Transport In Plants - Class 11 Medical Biology - Extra Questions
Differentiate between absorption and adsorption.
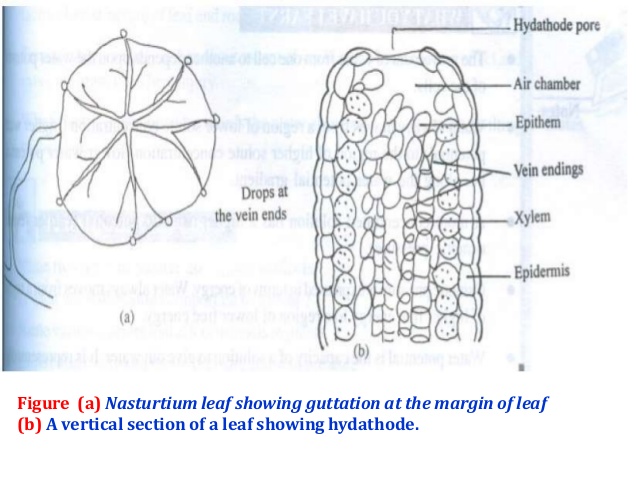
Loss of water as droplets from the margins of certain leaves is called ?
Differentiate between Guttation and bleeding.
Differentiate between guttation and bleeding in plants.
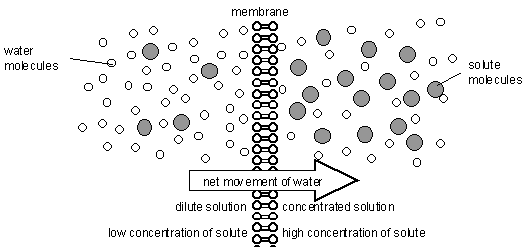
Osmosis is a special kind of diffusion, in which water diffuses across the cell membrane. The rate and direction of osmosis depends upon both _____.
The $$C_4$$ plants are twice as efficient as $$C_3$$ plants in terms of fixing $$CO_2$$ but lose only as much water as $$C_3$$ plants for the same amount of $$CO_2$$ fixed.
Diffusion is a slow process and is not dependent on a system. Why?
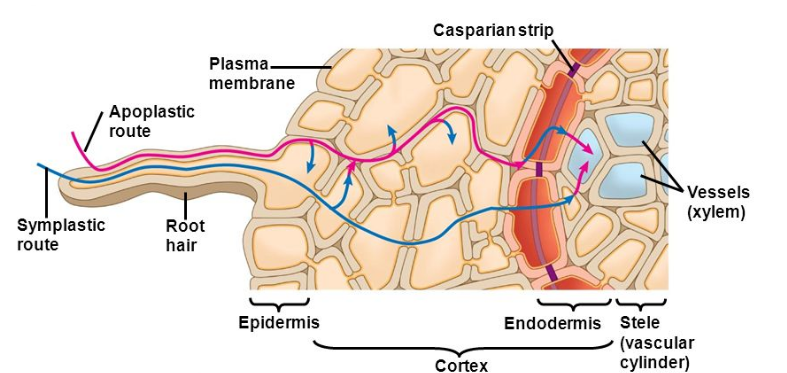
What are apoplast and symplast?
Osmosis is an example of active transport. True or False? Explain.
"Transpiration is necessary evil". Explain.
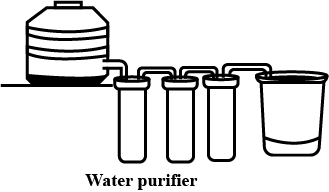
Which process takes place in the water purifier?
Give reasons for this sentence:
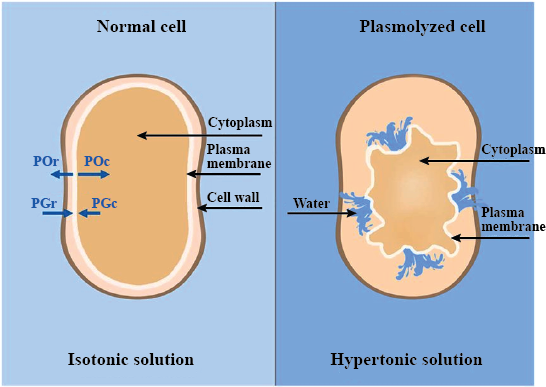
A plant cell when kept in a hypertonic salt solution for about $$30$$ minutes turns flaccid.
Differentiate between.
