Biomolecules - Class 11 Medical Biology - Extra Questions
Respiration is an anabolic and catabolic both. Justify the statement by giving example.
Anabolic reactions are always endergonic reactions. Justify this statement with an example.
Growth can be termed as an anabolic and catabolic process both. Justify the statement with a valid reason.
Catabolic reactions are exergonic reactions. Justify the statement with reason.
Why anabolic reactions are endergonic reactions?
Give an example for catalytic proteins.
Why are catabolic reactions always exergonic reactions?
Digestion is a catabolic process. Justify the statement with reason.
Man is an example of _________ organism.
What are the functions of proteins?
Mention the three differences between a living cell and a brick in a wall.
What is plasma?
Can you attempt building models of biomolecules using commercially available models (ball and stick models).
Who conducted in vitro synthesis of DNA ?
Choose the ODD one out of the following terms given and name the CATEGORY to which the others belong:
Phosphate, RNA, Sugar, Nitrogenous base.
Active transport is the one in which the ions outside the roots move in with expenditure of energy................
Some enzymes are named after the reaction, where they are used. What name is given to the class of enzymes which catalyze the oxidation of one substrate with simultaneous reduction of another substrate?
Nucleic acids exhibit secondary structure, justify with example.
Match the tissues/molecules mentioned in the list I with the options mentioned in the list II and select the correct option from the given codes.
