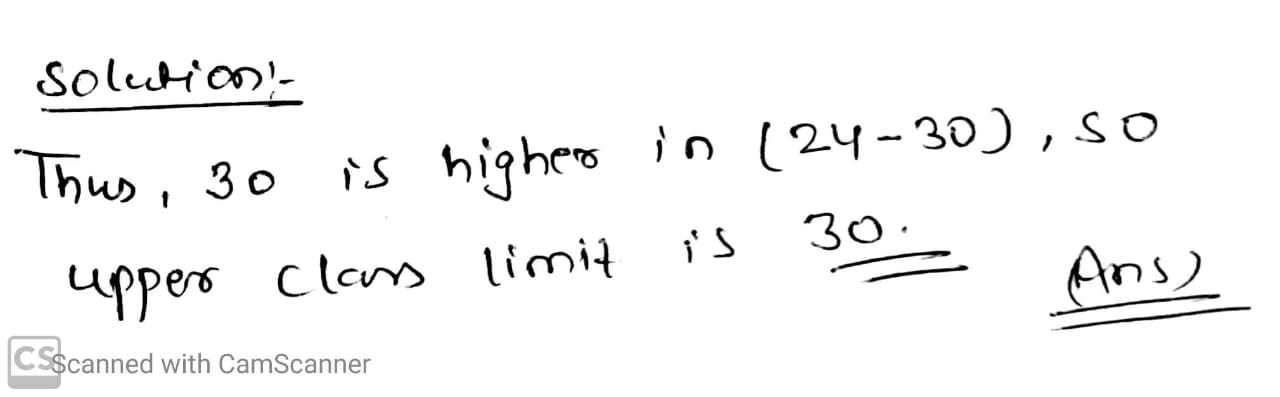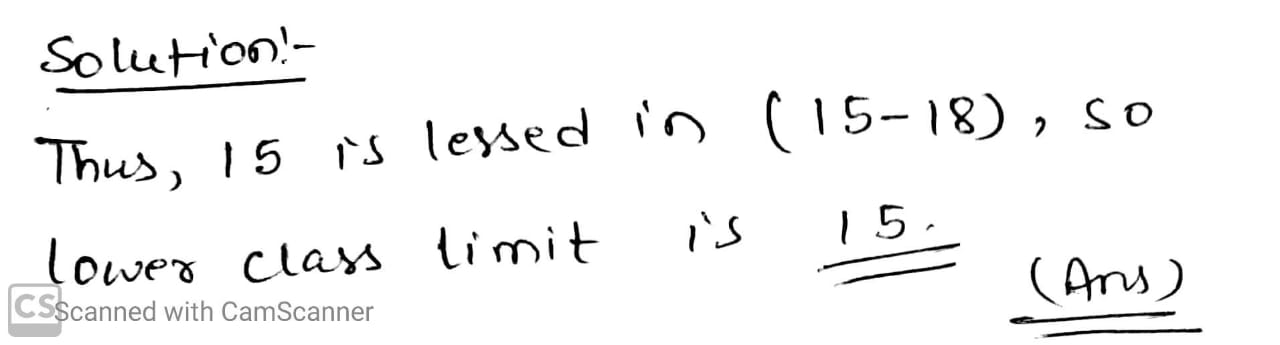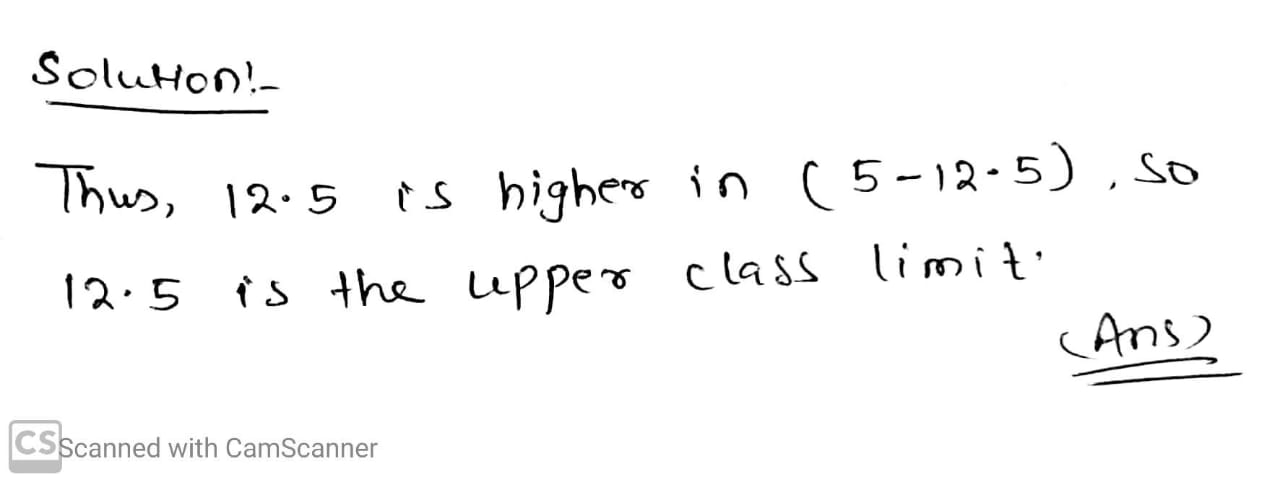Organisation Of Data - Class 11 Commerce Economics - Extra Questions
Define arrayed data.
Distinguish between raw data and arrayed data.
Fill in the blanks:
Data obtained in the ............... form is called raw data.
Complete the following cumulative frequency table:
| Class | Frequency | Less than type frequency |
| 0-10 | 2 | |
| 10-20 | 12 | |
| 20-30 | 20 | |
| 30-40 | 16 | |
| Total | 50 |
For the following raw data, form a discrete frequency distribution:
30,32,32,28,34,34,32,30,30,32,32,34,30,32,32,28,32,30,28,30,32,32,30,28 and 30
The marks scored by 55 students in a test are given below.
| Marks : | 0 - 5 | 5 - 10 | 10 - 15 | 15 - 20 | 20 - 25 | 25 - 30 | 30 - 25 |
| No. of students | 2 | 6 | 13 | 17 | 11 | 4 | 2 |
Given below are the cumulative frequencies showing the weights of 685 students of a school. Prepare a frequency distribution table.
| Weight (in kg ) | No. of students |
| Below 25 | 0 |
| Below 30 | 24 |
| Below 35 | 78 |
| Below 40 | 183 |
| Below 45 | 294 |
| Below 50 | 408 |
| Below 55 | 543 |
| Below 60 | 621 |
| Below 65 | 674 |
| Below 70 | 685 |
The numbers of members in the 40 families in Bhilar are as follows: 1, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 7, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 4, 6, 2, 3, 2, 1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 3,4, 5, 2, 4, 3, 2, 3, 5, 5, 4, 6, 2, 3, 5, 6, 4, 2. Prepare a frequency table and find the mean of members of 40 families.
Explain the meaning of the following terms: true class limits.
Following are the ages of 360 patients getting medical treatment in a hospital on a day :
| Age (in years ) : | 10 - 20 | 20 - 30 | 30 - 40 | 40 - 50 | 50 - 60 | 60 - 70 |
| No. of Patients : | 90 | 50 | 60 | 80 | 50 | 30 |
What is the class mark of the interval 27−32?
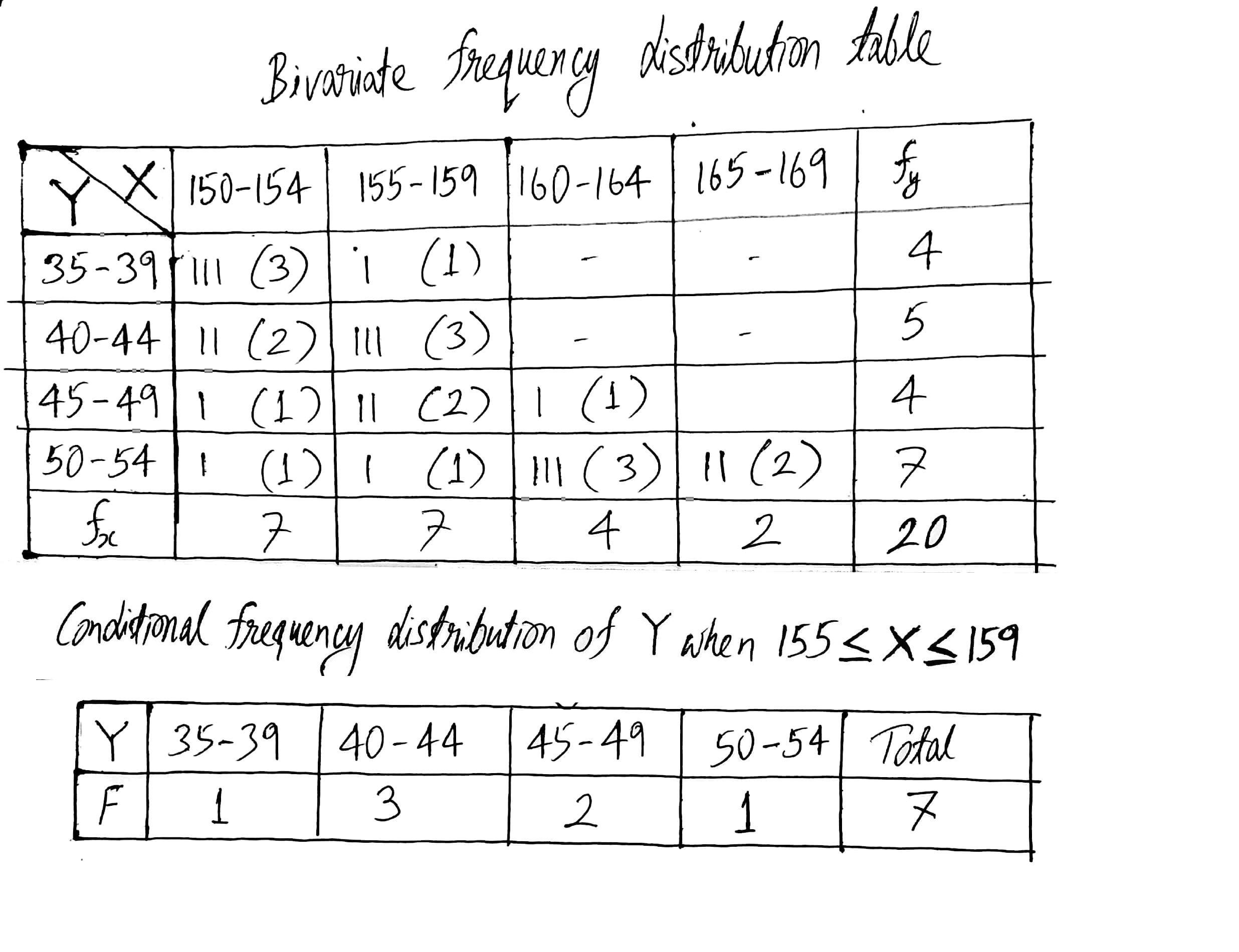
Following data gives height in cm(X) and weight in kgs(Y) of 20 boys. Prepare a bivariate frequency table taking class intervals 150−154, 155−159 etc., for X and 35−39, 40−44 etc., Y. Also find conditional frequency distribution of Y when 155≤X≤159
(152,40) (160,54) (163,52) (150,35)
(154,36) (160,49) (166,54) (157,38)
(159,43) (153,48) (152,41) (158,51)
(155,44) (156,47) (156,43) (166,53)
(160,50) (151,39) (153,50) (158,46).
