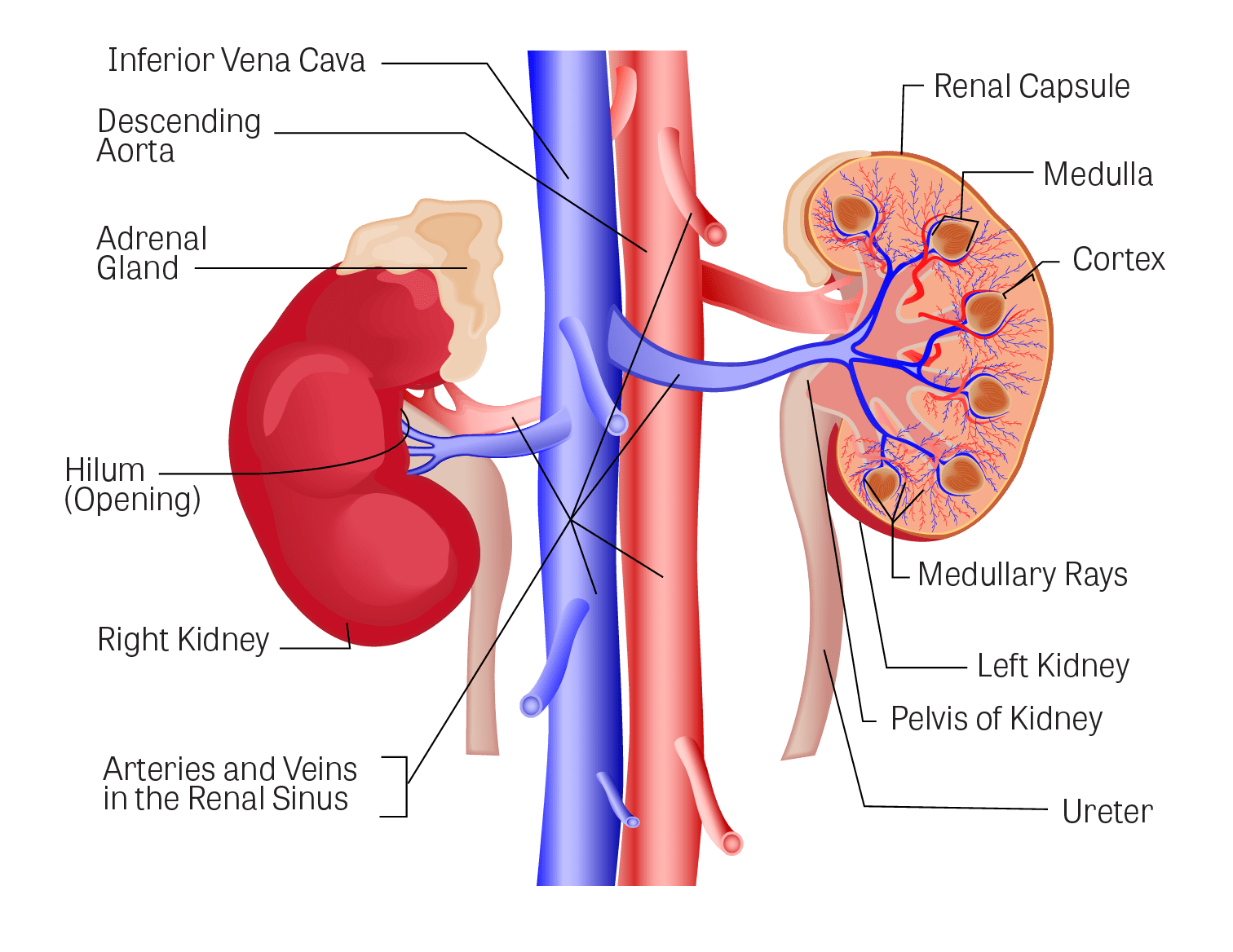
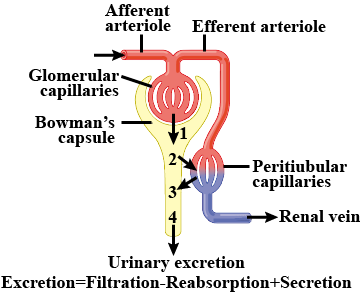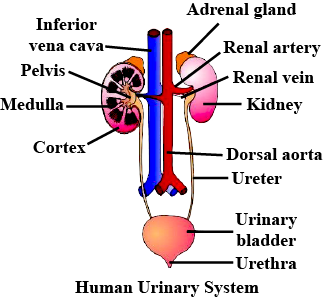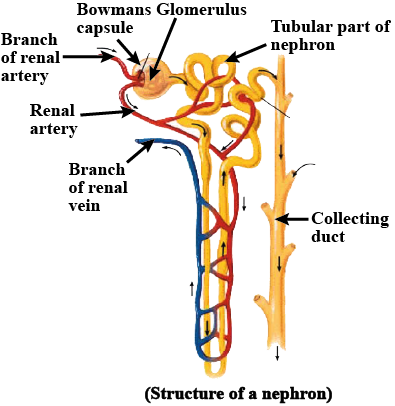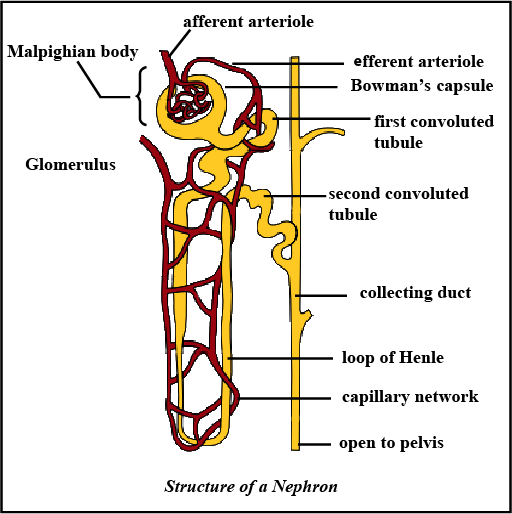Excretory Products And Their Elimination - Class 11 Medical Biology - Extra Questions
What is excretion? How do unicellular organisms remove their wastes?
Name the basic filtration unit present in the kidney.
Differentiate between the following pairs on the basis of what is mentioned in brackets:
Renal cortex and Renal medulla [Parts of the nephrons present].
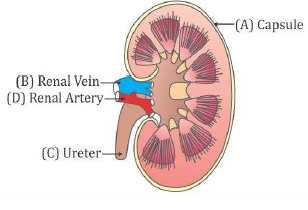
