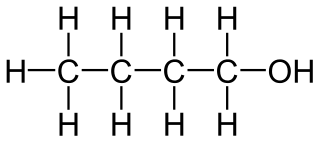
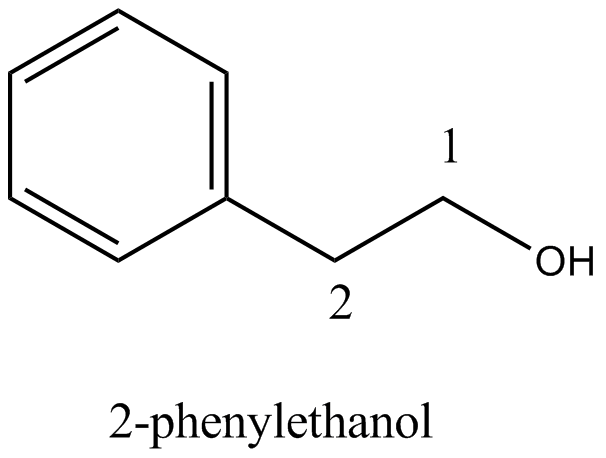
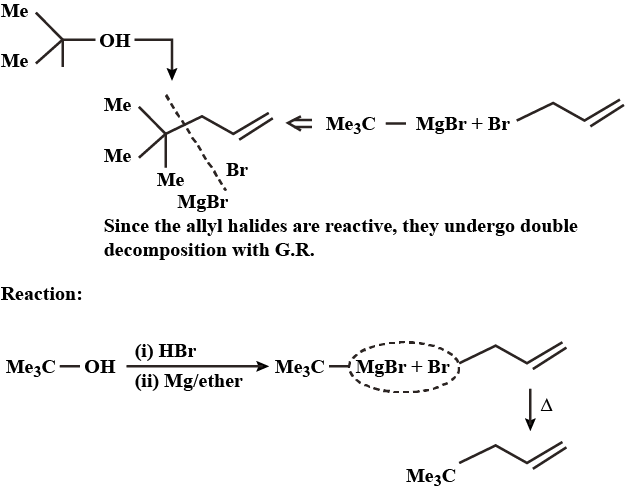
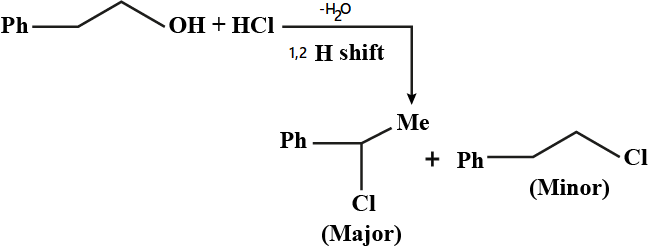
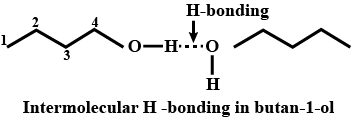
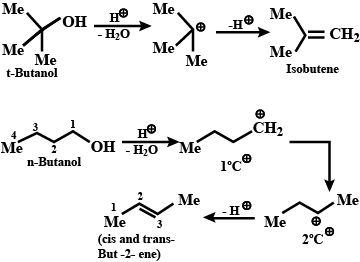
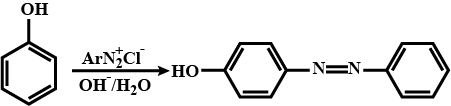
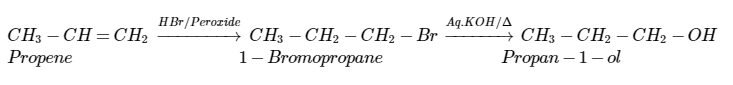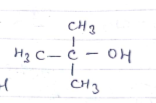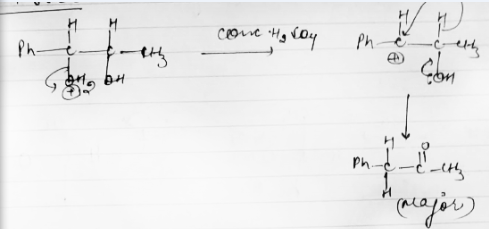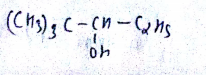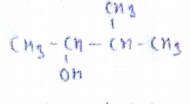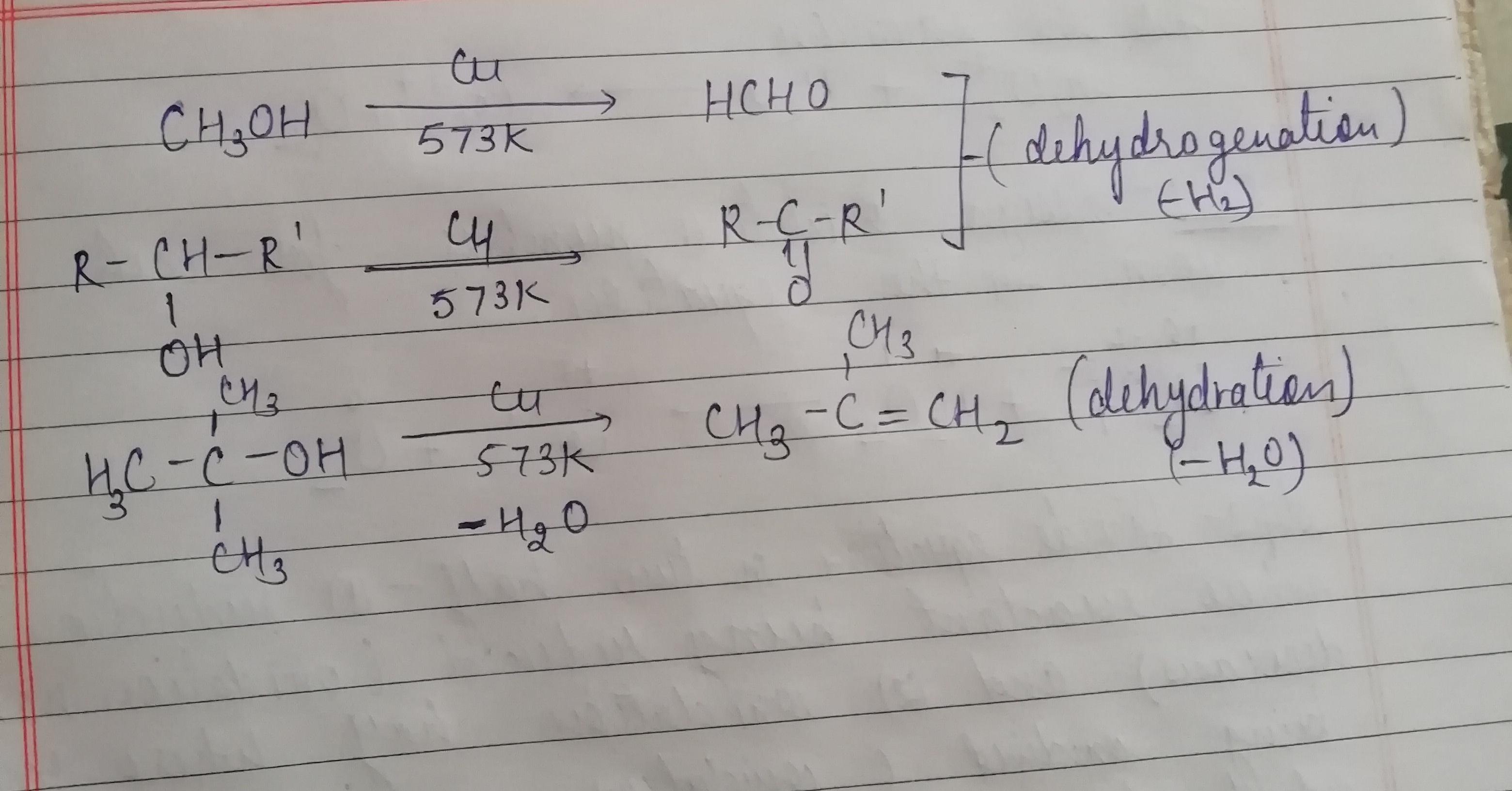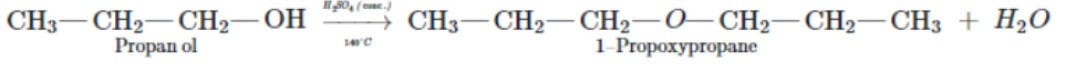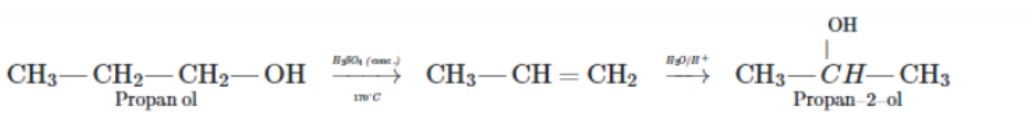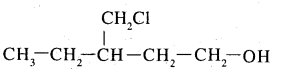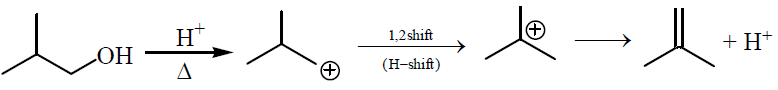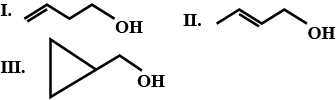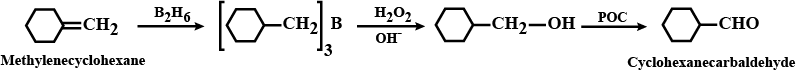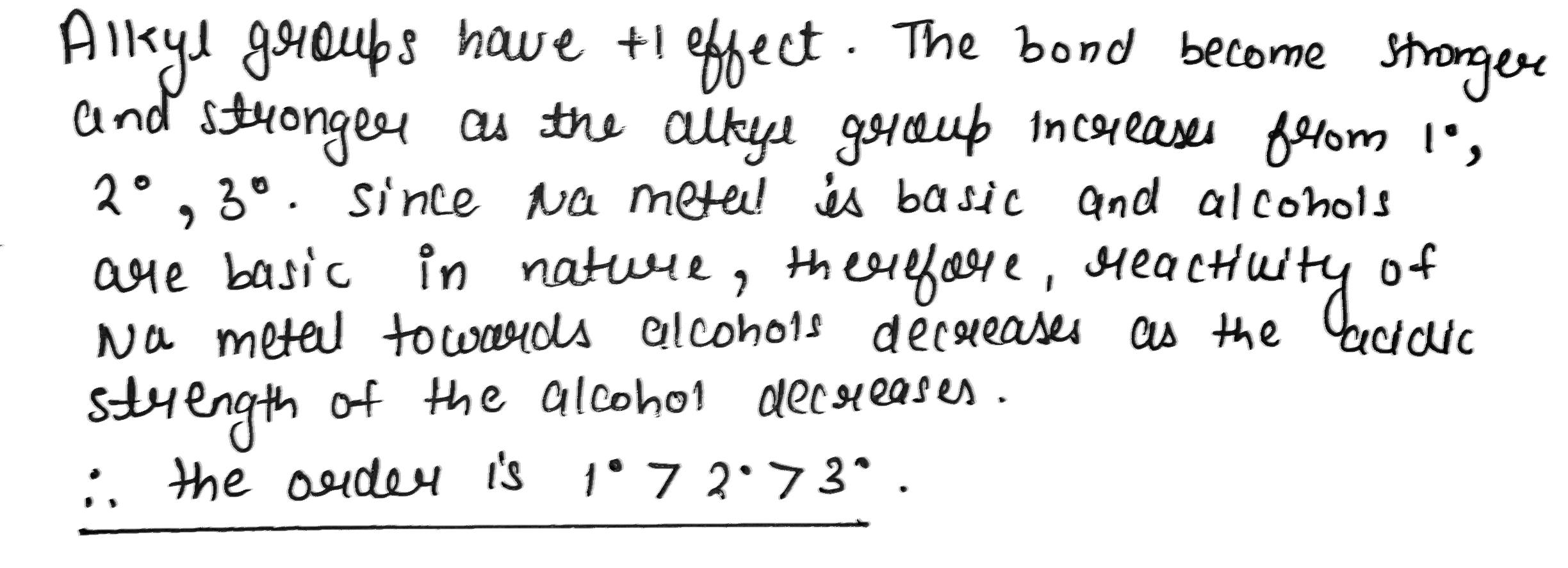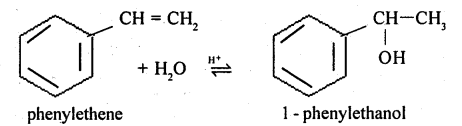Alcohols,Phenols And Ethers - Class 12 Engineering Chemistry - Extra Questions
