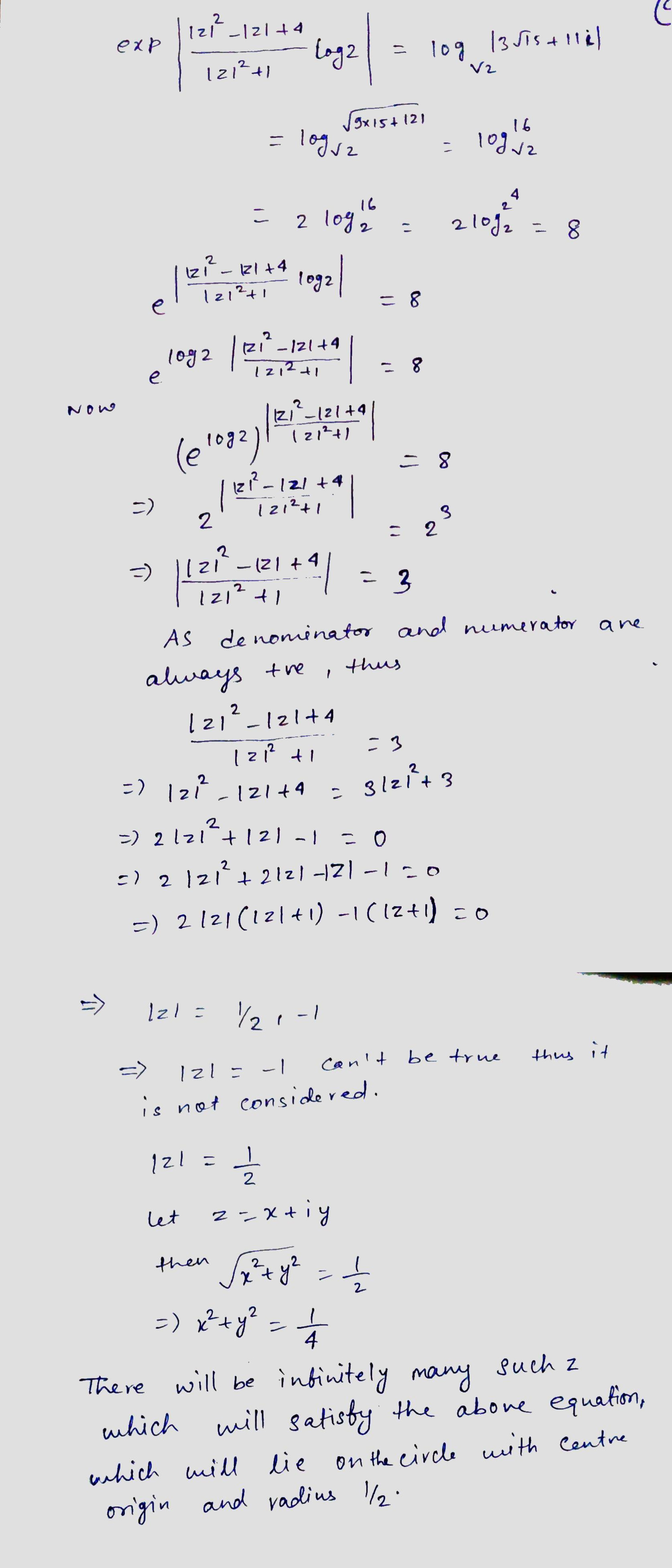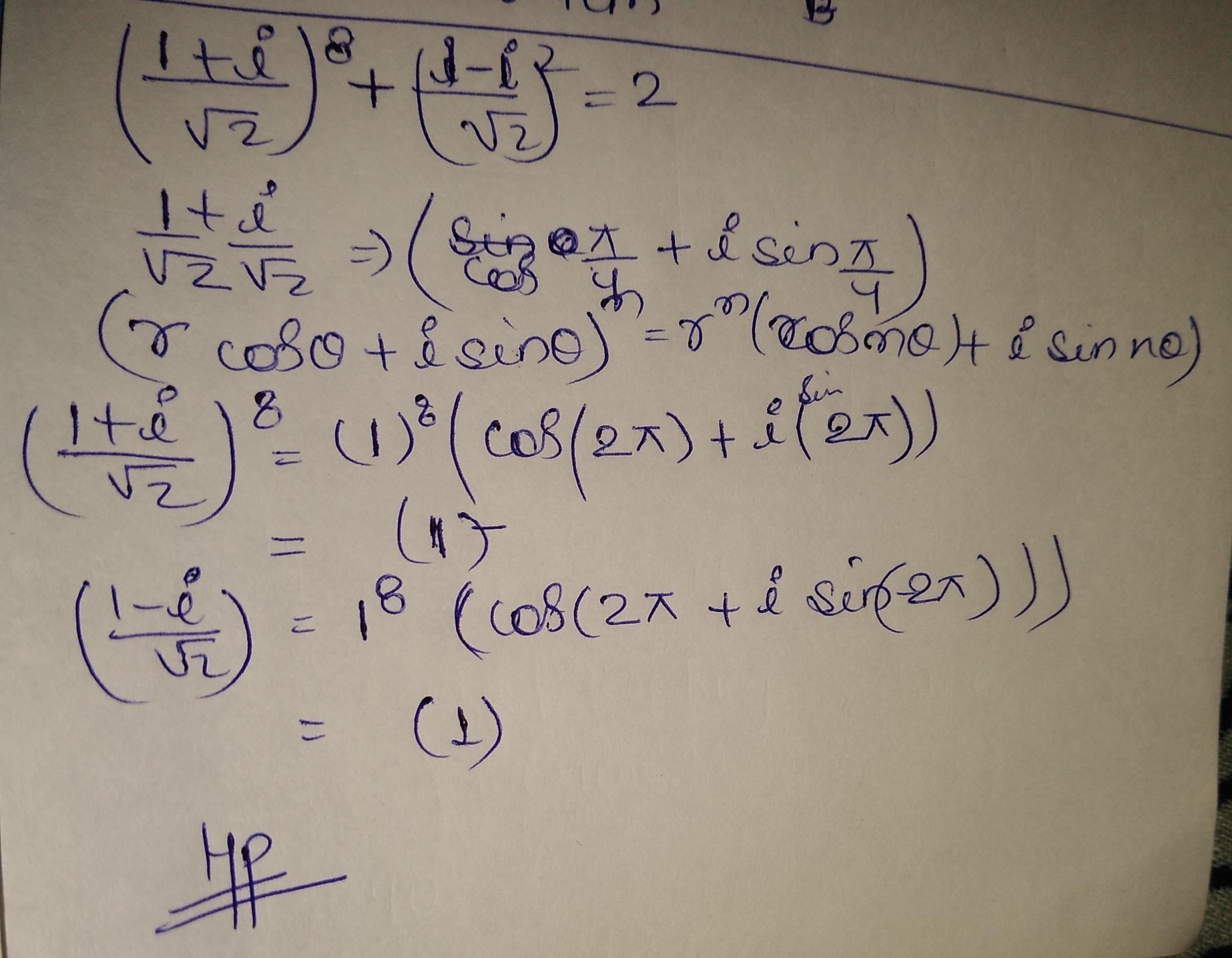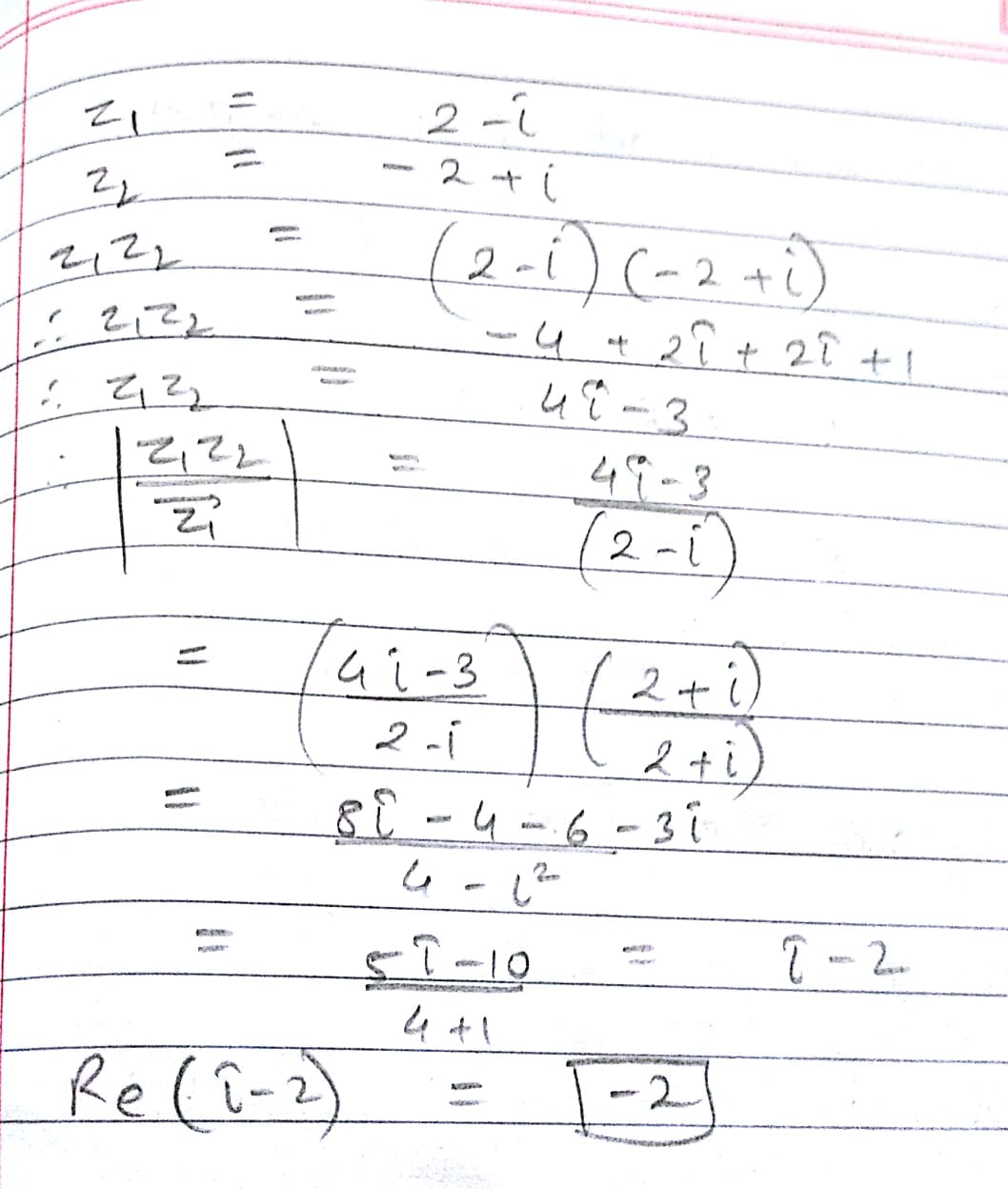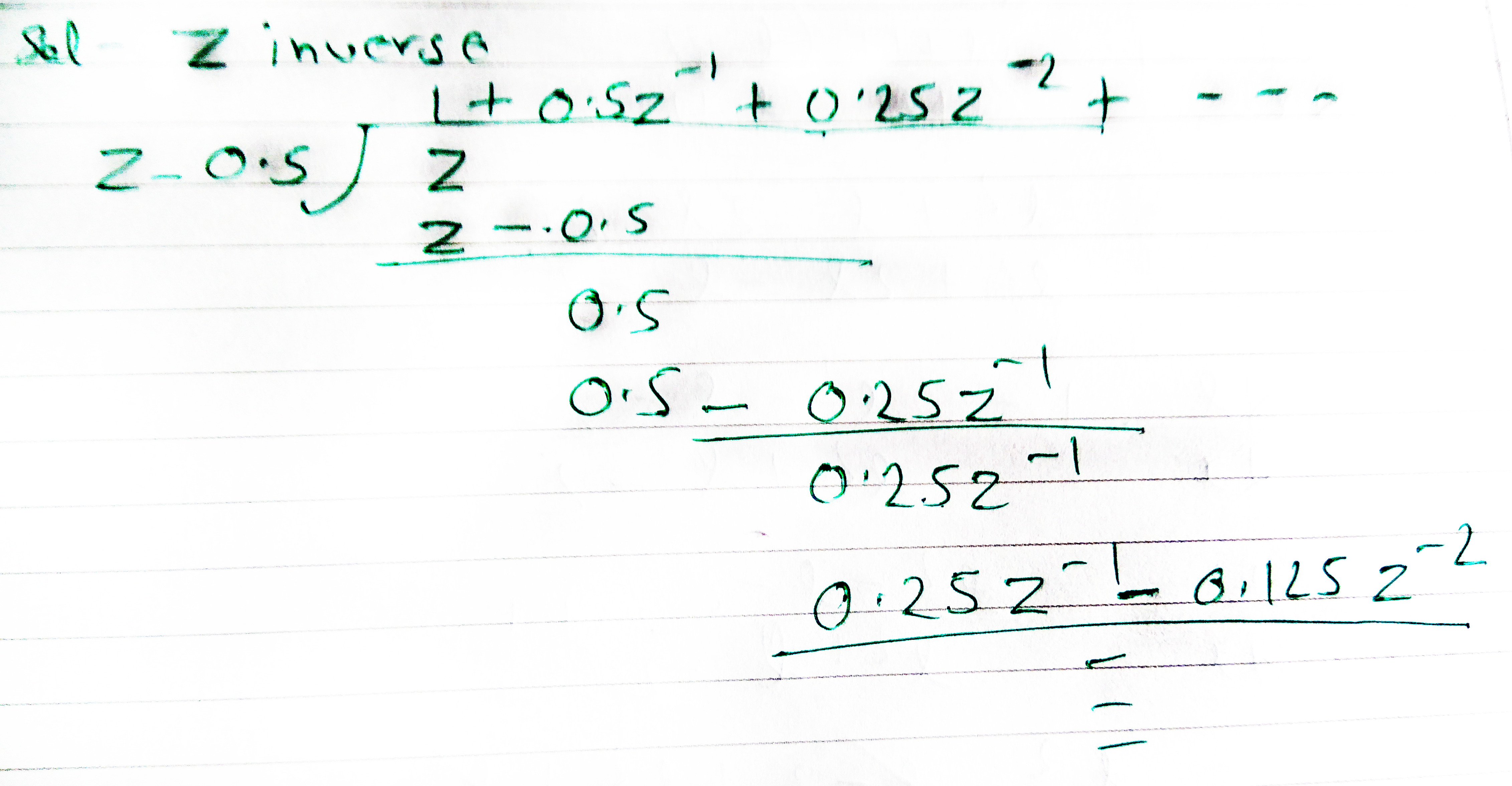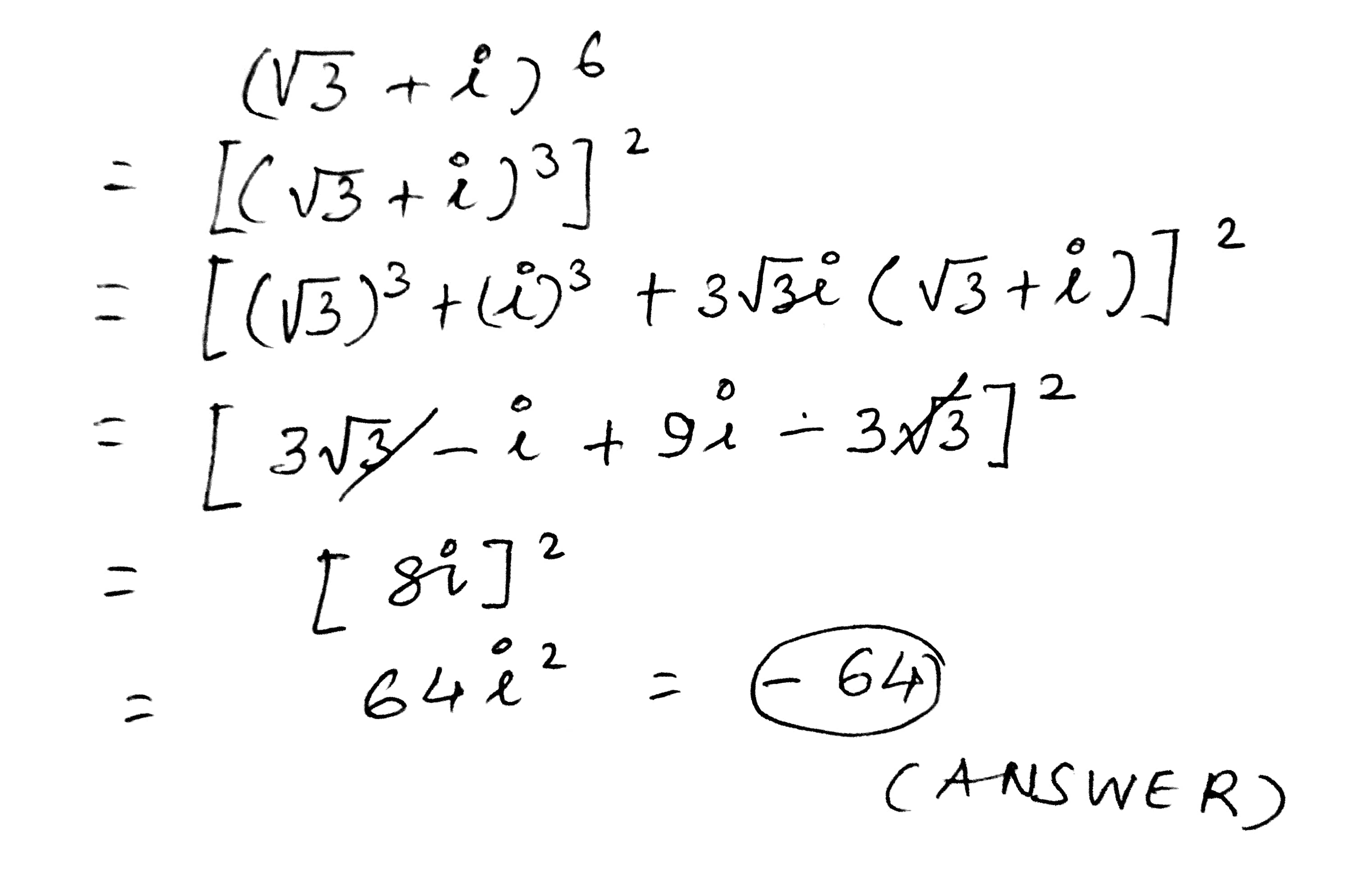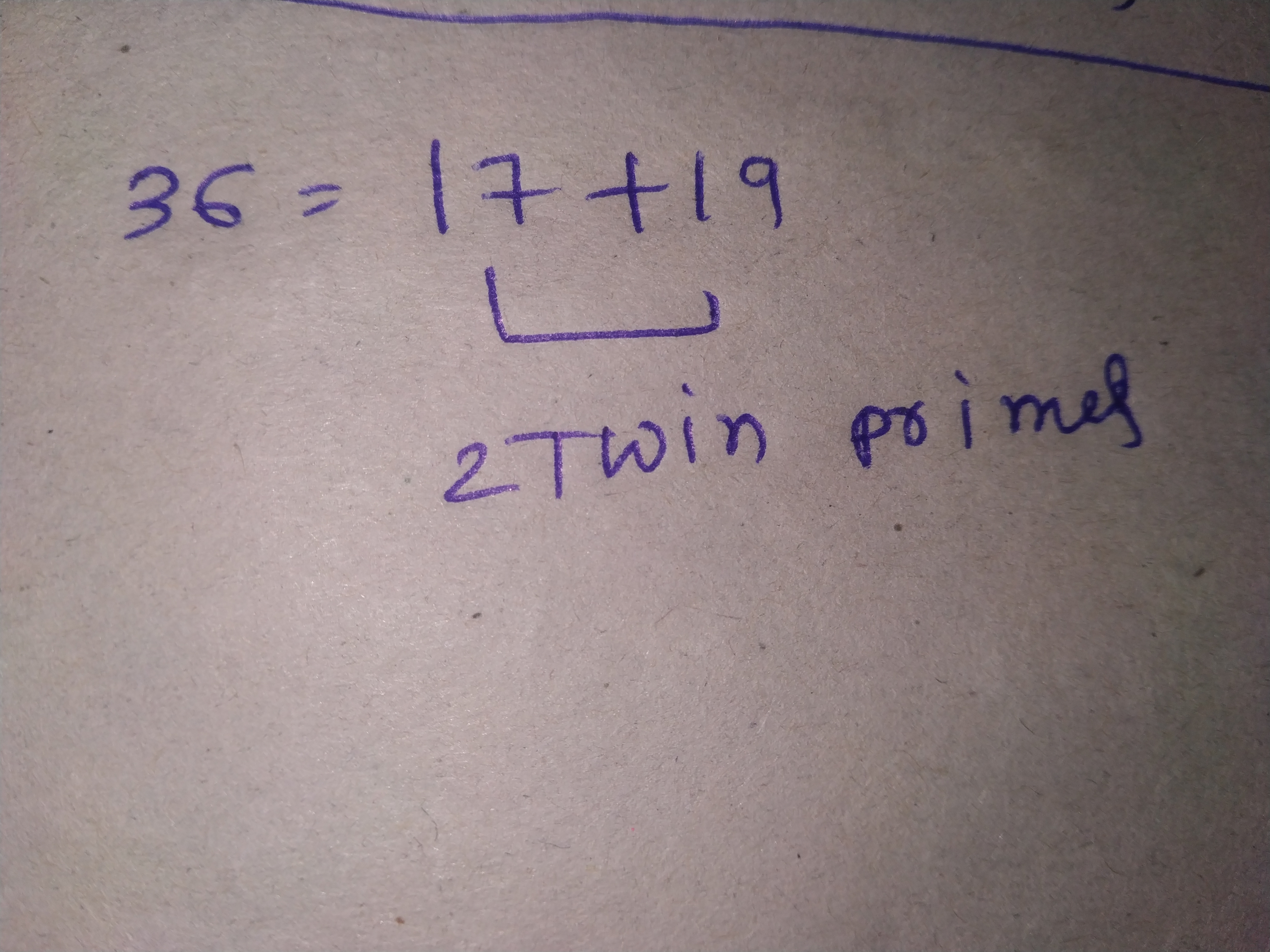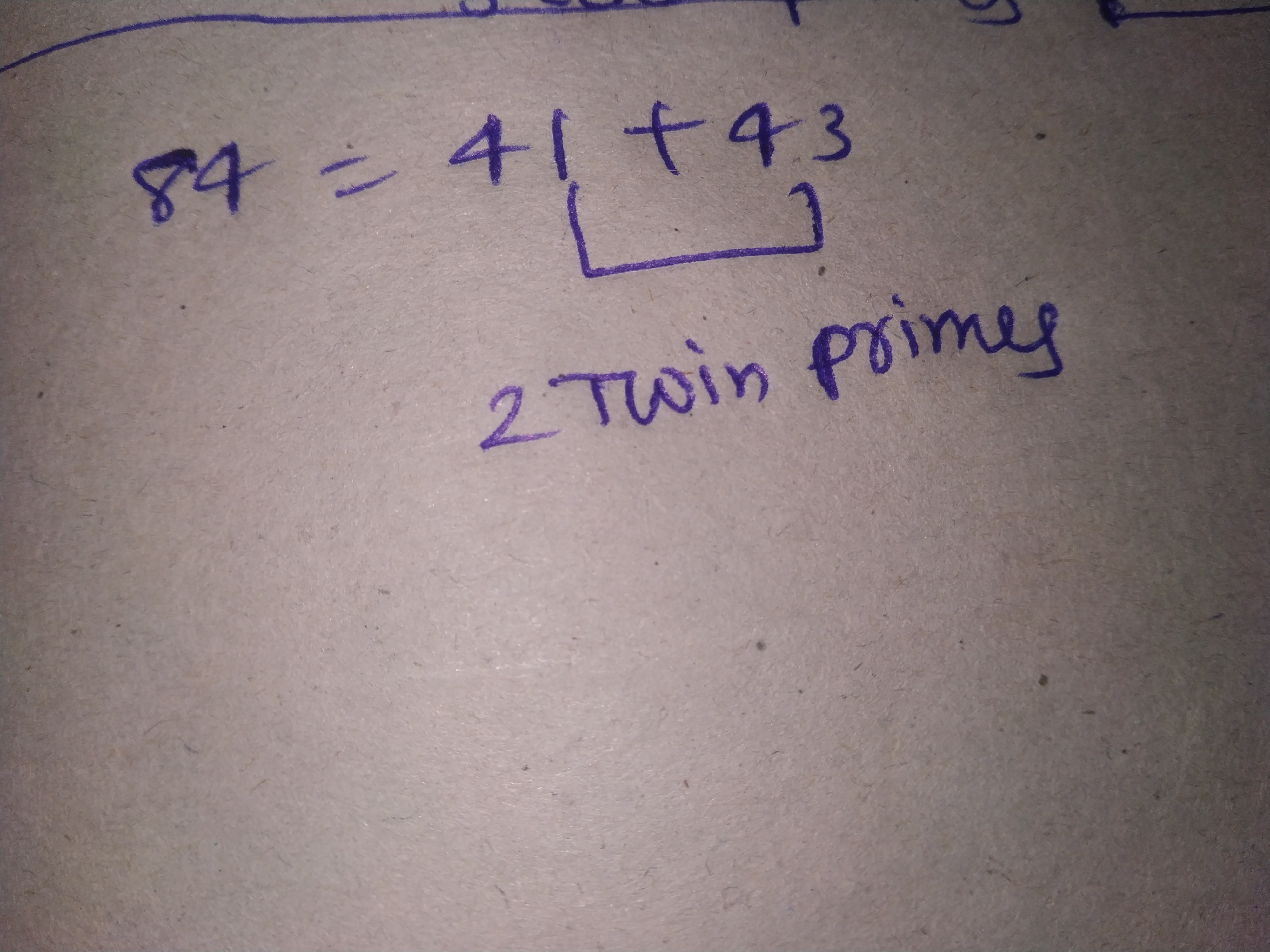Number Theory - Class 11 Commerce Applied Mathematics - Extra Questions
If $$Z_{1}$$ and $$Z_{2}$$ are two complex numbers and $$c> 0,$$ then prove that
