Photosynthesis In Higher Plants - Class 11 Medical Biology - Extra Questions
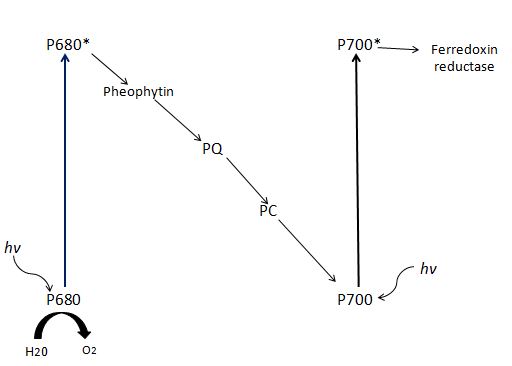
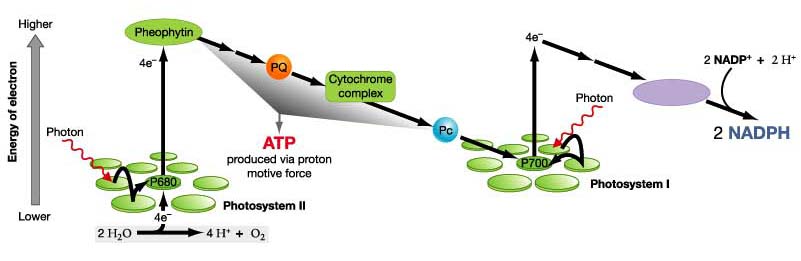
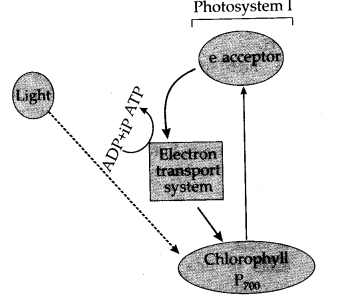
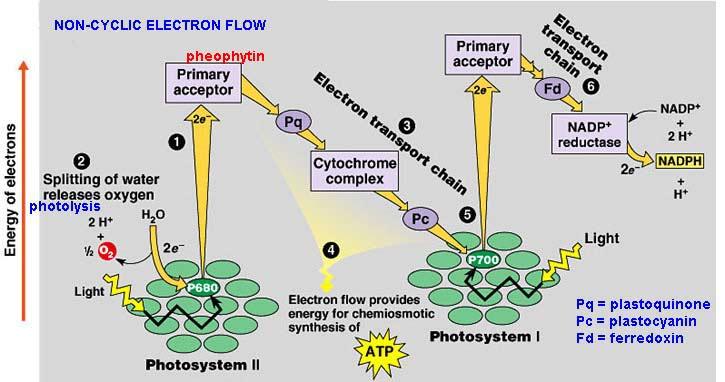
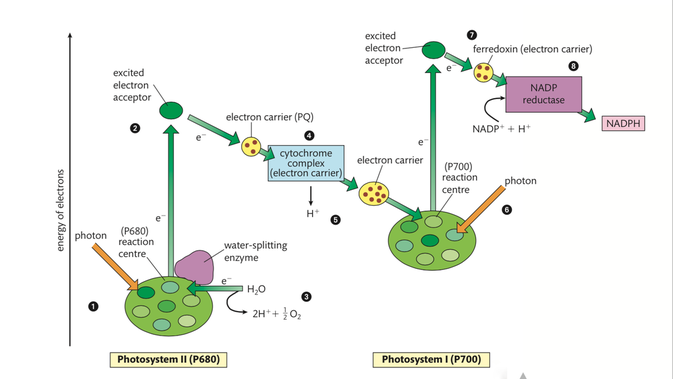
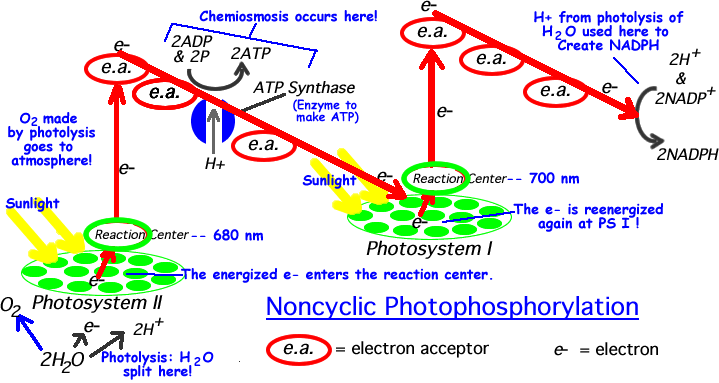
Write the schematic representation of Z-scheme of light reaction.
Do reactions of photosynthesis called, as 'Dark Reaction' need light? Explain.