List three main differences between DNA and RNA ?
Only .......... amino acids are present in the proteins
What are the structural units of nucleic acids?
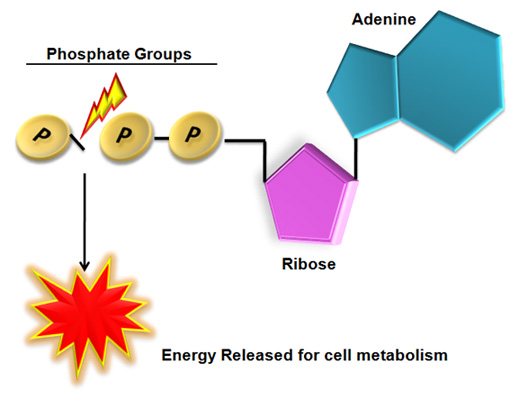
Name a molecule acting as energy currency in organisms
Differentiate between the following pairs on the basis of what is mentioned in brackets:
NADP and ATP [Expand the abbreviation].
Define metabolic waste.
Observe the given figure and answer the questions given below.
Which fraction would probably show the greatest amount of hydrolytic enzyme activity? Give a reason for your answer.
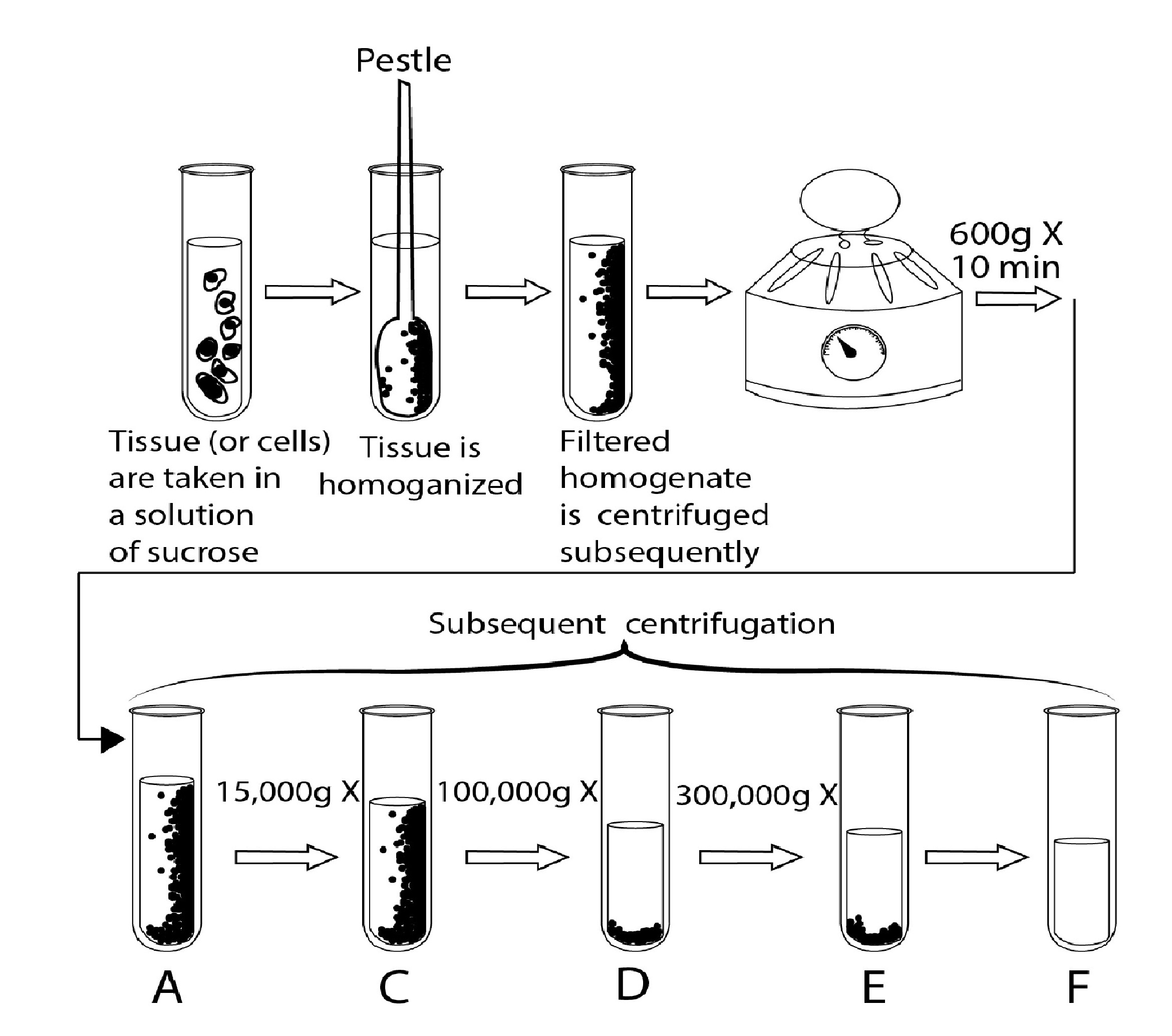
Observe the given figure and answer the questions given below.
Which fraction would you expect to produce most radioactively-labelled protein if labelled amino acids were added? Give a reason for your answer.

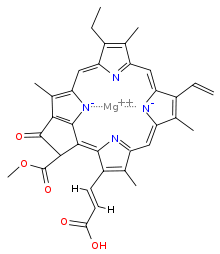
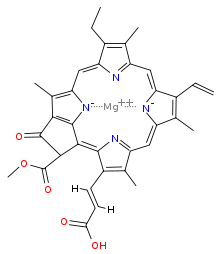
"Chlorophyll contains Mg and chlorine."
Answer whether the above statement is true or false. If true enter 1, else 0.
"Chlorophyll is an organometallic compound."Answer whether the above statement is true or false.
If true enter 1, else enter 0.
If true enter 1, else enter 0.
Name two structural polysaccharides which are found in fungi.
What is metabolism and what is its purpose?
What are macromolecules? Give examples of it.
Amino acids contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and _________.
Write differences between primary metabolism and secondary metabolism.
What are enzymes ?Give two examples with uses.
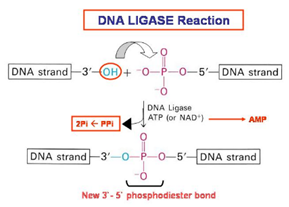
What is the action of ligases?