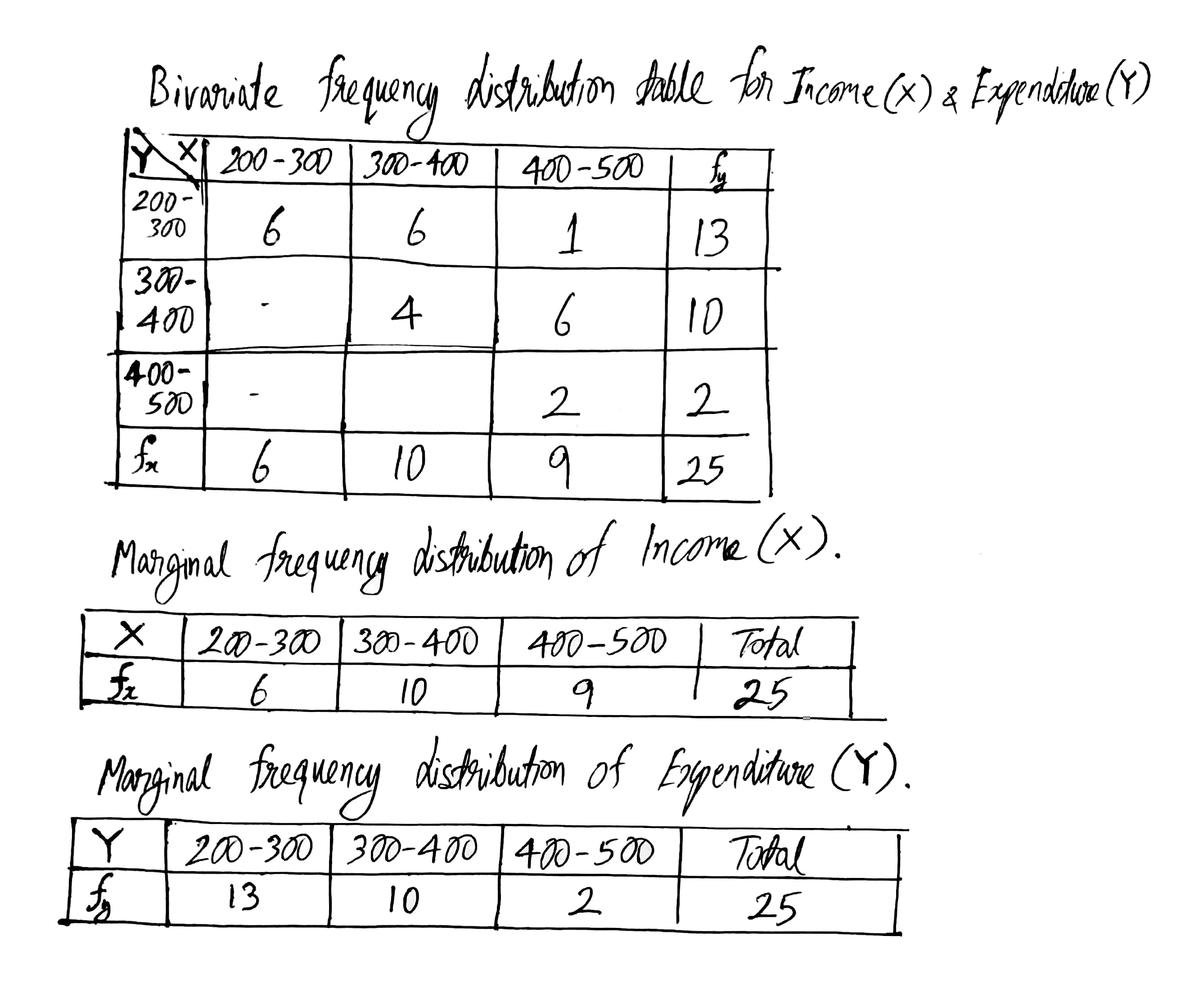
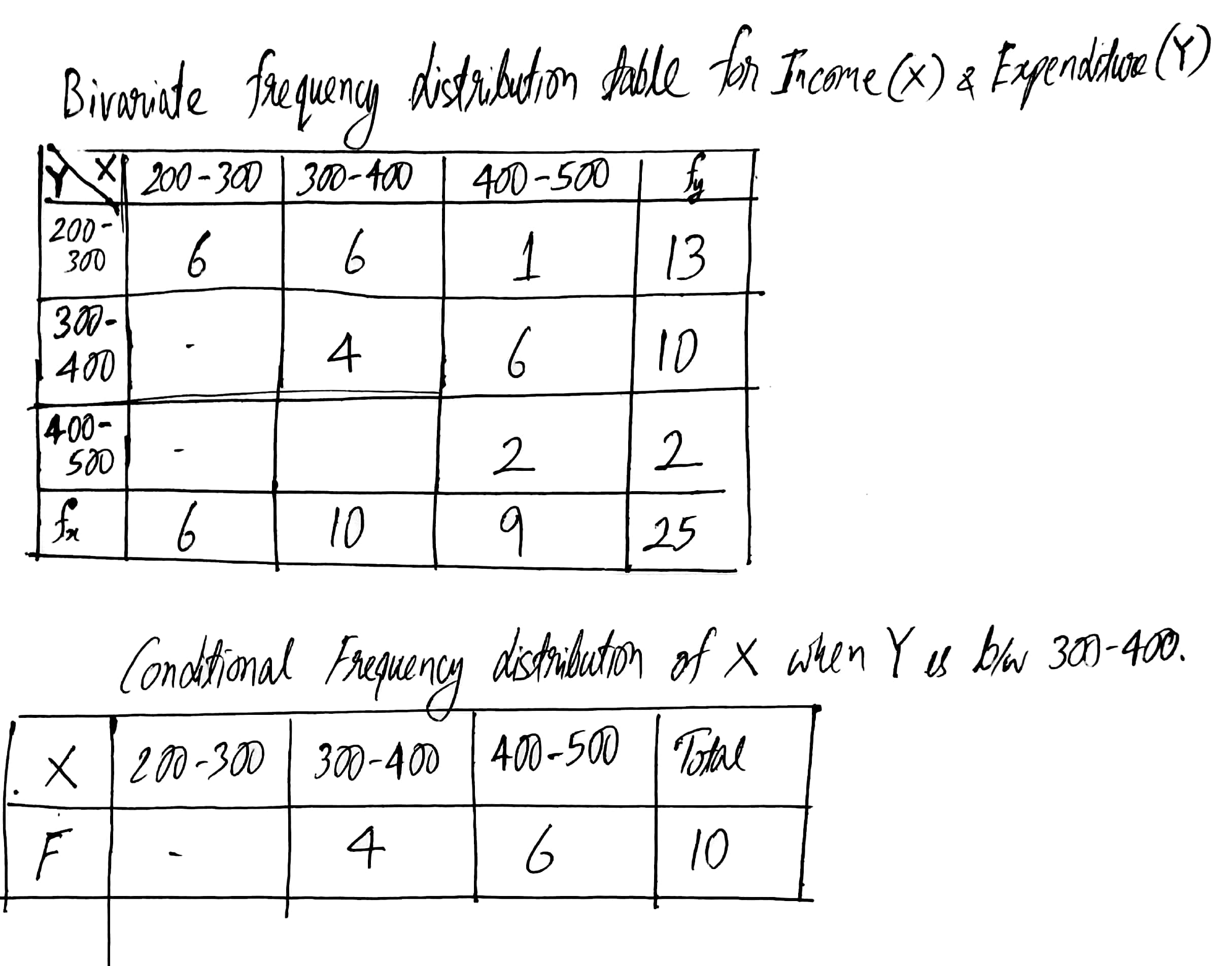
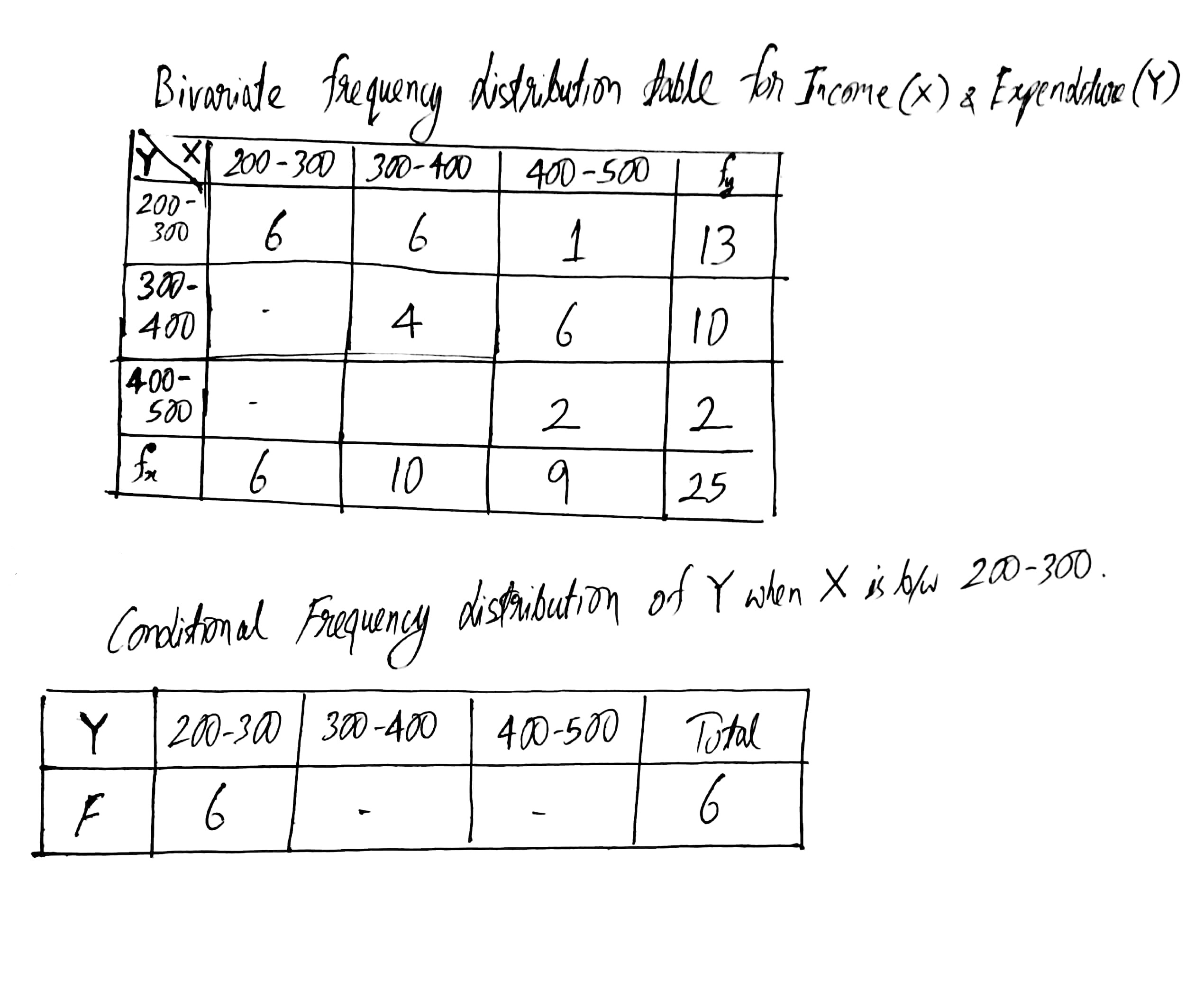
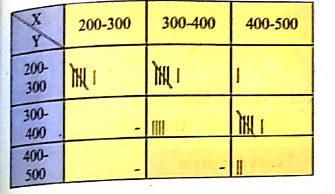
Following table gives income(X) and expenditure(Y) of 25 families.