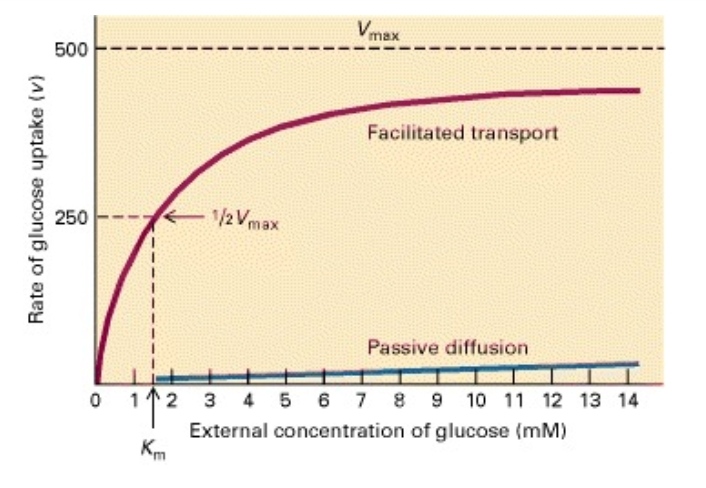
Facilitated diffusion and active transport
Explain the symplastic movement and apoplastic movement of water in the cell.
Why do molecules diffuse down their concentration gradients?
The water potential of pure water changes when solute is added to it
Define chemiosmosis.
Define guttation.
What is imbibition?
Briefly explain the following:
i) Osmosis
ii) Allele
iii) Pulse
iv) Reflex action
v) Synapse
Which of the following has highest water potential ? (i) 1 M Salt solution (ii) 1 M Sugar solution (iii) Distilled water (iv) 1 M Sugar solution with 2-3 bars pressure
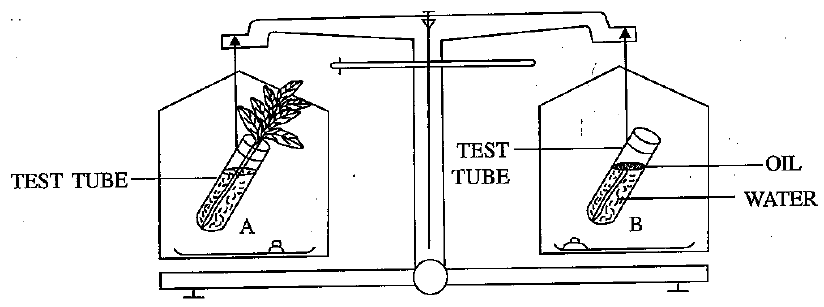
The figure given below represents experimental set up with a weighing machine to demonstrate a particular process in plants. The experimental set up was placed in bright sunlight. Study the diagram and answer the following questions:
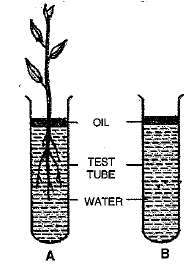
What is the purpose of keeping the test tube B in the experimental set up?
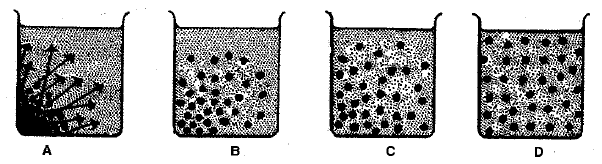
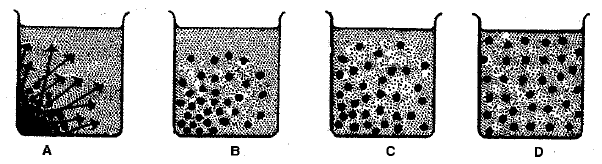
In an experimental set-up, a dye was placed at the bottom of a beaker filled with water as shown in figure A, below. After some time, the entire water in the beaker got coloured uniformly, as shown in figure D.
(a) Name and define the phenomenon shown in the experiment.
Differentiate between
Water potential and diffusion pressure deficit.
Fill in the blanks :
The water potential of pure water is ...............
What would be $$\Psi _p$$ of a flaccid cell?
Describe Uniporter Catalyzed Transport ?
When separated by a semipermeable membrane, water enters the sugar solution. What would you call the sugar solution as osmotically active or inactive?
Explain an activity to show that stem conducts water and other substances.
Distinguish uniport transport method from passive diffusion ?
What will happen if a plant cell is kept in solution of higher water potential?
A plant is transpiring rapidly. Will it show root pressure also?