How do you condemn the use of alcohol as a social practice.
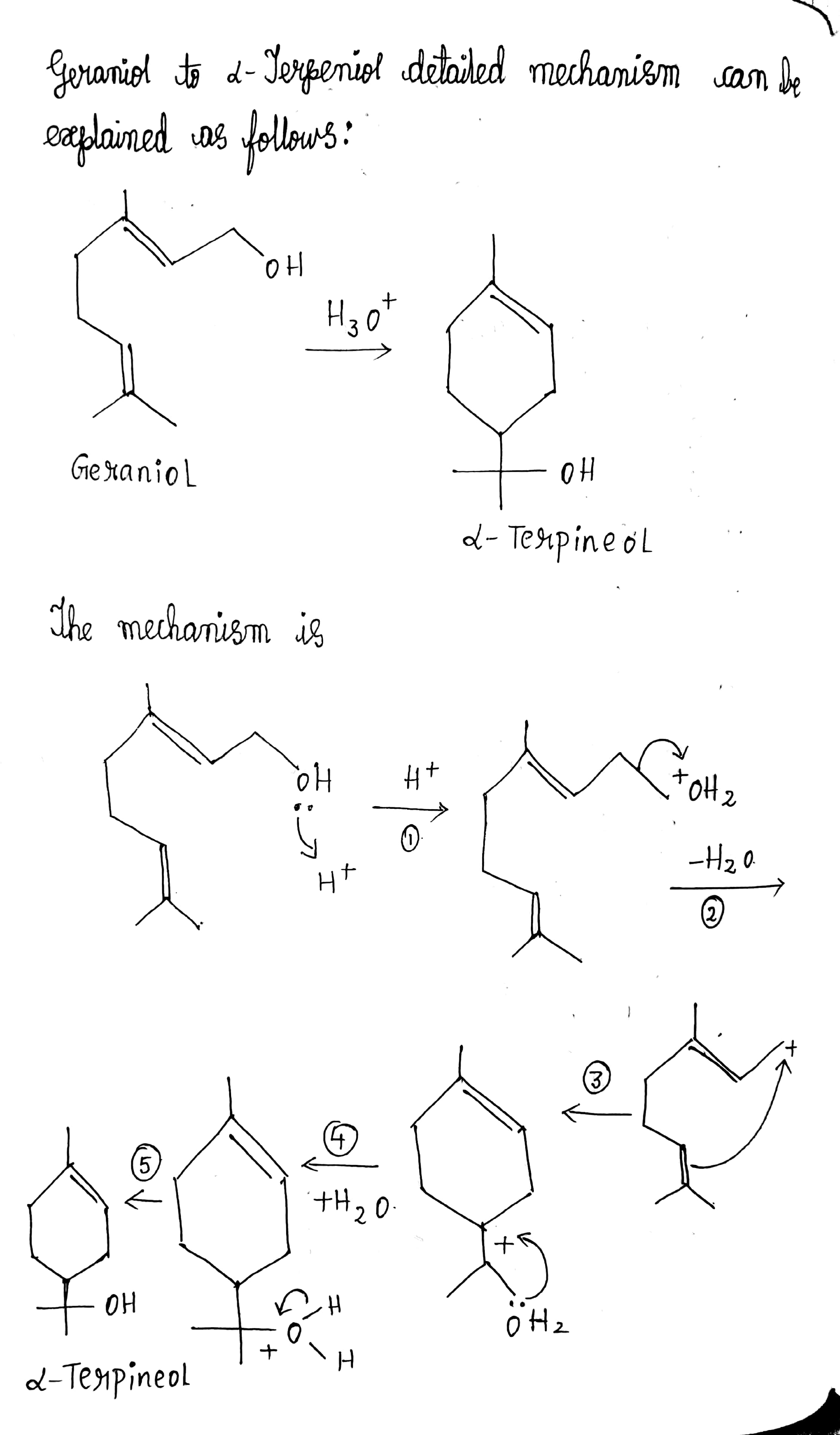
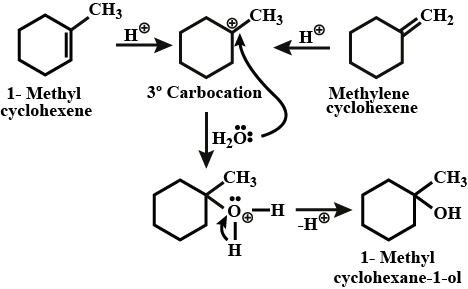
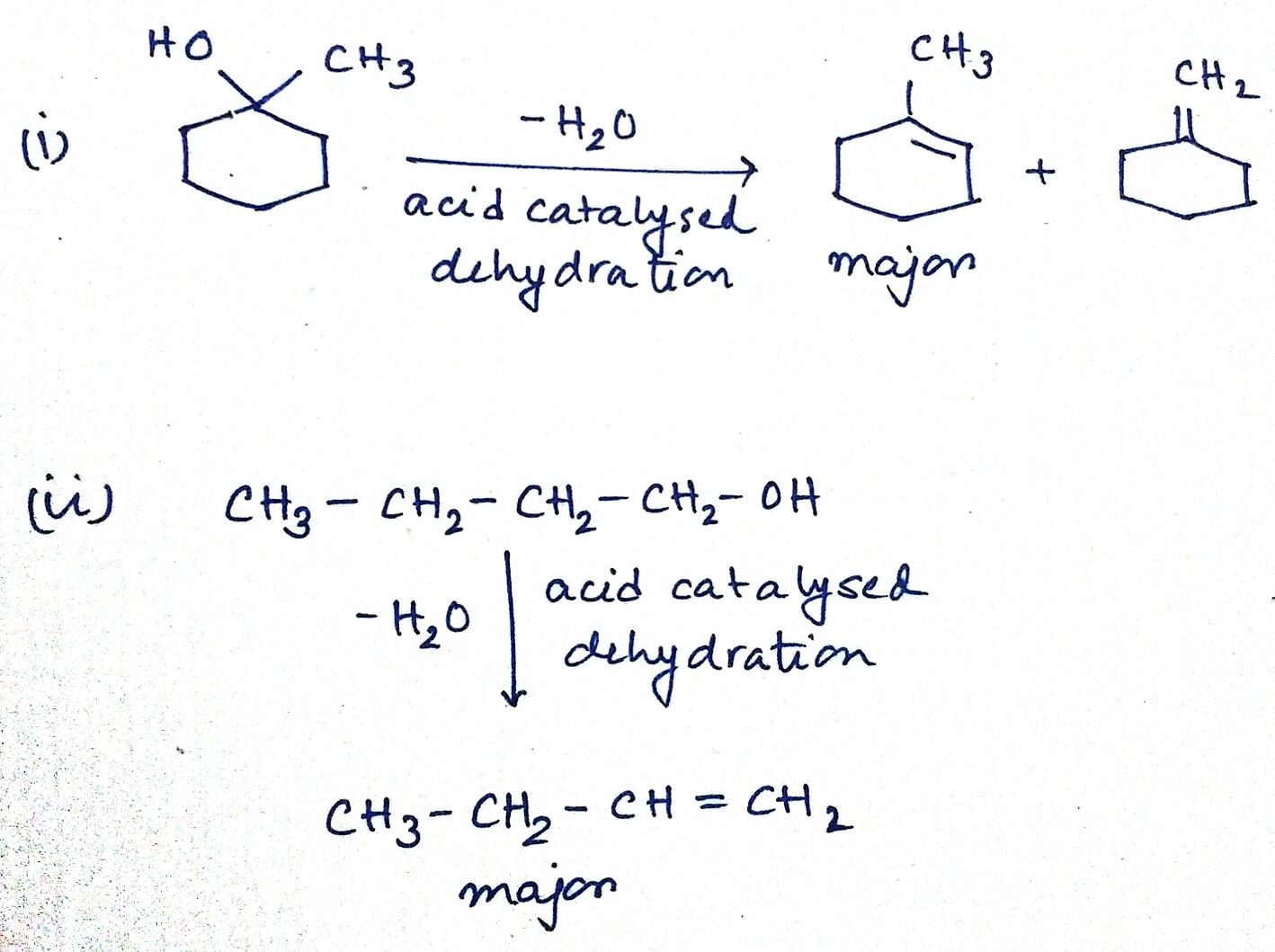
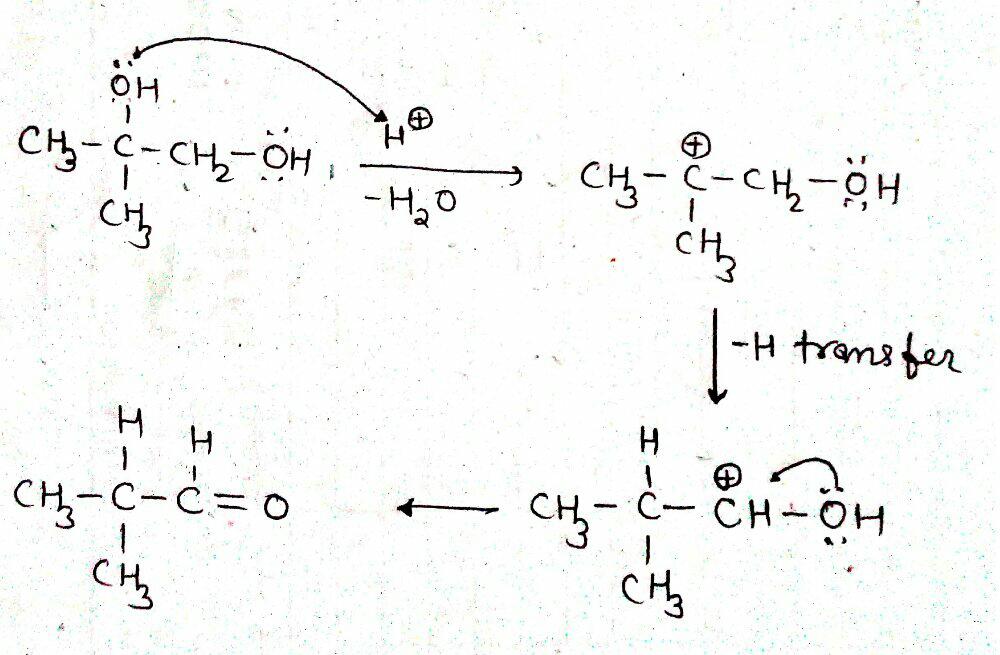
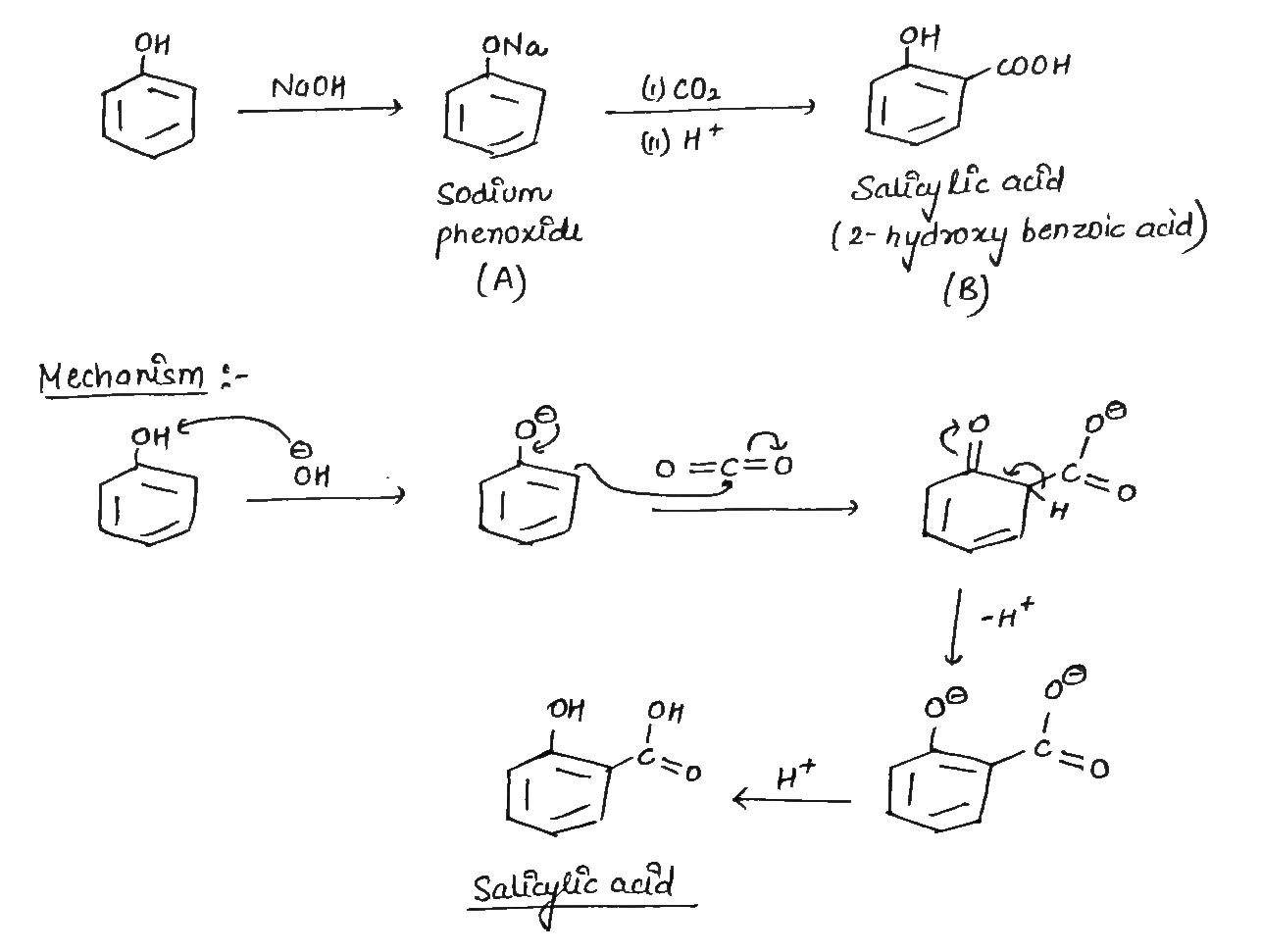
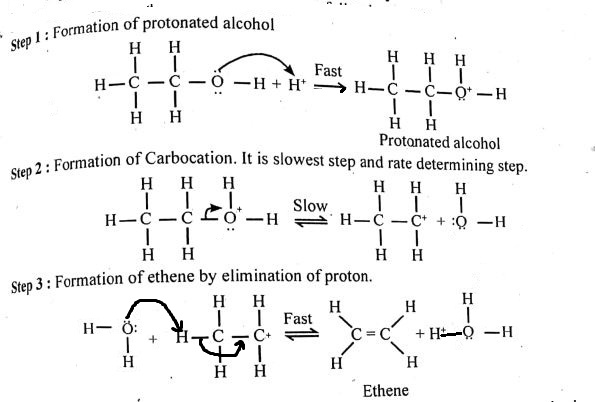
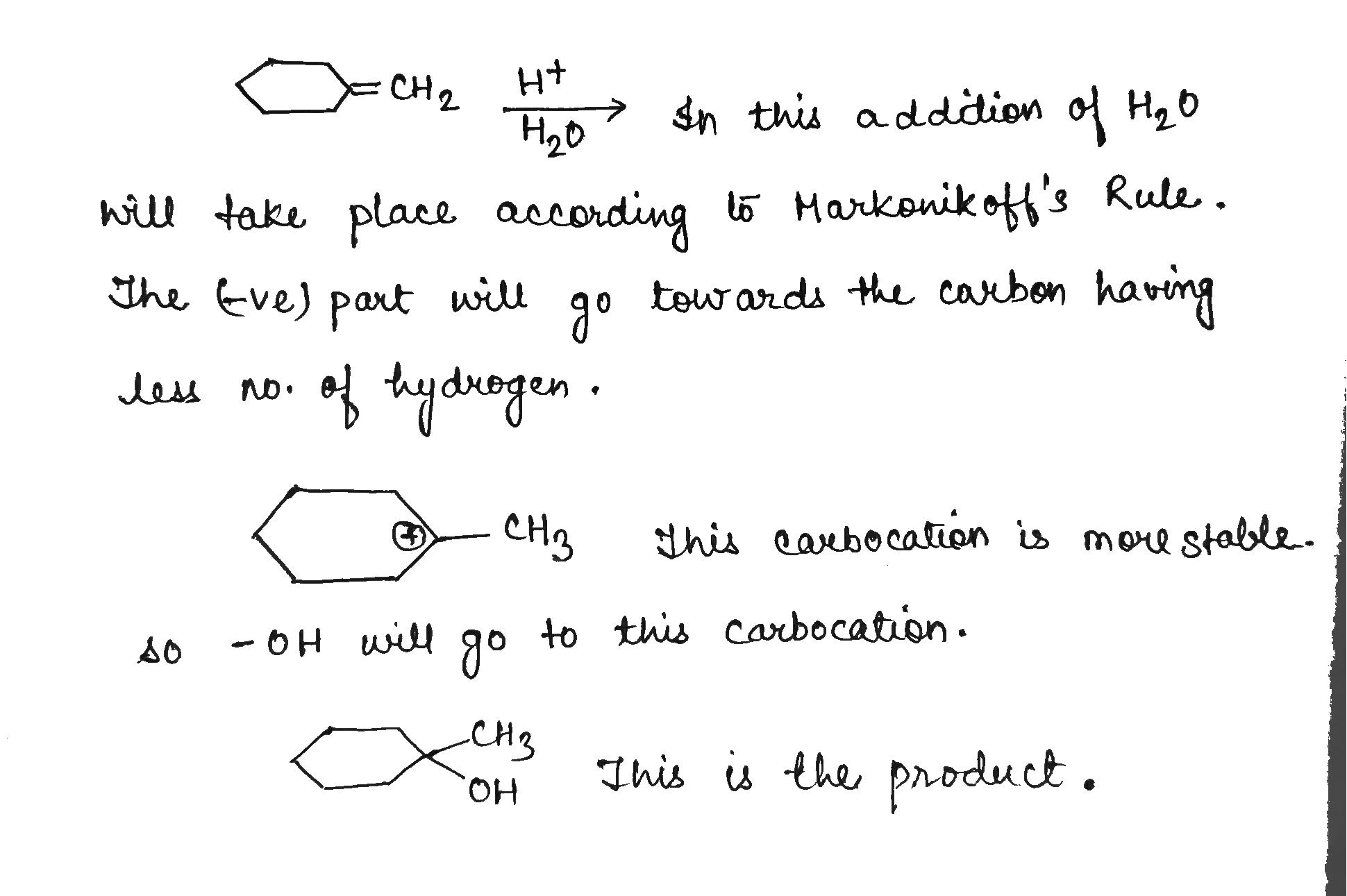
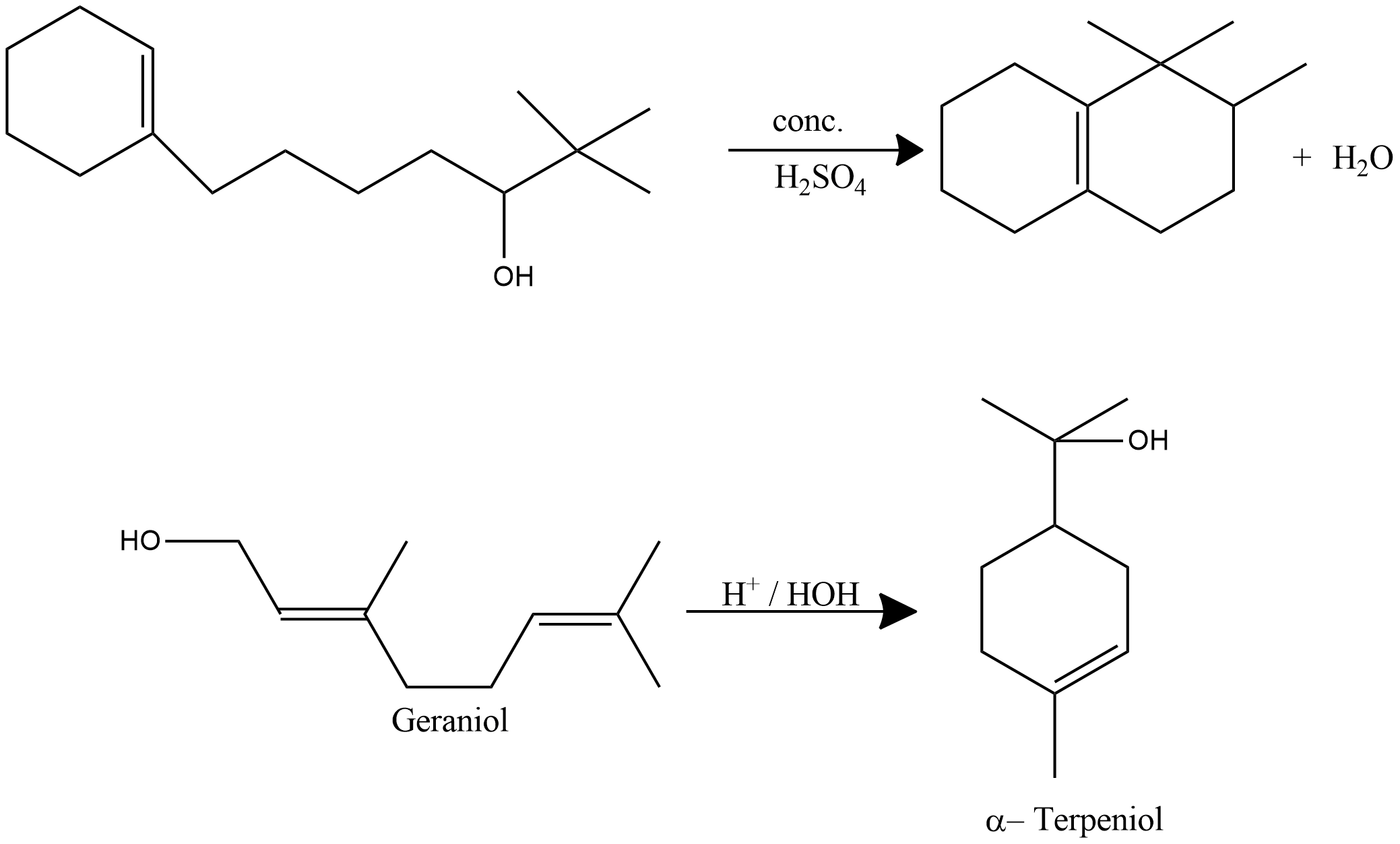
Write a reasonable and detailed mechanism for the following transformation.
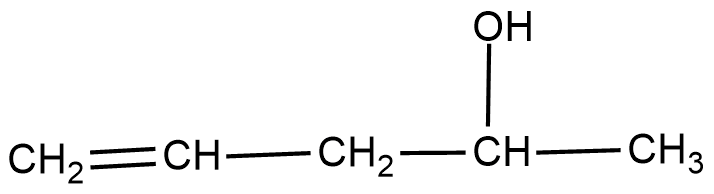
Write the IUPAC name.
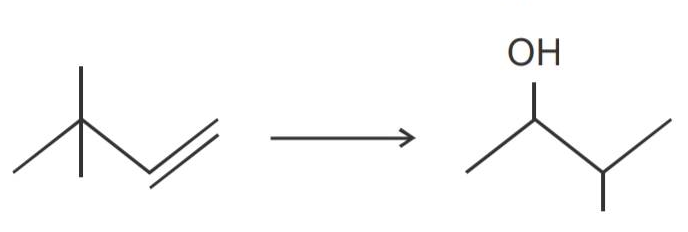
Write the name and formula of the second member of the carbon compounds having functional group-OH.
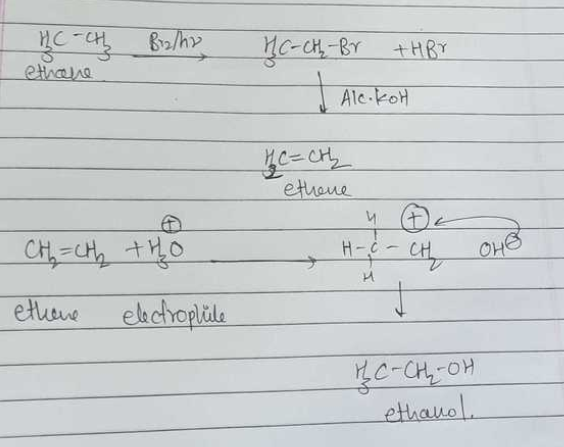
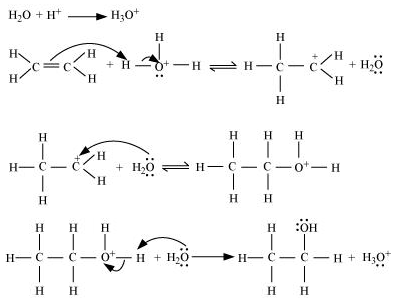
Write the mechanism for the preparation of ethanol form ethane.
