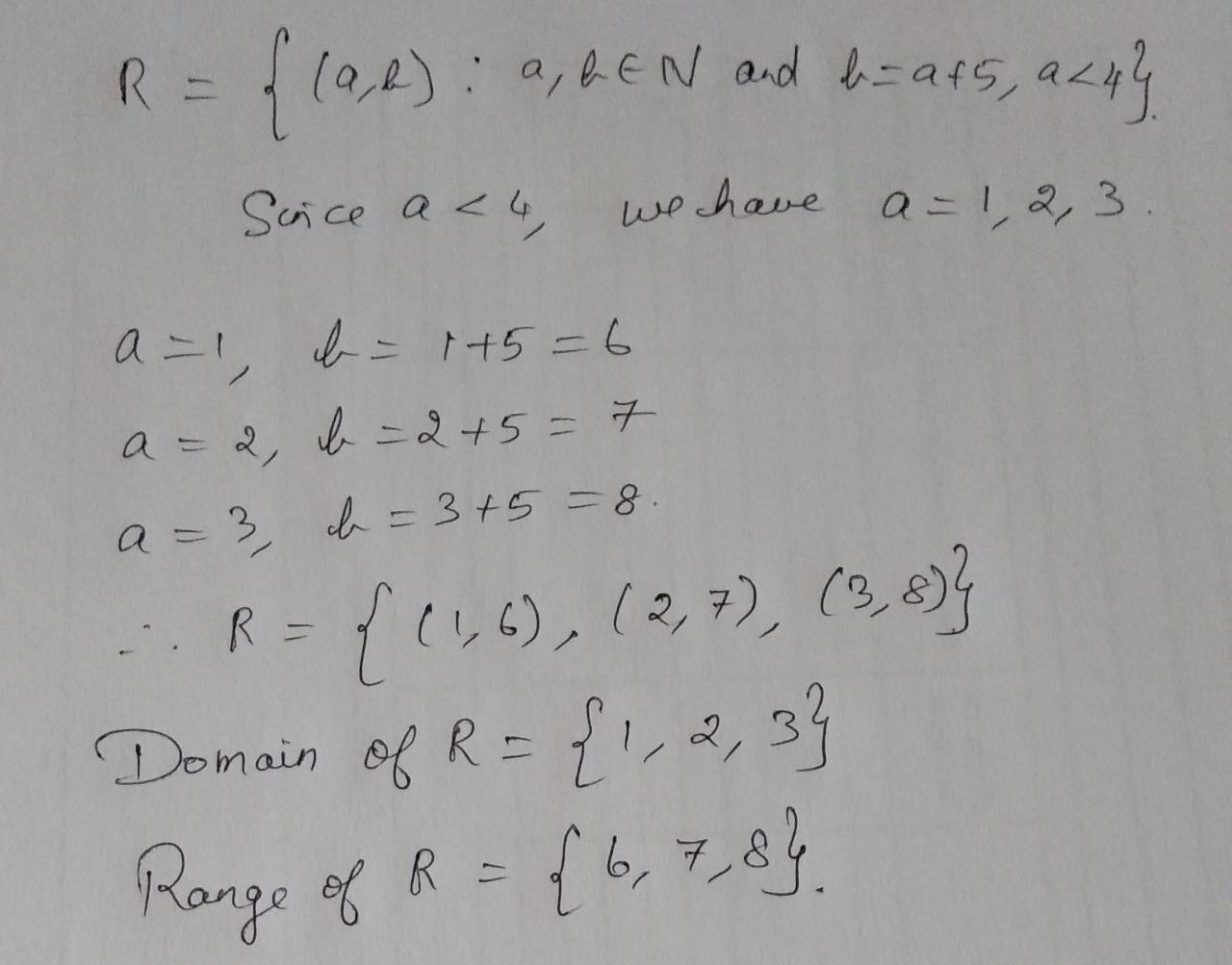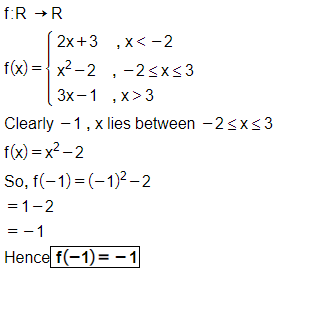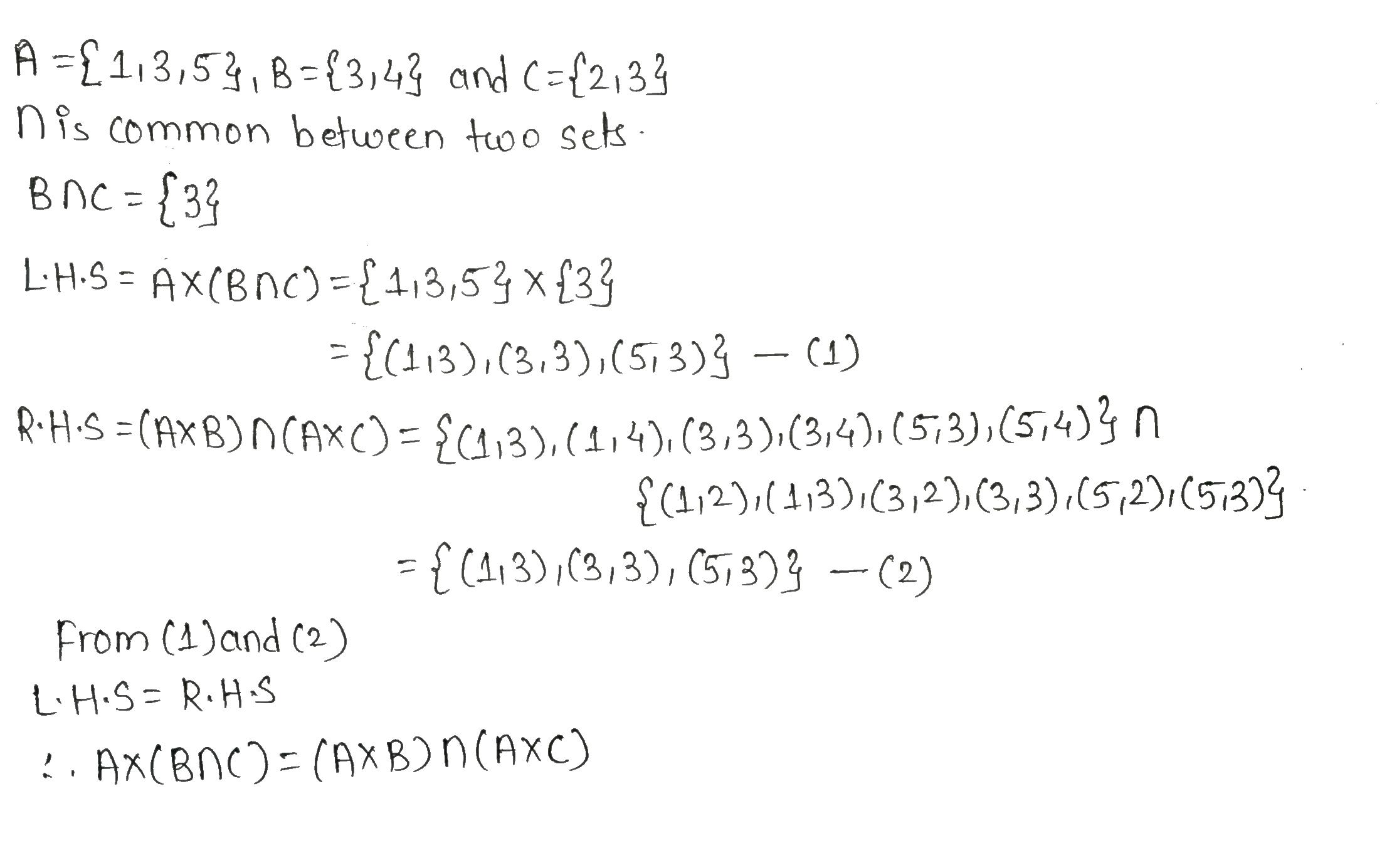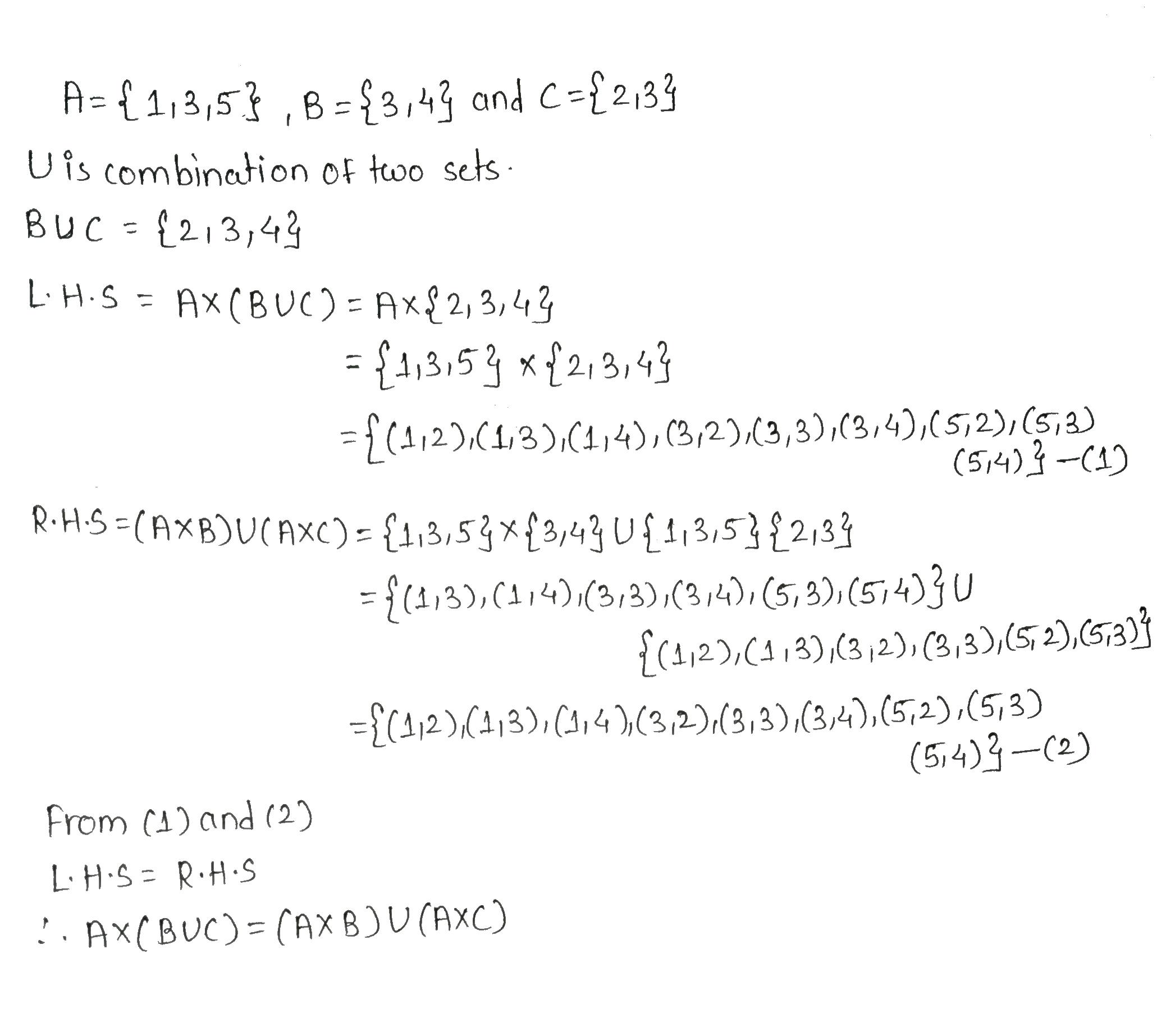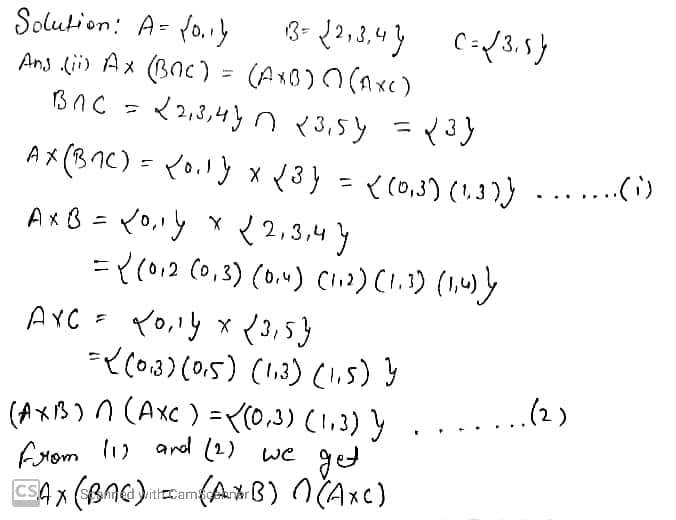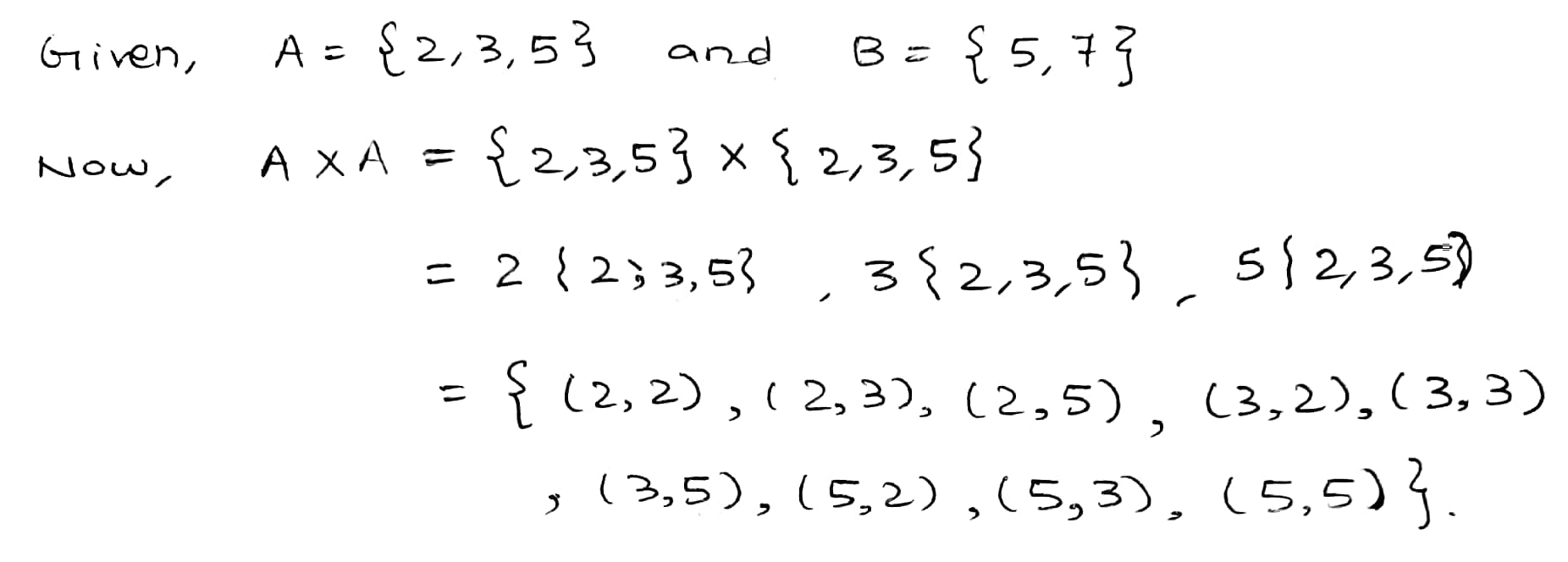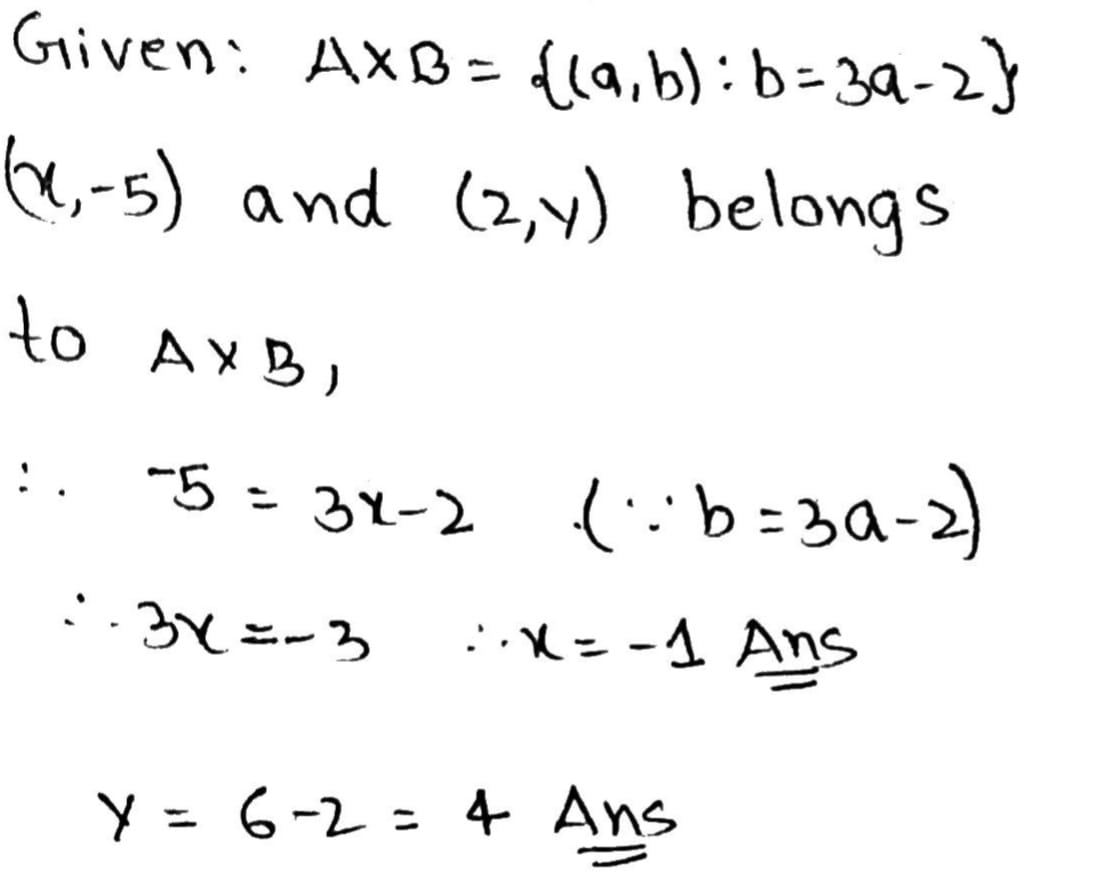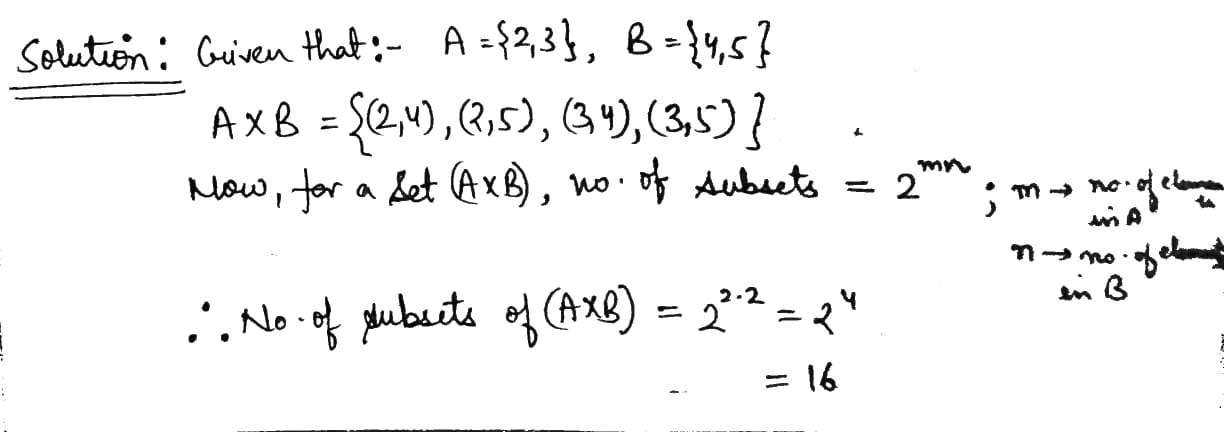