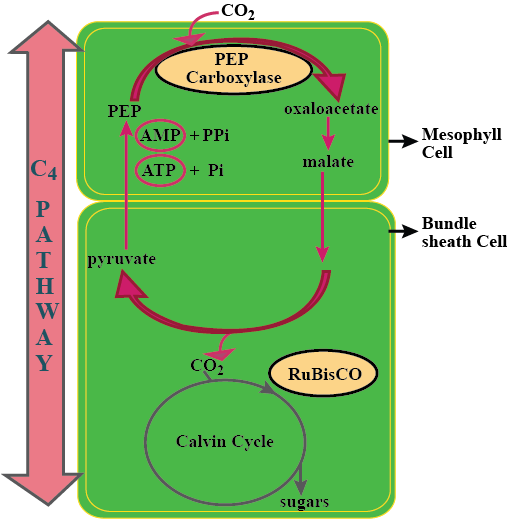
Some of these terms/chemicals are associated with the $$C_4$$ cycle. Explain.
Hatch slack pathway
How does a tree trunk exchange gases with the environment although it lacks stomata?
Some of these terms/chemicals are associated with the $$C_4$$ cycle. Explain.
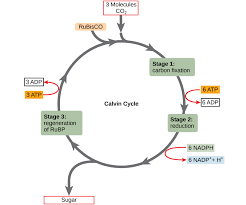
Calvin cycle
Observe the diagram and answer the following.
What is the first product of $$C_4$$ cycle?
Some of these terms/chemicals are associated with the $$C_4$$ cycle. Explain.
PEP carboxylase
Value Based Questions :
What chemical substances would be exchanged between the cytoplasm and the mitochondria? Indicate whether they are entering or leaving the mitochondria.
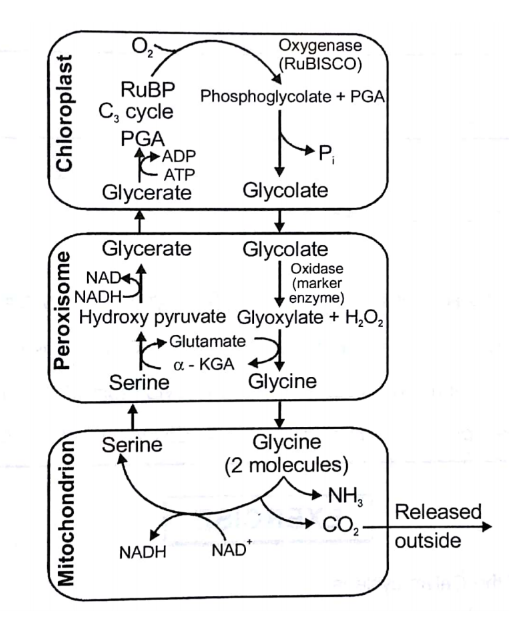
Does photorespiration release energy ?
Short /Long answer type question.
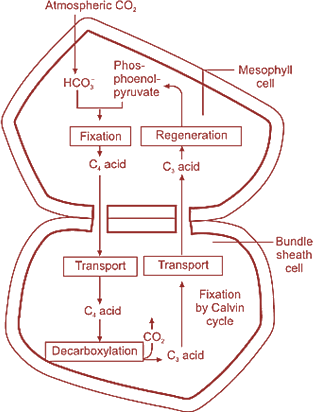
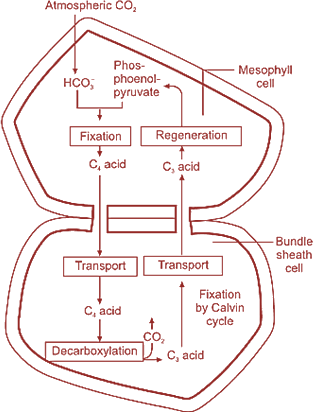
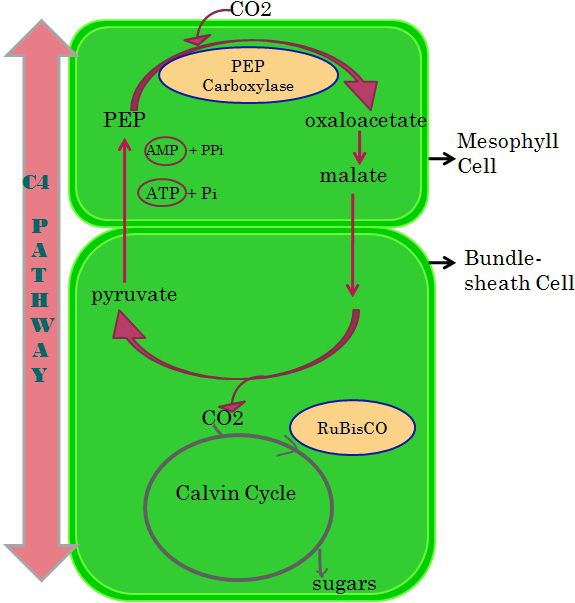
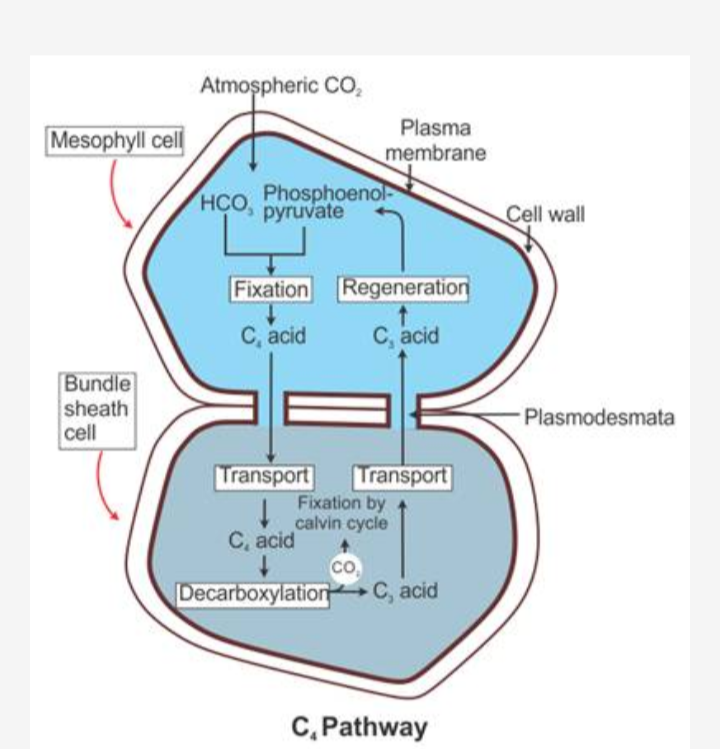
Give a schematic representation of the Hatch and Slack cycle ($$C_4$$ cycle).