What would be $$\Psi _p$$ of a plasmolysed cell ?
Compare the imbibing capacities of pea and wheat seeds.
How does carbon dioxide diffuse in submerged plants?
i) Solution of 'A' chamber has higher $$Psi$$ W.
ii) Solution of 'B' chamber has higher $$Psi \, s$$
iii) At equilibrium 'A' chamber will have lower $$Psi \,w$$
iv) Osmosis occurs in A $$\rightarrow$$ B direction.
How many above conclusions are incorrect with respect to given set up ?
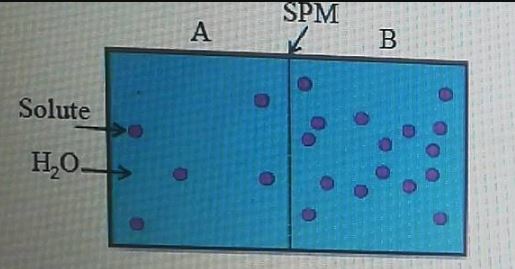
What is root pressure? How is it useful to plants?
State four differences between transpiration and guttation.
Write about respiration in mangroves that grow in marshylands.
Doors of house swell up in the rainy season due to what reasons?
Transpiration is a necessary evil. Justify.
The phenomenon by which living or dead plant cells absorb water by surface attraction.
The bending movements of certain flowers towards the sun and the sleep movements of certain plants at night are examples of ..................
What is root pressure?
What is the water potential value of pure water? If $$5$$ grams of sodium chloride is added, what will happen to its water potential value?
Define and explain water potential
Why do dry seeds imbibe water when placed in it?
Describe an activity to show the effect of low pressure and particulate nuclei over water vapours?
Briefly describe water potential. What are the factors affecting it?
Explain what will happen to a plant cell, if it is kept in a solution having higher water potential.
What is osmosis?
Given below is an experimental set up to demonstrate a particular process. Study the same and answer the following questions.
i. Name the physiological process being studied.
ii. Explain the process mentioned above.
iii. What is the aim of the above experiment?
iv. What would you observe in the experimental set up after an hour? Give a reason to support your answer.
v. Mention any three adaptations found in plants to overcome the physiological process mentioned in (i) above.
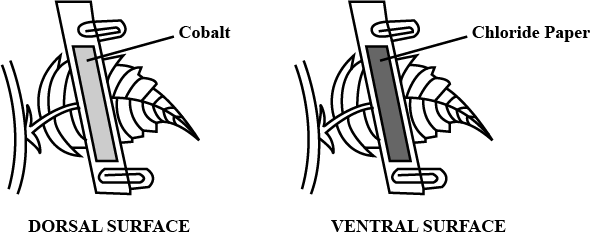
Define:
(i) Radial vascular bundle (ii) Rigor mortis (iii) Root pressure
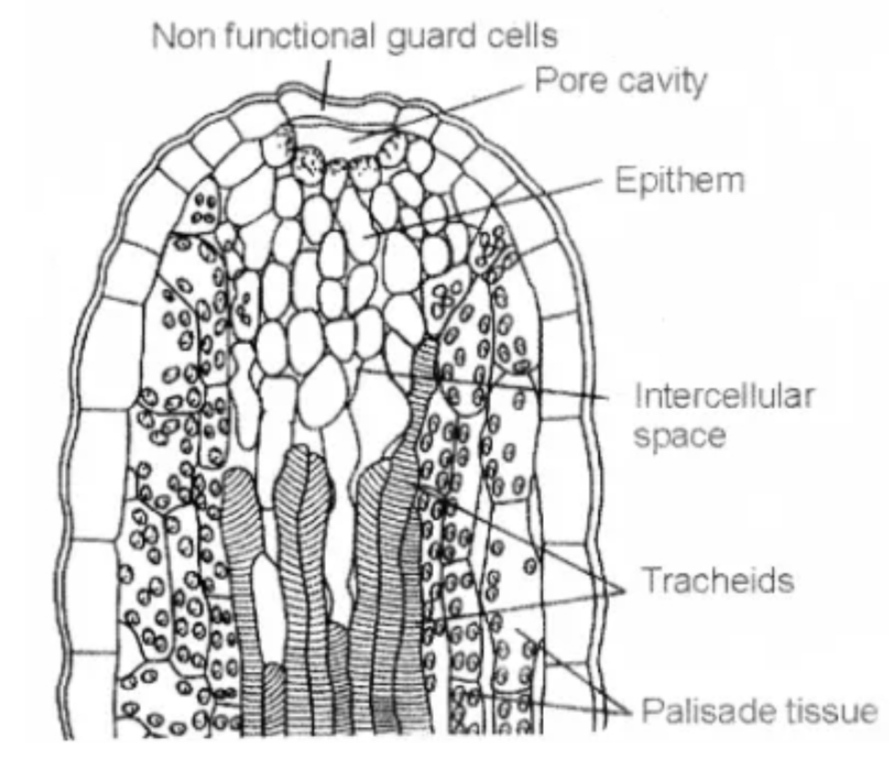
Explain the process of guttation with diagram.