$$\left | z_{1}+z_{2} \right |^{2}\leq \left ( 1+c \right )\left | z_{1} \right |^{2}+\left ( 1+c^{-1} \right )\left | z_{2} \right |^{2}$$
Let $$z_{1}$$ and $$z_{2}$$ be complex numbers such that $$z_{1}\neq z_{2}$$ and $$\left | z_{1} \right |=\left | z_{2} \right |.$$ If $$z_{1}$$ has positive real part and $$z_{2}$$ has negative imaginary part, then show that $$\displaystyle \frac{z_{1}+z_{2}}{z_{1}-z_{2}}$$ is purely imaginary.
Multiply $$3\sqrt { -7 } -5\sqrt { -2 } $$ by $$3\sqrt { -7 } +5\sqrt { -2 } $$
Find the modulus of complex number $$-2+2\sqrt{3}i$$.
Compute :
$$(1 \, + \, i)^{-1}$$
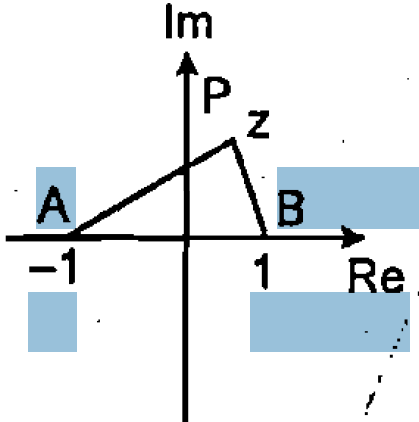
Locate the points representing the complex number for which $${ \log }_{ 1/2 }\dfrac { \left| z-1 \right| +4 }{ \left| z-1 \right| -2 } >1$$
compute.
