Locomotion And Movement - Class 11 Medical Biology - Extra Questions
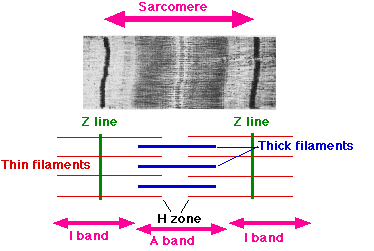
State whether the given statement is true or false.H-zone of striated muscle fibre represents both thick and thin filaments.
What lubricates the freely movable joint at the shoulder?
Differentiate between A-band and I-band.
Name the two special proteins which constitute the contractile filaments of a muscle fibre
Very short answer type.
Give one example each of fibrous joint and cartilaginous joint.
Very short answer type.
Why does the shoulder joint have more freedom of movement than any other joint in the body?
Which type of movable joint makes the hip joint?
What is a joint?
The place where two or more bones are connected is called a ______.
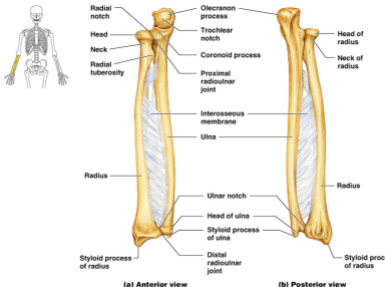
Which bone is bigger, the ulna or radius ?
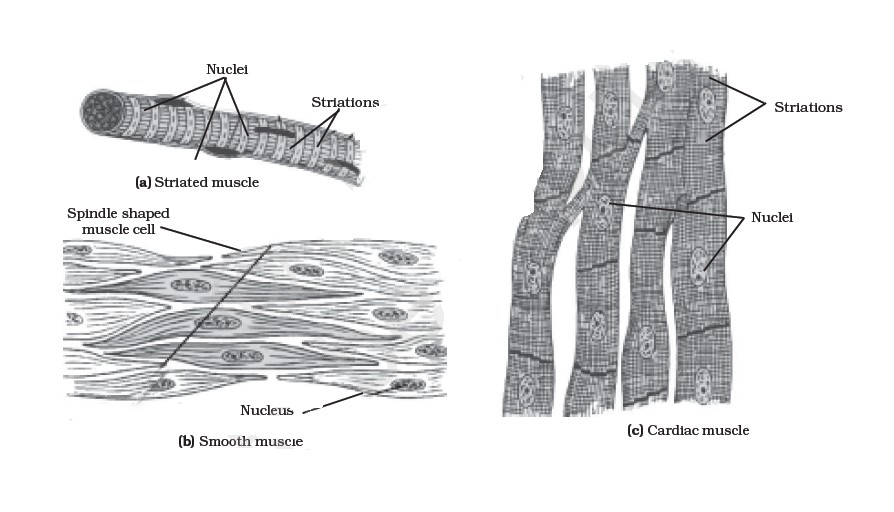
Draw a labelled diagram of various types of muscles found in the human body.
Thin filament of myofibril contains 2 F actins and two other proteins namely .......... and ...........
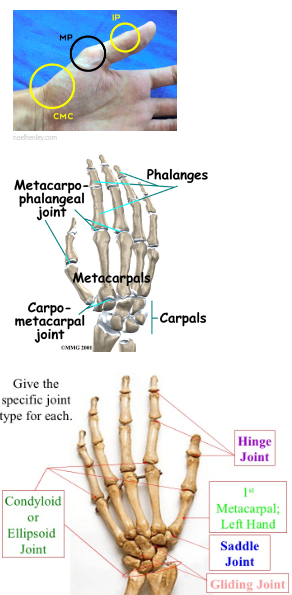
Name the type of joint between carpal/metacarpal of a thumb.
Name the type of joint between pubic bones in the pelvic girdle.
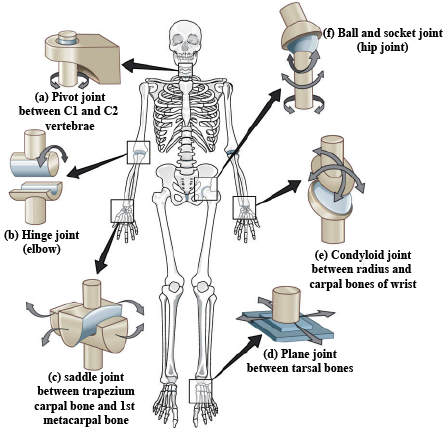
Name the type of joint between the following.