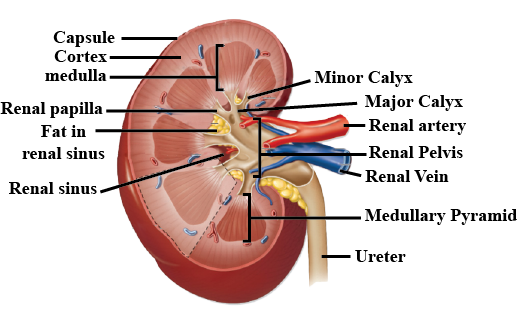
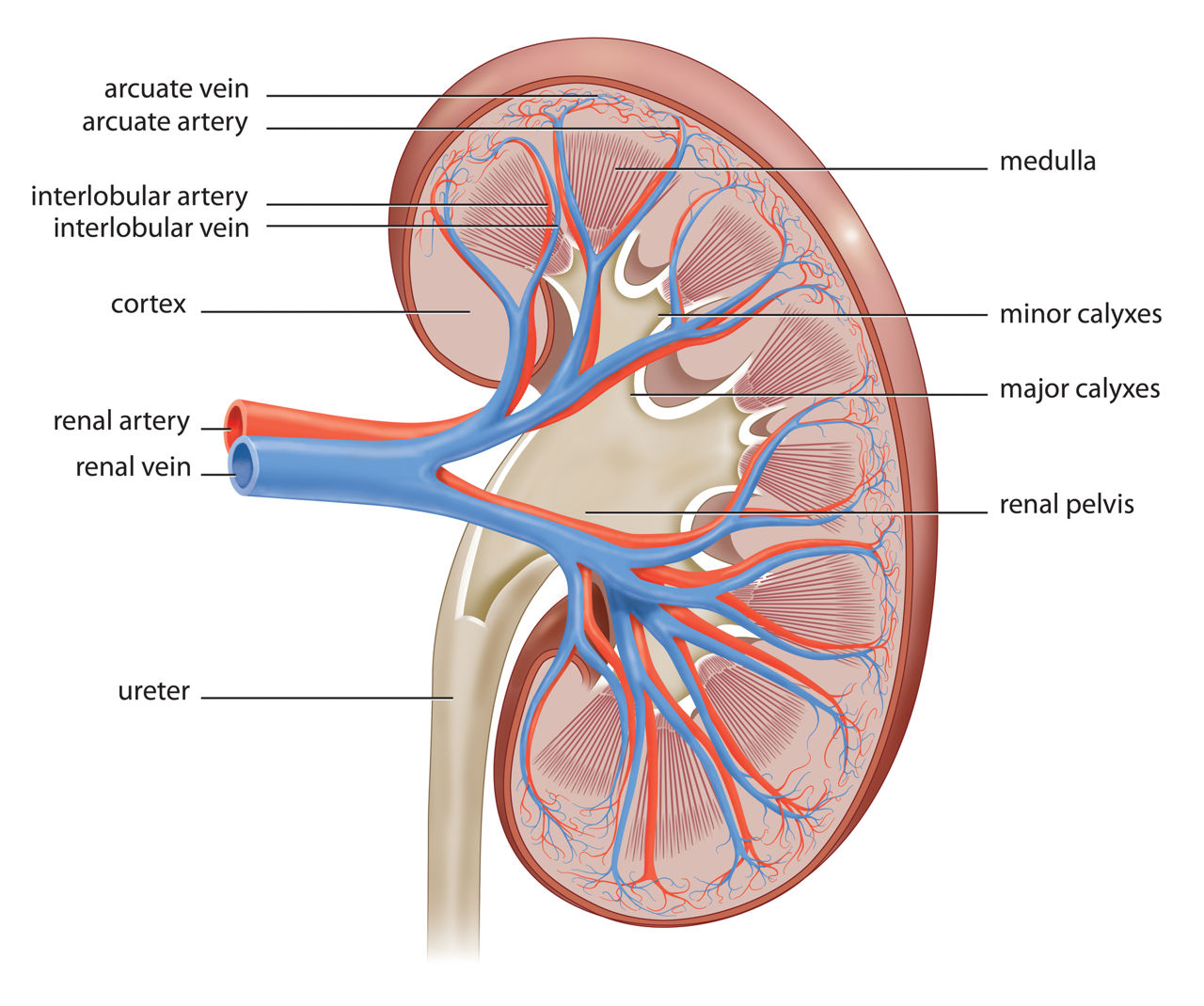
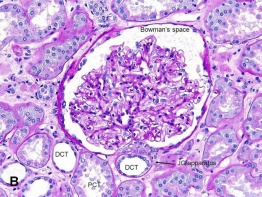
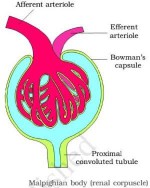
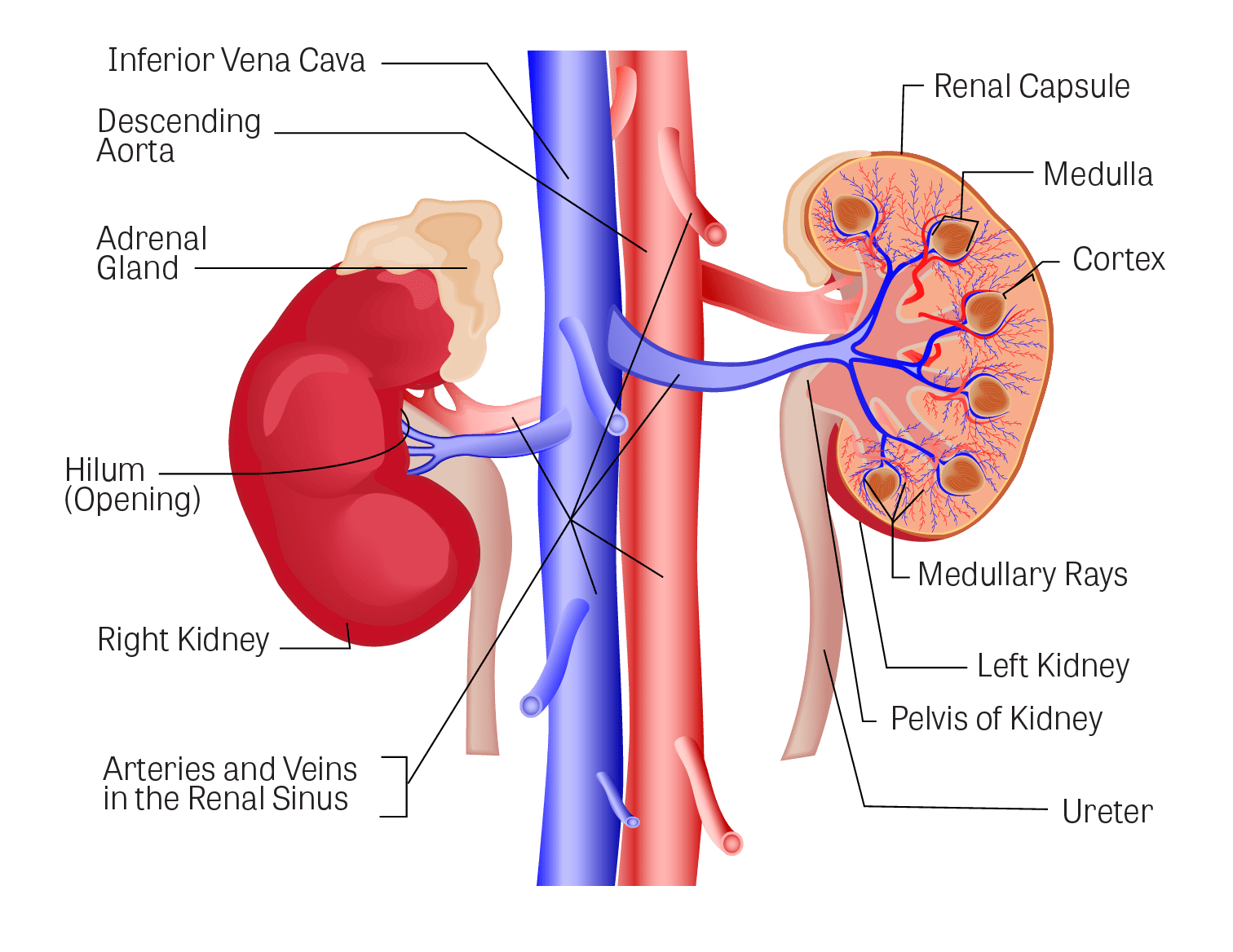
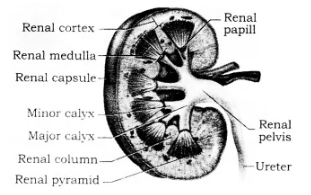
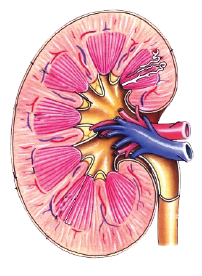
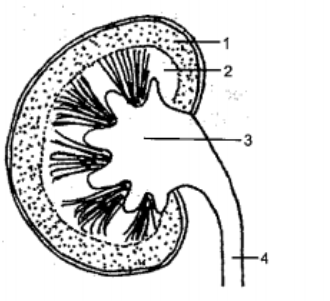
Look at the figure given. It is a section of human kidney as seen from the front.
Is it a longitudinal section or a cross-section?
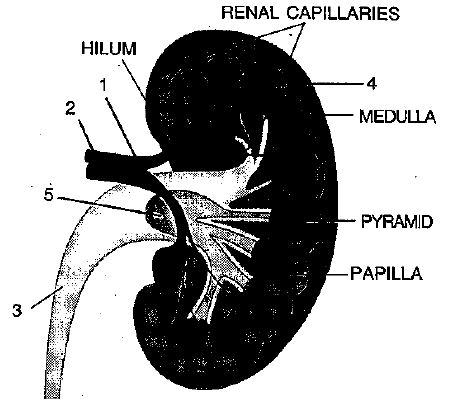
Define excretion.
A loop of capillary running parallel to the Henle's loop.
