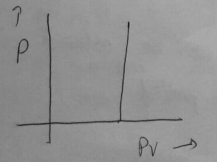States Of Matter - Class 11 Engineering Chemistry - Extra Questions
At $$27^0C$$ temperature 20 gm. $$H_2$$, 220 gm $$CO_2$$ and 140 gm $$N_2$$ are filled in a vessel having volume 2 litre. Find the total pressure in bar unit which gas is removed from the vessel so that pressure can be reduced by 50%.
What temperature would be necessary to double the volume of a gas STP if the pressure is decreased by 50%?
$$22.4$$ litres of a gas weighs $$70$$g at S.T.P. Calculate the weight (gm) of the gas if it occupies a volume of $$20$$ litres at $$27^o$$C and $$700$$mm Hg of pressure.
An evacuated glass vessel weighs $$50.0$$g when empty, $$148.0$$ gm when filled with a liquid of density $$0.98$$ g/mL and $$50.5$$ g when filled with an ideal gas at $$760$$ mm Hg at $$300$$k. Determine the molecular weight of the gas?
The molecular weights of oxygen and sulphur dioxide are $$32$$ and $$64$$ respectively. If $$1$$ litre of oxygen at $$15^o$$C and $$740$$ mm pressure contains $$N$$ molecules, the number of molecules in $$2$$ litre of sulphur dioxide under the same conditions of temperature and pressure will be:
500 mL of nitrogen at $$27^oC$$ are cooled to - $$5^oC$$ at the same pressure. Calculate the new volume.
Nitrogen gas is filled in a container of volume $$2.32L$$ at $$32^oC$$ and at $$4.7 atm$$ pressure. Calculate the number of moles of gas.[Write up to 3 decimal places]
The volume of given mass of a gas is $$0.6\ dm^3$$ at a pressure of $$101.325K\ Pa$$. Calculate the volume of the gas if its pressure is increased to $$142.860K\ Pa$$ at the same temperature. (Write answer up to 3 decimal places).
Calculate the volume occupied by $$5.25\ g$$ of nitrogen at $$26^{o}C$$ and $$74\cdot 2\ cm$$ of pressure.
$$1112\ dm^{3}$$ of dry carbon monooxide contains $$P$$ molecules. Calculate the number of molecules in $$336\ dm^{3}$$ of dry chlorides gas. Assume all measurement are made at the same temperature and pressure.
How much thermal energy should be added to $$3.45\ g\ Ne$$ in a $$10$$ liter flask to raise the tempereture from $$0^{o}C$$ to $$100^{o}C$$. (Atomic weight $$Ne=20.18$$)?
The mean kinetic energy of a molecule at $${ O }^{ 0 }C$$ is $$5.621\times { 10 }^{ -14 }erg$$. Calculate Boltzmann's constant. If the value of $$R=8.314\times { 10 }^{ 7 }erg$$, then calculate the no. of molecules present in one mole of gas.
Two flask of equal volume have been joined by a narrow tub of negligible volume. Initially both flasks are at 300 K containing 0.60 mole of $$O_2$$ gas at 0.5 atm pressure. One of the flask is then placed in a thermostat at 600 K. Calculate final pressure and the number of $$O_2$$ gas in each flask.
Write down the reason for the following:
a) Ink can be blotted with chalk.
b) Sweat can be blotted with tissue paper.
How many oxygen atoms combine with one carbon atom?
How many oxygen atoms combine with $$1000$$, carbon atom?
What is the law called which deals with the ratios of the volumes of the gaseous reactants and products?
Take water in a vessel and put a needle on the surface of water carefully.
a. Will the needle be immersed in water. Justify your answer.
b. Why do the water drops assume spherical shape?
Fill in the blanks
The average kinetic energy of the molecules of gas is directly proportional to the _________
What is the ideal gas equation? How can it be derived? Also, express it in terms of the density of the gas.
In the equation $$PV=RT$$, the value of $$R$$ in SI unit is (as nearest integer) :
At room temperature, ammonia gas at one atmosphere pressure and hydrogen chloride at $$P$$ atmospheric pressure allowed to effuse through identical pinholes from opposite ends of a glass tube of one metre length and uniform section. $$NH_{4}Cl$$ is first formed at a distance of $$60\ cm$$ from the end through which $$HCl$$ gas is sent in. What is the value of?
A polythene bag of $$3$$ litre capacity is filled by Helium gas (occupying $$Li$$ at $$0.3atm$$ and $$300K$$) at $$300K$$. Subsequently enough $$Ne$$ gas is filled to make total pressure $$0.4atm$$ at $$300K$$. Calculate ratio of moles of $$Ne$$ to $$He$$ in container.