The movement of water molecule from a region of higher concentration to a region of its lower concentration through a semi permeable membrane is called Osmosis.
a) In the above statement, how will you differentiate active transport from passive transport ?
Soil provides water and .............. to plants.
The loss of water in the form of droplets from the margins of leaves is called as what?
What is transpiration?
Match the columns :
Explain what will happen to a plant cell if it is kept in a solution having higher water potential?
What are the factors that affect the rate of diffusion ?
Why is energy required to develop root pressure?
Define osmosis.
What is water potential? Why is it negative in value?
Name the pores through which guttation occurs.
In an osmotic system, one chamber has a $$\Psi $$ of -1000 kPa while the other has -500 kPa. Which chamber has higher water potential ($$\Psi_w$$)?
Define transpiration. Name the types of transpiration. Give the mechanism of transpiration giving V.S. of leaf.
Set up an experiment to demonstrate root pressure.
The diagram given below represents a plant cell after being placed in a strong sugar solution. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow:
How can the above cell be brought back to its original condition? Mention the scientific term for the recovery of the cell.
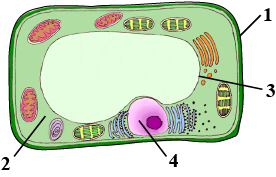
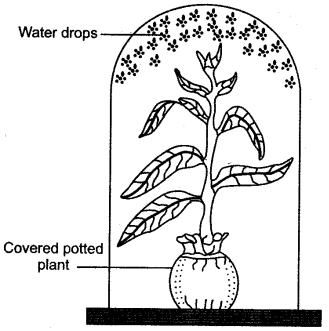
The diagrams given below represent the relationship between a mouse and a physiological process that occurs in green plants. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow:
Why did the mouse die in bell jar $$B$$?

The diagram given below represents a plant cell after being placed in a strong sugar solution. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow:
What is the state of the cell shown in the diagram?
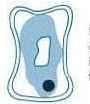
An experiment was set up as shown in the figure below. After some time, the water level in test tube A fell down but not in test tube B.
Why was there a fall in the water level of test tube A and not in that of test tube B?
What is guttation? Explain with the help of diagram of the vertical section of hydathode present on apical part of tomato or primula leaf.
Fill in the blank by choosing the correct alternative from those given in brackets.
When placed in a more concentrated solution, the cell contents will ............... (shrink/swell up)
Give appropriate biological or technical terms for the following.
Movement of molecules of a substance from their higher concentration to lower concentration when they are in direct contact.
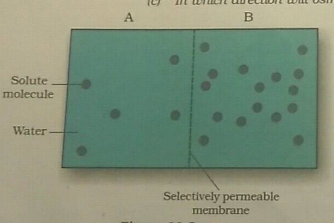
In an experimental set-up, a dye was placed at the bottom of a beaker filled with water as shown in figure A, below. After some time, the entire water in the beaker got coloured uniformly, as shown in figure D.
(b) In all the four figures, two kinds of molecules are shown symbolically larger and smaller. Which molecules are of the solute and which are of the solvent?
Larger ..................................................................
Smaller ..................................................................
Differentiate between Turgidity and Flaccidity.
The process by which the intact plant loses water in the form of droplets is called
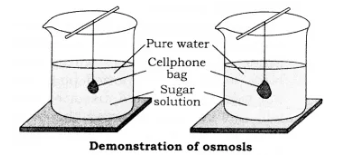
How you can demonstrate the phenomenon of osmosis in the laboratory?
Differentiate between osmosis and imbibition.
Demonstrate the phenomenon of transpiration.
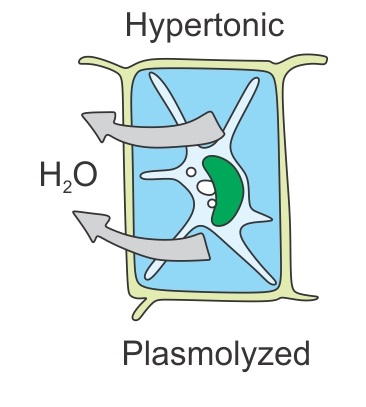
Define the term plasmolysis.