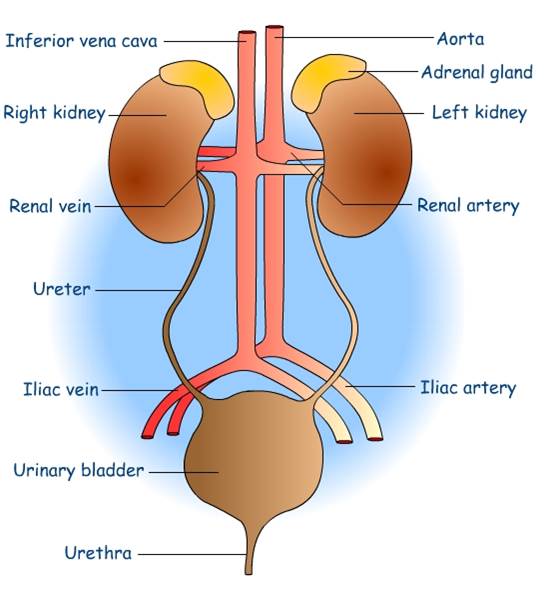
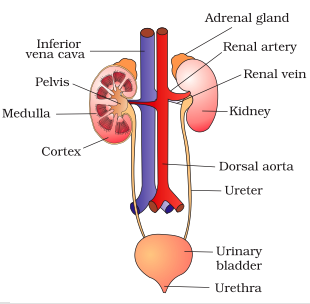
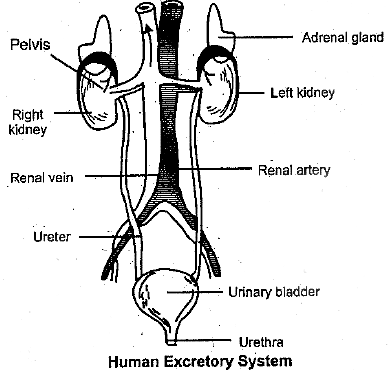
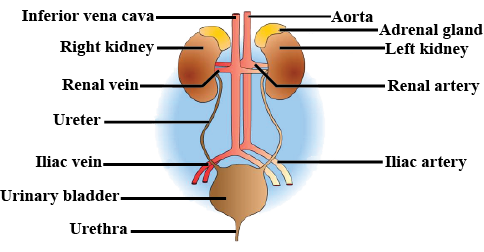
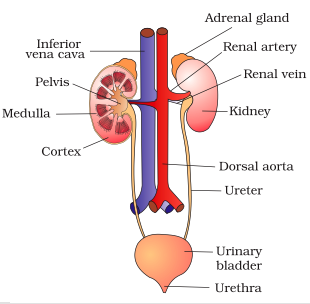
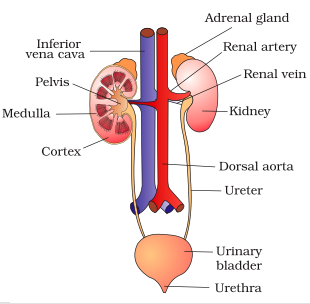
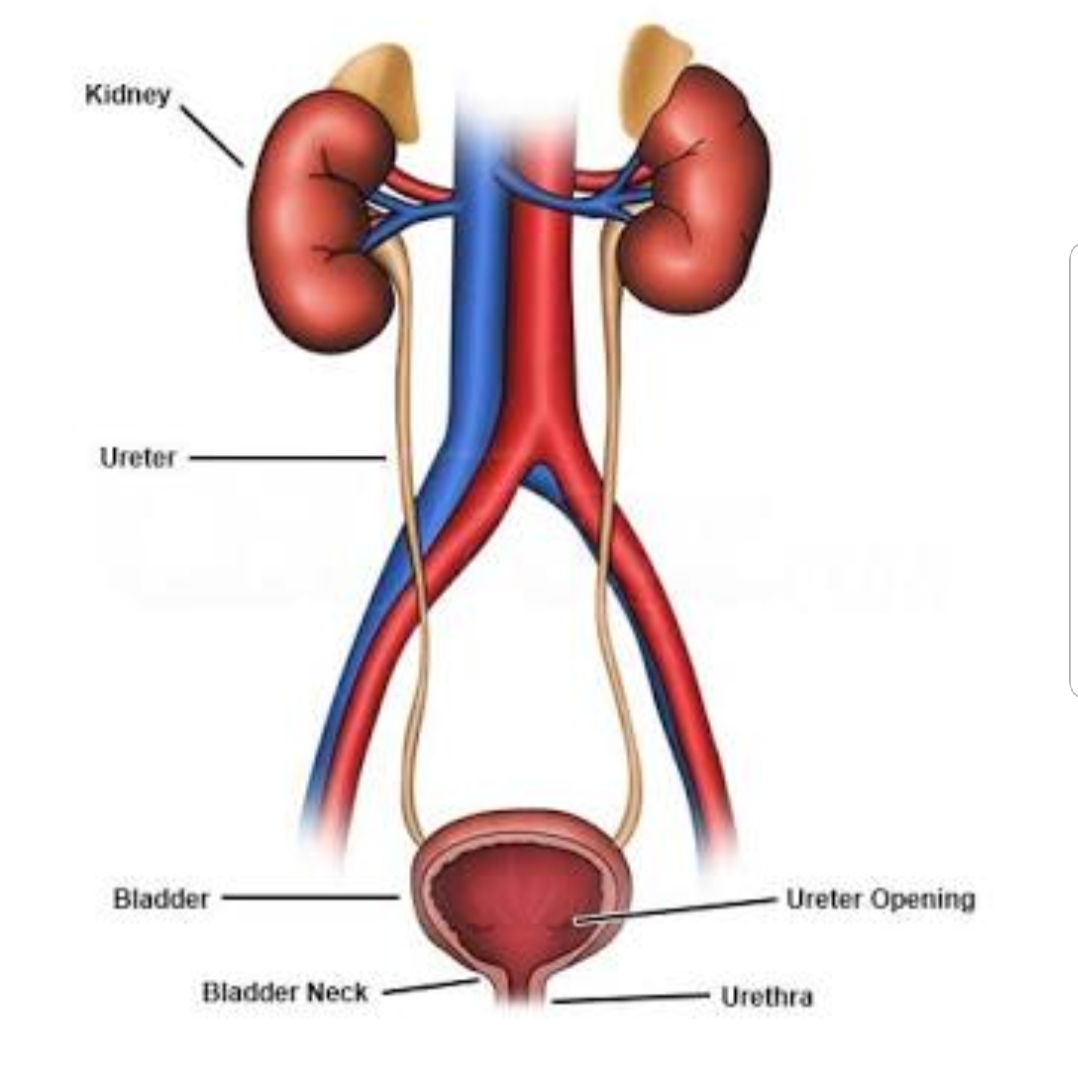
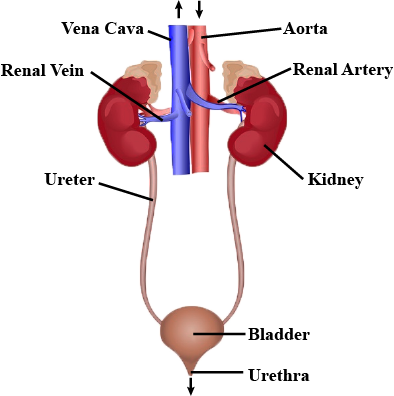
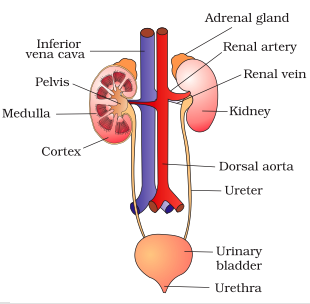
Write the name of excretory organs and draw a labelled diagram of excretory system in humans.
What is excretion?
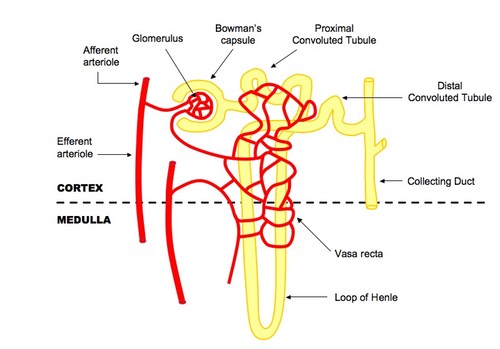
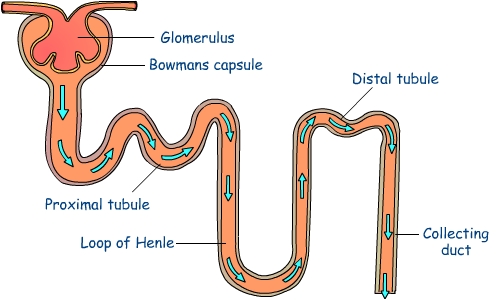
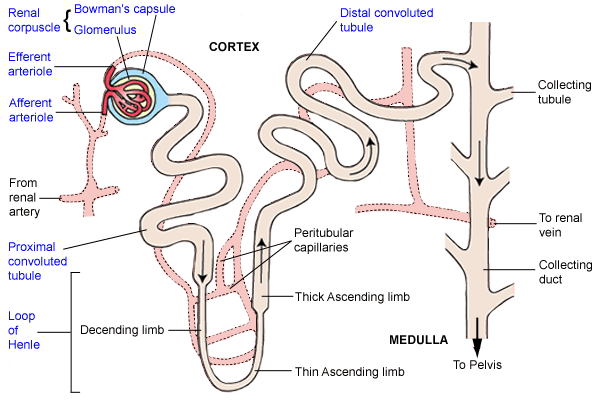
Draw the well labelled diagram of human nephron and define haemodialysis.
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
Desert mammals are adapted to water shortage by having nephrons with longer ..........
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
The network of capillaries, enclosed in a Bowmans capsule is called ..........
