Production And Costs - Class 11 Commerce Economics - Extra Questions
Complete the following table:
| Output (units) | Average Fixed Cost (Rs.) | Marginal Cost (Rs.) | Average Veriable Cost (Rs.) | Average Cost (Rs.) |
| 1 | 60 | 20 | ... | ... |
| 2 | ... | ... | 19 | ... |
| 3 | 20 | ... | 18 | ... |
| 4 | ... | 18 | ... | ... |
| 5 | 12 | ... | ... | 31 |
Explain the conditions of producer's equilibrium in terms of marginal revenue and marginal cost.
Explain the basic difference between the 'law of variable proportions', and 'returns to scale'.
What is meant by production function?
What is the basic difference between short run production function and long run production function?
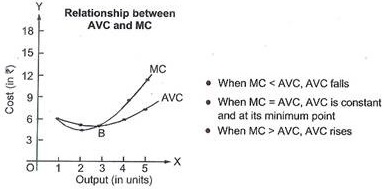
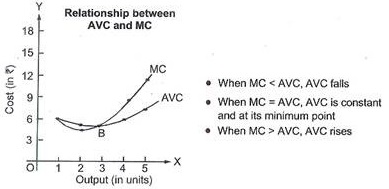
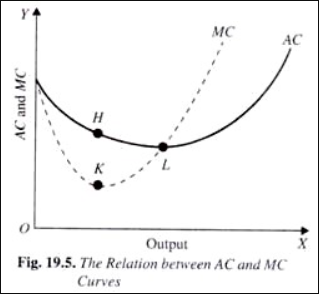
Why does marginal cost curve cut average cost curve only at its minimum point?
Define production cost.
Complete the following table:
| Output | AFC | TFC | TVC | MC |
| 0 | - | 50 | - | - |
| 1 | - | - | - | 10 |
| 2 | - | - | 18 | - |
| 3 | - | - | - | 6 |
| 4 | - | - | 32 | - |
Complete the following table:
| Output (Units) | ATC (Rs.) | AVC (Rs.) | MC (Rs.) |
| 1 | 54 | 30 | 30 |
| 2 | - | 24 | - |
| 3 | - | - | 24 |
| 4 | 33 | - | - |
Aslo find the value of TFC.
Why does the SMC curve cut the AVC curve at the minimum point of the AVC curve?
Marginal cost is always variable cost. Why?
A firm's average fixed cost of producing 2 units of a good is Rs. 9 and given below is its total cost schedule. Calculate its average variable cost and marginal cost for each of the given level of output.
| Output (Units) | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| TC (Rs.) | 23 | 27 | 30 |
At which point does the SMC curve cut the SAC curve? Give reason in support of your answer.
Consider a situation when $$10\%$$ increase in all inputs leads to $$12\% $$ increase in output. How does it impact the average cost? Is it a short period phenomenon or a long period phenomenon?
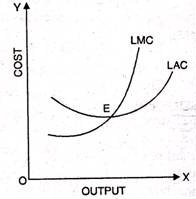
How do the long run marginal cost and the average cost curves look like?
"Stage of increasing returns (when MP is increasing) is economically redundant because the producer will not strike his equilibrium in this stage." Comment on the statement with justification.
Let the production function of a firm be:
$$ Q={ 5L }^{ 1/2 }{ K }^{ 1/2 } $$
Find out the maximum possible output that the firm can produce with 100 units of L and 100 units of K.
Let the production function of a firm be:
$$ Q={ 2L }^{ 2 }{ K }^{ 2 } $$
Find out the maximum possible output that the firm can produce with 5 units of L and 2 units of $$K$$.
FDI not only brings investment in the domestic economy, it also brings new technology. How would the availability of new technology (relating to auto industry) impact the short period production function of a car manufacturer in India?
"Discovery of natural gas in the international market leads to a cut in the petrol and diesel prices."
Explain the economic theory to analyse the impact of the statement on the cost of production of the transport firms in India. Also analyse its impact on the cost of transportation.
From the following data on the cost of production of a firm calculate TFC,AFC,TVC, AVC and MC:
| Output(kg) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| TC(Rs.) | $$60$$ | $$80$$ | $$100$$ | $$111$$ | $$116$$ | $$130$$ | $$150$$ |
Identify the different output levels which makes the different phases/stages of the operation of the law of variable proportions from the following data:
| Variable input | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| total product | 0 | 8 | 20 | 28 | 28 | 26 |
From the following data on the cost of production of a firm calculate (i) average fixed cost, (ii) average variable cost, and (iii) the marginal cost, of producing the 4th Unit.