What is Guttation?
What will be the direction of the movement of water when two solutions with $$\Psi_w = 0.2 MPa$$ and $$\Psi_w = 0.1 MPa$$ are separated by a selectively permeable membrane?
Why we should take germinating seeds in a conical flask for the experiment carbon dioxide is given out during the process of respiration?
How to compare the water potential and solute potential of two solutions?
Give biological reasons for the following:
A closed can of dried seeds bursts open if some water enters it by accidents.
Give reasons for the following:
Plasmolysis occurs in plant cells only and not in animal cells.
You took a fresh tomato and put it in a highly concentrated salt solution for 2 hr. Your little brother looked at it and stated, "The fat tomato is so thin now " What a magic?
(a) Define the phenomenon which has taken place.
(b) How does a cell wall help a plant to withstand hypotonic external media without bursting?
What do you mean by guttation ? Explain with example.
What would be $$\Psi_p$$ of a flaccid cell? Which organisms other than plants possess cell wall?
What is the role of diffusion in plant and animals
Which process plays an important role in gaseous exchange between cell?
If thickness of diffusion membrane is increased then what will happen?
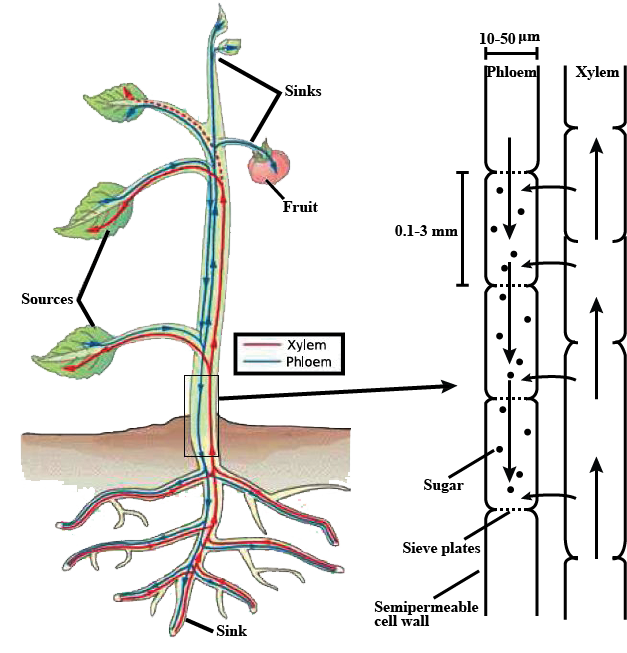
Describe the phloem transport from source to sink
The wooden doors gets jammed in rainy season ...
Bark of a tree is impervious to gases and water. Give reasons
The process by which water enters the root hair cell is ________
Differences between positive hydrostatic pressure gradient and negative hydrostatic pressure.
Describe the reaction of osmosis.
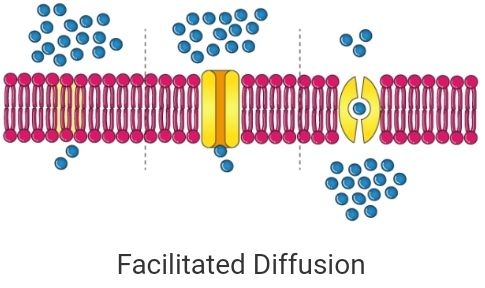
What is facilitated diffusion? How symport transport is different from antiport transport?
In which condition plant cell become flacid?
What occupies the space between the cell wall and the shrunken protoplast in the plasmolyzed cell?
State the term used for the transport of food from leaves to the other parts of a plant.
Name the process of loss of water in the form of vapour from the aerial parts of the plants.
Define Imbibition
Explain the process of translocation of food materials in plants.
Write note on
Root pressure
Root pressure
Define plasmolysis.
Define plasmolysis.
Define the following:
Osmosis
Define the following:
Plasmolysis
What is guttation? Explain with examples.
Explain root pressure in plants with the help of an experiment.
What is osmosis? Explain with the help of an experiment.
In a passive transport across a membrane, when two protein molecules move in opposite direction and independent of each other, it is called as _____.
Explain plasmolysis in a plant cell. Draw a diagram showing stages in plasmolysis.