$$[ (cos \theta \, + \, i \, sin \, \theta ) (\, cos \theta \, - \, i sin \theta ) ] = ?$$
Prove the identity,$$|1+z_1\bar{z_2}|^2+|z_1-z_2|^2=(1+|z_1|^2)(1+|z_2|^2)$$
Solve $$\left(\dfrac{1+i}{1-i}\right)^{24}$$
Prove the identity $$|1-z_1{z_2}|^2-|z_1-z_2|^2=(1-|z_1|^2)(1-|z_2|^2)$$
The HCF of two or more prime numbers is always __________
If $$\left( {a + ib} \right)\left( {c + id} \right) = A + iB$$, then show that $$\left( {{a^2} + {b^2}} \right)\left( {{c^2} + {d^2}} \right) = {A^2} + {B^2}$$.
If $$(a+ib)(c+id)=A+iB$$, then show that $$({a^2} + {b^2})({c^2} + {d^2}) = {A^2} + {B^2}$$
Define and Give one example of each :
a) Parallel lines
b) Intersecting lines
c) Perpendicular line
d) Prime Number
e) Twin Prime
f) Even Number
Find the values of the following:
$$(1+i\sqrt {3})^{3}$$
Find the value of $${(-1+\sqrt{-3})}^{2}+{(-1-\sqrt{-3})}^{2}$$.