Output(kg) 0 1 2 3 4 Total Cost (Rs.) $$80$$ $$102$$ $$122$$ $$140$$ $$156$$
| Output(kg) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Total Cost (Rs.) | $$80$$ | $$102$$ | $$122$$ | $$140$$ | $$156$$ |
Complete the following table:
| Output (Units) | Total Variable Cost (Rs.) | Average Variable Cost (Rs.) | Marginal Cost (Rs.) |
| 1 | $$20$$ | -- | -- |
| -- | -- | $$16$$ | $$12$$ |
| 3 | $$54$$ | -- | -- |
| -- | -- | $$20$$ | $$26$$ |
From the data calculate:
(i) average fixed cost, (ii) average variable cost, (iii) marginal cost.
| Output (kg) | $$0$$ | $$1$$ | $$2$$ | $$3$$ | $$4$$ | $$5$$ |
| Total Cost (Rs.) | $$40$$ | $$100$$ | $$120$$ | $$130$$ | $$150$$ | $$190$$ |
Complete the following table:
| Output (Units) | Total Cost (Rs.) | Total Variable Cost (Rs.) | Marginal Cost (Rs.) |
| $$0$$ $$1$$ $$2$$ | $$12$$ $$18$$ $$21$$ |
Using the following productions figures of a firm, derive the relationship between total product and marginal product.
| Units of Land | $$1$$ | $$1$$ | $$1$$ | $$1$$ | $$1$$ | $$1$$ | $$1$$ | $$1$$ | $$1$$ |
| Units of Labour | $$0$$ | $$1$$ | $$2$$ | $$3$$ | $$4$$ | $$5$$ | $$6$$ | $$7$$ | $$8$$ |
| $$TP$$ | $$0$$ | $$4$$ | $$11$$ | $$25$$ | $$37$$ | $$41$$ | $$43$$ | $$43$$ | $$41$$ |
Define production function. Distinguish between short run and long run production function.
Calculate MC, given the following information. Also, find AFC.
| Output (Units) | Total Variable Cost (Rs.) | Total Fixed Cost (Rs.) |
| $$0$$ $$1$$ $$5$$ | - $$400$$ $$1,600$$ | $$500$$ - - |
Answer the following question in $$4$$ sentences.
Write production function in the form of an equation.
Given below is the cost schedule of a firm. Its total fixed cost is $$Rs. 100$$. Calculate average variable cost and marginal cost at each given level of output.
| Output (Units) | $$1$$ | $$2$$ | $$3$$ | $$4$$ |
| Total Cost (Rs.) | $$350$$ | $$450$$ | $$610$$ | $$820$$ |
Following information is given about a firm:
| Output (Units) | $$0$$ | $$1$$ | $$2$$ | $$3$$ | $$4$$ | $$5$$ | $$6$$ |
| Total Cost (Rs.) | $$150$$ | $$300$$ | $$420$$ | $$600$$ | $$790$$ | $$1,000$$ | $$1,260$$ |
(i) AFC of producing $$3$$ units, (ii) AVC of producing $$4$$ units,
(iii) Least AC level of output, (iv) MC of producing $$5th$$ unit, and (v) TVC of producing $$6$$ units.
Complete the following table:
| Output (Units) | AFC (Rs.) | TFC (Rs.) | TVC (Rs.) | MC (Rs.) |
| $$0$$ $$1$$ $$2$$ $$3$$ $$4$$ | - - - - - | $$50$$ - - - - | - - $$18$$ - $$20$$ | - $$10$$ - $$6$$ - |
Define cost. Distinguish between fixed and variable costs. Give one example of each.
Answer the following project and Assignment oriented question.
Fill up the missing costs in the table given.
| Output in units | TFC | TVC | TC | AFC | AVC | AC |
| $$1$$ | $$50$$ | ? | $$70$$ | $$50$$ | ? | ? |
| $$2$$ | ? | $$30$$ | ? | $$25$$ | ? | $$40$$ |
| $$3$$ | $$50$$ | ? | $$90$$ | ? | $$13.33$$ | $$30$$ |
| $$4$$ | $$50$$ | $$60$$ | $$110$$ | $$12.5$$ | $$15$$ | $$27.5$$ |
| $$5$$ | $$50$$ | $$90$$ | ? | $$10$$ | $$18$$ | ? |
(For Blind students only)
Write the meaning of TFC, TVC, TC, AC and MC.
What do mean by variable factor?
What do mean by fixed factor?
Answer the following question in $$15$$ sentences.
Distinguish between total utility and marginal utility with the help of an example.