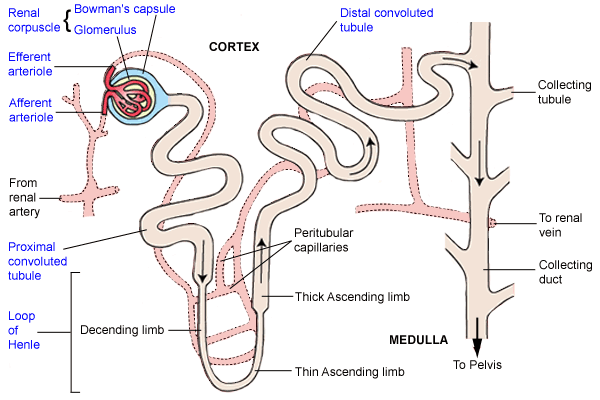
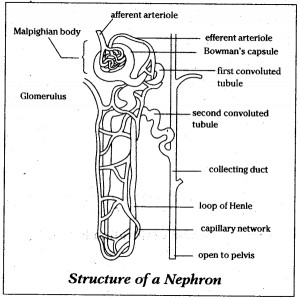
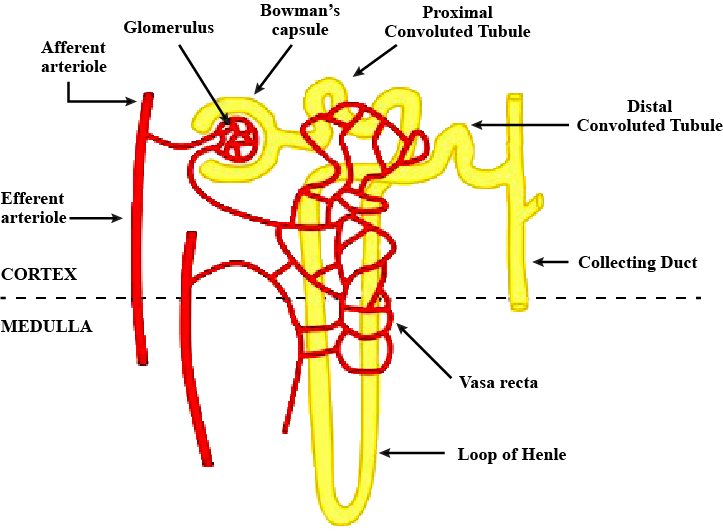
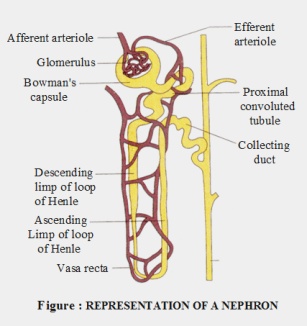
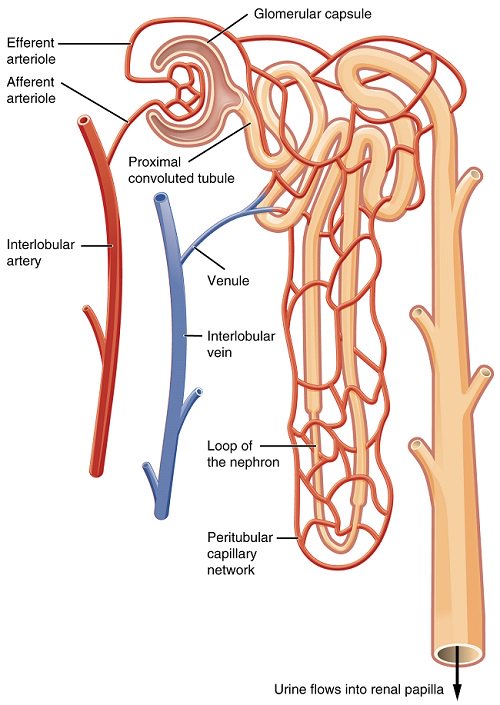
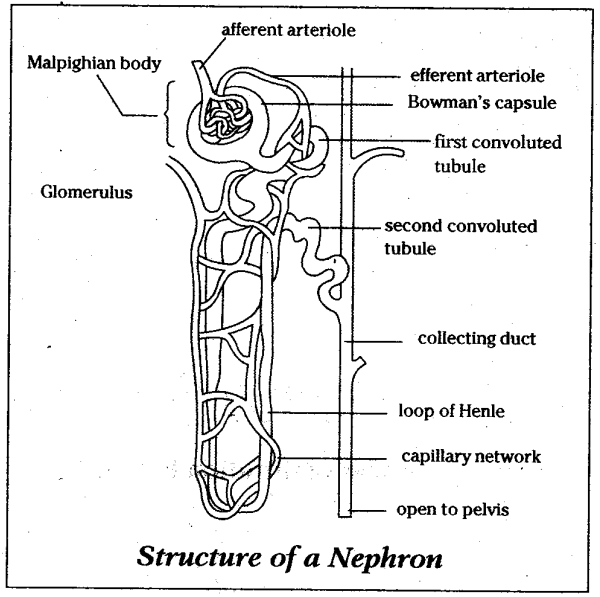
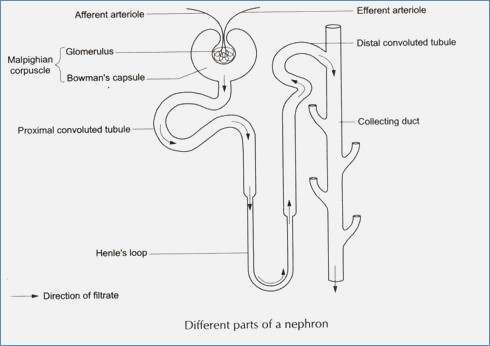
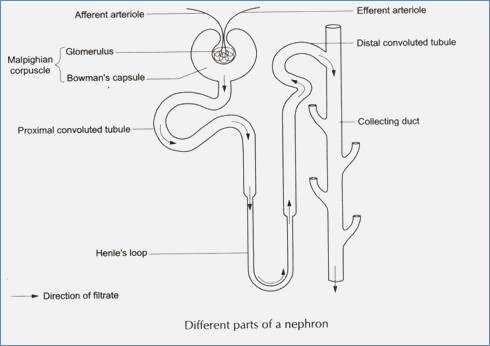
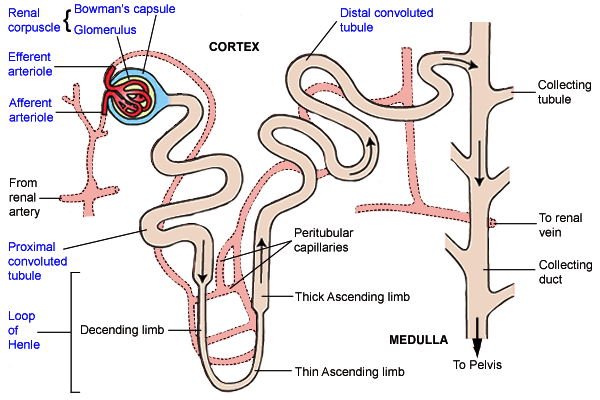
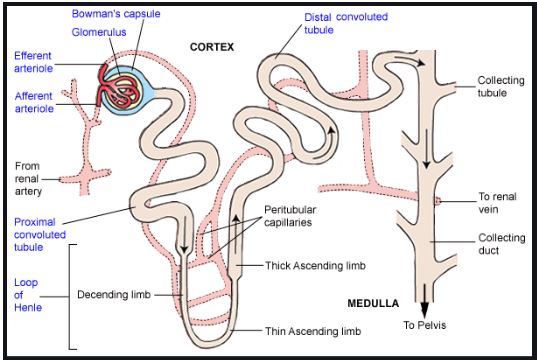
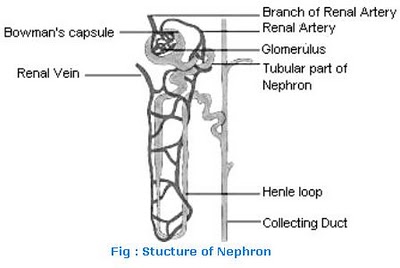
Name the different parts of a nephron.
Very short answer type.
What are the function performed by nephrons?
Mark the odd one in each of the following series
Renal pelvis, medullary pyramid, renal cortex
Explain the nature of excretory wastes.
The Bowman's capsule and glomerulus together form ________ body.
The structure and functional unit of kidney are _______.
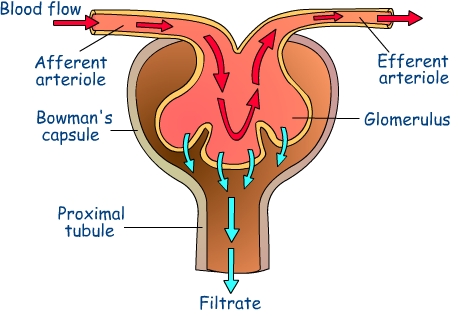
Draw a diagram to show the site of ultra-filtration and explain the process.
Where does Ultrafiltration process take place?
Match the right pairs.
Draw a labelled diagram of human excretory system.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of the human excretory system.
Draw a labelled diagram of a nephron. State the functions of glomerulitis, distal convoluted tubule and descending limb of Henle's loop
Name the structural and functional units of the kidney.
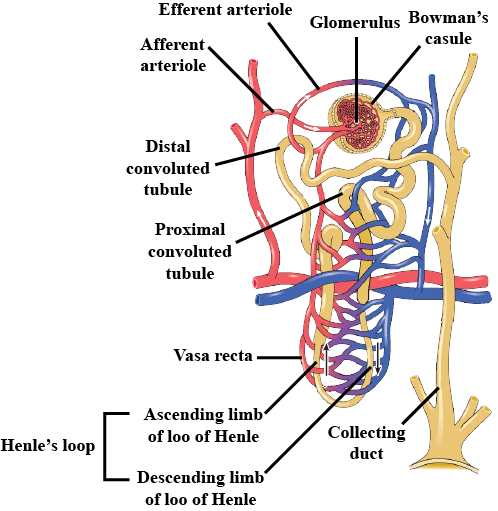
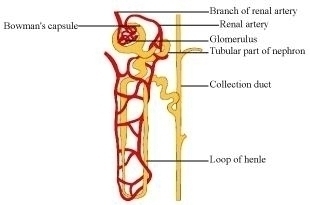
The given diagram represents a nephron and its blood supply. Study the diagram and answer the following questions:
Name the blood vessel which contains the least amount of urea in this diagrams.