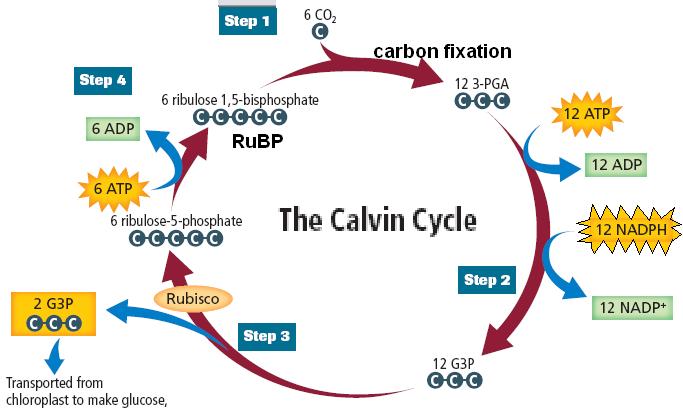
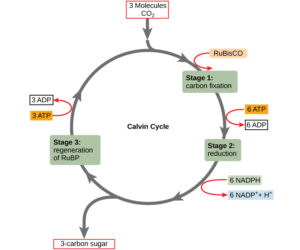
Define the calvin cycle?
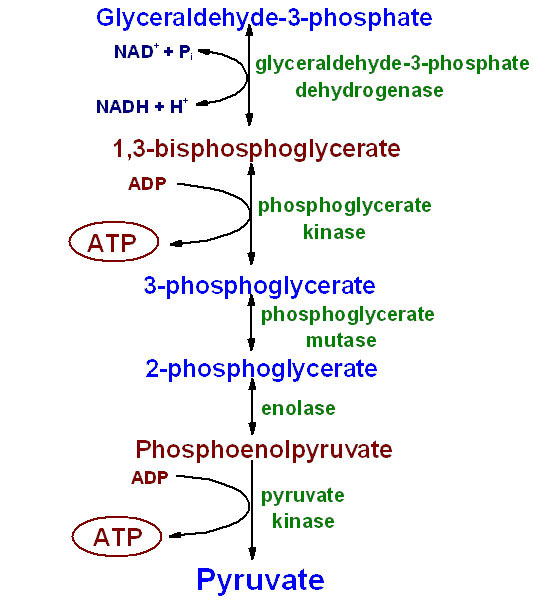
Give an account of carboxylation ($$CO_2$$ fixation) stage of Calvin cycle.