Answer the following question in $$4$$ sentences.
What are the four factors of production? And mention their rewards.
What is the shape of the average variable cost curve?
What is the relation between Average Variable Cost and Average Total Cost, if Total Fixed Cost is zero ?
Answer the following question in $$12$$ sentences.
The following table gives the TP schedule of labour. Find the corresponding average product and marginal product schedules.
| $$TP_L$$ | $$0$$ | $$15$$ | $$35$$ | $$50$$ | $$40$$ | $$48$$ |
| L | $$0$$ | $$1$$ | $$2$$ | $$3$$ | $$4$$ | $$5$$ |
What is the relationship between AC, AVC and MC?
What is the relationship between TVC and MC?
Define return to scale.
What are the assumptions of law of variable proportion?
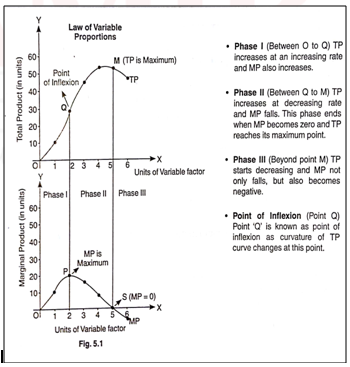
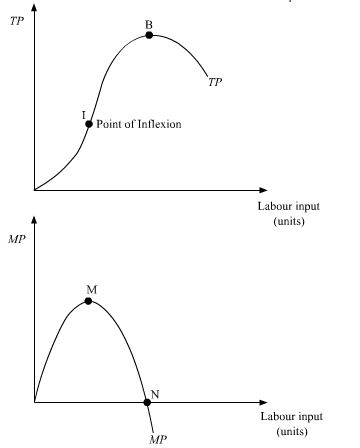
What is the relationship between TP and MP?
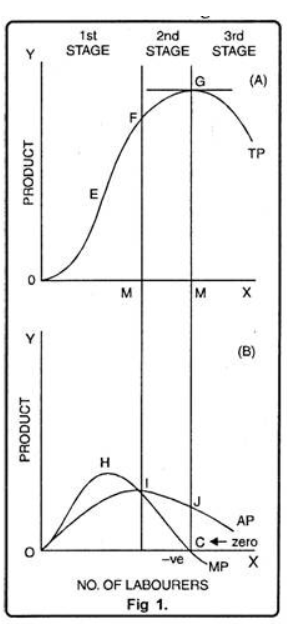
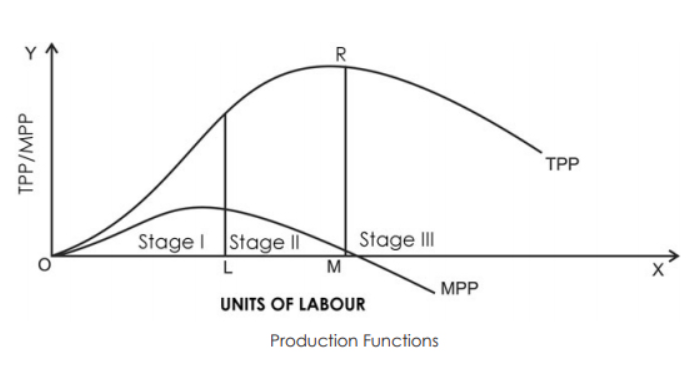
Explain the Law of Return of Factor. (use schedule and diagram)
When total product is at maximum point what will be the MP?
When TP decline then what will be MP?
What are the 3 stages of return to scale?
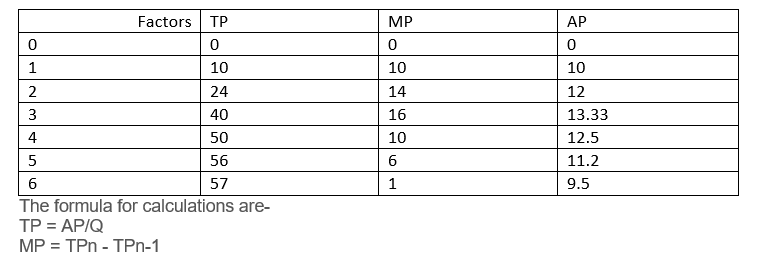
| Factors | TP | MP | AP |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 10 | - | 10 |
| 2 | 24 | - | 12 |
| 3 | 40 | 16 | 13.33 |
| 4 | - | 10 | - |
| 5 | - | 6 | 11.2 |
| 6 | 57 | 1 | 9.5 |
Explain the reasons behind the three phases of the law of variable proportions.
