Anatomy Of Flowering Plants - Class 11 Medical Biology - Extra Questions
Discuss the internal structure of monocot roots.
How open vascular bundles differ from closed vascular bundles?
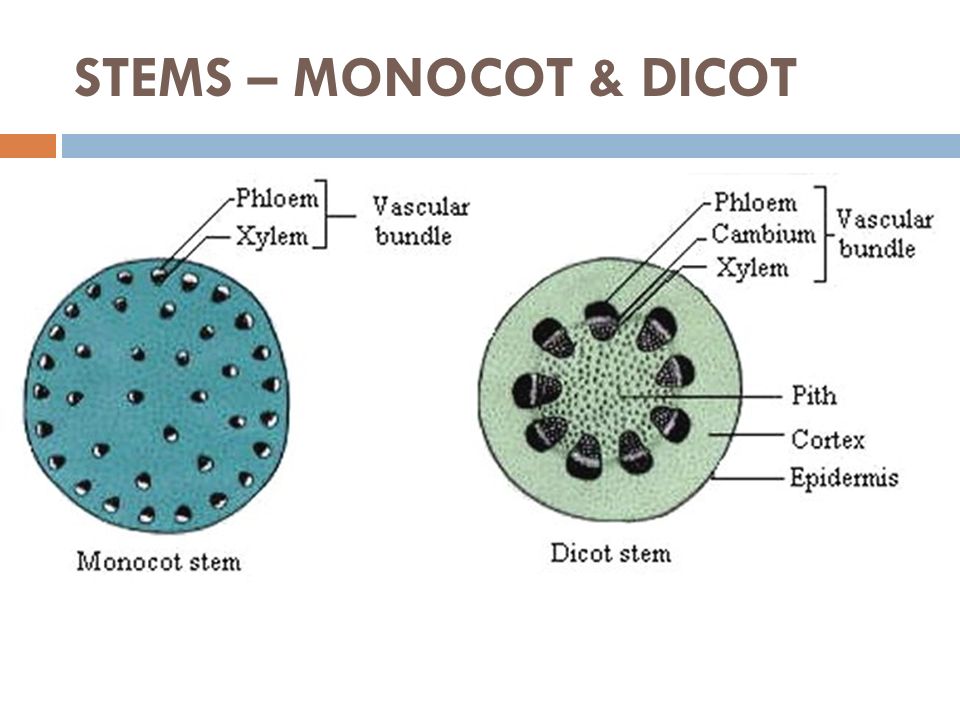
Mention two differences in the vascular bundles of sunflower and maize stems.
What is the difference between fibers and sclereids in plant histology? Give one example of each.
A T.S. of a trunk of a tree shows concentric rings which are known as growth rings. How are these rings formed?
What are medullary rays and what are their functions?
Answer the following with reference to the anatomy of dicot root.
Which type of cells constitute the cortex?
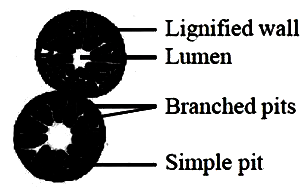
Give any four differences between tracheids and vessels.
How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
Which plant tissues are responsible for giving a plant strength and support?
What is eustele?
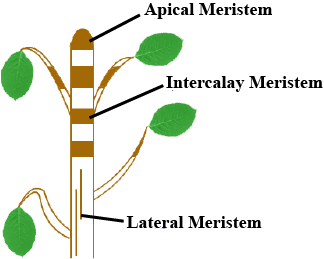
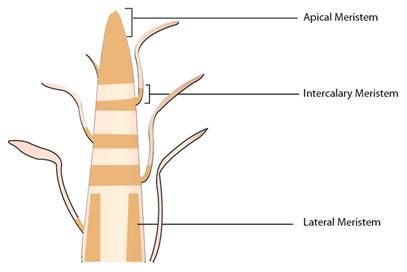
Define meristems.
What is an annual ring?
Name the different components of xylem and draw the living component of it.
Draw illustrations to bring out the anatomical difference between
(a) Monocot root and dicot root (b) Monocot stem and dicot stem
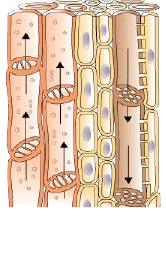
Why are xylem and phloem classified as complex tissues? Describe the structure of phloem.
What are passage cells?
Write any three functions of epidermal tissue system.
Give three anatomical differences between a monocot root and a dicot root.