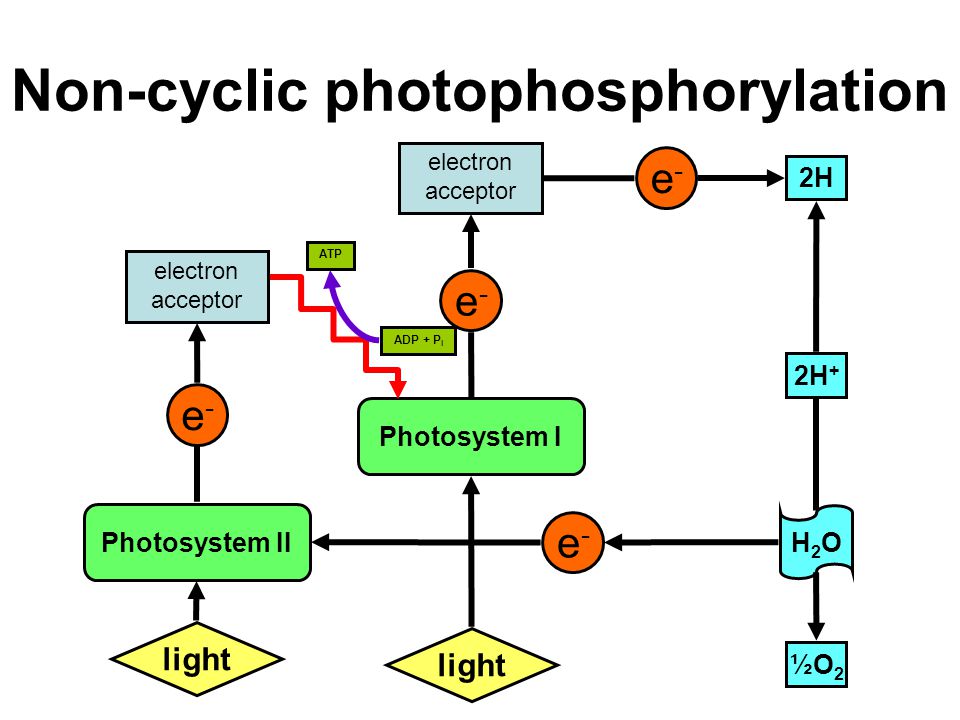
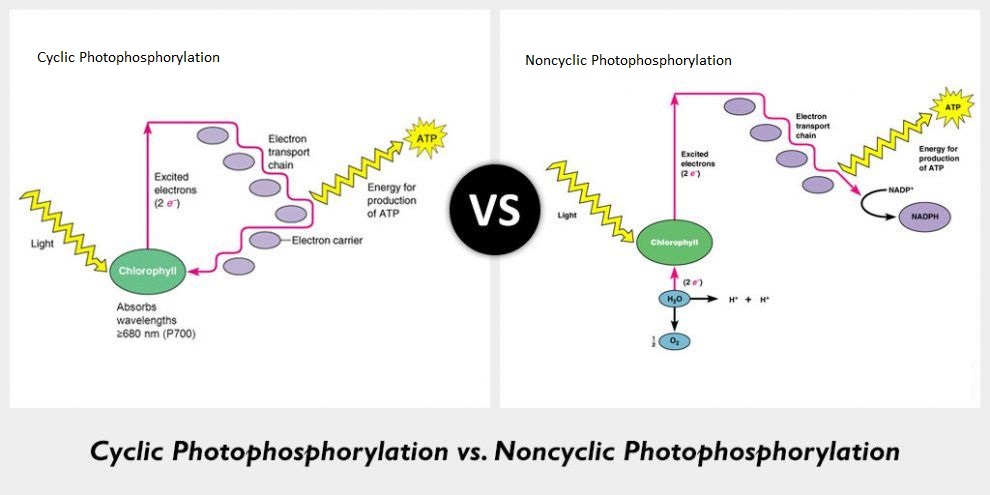
Why is non-cyclic photo phosphorylation considered as a non-cyclic pathway?
Explain the $$C_{4}$$ cycle of photosynthesis.
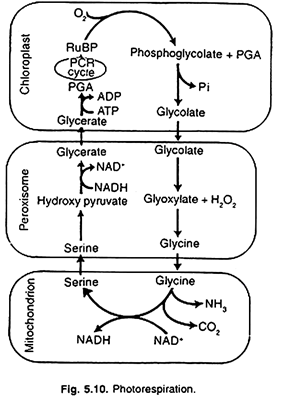
What is photorespiration? Explain it with diagrammatic representation.
Write three differences between $$C_3$$ and $$C_4$$ cycles.
What are the differences between $$C_{3}$$ and $$C_{4}$$ pathways?
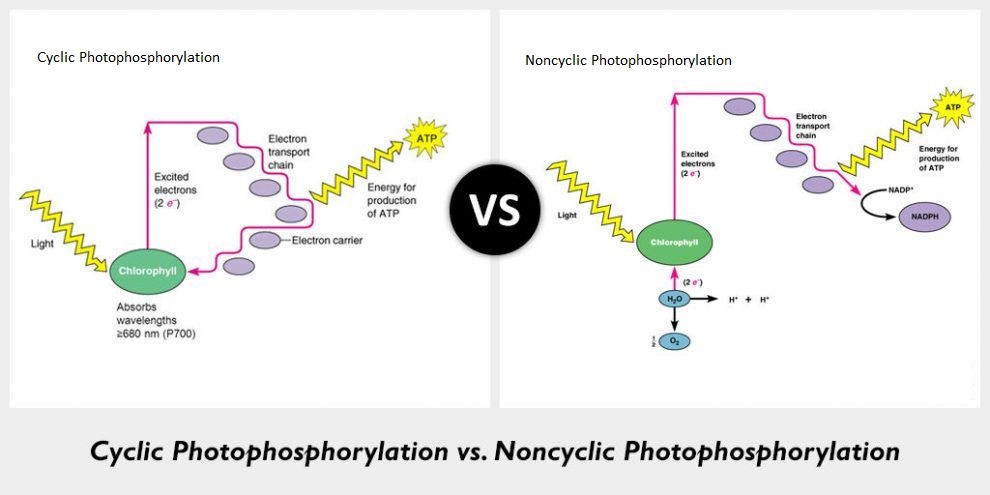
Differentiate between cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
Write any three differences between photo respiration and dark respiration.