Name the method which can give following product
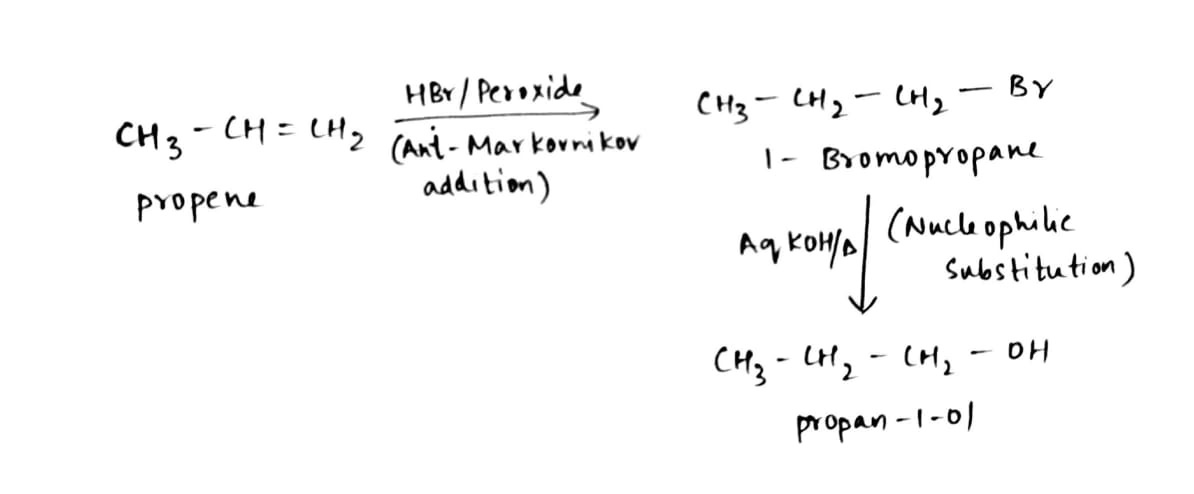
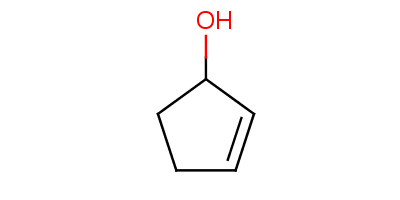
Propan-1-ol cannot be prepared by acid catalysed hydration of propane, then how is propene converted into propan-1-ol?
Write the stability of given alcohols
$$CH_3OH$$ , $$CH_3CH_2OH$$, $$CH_3CH_2CH_2OH$$
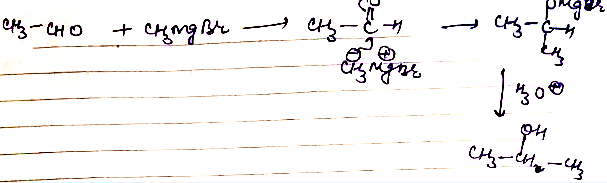
Identify missing products obtained in this reaction.
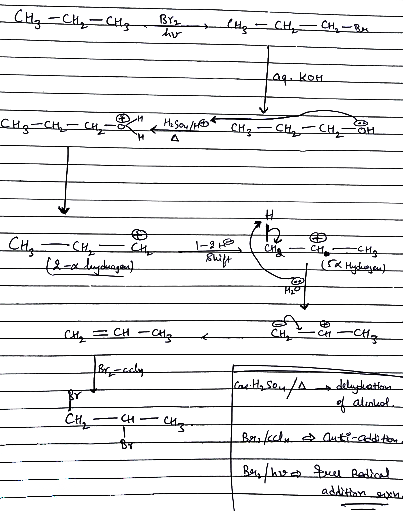
$$CH_{3}-CH_{2}-CH_{3}\xrightarrow{Br_{2}/hv}$$$$(A)\xrightarrow{aq KOH}(B)\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{H_{2SO_{4}}}(C)\xrightarrow[CCl_{4}]{Br_{2}}(D)$$
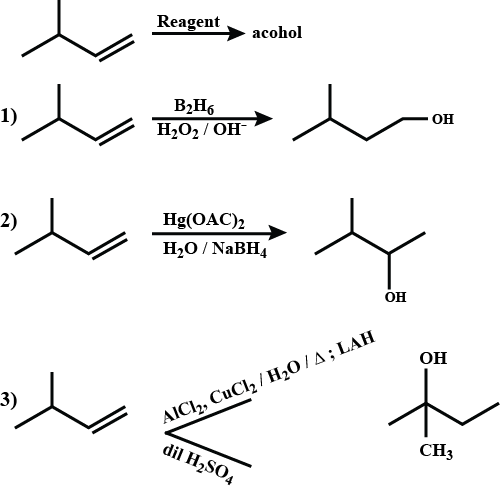
$$CH_3-\underset{\underset{\,\,\,\,CH_3}{|}}{C}H=CH_2\xrightarrow{Reagent}\,Alcohol$$Match the alcohol product with the suitable reagent.
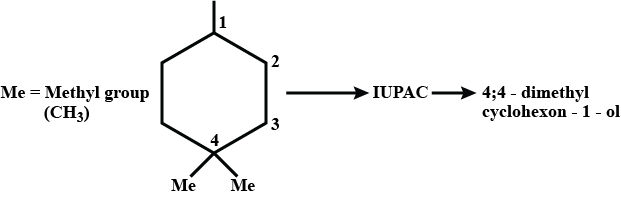
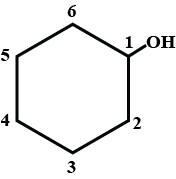
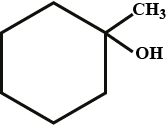
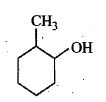
The given IUPAC name is 1,1-dimethylcyclohexane-3-ol
Is the above statement correct?

The name of the compound is Cyclopent-1-en-3-ol
If true enter 1, else enter 0.
The name of the compound is isobutyl alcohol.
If true enter 1, else enter 0.
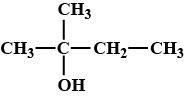
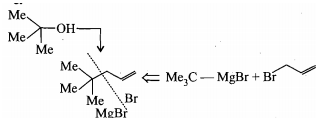
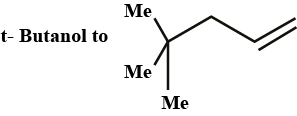
Convert t-Butanol to the given compound.
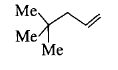
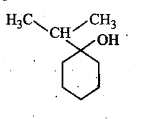
The given alcohol is _______ (primary/ secondary) alcohol.
(If your answer is primary type 1 else 2)

Suggest a sequence of reactions suitable for preparing propanol from $$2-propanol.$$
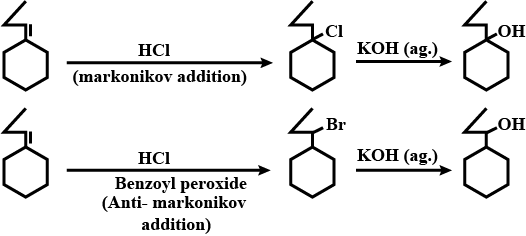
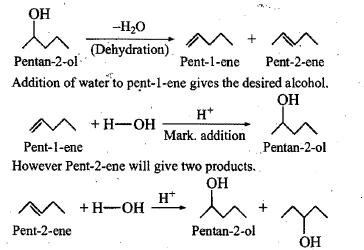
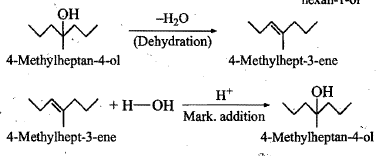
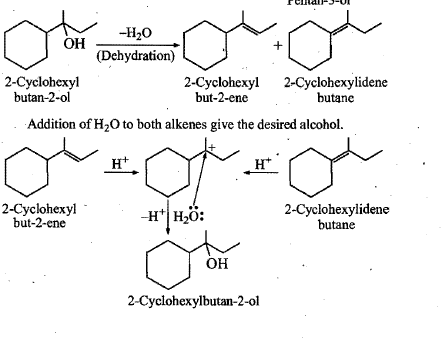
Show how would you synthesise the above alcohols from appropriate alkenes :
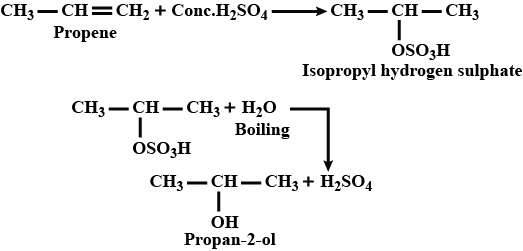
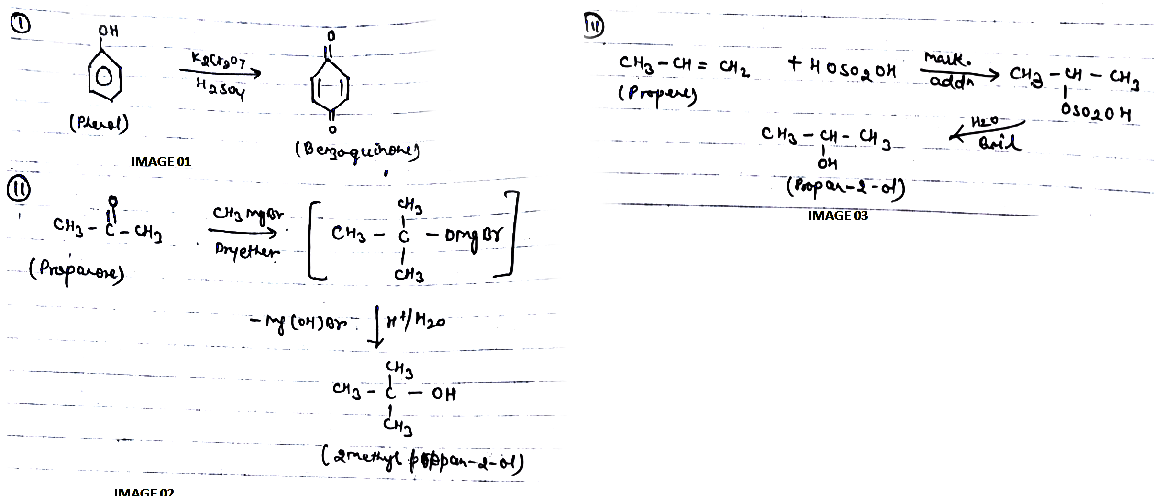
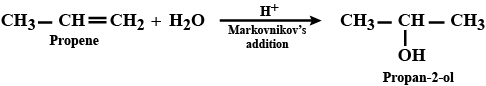
How are the following conversions carried out?Propen $$\displaystyle \rightarrow $$ Propan-2-ol
How would you synthesize an alcohol from appropriate alkenes?
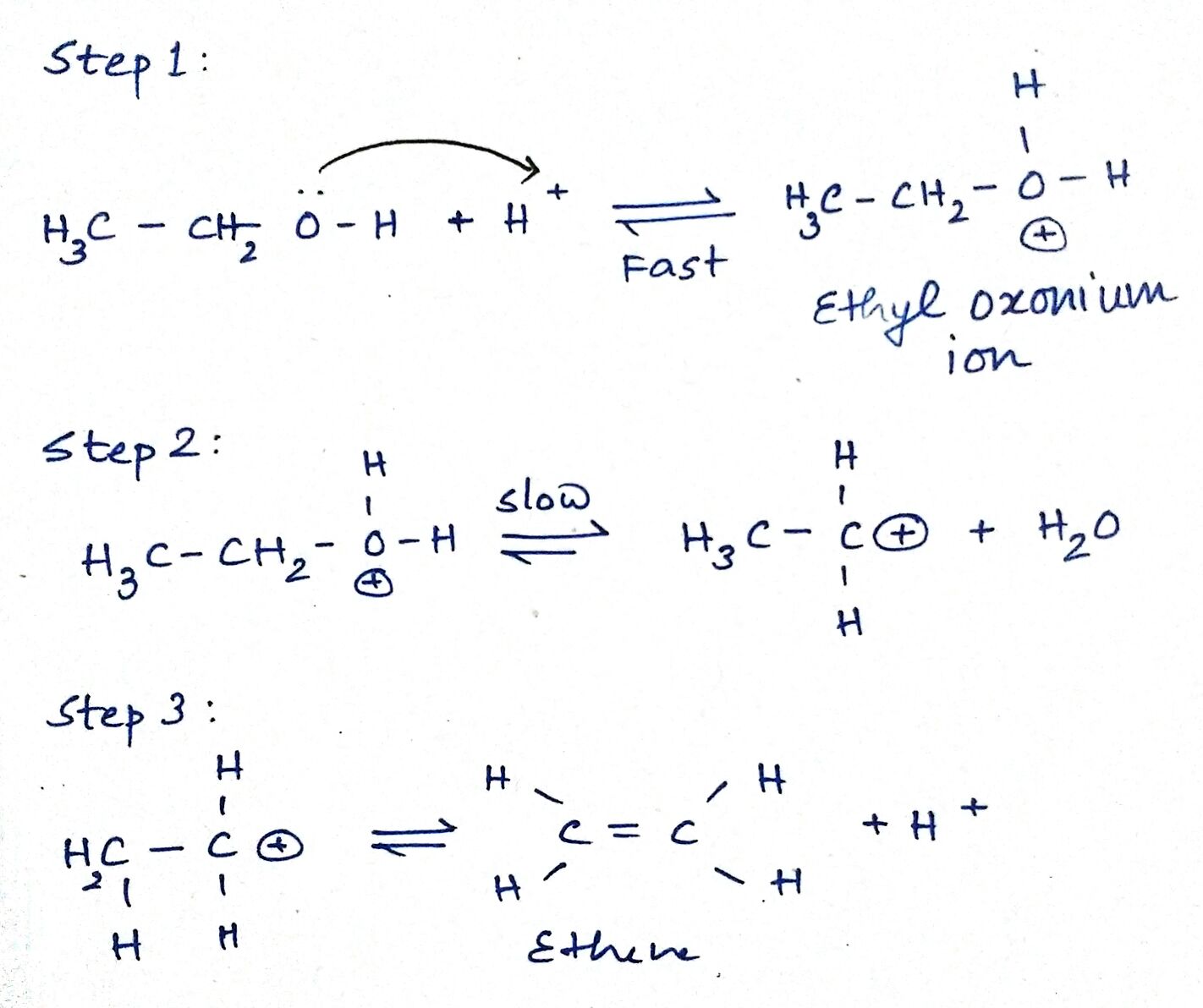
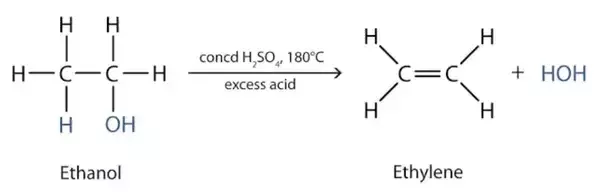
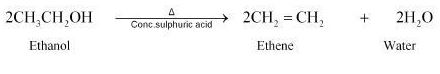
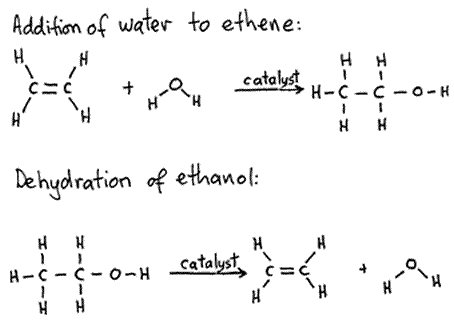
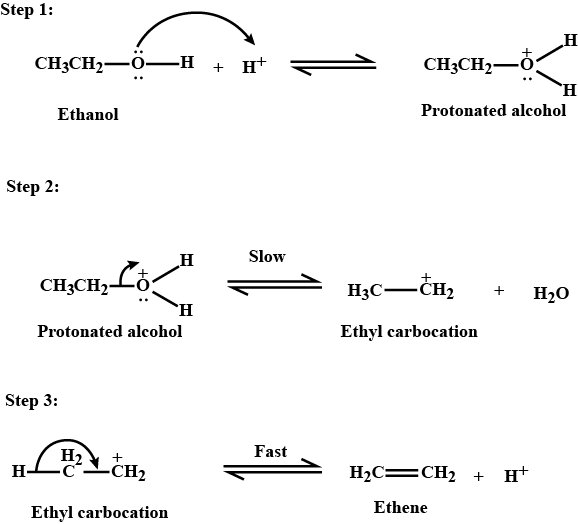
Writer the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene.
Write the equations involved in the following reaction.
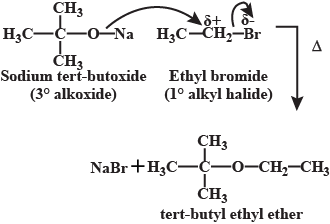
Williamson ether synthesis.
Match the column I with column II.
How can you synthesize Ethanol from Ethene?
Explain why is ortho nitrophenol more acidic than ortho methoxyphenol?
Show how will you synthesise:
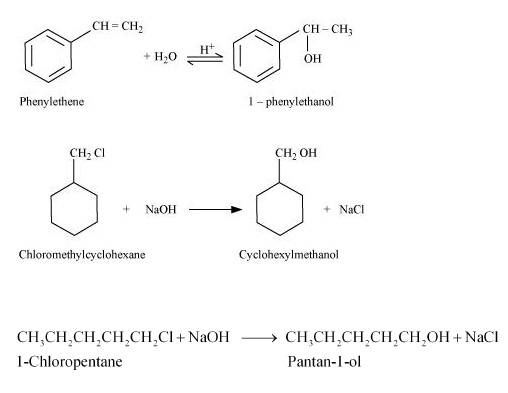
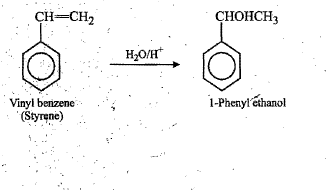
(i) 1-phenylethanol from a suitable alkene.
(ii) cyclohexylmethanol using an alkyl halide by an $$S_N2$$ reaction.
(iii) pentan-1-ol using a suitable alkyl halide.
Write the mechanism of hydration of ethene to yield ethanol.