Find the modules and the argument of the complex no $$Z=1+i$$
If $$a = \frac{{ - 1 + \sqrt {3i} }}{2}$$ , $$b = \frac{{ - 1 - \sqrt {3i} }}{2}$$ then show that $$\,\,{a^2} = b$$ and $$\,\,{b^2} = a$$.
$$z=2+3i$$ find $$|z|$$
Find the principal arguments of the following Complex Number
(i) $$5 + 5i$$
If $${z_1},{z_2} \in C,$$ then $$\left| {\dfrac{{{z_1}}}{{{z_2}}}} \right|$$.
Let $$Z = x + iy$$ and $$\omega = \dfrac {1 - iZ}{Z - i}$$. If $$|\omega| = 1$$, show that $$Z$$ is purely real.
Find the modulus of $$\frac{{1 + i}}{{1 - i}} - \frac{{1 - i}}{{1 + i}}$$
Solve: $$x^2 - (3\sqrt{2} - 2i)x - \sqrt{2}i = 0$$
State whether the given statement is true or false $$\overline{(z^{-1})} \, = \, (\bar{z})^{-1}$$
Express $$\dfrac{{5 + i\sqrt 2 }}{{2i}}$$ in the form of $$x + iy$$.
If $$\dfrac{{{{\left( {1 + i} \right)}^2}}}{{2 - i}} = x - iy,$$ then find the value of $$x + y$$.
Find the real and imaginary parts of the complex number z=$$\dfrac{3i^{20}-i^{19}}{2i-1}$$
If $${\left( {\frac{{1 + i}}{{1 - i}}} \right)^3} - {\left( {\frac{{1 - i}}{{1 + i}}} \right)^3} = x + iy$$, then find $$(x,\,y)$$,
For the complex number$$\sqrt { 37 } + \sqrt { - 19 }$$.Real part is $$\sqrt 37$$ and imaginary is $$\sqrt 19$$Enter 1 if true or 0 for false
What are twin-primes ?
Express the following in the form of a = ib, a,b$$\epsilon$$R $$i = \sqrt{-1}$$. State the values of a and b.
$$(1 + 2i)(-2 + i)$$
If ABC are angles of a triangle such that x = cis A, y = cis B, z = cis C, then find value of xyz
Give three pairs of prime numbers whose difference is $$2$$. [Remark: Two prime numbers whose difference is $$2$$ are called twin primes].
If $$z \neq 0$$ is a complex number,then prove that $$Re(z) = 0 \Longrightarrow Im(z^2)=0$$.
If $$(a + ib) (c + id) (e + if)(g +ih) = A + iB$$, then prove that $$(a^2 + b^2) (c^2 + d^2)(e^2 + f^2)(g^2 + h^2) = A^2 + B^2$$.
If $$z = x + iy$$ and $$w = \dfrac{(1 - iz)}{(z - i)}$$ and $$\left|w\right| = 1$$, then prove that $$z$$ is purely real.
If $$(x+iy)^3=u+iv$$, then prove that $$\displaystyle \frac{u}{x}+\frac{v}{y} =4(x^2 - y^2)$$.
If $$z_1$$ and $$z_2$$ are complex numbers and $$u = \sqrt{z_1z_2}$$, then prove that
$$\left|z_1\right| + \left|z_2\right| = \left|\displaystyle \frac{z_1 + z_2}{2}+u\right| + \left|\displaystyle \frac{z_1 + z_2}{2}-u\right|$$.
If $$ \left|z_1 + z_2\right| = \left|z_1\right| + \left|z_2\right|$$, then show that $$arg(z_1) = arg(z_2)$$.
If $$\left|z_1 - z_2\right| = \left|z_1\right| + \left|z_2\right|$$, then prove that $$arg(z_1) - arg (z_2) = \pi$$ . I
Find the minimum value of $$\left | 1+z \right |+\left | 1-z \right |.$$
$$2^{i}=e^{i(lnx)}$$.
Compute the modulus of complex number $$z=\sqrt5-2i$$
If $$\displaystyle a+ib=\dfrac { { \left( x+i \right) }^{ 2 } }{ { 2x }^{ 2 }+1 } $$, prove that $$\displaystyle { a }^{ 2 }+{ b }^{ 2 }=\dfrac { { \left( { x }^{ 2 }+1 \right) }^{ 2 } }{ { \left( 2x^2+1 \right) }^{ 2 } } $$.
Express $$\cfrac{2+i}{(1+i)(1-2i)}$$ in the form of $$a+ib$$. Find its modulus and argument.
Find the real and imaginary parts of the complex number $$\dfrac {a + ib}{a - ib}$$
Find the number of integral solution of $$(1-i)^x=2^x$$.
If $$z$$ and $$\alpha$$ complex numbers such that $$|z| = |\alpha| = r, r > 0$$ and $$\omega = \dfrac {z - \overline {\alpha}}{r^{2} + z\overline {\alpha}}$$, find $$Re(\omega)$$.
If the ratio $$\left (\dfrac {1 - z}{1 + z}\right )$$ is purely imaginary, then find value of $$|z|$$.
If $$a=\cfrac { 1+i }{ \sqrt { 2 } } $$, find the value of $${ a }^{ 6 }+{ a }^{ 4 }+{ a }^{ 2 }+1$$
If $$\left| { z }_{ 1 } \right| =2,\left| { z }_{ 2 } \right| =3,\left| { z }_{ 3 } \right| =4$$ and $$\left| 2{ z }_{ 1 }+3{ z }_{ 2 }+4{ z }_{ 3 } \right| =10$$, then absolute value $$8{ z }_{ 2 }{ z }_{ 3 }+27{ z }_{ 3 }{ z }_{ 1 }+64{ z }_{ 1 }{ z }_{ 2 }$$ must be equal to-
Find the points of the plane which satisfy the following equations.
$$\displaystyle \left | \, \frac{z \, - \, 2}{z \, + \, 3} \, \right | \, = \, 1.$$
Find the points of the plane which satisfy the following equations.