Find how many families have their income Rs. 300 and more and expenses Rs. 400 and less?
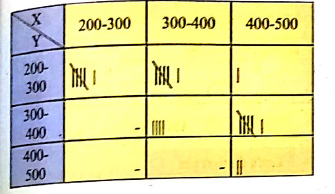
Following table gives income(X) and expenditure(Y) of 25 families.
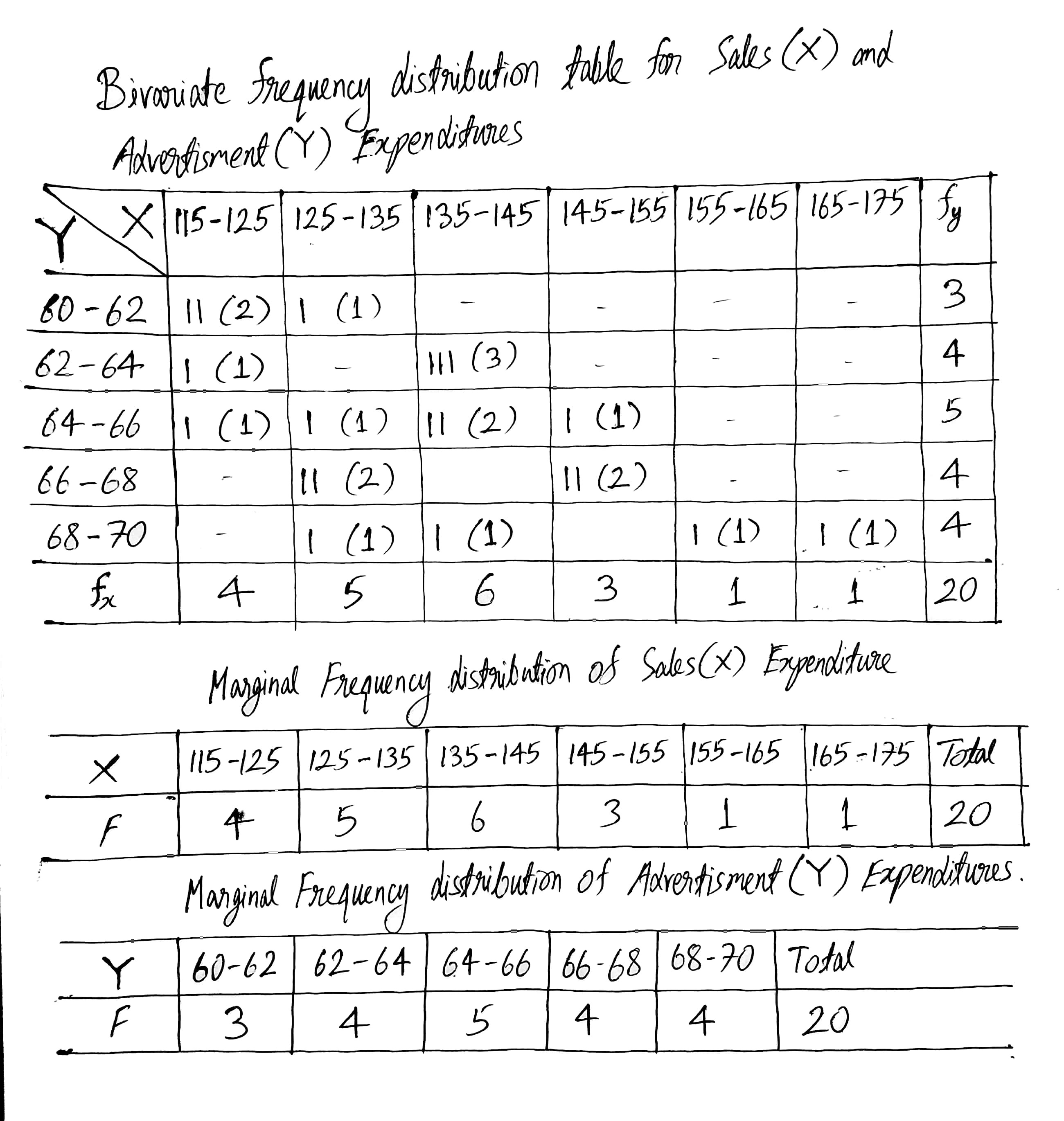
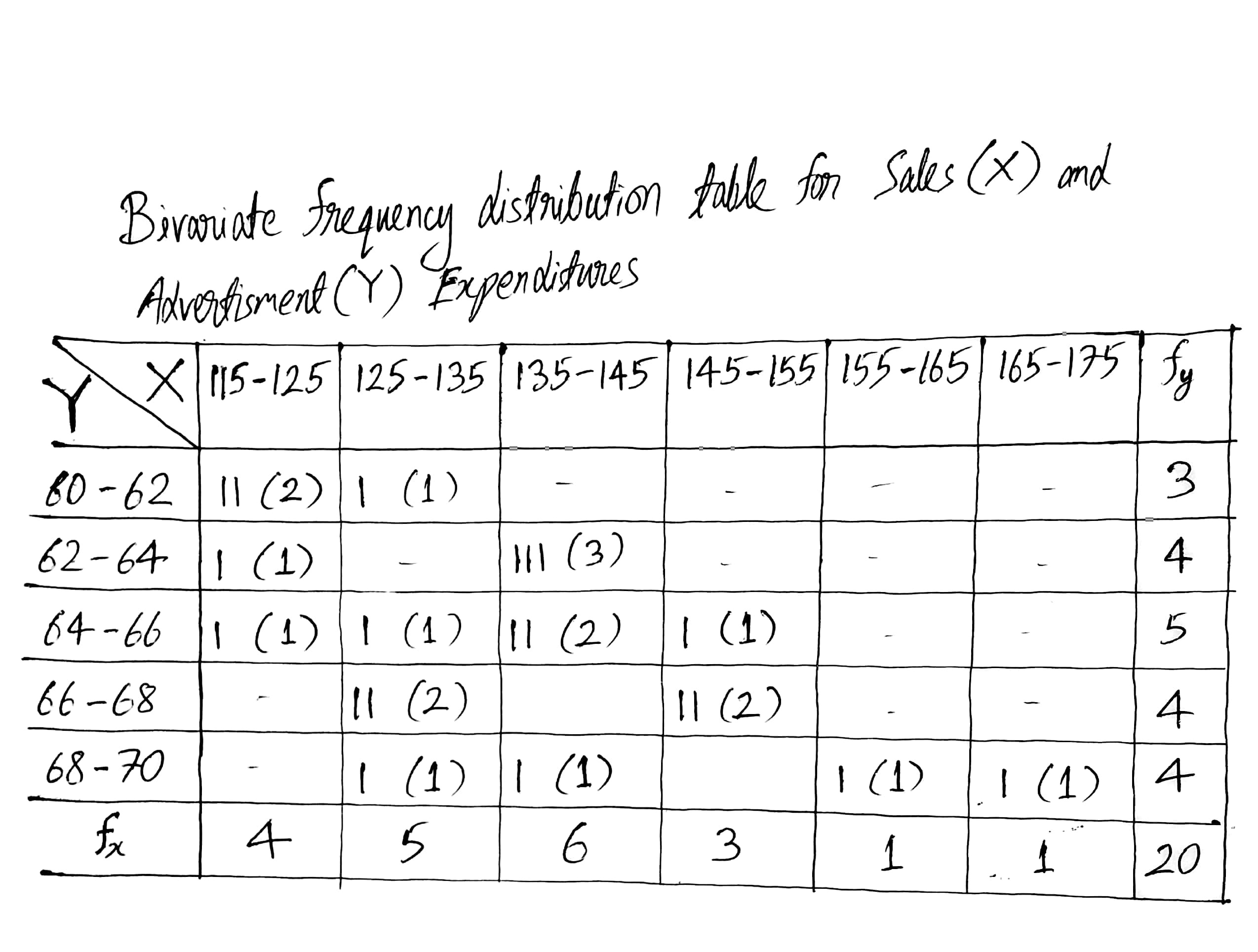
Find marginal frequency distribution of income and expenditure.