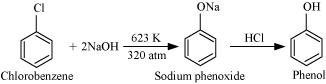
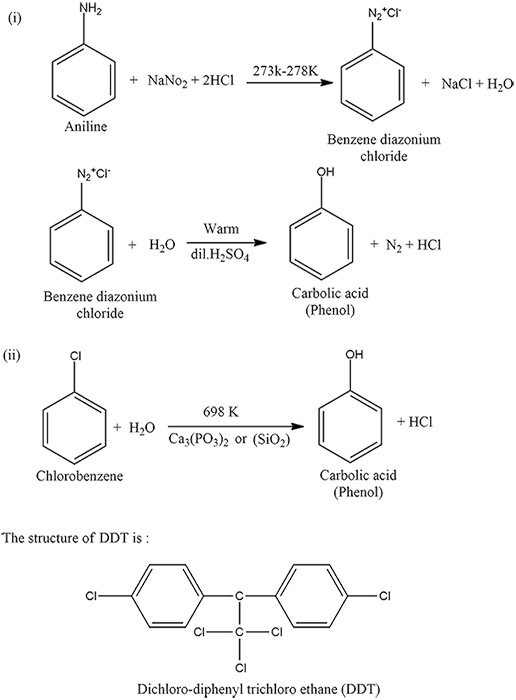
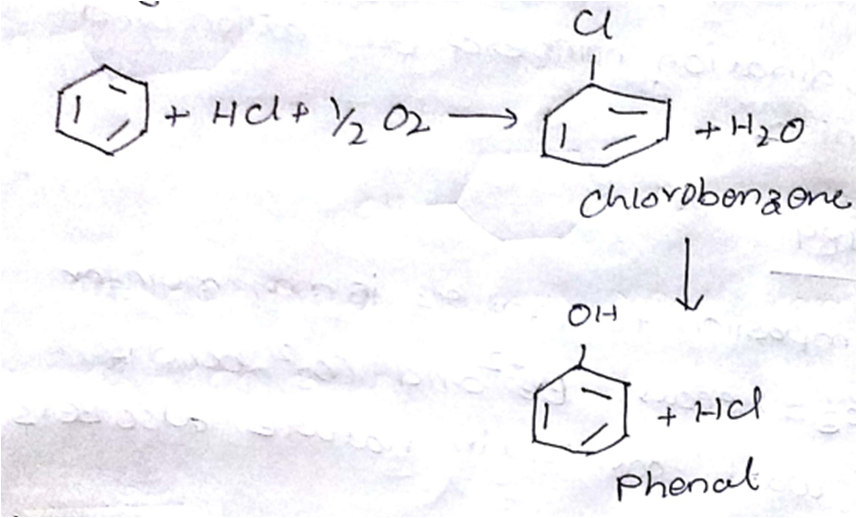
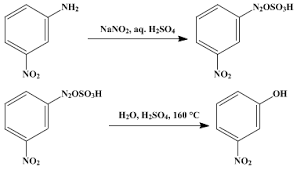
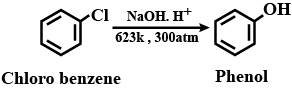
Write chemical reaction for the preparation of phenol from chlorobenzene.
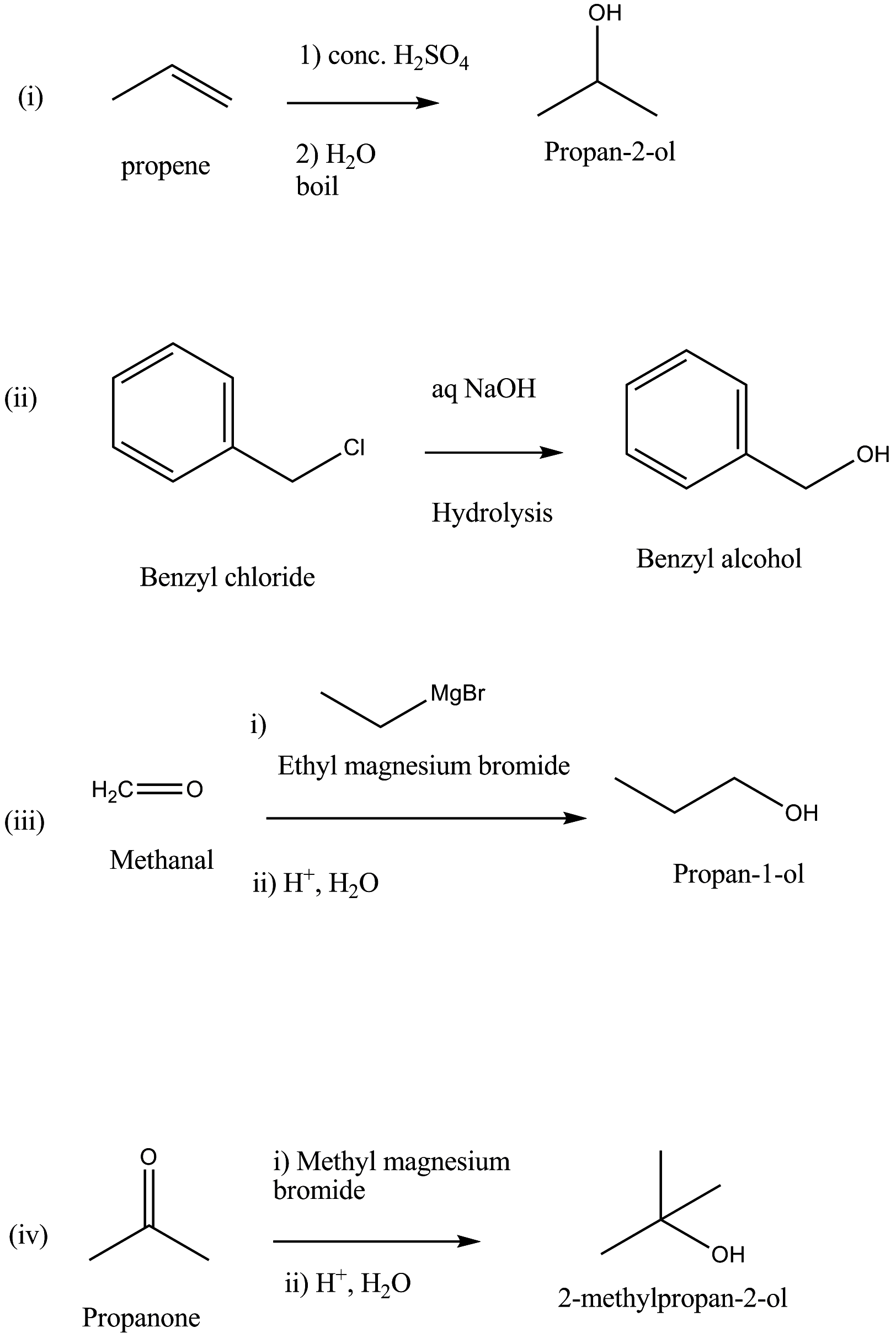
How are the following conversions carried out?
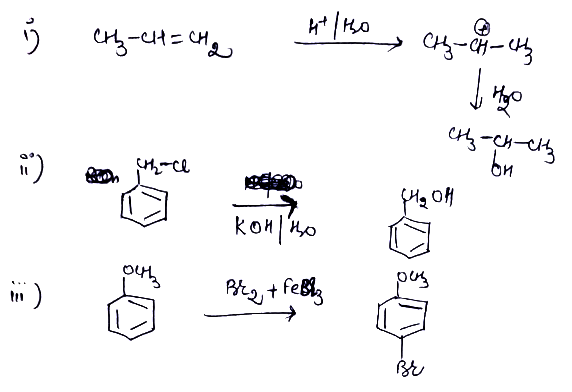
(i) Propene $$\longrightarrow$$ Propan-2-ol
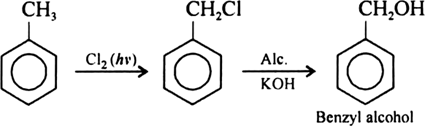
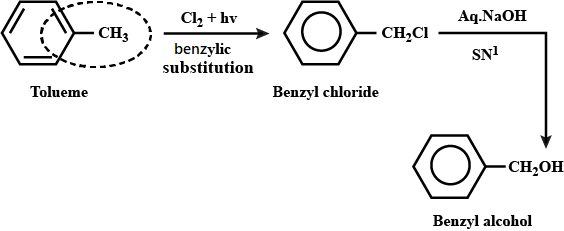
(ii) Benzyl chloride $$\longrightarrow$$ Benzyl alcohol
(iii) Ethyl magnesium chloride $$\longrightarrow$$ Propan-1-ol
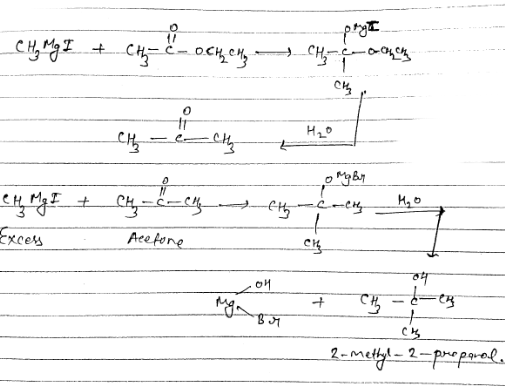
(iv) Methyl magnesium bromide $$\longrightarrow$$ 2-Methylpropan-2-ol
Show how would you synthesise the following alcohols from appropriate alkenes?
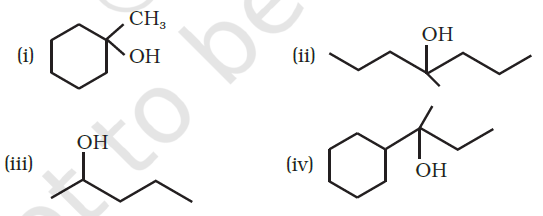
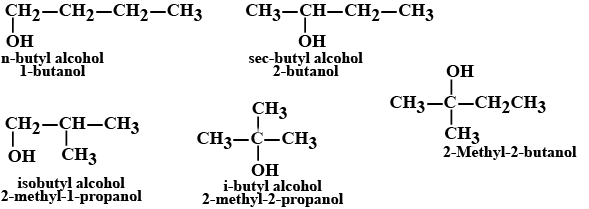
Write the name and structure of an alcohol with four carbon atoms in its molecule.
How will you convert:(i) Propene to propan$$-1-$$ol? (ii) Ethanal to propan-2-ol?
(ii) Ethanal to propan-2-ol?
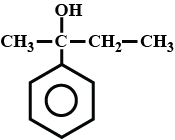
Write the IUPAC name of the given compound :
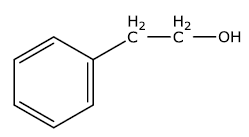
Draw the structure of major monohalo product in each of the following reactions.
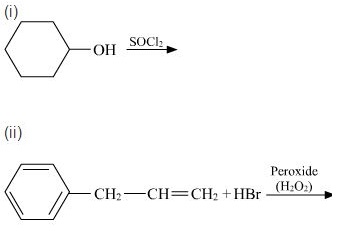
Write the equations involved in the following reactions:
(i) Reimer - Tietmann reaction
(ii) Williamson synthesis
Arrange the following compounds in the decreasing order of their boiling points.
a) Pentan-1-ol
b) 2-Methylbutan-2-ol
c) 3-Methylbutan-2-ol
Why do alcohols have higher boiling points than haloalkanes of the same molecular mass?
Arrange the following in the decreasing order of their boiling points:
$$\displaystyle CH_3CH_2OH, HOCH_2CH_2OH, CH_3CH_2Cl$$.
Can we dry ethanol by anhydrous $$CaCl_2$$?
Liquid alkalies as well as alcohols are added to water. What observation do you predict? Justify your prediction.
Ethyl alcohol and propane have nearly equal molecular weights. But, the former is a liquid with high boiling point and the latter is a gas with low boiling point. Give reason.
What is the major product when ethanol is treated with $$conc. H_{2}SO_{4}$$ at $$413\ K$$?
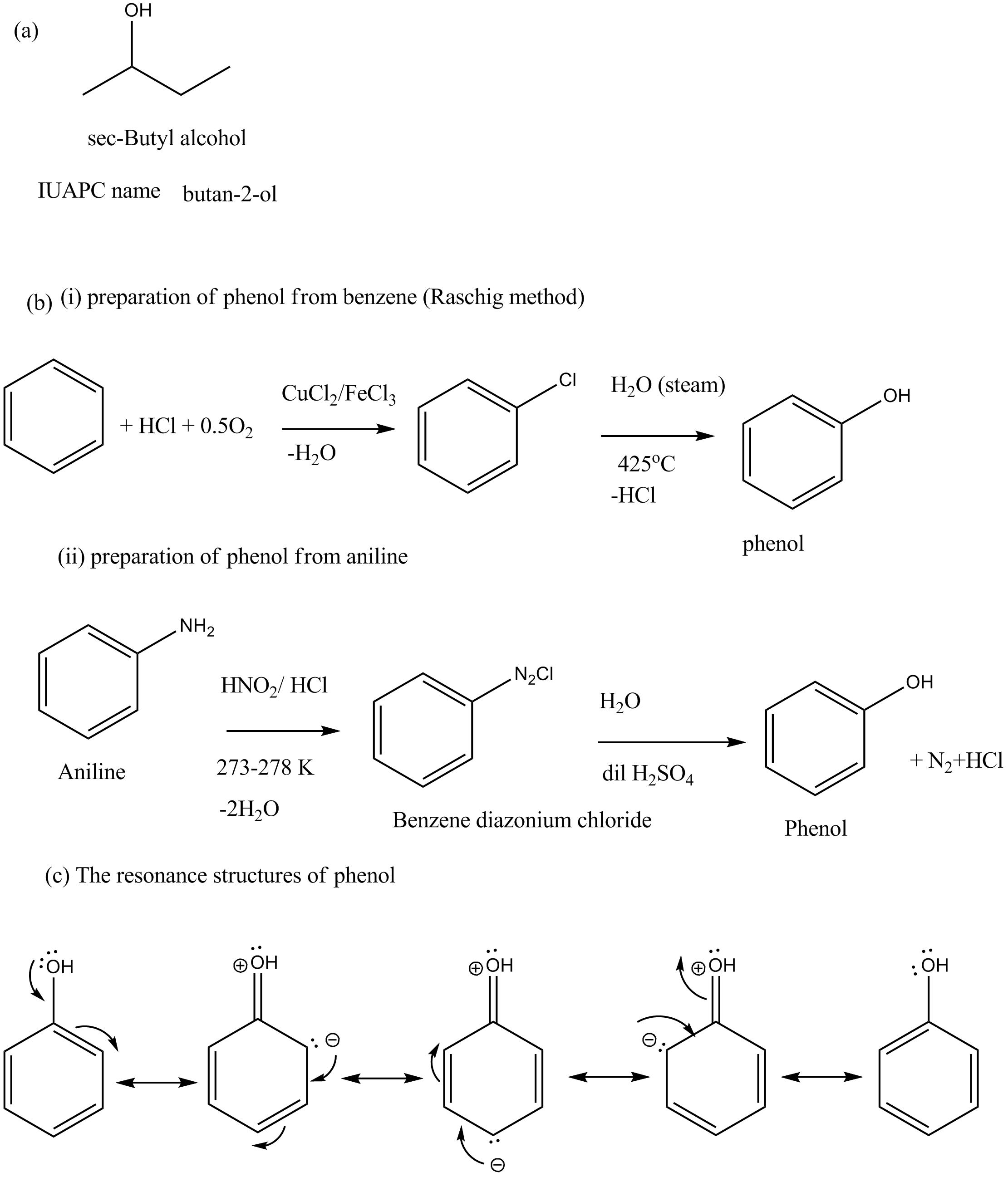
(a) Write the IUPAC name and structural formula of secondary-Butyl alcohol.
(b) Give equations for preparation of phenol from the following compounds:
(i) Benzene
(ii) Aniline.
(c) Write the resonance structures of phenol.
How is carbolic acid prepared from the following compound?
(i) Aniline
(ii) Chlorobenzene and steam at $$698$$K?
Draw structure of DDT. Write its environmental effects.
Mention two physical properties of carbolic acid.
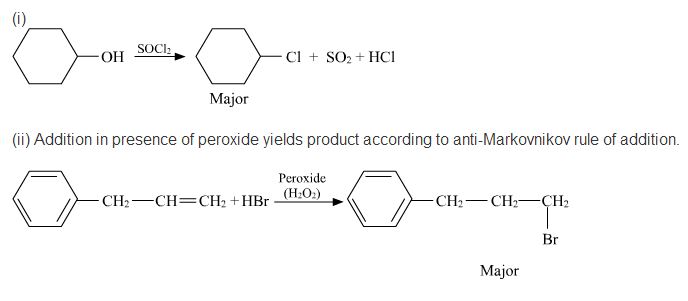
Write balanced chemical equations for the action of:
(1) Phosphorus trichloride on propan-2-ol
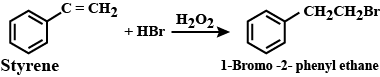
(2) Hydrogen bromide on styrene in the presence of a peroxide.
(3) Methyl bromide on silver propanoate.
(1) Phosphorus trichloride on propan-2-ol
(2) Hydrogen bromide on styrene in the presence of a peroxide.
(3) Methyl bromide on silver propanoate.
Write the chemical reactions of $$C_{2}H_{5}OH$$ with $$PCl_{3}$$ and $$PCl_{5}$$ separately
What is Williamson's Synthesis? Give equation.
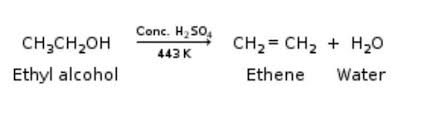
Ethanol is heated with excess concentrated $$H_2SO_4$$ at 443K.
i) Name the reaction that occurs and explain it.
ii) Write the equation for the above reaction.
iii) What is the product formed? What happens when this gas is passed through bromine water?
iv) When ethanol vapour is passed through bromine water, why does no change occur?
Match the following compounds with their functional groups:
| S.No | Compounds | Functional Groups |
| 1. | Alcohol | $$>C=O$$ |
| 2. | Aldehyde | $$-OH$$ |
| 3. | Ketone | $$-COOH$$ |
| 4. | Carboxylic acid | $$-CHO$$ |
Write a balanced equation using the correct symbols for these chemical reactions:
i) Action of hydrogen on ethene in the presence of nickel catalyst.
ii) Combustion of methane evolving carbondioxide and water.
iii) Dehydrogenation of ethanol.
iv) Decarboxylation of Sodium salt of ethanoic acid.
The organic compound A of molecular formula $$C_2H_4O_2$$ gives brisk effervescence with sodium bicarbonate solution. The sodium salt of A on treatment with soda lime gives a hydrocarbon B of molecular massIt belongs to the first member of the alkane family. What are A and B and how will you prepare A from ethanol?
How is diethyl ether prepared by continuous etherification process?