At a pressure of 3 atm air (treated an ideal gas) is pumped into the tubes of a cycle rickshaw. The volume of each tube at a given pressure is $$0.004{m}^{3}$$. One of the tubes gets punched and the volume of the tube reduces to $$0.0008{m}^{3}$$. Find the number of moles of air that have leaked out? [Assume that the temperature remains constant at 300K. $$ R=25/3J{ mol }^{ -1 }{ K }^{ -1 } $$]
A sample of gas occupies $$10 L$$ at $${ 127 }^{ o }C$$ and 1 bar pressure . The gas is cooed to $${ -73 }^{ o }C$$ at the same pressure. What will be the volume of the gas?
Helium gas at $$27^oC$$ is subjected to a pressure change from 5 atm to 2 atm at constant temperature. The initial volume of the gas was $$10 dm^3$$. Calculate the change in volume of gas in $$dm^3$$.
One mole of an ideal gas is subjected to a process in which $$P = \dfrac{1}{8.21}$$ $$V$$ where $$P$$ is in atm and a $$ V$$ in litre. If the process is operating from $$1$$ atm to finally $$10$$ atm (no higher pressure achieved during the process) then that would be the maximum temperature obtained & at what instant will it occur in the process.
A compound exists in the gaseous state both as a monomer $$(A)$$ and dimer $$(A_2)$$. The molecular weight of the monomer is $$48$$. In an experiment, $$96$$ g of the compound was confined in a vessel of volume $$33.6$$ litres and heated to $$273^0$$C. Calculate the pressure developed, if the compound exists as a dimer to the extent of $$50$$ per cent by weight, under these conditions. $$(R = 0.082)$$
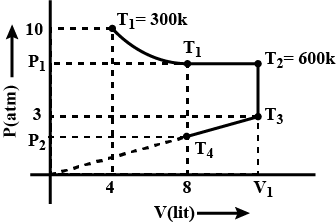
Fixed mass of a gas is subjected to the changes as shown is diagram, calculate $$T_3, T_4, P_1, P_2$$ and $$V_1$$ as shown is diagram. Considering gas obeys $$PV = nRT$$ equation.
One mole of $$NH_4Cl(s)$$ is kept in an open container & then covered with a lid. The container is now heated to $$600$$K where all $$NH_4Cl$$(s) dissociates into $$NH_3$$ and $$HCl(g)$$. If volume of the container is $$24.63$$ litres, calculate what will be the final pressure of gases inside the container. Also find whether the lid would stay or bounce off if it can with stand a pressure difference of $$5.5$$ atm. Assume that outside air is at $$300$$K and $$1$$ atm pressure.
Pressure of gas contained in a closed vessels is increased by $$0.4\%$$, when heated by $$^{ o }{ C }$$. Calculate its final temperature. Assume ideal nature.
The density of a gas is $$30^{o}C$$ and $$1.3\ atm$$ is $$0.027\ g/ cc$$. Find its $$M.W$$.
What volume of oxygen gas $$(O_2)$$ measured at $$0^0$$C and $$1$$ atm, is needed to burn completely $$1$$L, of propane gas $$(C_3H_8)$$ measured under the same conditions?
What is the density of helium at $$500^{o}\ C$$ and $$100\ mm$$ pressure?
A flask of $$2\ dm^{3}$$ capacity contains $$O_{2}$$ at $$101.325\ k Pa$$ and $$300\ K$$. The gas pressure is reduced to $$0.1\ Pa$$. Assuming ideal behaviour, answer the following:
i) What will be the volume of the gas which is left behind?
ii) What amount of $$O_{2}$$ and $$t$$ he corresponding number of molecules are left behind in the flask?
iii) In now $$2g$$ of $$N_{2}$$ is introduced, what will be the pressure of the flask
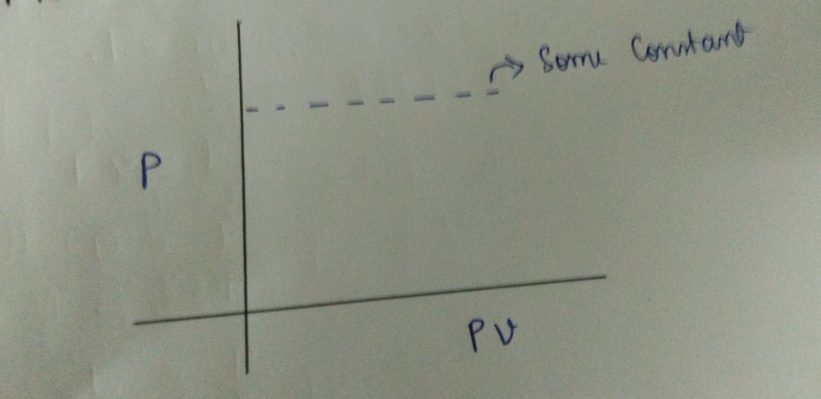
Plot between P vs PV.