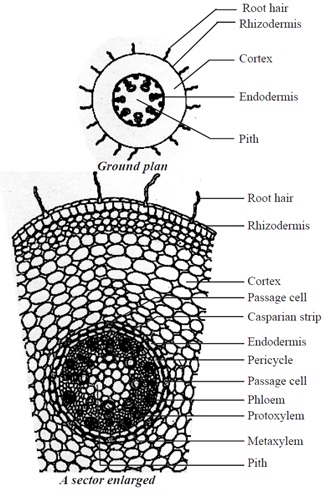
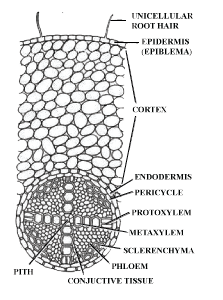
Describe the primary structure of monocot root.
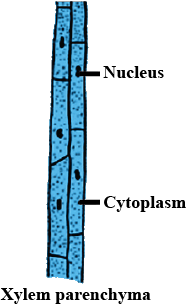
Observe the given picture.
a) Which portion forms clear cytoplasm and prominent nucleus?
b) Which functional portion is performing the function of conductivity?
c) Which portion is considered dead tissue?
d) Which portion stores starch and fats?
Answer the following questions in short.- Which ground tissue are you eating when you eat mashed potatoes?
- Which ground tissue makes the shell of a groundnut hard?
Draw and label brachysclereids.
Write any three anatomical differences between monocot root and dicot root
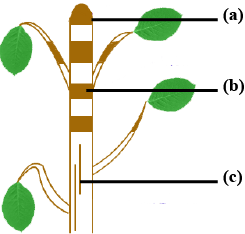
Answer the questions with respect to the given figure.
i) Copy the diagram and name the parts marked(a) to (c).
ii) Which part is responsible for elongation of the stem?
iii) Which part is responsible for secondary growth?
iv) Name the part which is responsible for elongation of internodes.
Which meristem does produce growth in length?
Why is cambium considered to be a lateral meristem?
Cut a transverse section of young stem of a plant from your school garden and observe it under the microscope. How would you ascertain whether it is monocot stem or dicot stem. Give reasons.
Differentiate fusiform initials and ray initials.
Name the most durable wood.
There are two unlabelled microscopic slides showing transverse sections of root and stem of a dicot plant. How will you differentiate between the two on the basis of the arrangement of the conducting tissue?
Define collateral vascular bundle.
Distinguish between Tracheid and vessel.
Define bicollateral vascular bundle.
What makes the apical meristem of the root sub-terminal?
What forms the cambial ring in a dicot stem during the secondary growth?
Differentiate between root apex and shoot apex.
Where is pericycle located in dicot root?
How are the xylem vessels arranged in dicot root?
Name and define the different types of vascular bundles.
Describe the structure and organisation of stem apex.
Briefly describe the anatomy of primary dicot root.
Differentiate between.
Collateral vascular bundle and concentric vascular bundle.
Short / Long answer type questions.
Give a brief account of complex tissue present in plants.
Short / Long answer type questions.
Answer the following with reference to the anatomy of dicot stem:
(i) Where exactly are the cambial cells located in the vascular bundles?, (ii) What is the name given to such a bundle, (iii) How are the xylem vessels arranged ?, (iv) What type of cells constitute the pith ?
Short / Long answer type questions .
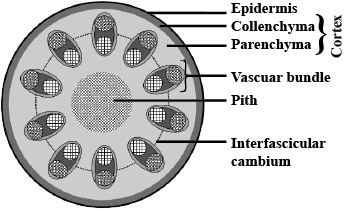
Give the anatomical (internal structure) differences between a dicot stem and a monocot stem.
Very short answer type.
What is an open type of vascular bundle?
State the location and function of collenchyma and sclerenchyma.
Draw a labelled diagram of the transverse section of a dicot root.
Explain the process of secondary growth in the stelar region of a dicot stem.
Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Select the odd one. Apical, Lateral, Intercalary, Epidermis
What are meristmatic and permanent tissue?
The tissues derived directly from the meristem of a embryo is called as ............
How many types of ground tissues are there? What are they? Write about parenchyma.
Distinguish between the following with suitable diagram:
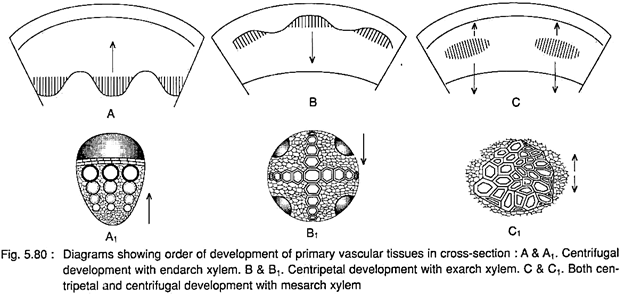
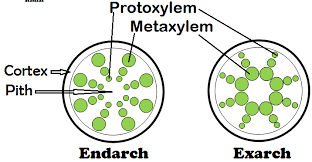
Exarch and endarch
Phellogen cuts off closely arranged parenchymatous cells on the outer side instead of cork cells. Why?