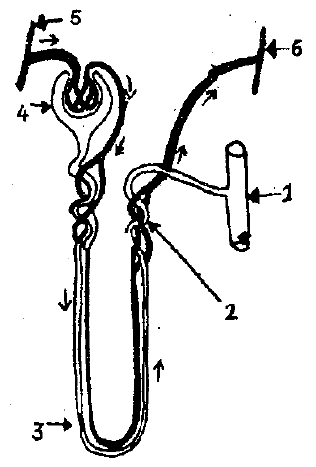
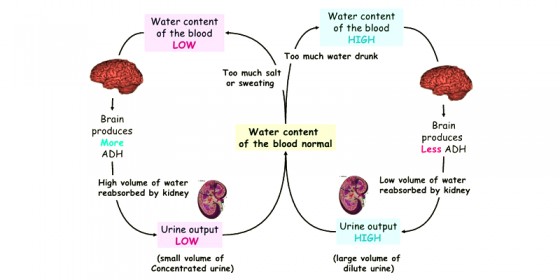
Why do terrestrial animals excrete hypertonic urine?
The given diagram represents a nephron and its blood supply. Study the diagram and answer the following questions:
State the reason for the high hydrostatic pressure in the glomerulus.
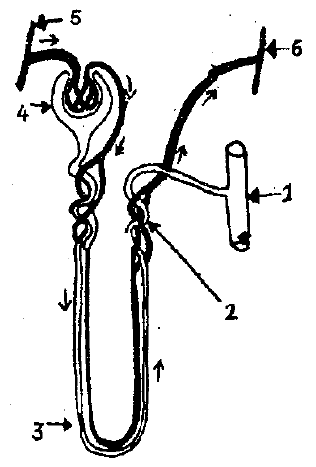
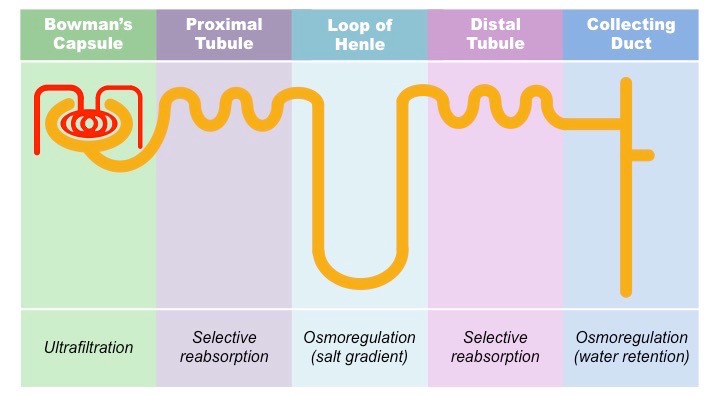
Write short notes on ultrafiltration and selective reabsorption.
Write short notes on nephron.
The given diagram represents a nephron and its blood supply. Study the diagram and answer the following questions:
Label parts 1, 2, 3, and 4.
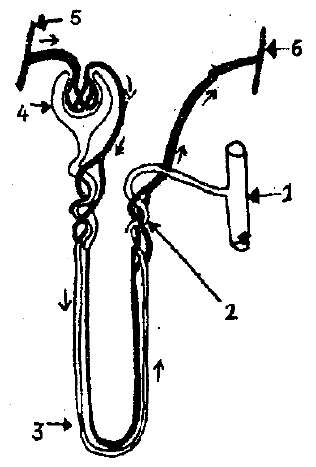
Observe the figure :
(a) Identify A and B.
(b) How the difference in size between A and B helps in the functioning of the kidney?
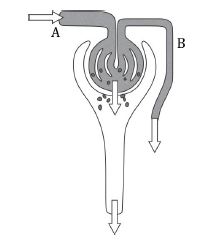
List out the various excretory organs found in the following:-
a) Sponges b) Roundworms c)Annelids d) crustaceans e) Insects f) Flatworms g) Echinoderms h) Cnidarians i) Molluscs j) Vertebrates
The tube arising from the notch of the kidney on the median side and connecting behind with the urinary bladder is __________.
Match the terms to these definitions:
(Excretion, micturition, hemodialysis, ureotelic, uricotelic, transport maximum, glomerular filtration rate, osmoregulation, renal threshold, nephron, countercurrent system, ultrafiltration)
.......... is the functional unit of a kidney
(Excretion, micturition, hemodialysis, ureotelic, uricotelic, transport maximum, glomerular filtration rate, osmoregulation, renal threshold, nephron, countercurrent system, ultrafiltration)
.......... is the functional unit of a kidney
What is Juxtaglomerular apparatus?
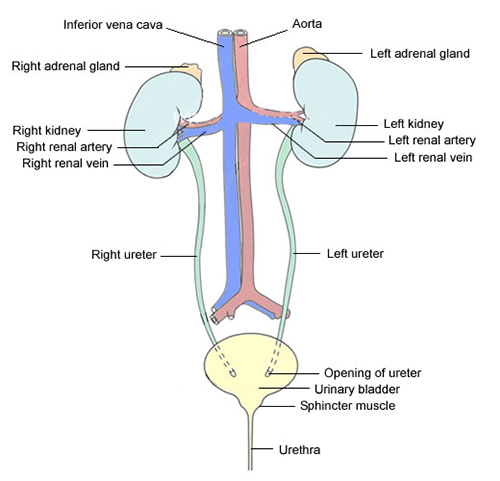
Draw a neat diagram of excretory system of human beings and label it:
(i) Left kidney
(ii) Urinary bladder
________ is the basic functional unit of the kidney.
A loop of capillary running parallel to the Henle's loop is known as
Indicate whether the given statement is true or false. Protein-free fluid is filtered from blood plasma into the Bowman's capsule.
Match the items of column I with those of column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Ammonotelism | (i) Birds |
| (b) Bowman's capsule | (ii) Water reabsorption |
| (c) Micturition | (iii) Bony fish |
| (d) Uricotelism | (iv) Urinary bladder |
| (e) ADH | (v) Renal tubule |
Copy the picture.
(a) Label the parts A, B and C.(b) Note down the functions of B, C and D.
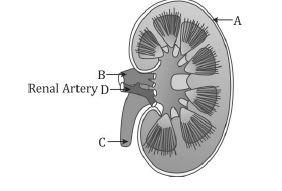
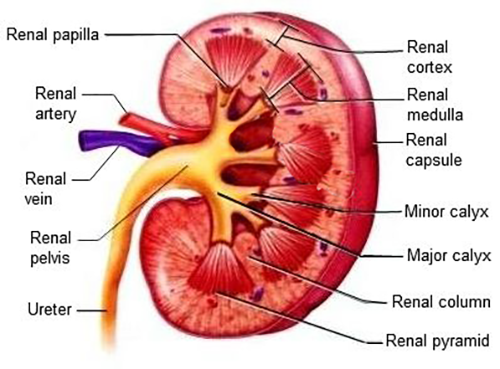
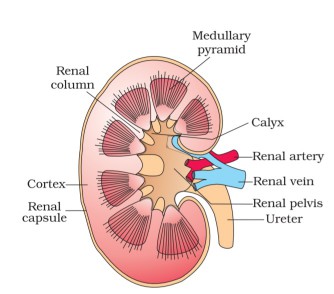
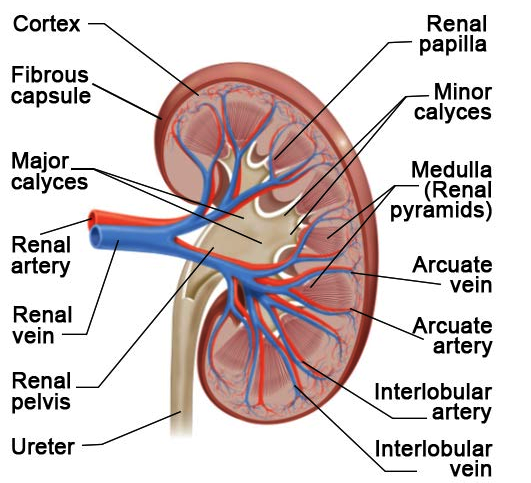
Draw well labelled diagram of L.S. of human kidney.
Draw a labelled diagram of the malpighian tubules transfer section.
Describe the structure of renal tubule with neatly labeled diagram.
State the exact location of the following structures.
Proximal convoluted tubule.
Write the functions of Bowman's capsule.
a) The diagram below shows the excretory system of a human being. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow.
i) Name the parts labelled 1, 2, 3 and 4.
ii) Give the main function of the parts labelled 5, 6, 7 and 8.
iii) Name the endocrine gland which could be added in the diagram and state its location/position.
Draw labelled diagram of a nephron. Explain the process of urine formation.
Give the biological technical term for the pigment providing colour to urine.
If there is a fault in the function of the 'Bowman's capsule, what will happen?
Draw a neat and well labelled diagram of human excretory system.
Draw the given diagram of L.S of kidney and label the following parts.
(a) Medullary pyramid
(b) Ureter
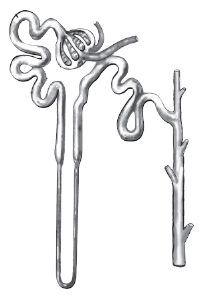
Draw the diagram and label any two parts mentioned below.