Write any four supplication of enzymes?
Explain the major classes of enzymes.
Name one element invariably found in proteins but not in all carbohydrates and lipids.
Name two scientists who proved experimentally that DNA is the genetic material.
What is the function of ATP in cell metabolism ? Explain with the aid of diagram, how its structure makes it possible.
Which is the principal mineral cation in the extracellular fluid.
Describe functions of polysaccharides in living organisms.
Match the following lists
Differentiate between ATP and AIDS based on their abbreviations.
Name the following :
The compound which stores energy in the cells.
Atoms\ions needed in very small amounts function mainly as .......... of enzymatic reactions.
.......... is invariably a component of amino acids, nucleic acids and chlorophylls.
Name the enzyme which possibly acts as an ion carrier.
Differentiate between.
Isomerases and transferases
The induced fit theory for enzyme action was given by..........
To which chemical group do all enzymes belong?
Value based questions.
Try to explain the following observations
When $$K^+$$ ions are removed from the medium surrounding red blood cells, sodium influx into the cells and potassium efflux increase dramatically.
Very Short Answer Types :
Name the two types of cell divisions occur in living cells.
What are proteins? Name the bond present in the proteins
Explain the process of formation of complex protein?
Match the following polymers with their possible monomers
The presence of thymine at the place of uracil also confers additional stability to DNA. How?
Why are proteins considered to be heteropolymers?
Why is plasma membrane also called as selectively permeable membrane?
What are the most common constituents of organic compounds found in organisms?
Give one example for a complex polysaccharide having amino sugars.
Condition A : Substrate X, specific for Enzyme E1, can be replaced by molecule C (which blocks the enzyme), if C is present in more concentration.
Condition B : Substrate Y can never bind to Enzyme E2, if molecule D binds to the enzyme.
a. At which sites are molecules C and D binding to the enzyme E1 and E2 respectivbely?
b. Which kind of inhibitors are C and D?
c. Describe another factor which can effect an enzyme's activity.
What are proteins? Describe the different biological function of proteins.
Who discovered nucleic acid? What was it called then?
Define : Inorganic inclusions of cell
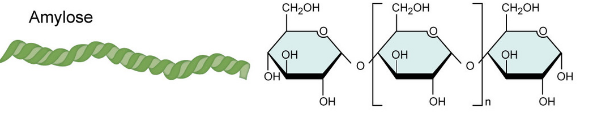
What is amylose?
Write a short note on metabolism.
What are biomolecules? How they are useful in day to day life?
Fill in the table basis of your observations in field trip.
| S. No. | Name of the plant | Secondary metabolites | Uses |
| A. | Neem | ||
| B. | Datura |
Explain factor effecting enzyme activity.
The energy currency of the cell is _________.
What are biomolecules?
What forms the backbone of a polynucleotide strand of a nucleic acid?
What is N-glycosidic linkage
What is the role of enzyme Taq polymerase in gene amplification ?
-S-S- bonds are found in which structure of proteins.
Out of respiration and photosynthesis which is anabolic and which is catabolic process. Why?
Briefly describe the factors affecting enzyme activity.
Explain the process of formation of complex proteins.
What are catabolic and anabolic processes?
What is the source of information for making proteins in the cell?
Define metabolism.
DNA and RNA are the two important nucleic acids present in our body. The study of DNA and RNA is very useful in research bodies.
A. What are the main structural differences between DNA and RNA?
B. What are nucleotides? Name the three components of nucleotides.
C. Mention the applications of studying DNA in different fields.
Explain in detail, classification of enzymes.
What are the biological functions of DNA and RNA? Do proteins affect the functioning of nucleic acids? Explain.
Can you attempt building models of biomolecules using commercially available atomic models (Ball and Stick models).
Find out and make a list of proteins used as therapeutic agents. Find other applications of proteins (e.g., cosmetics, etc.)