$$\displaystyle \left | \, \frac{z \, + \, i}{z \, - \, 3i} \, \right | \, = \, 1.$$
Simplify the following :
$$\dfrac{(1 \, - \, i)^3}{1 \, - \, i^3}$$
Express the following in the form A + iB :
$$\dfrac{1}{1 \, - \, \cos \theta \, + \, 2i \, \sin \theta}$$
Put the following in the form A + iB :
$$\dfrac{(a \, + \, ib)^2}{(a \, - \, ib)} \, - \, \dfrac{(a \, - \, ib)^2}{(a \, + \, ib)}$$
If $$Z_r \, = \, \left ( \cos\dfrac{r\pi }{10} \, + \, i \, \sin \dfrac{r\pi }{10}\right ).$$ Then, find the value of $$Z_1 \cdot Z_2 \cdot Z_3 \cdot Z_4 $$
If $$i{ z }^{ 3 }+{ z }^{ 2 }-z+i=0$$, then show that $$\left| z \right| =1$$.
$$The\quad complex\quad number\quad \cfrac { { 2 }^{ n } }{ { (1+i) }^{ 2n } } +\cfrac { { (1+i) }^{ 2n } }{ { 2 }^{ n } } ,\quad n\quad \in Z,\quad is\quad equal\quad to\quad $$
Find all the values of $$z$$ which satisfy the equation
exp$$\left| \dfrac { { \left| z \right| }^{ 2 }-\left| z \right| +4 }{ { \left| z \right| }^{ 2 }+1 } \log2 \right| ={ \log }_{ \sqrt { 2 } }\left| 3\sqrt { 15 } +11i \right| $$
Find the modulus and argument of the complex number:
$$\dfrac{1}{1+i}$$
For any two complex number $$z_1$$ and $$z_2$$ prove that $$Re(z_1z_2)= Rez_1Rez_2-I mz_1Imz_1$$
let $$z_1$$ and $$z_2$$ be two complex number such that $$|1-{z_1}z_2|^2-|z_1-z_2|^2=k\left(1-|z_1|^2\right)\left(1-|z_2|^2\right)$$ find the value of $$k$$
If $$\left( {a + ib} \right) = \frac{{1 + i}}{{1 - i}}$$ , then prove that $$\left( {{a^2} + {b^2}} \right) = 1$$
How solve and what is its meaning
$$z_{1}=2+3i$$
$$z_{2}=3+4i$$
$$\left|z_{1}+z_{2}\right|=?$$
Let $$\dfrac{1}{a+ib}=c+id$$ for non-zero $$a,b$$, then find $$c,d$$.
Find the modulus and the arguments of each of the complex numbers is $$z=-\sqrt{3}+i$$
Find real values of $$\theta $$ for which$$\left( {\dfrac{{4 + 3i\;\sin \theta }}{{1 - 2i\;\sin \theta }}} \right)$$ is purely real.
Prove that $${\left( {1 + i} \right)^4}{\left( {1 + \dfrac{1}{i}} \right)^4} = 16$$
$$\dfrac{4+3i}{(2+3i)(4-3i)}$$.
For any two complex numbers $$z_1,z_2$$ and any two real numbers a and b,
$$|az_1-bz_2|^2+|bz_1+az_2|^2=.....$$ .
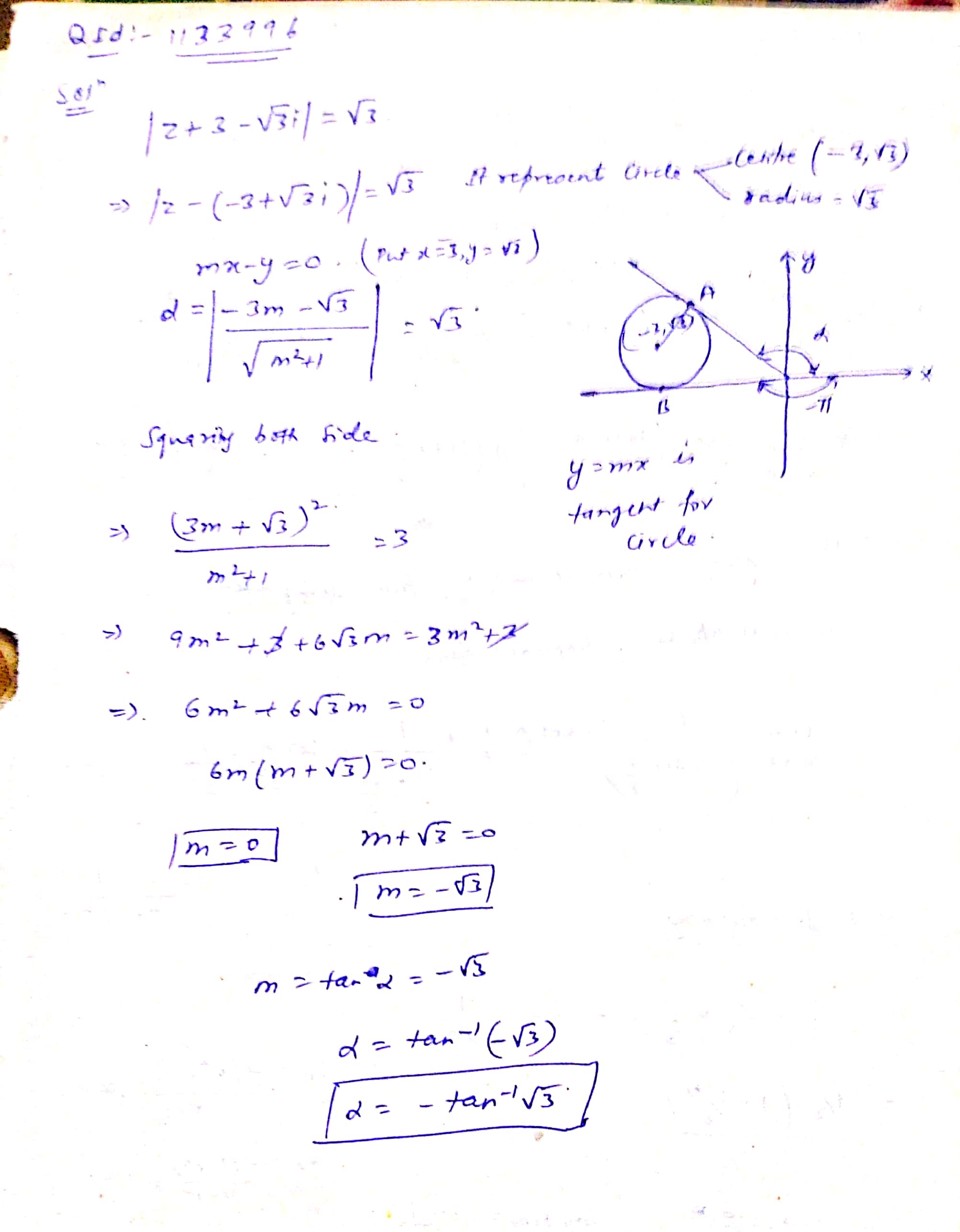
Among the complex numbers $$Z$$ satisfying the condition $$|z+3-\sqrt{3}i| = \sqrt{3}$$, find the number having the least positive argument.