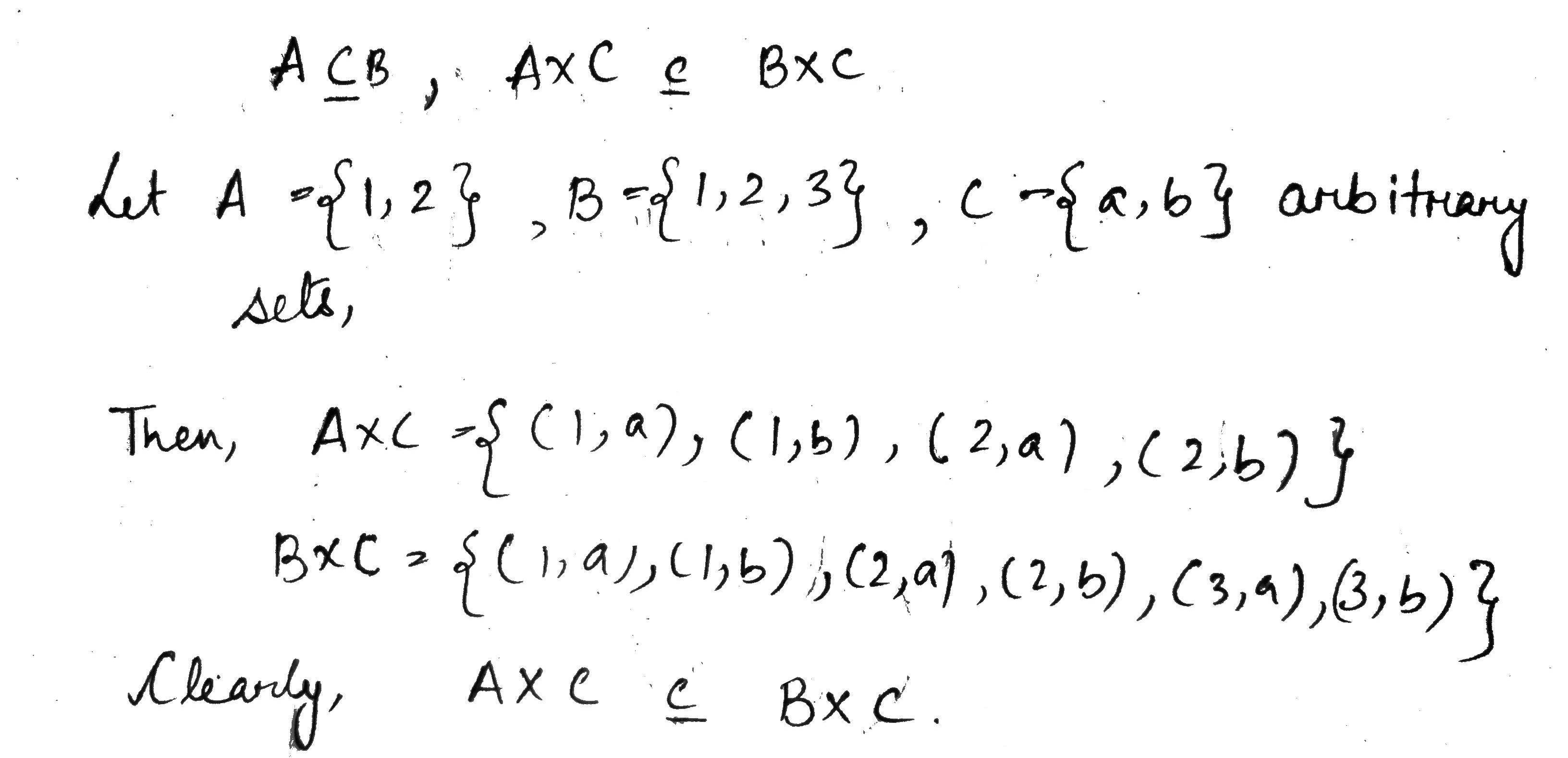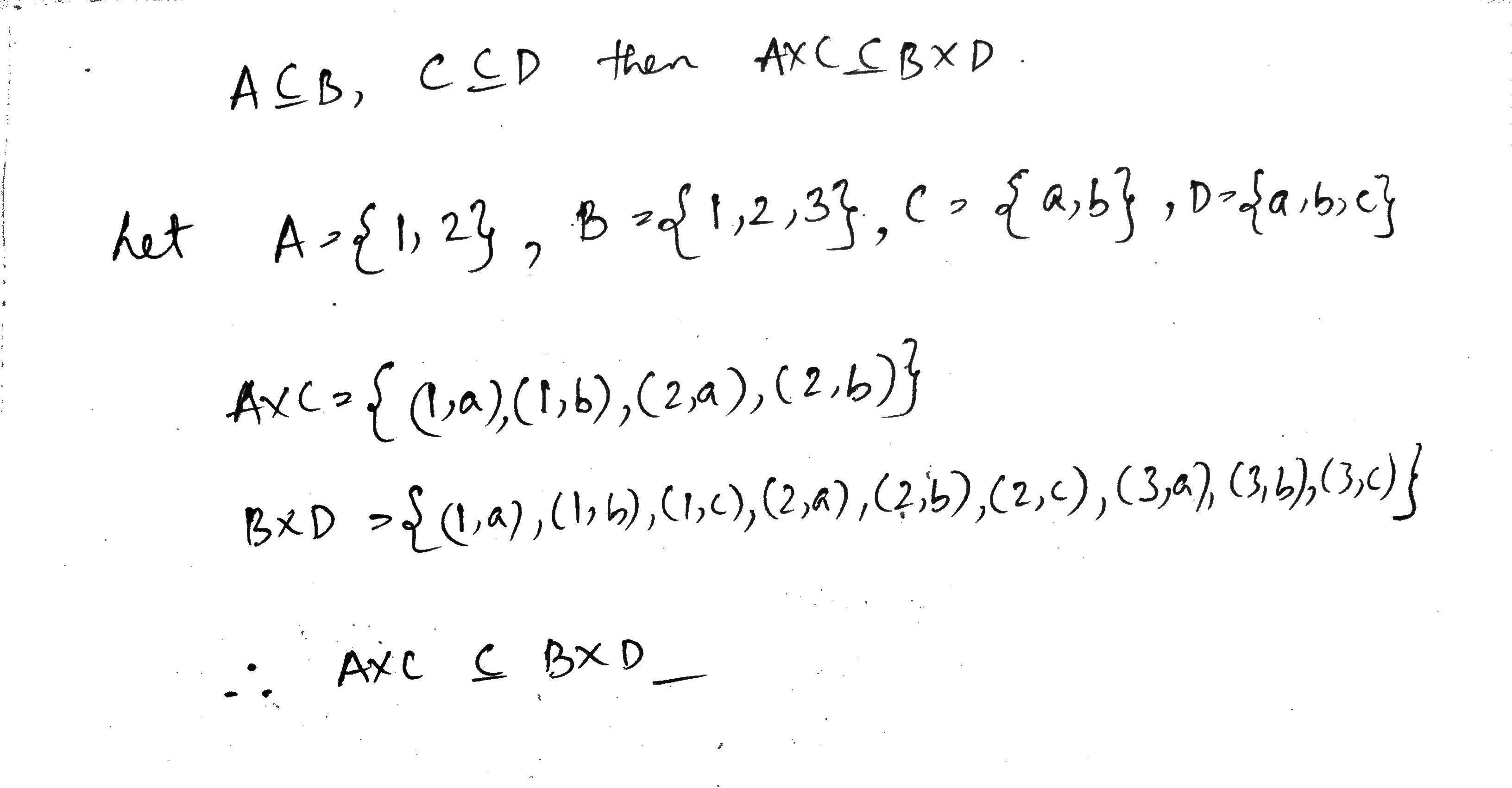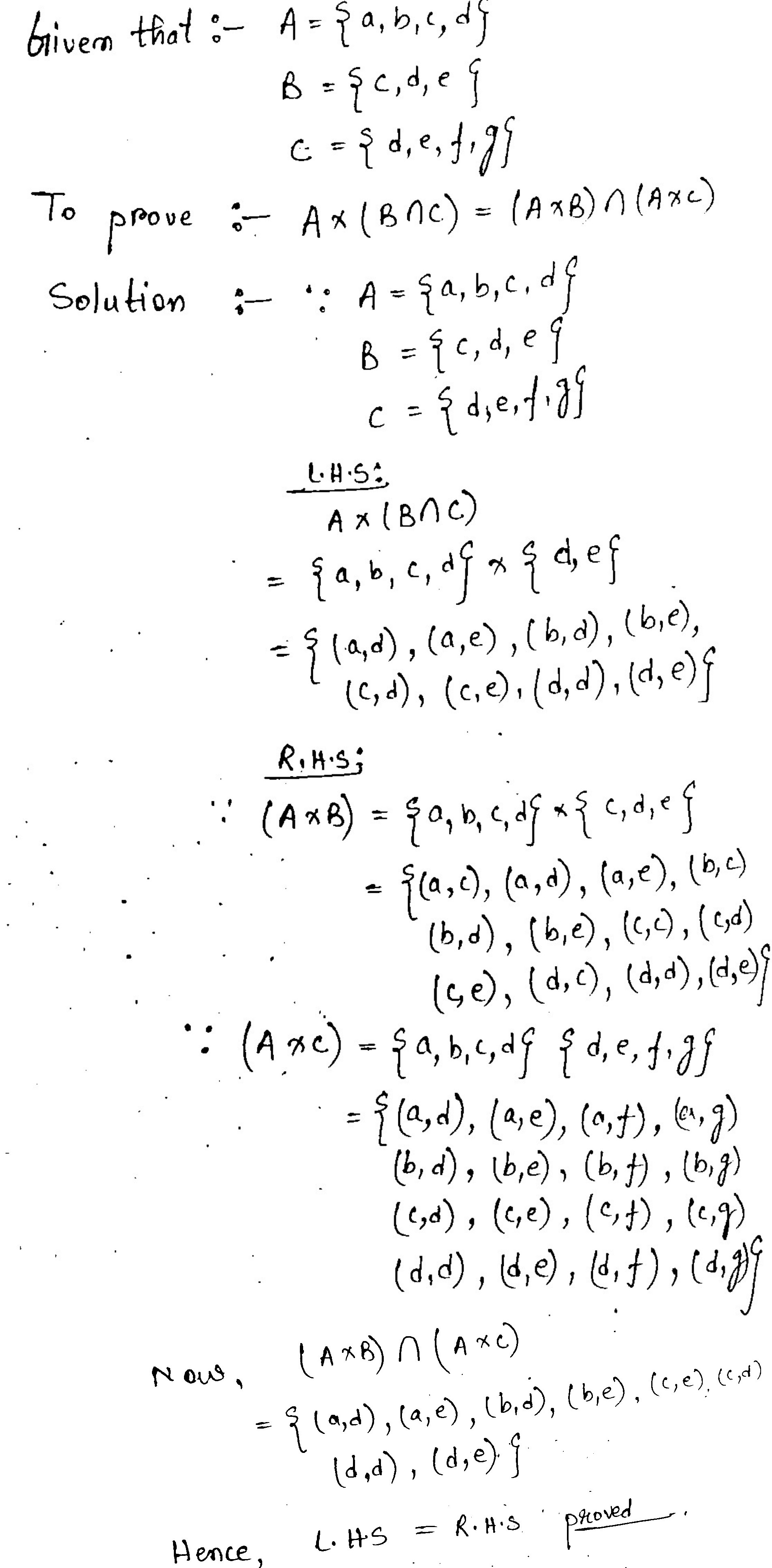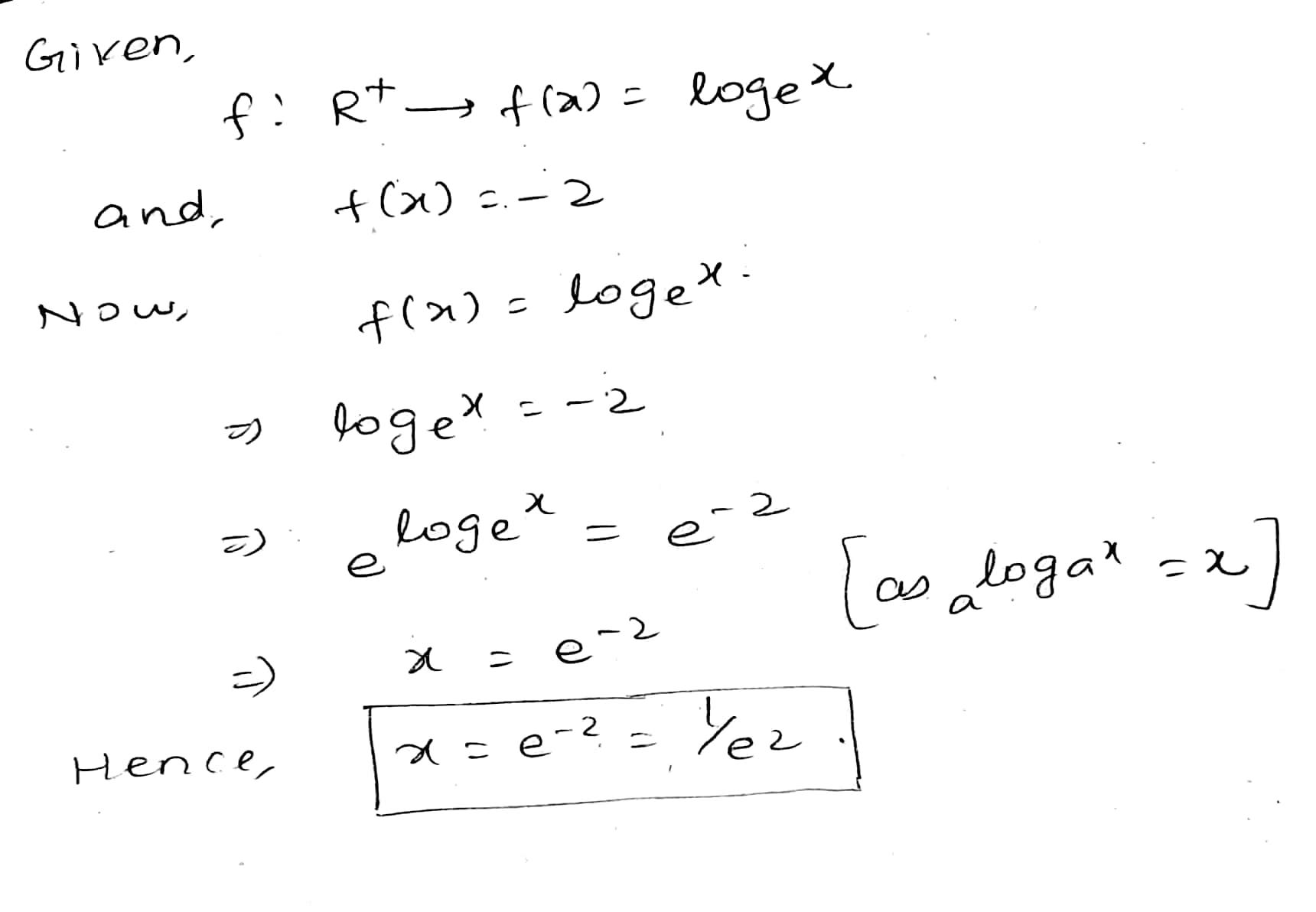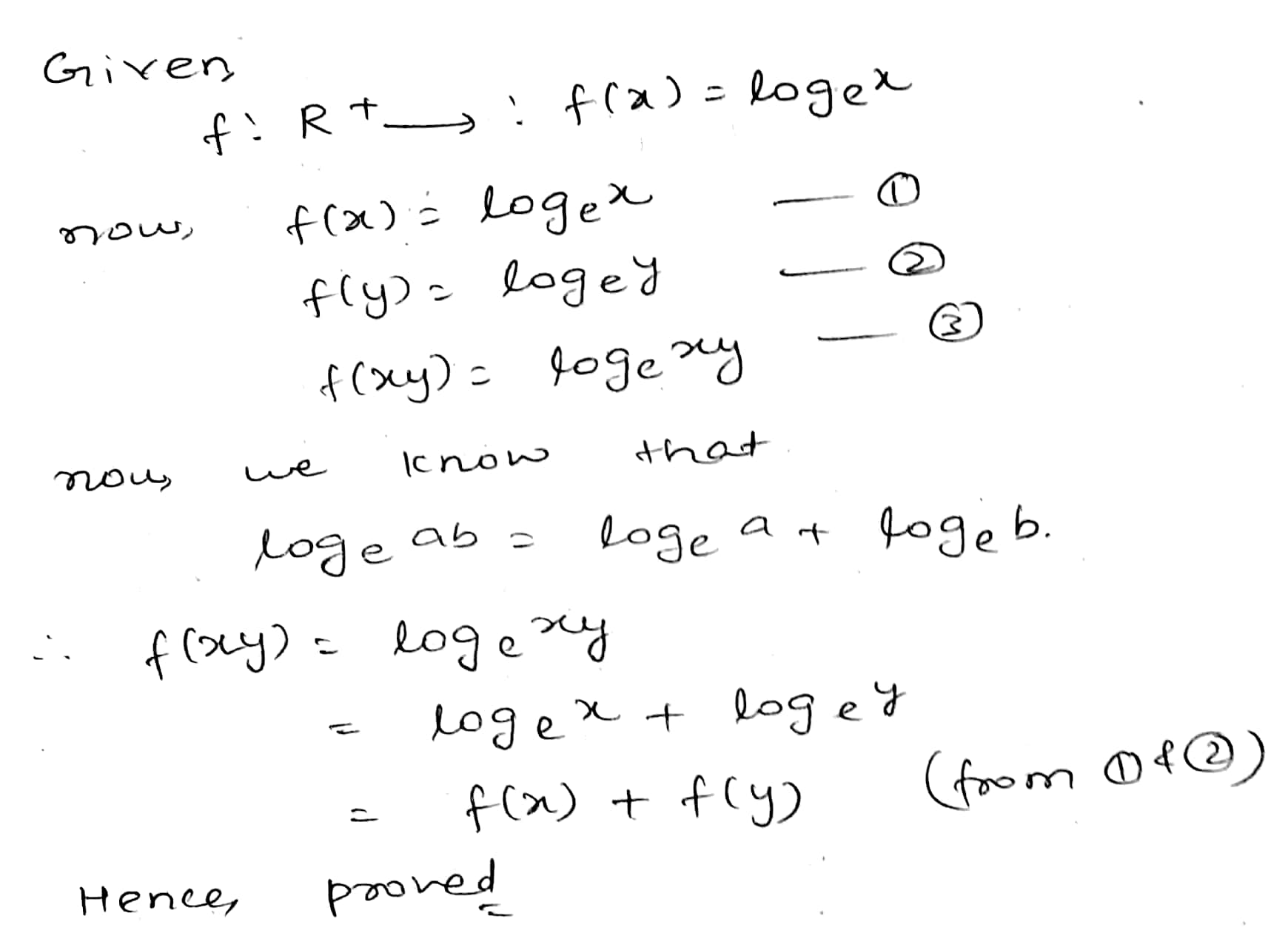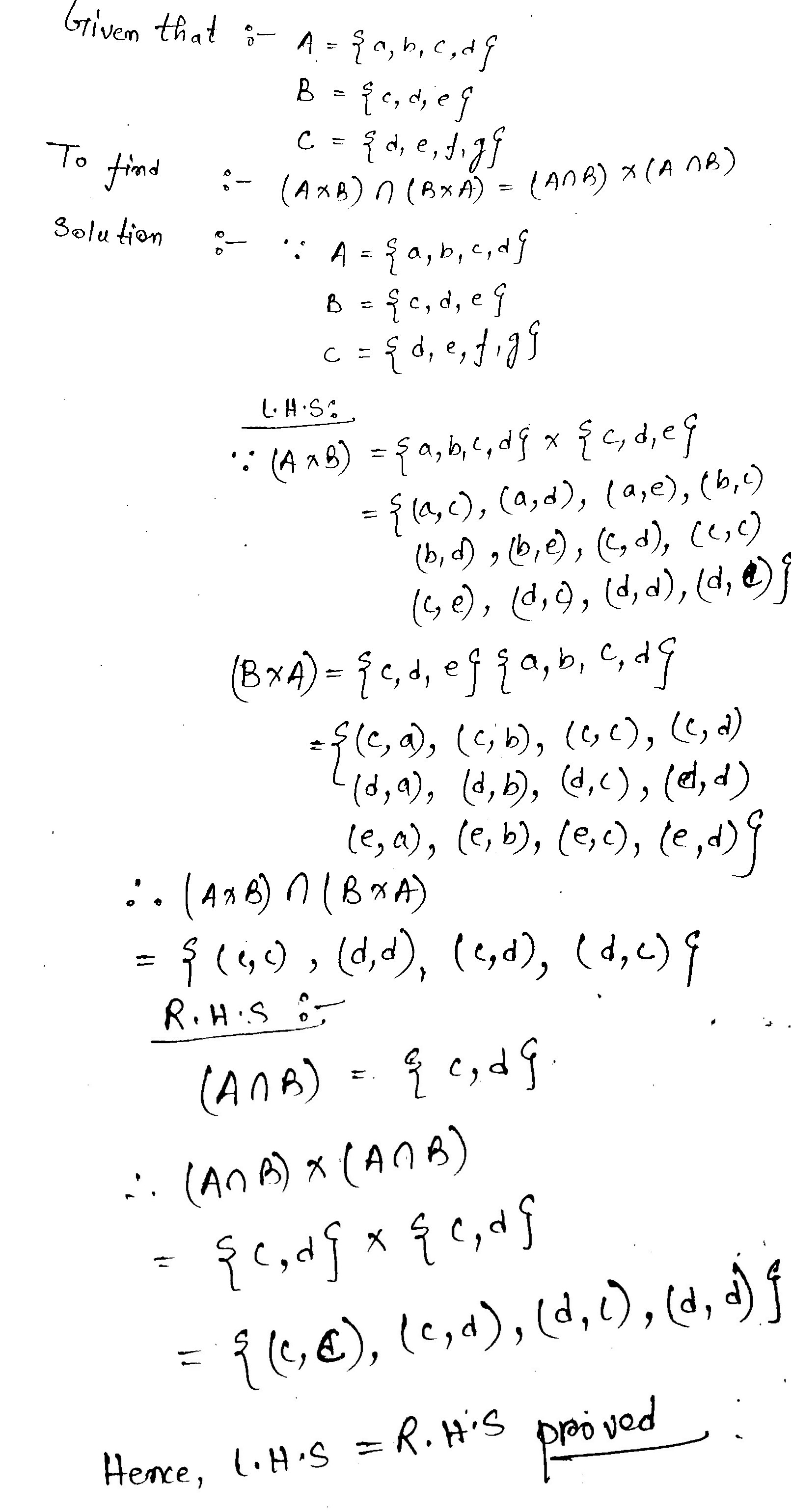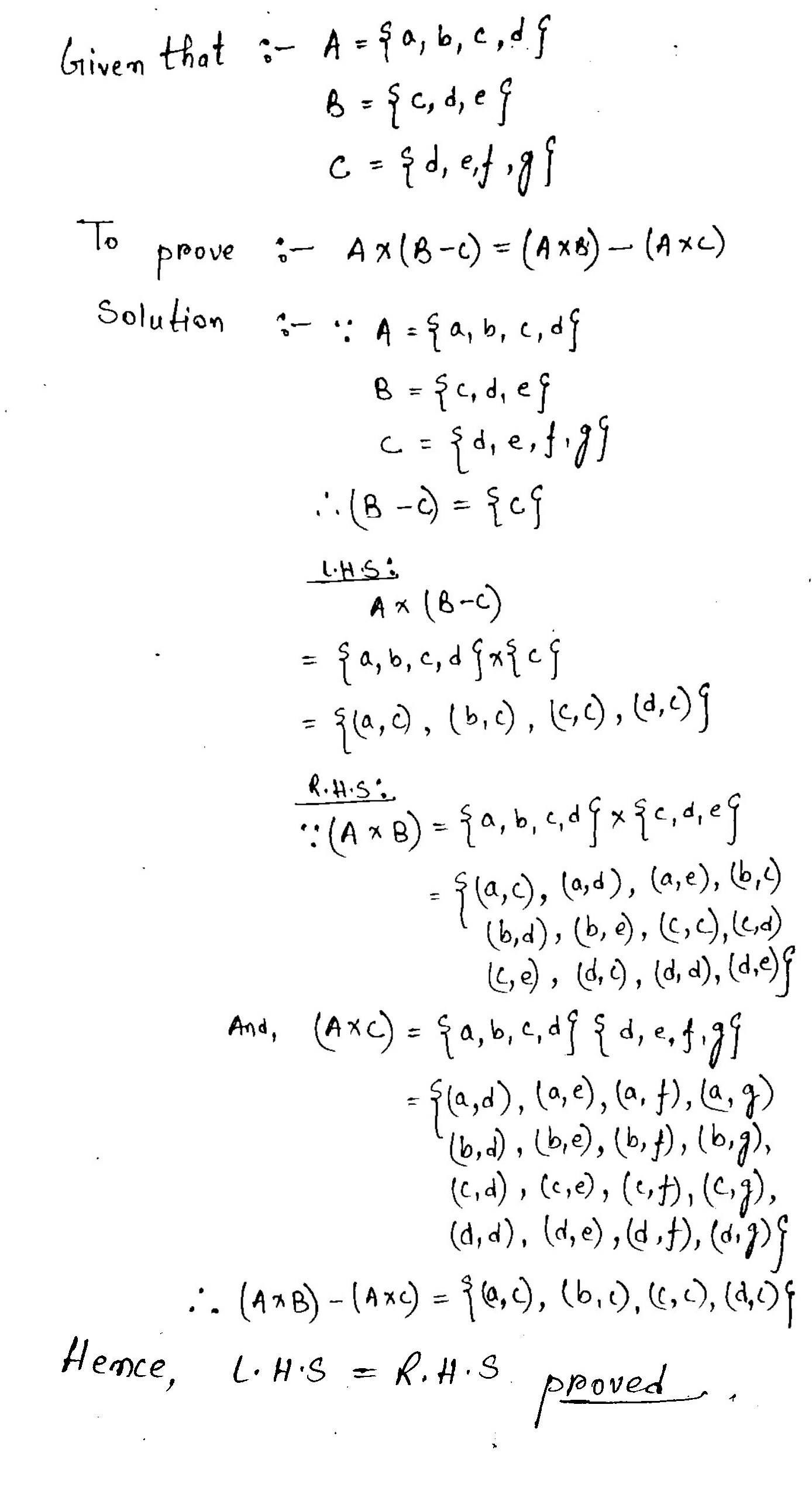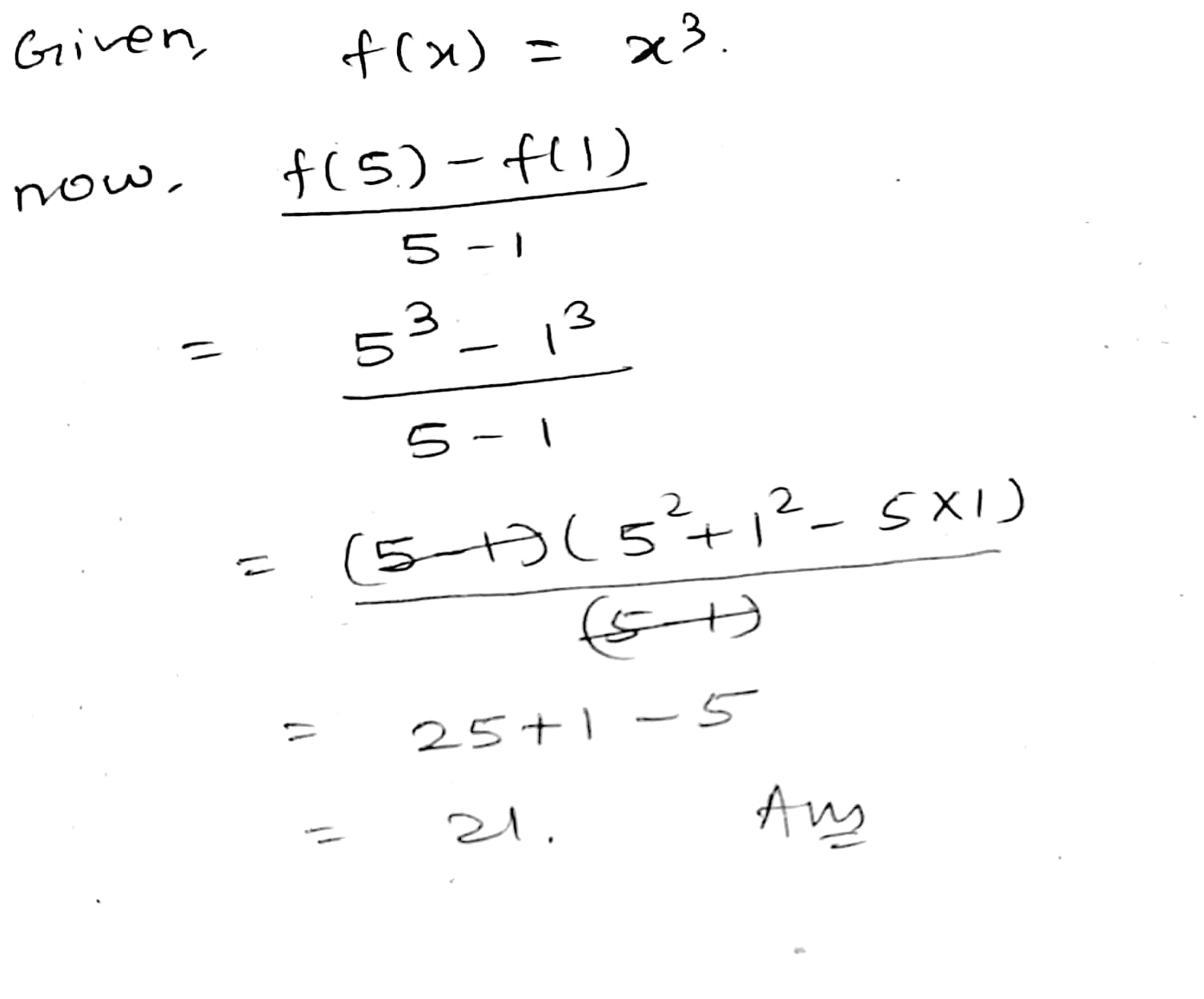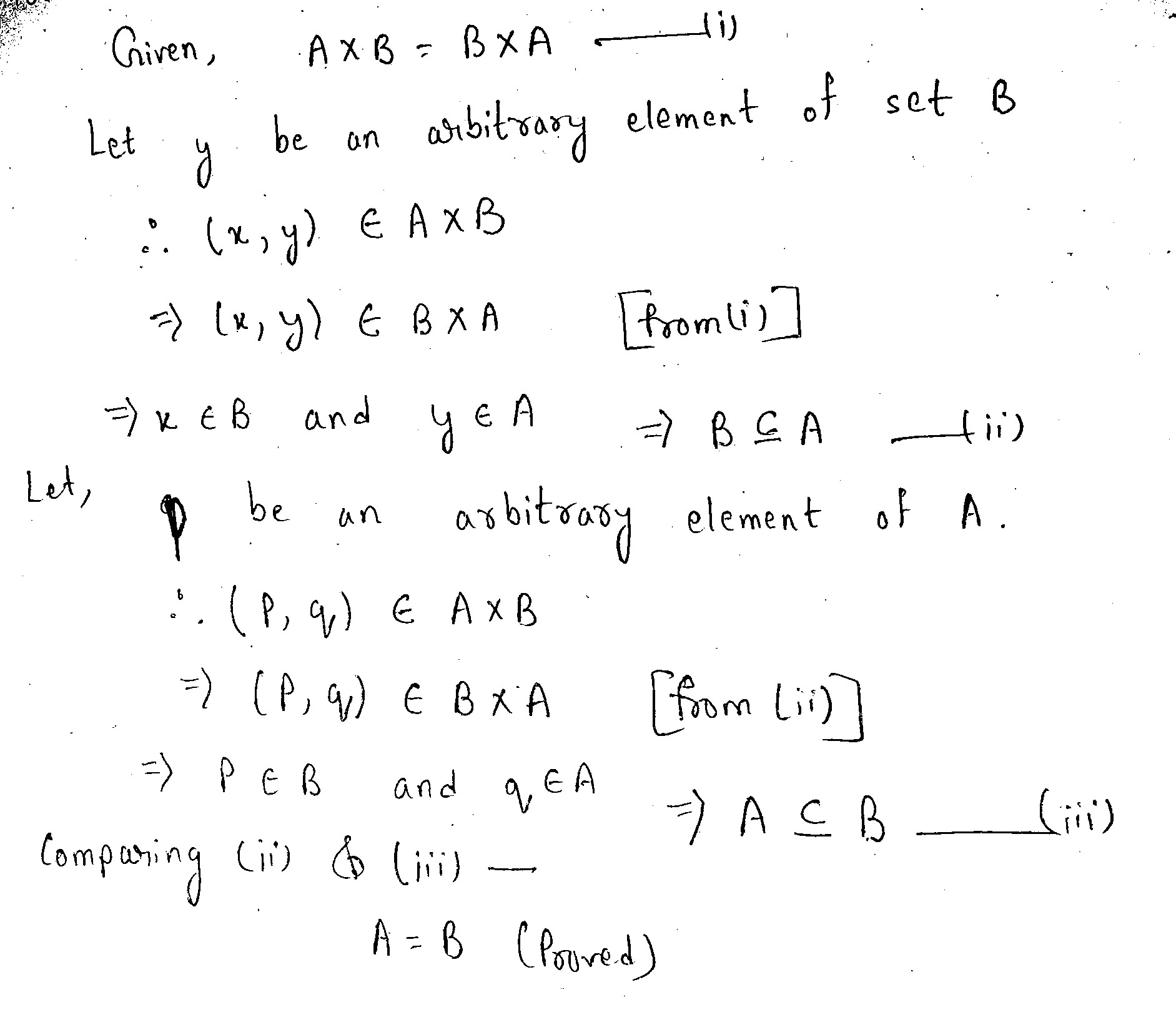