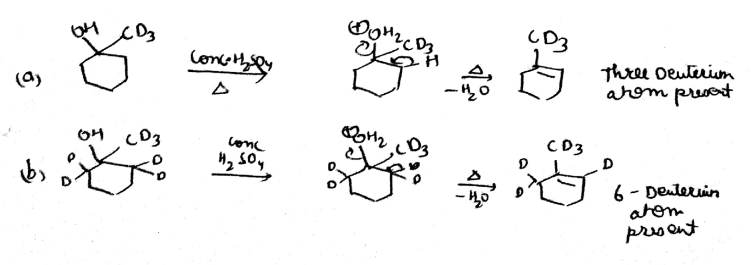
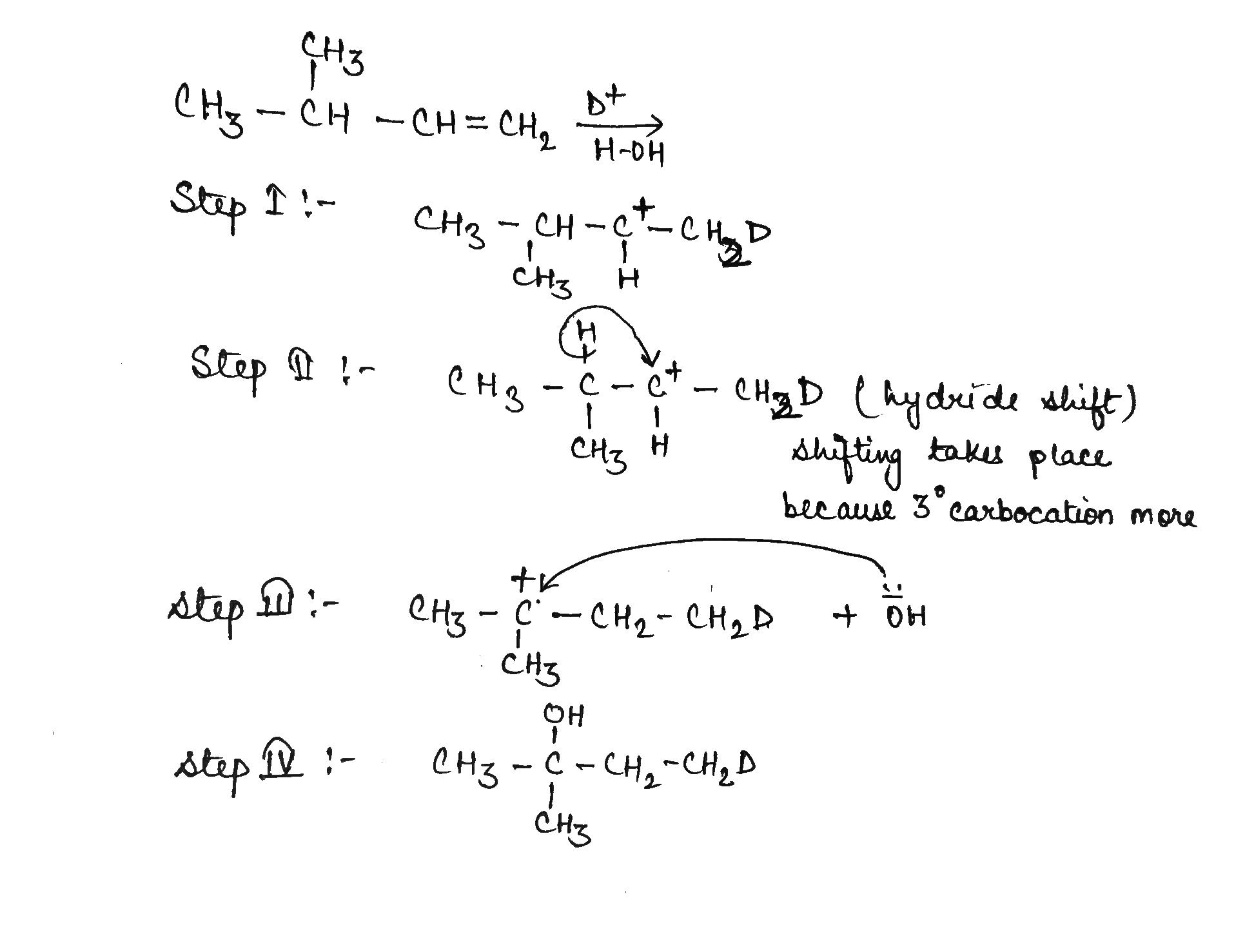
If the starting material is labeled with deuterium as indicated, how many total deuterium atoms will be present in the major elimination product of the above reactions?

A student prepared methanol in the laboratory by the addition of $$266\ g$$ of $$CO$$ and $$60\ g$$ of $$H_{2}$$, as shown below.
$$CO(g) + H_{2}(g) \rightarrow CH_{3}OH(l)$$
(a) Find out the limiting reagent.
(b) Calculate the amount of methanol produced and the amount of excess reactant remaining after the completion of the reaction.
Write the IUPAC name of the following.
$$CH_3-\!\!\!\!\!\!\overset{\,\,\,\,CH_3}{\overset{|}{\underset{\,\,\,\,\,C_2H_5}{\underset{|}{C}}}\!\!\!\!-}\,\underset{OH}{\underset{|}{C}H}-CH_3$$
How will you prepare isopropyl alcohol from propene?
IUPAC name of t-butyl alcohol ?
Find the reagents used for conversion.
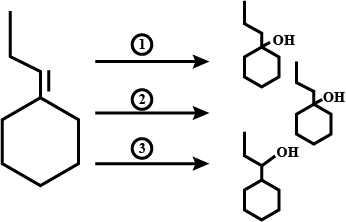
Carry out the following conversions:
(i) Phenol to benzoquinone.
(ii) Propanone to 2-Methylpropan-2-ol.
(iii) Propene to propan-2-ol.
How are the following conversions carried out ?
(i) Propene to propane-2-ol
(ii) Benzyl chloride to Benzyl alcohol
(iii) Anisole to p-Bromoanisole
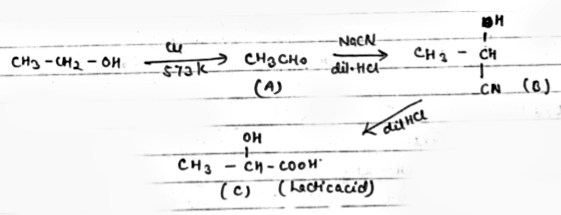
Identify the products 'A' 'B' and 'C' in the following reaction
$$CH_3 - CH_2 - OH \overset{Cu}{\underset{573 K}{\longrightarrow}}$$ A $$\overset{NaCN+ dil.HCl}{\longrightarrow}$$ B $$\underset{dil.HCl}{\longrightarrow} C$$?
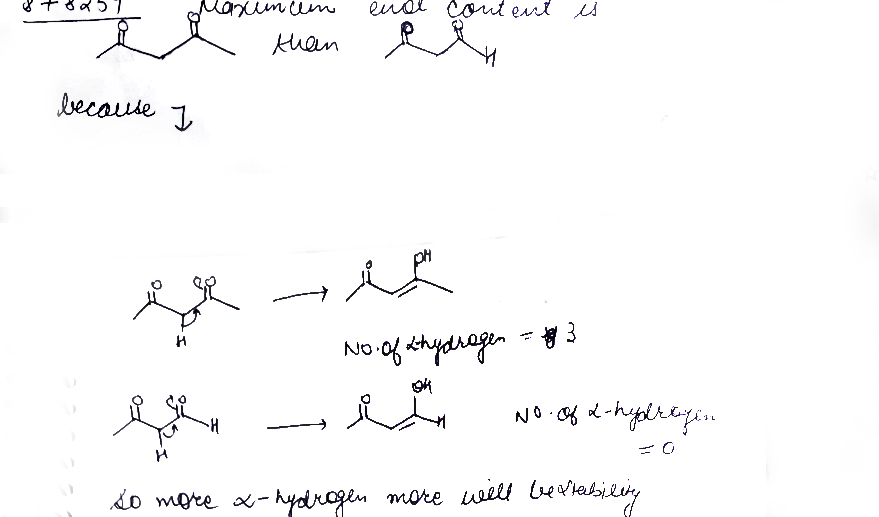
Maximum enol content is in ?
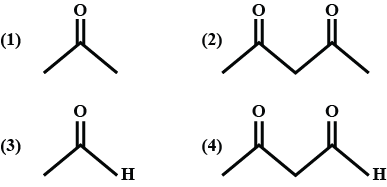
Give the IUPAC name of $${CH}_{3}-{CH}_{2}-CH(OH)-{CH}_{3}$$.
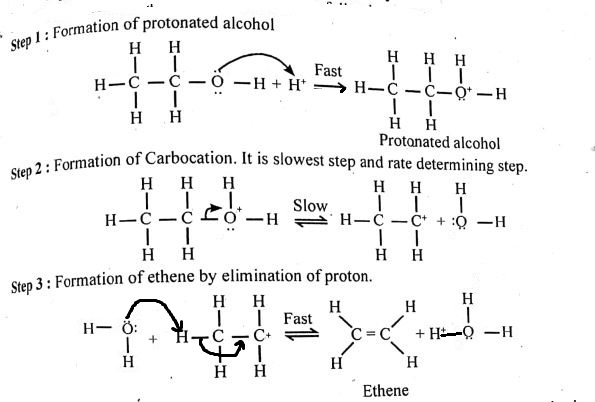
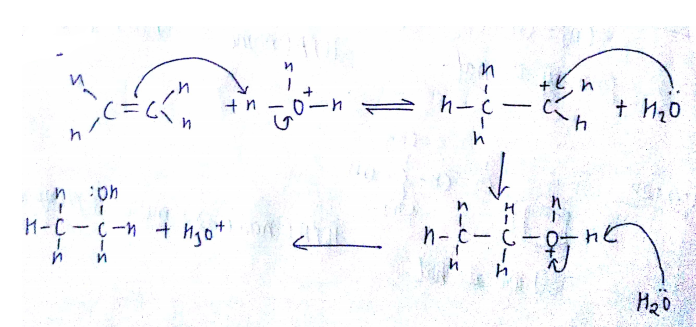
Write the three steps involved in the mechanism of acid catalysed dehydration of ethanol to ethene.
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound.
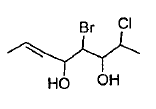
Give the IUPAC name of the following compound.
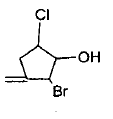
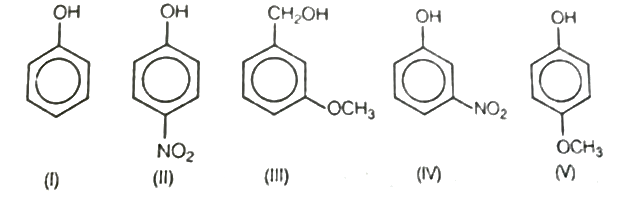
Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.
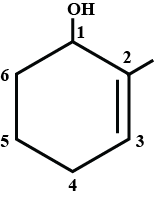
Write the IUPAC name of the given compound.
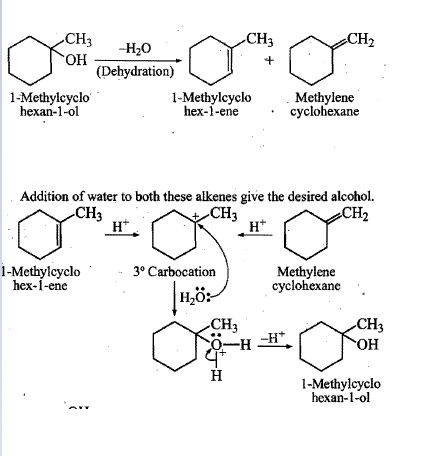
Predict the major product of acid catalysed dehydration:
(i) 1-methyl cyclohexanol
(ii) Butan-1-ol
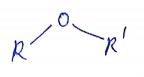
Write the general formula of ether.
$$H_2C=CH-CH_2OH$$Classify the following as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol.
Complete this reaction.
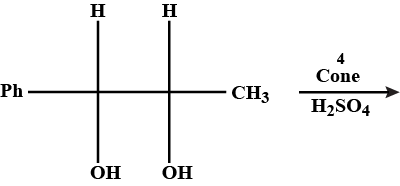
Convert 1-iodopropane to propan -1-ol.
Convert Ethanal to Isopropyl alcohol.
Give the IUPAC name for the following alcohols. Classify as primary or secondary or teritiary alcohol.

Give the IUPAC name for the following alcohols. Classify as primary or secondary or teritiary alcohol. $$(C_2H_5)_3C-OH$$
Give the IUPAC name for the following alcohols. Classify as primary or secondary or teritiary alcohol. $$(CH_3)_3C-\underset{\underset{\,\,\,OH}{|}}CH-C_2H_5$$
Give the IUPAC name for the following alcohols. Classify as primary or secondary or teritiary alcohol.
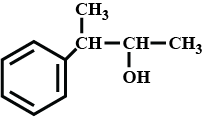
Write the mechanism of hydration of ethylene to ethyl alcohol.
Give the IUPAC name for the following alcohols. Classify as primary or secondary or teritiary alcohol. $$CH_2=CH-CH_2-CH_2-OH$$
Give the IUPAC name for the following alcohols. Classify as primary or secondary or teritiary alcohol.
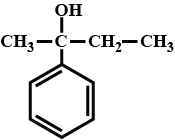
Give the IUPAC name for the following alcohols. Classify as primary or secondary or teritiary alcohol. $$CH_3 - \underset{\,\,\,OH}{\underset{|}{CH}} - \overset{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,CH_3}{\overset{|}{CH}} - CH_3$$
Write the iUPAC name of the following compound.
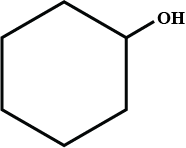
$$CH_2OHCH_2OH$$Write IUPAC name of the above compound.
Write the IUPAC names of phenols given.

Can you explain why is bimolecular dehydran not appropriate for the preparation of ethyl methyl ether?
The IUPAC name of the compound is:$$H_2=CH-\underset{\underset{\,\,\,CH_3}{|}}CH-\underset{\underset{\,\,\,\,\,C_2H_5}{|}}CH-\underset{\underset{\,\,OH}{|}}CH-CH_3$$
Arrange the following in increasing order of boiling points

Write the product $$(CH_{3})_{3}C-OH\xrightarrow[573 K]{Cu}$$
Write the IUPAC name of the given compound.$$H-\overset { H }{ \overset { | }{ \underset { H }{ \underset { | }{ C } } } } -\overset { H }{ \overset { | }{ \underset {O H }{ \underset { | }{ C } } } } -\overset { H }{ \overset { | }{ \underset { H }{ \underset { | }{ C } } } } -\overset { H }{ \overset { | }{ \underset { CH_3 }{ \underset { | }{ C } } } } -\overset { H }{ \overset { | }{ \underset { H }{ \underset { | }{ C } } } } -H$$
Arrange according boiling point: $$CH_3 \, CH_2 CH_3 , \, CH_3 CHO , \, CH_3 CH_2 OH, \, CH_3 OCH_3$$.
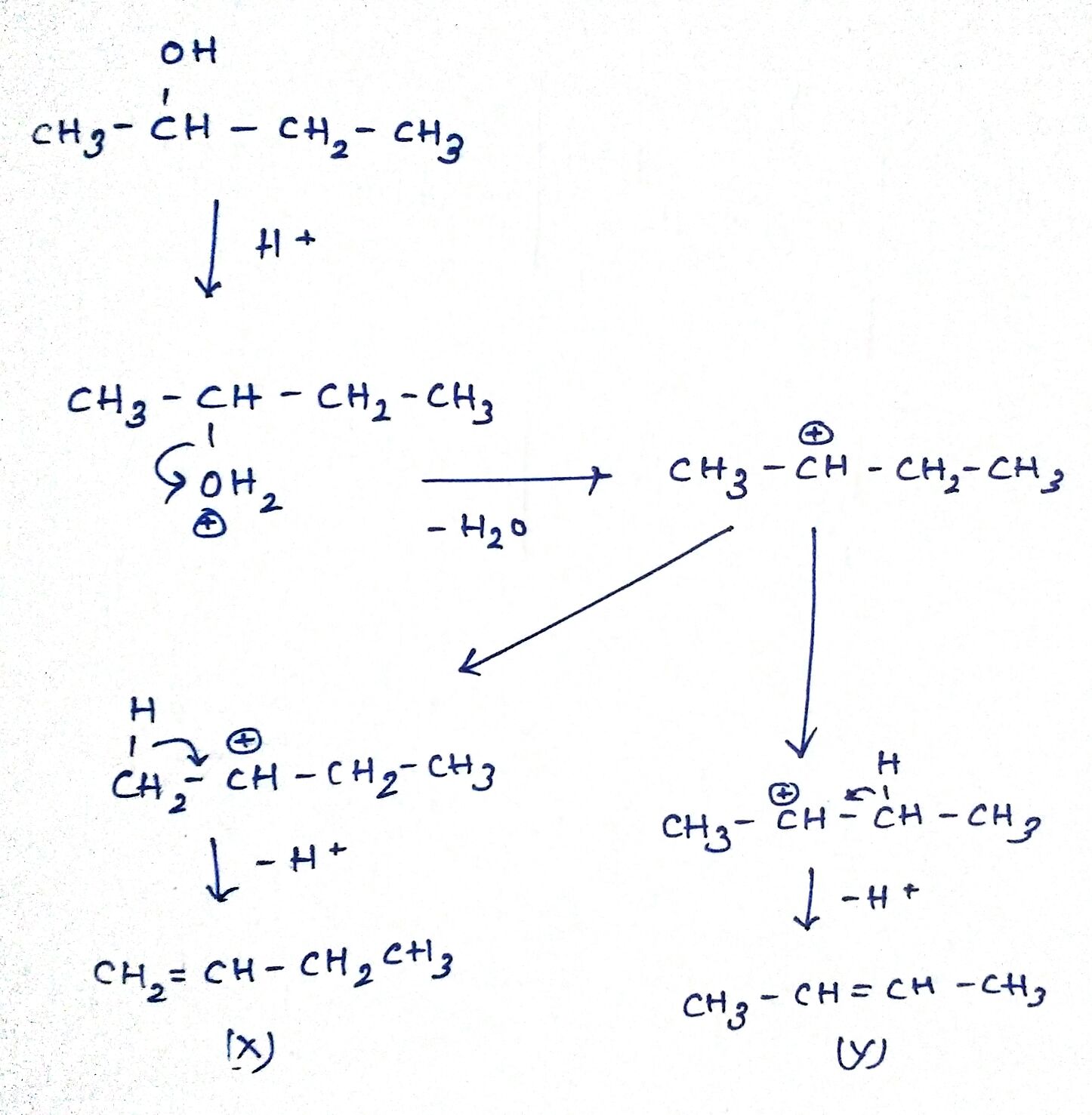
Identify X and Y.
$$\quad \quad \quad \quad OH\\ \quad \quad \quad \quad |\\ { CH }_{ 3 }-{ CH-CH }_{ 2 }{ CH }_{ 3 }\xrightarrow { 607.{ H }_{ 2 }SO_{ 4 },373k } \quad X+Y$$
What will be the product of the compound?
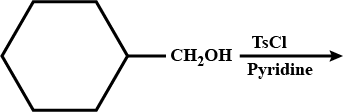
Write structures of the compound of following IUPAC name :
$$2-Methylbutan-2-ol$$
$$CH_3COOCH_2CH_3+CH_3MgI\rightarrow ?$$
How will you convect ethanol into ethylmethyl ketone?
How is phenol (carbolic acid) prepared from Rasching's process?
What is the action of following reagent on phenol?