At 300 K certain mass of a gas occupies 1 x $$10^{-1}dm^3$$ volume. Calculate its volume at 450K and at the same pressure.
One litre of a gas weighs $$2g$$ at $$300K$$ and $$1 atm$$ pressure. If the pressure is made $$0.75 atm$$ at which of the following temperatures will one litre of the same gas, weigh one gram?
300 ml of gas at $$27^0$$C is cooled to $$-3^0$$C at constant pressure, the final volume is:
Tempreture at the foot of a mountain is $$30^{0}C$$ and pressure is 760mm whereas at the top of the mountain these are $$0^{0}C$$ and 710mm.compair the densities of the air at the foot and the topof the mountain.
Find the temp. at which volume & pressure of $$28g$$ nitrogen gas becomes $${ 10dm }^{ 3 }$$ & $$2.46$$ atmosphere resp.
How does kinetic energy of photoelectron change when the intensity of radiation is increased?
11.35 litres of a gas at STP are found to have to have a mass of 8.5g. the number of mole of gas present in 34 g of gas is ?
Which law relates solubility of solvents with pressure?
Match the following gas laws with the equation representing them.
Give various forms of ideal gas equation.
Two flasks $$A$$ and $$B$$ have equal volumes. Flask $$A$$ contains $$H_2$$ and is maintained at $$300 K$$ while $$B$$ contains equal mass of $$CH_4$$ gas and is maintained at $$600 K$$. In which flask pressure is greater? How many times more?
Surface tension tends to minimise the surface area of a liquid. Suggest an experiment to prove this.
(Follow the pattern: Required materials, procedure, expected observation).
Define Dalton's law of partial pressure. Using this law, how is the pressure of dry gas determined?
Explain the following:
$$AlF_{3}$$ is a high melting solid whereas $$SiF_{4}$$ is a gas.
Estimate the average thermal energy of a helium atom at
(i) room temperature (27 $$\displaystyle ^{\circ}C$$),
(ii) the temperature on the surface of the Sun (6000 K),
(iii) the temperature of 10 million kelvin (the typical core temperature in the case of a star).
The heat absorbed during the isothermal expansion of an ideal gas against vacuum is
Match the Column-I with Column-II.
The pressure exerted by $$12g$$ of an ideal gas at temperature $${1}^{o}C$$ in a vessel of volume $$V$$ litre is one atm. When the temperature is increased by $$10$$ degrees at the same volume, the pressure increases by $$10$$%. Calculate the temperature $$t$$ and volume $$V$$. (Molecular weight of the gas$$=120$$)
Butane gas burns in air according to the following reaction, $$2{ C }_{ 4 }{ H }_{ 10 }+13{ O }_{ 2 }\longrightarrow 10{ H }_{ 2 }O+8{ CO }_{ 2 }$$.
Suppose the initial and final temperatures are equal and high enough so that all reactants and products act as perfect gases. Two moles of butane are mixed with $$13$$ moles of oxygen and then completely reached. Find the final pressure (if the volume remains unchanged and the pressure before the reaction is $${P}_{0}$$)?
$$2{ C }_{ 4 }{ H }_{ 10 }+13{ O }_{ 2 }\longrightarrow 10{ H }_{ 2 }O+8{ CO }_{ 2 }$$.
Suppose the initial and final temperatures are equal and high enough so that all reactants and products act as perfect gases. Two moles of butane are mixed with $$13$$ moles of oxygen and then completely reached. Find the final pressure (if the volume remains unchanged and the pressure before the reaction is $${P}_{0}$$)?
A sample of calcium carbonate is $$80\%$$ pure, $$25$$ gm of this sample is treated with excess of $$HCl$$. How much volume of $$CO_2$$ will be obtained at $$1$$ atm & $$273$$ K?
At constant temperature, a gas is at a pressure of $$1080$$ mm Hg. If the volume is decreased by $$40$$%, find the new pressure of the gas.