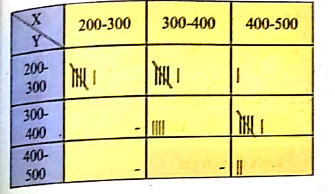
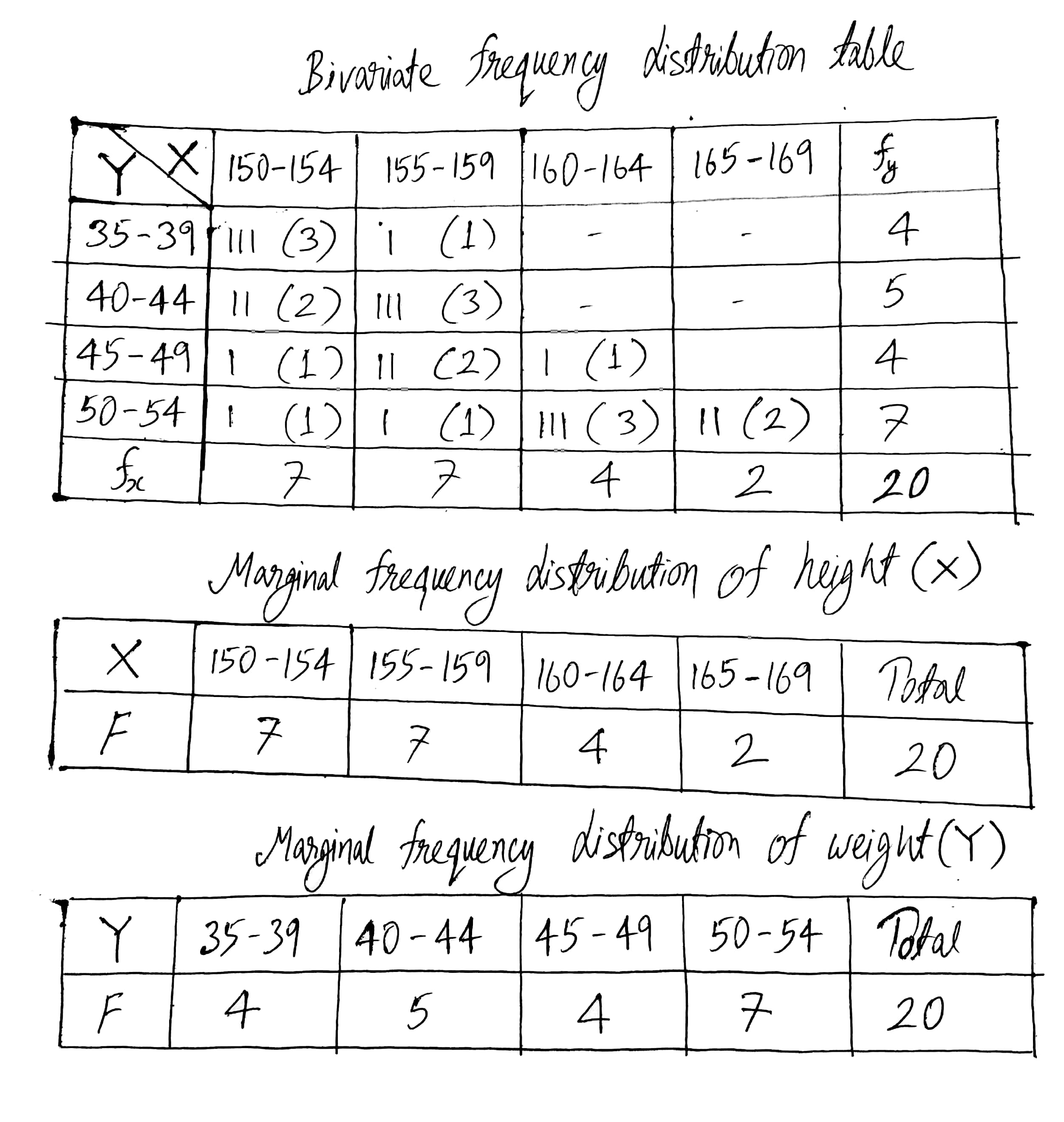
Following data gives height in cm(X) and weight in kgs(Y) of 20 boys. Prepare a bivariate frequency table taking class intervals 150−154, 155−159… etc., for X and 35−39, 40−44… etc., for Y. Also find marginal frequency distributions.
(152,40) (160,54) (163,52) (150,35)(154,36) (160,49) (166,54) (157,38)(159,43) (153,48) (152,41) (158,51)(155,44) (156,47) (156,43) (166,53)(160,50) (151,39) (153,50) (158,46).
(152,40) (160,54) (163,52) (150,35)
(154,36) (160,49) (166,54) (157,38)
(159,43) (153,48) (152,41) (158,51)
(155,44) (156,47) (156,43) (166,53)
(160,50) (151,39) (153,50) (158,46).
Following table gives income(X) and expenditure(Y) of 25 families.
Find conditional frequency distribution of X when Y is between 300−400.
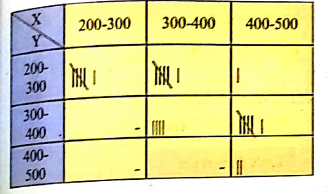
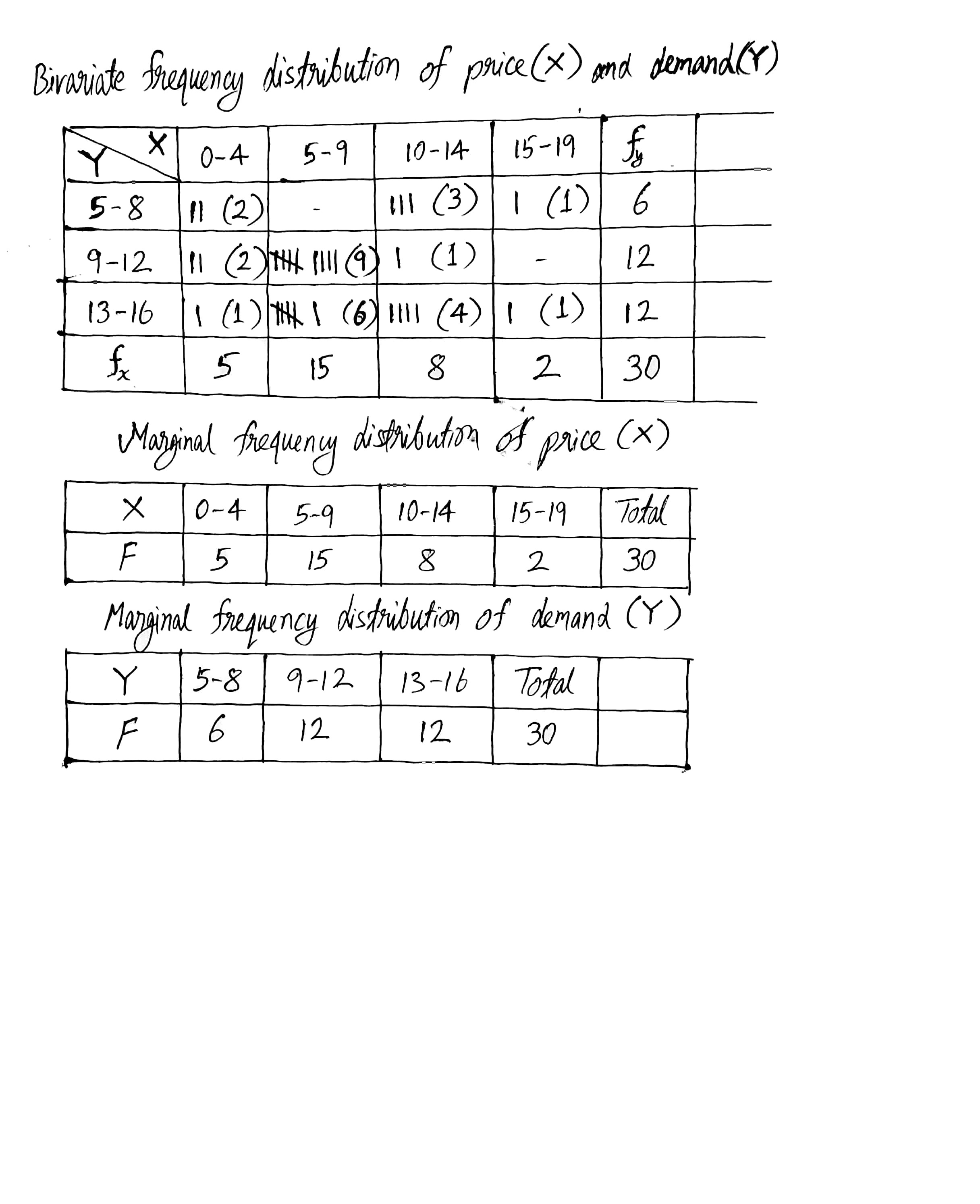
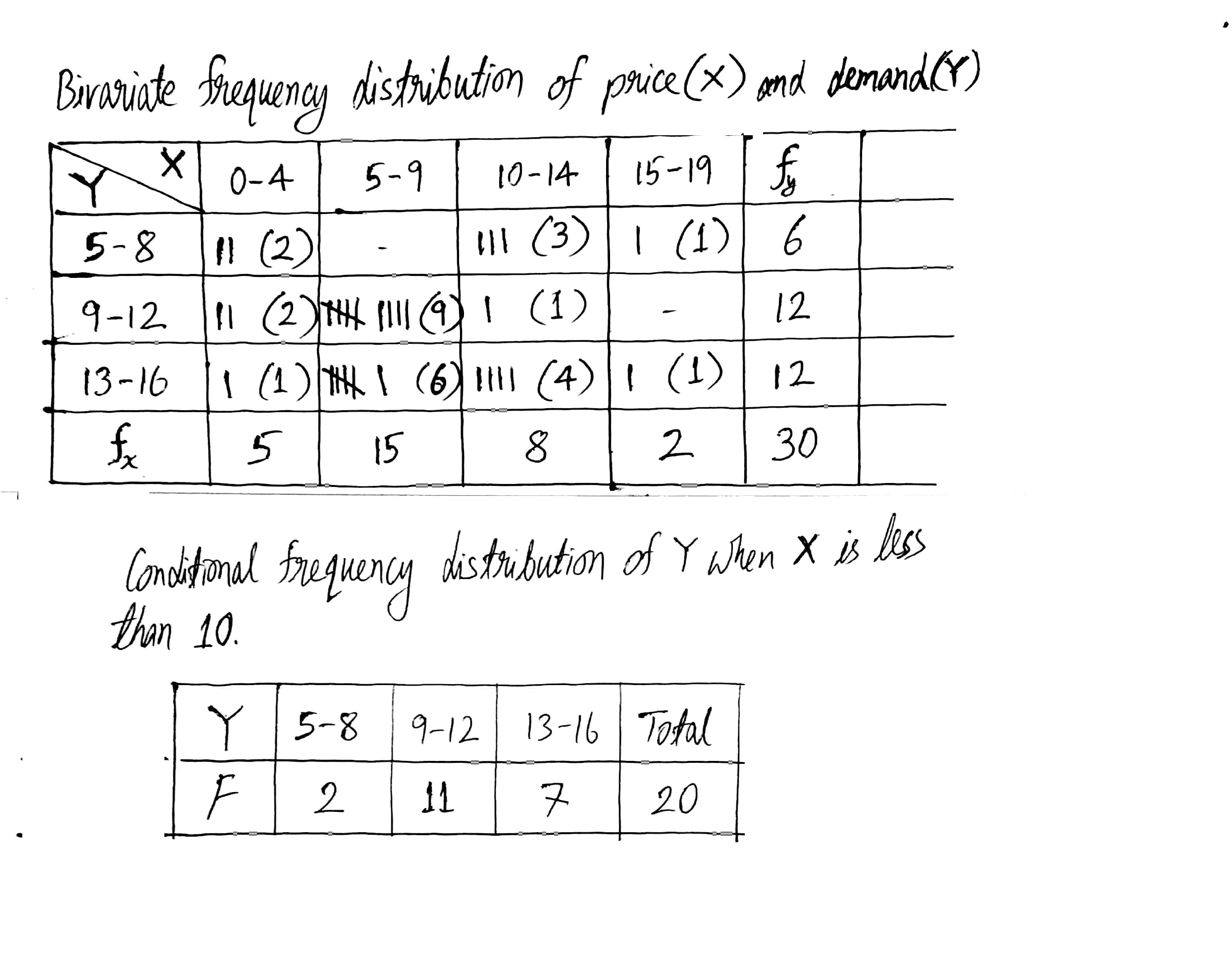
Following data gives the coded price(x) and demand(y) of a commodity.