Tabulate any eight differences between $$C_3$$ and $$C_4$$ plants/cycles.
State any three differences between photorespiration and dark respiration.
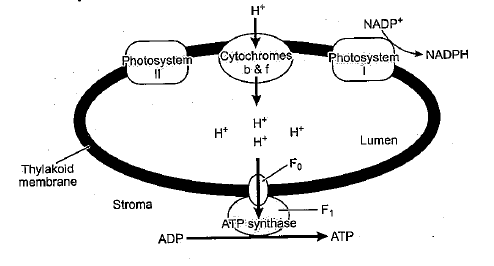
Explain chemiosmotic hypothesis for ATP synthesis.
Name the scientists who have contributed to the following.
(i) Reverse transcription.
(ii) Photorespiration.
(iii) Principle of limiting factors.
(iv) Photolysis of water.
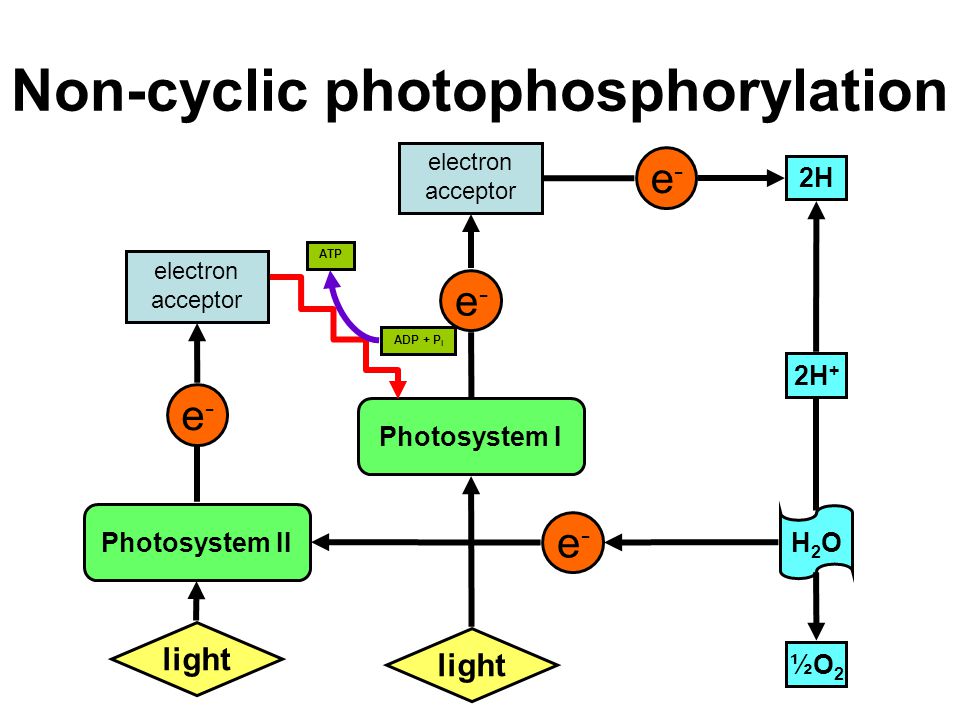
What is 'photophosphorylation'? Describe non-cyclic photo-phosphorylation with schematic representation. Give its significance.
Tabulate any four differences between C$$_3$$ and C$$_4$$ pathways.
Write differences between $$C_3$$ and $$C_4$$ .
With the help of biochemical reactions, explain the various phases of the Calvin cycle.
What is the site of formation of glycoxylate from glycolate?
By looking at a plant externally can you tell whether a plant is $$C_3$$ or $$C_4$$. Why and how ?
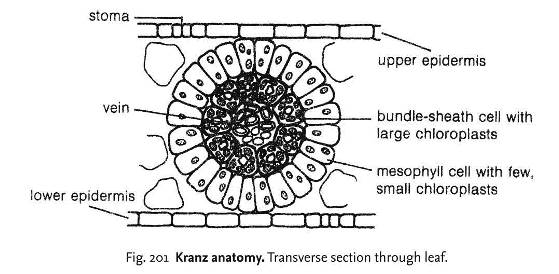
By looking at which internal structure of a plant can you tell whether a plant is $$C_3$$ or $$C_4$$? Explain.
Give comparison between the following :
(a) $$C_3$$ and $$C_4$$ pathways,
(b) Cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation.
(c) Anatomy of leaf in $$C_3$$ and $$C_4$$ plants.
Distinguish between
(a)Respiration and photorespiration.
(b) Cyclic photophosphorylation and non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
Define :(a) Photon (b) Quantum (c)$$C_3$$ plant (d) $$C_4$$ plant (e) Light Reaction (f) Photorespiration (g)Limiting Factor.
Name any two $$C_4$$ plants, Give anatomical characters of these plants.
Why is photorespiration also called $$C_2$$ cycle?
A plant is believed to be releasing oxygen during night time. Do you believe that the statement is true? Justify your answer with reason.
What is photorespiration ? How are photorespiratory losses overcome by $$C_4$$ plants ?