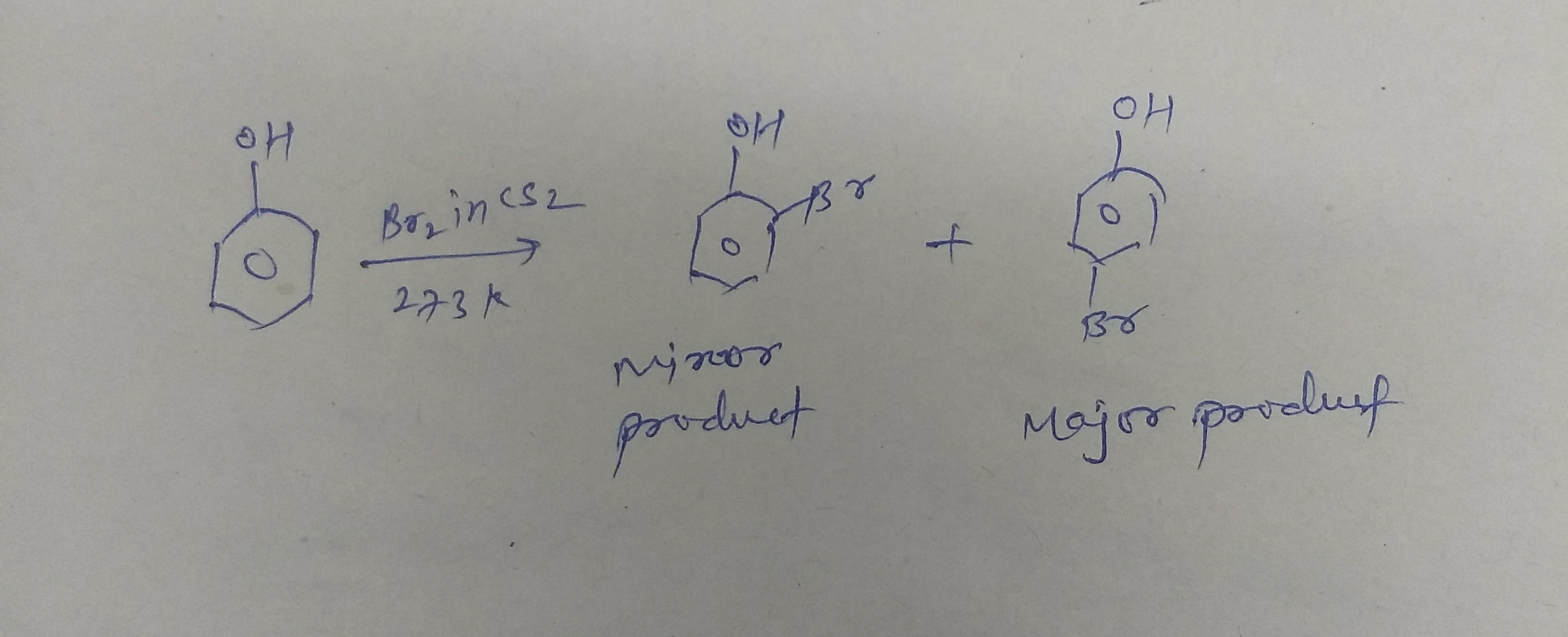
Bromine in $${ CS }_{ 2 }$$ at low temperature :
Bromine in $${ CS }_{ 2 }$$ at low temperature :
Give reasons :
o-nitrophenol is more volatile than p-nitrophenol
How the following conversion can be carried out?
Ethanol to propanenitrile
Toluene to benzyl alcohol
What are ethers?
Explain: Methanol is more soluble in water than Propan-1-ol.
Write the mechanism of the following reaction:
2CH$$_{3}$$CH$$_{2}$$OH $$\underrightarrow {{ H}^{ + } }$$ CH$$_{3}$$CH$$_{2}$$OCH$$_{2}$$CH$$_{3}$$
Give reasons:
p-nitro phenol is more acidic than p-methyl phenol.
Write the name of reactant used for the preparation ethyl t-butyl ether
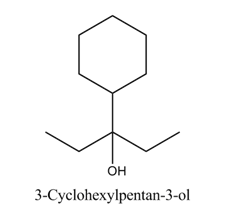
Write the structure of the compound whose IUPAC name is :
3 - Cyclohexylpentan - 3 - ol
Write IUPAC names of
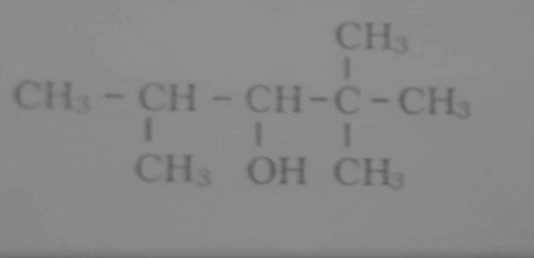
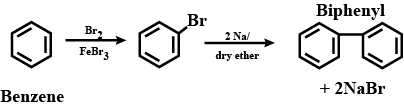
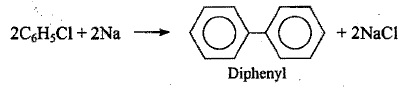
How are the following conversions carried out? (xviii) Benzene to diphenyl
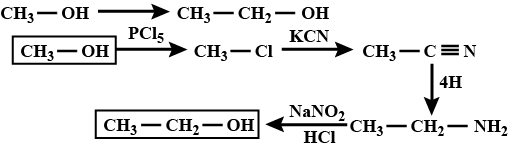
How to convert methanol into ethanol? Write chemical equations only.
Write down the dehydration products of the given alcohols.
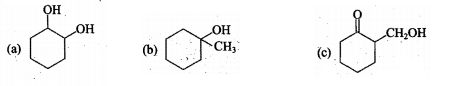
Dehydration of alcohol to form alkene is an ........ reaction.
What happens when :
Ethyl alcohol is heated at $$170^{\circ}C$$ with excess of $$conc. H_{2}SO_{4}$$?
Complete the following equations :
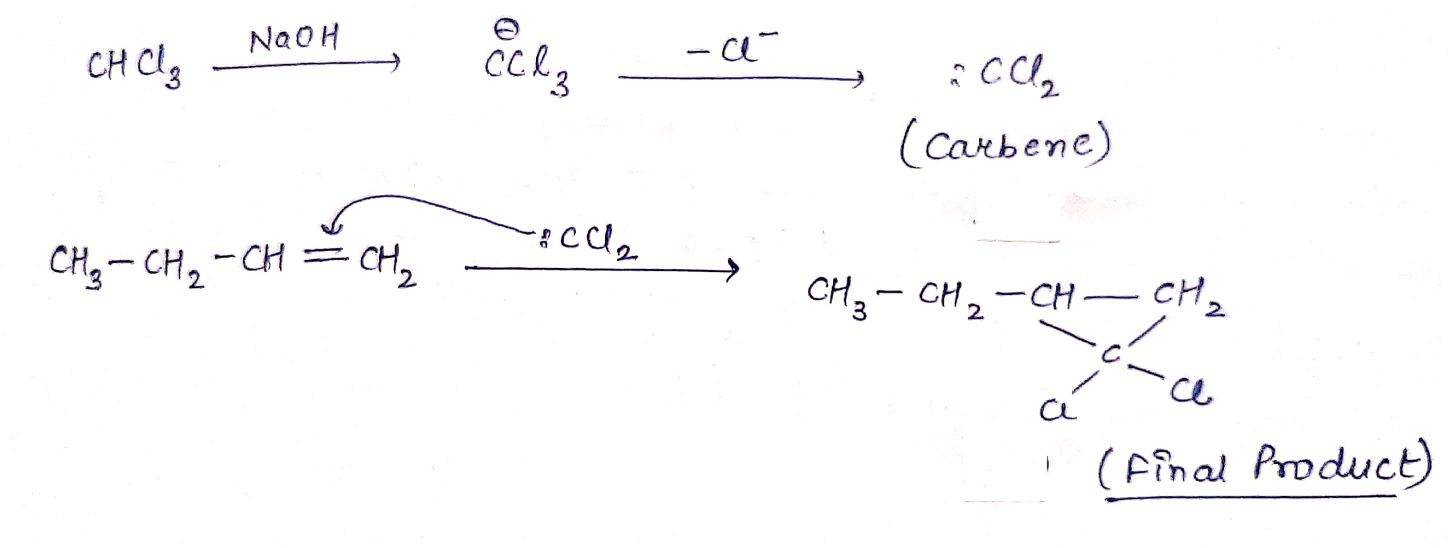
$$CH_{3}CH_{2} CH = CH_{2}\xrightarrow {CHCl_{3}} (A)\xrightarrow {NaOH} (B) $$.
$$CH_{3}CH_{2} CH = CH_{2}\xrightarrow {CHCl_{3}} (A)\xrightarrow {NaOH} (B) $$.
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds:
Isopropyl alcohol
The ease of dehydration of alcohols is in the order _________ $$>$$ secondary $$>$$ __________.
Boiling points of alcohols are ________ than those of corresponding alkanes.
Complete the above equation.
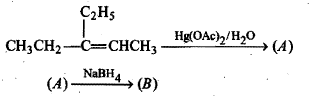
How will you obtain ethylene from ethyl alcohol?
Write IUPAC name of the following.
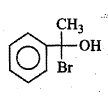
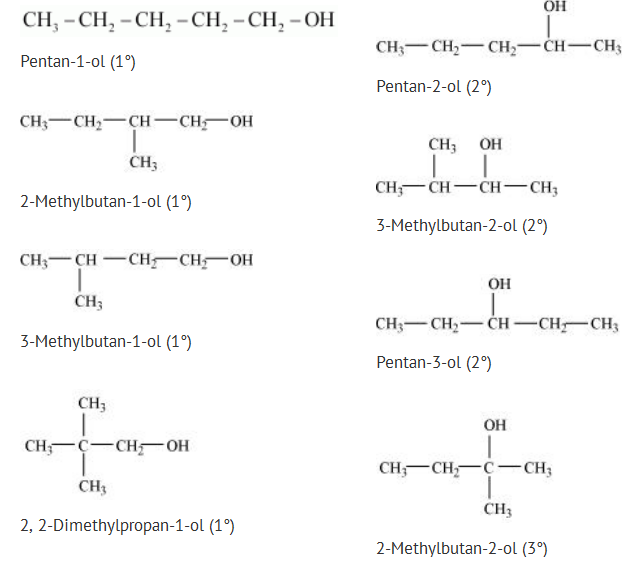
Write the structural formula and IUPAC names of the alcoholic isomers with molecular formula $$C_4H_{10}O$$.
How will you obtain iodoform from ethyl alcohol?
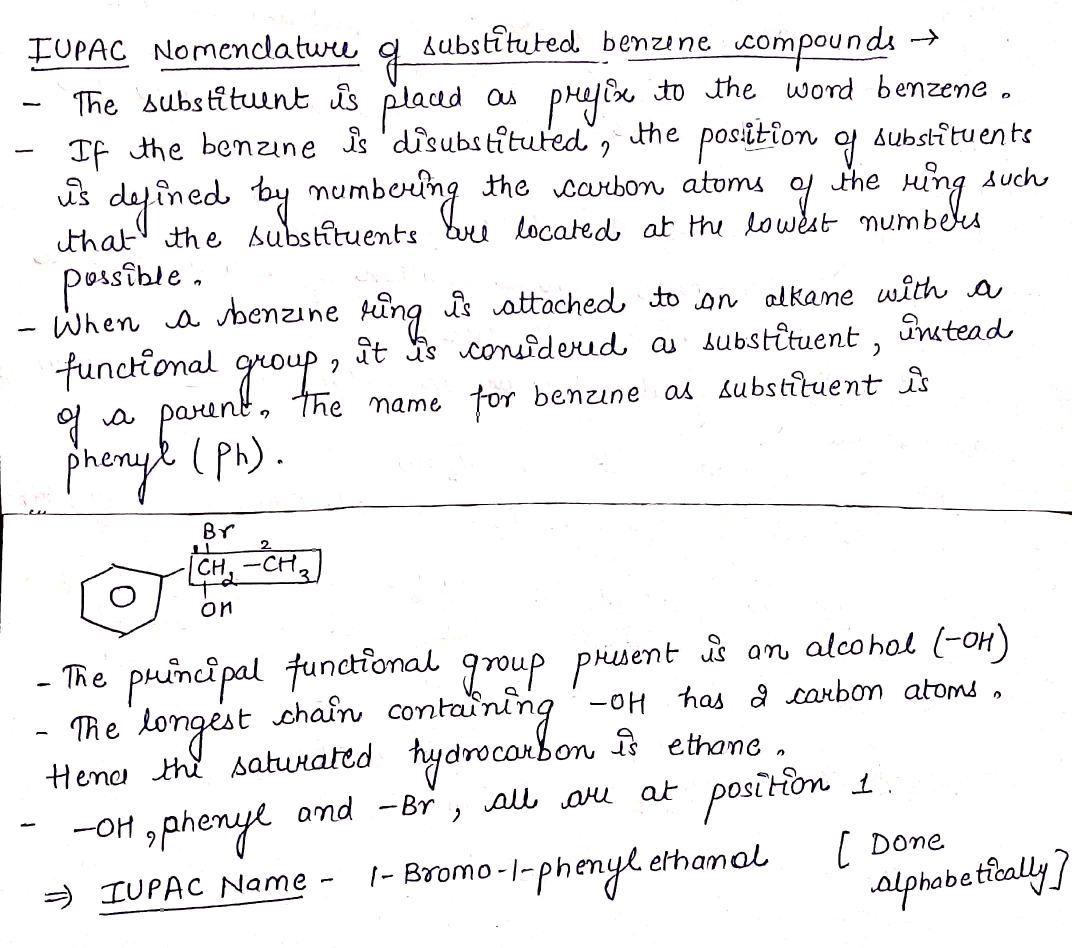
Write IUPAC name of the following.
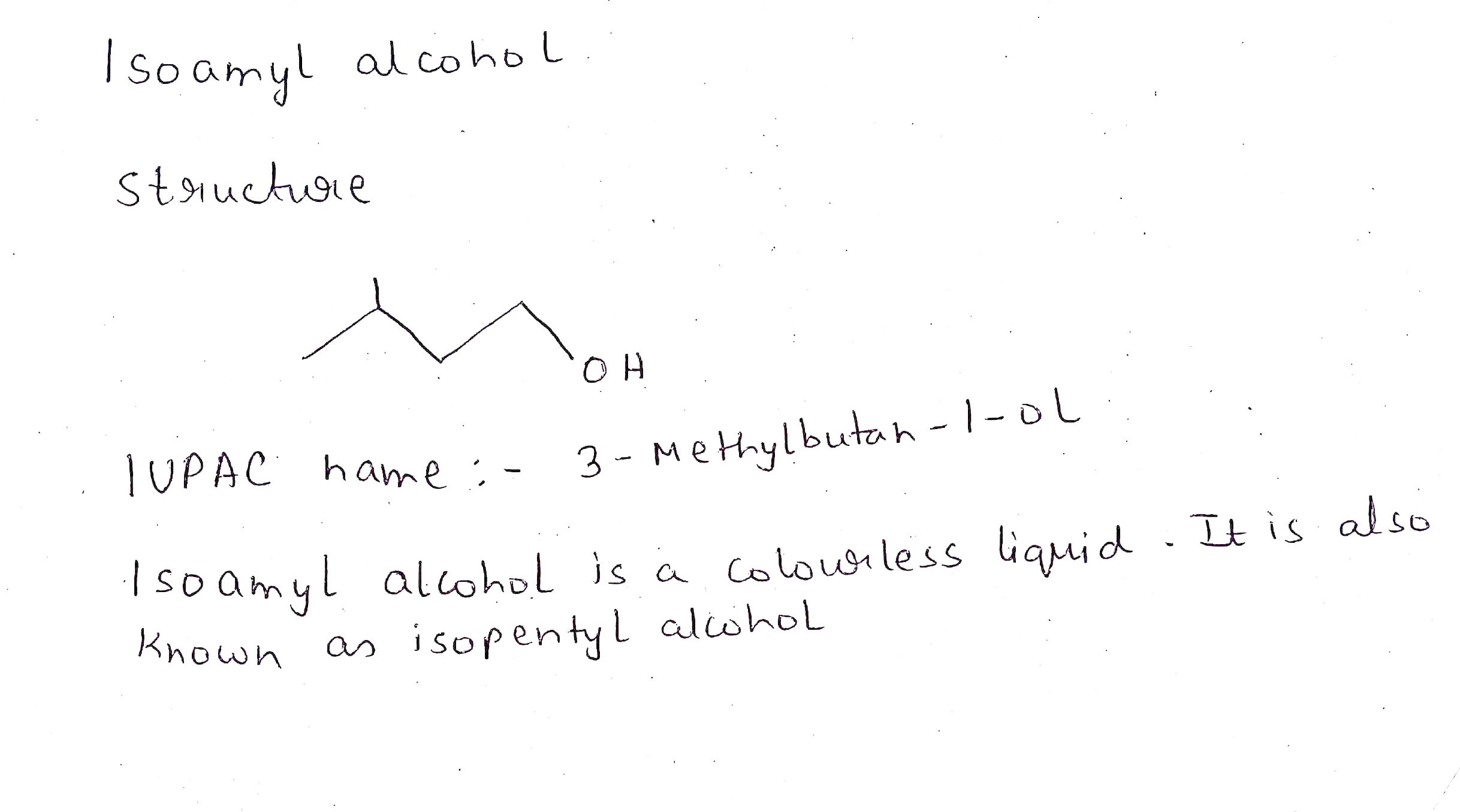
Isoamyl alcohol.
Isoamyl alcohol.
Write IUPAC name of the following.
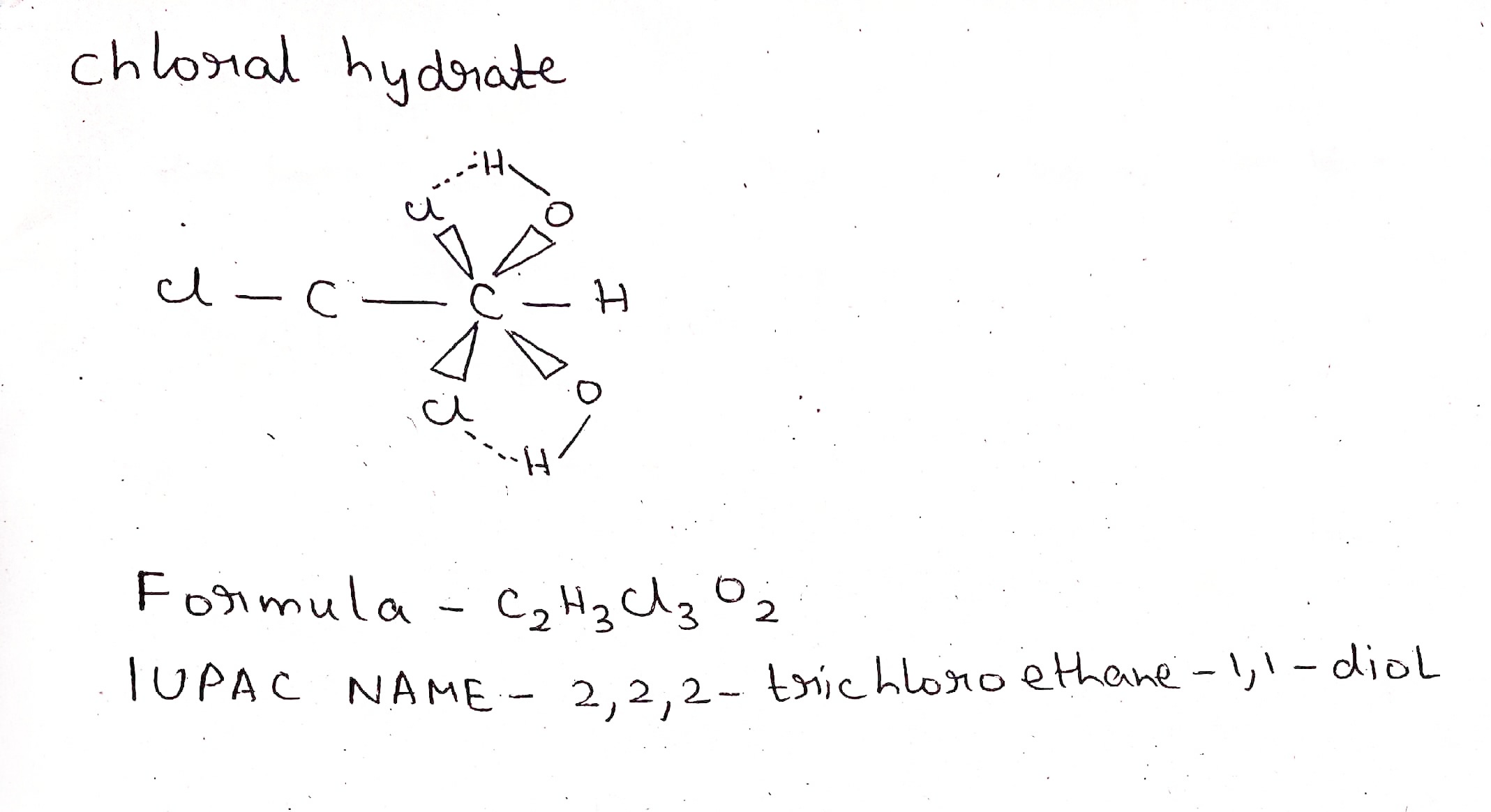
Chloral hydrate.