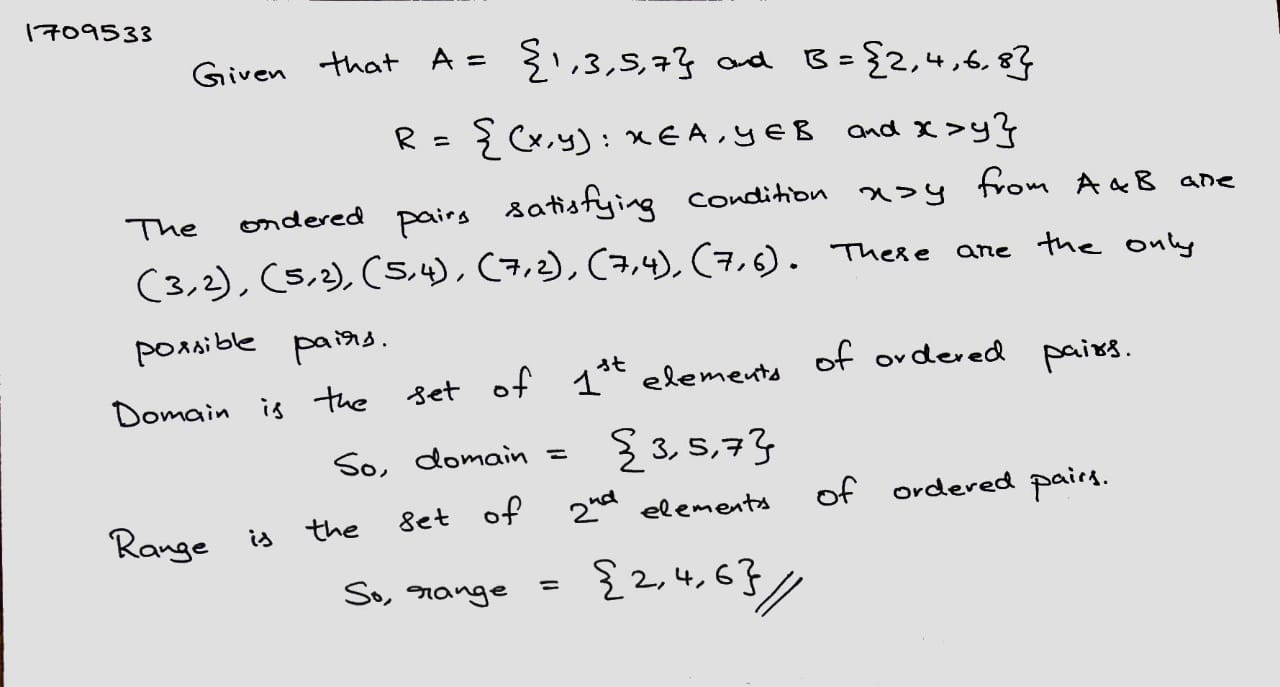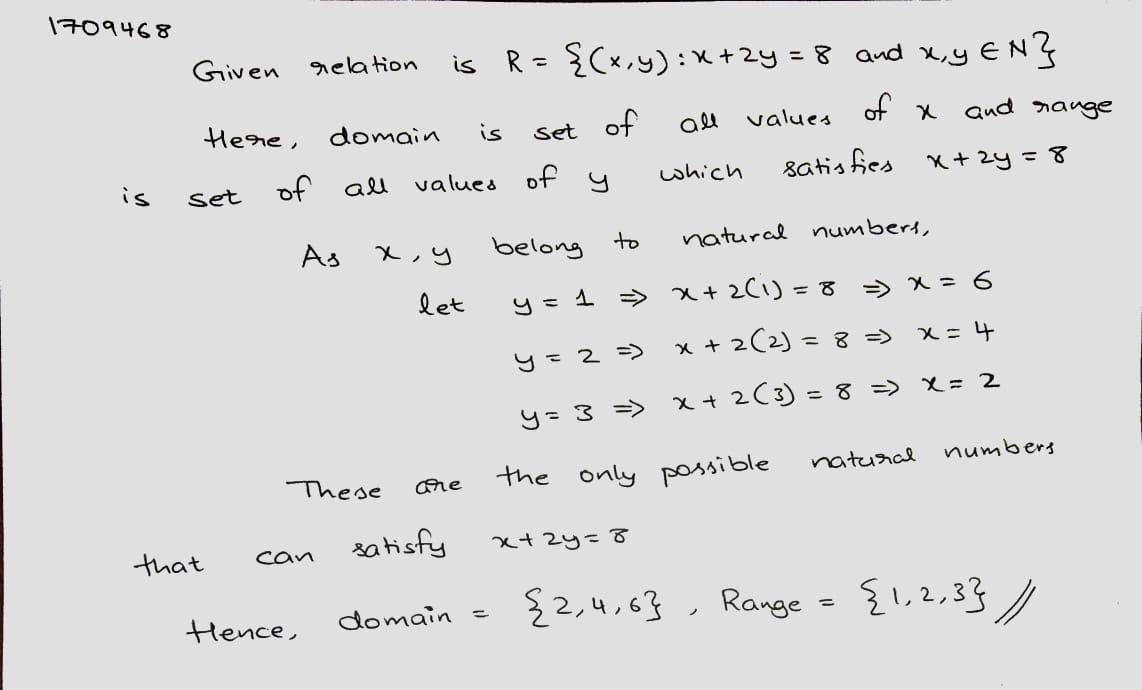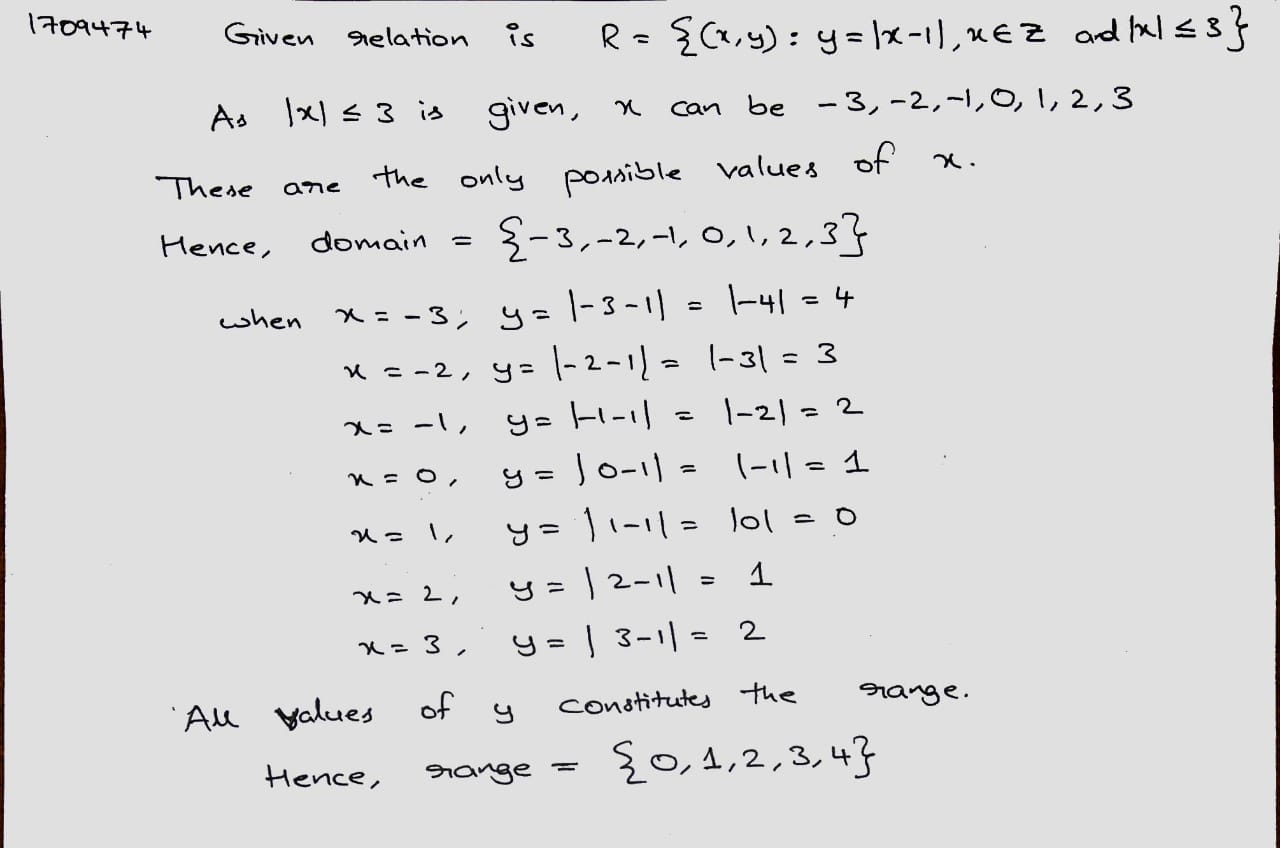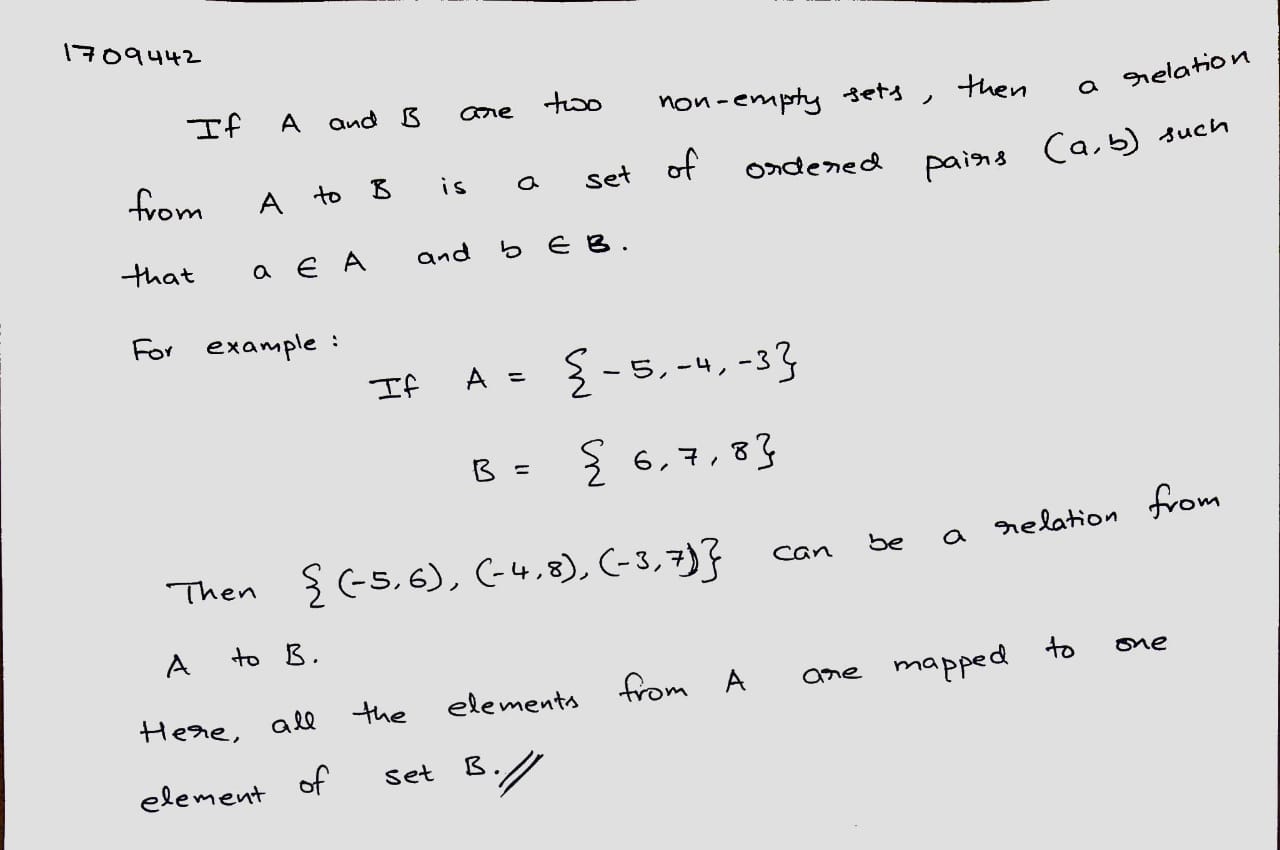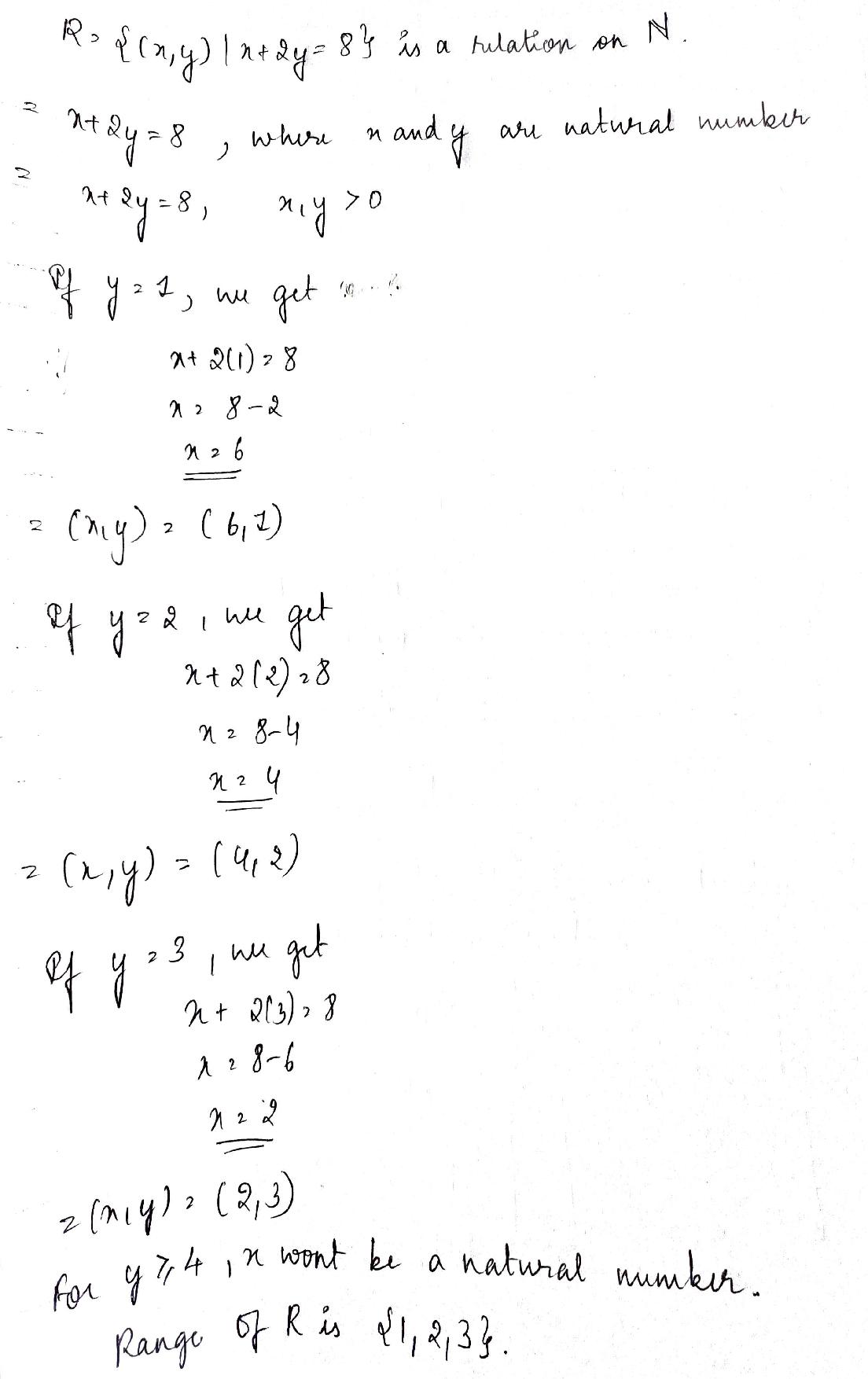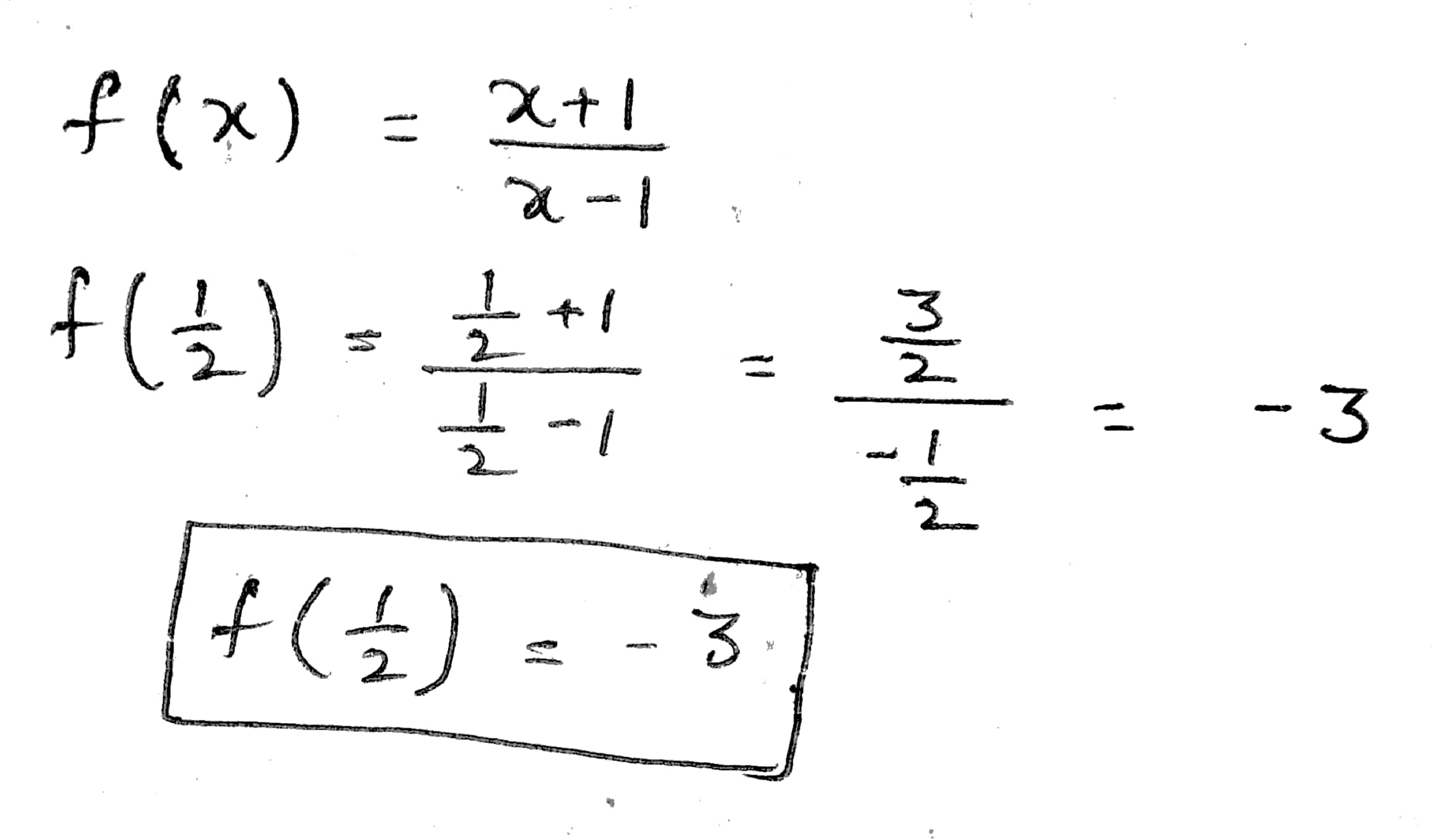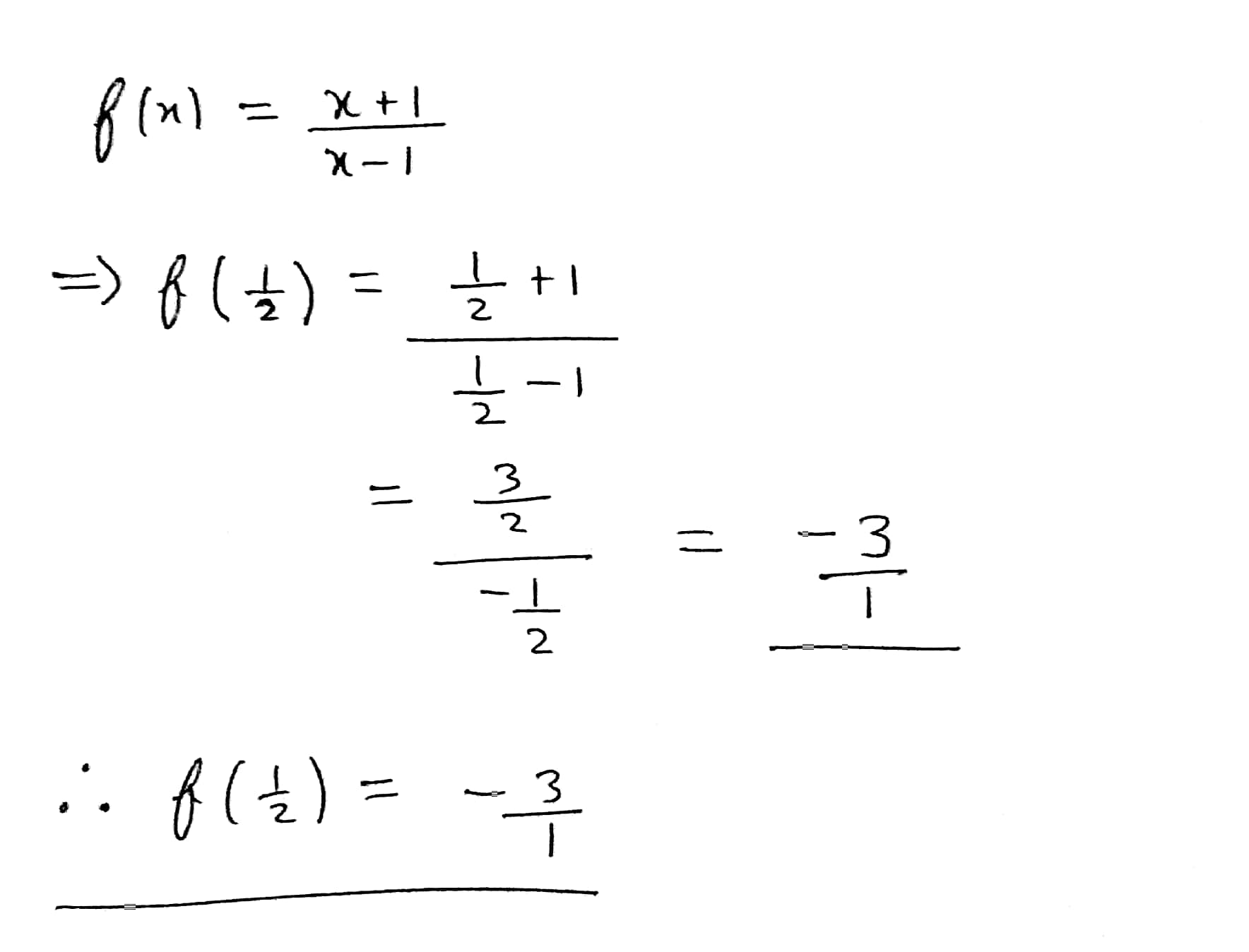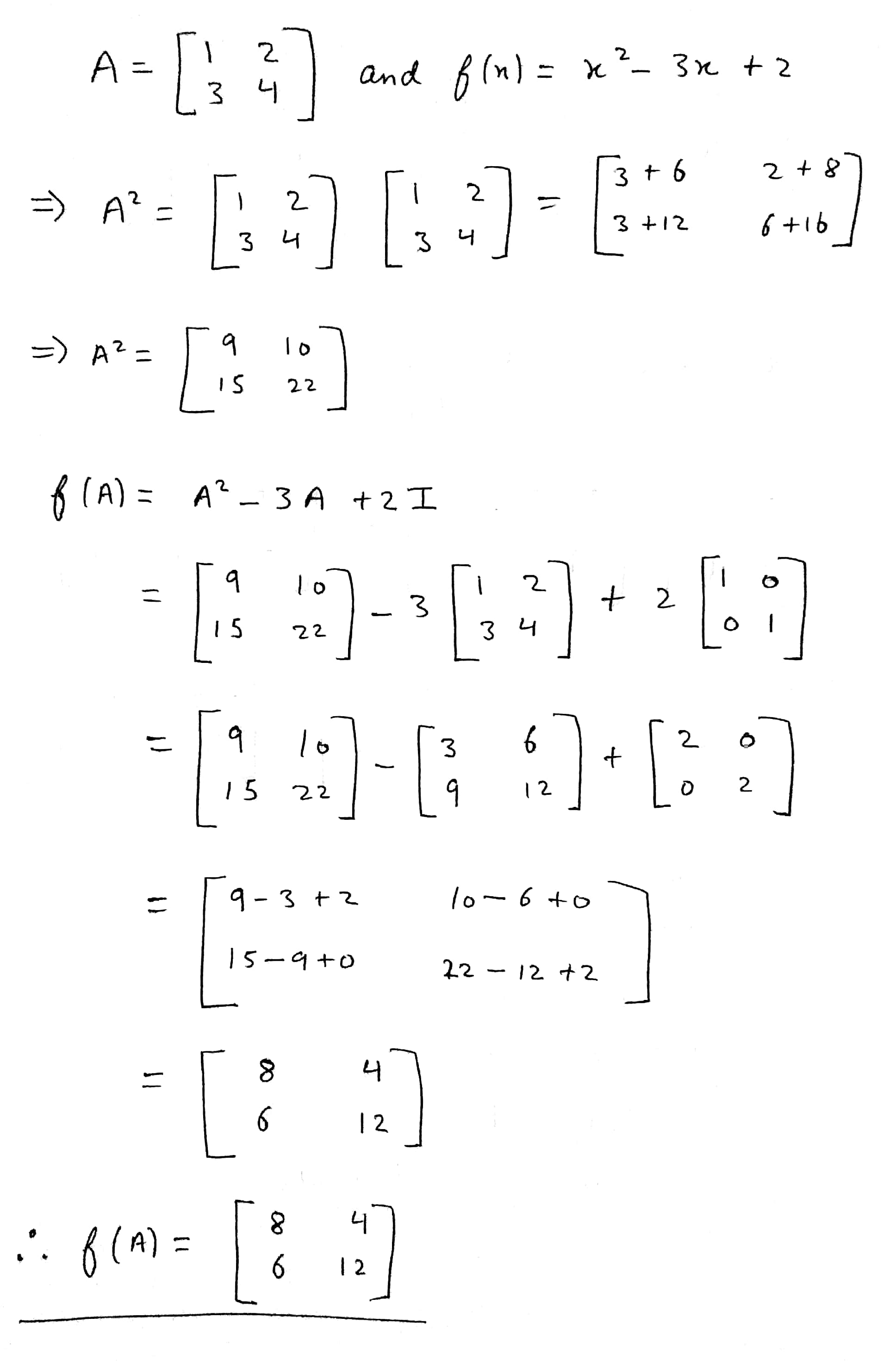