(a) Bowman's capsule
(b) Glomerulus
(c) Loop of Henle
(d) Collecting duct
'Master chemists' of our body are kidneys. Give reasons.
What are the different stages in Urine formation? Explain what happens in those stages.
What are the columns of Bertini?
Which organ is known as 'Master Chemist'? Why?
Define glomerular filtration.
Define homeostatic mechanism in a living organism.
Choose the correct answer from the four alternatives given in the brackets:
The process in which metabolic wastes are removed is
(Conduction, Excretion, Respiration, all of these)
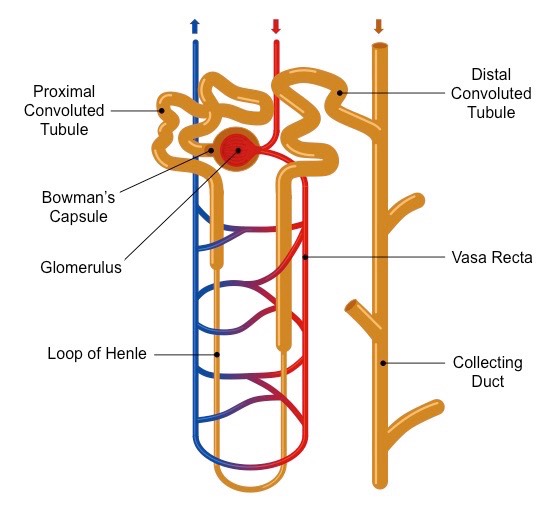
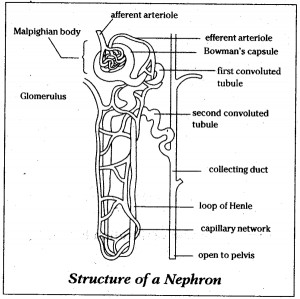
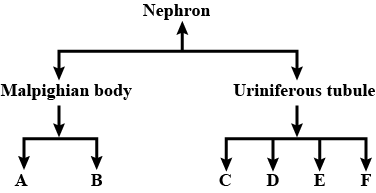
Observe the chart depicting the structure of a nephron.
(i) Mention the structures A to F
(ii) Explain the main function of a nephron.
Draw the diagram of human excretory system and label it.
Draw the L.S of kidney and label the parts.
(i) What are the structural and functional units of kidney?
(ii) Arrange the organs of the human excretory system in the correct order, based on the passage of urine.
Ureter, Urethra, Kidney, Urinary bladder.
Give significance of podocyte.
Draw a labelled diagram of excretory system of human.
Match the columns and find out the correct combination
Match the columns and choose the correct combination
Match
the columns
Select the proper option
Match the items of Column I with Column II
What is glomerular filtration? What is the normal filtration force in humans?
Define Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
What is a uriniferous tubule? How does it function?
Look at the figure given. It is a section of human kidney as seen from the front.
Name the parts numbered 1-5.
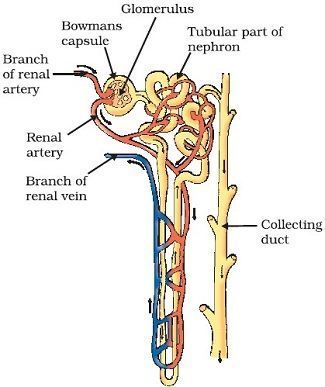
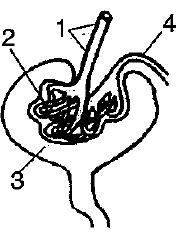
The diagram given is that of a structure present in a human kidney. Study the same and answer the question that follow.
Mention the three main steps involved in the formation of the fluid from part 2.

The diagram given is that of a structure present in a human kidney. Study the same and answer the question that follow.
a. What is the fluid that comes to part 2 called?
b. Name the main nitrogenous waste in it.

The diagram given is that of a structure present in a human kidney. Study the same and answer the question that follow.
a. What is the liquid entering part 1 called?
b. Name two substances present in this liquid that are reabsorbed in the tubule.

Correct the following statement by changing the underlined word/s.
Normal pale yellow color of the urine is due to the presence of pigment Melanin.
The diagram given is that of a structure present in a human kidney. Study the same and answer the question that follow.
Name the structure represented in the diagram.

Name the main nitrogenous metabolic waste excreted out by mammals including humans.
Define the following terms:
(a) Ultrafiltration
(b) Micturition
(c) Renal pelvis
(d) Urea
(e) Osmoregulation
Draw a well-labelled diagram of a human excretory system. Write the functions of
(a) Kidney
(b) Ureter
(c) Urinary bladder
Fill in the blanks in the following passage to make it a meaningful description.
In a nephron, the ________ flows through the ________ under great pressure. The reason for this great pressure is that the __________ (outgoing) _________ is narrower than the ___________ (incoming). This high pressure causes the ___________ part of the blood to filter out from the __________ into the __________ capsule.
Explain the terms ultrafiltration and selective absorption.
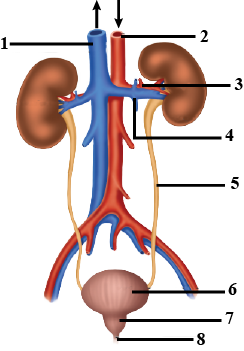
Given alongside is the figure of certain organs and associated parts in the human body. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
Name the two main organic constituents of the fluid that flows down the part labelled '3'.
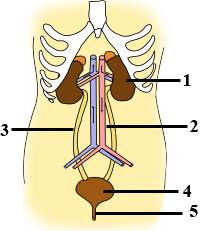
Given alongside is the figure of certain organs and associated parts in the human body. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
Name the parts numbered 1 to 5.
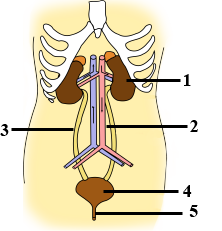
Given alongside is the figure of certain organs and associated parts in the human body. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
Name the structural and functional unit of the part marked '1'.
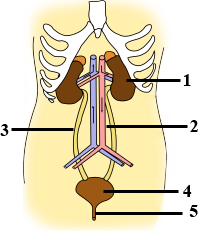
Look at the figure given. It is a section of human kidney as seen from the front.
Which area/part (give its name and the number given on the diagram) contains the following respectively:
(i) Malpighian capsule
(ii) The pyramids
(iii) Freshly collected urine
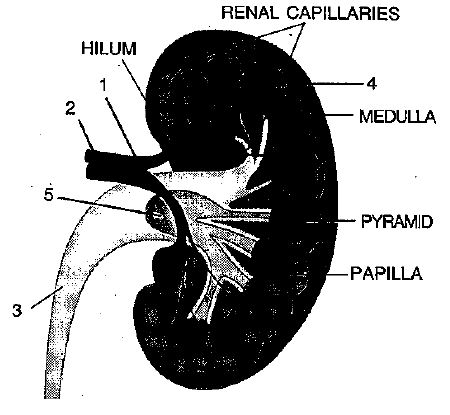
Study the diagram given alongside and then answer the questions that follow:
What is the technical term given to the process occurring in 2 and 3? Briefly describe the process.
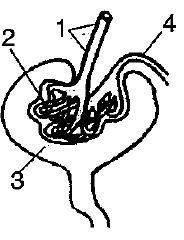
Given alongside is the figure of certain organs and associated parts in the human body. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
Name all the organ-systems shown completely or even partially.
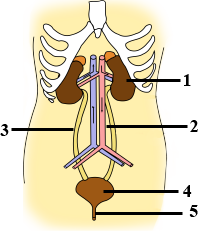
The given diagram represents a nephron and its blood supply. Study the diagram and answer the following questions:
Name the part of the nephron which lies in the renal medulla.
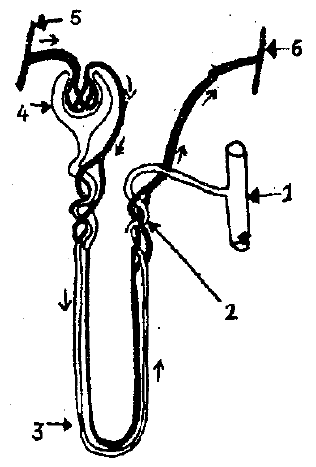
The given diagram represents a nephron and its blood supply. Study the diagram and answer the following questions:
Name the two main stages of urine formation.
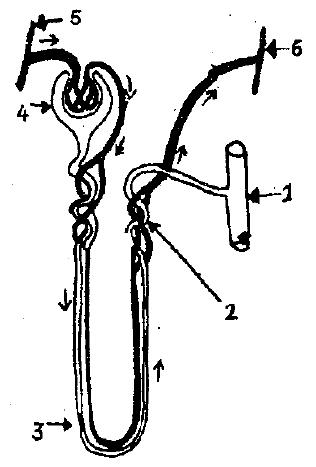
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
The yellow colour of urine is due to ..........
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
Kidney of a mammal resembles contractile vacuole of amoeba in expelling out..........
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
A condition in which the kidneys fail to form unine is called ..........
In which part of the nephron, does filtration take place?
Very short answer type.
Name the yellow coloured pigment present in urine.
Fill in the blanks with appropriate words.
Glycosuria is a condition that involves the excretion of large amount of..........
Write short notes on glomerular filtration rate.