Chloral hydrate.
Write IUPAC name of the following.
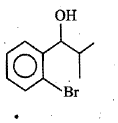
What happens when vapour of ethyl alcohol is passed through heated aluminium oxide at $$360^o$$C?
Write the equation for preparing ethyl alcohol in one step only from Ethylene.
The following name is inconsistent with the prevalent rules. Rename the compound in accordance with the accepted conventions:
$$2-Phenyl-3-butanol$$.
Explain the mechanism of the following reactions:
(a) Bromine on ethylene.
(b) $$HBr$$ on ethylene.
How will you obtain the following from propene?
$$n-Propyl\ alcohol$$.
$$n-Propyl\ alcohol$$.
Give the mechanism of :
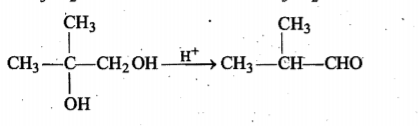
Outline a synthesis of alcohol from the indicated staring material.
Allyl alcohol from propene.
Outline a synthesis of alcohol from the indicated starting material.
Isopropyl alcohol from a hydrocarbon.
Write down the name and structure of the compound obtained by dehydration of ethyl alcohol.
Complete the following equations:
$$2C_{6}H_{5}Cl + Na \xrightarrow {Ether}$$.
Fill in the blanks:
Amongst the three isomers of nitrophenol, the one that is least soluble in water is ________.
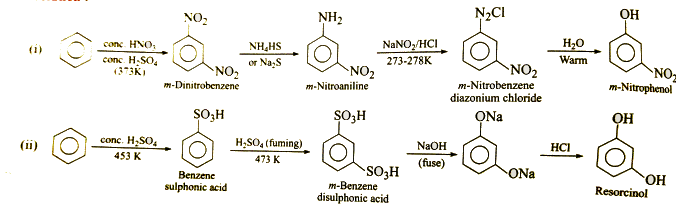
How will you prepare the following compounds from benzene?
Resorcinol.
With specific compounds write equations for the reactions involved in the following conversions:
An aromatic hydrocarbon to its hydroxy derivative.
How will you prepare the following compounds from benzene?
$$m-Nitrophenol$$.
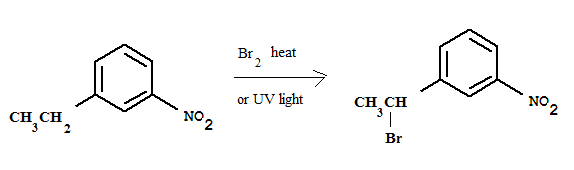
$$m-nitro\ ethyl \ benzene$$ on $$Br_2$$ and uv light,, What is the product ?
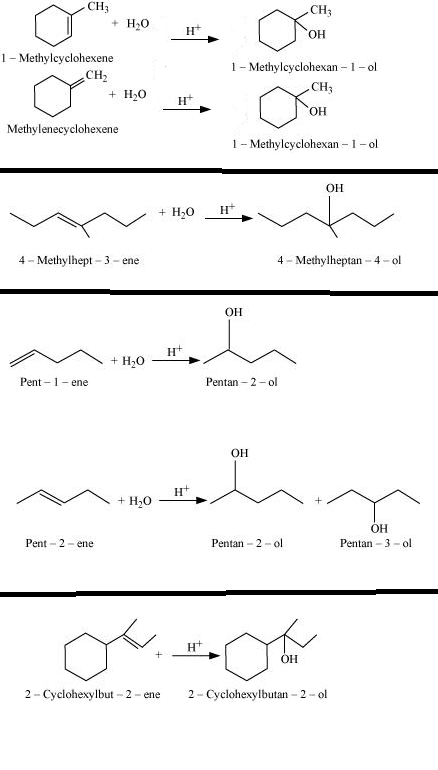
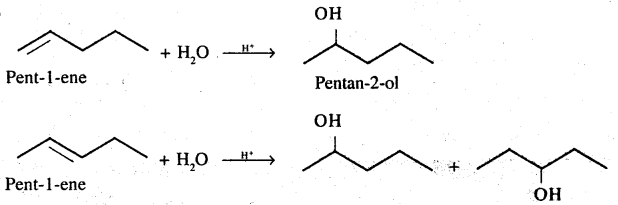
Give the major product of hydration of the above alkene.
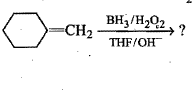
Give the major product of hydration of the following alkene.
$$C_3H_6(CH_3-CH=CH_2)\overset{H^+}{\underset{D_2O}{\rightarrow}}?$$
Identify the functional group present in the following compound and name it according to IUPAC system: $$CH_{3}OH$$.
Give the major product of hydration of the following alkene.
$$C_3H_6(CH_3-CH=CH_2)\overset{D^+}{\underset{D_2O}{\rightarrow}}?$$
Write the molecular formula of ethanol.
Give the major product of hydration of the following alkene.
$$C_3H_6(CH_3-CH=CH_2)\overset{D^+}{\underset{HOH}{\rightarrow}}?$$
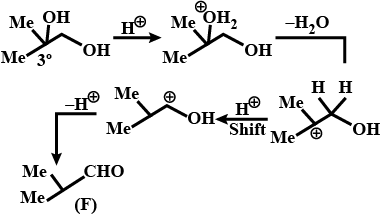
Identify (F)
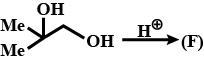
Write IUPAC name of the following compounds:
$$CH_3 - \underset{OH}{\underset{|}{CH}} - \underset{OH}{\underset{|}{CH}} - CH_3$$
Write IUPAC name of the following compounds:
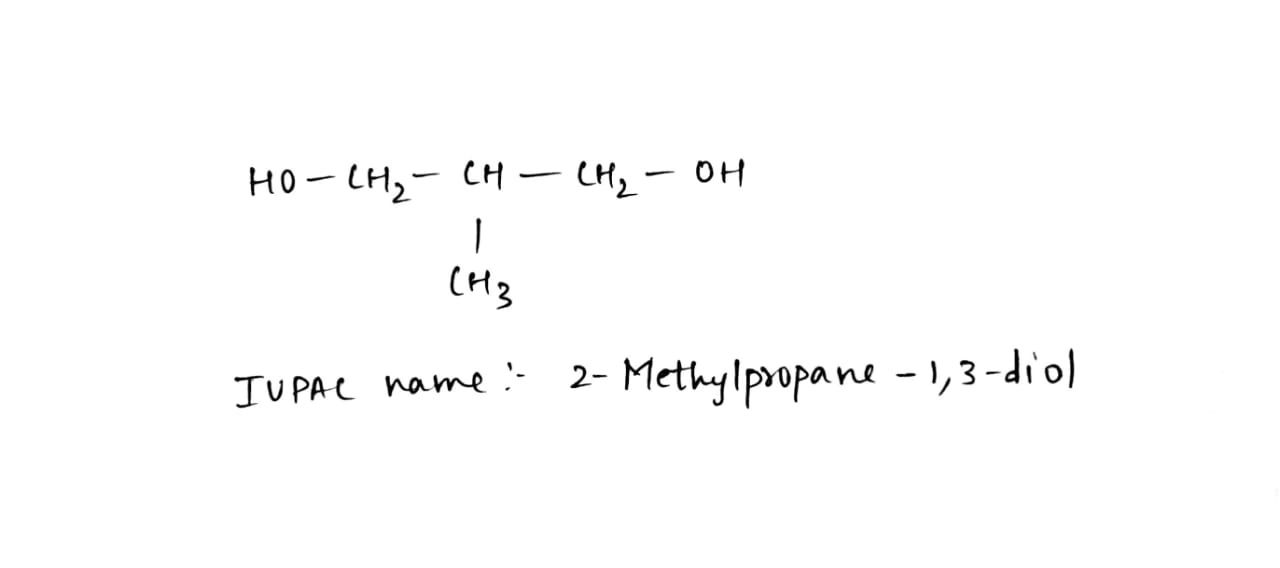
$$HO - CH_2 - \underset{OH}{\underset{|}{CH}} - CH_2 - OH$$
Write IUPAC name of the following compounds:
Identify A and B in the following reactions:
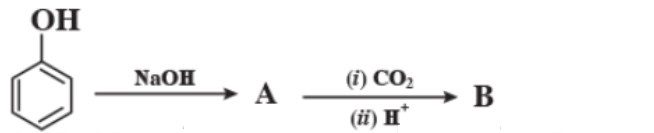
How are the following conversions carried out?
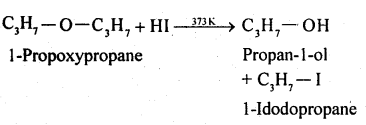
Propanol to 1-propoxypropane
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound:
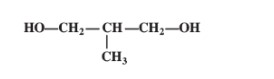
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound:
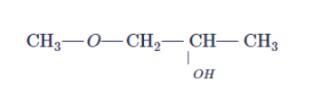
How are the following conversions carried out?
Propanol to propan-2-ol
Give Reasons:
Relative ease of dehydration of alcohols is $$3^\circ>2^\circ>1^\circ$$.
What is the effect of drinking methanol?
Write the main product(s) in each of the following reaction:
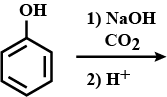
How do you obtain the following?
Propan-2-ol from propene
Give the trivial (common) names and the $$IUPAC$$ names of the following:
$$CH_{3}OH$$
Give the trivial (common) names and the $$IUPAC$$ names of the following:
$$C_{2}H_{5}OH$$
What are alcohols? State their sources
State the method of preparation of ethanol: by hydrolysis of ethene
Complete the reaction equation:
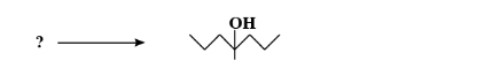
Name an organic compound which is: Called 'wood spirit
How do you convert the following:
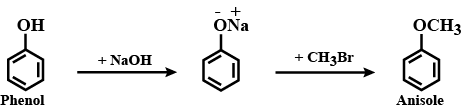
i) Phenol to Anisole
ii) Ethanol to Propan-2-ol
What is the molecular formula of the alcohol which can be derived from propane?
Name an organic compound which is: Made from water gas
Write structure of the compound whose IUPAC name is as follows:
$$3$$-Chloromethylpentan-l-ol
Draw the structures of all isomeric alcohols of molecular formula $$C_5H_{12}O$$ and give their IUPAC names.
Identify if pentanol is insoluble, partially soluble or highly soluble in water?
Write the general formula of alcohol.
Name the reagent used in the following reaction:
Dehydration of propan-2-ol to propene.
Show how would you synthesise the above alcohol from appropriate alkene?
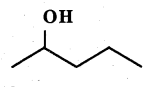
Write the equation of the reaction of hydrogen iodide with:
$$1$$-propoxypropane
$$1$$-propoxypropane
Write the structural formulae for the following IUPAC
propan-2ol
What happens when
chlorobenzene is subjected to hydrolysis
Write IUPAC name of the above compound:
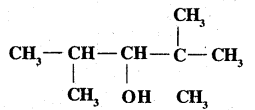
Explain the following with one example:
Dehydration
Dehydration
Write down the IUPAC name of the given compound.
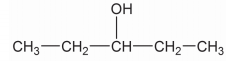
Write the IUPAC name of the following organic compound:
$$CH_3 - CH_2 - CH_2 - CH_2 - CH_2 - OH$$
Write the IUPAC name of ethyl alcohol.
Write down the IUPAC name of the compound given below:
$$CH_3 - CH_2 - CH_2 - OH$$
Write down the IUPAC name of the compounds given above and and then write the name of the isomerism exhibited by it.
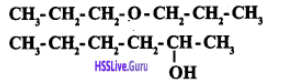
Can you write the $$IUPAC$$ names of these two compounds?
$$CH_2-OH, CH_3 -CH_2-OH$$
State how the following conversions can be carried out.
Ethene to Ethyl alcohol.
An optically active alcohol A $$\displaystyle \left ( C_{6}H_{10}O \right )$$ absorbs 2 mol of hydrogen per mole of A upon catalytic hydrogenation and gives a product B. The compound B is resistant to oxidation by $$\displaystyle CrO_{3}$$ and does not show any optical activity. Deduce the structures of A and B.
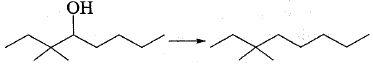
Conversion of given reaction to the given product will take place in how many step?
Match the compounds in Column I with their characteristics/tests/reactions (s) reagent(s)/stereochemistry/isomer(s) given in Column II. Matching can be one or more than one.
| Column I | Column II |
| Reaction | Product and name of the reaction |
Write the structrual formula of the major product in the following case:
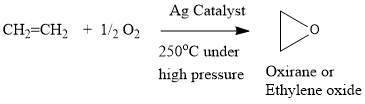
Ethene mixed with air is passed under pressure over a silver catalyst at $$250^{\circ} C$$.
Identify total number of 1, 2 shift during following dehydration reaction ?
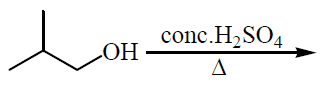
Explain the following with an example.
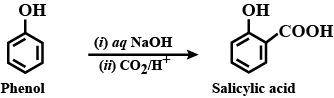
(i) Kolbes reaction.
(ii) Reimer-Tiemann reaction.
(iii) Williamson ether synthesis.
(iv) Unsymmetrical ether.
(i) Draw the structures of all isomeric alcohols of molecular formula $$C_5H_{12}O$$ and give their IUPAC names.
(ii) Classify the isomers of alcohols in above question as primary, secondaryand tertiary alcohols.
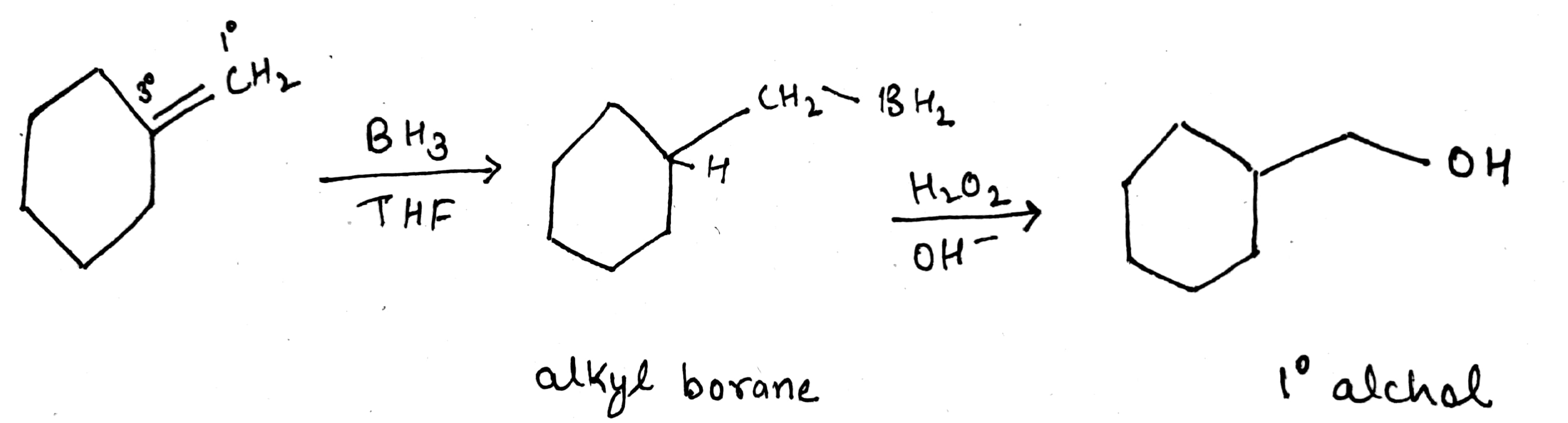
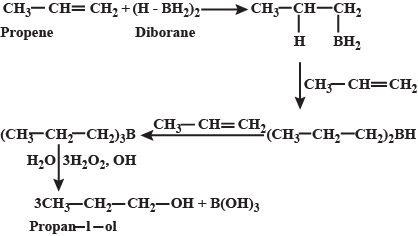
What is meant by hydroboration-oxidation reaction? Illustrate it with an example.
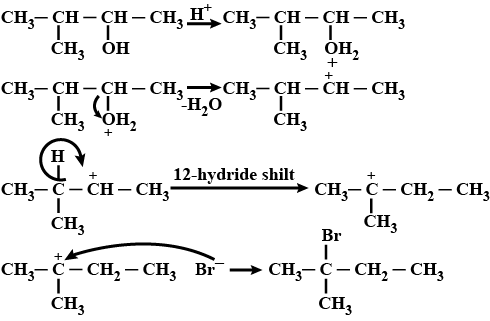
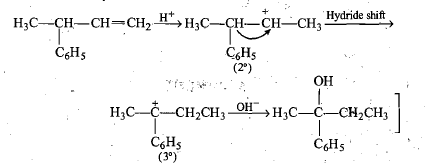
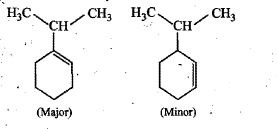
When 3-methylbutan-2-ol is treated with HBr, the following reaction takes place:
Give a mechanism for this reaction.
(Hint : The secondary carbocation formed in step II rearranges to a more stable tertiary carbocation by a hydride ion shift from 3rd carbon atom.)