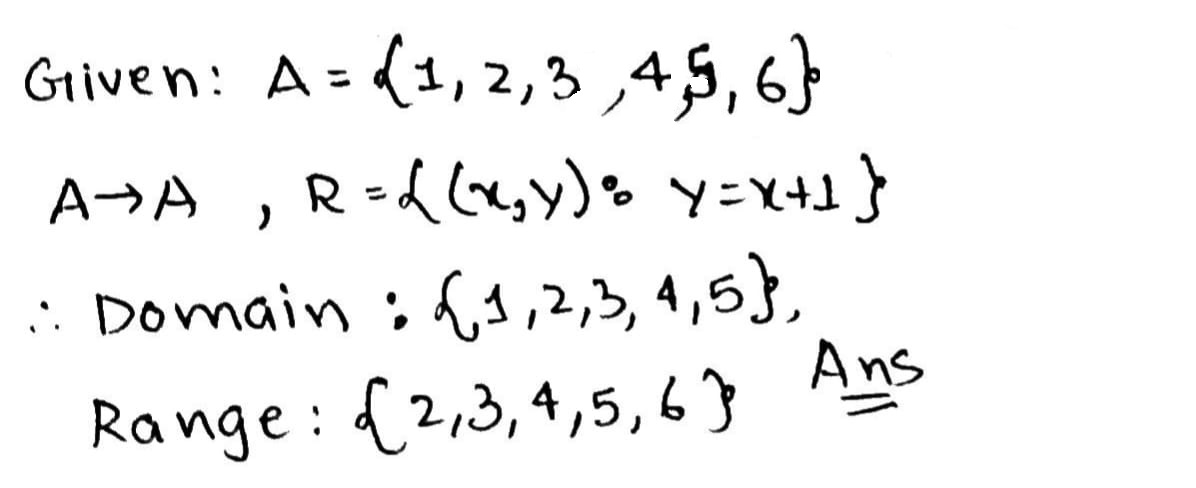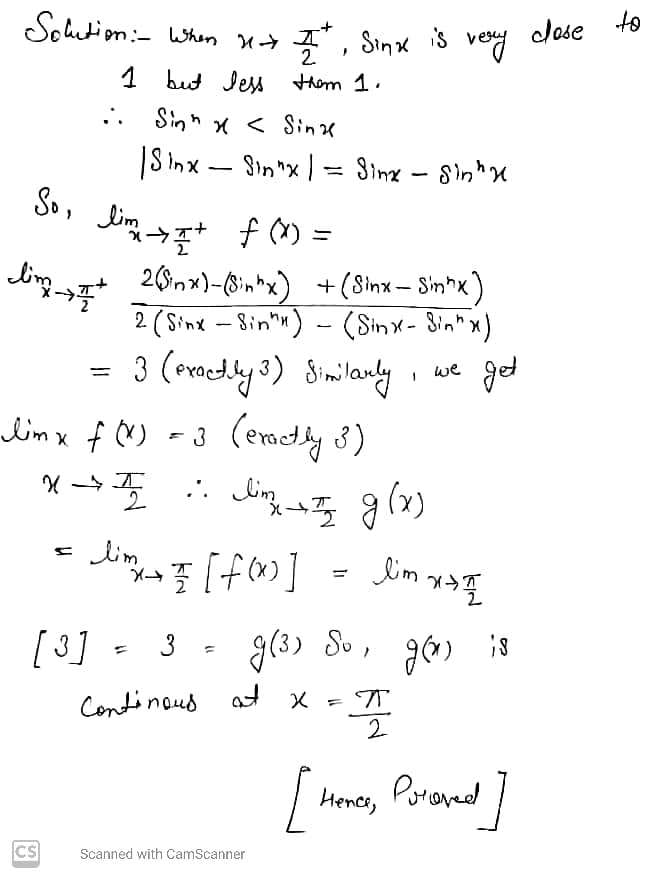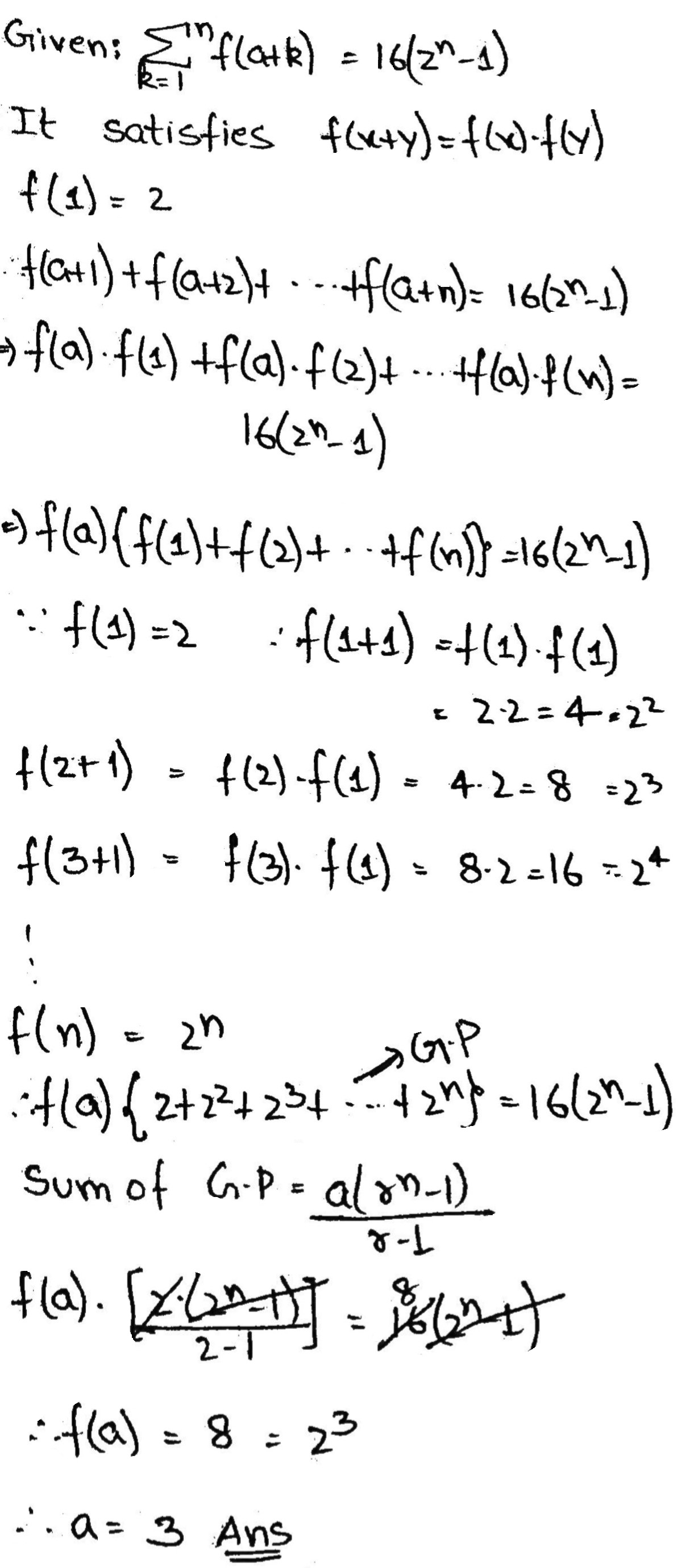Relations And Functions - Class 11 Engineering Maths - Extra Questions
$$\displaystyle f\left ( x \right )=1 $$ and $$ \phi \left ( x \right )=\sin ^{2}x+\cos ^{2}x.$$
Show that both functions are equal?