Mark the odd one in each of the following series
Afferent arteriole, Henle's loop, vasa recta, efferent arteriole.
Mark the odd one in each of the following series
glomerular filtration, antidiuretic hormone, hypertonic urine, collecting duct
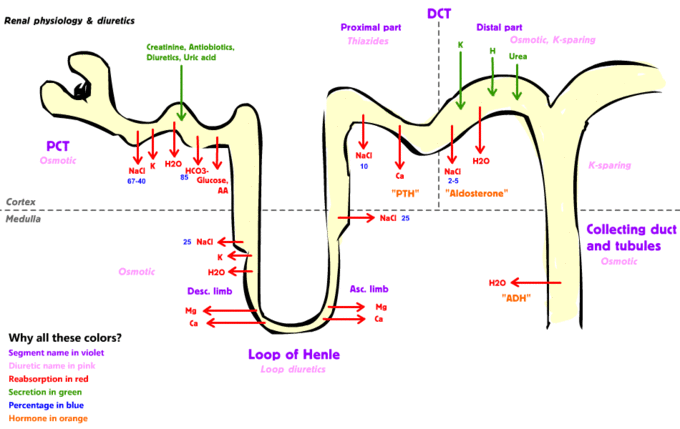
What are the different stages of urine formation? Explain the role of glomerulus of nephron-in the formation of urine.
Describe the structure and physiology of the kidney of a mammal.
Differentiate between the following:Ascending and descending limbs of Henle's loop.
Mark the odd one in each of the following series
Proximal convoluted tubule, distal convoluted tubule, Henle's loop, renal corpuscle.
How is the structure of kidney related to the function of excretion? Describe the process of urine formation in humans.
What happens to glomerular filtration rake (GF1t) if blood pressure in the kidneys increases?
The concentration of glucose in plasma is 100 mg/100 mL, and the GFR is 125 mL/min. How much glucose is filtered per minute?
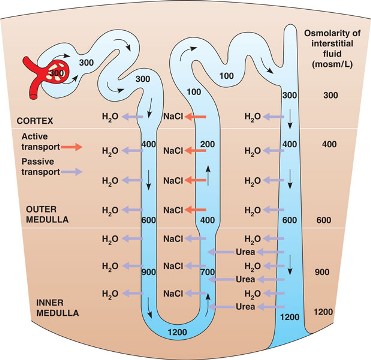
Why is that the urine excreted during summer months is hypertonic?
Draw a labelled histological diagram of the kidney. Describe how selective reabsorption takes place in the kidney tubule.
Draw a labelled diagram of the sagittal section of the human kidney.
Value based questions.
Imagine a water molecule has just entered the proximal convoluted tubule of the nephron
that will eventually be part of the urine. What parts of the nephron will it travel through (in order) before it reaches the renal pelvis?
Differentiate between proximal and distal convoluted tubules. (Based on their position)
Which organs are associated with a major excretory system in mammals? Describe briefly the structure of a nephron.
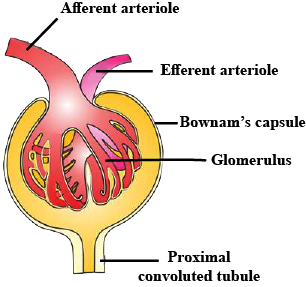
Show the structure of a renal corpuscle with the help of a diagram.
Short / Long answer type questions.
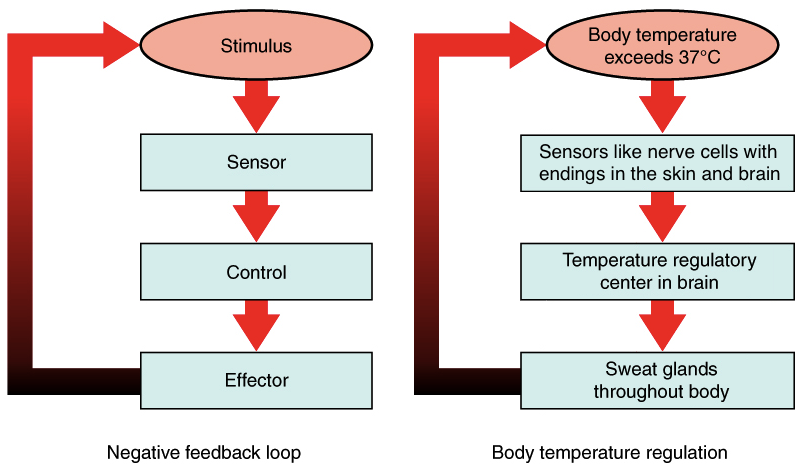
What is feedback control? Illustrate feedback mechanism of homeostasis by an example of hormones.
Give a brief account on human excretory system. Add a note on vertical section of kidney.
What is homeostasis?
Name any two substances which are selectively reabsorbed from the tubules of a nephron.
What is the tube that passes urine to outside of the body?
How does the blood come out of the capillary and come in contact with the Bowman's capsule so as to form filtrate?
Describe the process of ultrafilteration.
Describe Malpighian body. Explain its role in urine formation.
Given is a jumbled list of the parts of a certain body structure - Loop of Henle, Bowman's capsule, convoluted tubule, glomerulus, proximal convoluted tubule.
(i) Name the structure to which the listed parts belong.
(ii) Rearrange the parts in their proper sequence from the starting point to where they end.
Define excretion. Describe the structure of nephron. Write a note on the physiology of urine formation.
Describe the human excretory system. Write a note on vertical section of kidney.
The blood vessel which-
(a) Enters the malpighian corpuscles
(b) Leaves the malpighian corpuscles
Define excretion. Explain mechanism of urine formation.
The organs of excretion in arthropoda is __________
What is meant by excretion? Explain the process OR Describe the mechanism of urine formation.
Which part of Nephron is not permeable for water ?

Mention the differences between egestion and excretion.
Write the special characteristics/features of the human excretory system
What happens to glucose which enters the nephron along with filterate during excretion in human beings? State two vital functions of kidney.
What will happen if their is no tubular reabsorption in the nephrons of kidneys?
Draw a neat and correct diagram of the of the human kidney and label it.
Name the organ in man concerned with maintaining water balance in the body.
What is meant by osmoregulation? How is it maintained in human body?
Which cell organelle detoxifies poisons and drugs in the liver of vertebrates?
Describe the structure and functioning of nephrons.
Differentiate protonephridia from metanephridia.
What is tubular secretion? Name the substances secreted through the renal tubules.
Draw the structure of a nephron and label the following ; Glomerulus ,Bowman capsule, renal artery, collecting duct,
b) What happen to glucose that enters the nephron along with the filtrate
Give reasons for this sentence:
Urine is formed from alkaline blood but it is acidic in nature.
Draw the structure of nephorons are also labelled
What is malpighian body?
Draw a labelled structure of nephron.
Draw the structure of a nephron and label glomerulus, Bowman's capsule, renal artery, collecting duct.
b) What happen to glucose that enters the nephron along with the filtrate?
What is the unit of excretory system?
Where does the initial production of urine occurs?
With the help of a well labelled diagram, describe the structure of nephron
Explain in your own words.
How does excretion occur in human beings?
What is the role of fluid filtered out in Bowman's capsule?
Mention the functions of
(a) Proximal convoluted tubule
(b) Henle's loop
(c) Distal convoluted tubule
(a) Proximal convoluted tubule
(b) Henle's loop
(c) Distal convoluted tubule
What is glomerulus? What role does it plays during urine formation?
Briefly describe the structure and functions of nephron with neat labelled diagram.
What causes the liquid part of blood to filter out from the glomerulus into the renal tubule?
Explain about composition of urine?
Explain excretion in human beings.
Draw a labelled diagram of nephron.
What is mainly digested by stomach of man?
Read the following table and answer the following questions.
| Sl. No. | Structure | Location |
| 1. | Tricuspid valve | Right auriculo-ventricular aperture |
| 2. | Guard cells | Epidermis of leaves |
| 3. | Glomerulus | Nephron |
| 4. | Alveoli | Lungs |
| 5. | Acrosome | Above the head of a sperm |
Draw and label the diagram.
Nephron
Unscramble the given words below to get the correct word using the clues given against them.
RETECOXNI: Waste products are removed by this process
Name the process and the organ which helps in removing the following wastes from the body.
a) Carbon dioxide
b) Undigested food
c) Urine
d) Sweat
Explain the structure of kidney.
Arrange the terms in correct sequence:
Glomerulus, renal vein. efferent arterioles, renal artery, afferent arterioles, secondary capillaries.
Explain the internal structure of the kidney?
Label the different components of actin filament in the diagram given below.

Describe the structure and functioning of nephrons.
Explain the structure of a nephron.
Name two actively transported substances in Glomerular filtrate.
Which is the functional unit of kidney?
Explain the organs involved in excretion, other than kidney.
Explain why the composition of glomerular filtrate is not the same as urine.
What is Ultrafiltration?
What is the main role of kidneys in the body?
Name the organs that form the excretory system in human beings.
Write the name of the excretory unit in the kidney.
The glomerular filtrate in the loop of Henle gets concentrated in the descending and then gets diluted in the ascending limbs. Explain.
What is the malpighian body?
Label the parts marked 2 andMention the function of part 5.