| Price | 5 | 7 | 9 | 8 | 10 | 7 | 9 | 8 | 5 | 11 | 11 | 10 | 2 | 3 | 9 |
| Demand | 9 | 15 | 13 | 15 | 14 | 10 | 11 | 14 | 10 | 14 | 6 | 14 | 15 | 11 | 12 |
| Price | 2 | 4 | 3 | 14 | 6 | 10 | 7 | 15 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 11 | 14 | 15 |
| Demand | 6 | 11 | 8 | 11 | 10 | 15 | 9 | 15 | 13 | 9 | 14 | 10 | 7 | 5 | 6 |
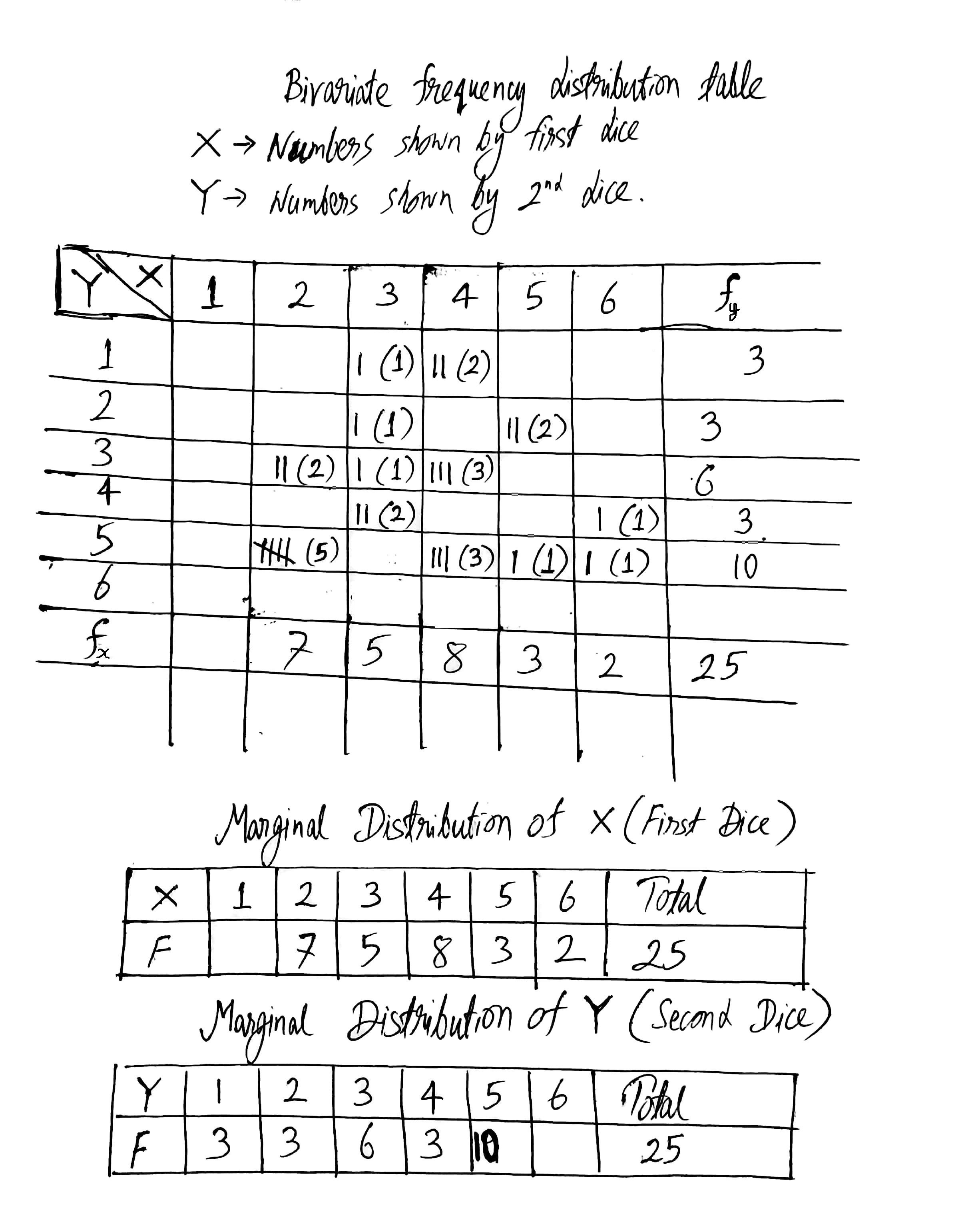
Two dice are thrown simultaneously 25 times. The following pairs of observations are obtained.
(2,3) (2,5) (5,5) (4,5) (6,4) (3,2) (5,2) (4,1) (2,5) (6,1) (3,1) (3,3) (4,3) (4,5) (2,5) (3,4) (2,5) (3,4) (2,5) (4,3) (5,2) (4,5) (4,3) (2,3) (4,1).
Prepare a bivariate frequency distribution table for the given data. Also obtain the marginal distributions.
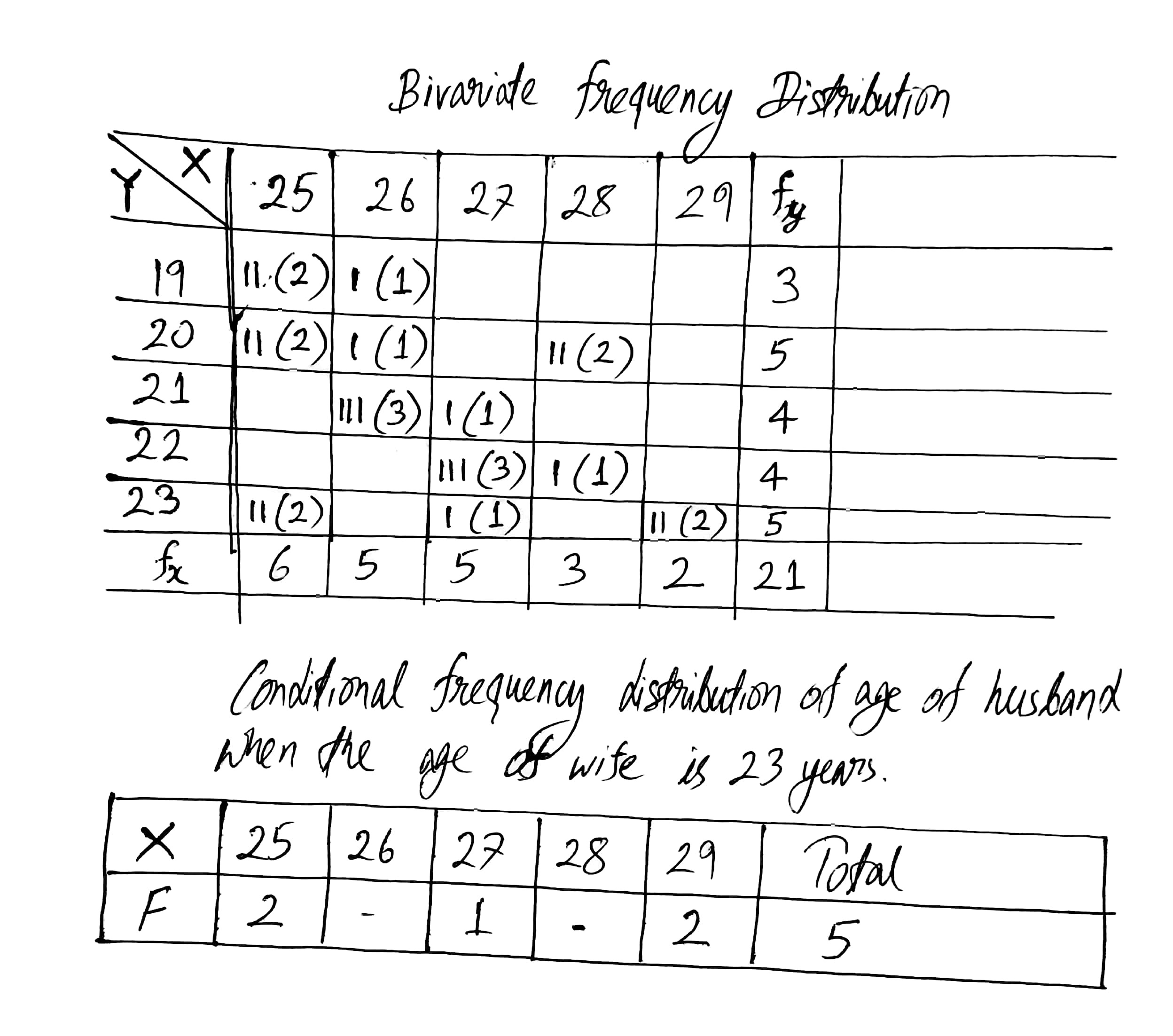
Following data gives the age of husbands(X) and age of wives(Y) in years. Construct a bivariate frequency distribution table and find the marginal distributions.