State whether the given statement is true or false. If true enter $$1$$ or else enter $$0$$.
$$(x, y)$$ is an ordered pair, whose first component is $$x$$ and the second component is $$y$$.
The cartesian product $$A\times A$$ has $$9$$ elements among which are found $$(-1, 0)$$ and $$(0, 1)$$. Find the set $$A$$ and the remaining elements of $$A\times A$$.
If $$x$$ is real, then find the solution set of $$\sqrt{x+1}+\sqrt{x-1}=1$$.
Use the elements of set A ={x, y, z} to form all possible ordered pairs. Find the number of elements in the ordered pair.
Given below are some points, with their co-ordinates.
$$P(4, 3), Q(-3, 2), R(5, 1), S(0, -4)$$ What is the $$y-$$coordinate of point $$R$$ ?
State whether each of the following statements are true or false. If the statement is false rewrite the given statement correctly
(i) If $$P = \{m, n\}$$ and $$Q = \{n, m\}$$ then $$\displaystyle P\times Q = \{(m, n), (n, m)\}$$
(ii) If $$A$$ and $$B$$ are non-empty sets then $$\displaystyle A\times B$$ is a non-empty set of ordered pairs $$(x, y)$$ such that $$\displaystyle x\in A$$ and $$\displaystyle y\in B$$
(iii) If $$A = \{1, 2\}, B = \{3, 4\}$$ then $$\displaystyle A\times \left ( B\cap \phi \right )=\phi $$
If $$\displaystyle \left ( \frac{x}{3}+1,y-\frac{2}{3} \right )=\left ( \frac{5}{3},\frac{1}{3} \right )$$ find the values of x and y
Find the number of ordered pairs in $$R o R$$ ?
$$A = \{1, 2, 3, 5\}$$ and $$B = \{4, 6, 9\}$$. Define a relation $$R$$ from $$A$$ to $$B$$ by $$R = \{(x, y):$$ the difference between $$x$$ and $$y$$ is odd $$\displaystyle x\in A, y\in B\}$$. Write $$R$$ in roster form
Let $$A = \{1, 2, 3, 4, 6\}$$ and $$R$$ be the relation on $$A$$ defined by $$\{(a, b): a, \displaystyle b\in A\ , b$$ is exactly divisible by $$a\}$$
(i) Write $$R$$ in roster form
(ii) Find the domain of $$R$$
(iii) Find the range of $$R$$
State whether the given statement is true or false. If true enter $$1$$ or else enter $$0$$. $$(x, y)$$ is an ordered pair whose components are $$x$$ and $$y$$.
Let $$A$$ and $$B$$ be two sets such that $$n(A) = 3$$ and $$n(B) = 2$$. If $$(x, 1), (y, 2), (z, 1)$$ are in $$\displaystyle A\times B$$ find $$A$$ and $$B$$ where $$x, y$$ and $$z$$ are distinct elements
Suppose $$3$$ bulbs are selected at random from a lot. Each bulb is tested and classified as defective $$(D)$$ or non-defective $$(N)$$. Write the sample space of this experiment?
Let $$A =\{x, y, z\}$$ and $$B = \{1, 2\}$$. Find the number of relations from $$A$$ to $$B$$.
Determine the domain and range of the relation $$R$$ defined by $$R = \{(x, x + 5) : \displaystyle x\in \{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5\}\}$$
Write the relation $$R = \{(x,\displaystyle x^{3}): x\mbox{ is a prime number less than 10}\}$$ in roster form
For the given function F= { (1, 3), (2, 5), (4, 7), (5, 9), (3, 1) }, write the domain and range.
If $$k$$ is given a real constant $$f(x)$$ is a real quadratic in '$$x$$ such that $$f(x + k) = f(-x)$$. The coefficient of $$x^2$$ is $$1$$. Find $$f(x)$$.
A function $$f : [-3, 7) \rightarrow R$$ is defined as follows
$$f(x)=\left\{\begin{matrix}4x^2-1; & -3 \leq x < 2 \\ 3x-2; & 2\leq x\leq 4 \\ 2x-3; & 4 < x < 7 \end{matrix}\right.$$
(i) $$f(5)+f(6)$$
(ii) $$ f(1)-f(3)$$
(iii) $$ f(-2)-f(-4)$$
(iv) $$\dfrac{f(3)+f(1)}{2f(6)-f(1)}$$
Let R be a relation from A = {1,2,3,4} to B = {1,3,5} i.e. (a,b) $$\epsilon$$ R if a < b then find R o $$R^{-1}$$
If $$G=\left\{ 7,8 \right\} $$ and $$H=\left\{ 5,4,2 \right\} $$, find $$H\times G$$.
Let $$S=\{1,2,3\}$$ and a relation $$R$$ is defined by $$aRb$$ iff $$a=b$$ then find $$R$$.
If $$f(x)=\log_e\sec x$$ and $$\phi(x)=\log_e\tan x$$ then prove that $$e^{2f(x)}-e^{2\phi(x)}=1$$.
Find the domain of definations of the following functions:
$$f(x)=\sqrt {1-\sqrt {1-x^{2}}}$$
Let $$A = \left\{ {1,2,3,4} \right\}$$ and $$R$$ is a relation on $$A$$ such that $$R = \left\{ {\left( {a,b} \right):a = 2b} \right\}$$
If $$A = \{a, b, c\}$$ , $$B = \{1, 2\}$$ , then find $$A \times B , \, B \times A \, and \, A \times A$$
If the relation $$R: A \rightarrow B$$ where $$A = \{1, 2, 3, 4\}, B = \{1, 3, 5\}$$ is defined by $$R = \{(x, y): x < y, x \in A, y \in B\}$$ then find $$R$$ and $$R^{-1}$$.
If $$P = \{a , b\}$$ and $$Q = \{x, y, z\}$$, show that $$P \times Q \neq Q \times P.$$
Let $$A=\{1,-1\}$$. Then find $$A\times A$$.
Given $$R = \{(x, y): x, y \in W, x^2 + y^2 = 25\}$$, where $$W$$ is the set of all whole numbers. Find the domain and range of $$R$$.
If $$R = \{(x, y)|y = 2x + 7|$$, where $$x \in R$$ and $$-5 \le x \le 5\}$$ is relation, find the domain of $$R$$.
If $$f(x) = x + (1/x)$$, show that $$\{f(x)\}^3 = f(x^3) + 3f(1/x)$$
If $$A = \{0, 1\}$$ and $$B = \{1, 2, 3\}$$, show that $$A \times B \neq B \times A$$
Let $$A = \{1, 2, 3\}$$. Find the number of relations from $$A$$ to $$A.$$
The Cartesian product $$P\times P$$ has $$16$$ elements among which two elements are $$(a,b)$$ and $$(c,d)$$. Find the set $$P$$ and the remaining elements of $$P\times P$$
If $$\dfrac{1}{{\left| a \right|}} > \dfrac{1}{b}$$, then $$\left| a \right| < b$$, where a & b are non-zero real numbers.
Let A = {1,2} and B = {3,4}. Find the number of relations from A to B.
Find the domain and range of the following real functions:
i) $$f(x) = -|x|$$
ii) $$f(x) = \sqrt{9 - x^2}$$
If $$f\left( x \right) = {x^3} - \frac{1}{{{x^3}}}$$, prove that $$f\left( x \right) + f\left( {\frac{1}{x}} \right) = 0$$
Find domain and range of
$$R = \{ (a, b) / a \in N, \, \, \, a < 5 \, \, \text{ and} \, \, b = 2\}$$
If $$A=\left\{ 3,4 \right\} \quad and\quad B=\left\{ 1,2 \right\} $$ then of $$A\times B$$ is .
Determine the domain and the range of the relation $$R$$ defined by $$R=\{ \left( x+1,\quad x+5 \right) :x\in \{ 0,\quad 1,\quad 2,\quad 3,\quad 4,\quad 5\}\}$$
Show that the relation $$R$$ in the set $$Z$$ of integers given by
$$R=\left\{(a,b):2\ divides\ a-b\right\}$$
If $$ p(x)=ix^2+5x+8$$, then $$p{(-1)}$$=
The value of $$x$$ satisfying the equation $$-3(x+6)=24$$ ?
Let $$f:R\rightarrow R$$ be defined as $$f(x)=10x+7$$. Find the function $$g:R\rightarrow R$$ such that $$gof=fog=I_{R}$$.
If $$f(x)=\cfrac{\sin{([x]\pi)}}{{x}^{2}+x+1}$$, where $$[x]$$ denotes the integral part of $$x$$. Show that $$f(x)$$ is a constant function.
If $$A=\left\{1,2\right\}$$, form the set $$A\times A\times A$$.
If $$A = \left\{ {1,2} \right\},B = \left\{ {x:x \in N\,\,and\,\,{x^2} - 9 = 0} \right\},$$ Find $$A \times B.$$
If $$A\times B=\left\{\left(a,1\right),\left(b,3\right),\left(a,3\right),\left(b,1\right),\left(a,2\right),\left(b,2\right)\right\}$$.Find $$A$$ and $$B$$
Find $$x$$ and $$y$$ if $$\left(x+3,5\right)=\left(6,2x+y\right)$$
Let $$R$$ be relation from $$Q$$ to $$Q$$ defined by $$R=\left\{(a,b):a,b\ \in \ Q\ and\ a-b\ \in \ Z\right\}$$.
Show that :
$$(a,b)\ \in \ R$$ implies that $$(b,a)\ \in \ R$$.
Find the relations between $$a$$ and $$b$$, so tat the function $$f$$ defined by:
$$f\left( x \right)=\begin{cases} ax+1, \\ bx+3, \end{cases}\begin{matrix} if\ x\le 3 \\ if\ x>3 \end{matrix}$$
is continuous at $$x=3$$.
If $$A=\left\{a,b\right\}$$ and $$B=\left\{1,2,3\right\}$$ find $$\left(A\times B\right)\cap\left(B\times\,A\right)$$
The cartesian product $$A\times A$$ has $$9$$ elements among which are found $$\left(-1,0\right)$$ and $$\left(0,1\right)$$.Find the set $$A$$ and the remaining elements of $$A\times A$$
If $$A=\left\{1,3,5,6\right\}$$ and $$B=\left\{2,4\right\}$$.Find $$A\times\,B$$ and $$B\times \,A$$
Let $$R$$ be relation from $$Q$$ to $$Q$$ defined by $$R=\left\{(a,b):a,b\ \in \ Q\ and\ a-b\ \in \ Z\right\}$$.
Show that :
$$(a,b)\ \in \ R$$ and $$(b,c)\ \in R$$ implies that $$(a,c)\ \in \ R$$.
Find the values of $$a$$ and $$b$$ if $$\left(3a-2,b+3\right)=\left(2a-1,3\right)$$
If $$A=\left\{a,b\right\}$$ and $$B=\left\{1,2,3\right\}$$ find $$A\times A$$ and $$B\times\,B$$
List the relation R defined by $$R=\left \{ (a,b):a\leq b^{3} \right \}$$ in Roaster form. $$a,b \in N$$
If $$A=\left\{a,b\right\}$$ and $$B=\left\{1,2,3\right\}$$ find $$A\times B$$ and $$B\times\,A$$
Let $$R=\left\{ \left( a,{ a }^{ 3 } \right) :\text{a is a prime number less than }\ 5 \right\} $$ be a relation. Find the range of $$R$$.
Write the domain of the relation $$R$$ defined on the set $$\mathbb{Z}$$ of integers as follows:
$$(a,b)\in R\Leftrightarrow {a}^{2}+{b}^{2}=25$$
If $$R=\left\{ (x,y):x+2y=8 \right\} $$ is a relation on $$N$$, then write the range of $$R$$.
If $$R=\left\{ (x,y):{ x }^{ 2 }+{ y }^{ 2 }\le 4;x,y\in \mathbb{Z} \right\} $$ is a relation on $$\mathbb{Z}$$, write the domain of $$R$$.
Write the identity relation on set $$A=\left\{ a,b,c \right\} $$.
Find the domain and range of each of the following real value functions:
$$f(x)= |x-1|$$
There are four men and six women on the city councils. If one council number is selected for a committee at random, how likely that it is a woman
Enter 1 if it is true else enter 0.For the relation $$\displaystyle R = \{ (-1, 1), (1, 1), (-2, 4), (2, 4), (3, 9)\}$$ is dom $$\displaystyle (R) = \{-2, -1, 1, 2, 3\}$$ and range $$\displaystyle (R) = \{1, 4,9\}$$.
Let the relation $$R$$ be defined in $$N$$ by $$aRb$$ if $$2a+3b=30$$. Then $$R=$$ ....
Let the relation $$R$$ be defined on the set $$A=\left\{ 1,2,3,4,5 \right\} $$ by $$R={(a,b):a^2b^2 < 8}.$$ Then $$R$$ is given by ______.
For the set $$A=\left\{1,2,3\right\}$$, define a relation $$R$$ in the set $$A$$ as follows:
$$R=\left\{(1,1),(2,2),(3,3),(1,3)\right\}$$
Write the ordered pairs to be added to $$R$$ to make it the smallest equivalence relation.
Let $$R$$ relation defined on the set of natural number $$N$$ as follows:
$$R=\left\{(x,y): x\in \ N, y\in \ N, 2x+y=41\right\}$$. Find the domain and rang of the relation $$R$$. Also verify $$R$$ is reflexive, symmetric and transitive.
If $$R$$ be a relation $$<$$ from $$A=\{1,2,3,4\}$$ to $$B=\{1,3,5\}$$ i.e., $$(a,b) \in$$ R if $$a<b$$, then find $$ROR^{-1}$$
Let $$A=\left \{ 1, 2, 3, 4 \right \}$$ and $$B=\left \{ x, y, z \right \}$$. Consider the subset $$R=\left \{ (1, x),(1,y),(2,z),(3,x) \right \}$$of $$A\times B.$$ Is R, a relation from A to B? If yes, find domain and range of R. Draw arrow diagram of R and represent R in a tabular form.
If $$f: R\rightarrow R$$ defined by $$f(x)=x^2+1$$, then the values of $$f^{-1}(17)$$ are a and b, then a+b =?
For each set of ordered pairs below, state whether it is a function or not give reasons(i){(3, 2), (4, 2), (5, 2)}
if a function enter 1 else 0
if a function enter 1 else 0
If $$x, y\in \left [ 0, 2\pi \right ]$$, then find the total number of ordered pairs $$\left ( x, y \right )$$ satisfying the equation $$\sin x\cos y=1$$
Let a relation R be defined by
$$\displaystyle R= \left \{ \left ( 4,5 \right ), \left ( 1,4 \right ), \left ( 4,6 \right ), \left ( 7,6 \right ), \left ( 3,7 \right ) \right \}$$ then find $$\displaystyle R o R$$
Given a relation $$\displaystyle R=\left \{ \left ( 1,2 \right ),\left ( 2,3 \right ) \right \}$$ on the set of natural numbers,Find the minimum number of ordered pairs should be added so that the enlarged relation is symmetric,transitive and reflexive.
Use elements of set P = {2 , 3} to find the number of all possible ordered pairs.
Let $$A$$ and $$B$$ be two sets such that $$\displaystyle A\times B$$ Consists of $$6$$ elements. If three elements of $$\displaystyle A\times B$$ are $$\displaystyle \left ( 1,4 \right ),\left ( 2,6 \right ),\left ( 3,6 \right )$$ then $$\:B\times A$$. is $$=\left \{ \left ( a,1 \right ),\left ( 6,1 \right ),\left ( 4,d \right ),\left ( c,2 \right ) ,\left ( 4,3 \right )\left ( b,3 \right )\right \}$$. Find $$a+b+c+d$$
Given $$A = \{5, 6, 7\}$$ and $$B = \{3, 4\}$$. Form all possible ordered pairs and write the total number of ordered pairs formed so that both the components are from B.
Let $$A = \{1, 2\}$$ and $$B = \{2, 3, 4\}$$.If $$ B \times B= \{(2,2), (2,3),(2, 4), (3,2), (3,3), (3,4) , (4,2), (4,3), (4,4)\}$$. Please enter $$1$$ or else $$0$$.
Please enter $$1$$ or else $$0$$.
Let $$A = \{1, 2\}$$ and $$B = \{2, 3, 4\}$$, then $$B \times A=\{(2,1),(2,2), (3,1), (3,2),(4,1),(4,2)\}$$. If true enter $$1$$, or else enter $$0$$.
Let $$A = \{1, 2\}$$ and $$B = \{2, 3, 4\}$$, then $$ A \times A = \{ (1,1), (1,2),(2,1), (2,2)\}$$. If true enter $$1$$, or else enter $$0$$.
Let $$A = \{1, 2\}$$ and $$B = \{2, 3, 4\}$$, then $$ A \times B = \{ (1,2), (1,3),(1, 4), (2,2), (2,3), (2,4) \}$$. If true enter $$1$$, or else enter $$0$$.
Given $$A = \{5, 6, 7\}$$ and $$B = \{3, 4\}$$. Form all possible ordered pairs and write the total number of ordered pairs formed. So that :
Both the components are from AFind the total number of such pairs.
If $$A = \{x, y\}$$ and $$B = \{y, x\}$$ ; then $$A \times B = ?$$ What are the number of elements of such set?
If $$A =$$ {$$x$$ : $$x \,\,\in\,\, W$$, $$3 \leq x < 6$$}, $$B = \{3, 5, 7\}$$ and $$C = \{2, 4\}$$; find : $$(A - B) \times C$$
If P = {a, b, c} and Q = {b, c, d} ; find number of elements in $$(P \cap Q) \times P$$
Given $$A = \{ x \in W : 7 \le x \leq 10 \}, $$ find $$ A \times A.$$
If $$M=\{x : x \,\,\epsilon\,\, N, 1 < x \leq 4\}$$ and $$N = \{y : y\,\,\epsilon\,\,W, y < 3\}$$; Find: $$n(N$$ $$\times$$ $$N$$).
Given $$M = (0, 1, 2)$$ and $$N = (1, 2, 3)$$. Find $$(M \cup N)\times (M - N)$$
If $$M=\{x : x \,\,\epsilon\,\, N, 1 < x \leq 4\}$$ and $$N = \{y : y\,\,\epsilon\,\,W, y < 3\}$$; find M $$\times$$ N :Also find the number of such ordered pairs.