Define Imbibition.
Define the following:
Diffusion
Water moves up against gravity and even for a tree of 20m height. the tip receives water within two hours. The most important physiological phenomenon which is responsible for the upward movement of water is _____.
Define the terms:
(a) Semi-permeable membrane
(b) Osmosis
Define transpiration.
Given below is a table. Fill in the gaps.
Property simple diffusion facilitated transport Active Transport
| Property | Simple diffusion | Facilitated transport | Active transport |
| Highly selective | _____ | Yes | _____ |
| Uphill transport | _____ | _____ | Yes |
| Requires ATP | _____ | _____ | _____ |
Define water potential and solute potential.
If one wants to find minerals and in the form. they are mobilised in the plant. How will an analysis of the exudate help?
Define Uniport, Symport and Antiport. Do they require energy?
Water molecule is very polar. Polar end of molecule attracts opposite charges on another water molecule (acts like magnet). How will you explain this property of water with reference to upward movement of water? Comment on the upward movement of water given the intermolecular hydrogen bonding in water.
Differentiate between Apoplast and Symplast pathways of water movement. Which of these would need active transport?
Differentiate between active and passive absorption of minerals.
Name the scientist(s) who proposed the principle of active $$K^+$$ transport.
Write a note on guttation.
What are the factors affecting the rate of diffusion?
What happens when a pressure greater than the atmospheric pressure is applied to pure water or a solution?
Differentiate between the following:
(a) Diffusion and Osmosis
(b) Transpiration and Evaporation
(c) Osmotic Pressure and Osmotic Potential
(d) Imbibition and Diffusion
(e) Apoplast and Symplast pathways of movement of water in plants.
(f) Guttation and Transpiration.
Explain why pure water has the maximum water potential.
(a) With the help of well-labelled diagrams, describe the process of plasmolysis in plants, giving appropriate examples.
(b) Explain what will happen to a plant cell if it is kept in a solution having higher water potential.
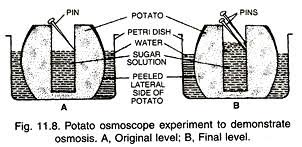
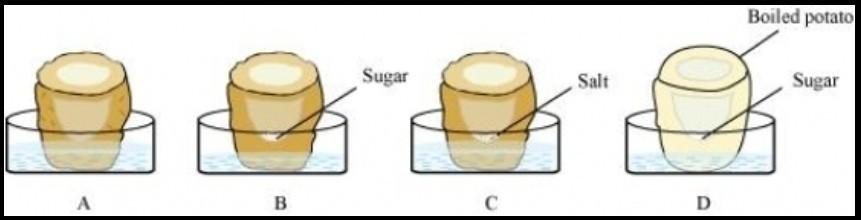
Carry out the following osmosis experiment:
Take four peeled potato halves and scoop each one out to make potato cups. One of these potato cups should be made from a boiled potato. Put each potato cup in a trough containing water. Now,
(a) Keep cup A empty.
(b) Put one teaspoon sugar in cup B.
(c) Put one teaspoon salt in cup C.
(d) Put one teaspoon sugar in the boiled potato cup D.
Keep these for two hours. Then observe the four potato cups and answer the following:
(i) Explain why water gathers in the hollowed portion of B and C.
(ii) Why is potato A necessary for this experiment?
(iii) Explain why water does not gather in the hollowed-out portions of A and D.
(b) Put one teaspoon sugar in cup B.
(c) Put one teaspoon salt in cup C.
(d) Put one teaspoon sugar in the boiled potato cup D.
(ii) Why is potato A necessary for this experiment?
(iii) Explain why water does not gather in the hollowed-out portions of A and D.
Briefly explain the following terms.
(i) Genes
(ii) Cytokinesis in plant cells
(iii) Guttation
(iv) Diabetes insipidus
(v) Disinfectants
Define the term water potential. What are its components? Explain.
Explain plasmolysis and bring out its significance.
What is meant by facilitated transport?
In passive transport method, transport of molecules takes place --------- the concentration gradient.
Define symport and antiport.
Give a scientific term for each of the following.
(i) A single isolated contraction of muscle fibre.
(ii) Inhibition of the growth of the lateral bud by terminal bud.
(iii) Specialised structure through which guttation occurs.
(iv) Development of embryo from the egg without the process of fertilization.
(v) Process of splitting of water molecules during photosynthesis.
(vi) Passing out of urine.