Show that:
$$\left(\dfrac{1+i}{\sqrt{2}}\right)^{8}+\left(\dfrac{1-i}{\sqrt{2}}\right)^{8}=2$$
Find the value of $${ x }^{ 3 }+2{ x }^{ 2 }-3x+21$$ if $$x=1+2i$$
Let $$z_{1}=2-i,z_{2}=-2+i$$. Find $$Re\left(\dfrac {z_{1} z_{2}}{ \vec {z_{1}}}\right)$$
Find the expanded form when $$z$$ is divided by $$z-0.5$$
Show that if $$\left| \dfrac { z - 3 i } { z + 3 i } \right| = 1 ,$$ then $$z$$ is a real number.
If $$|z-1|+|z-3| \le 8$$, then find the range of $$|z-4|$$.
Express the following in the form of a = ib, a,b$$\epsilon$$R $$i = \sqrt{-1}$$. State the values of a and b. $$(1+i)(1-i)^{-1}$$
Show that $$(-1 + \sqrt 3 i)^3$$ is a real number.
Express $$(5-3i)^{3}$$ in the form $$a+ib$$.
Simplify: $$\left( -\sqrt { 3 } +\sqrt { -2 } \right) \left( 2\sqrt { 3 } -i \right) $$=(a + ib)$$\left( -\sqrt { 3 } +\sqrt { -2 } \right) $$. Find value of a and b.
Simplify and express the result in the form of $$a+ib$$
$$(\sqrt{3}+i)^6$$
Find the possible missing twins for the following number so that they become twin primes.
$$89$$.
Express the following number as the sum of twin primes.
$$36$$.
Find the possible missing twins for the following number so that they become twin primes.
$$101$$.
Find the possible missing twins for the following number so that they become twin primes.
$$29$$.
Evaluate $$(\sqrt {-36}\times \sqrt{-25})$$.
Define twin prime numbers.
Given the output of the following,when num1 = 4, num2 = 3, num3 = 21. num1 + = num2 + num3 print (num1)2. num1 = num1 * (num2 + num3) print (numl)3. num1 = num2* (num2 + num 3) print(num1)4. num1 = '5' + '5' print (numl)
1. num1 + = num2 + num3
print (num1)2. num1 = num1 * (num2 + num3)
print (numl)3. num1 = num2* (num2 + num 3)
print(num1)
4. num1 = '5' + '5'
print (numl)Prove that if $$\displaystyle x \, + \,\frac{1}{x} \, = \, 2 \, cos \, \alpha, \, then \, x^n \, + \, \frac{1}{x^n} \, = \, 2 \, cos \, n\alpha.$$
Given: $${ z }_{ 1 }+{ z }_{ 2 }+{ z }_{ 3 }=A;{ z }_{ 1 }+{ z }_{ 2 }w+{ z }_{ 3 }{ w }^{ 2 }=B;{ z }_{ 1 }+{ z }_{ 2 }{ w }^{ 2 }+{ z }_{ 3 }{ w }^{ }=C$$ where $$w$$ is cube rott of unity
Prove: $${ \left| A \right| }^{ 2 }+{ \left| B \right| }^{ 2 }+{ \left| C \right| }^{ 2 }=3\left( { \left| { z }_{ 1 } \right| }^{ 2 }+{ \left| { z }_{ 2 } \right| }^{ 2 }+{ \left| { z }_{ 3 } \right| }^{ 2 } \right) $$
Perform the indicated operations.
$$\displaystyle (- \, 1 \, + \, \sqrt{3i})^3.$$
Solve $$\left(\dfrac {1}{1-4i}-\dfrac {2}{1+i}\right)\left(\dfrac {3-4i}{5+i}\right)$$
Solve $$\dfrac {1}{1+i}$$
Express the following number given in the form $$a+ib$$.
$$(5i)\left(-\dfrac{3}{5}i\right)$$.
If $$|z + 1| = z + 2 (1 + i)$$, then find $$z$$.
Define twin primes.Determine twin primes between $$ 50 $$ and $$ 1000 $$
What are twin-primes? Write all pairs of twin-primes between $$50$$ and $$100$$.
Express the following number as the sum of twin primes.
$$120$$.
Express the following number as the sum of twin primes.
$$84$$.
Class 11 Commerce Applied Mathematics Extra Questions
- Basics Of Financial Mathematics Extra Questions
- Circles Extra Questions
- Descriptive Statistics Extra Questions
- Differentiation Extra Questions
- Functions Extra Questions
- Limits And Continuity Extra Questions
- Logarithm And Antilogarithm Extra Questions
- Mathematical And Logical Reasoning Extra Questions
- Number Theory Extra Questions
- Numerical Applications Extra Questions
- Permutations And Combinations Extra Questions
- Probability Extra Questions
- Relations Extra Questions
- Sequences And Series Extra Questions
- Set Theory Extra Questions
- Straight Lines Extra Questions
- Tangents And Its Equations Extra Questions