(a) Atlas/axis(b) Carpal/metacarpal of thumb(c) Between phalanges(d) Femur/acetabulum(e) Between cranial bones(f) Between pubic bones in the pelvic girdle
In a muscle fibre, Ca $$^{++}$$ is stored in
Write true or false. If false change the statement so that it is true.
(a) Actin is present in thin filament.(b) H-zone of striated muscle fibre represents both thick and thin filaments.(c) Human skeleton has 206 bones.(d) There are 11 pairs of ribs in man.(e) Sternum is present on the ventral side of the body.
(b) H-zone of striated muscle fibre represents both thick and thin filaments.
(c) Human skeleton has 206 bones.
(d) There are 11 pairs of ribs in man.
(e) Sternum is present on the ventral side of the body.
Name the type of joint between cranial bones.
Match the following
| Column I | Column II |
| Smooth muscle | Myoglobin |
| Tropomyosin | Thin filament |
| Red muscle | Sutures |
| Skull | Involuntary |
Define the term physiotherapy.
If there are no joints then will it be possible to move?
Define botulism. Name the bacterium responsible for botulism.
Can we bend our body at every part?
Give an example of fixed joint.
The skeletal system has many other functions besides helping in movements. Explain
Name the places where two parts of the body are seen to be joined together.
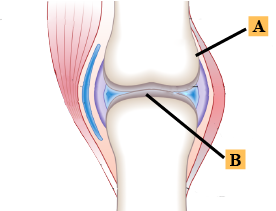
Name the joint, label part A and B and write their functions.
Name the type of joint between the cranial bones.
Short / Long answer type questions.
Describe the structure of a myofibril of a striated muscle.
Short / Long answer type questions.
Intramembranous ossification involves the formation of bone directly on or within loose fibrous connective tissue membranes.Which bones of the body develop by intramembranous ossification?
Very short answer type.
Name the structure by which Haversian canals of a bone are interconnected.
What is a joint? Describe various types of joints with suitable examples.
Match the terms to these definitions.
Abductor, adductor, false rib, joint, supinator, rigor mortis, motor, end-plate, spasm, pronator, muscle twitch
.......... is a point where two or more bones meet.
Give the difference between voluntary and involuntary muscles.
Describe any two types of cartilaginous joint giving examples.
Differentiate between skeletal and smooth muscles.
What is a joint? Describe various kinds of joint found in our body.
Describe the structure of actin and myosin filaments.(The Length Sarcomere is $$2.5\mu m($$.Actin rod $$=1\mu m,)$$ myosin$$=1.5\mu m$$ $$1$$Myosin filament & $$1$$ Actin filament is surrounded by $$3$$ Myosin filament.)
How is tetany cousted?
Explain how the skeletal systems performs the following.
Support.
Which tissue is affected by Myasthenia gravis? What is the underlying cause?
Write the type of joint which is used for the following movement:
A person lifts weights to build up his biceps.
Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles. Give one example of each type.
Answer the following.
How many types of muscles are there? Which are those types?
How many types of muscles are there? Which are those types?
A muscle fibre tapers at both ends and does not show striations. Name the muscle fibre.
Why is the skeletal system so important ?
What is osteoporosis?
Name the different types or joints? Give one example of each type.
What type of joint is the thumb?
Where does the spinal cord typically terminate?
What type of joint is found in the neck?
Why is the anatomical position of the body important?
Which is likely to heal faster, a bone injury or a cartilage injury?
Where is the "funny bone " located ?
What is the function of the muscular system?
Write briefly about the biological importance of Fibrous joints.
Thin filament of myofibrils contains $$2$$ 'F' actins and two other proteins namely ............ and ............
Write briefly about the biological importance of Synovial joints.