| X | 27 | 25 | 28 | 26 | 29 | 27 | 28 | 26 | 25 | 25 | 27 |
| Y | 21 | 20 | 20 | 21 | 23 | 22 | 20 | 20 | 19 | 19 | 23 |
| X | 26 | 29 | 25 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 28 | 25 | 27 | 26 | |
| Y | 19 | 23 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 22 | 23 | 22 | 21 |
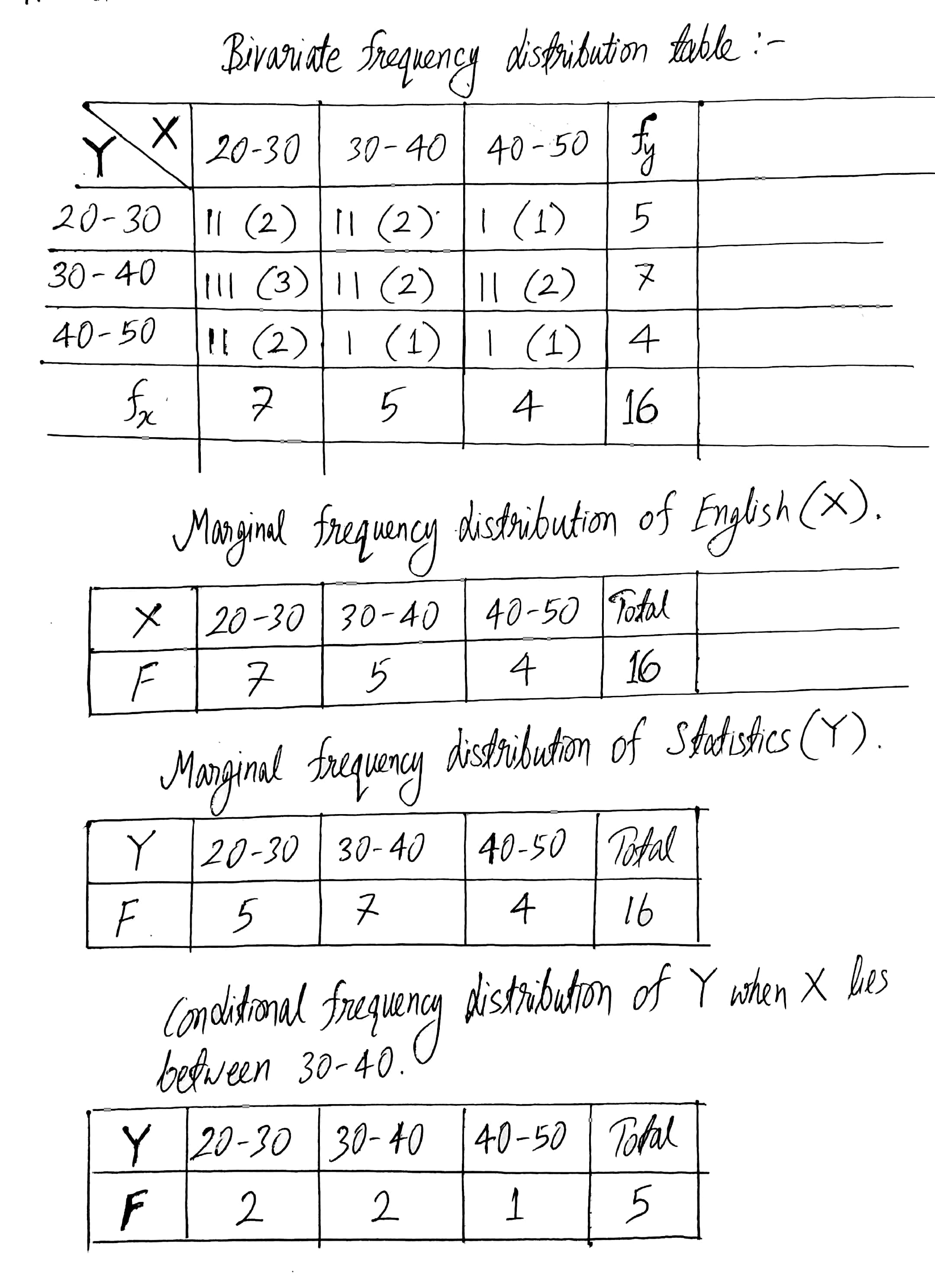
Construct a bivariate frequency distribution table of the marks obtained by students in English(X) and Statistics(Y).
| Marks in Statistics(X) | 37 | 20 | 46 | 28 | 35 | 26 | 41 | 48 | 32 | 23 | 20 | 39 | 47 | 33 | 27 | 26 |
| Marks in English(Y) | 30 | 32 | 41 | 33 | 29 | 43 | 30 | 21 | 44 | 38 | 47 | 24 | 32 | 31 | 20 | 21 |
Following table gives income(X) and expenditure(Y) of 25 families.
Find conditional frequency distribution of Y when X is between 200−300.
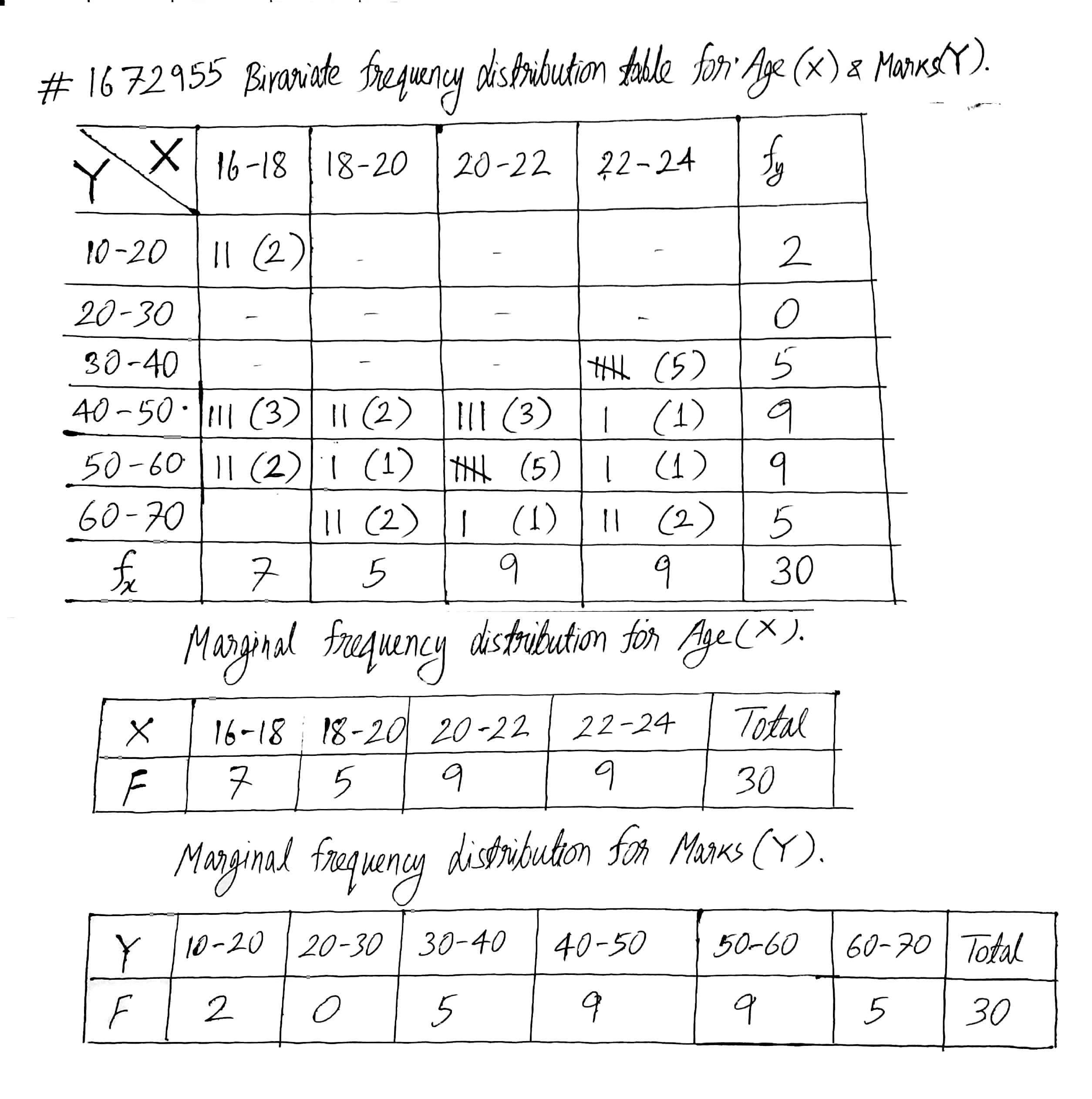
Following data gives the age in years and marks obtained by 30 students in an intelligence test.