Give three ways in which phloem tubes differs from the xylem vessels.
cells which can secret substances at the epithelial tissue folds inward
What are the various protective tissues present in plants? Explain with the help of examples.
Arrested flower development.
Give reasons.
Intercellular spaces are absent in sclerenchymatous tissue.
Name the tissue found in the husk of a coconut. List two characteristics of the tissue.
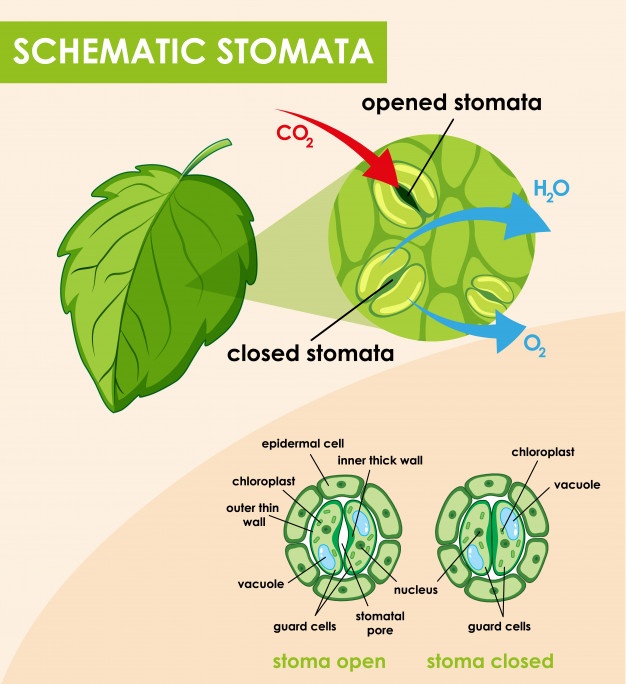
The stomatal pore is guarded by two bean-shaped guard cells. Are there other types of cells that are part of the stomatal complex? How is their presence in the vicinity of guard cells functionally effective?
Write the name of the following tissue.
Tissue responsible for increasing the height of plants.
Tissue responsible for increasing the height of plants.
Explain the structure and functions of xylem?
Protoxylem is the first formed xylem. If the protoxylem lies next to phloem what kind of arrangement of xylem would you call it?
Name the chief mechanical supporting tissue in plants.
The cross-section of a plant material showed the following features when viewed under the microscope.
(a) The vascular bundles were radially arranged.
(b) Four xylem strands with exarch condition of protoxylem.
To which organ should it be assigned?
What part of the plant would show the following:
(a) Radial vascular bundle
(b) Polyarch xylem
(c) Well developed pith
Distinguish between open and closed vascular bundles.
State the location and function of different types of meristematic tissues in plants.
What is a periderm? How does periderm formation take place in the dicot stems?
Cork cambium forms tissues that form the cork. Do you agree with this statement? Explain.
Draw and label the diagram of the T.S. of stem.
Distinguish between Phellem and phelloderm.
Distingusih between Fascicular cambium and interfascicular cambium.
Distinguish between Softwood and hardwood.
Draw a labelled diagram of T.S. of dicot root. Give four differences between internal structure of dicot and monocot root.
Differentiate between .
Open bundle and closed bundle
Differentiate between.
Amphicribal vascular bundle and amphivasal vascular bundle
Very short answer type :
What is a bicollateral vascular bundle ?
Very short answer type :
Why is propagation through grafting not successful in monocots ?
Define fascicular cambium and interfascicular cambium.
Class 11 Medical Biology Extra Questions
- Anatomy Of Flowering Plants Extra Questions
- Animal Kingdom Extra Questions
- Biological Classification Extra Questions
- Biomolecules Extra Questions
- Body Fluids And Circulation Extra Questions
- Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Extra Questions
- Cell Cycle And Cell Division Extra Questions
- Cell The Unit Of Life Extra Questions
- Chemical Coordination And Integration Extra Questions
- Digestion And Absorption Extra Questions
- Excretory Products And Their Elimination Extra Questions
- Locomotion And Movement Extra Questions
- Mineral Nutrition Extra Questions
- Morphology Of Flowering Plants Extra Questions
- Neural Control And Coordination Extra Questions
- Photosynthesis In Higher Plants Extra Questions
- Plant Growth And Development Extra Questions
- Plant Kingdom Extra Questions
- Respiration In Plants Extra Questions
- Structural Organisation In Animals Extra Questions
- The Living World Extra Questions
- Transport In Plants Extra Questions