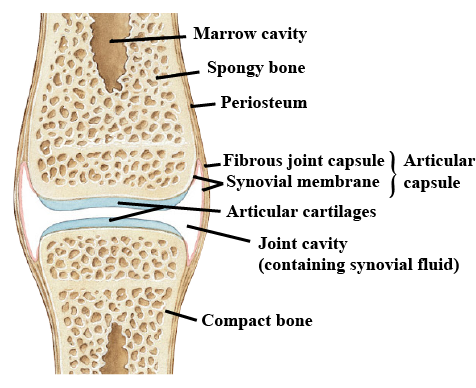
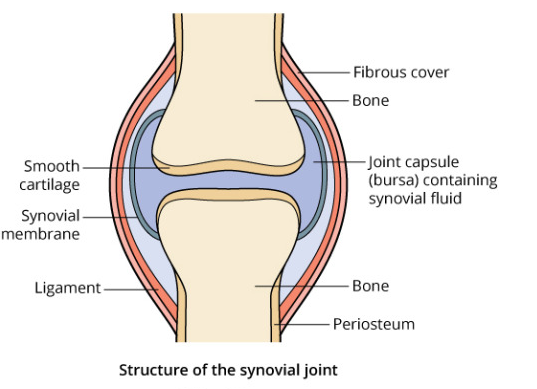
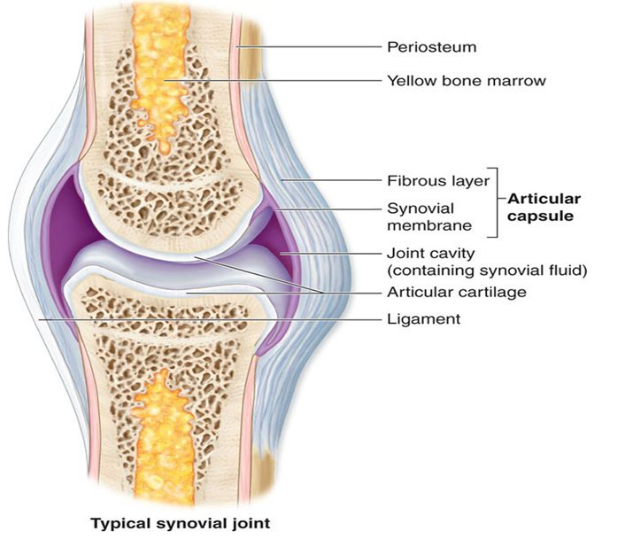
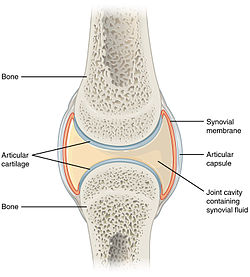
Name the fluid present in the joint capsule. What is its function?
Describe the structure of synovial joint with the help of a neat labelled diagram.
How does calcium affect the process of muscle contraction?
SHORT ANSWER TYPE
Some people in old age complain of stiff joints. What do you think could be a possible reason for it ?
Short/ Long answer type questions.
How is the structure of a sarcomere suitable for the contractility of the muscle? Explain its function according to sliding filament theory.
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
The skull bones are joined at the sutures by .......... tissue while the bodies of vertebrae are joined by .......... tissue.
A synovial cavity is found in .......... joint.
Short/ Long answer type questions.
When two stimuli are applied to the muscle with the second following the first closely enough in time, a large contraction occurs on the application of the second stimulus. Explain.
What are the different types of joints ? Give one example of each type
Which of the following is contractile protein
a) Myosin b) Actin
Mention any two contractile proteins.
Match the following and mark the correct option
Describe typical synovial joint with a neat labelled diagram.
What is the function of the joint (1)?
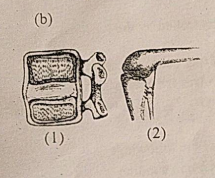
Describe any two types of cartilaginous joints giving examples.
An elderly woman slipped in the bathroom and had severe pain in her lower back. After X-ray examination doctors told her it is due to a slipped disc. What does that mean? How does it affect our health?
Class 11 Medical Biology Extra Questions
- Anatomy Of Flowering Plants Extra Questions
- Animal Kingdom Extra Questions
- Biological Classification Extra Questions
- Biomolecules Extra Questions
- Body Fluids And Circulation Extra Questions
- Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Extra Questions
- Cell Cycle And Cell Division Extra Questions
- Cell The Unit Of Life Extra Questions
- Chemical Coordination And Integration Extra Questions
- Digestion And Absorption Extra Questions
- Excretory Products And Their Elimination Extra Questions
- Locomotion And Movement Extra Questions
- Mineral Nutrition Extra Questions
- Morphology Of Flowering Plants Extra Questions
- Neural Control And Coordination Extra Questions
- Photosynthesis In Higher Plants Extra Questions
- Plant Growth And Development Extra Questions
- Plant Kingdom Extra Questions
- Respiration In Plants Extra Questions
- Structural Organisation In Animals Extra Questions
- The Living World Extra Questions
- Transport In Plants Extra Questions