| Age | 16 | 17 | 22 | 19 | 21 | 16 |
| Marks | 16 | 19 | 39 | 50 | 48 | 41 |
| Age | 21 | 20 | 20 | 23 | 22 | 19 |
| Marks | 59 | 44 | 42 | 62 | 37 | 67 |
| Age | 23 | 20 | 22 | 22 | 23 | 22 |
| Marks | 45 | 57 | 35 | 37 | 38 | 56 |
| Age | 17 | 18 | 16 | 21 | 19 | 20 |
| Marks | 54 | 61 | 47 | 67 | 49 | 56 |
| Age | 17 | 18 | 23 | 21 | 20 | 16 |
| Marks | 51 | 42 | 65 | 56 | 52 | 48 |
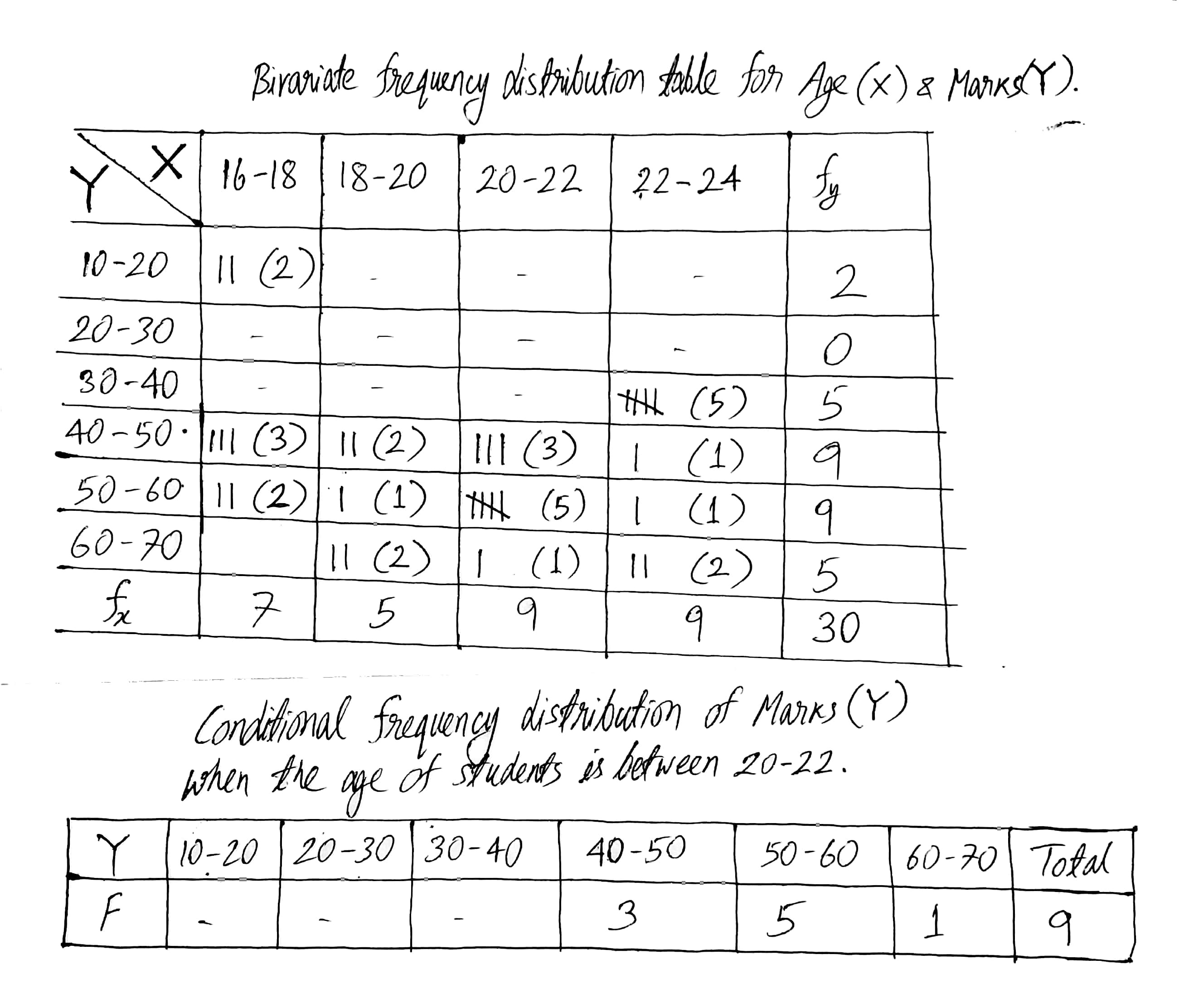
Following data gives the age in years and marks obtained by 30 students in an intelligence test.
| Age | 16 | 17 | 22 | 19 | 21 | 16 |
| Marks | 16 | 19 | 39 | 50 | 48 | 41 |
| Age | 21 | 20 | 20 | 23 | 22 | 19 |
| Marks | 59 | 44 | 42 | 62 | 37 | 67 |
| Age | 23 | 20 | 22 | 22 | 23 | 22 |
| Marks | 45 | 57 | 35 | 37 | 38 | 56 |
| Age | 17 | 18 | 16 | 21 | 19 | 20 |
| Marks | 54 | 61 | 47 | 67 | 49 | 56 |
| Age | 17 | 18 | 23 | 21 | 20 | 16 |
| Marks | 51 | 42 | 65 | 56 | 52 | 48 |
Find marginal frequency distributions.
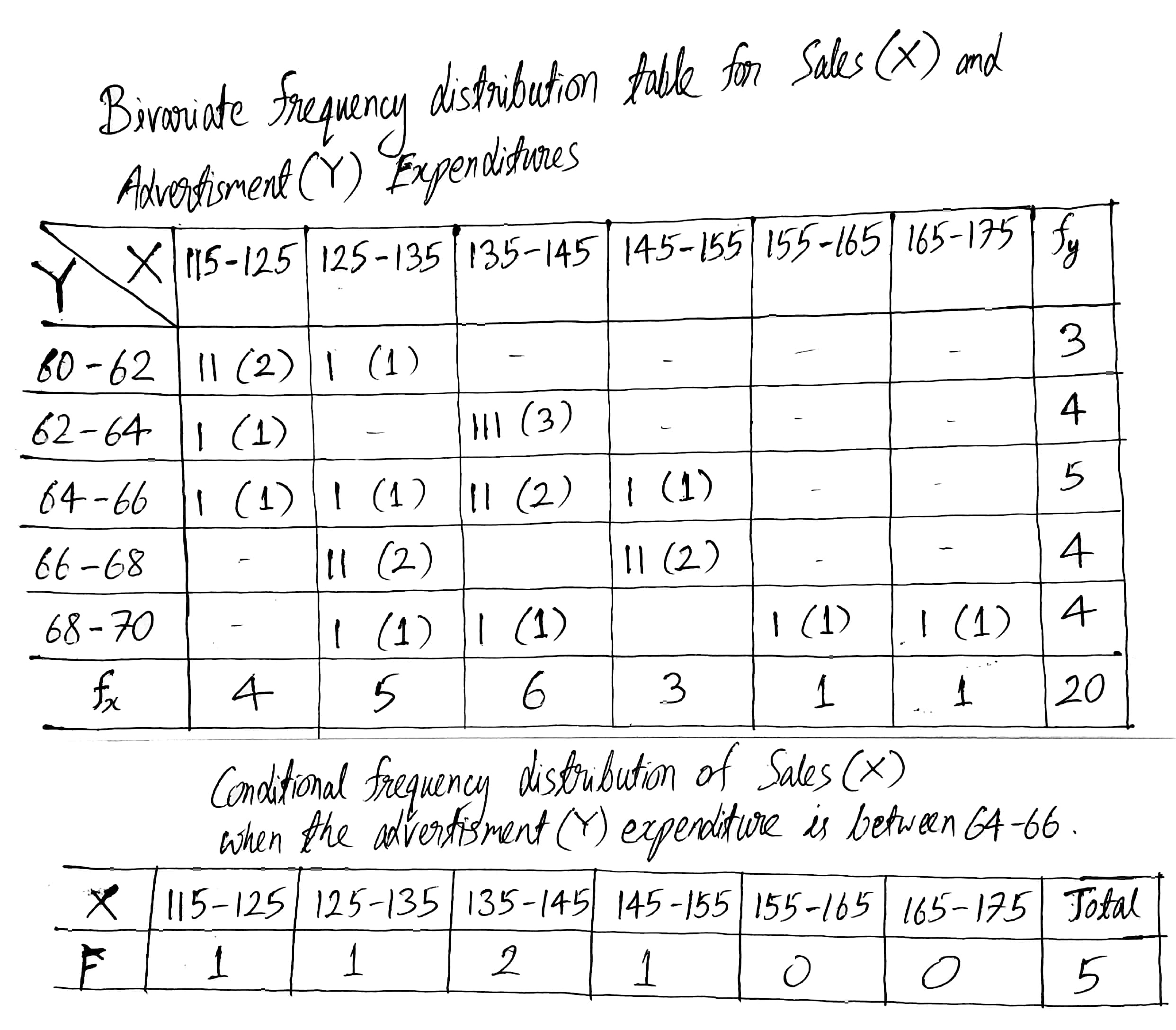
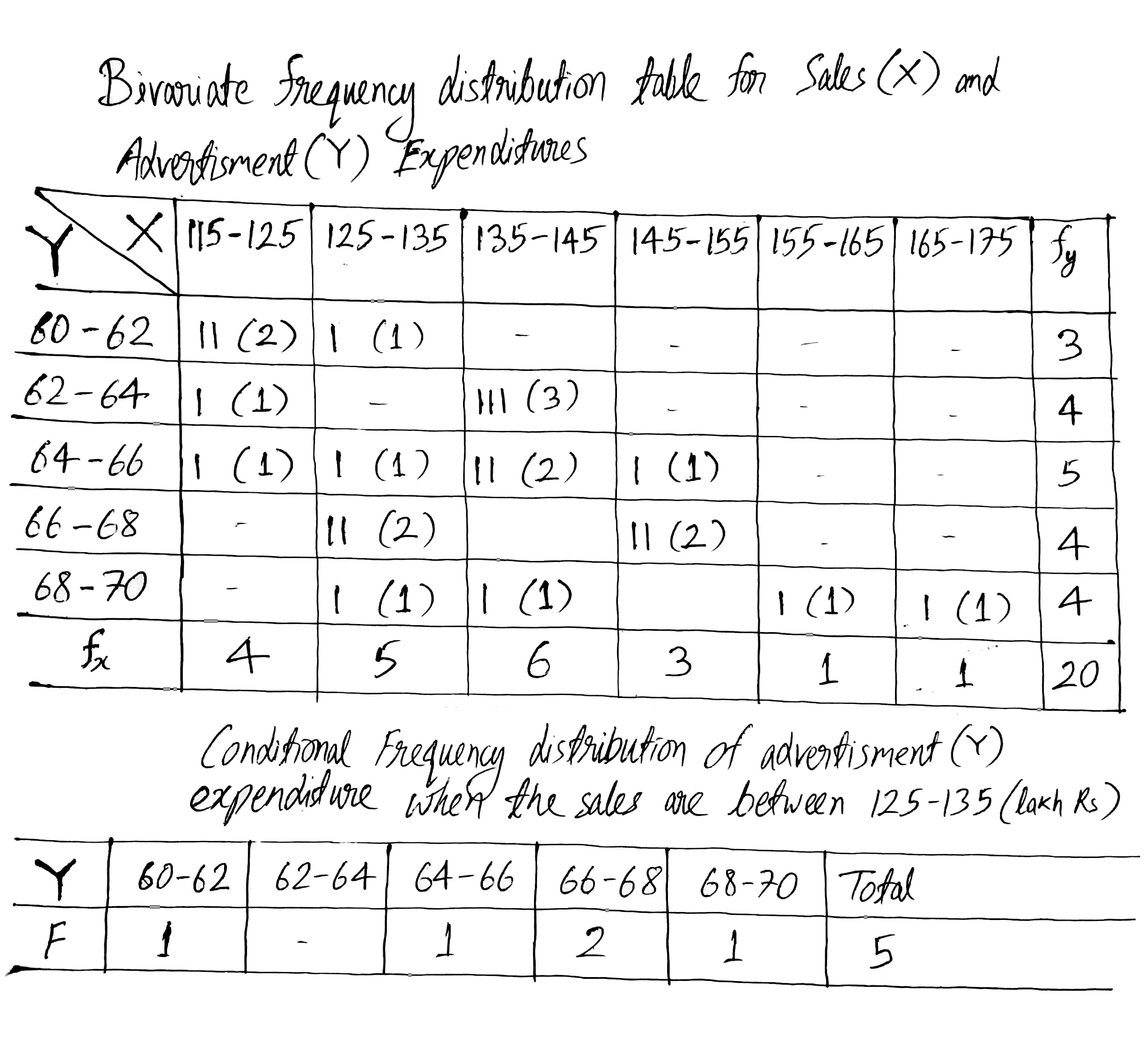
Conditional frequency distribution of Sales when the advertisement expenditure is between 64−66. (Thousand Rs.)