Name the following:
(a) A chordate animal having flame cells as excretory structures.(b) Cortical portions projecting between the medullary pyramids in the human kidney.(c) A loop of capillary running parallel to the Henle's loop.
(b) Cortical portions projecting between the medullary pyramids in the human kidney.
(c) A loop of capillary running parallel to the Henle's loop.
Compare the functioning of alveoli in the lungs and nephrons in the kidneys with respect to their structure and functioning.
Explain the Human Excretory System with the help of suitable diagram.
Mention the exact location of the following structures:
$$(i)$$ Thylakoids
$$(ii)$$ Organ of Corti
$$(iii)$$ Lenticels
$$(iv)$$ Bicuspid valve
$$(v)$$ Loop of Henle
Differentiate between the following pairs on the basis of what is mentioned in brackets :
(i) Photolysis and Photophosphorylation. (Definition)
(ii) Bicuspid valve and Tricuspid valve. (Function)
(iii) Vasectomy and Tubectomy. (Explain)
(iv) Cerebrum and Spinal cord. (Arrangement of nerve cells)
(v) Bowman's capsule and Malpighian capsule. (Parts included)
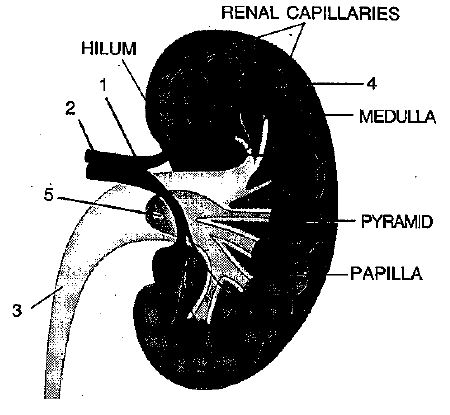
The diagram given shows a section of a human kidney. Study the diagram carefully and answer the questions that follow:
$$(i)$$ Label the parts numbered $$1$$ to $$4$$.
$$(ii)$$ Why does part '$$2$$' have striped appearance?
$$(iii)$$ What is the fluid that passes down part '$$4$$'? Name the main nitrogenous waste present in it.
$$(iv)$$ Mention the structural and functional units of kidneys.
$$(v)$$ Name the two major steps in the formation of the fluid mentioned in $$(iii)$$.
Sketch a labelled L. S. of human kidney.
Which is the basic filtration unit in the human excretory system?
The Master chemists of our body are the kidneys. Justify.
(i) Kidneys filter all chemicals in the body.
(ii) Kidneys maintain the chemical composition of blood.
(iii) Kidneys eliminate all chemicals absorbed by the body.
(iv) Kidneys store the chemicals accumulated in the body.
Sketch and label structure of nephron.
Describe the excretory system of man giving the structure of a nephron.
Match column I with column II regarding human excretory system. Choose the correct option.
Study the diagram given alongside and then answer the questions that follow:
Name the region in the kidney where the above structure is present?label the parts 1, 2, 3,4.
Short / Long answer type questions .
What do you understand by Homeostasis ? Write the name of scientist who used this word for the first time.
Write short notes on the renal threshold.
What are the factors that favour glomerular filtration ?
Describe the role of liver, lungs and skin in excretion.
Given below are five groups of five terms in each. Arrange the terms in each group in their proper sequence.
I.Renal Pelvis, Urethra, Ureter Kidney Urinary Bladder
ii. Sodium ions move into the axon, Repolarisation. Polarisation, Stimulus, Depolarisation
iii. ATP is produced, guard cells photosynthesise during the day guard cells become more turgid. guard cells become hypertonic, Potassium ions are actively pumped into the guard cells
iv Efferent ducts, Network of ducts, Seminiferous tubules. Urethra, Vas deferens v. Response, Effector Brain or Spinal Cord, Receptor Stimulus
Mention any two substances which are selectively reabsorbed as the filtrate flows along the tubular paths of this unit.
Which of Maya's organs is not working properly? (brain/heart/kidneys)
Cup shaped structure of renal tubule where ultrafiltration occurs.
Given is an example of a certain structure and its special functional activity.
"Kidney and excretion."
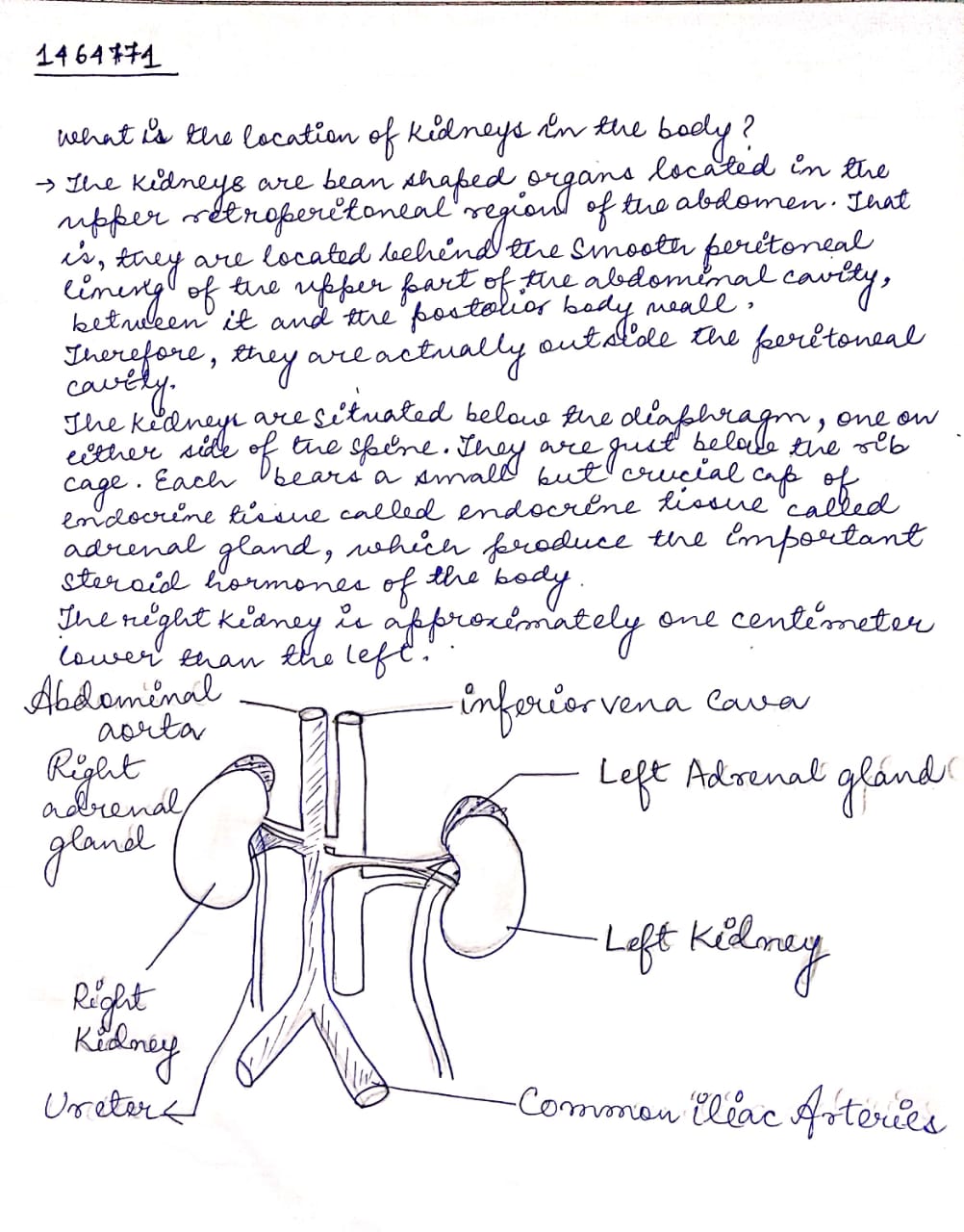
What is the location of kidneys in the body?
Describe the structure and functioning of nephrons.
Name the structure help in excretion and osmoregulation in Earthworm and Cockroach.
What is the function of the kidneys in excretion? Explain with the help of a diagram.
A. List the three major steps involved in the formation of urine.
B. Name the excretory unit of a kidney.
C. State the two functions of the human kidney.
D. What is the composition of urine?
Class 11 Medical Biology Extra Questions
- Anatomy Of Flowering Plants Extra Questions
- Animal Kingdom Extra Questions
- Biological Classification Extra Questions
- Biomolecules Extra Questions
- Body Fluids And Circulation Extra Questions
- Breathing And Exchange Of Gases Extra Questions
- Cell Cycle And Cell Division Extra Questions
- Cell The Unit Of Life Extra Questions
- Chemical Coordination And Integration Extra Questions
- Digestion And Absorption Extra Questions
- Excretory Products And Their Elimination Extra Questions
- Locomotion And Movement Extra Questions
- Mineral Nutrition Extra Questions
- Morphology Of Flowering Plants Extra Questions
- Neural Control And Coordination Extra Questions
- Photosynthesis In Higher Plants Extra Questions
- Plant Growth And Development Extra Questions
- Plant Kingdom Extra Questions
- Respiration In Plants Extra Questions
- Structural Organisation In Animals Extra Questions
- The Living World Extra Questions
- Transport In Plants Extra Questions