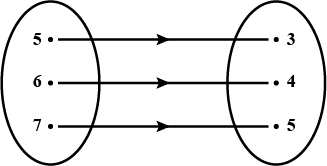
$$\displaystyle R_{4}= \left \{ \left ( 1,3 \right ), \left ( 2,5 \right ), \left ( 4,7 \right ), \left ( 5,9 \right ), \left ( 3,1 \right ) \right \}$$
Is it a mapping?
If it is true enter 1, else enter 0.
Given ordered pairs : (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6), (6, 7), (8, 4), (8, 5), (8, 6), (8,8).Use these ordered pairs to find the following relation :$$R_4$$ = "is greater than"
Given ordered pairs : (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6), (6, 7), (8, 4), (8, 5), (8, 6), (8,8).
Use these ordered pairs to find the following relation :
Given ordered pairs : (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6), (6, 7), (8, 4), (8, 5), (8, 6), (8,8).Find the ordered pair(s) from above given list which satisfies the following relation.$$R_3$$ = "is one less than"
Given ordered pairs : (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6), (6, 7), (8, 4), (8, 5), (8, 6), (8,8).
Find the ordered pair(s) from above given list which satisfies the following relation.
Given A = {8, 9, 10, 12}, B = {2, 3, 4, 5} and the relation R from A to B means : "is multiple of" :
Write the domain range of relation R.
Let $$\displaystyle A=\left \{ 1,2,3,4,5 \right \},B=\left \{ 1,3,5,7,9,10,17,26,30 \right \}$$ Which of the following sets of ordered pairs are (i) relations (ii) functions (iii) neither,from A to B
(a)$$\displaystyle R_{1}=\left \{ \left ( 1,3 \right ),\left ( 3,3 \right ),\left ( 5,17 \right ) ,\left ( 1,2 \right )\right \}$$
(b) $$\displaystyle R_{2}=\left \{ \left ( 3,7 \right ),\left ( 4,5 \right ),\left ( 5,30 \right ) \right \}$$
(c) $$\displaystyle R_{3}=\left \{ \left ( x,y \right ):x \epsilon A,y \epsilon B,x+y=8 \right \}$$
(d) $$\displaystyle R_{4}=\left \{ \left ( x,y \right ):x \epsilon A,y\epsilon B,y=x^{2}+1 \right \}$$ (e)$$\displaystyle R_{5}=\left \{ \left ( x,y \right ):x\epsilon A,y\epsilon B,y=2x-1 \right \}$$
Find the number of ordered pairs in $$\displaystyle R^{-1} o R.$$
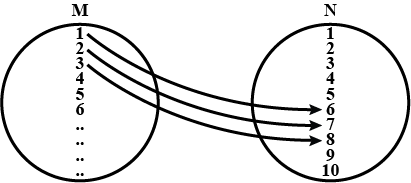
Write the relation, represented by the arrow diagram given below, in roster form. Also, write the domain and range of the relation.
Given ordered pairs : (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6), (6, 7), (8, 4), (8, 5), (8, 6), (8,8).Use these ordered pairs to find the following relation :$$R_2$$ = "is equal to"
Given ordered pairs : (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6), (6, 7), (8, 4), (8, 5), (8, 6), (8,8).
Use these ordered pairs to find the following relation :
Given ordered pairs : (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6), (6, 7), (8, 4), (8, 5), (8, 6), (8,8).Use these ordered pairs to find the following relation :$$R_1$$ = "is less than"
Given ordered pairs : (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6), (6, 7), (8, 4), (8, 5), (8, 6), (8,8).
Use these ordered pairs to find the following relation :
Let $$f$$ be a function from the set of positive integers to the set of real number such that
(i) $$f(1)=1$$
(ii) $$\displaystyle \sum_{r=1}^{n} rf(r) =n(n+1)f(n),\forall n\geq 2$$
then find the value of $$2126 f(1063)$$
Let $$\displaystyle f\left ( x \right )=\frac{9^{x}}{9^{x}+3}$$. Show $$f(x)+f(1-x)=1$$, and hence evaluate $$\displaystyle f\left ( \frac{1}{1996} \right )+f\left ( \frac{2}{1996} \right )+f\left ( \frac{3}{1996} \right )+...+f\left ( \frac{1995}{1996} \right )$$.
Which of the following are identity relations of set $$A = \{1, 2, 3\}$$
1.$$\displaystyle R_{1}=\left \{ (1,1),(2,2) \right \}$$2.$$R_{2}=\left \{ (1,1),(2,2)(3,3),(1,3) \right \}$$3.$$R_{3}=\left \{ (1,1),(2,2),(3,3) \right \}$$
Let $$A=\{1, 3, 5, 7\}$$ and $$B = \{2, 4, 6, 8\}$$ be two sets $$R$$ be a relation from $$A$$ to $$B$$ defined by the phrase $$\displaystyle “(x,y)\in R\Rightarrow x>y".$$ Find relation $$R$$ and its domain and range.
Define a sequence $$\left<f_0(x),\,f_1(x),\,f_2(x),\dots\right>$$ of functions by $$f_0(x)=1,\;f_1(x)=x,\; \ \ \begin{pmatrix}f_n(x)\end{pmatrix}^2-1=f_{n+1}(x)f_{n-1}(x)$$, for $$n\,\ge\,1$$. Prove that each $$f_n(x)$$ is a polynomial with integer coefficients.
Solve the
$$2\dfrac{1}{5}-\dfrac{-1}{3}$$
The cartesian product $$\displaystyle A\times A$$ has $$9$$ elements among which are found $$(-1, 0)$$ and $$(0, 1)$$. Find the set $$A$$ and the remaining elements of $$\displaystyle A\times A$$
Let $$A = \{1, 2, 3, .... , 14\}$$. Define a relation $$R$$ from $$A$$ to $$A$$ by $$R = \{(x, y): 3x - y = 0$$ where $$x, y \displaystyle \in A\}$$. Write down its domain, co-domain and range.
If $$G = \{7, 8\}$$ and $$H = \{5, 4, 2\}$$, find $$\displaystyle G\times H $$ and $$\displaystyle H\times G $$.
Define a relation $$R$$ on the set $$N$$ of natural numbers by $$R = \{(x, y): y = x + 5, x$$ is a natural number less than $$4; x, \displaystyle y\in N\}$$. Depict this relationship using roster form. Write down the domain and the range.
Let $$f, g$$ : $$\displaystyle R\rightarrow R$$ be defined respectively by $$f(x) = x + 1, g(x) = 2x - 3$$. Find $$f + g, f - g$$ and $$\displaystyle \frac{f}{g}$$
Let $$R$$ be the relation on $$Z$$ defined by $$R =$$ $$\{(a, b): a, b \in Z, a -b$$ is an integer$$\}$$. Find the domain and range of $$R.$$
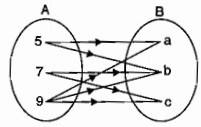
The figure shows a relationship between the sets $$P$$ and $$Q$$. Write this relation in
(i) in set-builder form (ii) roster form
If $$A = \{2, 4, 6, \}$$, $$B = \{5, 7, 1, 9\}$$.
Let R be the relation ‘is less than’ from A to B. Find Domain (R) and Range (R).
If $$R = \left \{(x, y) : x + 2y = 8\right \}$$ is a relation on $$N,$$ write the range of $$R.$$
If $$f(x)=4-3x$$, find $$f(-5)$$ and $$f(13)$$
In the problem below, $$f(x)={x}^{2}$$ and $$g(x)=4x-2$$
Find the following function:
$$(f\times g)(x)$$
Find the following function:
A function $$f : (-3, 7)\rightarrow R$$ is defined as follows:
$$f(x) = \left\{\begin{matrix} 4x^{2} -1;& -3 \leq x < 2\\ 3x - 2; & 2\leq x \leq 4\\ 2x - 3; & 4 < x \leq 6\end{matrix}\right.$$
Find:
$$f(1) - f(-3)$$
A function $$f : (-3, 7)\rightarrow R$$ is defined as follows:
$$f(x) = \left\{\begin{matrix} 4x^{2} -1;& -3 \leq x < 2\\ 3x - 2; & 2\leq x \leq 4\\ 2x - 3; & 4 < x \leq 6\end{matrix}\right.$$
Find:
$$\dfrac {f(3) + f(-1)}{2f(6) - f(1)}$$
A function $$f : [-7, 6) \rightarrow R$$ is defined as follows
$$f(x)=\left\{\begin{matrix}x^2+2x+1; &-7 \leq x < -5 \\ x+5;& -5\leq x\leq 2 \\ x-1;& 2 < x < 6 \end{matrix}\right.$$
(iii) $$ 2f(-4)+3f(2)$$
(ii) $$f(-7)-f(-3)$$
(iv) $$\dfrac{4f(-3)+2f(4)}{f(-6)-3f(1)}$$
A function $$f : (-3, 7)\rightarrow R$$ is defined as follows:
$$f(x) = \left\{\begin{matrix} 4x^{2} -1;& -3 \leq x < 2\\ 3x - 2; & 2\leq x \leq 4\\ 2x - 3; & 4 < x \leq 6\end{matrix}\right.$$
Find:
$$f(-2) - f(4)$$
Let $$ f(x)=\sqrt{x+\sqrt{0+\sqrt{x+\sqrt{0+\sqrt{x+......}}}}}$$.If $$f(a)=4$$ and$$ f(a)=\dfrac{p}{q}$$ where p and q are relatively prime natural numbers then $$ (a > 0)(p+q)$$ is equal to
Let $$\quad f(x)=\sqrt { \cfrac { { x }^{ 2 }+ax+4 }{ { x }^{ 2 }+bx+16 } } $$ is defined for all real $$x$$, then find the number of possible ordered pairs $$(a,b)$$ (where $$a,b\in I$$)
Which term of the A.P. $$3,10,17,......$$ wil be $$84$$ more than its $$13$$th term?
Find the intervals of monotocity of the function $$f(x)=2x^2-\log |x|, x\neq 0$$.
A function $$f(x)$$ is defined as $$f(x) = x^{2} + 3$$. Find $$f(0), f(1), f(x^{2}), f(x + 1)$$ and $$f(f(1))$$.
If A = {a, b, c, d}, B={1, 2, 3}, find whether or not the following sets of ordered pairs are relations from A to B or not
(a) $$R_1$$ ={(a, 1), (a, 3)}
(b) $$R_2$$ = { (b, 1), (c, 2), (d, 1)}
(c) $$R_3$$ = {(a, 1), (b, 2),( 3, c)}
N is the set of positive integers and ~ be a relation on $$N\times N $$ defined (a, b) ~ (c, d) iff ad = bc.Is it equivalence relation.
A class has $$175$$ students. The following table shows the number of students studying one or more of the following subjects in this class :
| Subject | Number of students |
| Mathematics | $$100$$ |
| Physics | $$70$$ |
| Chemistry | $$46$$ |
| Mathematics and Physics | $$30$$ |
| Mathematics and Chemistry | $$28$$ |
| Physics and Chemistry | $$23$$ |
| Mathematics, Physics and Chemistry | $$18$$ |
Suppose $$f$$ is the collection of all ordered pairs of real numbers and x = 6 is the first element of some ordered pair in $$f$$. Suppose the vertical line through x = 6 intersects the graph of $$f$$ twice. Is $$f$$ a function? Why or why not?
If $$X= \{1, 2, 3, 4, 5\}$$ and $$Y = \{ 1, 3, 5, 7,9\}$$ determine which of the following sets are (i) mappings (ii) relations (ii) neither of X to Y.
(a) $$R_1 = { (x, y): y = x + 2 , x \in X, y \in Y}$$
(b) $$R_2$$ $$= \{ (1, 1), ( 2, 1), (3, 3), (4, 3), ( 5, 5)\}$$
(c) $$R_3$$ $$= \{ (1, 1), (1, 3), (3, 5), (3, 7), (5, 7)\}$$
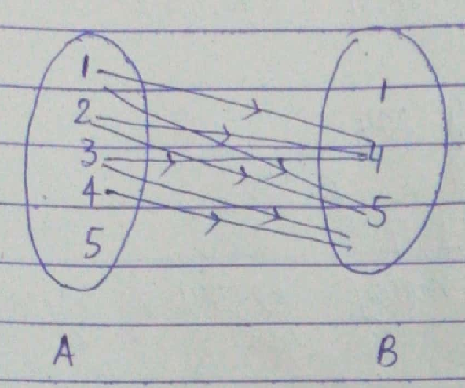
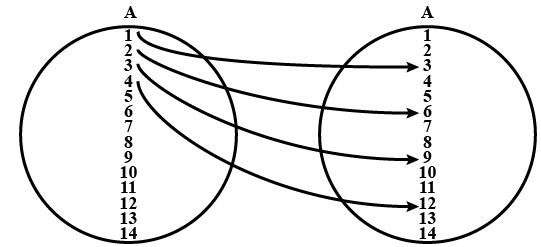
(d) $$R_4$$ $$= \{ (1, 3), (2, 5), (4, 7), (5, 9), (3, 1)\}$$
Let a relation R be defined by
R = {(4, 5), ( 1, 4), ( 4, 6), (7, 6), (3, 7)}.
Find (i) R o R (ii) $$R^{-1}$$ o R.
Let $$A= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}$$, $$B = { 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 10, 17, 26, 30}.$$ Which of the following sets of ordered pairs are (i) relations (ii) functions (iii) neither, from A to B
(a) $$R_1$$= {(1, 3), (3, 3), (5, 17), (1, 2)}
(b) $$R_2$$ = {(3, 7), (4, 5), ( 5, 30)}
(c) $$R_3 = {(x, y): x \in A, y \in B, x+y =8}$$
(d) $$R_4 = {(x, y): x \in A, y \in B, y=x^2+1}$$
(e) $$R_5 = {(x, y): x \in A, y \in B, y=2x-1}$$
The following relation is defined on the set of real numbers. $$aRb$$ if $$|a - b| > 0$$.
Let, $$f(x+1)=2x^2-3x-1$$, then find the value of $$f(0)$$ and $$f(x+2)$$.
If $$f(x) = x+7 $$ and $$g(x) = x-7$$, $$x \in R $$, find $$(fog)(7)$$. function $$f:R \rightarrow R$$ defined by $$f(x) = \frac{3x+5}{2}$$ is an invertible function, find $$f^{-1}$$
$$f:[0,2] \rightarrow R $$ is defined as $$ f(x) = \sqrt{x^3 +2 - 2\sqrt{x^3 + 1}} + \sqrt{x^3 +10 - 6\sqrt{x^3 + 1}} $$ and $$g(x) = \int f(x) dx.$$ if $$ g(1) = 3$$ then $$g(\frac{1}{3}) = $$
Let $$f(x)=\cos(\log x)$$ the prove that $$f(x).f(y)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left[f\left(\dfrac{y}{x}\right)+f(xy)\right]$$.
If $$(2.3)^{x} = (0.23)^{y} =1000$$ then find the value of $$\dfrac{1}{x} -\dfrac{1}{y}$$
Let $$R$$ be a relation $$ < $$ from $$A={1,2,3,4}$$ to $$B={1,3,5},i.e.,(a,b) \in R \Leftrightarrow a < b$$ , then $$R o R^{-1}$$ is:
a) {$$(1,3),(1,5),(2,3),(2,5),(3,5),(4,5)$$}
b) {$$(3,1),(5,1),(3,2),(5,2),(5,3),(5,4)$$}
Let $$A = \{1, 2\}$$ and $$B = \{3, 4\}$$. Find the number of relations from $$A$$ to $$B$$.
Verify$$A=\{1,2\}$$
$$B=\{1,2,3,4\}$$$$C=\{5,6\}$$$$D=\{5,6,7,8\}$$. Prove $$A\times (B \cap C)=(A\times B) \cap (A\times C)$$
A relation R is defined on the set $$z$$ of integers as follows. $$(x, y)\in R\Leftrightarrow x^2+y^2=25$$. Express $$R$$ and $${R}^{-1}$$ as the set of ordered pairs and hence find their respective domains.
Let $$A=\left\{x,y,z\right\}$$ and $$B=\left\{1,2\right\}$$. Find the number of relations from $$A$$ to $$B$$.
If $$A =\left\{2, 4, 6, 9\right\}, B = \left\{4, 6, 18, 27, 54\right\}$$ and a relation $$R$$ from $$A$$ to $$B$$ is defined by $$R = \{(a, b) : a \, \in \, A, \, b \, \in \, B, \,\,\, a \, \,\text{is a factor of b and }\ a < b\}$$
If $$f(x)=\dfrac{1}{1-x}$$, show that $$f[f\{f(x)\}]=x$$.
Let $$R$$ be a relation in $$N$$ defined as $$R = \{(x, y) \in \, N \times N : \, x + 2y = 39\}$$ Find the domain, co-domain and range of $$R$$. Also write $$R^{-1}$$ in roster form.
Let $$A=\{1,2,3\}$$ and $$B=\{3,4\}$$ then find $$A\cap B$$ and then find $$A\times (A\cap B)$$.
If $$f(x)=2x-5$$, then what is the value of $$f(2)+f(5)$$?
If $$f(x) = x^2- 3x +4$$, then find the value of x satisfying $$f(x) = f( 2x+1).$$
If $$A = {2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}$$ given by $$R = \left\{ \left( x,y \right) :x\in A,y\in A\ and \ divides\ y \right\}$$ then find the domain and range of $$R$$.
If $$f\ {(x)}= \dfrac { \dfrac { 1 }{ x } +1 }{ \dfrac { 1 }{ x } -1 } $$ then the value of $$f\ {(x)}+f\ {(-x)}$$ is
If $$R=\{ (1,-1),(2,-2),(3,-1)\} $$ is relation, then find the range of R.
If $$f(x) = \dfrac{(x - 1)}{(x + 1)}$$ then prove that $$f(2x) = \dfrac{3f(x) + 1}{f(x) + 3}$$
Find the value$$ \left| 7 \right|\times\left| -4\right|\times \left|4-9 \right|\times \left|7 \right|\times \left| -4 \right|\times \left|4-9 \right|$$
Let $$'*'$$ be a binary operation on set Q of rational number defined as $$a*b=\dfrac{ab}{5}$$. Write the identity for $$'*'$$, if any.
Find range & domain of following $$\sqrt {4 - {x^2}} $$
If $$f\left( x \right) = x + \dfrac{1}{x}$$, prove that $${\left( {f\left( x \right)} \right)^3} = f\left( {{x^3}} \right) + 3f\left( {\dfrac{1}{x}} \right)$$
If $${e^{f\left( x \right)}} = \dfrac{{10 + x}}{{10 - x}},x \in \left( { - 10,0} \right)$$ and $$f\left( x \right) = k.f\left( {\dfrac{{200x}}{{100 + {x^2}}}} \right)$$ then $$k$$ =
Let $$A=\{-1,1\}$$ then find $$A\times A$$.
If $$A=\left\{1,2,3\right\}$$ and $$B=\left\{3,4\right\}$$ and $$C=\left\{1,3,5\right\}$$.Find $$\left(A\times\,B\right)\cap\left(A\times\,C\right)$$
The simplified form of $$\left ({\dfrac {x(x - 5y)} {{x^2} - 6xy + 5{y^2}} } \times {\dfrac {(x + y)(x - y)} {{x^2} + xy}}\right )$$ is
The number of relations from $$A = \{ 2,6 \}$$ to $$B = \{ 1,3,5,6,7 \}$$ that are not functions from A to $$B$$ is
$$y=\dfrac{x-2}{2x+3}$$Express in the form $$f(x,y) = 0$$
Let $$A=\left\{1, 2, 3, 4, 5\right\}$$ and $$B=\left\{1, 4, 5\right\}$$. Let $$R$$ be a relation 'is less than' from $$A$$ to $$B$$. Find the domain, co domain and range of $$R$$.
A function $$f\::\:R\rightarrow R$$ satisfy the equation $$f\left(x\right)f\left(y\right)-f\left(xy\right)=x+y$$ for all $$x,y\in R$$ and $$f\left(y\right)>0$$, then ?
If the function $$f(x)$$ given by $$f(x)=\begin{cases}3ax+b & if \, x > 1 \\ 11 & if\, x=1 \\5ax-2b & if \, x < 1\end{cases}$$ is continuous at x=1, then find the values of a and b.
For x $$\in$$ R, the range of the given expression $$\dfrac{x^2 + 34x - 71}{x^2 + 2x - 7}$$ is
Number of solutions satisfying $$| x | + | x - 2 | \leq 2$$ for $$x \in R$$ is
Let $$f:$$ $$R \rightarrow R$$ be given by $$f ( x ) = x ^ { 2 } + 3 .$$ Find ( a ) $$\{ x : f ( x ) = 28 \}$$ ( b ) the pre-images of $$39$$ and $$2$$ under $$f.$$
Find the range
$$f(x)=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x-5}}$$
Find the domain of $$\cos^{-1}[X]$$ where $$[X]$$ is the greatest integer functions.
Find the domain and range of the following real functions :
$$f ( x ) = - | x |$$
If $$A=\left\{1,2,3\right\}$$ and $$B=\left\{3,4\right\}$$ and $$C=\left\{1,3,5\right\}$$.Find $$A\times\left(B\cup\,C\right)$$
$$n ( A ) + n ( B ) - n ( A \cap B ) =$$
Is $$a\leq a^2$$, $$a\in R$$ true? Why or why not?