Define : Tyndall effect / Brownian movement / Imbibition / Diffusion / DPD / Osmosis / Hypertonic solution / Hypotonic solution / Isotonic solution / Plasmolysis / Osmotic pressure / Turgor pressure / Wall pressure / Water potential / Permeability.
Define Diffusion/ Osmosis ?
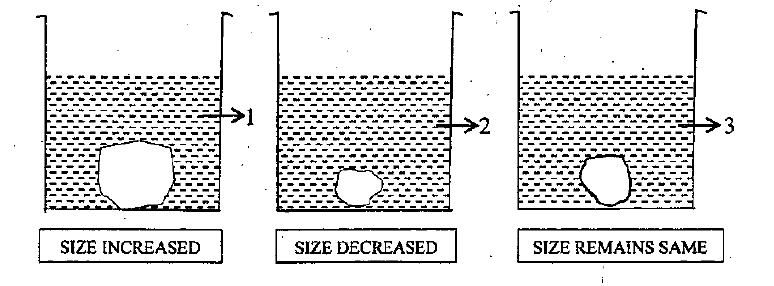
A candidate in order to study the process of osmosis has taken 3 potato cubes and put them in 3 different beakers containing 3 different solutions. After 24 hours, in the first beaker the potato cube increased in size, in the second beaker the potato cube decreased in size and in the third beaker there was no change in the size of the potato cube. The following diagram shows the result of the same experiment:
Give the technical terms of the solutions used in beakers,2 and 3.
Differentiate between the following:
(a) Turgor pressure and wall pressure
(b) Imbibition and osmosis
Differentiate between
Hygroscopic Water and capillary Water.
In the given diagram, which cell has maximum absorbing capacity?
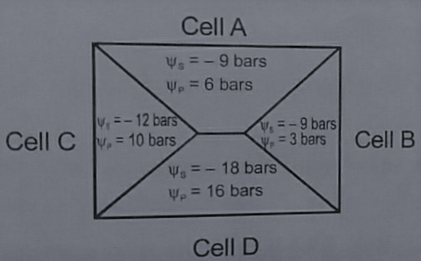
Give the direction for the flow of water in the given diagram.

If one chamber has a $$\Psi_w $$ of - 2000 kPa, and the other - 1000 kPa, which is the chamber that has the higher $$\Psi $$ ?
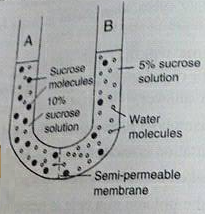
Differentiate Between
Osmotic potential and matrick potential
What will happen if dry kidney beans are left in pure water for sometime?
What will happen if a deshelled egg is kept in saline water?
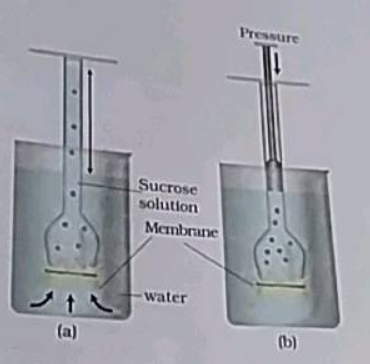
Study the experimental set up in figure and then answer the questions that follow:
a) What phenomenon is being studied by this set up?
b) Explain the phenomenon mentioned in (a) above
c) What is meant by 'semipermeable' membrane?
d) What will you observe in the set up after about half an hour? Give a reason for your answer.
How does the pressure extend by a liquid change with the depth?
Describe pressure potential.
You soak seeds of bean and observe them after 2-3 days. What will he your observations?
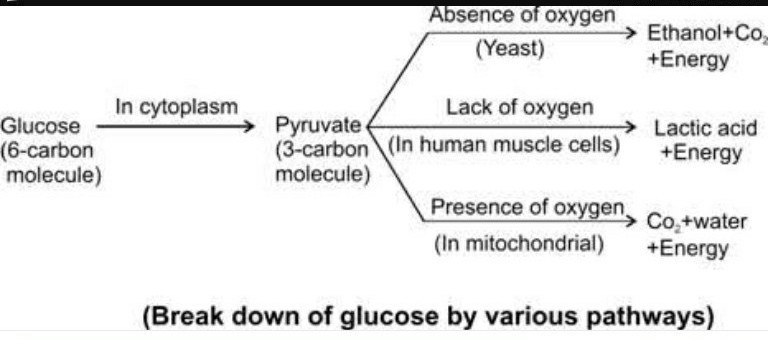
Draw a flowchart to show the breakdown of glucose by various pathways.