How many molecules of $$CO_2$$ gas is passed in $$900$$ml water at $$298$$ K temperature . The value of $$K_H$$ is $$6.02 \times 10^{-4}$$ bar and partial pressure of $$CO_2$$ gas is $$ 2 \times 10^{-8} bar $$:
Calculate the total pressure of a mixture of 8 g of oxygen and 4g of hydrogen confined in vessel of $$1d{ m }^{ 3 }$$ at $${ 27 }^{ 0 }C$$.
$$\left( R=0.083\quad bar\quad d{ m }^{ 3 }{ k }^{ -1 }{ mol }^{ -1 } \right) $$
A certain mass of gas occupied $$850ml$$ at a pressure of $$760\ mm$$ of $$Hg$$. On increasing the pressure it was found that the volume of the gas was $$75%$$ of its initial value. Assuming constant temperature, find the final pressure of the gas?
A gas cylinder containing cooking gas can withstand a pressure of $$14.9$$ atm. The pressure guage of the cylinder indicates $$12$$ atm at $$27^{o}C$$. Due to sudden fire in the building, its temperature stats rising. At what temperature cylinder will explode?
$$500 ml$$ of a gas A exerts a pressure $$600 torr$$ in a vessel. $$400 ml$$ of a gas B exerts a pressure $$200 torr$$ in another vessel. If the $$2$$ gases are mixed in a $$3 L$$ vessel then the total pressure of the gas is?
The density of a mixture of $$O_2$$ and $$N_2$$ gases at $$1$$ atm and $$273$$K is $$0.0013$$ gm/ml. If partial pressure of $$O_2$$ in the mixture is A then calculate value of $$25$$A.
One mole of $$N_2O_4(g)$$ at $$300$$K is kept in a close container under one atmosphere. It is heated $$600$$K when $$20\%$$ by mass of $$N_2O_4(g)$$ decomposes to $$NO_2(g)$$. The resultant pressure is:
28.32 litres of chorine were libereted at noramal condition of tempreture and pressure. calculate the volume of the gas at $$12^{0}C$$ and780mm pressure.
One litre gas at 40 K and 300 atm pressure is compressed to a pressure of 600 atm and 200 K. the comressibillity factor is changed from 1.2 to 1.6 respectively.calculate the final volume of the gas ?
A mixture of $$90$$ $$mole%$$ oh $${H}_{2}$$ $$10$$ $${%}_{2}$$ $${D}_{2}$$ at $$298\ K$$ and a pressure of $$1$$ atm is allowed to effuse through a small orifice of area $$03\ {mm}^{2}.$$ Calculate the composition of the initial gas that passes through.
At constant temperature $$250\ mL$$ of argon at a $$760\ mm\ Hg$$ pressure and $$60\ mL$$ of nitrogen at $$500\ mm$$ pressure are put together in one litre flask. The final pressure is _________ $$mm\ Hg$$.
An unspecified quantity of an ideal gas was at initial pressure of $$5$$ atm and temperature of $$303$$K. The gas is expanded at $$303$$K until the volume has increased by $$60\%$$ of the initial value. Next, the quantity of the gas in the vessel is increased by $$20\%$$ of the initial value while the volume is maintained constant. Finally, the temperature is adjusted at constant volume until the gas pressure is again $$5$$ atm. What is the final temperature, in Kelvin?
At $$627^oC$$ and $$1\ atm, SO_3$$ partially dissociates into $$SO_2$$ and $$O_2$$. One litre of the equilibrium mixture weighs $$0.94\ g$$ under the above conditions. Calculate the partial pressures of the constituent gases in the mixture.
In a gravity free cabin, a non-conducting liquid of surface tension T and possessing uniform volume charge density p is sprayed into large number of drops. After spraying, the drops float around in the cabin and keep on breaking apart into smaller drops and coalescing into larger drops. While floating, the electrostatic forces between the drops are negligible. Estimate radius of the drops when their number reaches a stable value.
The sap in trees, which consists mainly of water in summer, rises in a system of capillaries of radius $$r=2.5 \times 10^{-5}m$$. The surface tension of sap is $$T=7.28 \times 10^{-2}Nm^{-1}$$ and the angle of contact is $$0^{\circ}$$. Does surface tension alone account for the supply of water to the top of all trees?
Class 11 Engineering Chemistry Extra Questions
- Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure Extra Questions
- Classification Of Elements And Periodicity In Properties Extra Questions
- Environmental Chemistry Extra Questions
- Equilibrium Extra Questions
- Hydrocarbons Extra Questions
- Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles And Techniques Extra Questions
- Redox Reactions Extra Questions
- Some Basic Concepts Of Chemistry Extra Questions
- Some P-Block Elements Extra Questions
- States Of Matter Extra Questions
- Structure Of Atom Extra Questions
- Thermodynamics Extra Questions