If $$a,b,c\in{R}^{+}$$ such that $$a+b+c=18$$, then the maximum value of $${a}^{2}{b}^{3}{c}^{4}$$ is
If $$f ( x ) = \frac { a ^ { x } + a ^ { - x } } { 2 }$$ then $$f ( x + y ) f ( x - y )$$ is equal to:
A relation $$R$$ is defined from a set $$A=[2,3,4,5]$$ to a set $$B=[3,6,7,10]$$ as follows:
$$(x,y)\in R\Leftrightarrow x$$ is relatively prime to $$y$$.Express R as a set of ordered pairs and determine its domain and range.
If $$A=\left\{1, 2, 4,5\right\} $$ and $$B=\left\{a,b\right\}$$ Find the total number of relations from $$A$$ to $$B$$.
Write the relations as sets of ordered pairs $$\left\{\left(x,y\right) : y = 3x, x\in \left\{1,2,3\right\}, y\in \left\{3,6,9,12\right\}\right\} $$
If $$A={1, 2, 4} $$ and $$B={a, b}$$ Find the total number of relations from A to B.
If f = {(4, 5), (5, 6), (6, -4) and g = {(4, -4), (6, 5),(8, 5)} then find$$ A)f+g\ \ \ \ B)f-g\ \ \ \ C)2f+4g\ \ \ \ D)f+4\ \ \ \ E)fg\ \ \ \ F)f/g\ \ \ \ G)|f| \ \ \ \ H)\sqrt{f}\ \ \ \ I)f^2\ \ \ \ G)f^3$$
If $$f:A\rightarrow A$$, then range of $$f$$ where $$A=\left\{1,2,3,4\right\}$$ and $$f\left(x\right)={x}^{2}+x+2$$
If $$f\left(x\right)={x}^{2}+2x+3,$$ then find $$\dfrac{f\left(x+h\right)-f\left(x-h\right)}{h},\,\,h\neq 0$$
Let $$X=\left\{1,2,3,4,5\right\}$$.If the relation $$g=\left\{\left(1,2\right),\left(2,3\right),\left(3,4\right),\left(4,5\right),\left(5,1\right)\right\}$$ on $$X$$ is a function from $$X$$ to $$X$$.then find $$g\left(g\left(g\left(2\right)\right)\right)$$
If $$f\left(x\right)+f\left(\dfrac{1}{x}\right)=f\left(x\right)f\left(\dfrac{1}{x}\right)$$ and $$f\left(3\right)=28$$ find $$f\left(\dfrac{1}{3}\right)$$
If $$A \times B = \left\{ {\left( {p,q} \right),\left( {p,r} \right),\left( {m,q} \right),\left( {m,r} \right)} \right\}$$
Find A and B
If $$f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}$$ the show that $$f\left(x\right)+f\left(\dfrac{1}{x}\right)=0$$
Find whether $$f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{{a}^{x}+1}{{a}^{x}-1}$$ is even, odd or neither odd nor even.
If $$\dfrac { 4 }{ x } <\dfrac { 1 }{ 3 },$$ what is the possible range of value for $$x$$?
Let $$X=\left\{1,2,3,4,5\right\}$$.If the relation $$g=\left\{\left(1,2\right),\left(2,3\right),\left(3,4\right),\left(4,5\right),\left(5,1\right),\right\}$$ on $$X$$ is a function from $$X$$ to $$X$$.then find $$g\left(g\left(g\left(4\right)\right)\right)$$
Let $$f(x)=\left\{\begin{matrix} x^3+x^2+10x, & x < 0\\ x^2e^x, & x\geq 0\end{matrix}\right.$$. Investigate the behaviour of the function for $$x\in R$$.
The domain of $$f(x)=\sqrt { x-2-2\sqrt { x-3 } } -\sqrt { x-2+2\sqrt { x-3 } } $$
Find the range of $$\ln{\left[{\left\{x\right\}}^{2}+3\left\{x\right\}+2\right]}$$ where $$\left\{x\right\}$$ is a fractional function.
Find the range of $$f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{\left\{x\right\}}{\left\{x\right\}+1}$$
Let $$f:R\rightarrow R$$ be defined by $$f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x+1}{{x}^{2}+2},\,x\in \,R$$.Find $$f\left(4\right)$$
Let $$f:R\rightarrow R$$ be defined by $$f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x+1}{{x}^{2}+2},\,x\in \,R$$.Find $$f\left(0\right)$$
If $$n(A)=15, n(A\cup B)=29, n(A\cap B)=7$$ then $$n(B)=$$?
Let $$A$$ and $$B$$ be two sets such that $$n\left(A\right)=5$$ and $$n\left(B\right)=2$$.If $$a,b,c,d,e$$ are distinct and $$\left(a,2\right),\left(b,3\right),\left(c,2\right),\left(d,3\right),\left(e,2\right)$$ are in $$A\times B$$,find $$A$$ and $$B$$
Express $$A=\left\{\left(a,b\right):2a+b=5,a,b\in\,W\right\}$$ as the set of ordered pairs.
Suppose that f(x) is a function of the form f(x)= $$\frac{ax^{8}+bx^{6}+cx^{4}+dx^{2}+15x+1}{x}(x\neq 0)$$ If f(5)=-28 then the value of f(-5) /14 is equal to
$$f=\{(4,3),(6,7)\}\ \ \ g=\{(4,9),(6,5)\}$$ find $$f+g$$
If $$f(x+y)=f(x).f(y)$$ then prove that $$f\left( x \right) ={ \left[ f\left( 1 \right) \right] }^{ x }$$
If $$f(x+y)=f(x)+f(y)$$. Then prove that $$f(x)=x.f(1)$$
Let $$|X|$$ denote the number of elements in a set $$X$$.let $$S=\{1,2,3,4,5,6\}$$ be a sample space ,where each elements is equally likely to occur.If A and B are independent events associated with $$S$$, then the number of ordered pairs $$(A,B)$$ such that $$1\le |B|<|A|$$ equals.
Let $$f:R^+ \to R$$, where $$R^+$$ is the set of all positive real numbers, be such that $$f(x)=\log_e x$$.
Determine
whether $$f(xy)=f(x)+f(y)$$ holds.
Find the domain and range of each of the following real value functions:
$$f(x)= -|x|$$
Which one of the given relations on $$A=\left\{ 1,2,3 \right\} $$ is a function?
$$f=\left\{ \left( 1,3 \right) ,\left( 2,3 \right) ,\left( 3,2 \right) \right\} $$, $$g=\left\{ \left( 1,2 \right) ,\left( 1,3 \right) ,\left( 3,1 \right) \right\} $$
what is the fundamental difference between a relation and a function? Is every relation a function?
Find the domain and range of each of the following real value functions:
$$f(x)=\sqrt {x-1}$$
Find the domain of each of the following real valued functions of real variable:
$$f(x)=\dfrac {x^2+2x+1}{x^2-8x+12}$$
Determine the domain and range of the relation R defined by $$R=\{(x, x+5):x\in \{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5\}\}$$.
Let $$f:(0, \infty)\to R$$ and $$g:R\to R$$ be defined by $$f(x)=\sqrt x$$ and $$g(x)=x$$. Find $$f+g, f-g, fg$$ and $$\dfrac {f}{g}$$.
Determine the domain and range of the relation R defined by $$R=\{(x, x^3):x$$ is a prime number less than $$10\}$$.
Let $$A=\{1, 2\}$$ and $$B=\{3, 4\}$$. Find the total number of relations from A into B.
A relation R is defined from a set $$A=\{2, 3, 4, 5\}$$ to a set $$B=\{3, 6, 7, 10\}$$ as follows:
$$(x, y)\in R\Leftrightarrow x$$ is relatively prime to y.
Express R as a set of ordered pairs
Write the following relation as the sets of ordered pairs.
A relation R on the set $$\{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7\}$$ defined by $$(x, y)\in R\Leftrightarrow x$$ is $$\{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7\}$$ defined by $$(x, y)\in R\Leftrightarrow x$$ is relatively prime to y.
Let $$A=\{1, 2\}$$ and $$B=\{3, 4\}$$. Find the total number of relations from A into B.
Determine the domain and range of the following relations.
$$S=\{(a, b): b=|a-1|, a\in Z$$ and $$|a|\leq 3\}$$.
Determine the domain and range of the relation R defined by $$R=\{(x, x+5):x\in \{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5\}\}$$.
Determine the domain and range of the following relation.
$$R=\{(a, b):a\in N, a < 5, b=4\}$$.
Determine the domain and range of the following relation.
$$R=\{(a, b):a\in N, a < 5, b=4\}$$.
Let $$A=\{a, b\}$$. List all relations on A and find their number.
Determine the domain and range of the following relations.
$$S=\{(a, b): b=|a-1|, a\in Z$$ and $$|a|\leq 3\}$$.
Let $$A=\{x, y, z\}$$ and $$B=\{a, b\}$$. Find the total number of relations from A into B.
Let R be the relation on Z defined by $$R=\{(a, b):a, b\in Z, a-b$$ is an integer$$\}$$. Find the domain and range of R.
Let $$A=\{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6\}$$. Let R be a relation on A defined by $$R=\{(a, b):a, b\in A, b$$ is exactly divisible by a$$\}$$ Find the range of R.
Let $$A=\{1, 2, 3,....., 14\}$$. Define a relation on a set A by $$R=\{(x, y): 3x-y=0$$, where $$x, y\in A\}$$.
Depict this relationship using an arrow diagram. Write down its domain, co-domain and range.
Answer the following question in one word or one sentence or as per the exact requirement of the question. If $$R=\{(x, y):x, y\in Z, x^2+y^2\leq 4\}$$ is a relation defined on the set Z of integers, then write domain of R.
Let $$A=\{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6\}$$. Let R be a relation on A defined by $$R=\{(a, b):a, b\in A$$, b is exactly divisible by a$$\}$$. Find the domain of R.
$$A=\{1, 2, 3, 5\}$$ and $$B=\{4, 6, 9\}$$. Define a relation R from A to B by $$R=\{(x, y):$$ the difference between x and y is odd, $$x\in A, y\in B\}$$. Write R in Roster form.
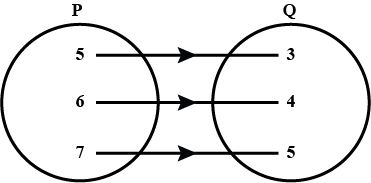
Define a relation R on the set N of natural numbers by $$R=\{(x, y):y=x+5$$, x is a natural number less than $$4, x, y\in N\}$$.
Depict this relationship using (i) roster form (ii) an arrow diagram. Write down the domain and range or R.
Answer the following question in one word or one sentence or as per exact requirement of the question.
If $$R=\{(x, y): x, y\in W, 2x+y=8\}$$, then write the domain and range of R.
Determine the domain and range of the relation R defined by $$R=\{(x, x^3):x$$ is a prime number less than $$10\}$$.
Determine the domain and range of the following relations.$$S=\{(a, b): b=|a-1|, a\in Z$$ and $$|a|\leq 3\}$$.
If $$f(x)+f(x+4)=f(x+2)+f(x+6)$$ then find the period of $$f(x)$$.
Answer the following question in one word or one sentence or as per exact requirement of the question.
If $$A=\{1, 3, 5\}$$ and $$B=\{2, 4\}$$, list the elements of R, if $$R=\{(x, y):x, y\in A\times B$$ and $$x > y\}$$.
Let $$R=\{(x, y):x+2y=8\}$$ be a relation on N. Write the range of R.
Find the domain and range of the relation
$$R=\{(-1, 1), (1, 1), (-2, 4), (2, 4)\}$$.
Let $$R=\{(a, a^3):a$$ is a prime number less than $$10\}$$. Find dom(R).
Let $$R=\{(a, a^3):a$$ is a prime number less than $$10\}$$. Find R.
Let $$R=\{(a, a^3):a$$ is a prime number less than $$10\}$$. Find range (R).
Let $$R=\{(a, a^3):a$$ is a prime number less than $$5\}$$. Find the range of R.
Let $$f: R\rightarrow R: f(x)=3x+2$$, find $$f\{f(x)\}$$.
Let $$f: R\rightarrow R$$ be defined by
$$f(x)=\left\{\begin{matrix} 2x+3, & when & x < -2\\ x^2-2, & when & -2\leq x\leq 3\\ 3x-1, & when & x > 3\end{matrix}\right.$$
Find $$f(2)$$.
Let $$R=\{\left(a, \dfrac{1}{a}\right):a\in N$$ and $$1 < a < 5\}$$. Find the doman and range of R.
Let $$f: R\rightarrow R$$ be defined by
$$f(x)=\left\{\begin{matrix} 2x+3, & when & x < -2\\ x^2-2, & when & -2\leq x \leq 3\\ 3x-1, & when & x >3\end{matrix}\right.$$
Find $$f(-3)$$.
Let $$R=\{(a, b):b=|a-1|, a\in Z$$ and $$|a| < 3\}$$. Find the domain and range of R.
Let $$f: R\rightarrow R$$ be defined by
$$f(x)=\left\{\begin{matrix} 2x+3, & when & x < -2\\ x^2-2, & when & -2\leq x \leq 3\\ 3x-1, & when & x > 3\end{matrix}\right.$$
Find $$f(4)$$.
Let $$R=\{(a, b):a, b\in N$$ and $$a+3b=12\}$$. Find the domain and range of R.
Let $$R=\{(a, b):a, b\in N$$ and $$b=a+5, a < 4\}$$. Find the domain and range of R.
For any sets $$\displaystyle A, B$$ and $$\displaystyle C$$, prove that:
$$\displaystyle A \times (B \cup C) = (A \times B)\cup (A \times C)$$
Let $$f:R\rightarrow R$$ be defined by
$$f(x)=\left\{\begin{matrix} 2x+3, & when & x < -2\\ x^2-2, & when & -2\leq x \leq 3\\ 3x-1, & when & x > 3\end{matrix}\right.$$
Find $$f(-1)$$.
If $$\displaystyle A = \{1, 3, 5\}, B = \{3, 4\}$$ and $$\displaystyle C = \{2, 3\}$$, verify that
$$\displaystyle A \times (B \cap C) = ( A \times B) \cap (A \times C)$$
If $$\displaystyle A = \{1, 3, 5\}, B = \{3, 4\}$$ and $$\displaystyle C = \{2, 3\}$$, verify that
$$\displaystyle A \times (B \cup C) = ( A \times B) \cup (A \times C)$$
Let $$\displaystyle A = \{ x \in W : x < 2 \}, B = x \in N : 1 < x \leq 4\}$$ and $$\displaystyle C = \{3, 5\}$$. Verify that :
$$\displaystyle A \times (B \cap C) = (A \times B) \cap (A \times C)$$
If $$\displaystyle A = \{2, 3, 5\}$$ and $$\displaystyle B = \{5, 7\}$$, find $$A \times A$$ and enter the number of elements of it.
Let $$\displaystyle A \times B = \{ (a, b) : b = 3a - 2\}.$$ If $$\displaystyle (x, -5)$$ and $$\displaystyle (2, y)$$ belong to $$\displaystyle A \times B $$, find the values of $$\displaystyle x $$ and $$\displaystyle y$$.
If the answer is $$\displaystyle x = -1, y = 4$$ then $$1,$$ else $$0$$
Let $$\displaystyle A = \{2, 3 \}$$ and $$\displaystyle b = \{ 4, 5\}$$. Find $$\displaystyle (A \times B)$$. How many subsets will $$\displaystyle (A \times B)$$ have?
Enter 1 if it is true else enter 0.If $$\displaystyle A = \{2, 3, 5\}$$ and $$\displaystyle B = \{5, 7\}$$, then $$\displaystyle A \times B = \{(2, 5), (2, 7), (3, 5), (3, 7), (5, 5), (5, 7)\}$$
Enter 1 if it is true else enter 0.
If $$\displaystyle A = \{2, 3, 5\}$$ and $$\displaystyle B = \{5, 7\}$$, find $$B \times B$$ and enter the value of no of pair which contain the same element.
If $$\displaystyle A = \{2, 3, 5\}$$ and $$\displaystyle B = \{5, 7\}$$, find:
$$B \times A$$
Let $$\displaystyle A = \{ x \in W : x < 2 \}, B = x \in N : 1 < x \leq 4\}$$ and $$\displaystyle C = \{3, 5\}$$. Verify that :
$$\displaystyle A \times (B \cup C) = (A \times B) \cup (A \times C)$$
Let $$\displaystyle A = \{-3, -1\}, B = \{1, 3\}$$ and $$\displaystyle C = \{3, 5\}$$. Find $$\displaystyle A \times B$$, and enter the value of number of elements of it.
If $$\displaystyle A$$ and $$\displaystyle B$$ are nonempty sets, prove that
$$\displaystyle A \times B = B \times A \iff A = B$$.
If $$\displaystyle A = \{5, 7\}$$, find $$\displaystyle A \times A$$ and enter the value of number of elements of it.
If $$\displaystyle A \subseteq B$$, prove that $$\displaystyle A \times C \subseteq B \times C$$ for any set $$\displaystyle C$$.
For any sets $$\displaystyle A, B$$ and $$\displaystyle C$$, prove that:
$$\displaystyle A \times (B - C) = (A \times B)- (A \times C)$$
If $$\displaystyle A \subseteq B$$ and $$\displaystyle C \subseteq D$$ then prove that $$\displaystyle A \times C \subseteq B \times D$$.
Let $$\displaystyle A = \{-3, -1\}, B = \{1, 3\}$$ and $$\displaystyle C = \{3, 5\}$$. Find $$\displaystyle A \times (B \times C)$$ and enter the value of number of elements of it.
For any sets $$\displaystyle A, B$$ and $$\displaystyle C$$, prove that:
$$\displaystyle A \times (B \cap C) = (A \times B)\cap (A \times C)$$
Let $$\displaystyle A = \{-3, -1\}, B = \{1, 3\}$$ and $$\displaystyle C = \{3, 5\}$$. Find $$\displaystyle B \times C$$ and enter the value of number of elements of it.
Lets $$\displaystyle A = \{1, 2\}$$ and $$\displaystyle B = \{2, 3\}$$. Then, write down the no. of all possible subsets of $$\displaystyle A\times B$$.
Let $$\displaystyle A = \{a, b, c, d\}, B = \{c, d, e\}$$ and $$\displaystyle C = \{d, e, f, g \}$$. Then verify each of the following identities:
$$\displaystyle A \times (B \cap C) = ( A \times B ) \cap (A \times C)$$
Let $$ R^+ $$ be the set all positive real numbers.
Let $$ f : R^+ \rightarrow : f(x) = log_ex $$
Find $$ \{x:x \epsilon R^+ and f(x) = -2 \}$$
Let $$ R^+ $$ be the set all positive real numbers.
Let $$ f : R^+ \rightarrow : f(x) = log_ex $$
Find out whether $$f(xy) = f(x) +f (y)$$ for all $$ x, y \epsilon R^+ $$
Let $$\displaystyle A = \{2, 3, 5\}$$ and $$\displaystyle R = \{(2, 3), (2, 5), (3, 3), (3, 5)\}$$.
Show that $$\displaystyle R$$ is a binary relation on $$\displaystyle A$$. Which element is common between domain and range of $$R$$.
Let $$\displaystyle A = \{a, b, c, d\}, B = \{c, d, e\}$$ and $$\displaystyle C = \{d, e, f, g \}$$. Then verify each of the following identities:
$$\displaystyle (A \times B) \cap ( B \times A) = ( A \cap B) \times ( A \cap B)$$
Let $$\displaystyle A = \{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 \}$$ and let $$\displaystyle R = \{(a, b): a, b \in A$$ and $$2a + 3b = 12\}$$.
Express $$\displaystyle R$$ as a set of ordered pairs. Show that $$\displaystyle R$$ is a binary relation on $$\displaystyle A$$.
Which element is common between domain and range.
Let $$\displaystyle A = \{a, b, c, d\}, B = \{c, d, e\}$$ and $$\displaystyle C = \{d, e, f, g \}$$. Then verify each of the following identities:
$$\displaystyle A \times (B - C) = (A \times B ) - ( A \times C )$$
If $$ f(x) = x^3 $$, find the value of $$ \frac{ {f(5) - f(1) } }{ (5-1)} .$$
If $$ f(x) = \dfrac {x+1}{x-1} $$ then show that $$ f[\left\{ f(x) \right\} ]=x$$
Let $$\displaystyle R $$ be a relation on $$\displaystyle Z $$, defined by $$\displaystyle (x, y) \in R \iff x^2 + y^2 = 9$$. Then, write $$\displaystyle R $$ as set of ordered pairs. How many elements are there in its domain?
If $$ f(x) = \frac {x-1}{x+ 1} $$ then show that $$ f( \frac {1}{x}) = - f(x) $$
If $$ f(x) = x^3 - \frac {1}{x^3} $$ then show that $$ f(x) + f( \frac {1}{x}) = 0 $$
Find the domain and range of $$ f(x) = \dfrac {1}{x} $$.
If $$ f (x) =x^2 - 3x + 4 $$ and $$ f(x) = f(2x+ 1) $$, find the values of $$x $$.
If $$ f(x) = \frac {1}{(1-x)} $$ then show that $$ f[f\left\{ f(x) \right\} ]=x$$
If $$ f(x) = \dfrac {x-1}{x+ 1} $$ then show that $$ f ( \frac {-1}{x} ) = \frac {-1}{f(x)} $$
If $$ f(x) = \frac {1}{(2x+ 1)} and x \neq \frac {-1}{2} $$ then prove that $$ f\left\{ f(x) \right\} = \frac {2x+ 1}{2x+ 3} $$, when it is given that $$ x \neq \frac {-3}{2} $$
If $$\displaystyle A = \{5 \}$$ and $$\displaystyle B = \{5, 6\}$$, write down all possible subsets of $$\displaystyle A \times B$$.