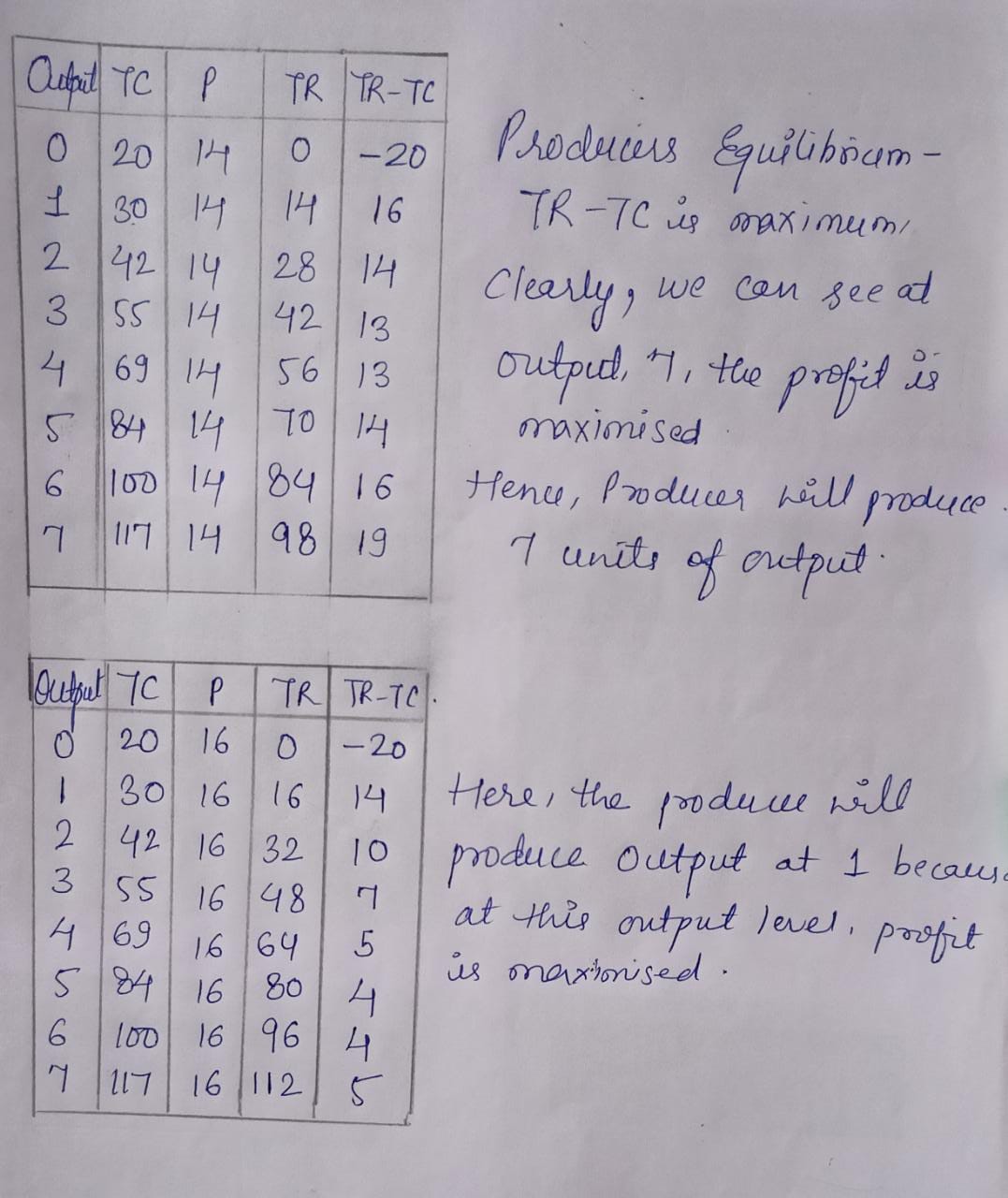
The perfectly competitive firm has the following cost function:
| Total output | Total cost |
| 0 | 20 |
| 1 | 30 |
| 2 | 42 |
| 3 | 55 |
| 4 | 69 |
| 5 | 84 |
| 6 | 100 |
| 7 | 117 |
Show the relationship between marginal cost (MC) and average cost (AC) through graphs.