Name the first stable product of $$C_4$$ cycle ?
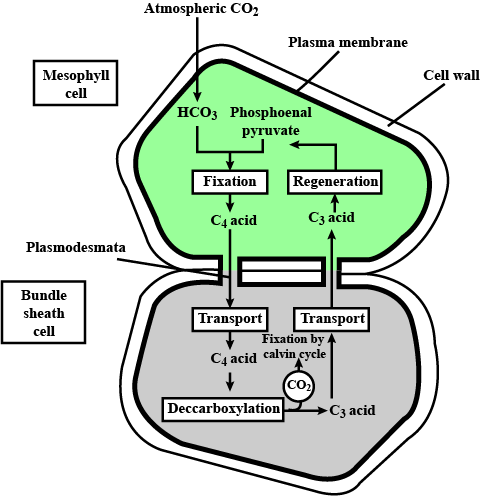
Specify how $$C_4$$ photosynthetic pathway increases $$CO_2$$ concentration in bundle sheath cells of sugarcance.
What is the difference between chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b?
Give the importance of $$C_4$$ plants.
Where does non-cyclic photophosphorylation take place ? Describe the process. Why is process referred to as non-cyclic ?
Describe the mechanism of Hatch and Slack pathway in $$C_4$$ plants.
Describe $$C_3$$ pathway of photosynthesis. How does it differ from $$C_4$$ pathway?
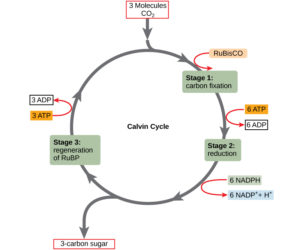
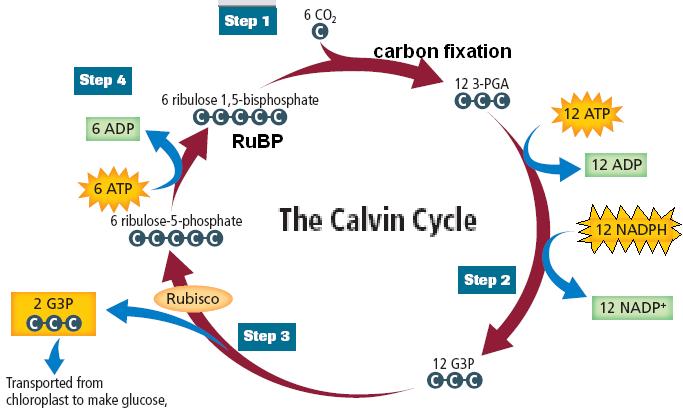
Define carbon fixation in plants. What was the contribution of Melvin Calvin. Describe the three phases of Calvin cycle.
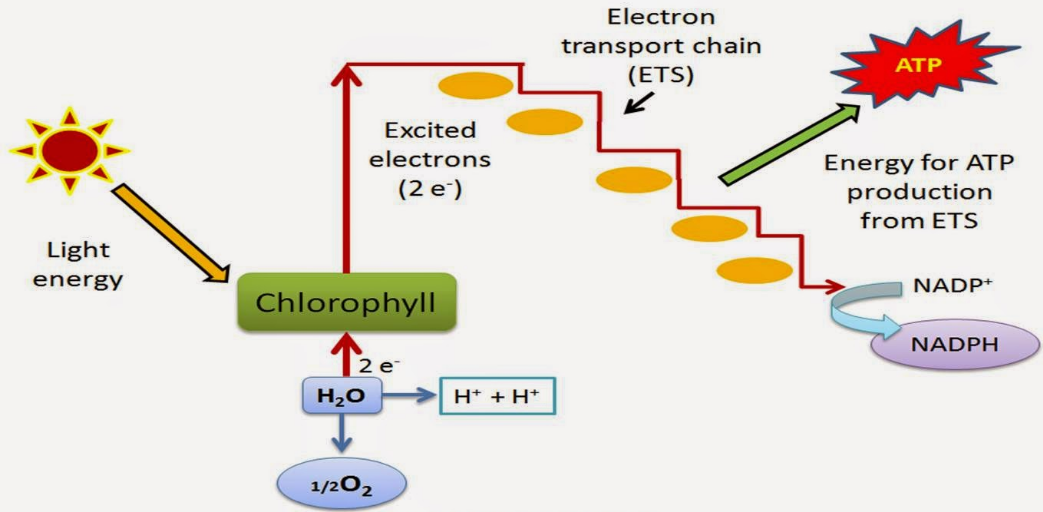
How are ATP, NADPH and oxygen produced in noncyclic photophosphorylation.
Name any two $$C_4$$ plants. Describe how carbon dioxide is fixed in such plants.
What is photorespiration ? Explain the mechanism and its significance.
What is meant by photophosphorylation ? Discuss the cyclic photophosphorylation.
Calvin cycle consists of three phases. What are they? Explain the significance of each of them.
What is the disadvantage of photorespiration? Explain how the photorespiratory losses are overcome in plants like sugarcane.
Where does cyclic photophosphorylation take place in the leaves ? Why is this process called cyclic? Describe cyclic photophosphorylation.