What is ribozyme?
Find out a qualitative test for proteins, fats and oils, amino acids and test any fruit juice, saliva, sweat and urine for them.
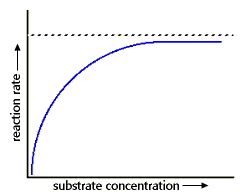
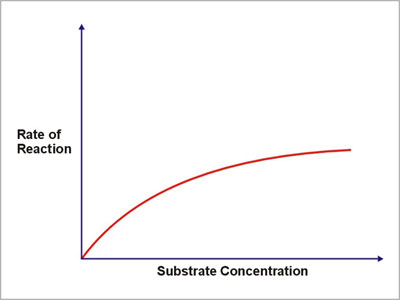
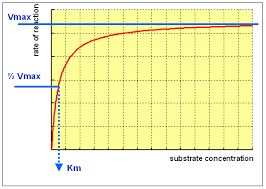
How does the substrate concentration affect the velocity of enzyme reaction?
List the major biomolecules which make up the cell.
What does an enzyme do in terms of energy requirement of a reaction? What would happen if the enzyme did not play this role?
Name the following :
(a) Energy currency of the cell
(b) Oxidative breakdown of carbohydrates to release energy
(c) An organism which respires throughout life anaerobically
(d) A common phase to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration
(e) Aerobic respiration requires
(f) A chemical which removes $$CO_{2}$$ from the air
Write the full forms of ATP and ADP
If you study the effect of substrate concentration on an enzymatic reaction, what kind of curve would you obtain?
What are the factors which influence enzyme activity? Discuss them in brief.
Match the terms to these definitions
Cofactor, coenzyme, holoenzyme, apoenzyme, ligases, lyases, transferases, isozymes, zymogens, competitive inhibitor, non-competitive inhibitor, activation energy
..........enzymes which catalyse the linking together of compounds utilising the energy from ATP
Which enzymes has more affinity towards substrate?
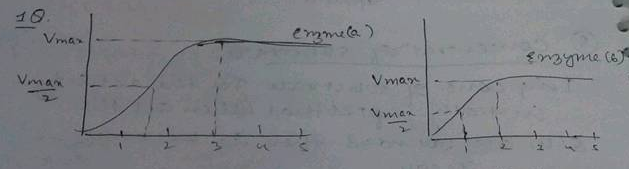
Why proteins are called biological polymer?
Select the correct match of enzymes listed, their site of action, their substrate and optimum $$pH$$
| Enzyme | Site of action | Substrate | pH |
| Amylopsin | Pancreas | Starch | $$7.8$$ |
| Trypsinogen | Duodenum | Peptones | $$6.8$$ |
| Nucleotidase | Small intestine | Nucleoside | $$6.8$$ |
| Carboxypeptidase | Small intstine | Polypeptide | $$7.8$$ |
Explain the classification of enzymes.
Class 11 Medical Biology Extra Questions
- Anatomy Of Flowering Plants Extra Questions
- Animal Kingdom Extra Questions
- Biological Classification Extra Questions
- Biomolecules Extra Questions
- Body Fluids And Circulation Extra Questions
- Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Extra Questions
- Cell Cycle And Cell Division Extra Questions
- Cell The Unit Of Life Extra Questions
- Chemical Coordination And Integration Extra Questions
- Digestion And Absorption Extra Questions
- Excretory Products And Their Elimination Extra Questions
- Locomotion And Movement Extra Questions
- Mineral Nutrition Extra Questions
- Morphology Of Flowering Plants Extra Questions
- Neural Control And Coordination Extra Questions
- Photosynthesis In Higher Plants Extra Questions
- Plant Growth And Development Extra Questions
- Plant Kingdom Extra Questions
- Respiration In Plants Extra Questions
- Structural Organisation In Animals Extra Questions
- The Living World Extra Questions
- Transport In Plants Extra Questions