Prove that $$\displaystyle A \times B = B \times A \implies A = B$$.
Let $$\displaystyle A = \{ a, b\}$$. List all relations on $$\displaystyle A$$ and find their number.
Find the domain and range of $$ f(x) = \dfrac {1}{2 -sin x} $$
Let $$\displaystyle R = \{( x, x^2) : x $$ is a prime number less than $$\displaystyle 10 \}$$.
Find dom $$\displaystyle (R)$$ and range $$\displaystyle (R)$$.
Find the domain and range of $$ f(x) = \dfrac {x-3}{2-x} $$.
Let $$\displaystyle A = \{1, 2, 3\}$$ and $$\displaystyle B = \{4\}$$.
How many relations can be defined from $$\displaystyle A $$ to $$\displaystyle B$$?
Find the domain and range of $$ f(x) = \dfrac {x^2 -16}{x -4} $$.
Find the domain and range of $$ f(x) = \dfrac {x^2 -9}{x- 3}$$
Let $$\displaystyle A$$ and $$\displaystyle B$$ be two nonempty sets.
What do you mean by the domain and range of a relation?
Number of positive integers $$ x $$ for which $$ f(x)=x^{3}-8 x^{2}+20 x-13 $$ is a prime number is.
Let $$\displaystyle A = \{ 1, 3, 5, 7\}$$ and $$\displaystyle B = \{2, 4, 6, 8\}$$.
Let $$\displaystyle R = \{(x, y) : x \in A, y \in B \ and \ x > y \}$$.
Find dom $$\displaystyle (R)$$ and range $$\displaystyle (R)$$.
Find the domain and range of each of the relations given below:
$$\displaystyle R = \{ (x, y) : x + 2y = 8$$ and $$\displaystyle x, y \in N\}$$.
Find the domain and range of each of the relations given below:
$$\displaystyle R = \{ (x, y) : y = |x - 1|, x \in Z$$ and $$\displaystyle |x|\leq 3\}$$.
Define a relation $$\displaystyle R$$ from $$\displaystyle Z $$ to $$\displaystyle Z $$, given by
$$\displaystyle R = \{ (a, b) : a, b \in Z $$ and $$\displaystyle (a - b)$$ is an integer $$\displaystyle \}$$.
Find dom $$\displaystyle (R)$$ and range $$\displaystyle (R)$$
Let $$\displaystyle A = \{ 2, 4, 5\}$$ and $$\displaystyle B = \{1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8\}$$.
Let $$\displaystyle R = \{(x, y) : x \in A, y \in B \ and \ x$$ divides $$\displaystyle y \}$$.
How many common elements are there between dom $$\displaystyle (R)$$ and range $$\displaystyle (R)$$.
Let $$\displaystyle A$$ and $$\displaystyle B$$ be two nonempty sets.
What do you mean by a relation from $$\displaystyle A$$ to $$\displaystyle B$$?
Let $$f : R \rightarrow R f(x^2 + x + 3) + 2f(x^2 - 3x + 5) = 6x^2 - 10x + 17 \space \forall \space x \epsilon \space R$$, then the value of f(5) is
If $$R=\left \{ \left ( x,y \right ):x+2y=8 \right \}$$ is a relation on $$N$$, write the range of $$R$$.
Let $$A=\left\{a,b,c \right\}$$ and the relation $$R$$ be define on $$A$$ as follows:
$$R=\left\{(a,a),(b,c),(a,b)\right\}$$.
Then, write the minimum number of ordered pairs to be added in $$R$$ to make $$R$$ reflexive and transitive.
If $$f:R \rightarrow R$$ is defined by $$f(x)=x^2-3x+2$$, find $$f(f(x))$$
Let R be a relation from N to N defined by R = {(a, b) : a, b $$\epsilon$$ N and a = $$b^2$$}. Are the following true?
(ii) (a, b) $$\epsilon$$ R, implies (b, a) $$\epsilon$$ R
Let A = {1, 2, 3...14}. Define a relation R from A to A by R = {(x, y) : 3x - y = 0}, where x, y $$\epsilon$$ A. Write down its domain, codomain and range.
Show that the relation $$R$$ in the set
$$A=\left\{ x \in Z :0 \le x \le 12 \right\}$$, given by
$$R=\left\{ (a, b): | a-b| \ is\ a\ multiple\ of\ 4 \right\}$$
Is $$g=\left\{(1,1),(2,3),(3,5),(4,7) \right\}$$ a function? If $$g$$ is described by $$g(x)=\alpha x +\beta$$, then what value should be assigned to $$\alpha$$ and $$\beta$$.
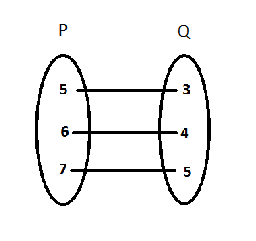
The given figure shows a relationship between the sets P and Q. Write this relation
(i) in set-builder for.
(ii) in roster form.
What is its domain and range?
If $$f: R\to R$$ is defined by $$f(x)=x^2 -3x+2$$, write $$f(f(x))$$.
Let R be a relation from N to N defined by R = {(a, b) : a, b $$\epsilon$$ N and a = $$b^2$$}. Are the following true?
(i) (a,a) $$\epsilon$$ R, for all a $$\epsilon$$ N
Let R be a relation from N to N defined by R = {(a, b) : a, b $$\epsilon$$ N and a = $$b^2$$}. Are the following true?
(iii) (a, b) $$\epsilon$$ R, (b, c) $$\epsilon$$ R implies (a, c) $$\epsilon$$ R.
Justify your answer in each case.
If $$A=\left\{1,2,3 \right\}$$ and $$f, g$$ are relation corrosponding to the subset of $$A\times A$$ indicated against them, which of $$f, g$$ is a function? Why?
$$f=\left\{(1,3),(2,3),(3,2)\right\}$$
$$g=\left\{(1,2),(1,3),(3,1)\right\}$$
If $$R$$ is the set of all real numbers, what do the Cartesian products $$R \times R$$ and $$R \times R \times R$$ represent?
Let $$A=\left\{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6\right\}$$. Define a relation $$R$$ from $$A$$ to $$A$$ by $$R =\left\{(x, Y): y=x+1\right\}$$
Write down the domain, condomain and range of $$R$$
If $$(x+1, y-2)=(3, 1)$$, find the values of $$x$$
Let $$A=\left\{ 1, 2, 3,.......14\right\}$$. Define a relation $$R$$ from $$A$$ to $$A$$ by $$R =\left\{ (x, y):3x-y=0, x, y \in A\right\}$$. Write down its domain, co-domain and range.
Define range of a relation.
If $$P=\left\{ a, b, c \right\}$$ and $$Q=\left\{ r \right\}$$, from $$P \times Q$$ and $$Q \times P$$. Are these two products equal?
Define ordered pair.
Define domain of a relation.
If $$\left( \dfrac x3+1, y-\dfrac 23 \right)=\left( \dfrac 53, \dfrac 13 \right)$$ find x and y
Let $$A=\left\{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 \right\}$$. Let $$R$$ be the relation on $$A$$ defined by $$\left\{(a, b): a, b \in A, b\right.$$ is exactly divisible by $$a\left. \right\}$$,
Find the domain of $$R$$
Let $$R$$ be a relation from $$Q$$ to $$Q$$ defined by $$R=\left\{(a, b)\ a, b\in Q\right.$$ and $$\left.a-b \in Z \right\}$$. Show that $$(a, a)gR$$, for all $$a \in Q$$
If A = {1 , 2 , 3} B = { 4 , 5 , 6} , then which of the following is relation from A to B ? Justify your answer also.
$$ {( 1 , 6) , (2 , 6) ( 3 , 6) } $$
Let $$A=\left\{ \right.1, 2, 3, 4), B=\left\{1, 5, 9, 11, 15, 16\right\}$$ and $$f=\left\{ (1, 5), (2, 9), (3, 1), (4, 5), (2, 11)))\right.$$.
Is the following true?
$$f$$ is a relation from $$A$$ to $$B$$
Justify your answer.
If A = {1 , 2 , 3} B = { 4 , 5 , 6} , then which of the following is relation from A to B ? Justify your answer also.
$$ ( 1 , 4), (3 , 5), (3 , 6 )$$
Let $$N$$ be the set of natural numbers and the relation $$R$$ be defined on $$N$$ such that $$R=\left\{ (x, y):y=2x, x, y\in N \right\}$$. What is the domain, co-domain and range of $$R$$?
Is this relation a function?
If A = {1 , 2 , 3} B = { 4 , 5 , 6} , then which of the following is relation from A to B ? Justify your answer also.
$$ { (1 , 5), ( 3 , 4) ( 5 , 1), (3 ,6)} $$
Let $$A=\left\{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 \right\}$$. Let $$R$$ be the relation on $$A$$ defined by $$\left\{(a, b): a, b \in A, b\right.$$ is exactly divisible by $$a\left. \right\}$$,
Find the range of $$R$$
Express the following relation in the rules from defined in N:
$$ {(2 , 3) , ( 4 , 2) , (6 , 1) , } $$
If a relation $$ \phi$$ RR from set C of complex numbers to a set R of real numbers is so defined that $$ x \phi y \Leftrightarrow |x| = y $$
$$ ( 1 + i) \phi 3 $$
Express the following relation in the rules from defined in N:
$$ {(1 , 3) , ( 2 , 5) , (3 , 7) , (4 , 9).........} $$
In in a set of integers Z , a relation R is defined in such a way that $$ x Ry \Leftrightarrow x^{2} + y^{2} = 25 $$ , then write R and $$ R^{-1}$$ in the from of a set order pairs and also write their domain .
If a relation $$ \phi $$ RR from set C of complex numbers to a set R of real numbers is so defined that $$ x \phi y \Leftrightarrow |x| = y $$
$$ 3 \phi (-3) $$
If a relation $$ \phi $$ RR from set C of complex numbers to a set R of real numbers is so defined that $$ x \phi y \Leftrightarrow |x| = y $$
$$ ( 2 + 3i) \phi 13 $$
If A = {1 , 2 , 3} B = { 4 , 5 , 6} , then which of the following is relation from A to B ? Justify your answer also.
$$ {( 2 , 4), (2 , 6)( 3 , 6)( 4 , 2)}$$
A relation R from set A = { 2 , 3 , 4 , 5) to set B = { 3 , 6 , 7 , 10 } is defined in such a way that $$ xRY \Leftrightarrow x $$ is a prime number related to y . Write relation R in the set from order pairs and also fined domain and range of if.
If A = {1 , 2 , 3} B = { 4 , 5 , 6} , then which of the following is relation from A to B ? Justify your answer also.
$$ A \times B $$
Express the following relation in the rules from defined in N:
$$ {(2 , 1) , ( 3 , 2) , (4 , 3) ,( 5 , 4)....... }$$
Express the following relations in the from of sets or orders pairs :
$$ R_{2} $$ is relation from set A = {8 ,9 , 10 , 11 } to set B = (5 , 6 , 7 8} such that " y = x - 2
If $$f : R \rightarrow R , f (x) = x^{2} ,$$ then find
$$\{ x | f (x) = 4 \}$$
If f : R \rightarrow R , f (x) = x^{2} ,$$ then find
{ y | f (y) = - 1 }
Any relation P is defined in set R0 of non zero real numbers by following ways :
$$ xPy \Leftrightarrow x^{2} + y^{2} = 1 $$
If a relation $$ \phi $$ RR from set C of complex numbers to a set R of real numbers is so defined that $$ x \phi y \Leftrightarrow |x| = y $$
$$ ( 1 + i) \phi 1 $$
Express the following relations in the from of sets or orders pairs :
$$ R_{1} $$ is relation from set A = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 } to set B = (1 , 2 , 3} such that "x = 2y "
Express the following relations in the from of sets or orders pairs :
$$ R_{3} $$ is relation from set A = {0 , 1 , 2......10} defined by 2x + 3y = 12.
Any relation P is defined in set R0 of non zero real numbers by following ways :
$$ xPy \Leftrightarrow + xy = 1 $$
Any relation P is defined in set $$R_o$$ of non zero real numbers by following ways :
$$ xPy \Leftrightarrow ( x + y) $$ is a rational number.
Express the following relations in the from of sets or orders pairs :
$$ R_{3} $$ is relation from set A = {5 , 6 , 7 ,8} to set B = { 10 , 12 , 15 , 16 , 18} is defined such that "x is divisor of y''
If A = { 1 ,2} , then write all non - zero relations defined in A.
Find the domain and range of the following relations
$$ R_{1} = \left \{ ( x ,y) : x , y \in N , x + y = 10\right \} $$
In the set of real numbers R , two relations $$R_{1} and R_{2}$$ can be defines as
$$ aR_{1}b \Leftrightarrow a - b >0 $$
In the set of real numbers R , two relations $$R_{1} and R_{2}$$ can be defines as
$$ aR_{2}b \Leftrightarrow |a| \leq b $$
In the set of real numbers R two , relations $$ R_{1} and R_{2}$$ are defined as
$$ aR_{1}b \Leftrightarrow |a| = |b| $$
Find the domain and range of the relaton R
$$ R = { ( x + 1, x + 5)} : x \in { 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5} $$
Solve :
$$f(x) = 5 - 3x $$
Find $$f(16)$$.
In the set of real numbers R two , relations $$ R_{1} and R_{2}$$ are defined as
$$ aR_{1}b \Leftrightarrow |a| \leq |b| $$
If statement is $$P(n): (n+ 3) < 2^{n+3}$$ then write $$P(4)$$.
Given $$A = \{5, 6, 7\}$$ and $$B = \{6, 8, 10\}$$, then : $$(A \cup B)\times B$$Find the number of elements in the above set obtained.
If $$A = \{5, 6, 7, 8\}$$ and $$B =\{6, 8, 10\}$$ find total elements in $$(A \cup B) \times (A \cap B)$$.
If the ordered pairs $$(a - 3, a + 2b)$$ and $$(3a - 1, 3)$$ are equal, find the value of $$a+b$$.
Given $$A = \{2, 3, 5\}$$ and $$B = \{6, 10, 14, 18\}$$ ; find the number of elements in relation $$R$$ such that $$R=\{(x, y) \,\,\epsilon\,\, A \times B,x < y \text{ and }\displaystyle \frac{y}{x} \,\,\epsilon \,\,N \}$$
If $$M=\{x : x \,\,\epsilon\,\, N, 1 < x \leq 4\}$$ and $$N = \{y : y\,\,\epsilon\,\,W, y < 3\}$$; find : N $$\times$$ MAlso find the number of such ordered pairs.
Let $$f:R-\left\{ 1 \right\} \rightarrow R$$ be defined $$f(x)=\cfrac { x+1 }{ x-1 } $$, show that $$f(x)+f\left( \cfrac { 1 }{ x } \right) =0$$ for $$\left( x\neq 0 \right) $$.
If $$f(x) = 2e^{x} - c\ ln\ x$$ monotonically increases for every $$x\epsilon (0, \infty)$$, then the true set of values of $$c$$ is ?
If $$f\left( x \right) = \cos \left( {\log x} \right)$$, than show that $$f\left( {\frac{1}{x}} \right).f\left( {\frac{1}{y}} \right) - \frac{1}{2}\left[ {f\left( {\frac{x}{y}} \right) + \left( {xy} \right)} \right]$$
Solve : $$f(x) = \dfrac{x^2 +2}{x^2 + 4}$$
If $$f\left(x\right)=x+2,\,g\left(x\right)={x}^{2}-x-2,$$ then find $$\dfrac{g\left(1\right)+g\left(2\right)+g\left(3\right)}{f\left(-4\right)+f\left(-2\right)+f\left(2\right)}$$
Find the range of $$f\left(x\right)={\sin}^{-1}{\left(\ln{\left[x\right]}\right)}+\ln{\left({\sin}^{-1}{\left[x\right]}\right)},$$ where $$\left[x\right]$$ is the greatest function.
If f(x) = $$\frac{x + 1}{x - 1}$$; then f($$\frac{1}{2}$$)
If f(x) = $$\frac{x + 1}{x - 1}$$; then f($$\frac{1}{2}$$)=
Let $$f : R-\{2\} \rightarrow R$$ be defined by $$f(x)=\dfrac{x^{2}-4}{x-2}$$and $$g: R \rightarrow R$$ be defined by $$g(x)=x+2$$ . Find whether $$f \equiv g$$ or not.
Let f(x)=$$\frac{ax+b}{cx+d}$$.Then fof(x)=x provided that.
What do you mean by a binary relation on a set $$\displaystyle A$$?
Define the domain and range of a relation on $$\displaystyle A$$.
For any sets $$\displaystyle A$$ and $$\displaystyle B$$, prove that:
$$\displaystyle (A \times B) \cap ( B \times A) = (A \cap B) \times (B \cap A)$$.
Let $$\displaystyle A = \{ 2, 3, 4, 5\}$$ and $$\displaystyle B = \{3, 6, 7, 10\}$$.
Let $$\displaystyle R = \{(x, y) : x \in A, y \in B $$ and $$\displaystyle x $$ divides $$\displaystyle y \}$$.
Which element is common between the domain and range?
If $$ A = \left( \begin{array} { l l } { 1 } & { 2 } \\ { 3 } & { 4 } \end{array} \right) \& f ( x ) = x ^ { 2 } - 3 x + 2 . $$ find f ( A )
Let $$\displaystyle A = \{ 1, 2, 3, 4, 6\}$$ and let $$\displaystyle R = \{(a, b) : a, b \in A $$ and $$\displaystyle a $$ divides $$\displaystyle b \}$$.
Enter 1 if both dom $$\displaystyle (R)$$ and range $$\displaystyle (R)$$ are same else enter 0
Let $$\displaystyle A = \{2, 3 \}$$ and $$\displaystyle B = \{ 3, 5 \}$$.
How many relations can be defined from $$\displaystyle A $$ to $$\displaystyle B $$?
Let $$\displaystyle A = \{ 1, 2, 3, 5, 6\}$$
Define a relation $$\displaystyle R $$ from $$\displaystyle A $$ to $$\displaystyle A $$ by $$\displaystyle R = \{ (x, y) : y = x + 1 \}$$. How many common elements are there in between dom $$\displaystyle (R)$$ and range $$\displaystyle (R)$$.
Let $$\displaystyle R = \{ (x, y): x, y \in Z$$ and $$\displaystyle x^2 + y^2 \leq 4 \}$$.
Enter 1 if dom $$\displaystyle (R) $$ and range $$\displaystyle (R)$$ are same else enter 0
Let $$ fx=\begin{cases} x^{ 2 }-4x+3,\quad x<3 \\ x-4,\quad x\geq 3 \end{cases}\quad and\quad g(x)=\begin{cases} x-3,\quad x<4 \\ x^{ 2 }+2x+2,\quad x\geq 4 \end{cases}$$
Describe the function $$ f / g $$ and find its domain.
Let f(x) be a function satisfying the condition f(-x)=f(x) for all real x. if f(0)exists ,find its value
Let $$\displaystyle R = \{(x, x + 5) : x \in \{0,1, 2, 3, 4, 5\} \}$$
Find dom $$\displaystyle (R)$$ and range $$\displaystyle (R)$$. And enter the common element between them.
If $$g(x) = \left\{\begin{matrix} [f(x)], & x \in (0, \pi/2) \cup (\pi / 2, \pi) \\ 3, & x=\pi/2 \end{matrix}\right.$$
and $$f(x) = \dfrac{2(\sin x - \sin^n x) + |\sin x - \sin^n x|}{2(\sin x - \sin^n x) - |\sin x - \sin^n x|}, n \in N$$
Where $$[\cdot]$$ denotes the greatest integer function. Prove that $$g(x)$$ is continuous at $$ x=\pi /2$$ when $$n>1$$.
Consider the set $$A=(1,2,3)$$ and $$R$$ be the smallest equivalence relation on $$A$$, then $$R=$$ ______
Let $$Z$$ be the set of integers and $$R$$ be the relation defined in $$Z$$ such that $$aRb$$ if $$a-b$$ is divisible by $$3$$. Then $$R$$ partitions the set $$Z$$ into ______ pairwise disjoint subsets.
Solve :
$$f(x) = 5 - 3x $$
Find $$ff(x)$$, in its simplest form.
Define a Cartesian product of two sets.
Solve :
$$f(x) = 5 - 3x $$
Find $$ f (x + 2) $$.
If f is a function satisfying
$$f(x + y) = f(x) f(y) \forall x, y \epsilon N$$ such that $$f(1) 3$$ and $$\sum_{x}^{n} = 1 f(x) = 120$$ find the value of n.
Find the natural number a for which $$\sum_{k=1}^{n}f(a + k) = 16(2^n -1)$$, where the function f satisfies the relation f(x+y) = f(x) f(y) for all natural numbers x, y and further f(1) = 2.
Class 11 Engineering Maths Extra Questions
- Binomial Theorem Extra Questions
- Complex Numbers And Quadratic Equations Extra Questions
- Conic Sections Extra Questions
- Introduction To Three Dimensional Geometry Extra Questions
- Limits And Derivatives Extra Questions
- Linear Inequalities Extra Questions
- Mathematical Reasoning Extra Questions
- Permutations And Combinations Extra Questions
- Principle Of Mathematical Induction Extra Questions
- Probability Extra Questions
- Relations And Functions Extra Questions
- Sequences And Series Extra Questions
- Sets Extra Questions
- Statistics Extra Questions
- Straight Lines Extra Questions
- Trigonometric Functions Extra Questions