Compare $$C_4$$ and $$C_3$$ pathways of $$CO_2$$ fixation during photosynthesis. Give well labelled schematic sketch of $$C_4$$ pathway.
What is used, produced, and accomplished by the Calvin-Benson cycle?
Where does Calvin cycle take place in chloroplast ? Explain the cycle.
Write the short notes on $$C_4$$ and $$C_3$$ plant.
Name the following :
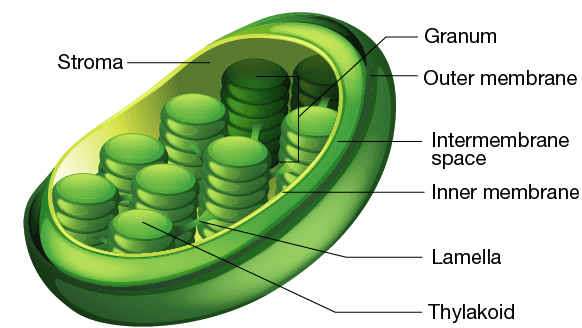
The part of chloroplast where the dark reaction of photosynthesis takes place.
A potted plant was taken in order to prove a factor necessary for photosynthesis. The potted plant was kept in the dark for 24 hours. One of the leaves was covered with black paper in the centre. The potted plant was then placed in sunlight for a few hours.
Draw a neat diagram of a chloroplast and label its parts.
Fill in the blanks with the appropriate answer from the choices given in the brackets.
The dark reaction of photosynthesis is known as ............... (Hill reaction, cyclic phosphorylation, Calvin cycle).
Fill in the blanks with the appropriate answer from the choices given in the brackets.
Stroma is the ground substance in ............... (cytoplasm, chloroplast, ribosomes).
Short answer type questions
Describe the chemiosmotic mechanism of ATP synthesis
Explain why respiration is said to be the reverse of photosynthesis.
Short / Long answer type questions .
What.is the role of ATP in energy transformations within living organisms?
Write the full form of G-6-PD
Give a schematic representation of non-cyclic photophosphorylation showing both the photosystems.
Discuss the major events in the Calvin cycle.
A green plant starts evolving carbon dioxide instead of oxygen on a hot summer day. Explain.
Describe the flow of electrons in non-cyclic photophosphorylation and compare it with that of cyclic photophosphorylation.
Very short answer type.
Explain $$CO_2$$ compensation point
Define photo-oxidation and photorespiration.
Explain Kranz Anatomy.
Give an example of a plant exhibiting Kranz Anatomy.
What is the use of ATP binding site?
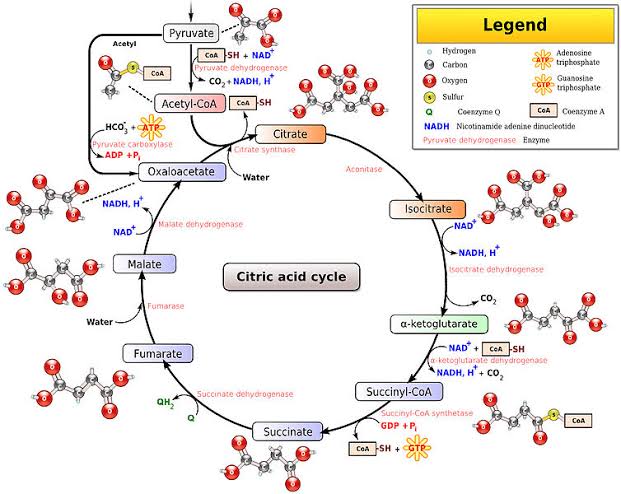
What is tricarboxylic acid cycle? Describe its different steps.
Name the three organelles involved in photorespiration.
In $$C4$$ cycle to get 1 Molecule of glucose. How many $$ATP$$ and $$NADPH_2$$ are required.
What is Glucocorticoids?
Name the following :
A photosynthetic stage which may take place in the presence and absence of light.
You would recollect from previous unit that the mesophyll cells in the leaves, have a large number of chloroplasts. Usually the chloroplasts align themselves along the walls of the mesophyll cells, such that they get the optimum quantity of the incident light. When do you think the chloroplasts will be aligned with their flat surfaces parallel to the walls ? when would they be perpendicular to the incident light ?
Why is photorespiration is considered as a destructive activity?
Explain $$CO_2$$ fixation by the Calvin-Benson cycle?
What is the importance of the following processes occurring during photosynthesis in plant.
Emission of electrons from chlorophyll.
Photolysis of water.
The G-actin polymerises to form the F-actin in the presence of ____________
With the help of a diagram explain Z scheme of light reaction
Explain Calvin cycle.
What is the primary acceptor of $$CO_2$$ in $$C_4$$ plants? What is the first compound formed as a result of primary carboxylation in the $$C_4$$ pathway?
Write the differences between $$C_3$$ and $$C_4$$ pathway.
Find out how Melvin Calvin worked out the complete biosynthetic pathway for synthesis of sugar.
Write five differences between $$C_3$$ and $$C_4$$ plants.