Following data gives the coded price(x) and demand(y) of a commodity.
| Price | 5 | 7 | 9 | 8 | 10 | 7 | 9 | 8 | 5 | 11 | 11 | 10 | 2 | 3 | 9 |
| Demand | 9 | 15 | 13 | 15 | 14 | 10 | 11 | 14 | 10 | 14 | 6 | 14 | 15 | 11 | 12 |
| Price | 2 | 4 | 3 | 14 | 6 | 10 | 7 | 15 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 11 | 14 | 15 |
| Demand | 6 | 11 | 8 | 11 | 10 | 15 | 9 | 15 | 13 | 9 | 14 | 10 | 7 | 5 | 6 |
Also find conditional frequency distribution of y when x is less than 10.
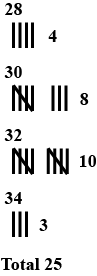
Prepare a frequency table of the following ages (in years) of 30 students of class VIII in your school:
13,14,13,12,14,13,14,15,13,14,13,14,16,12,14
13,14,15,16,13,14,13,12,17,13,12,13,13,13,14
Following figures relate the weekly wages (in Rs.) of 15 workers in a factory:
300,250,200,250,200,150,350,200,250,200,150,300,150,200,250
Prepare a frequency table.
Which mark is occurring more frequently?
Construct a bivariate frequency distribution table for the given data by taking classes 115−125, 125−135,... etc., for sales and 60−62,62−64,... etc., for advertisement expenditure.
Conditional frequency distribution of advertisement expenditure when the sales are between 125−135. (lakh Rs.)
Fill in the blanks:
Arranging the numerical figures in ascending or descending order is called an .............
Define the term Raw data
Define the term Array
Define the term:
Array.
Arrange the following as an array (in descending order):
0,2,0,3,4,1,2,3,5
Arrange the following as an array (in ascending order):
6.3,5.9,9.8,12.3,5.6,4.7
Upper clas limit of 24−30 is _______
Fill in the blanks:
Lower class limit of 15−18 is
A die is thrown 25 times and the scores were as given below:
2,1,4,6,2,3,1,5,6,3,4,5,2,1,6,6,6,3,2,2,2,4,3,2,2
Construct data array.
Arrange the following as an array (in descending order):
9.1.3.7.5.6.8.3.11.5.10.6
Arrange the following as an array (in ascending order):
7,5,15,12,10,11,16
Uses the table given to find:
The upper and lower limits of the fifth class
If the upper limit and the lower limits of a class interval are 16 and 10; the class interval is ____
Upper limit of 5−12.5 is _____
Find the actual lower class limits, upper class limits and the mid-values of the classes:
10−19,20−29,30−39, and 40−49.
Fill in the blanks:
In the class interval 35−46; the lower limit is ....... and the upper limit is.....
Data personally collected by an investigator is ____________ data.
Classification data based on the geographical differences of the data is ________.
Define raw data. What is bivariate and univariate distribution? Explain.
The number of books in different shelves of a library are as follows :
30,32,28,24,20,25,38,37,40,45,16,20
19,24,27,30,32,34,35,42,27,28,19,34,
38,39,42,29,24,27,22,29,31,19,27,25
28,23,24,32,34,18,27,25,37,31,24,23,
43,32,28,31,24,23,26,36,32,29,28,
Prepare a cumulative frequency distribution table using 45 - 49 as the last class-interval.
Explain the difference between a frequency distribution and a cumulative frequency distribution.
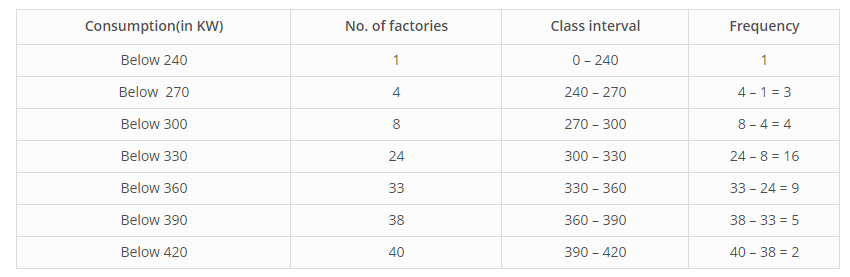
The following cumulative frequency distribution table shows the daily electricity consumption (in kW) of 40 factories in an industrial state : Represent this as a frequency distribution table.
| Consumption (in kW) | No. of Factories |
| Below 240 | 1 |
| Below 270 | 4 |
| Below 300 | 8 |
| Below 330 | 24 |
| Below 360 | 33 |
| Below 390 | 38 |
| Below 420 | 40 |
The marks scored by 40 students of class IX in mathematics are given below:
81,55,68,79,85,43,29,68,54,73,47,35,72,64,95,44,50,77,64,35,79,52,45,54,70,83,62,64,72,92,84,76,63,43,54,38,73,68,52,54.
Prepare a frequency distribution with class size of 10 marks.
Prepare a frequency distribution with class size of 10 marks.
Define the following terms: Frequency distribution
The heights (in cm) of 30 students of class IX are given below:
155,158,154,158,160,148,149,150,153,159,161,148,157,153,157,162,159,151,154,156,
152,156,160,152,147,155,163,155,157,153.
Prepare a frequency distribution table with 160-164 as one of the class intervals.
Define the following terms :
True class limits
The water bills (in RS) of 32 houses in a certain street for the period 1.1.98 to 31.3.98 are given below :56,43,32,38,56,24,68,85,52,47,35,58,63,74,27,84,69,35,44,75,55,30,54,65,45,67,95,72,43,65,35,
Tabulate the data and present the data as a cumulative frequency table using 70 - 79 as one of the class intervals.
Tabulate the data and present the data as a cumulative frequency table using 70 - 79 as one of the class intervals.
Following figures relate the weekly wages (in Rs.) of 15 workers in a factory:
300,250,200,250,200,150,350,200,250,200,150,300,150,200,250
Prepare a frequency table.
How many workers are getting the minimum wages?
Following figures relate the weekly wages (in Rs.) of 15 workers in a factory:
300,250,200,250,200,150,350,200,250,200,150,300,150,200,250
Prepare a frequency table.
What is the range in wages (in Rs)?
Following figures relate the weekly wages (in Rs.) of 15 workers in a factory:
300,250,200,250,200,150,350,200,250,200,150,300,150,200,250
Prepare a frequency table.
How many Workers are getting Rs 350?
Following figures relate the weekly wages (in Rs.) of 15 workers in a factory:
300,250,200,250,200,150,350,200,250,200,150,300,150,200,250
Prepare a frequency table.
What is the highest mark?
Class 11 Commerce Economics Extra Questions
- Collection Of Data Extra Questions
- Correlation Extra Questions
- Index Numbers Extra Questions
- Introduction To Economics Extra Questions
- Introduction To Microeconomics Extra Questions
- Market Equilibrium Extra Questions
- Measures Of Central Tendency Extra Questions
- Measures Of Dispersion Extra Questions
- Non-Competitive Markets Extra Questions
- Organisation Of Data Extra Questions
- Presentation Of Data Extra Questions
- Production And Costs Extra Questions
- Theory Of Consumer Behaviour Extra Questions
- The Theory Of The Firm Under Perfect Competition Extra Questions
- Use Of Statistical Tools Extra Questions