Study the given table and answer the following the following questions:
| Capital | Resources (labour) | TP (Quintals) | MP (Quintals) | AP (Quintals) |
| 30 | 1 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| 30 | 2 | 25 | 15 | 12.5 |
| 30 | 3 | 37 | 12 | 12.3 |
| 30 | 4 | 47 | 10 | 11.8 |
| 30 | 5 | 55 | 8 | 11.0 |
| 30 | 6 | 60 | 5 | 10.0 |
| 30 | 7 | 63 | 3 | 9.0 |
| 30 | 8 | 63 | 0 | 7.9 |
| 30 | 9 | 62 | -1 | 6.8 |
Why does Total Product start to fall, if production continues by a producing firm in short run, even after Marginal Product becomes zero?
Explain the law of variable proportion with the help of the diagram.
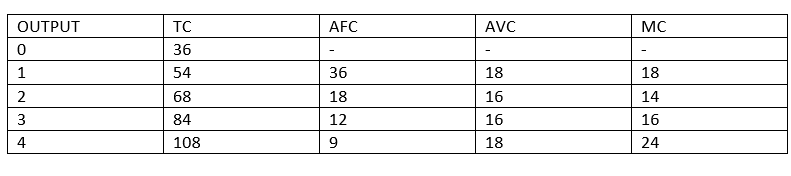
Calculate the following-
| Output | TC | AFC | AVC | MC |
| 0 | 36 | - | - | - |
| 1 | - | - | - | 18 |
| 2 | - | - | - | 14 |
| 3 | - | - | 16 | - |
| 4 | - | - | - | 24 |
Calculate total fixed cost, total variable cost, and marginal cost from the following:
| Output (units) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Total cost Rs. | 10 | 18 | 22 | 28 | 40 |
Critically examine the law of variable proportions.
Complete the following cost schedule: Quantity (in units) Total cost (Rs.) Total variable cost (Rs.) Average Variable Cost (Rs.) 0 200 0 __ 1 __ __ __ 2 __ 180 __ 3 __ __ 80 4 490 __ __
| Quantity (in units) | Total cost (Rs.) | Total variable cost (Rs.) | Average Variable Cost (Rs.) |
| 0 | 200 | 0 | __ |
| 1 | __ | __ | __ |
| 2 | __ | 180 | __ |
| 3 | __ | __ | 80 |
| 4 | 490 | __ | __ |
From the following total cost revenue schedule of a film, find out the level of output, using marginal cost and marginal revenue approach, at which the firm would be in equilibrium. Given reasons for your answer.
| Output (units) | Total Revenue (Rs.) | Total Cost (Rs.) |
| 1 | 10 | 8 |
| 2 | 18 | 15 |
| 3 | 24 | 21 |
| 4 | 28 | 25 |
| 5 | 30 | 33 |
Give the meaning and characteristics of production possibility frontier.
Given the behaviour of marginal product and total product as more and more units of only one input are employed while keeping other inputs as constant.
How is the development of an SEZ (special economic zone) expected to influence the cost structure of a firm?
Answer the following question in $$20$$ sentences.
A Firms SMC schedule in shown in the following table. TFC is Rs. $$100$$, find TVC, TC, AVC and SAC schedules of the firm.
| Q | $$0$$ | $$1$$ | $$2$$ | $$3$$ | $$4$$ | $$5$$ | $$6$$ |
| SMC | - | $$500$$ | $$300$$ | $$200$$ | $$300$$ | $$500$$ | $$800$$ |
What are the different phases in the Law of Variable Proportions in terms of marginal product? Give reason behind each phase. Use diagram.
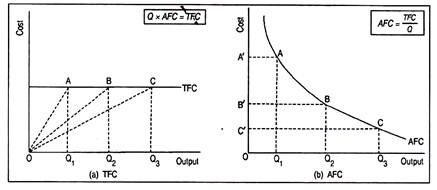
What does the average fixed cost curve look like? Why does it look so?
Average cost of production must ultimately rise when the level of output continues to expand, no matter it is related to short period production function or long period production function. Then, where is the difference between the two types of production functions?
Can there be some fixed cost in the long run? If not, why?
Class 11 Commerce Economics Extra Questions
- Collection Of Data Extra Questions
- Correlation Extra Questions
- Index Numbers Extra Questions
- Introduction To Economics Extra Questions
- Introduction To Microeconomics Extra Questions
- Market Equilibrium Extra Questions
- Measures Of Central Tendency Extra Questions
- Measures Of Dispersion Extra Questions
- Non-Competitive Markets Extra Questions
- Organisation Of Data Extra Questions
- Presentation Of Data Extra Questions
- Production And Costs Extra Questions
- Theory Of Consumer Behaviour Extra Questions
- The Theory Of The Firm Under Perfect Competition Extra Questions
- Use Of Statistical Tools Extra Questions