Why photorespiration does not take place in C$$_4$$ plants?
$$CO_2$$ fixation rate in under high light condition in $$C_3$$ & $$C_4$$ is:
Six turns of Calvin cycle are required to generate one mole of glucose. Explain.
Some of these terms/chemicals are associated with the $$C_4$$ cycle. Explain.
Bundle sheath cells
A process is occurring throughout the day, in 'X' organism. Cells are participating in this process. During this process ATP. $$CO_2$$ and water evolved. It is not a light dependent process.
(a) Name the process.
(b) Is it a catabolic or an anabolic process?
(c) What could be the raw material of this process?
Give comparison between the following:
(a) C$$_3$$ and C$$_4$$ pathways
(b) Cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation
(c) Anatomy of leaf in C$$_3$$ and C$$_4$$ plants.
Even though a very few cells in a C$$_4$$ plant carry out the biosynthetic Calvin pathway, yet they are highly productive. Can you discuss why?
What are phytoplankton?
Explain Calvin cycle with the help of diagram.
Tabulate any eight differences between C$$_3$$ and C$$_4$$ cycles.
Describe the cyclic photophosphorylation. What is the purpose of proton gradient during the process in thylakoids?
RuBisCo is an enzyme that acts both as a carboxylase and oxygenase. Why do you think RuBisCO carries out more carboxylation in $$C_4$$ plants ?
(i) How many turns of dark reaction yield one molecule of glucose ?
(ii) Explain main chemical steps that take place in the dark reaction or Calvin cycle of photosynthesis.
Even though a very few cells in a $$C_4$$ plant carry out biosynthetic Calvin pathway, yet they are highly productive. Can you discuss why ?
What is Kranz anatomy? Write a note on photosynthesis of those plants in which this anatomy is found.
(a) Schematically represent non-cyclic photophosphorylation in Angiosperms, giving all the components.
(b) Why is the process called non-cyclic ?
What is photophosphorylation ? Distinguish between cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation. Give schematic sketches of both.
(a) Give a schematic outline of photorespiration.
(b)Differentiate between photophosphorylation and photorespiration.
Very short answer type :
Mention the most significant function of bundle sheath.
Can ribulose biphosphate (RuBP) combine with both carbon dioxide and oxygen gas?
Short /Long answer type question.
Enlist the steps involved in $$C_4$$ pathhway of fixation. Explain how plants overcome the photo-respiratory losses by this mechanism.
Application based questions
Suggest some habitats in which (a) light intensity or (b) temperature might be limiting factors in photosynthesis.
Short /Long answer type question.
Trace the non-cyclic electron pathway (Z-scheme), naming and explaining all the events that occur as the electrons move from water to $$NADP^+$$
Short /Long answer type question.
Trace the cyclic electron pathway, naming and explaining the main events that occur as electrons cycle.
Short /Long answer type question.
What is the Z-scheme of photosynthesis ? What are the products of photoreaction and how they are used in the process of $$CO_2$$ fixation ?
Short /Long answer type question.
How the tracer technique is useful in determining the reaction sequence of the metabolic process? Explain with the help of Calvin cycle.
Very short answer type.
Give the exact location and function of grana
Write notes on
(a) Emerson enhancement effect(b) Warburg effect(c) Red drop(d) Photorespiration.
Explain the Hatch-Slack pathway.
How does the length of a neuron affect the speed with which the nerve impulse Travels along it?
$$C4$$ plants ultimately use RUBISCO, yet have lower rate of photorespiration than do $$C_3$$ plants. Explain.
Calculate how many ATP are synthesised and deduct the number of ATP utilised during glycolysis.
Whether Photorespiration is present at low light intensities.
Granules, cyanophycean granules and glycogen granules. Gas vacuoles are found in blue green and purple and green photosynthetic bacteria.
What do you understand by photophosphorylation? Explain the process in detail.
Give the diagrammatic representation of $$C_4$$ cycle.
With the help of a suitable diagrammatic representation explain HSK pathway.
In $$C_4$$ pathway carboxylation occurs twice. Discuss.
During photorespiration oxidation, deamination and decarboxylation all takes place in :-
Class 11 Medical Biology Extra Questions
- Anatomy Of Flowering Plants Extra Questions
- Animal Kingdom Extra Questions
- Biological Classification Extra Questions
- Biomolecules Extra Questions
- Body Fluids And Circulation Extra Questions
- Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Extra Questions
- Cell Cycle And Cell Division Extra Questions
- Cell The Unit Of Life Extra Questions
- Chemical Coordination And Integration Extra Questions
- Digestion And Absorption Extra Questions
- Excretory Products And Their Elimination Extra Questions
- Locomotion And Movement Extra Questions
- Mineral Nutrition Extra Questions
- Morphology Of Flowering Plants Extra Questions
- Neural Control And Coordination Extra Questions
- Photosynthesis In Higher Plants Extra Questions
- Plant Growth And Development Extra Questions
- Plant Kingdom Extra Questions
- Respiration In Plants Extra Questions
- Structural Organisation In Animals Extra Questions
- The Living World Extra Questions
- Transport In Plants Extra Questions