Why Is solute potential always negative? Explain $$y_w = y_z + y_p$$
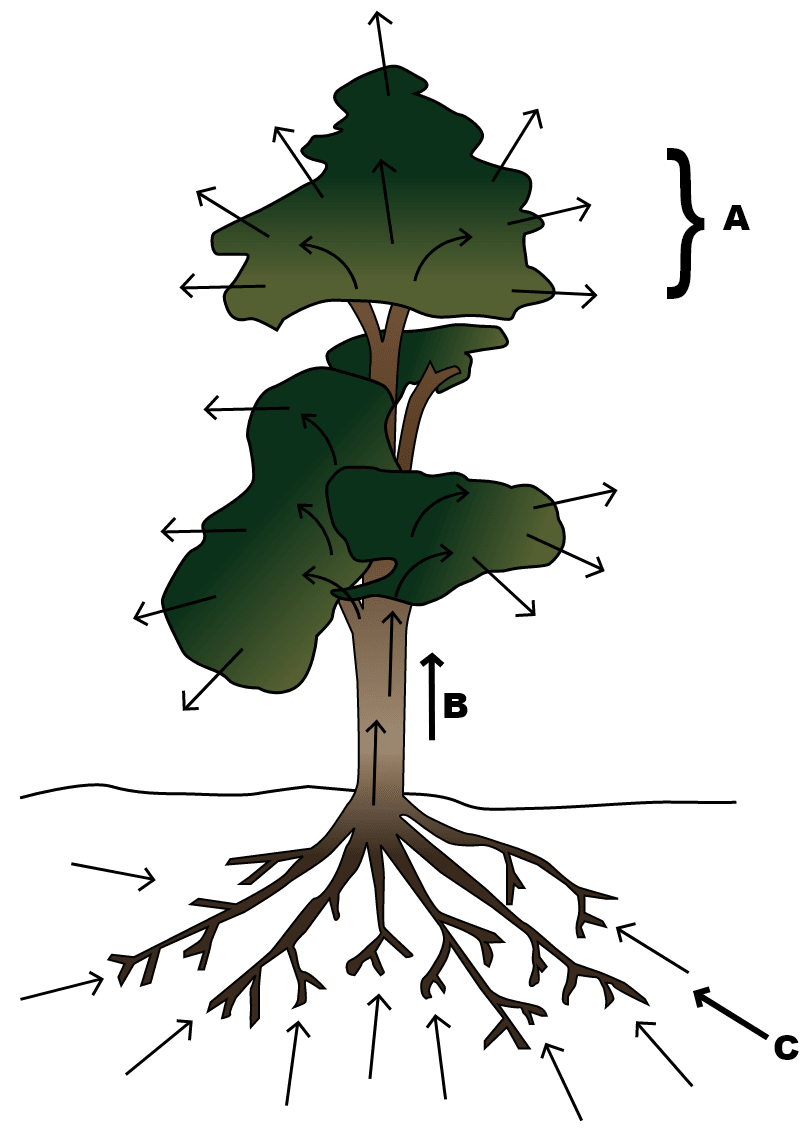
(a) An outline sketch of a tree is shown in the diagram below. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
(i) Name the phenomenon that is labelled A in the diagram.
(ii) Explain the phenomenon occurring in A.
(iii) What is the importance of this phenomenon in plants?
(iv) Explain the role of any three external factors that will increase the rate of the phenomenon.
(v) What do the direction of arrows in B and C indicate?
Class 11 Medical Biology Extra Questions
- Anatomy Of Flowering Plants Extra Questions
- Animal Kingdom Extra Questions
- Biological Classification Extra Questions
- Biomolecules Extra Questions
- Body Fluids And Circulation Extra Questions
- Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Extra Questions
- Cell Cycle And Cell Division Extra Questions
- Cell The Unit Of Life Extra Questions
- Chemical Coordination And Integration Extra Questions
- Digestion And Absorption Extra Questions
- Excretory Products And Their Elimination Extra Questions
- Locomotion And Movement Extra Questions
- Mineral Nutrition Extra Questions
- Morphology Of Flowering Plants Extra Questions
- Neural Control And Coordination Extra Questions
- Photosynthesis In Higher Plants Extra Questions
- Plant Growth And Development Extra Questions
- Plant Kingdom Extra Questions
- Respiration In Plants Extra Questions
- Structural Organisation In Animals Extra Questions
- The Living World Extra Questions
- Transport In Plants Extra Questions