Write IUPAC name of the given compound:

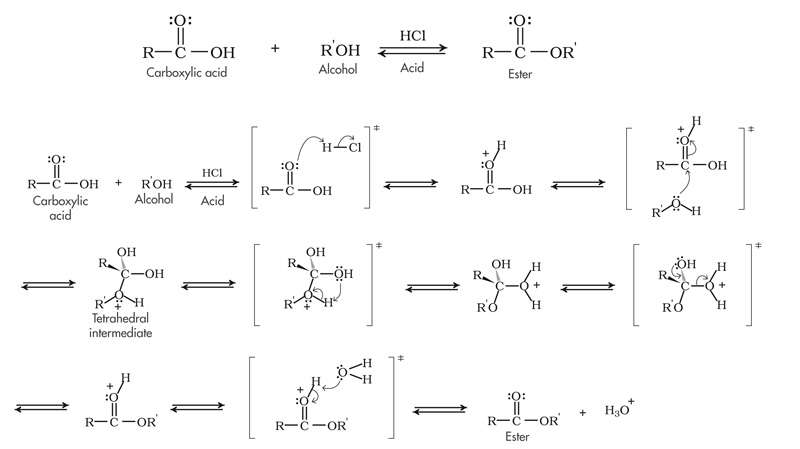
Explain the mechanism of esterification. Write the reactions involved in dehydration of $${1}^{o}$$, $${2}^{o}$$ and $${3}^{o}$$ alcohols.
Write the correct pair of reactants for the preparation of t-butyl ethyl ether by Williamson synthesis.
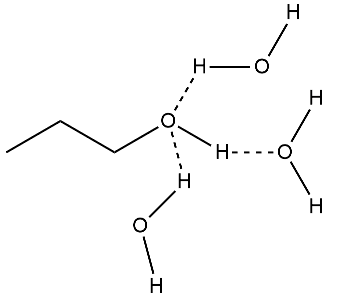
Explain how Alcohols of lower molecular mass are soluble in water.
Write two methods of preparation of methyl alcohol. Describe giving diagram. Give such a test of methyl alcohol which is not given by ethyl alcohol which is not given by ethyl alcohol. Give the chemical reactions.
$${C_6}{H_5}Cl\xrightarrow[High\,\,temperature\,\, and\,\, pressure]{NaOH}A \xrightarrow{HCl}B$$
Identify $$A$$ and $$B$$ in the above reaction.
a) Write the mechanism of acid catalysed dehydration of ethanol to ethene.
b) Between phenol and alcohol which is more acidic? Why?
Complete the following reaction
Propene $$\xrightarrow[H_2O, \Delta]{H_2SO_4} A$$
Name the following
(1) Thte non-sublimable solid from a mxiture of iodine and potassion nitrate.
(2) The heavier liquid component from -mercury and water
(3) The lower boiling point component from methyl alcohol and water.
(4) The compound containing one atom of sulphur and two atoms of oxygen
(5) An acid whose formula is $${H}_{2}{CO}_{3}$$
Explain the following behaviours :
(i) Alcohols are more soluble in water than the hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses.
(ii) Ortho-nitrophenol is more acidic than ortho-methoxyphenol.
(iii) Cumene is a better starting material for the preparation of phenol.
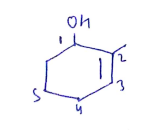
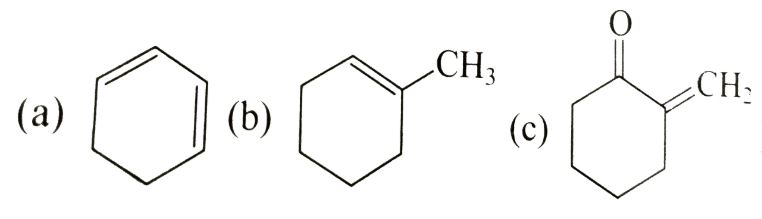
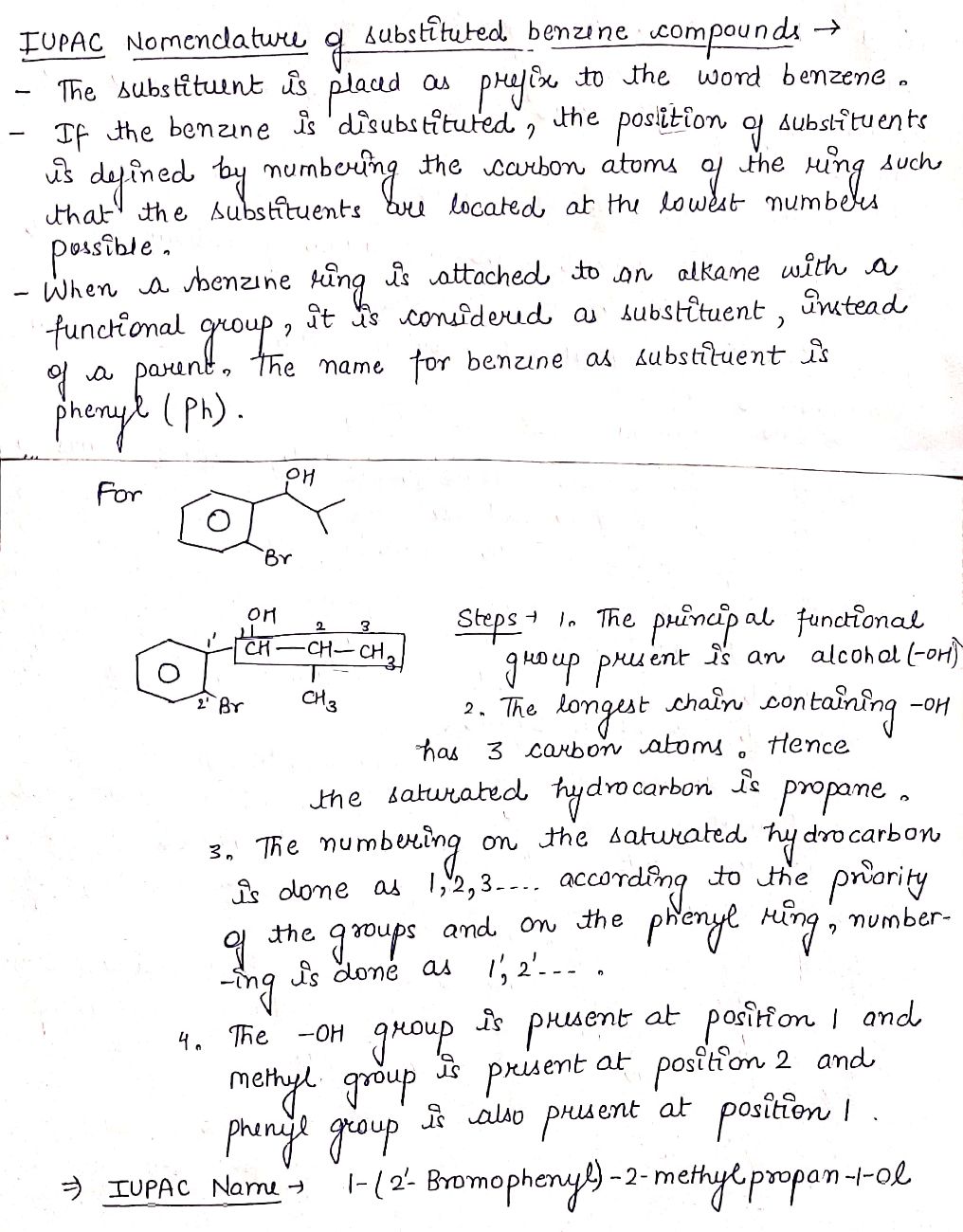
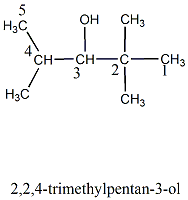
Write the IUPAC name of the compound in the picture.

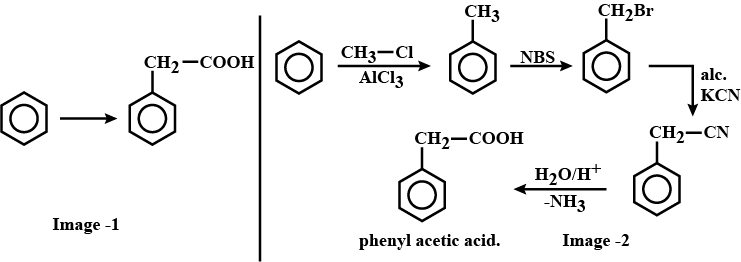
How will you prepare the compounds from benzene ? You may any inorganic regent and any organic reagent having not more than carbon atom
Phenylacetic acid
Discuss the mechanism of the following reactions:
(A) Dehydration of alcohols to form alkenes.
Complete the following equation.
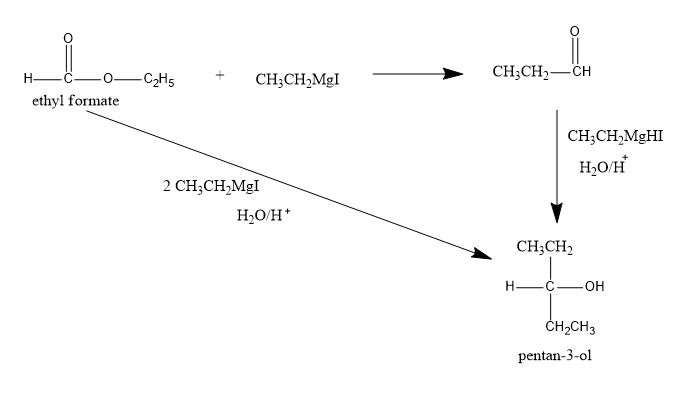
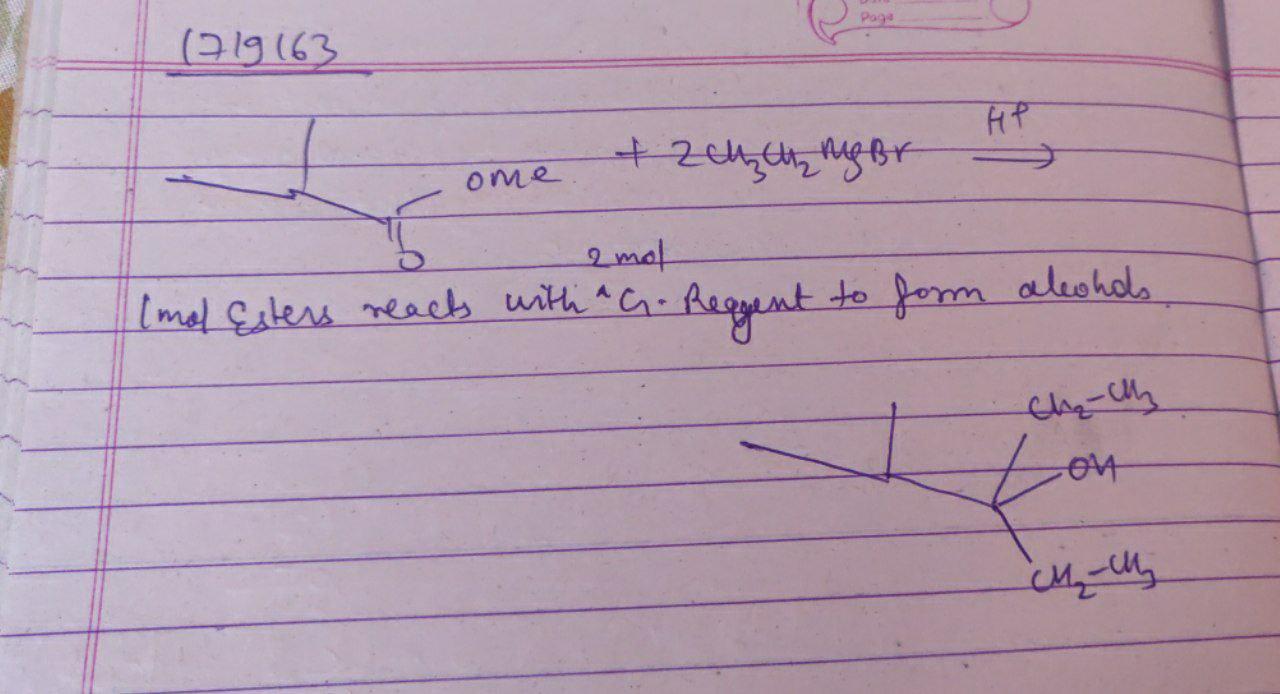
$$H-\overset{\overset{\displaystyle O}{||}}{C}-OEt+2CH_3CH_2MgI\overset{H_2O/H^+}{\rightarrow}(A)$$.
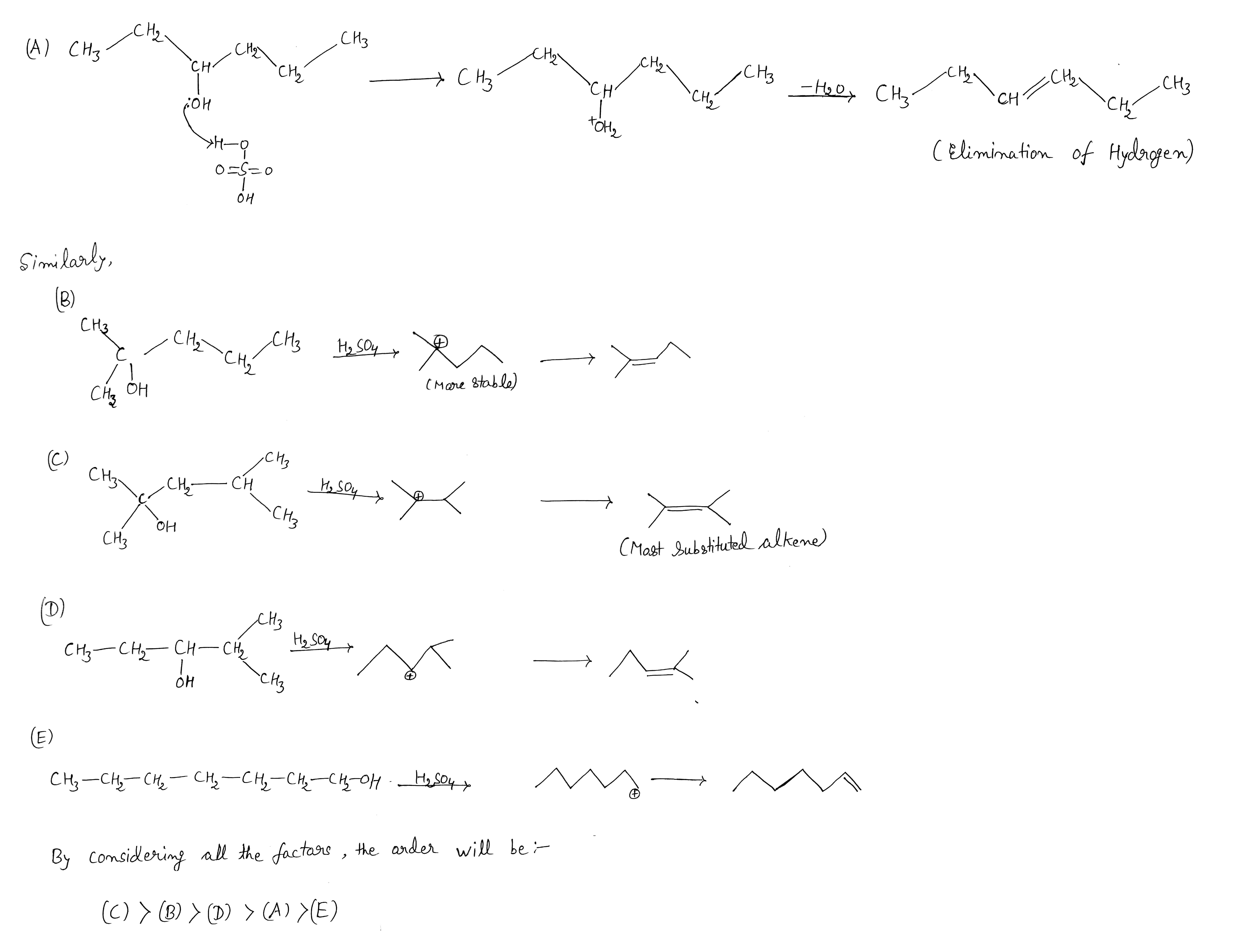
Arrange the following in decreasing order of rate of dehydration with conc. $$H_2SO_4$$:
(A) $$CH_3CH_2CH(OH)CH_2CH_2CH_3$$
(B) $$(CH_3)_2C(OH)CH_2CH_2CH_3$$
(C )$$(CH_3)_2C(OH)CH(CH_3)_2$$
(D) $$CH_3CH_2CH(OH)CH(CH_3)_2$$
(E) $$CH_3CH_2CH_2CH_2CH_2CH_2CH_2OH$$
Complete the following equation.
$$RCH=CH_2\overset{Hg(OAc)_2}{\underset{THF, -H_2O}{\rightarrow}}(A)\overset{NaBH_4}{\rightarrow}(B)$$.
Complete the following equation.
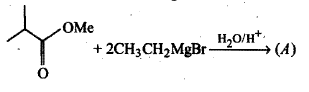
Answer the following.
What is the name of carbinol?
Outline a synthesis of alcohol from the indicated starting material.
$$1$$-Phenylethanol from styrene(vinyl benzene).
How will you obtain?
Ethanol from acetylene.
Show, how would you synthesize the following alcohol from appropriate alkene?
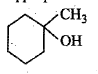
Show, how would you synthesize the following alcohol from appropriate alkene?
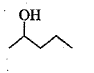
Show, how would you synthesize the following alcohol from appropriate alkene?
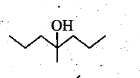
Show, how would you synthesize the following alcohol from appropriate alkene?
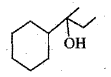
Give reasons for the following.
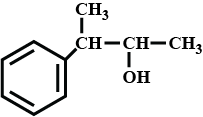
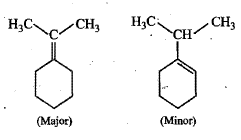
Hydration of $$3$$-phenylbut-$$1$$-ene in dil. $$H_2SO_4$$ forms $$2$$-phenylbutan-$$2$$-ol instead of $$3$$-phenylbutan-$$2$$-ol.
Give the major product of hydration of the following alkene.
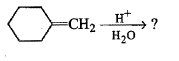
Write down the dehydration product of the following.
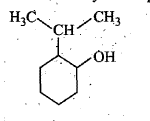
Give the major product of hydration of the following alkene.
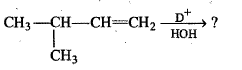
Write down the dehydration product of the following.
Write down the dehydratiom product of the following.
Convert the following:
Toluene to benzyl alcohol
Complete the above :

Convert the following
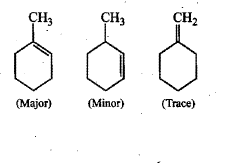
Identify the major and minor products.
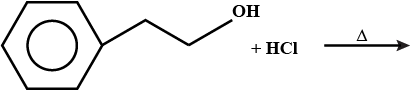
Write the structural formula for each of the following.
Three $$1^{\circ}$$ alcohols with the formula $$C_{4}H_{8}O$$.
Why is there a large difference in th boiling points of butanal and butan-1-ol?
Which of the following is the correct method for synthesising methyl-t-butyl ether and why ?
$$i$$. $$(CH_{3})_{3}CBr + NaOMe\rightarrow$$
$$ii$$. $$CH_{3}Br + NaO-t-Bu\rightarrow$$
Give Reason for the following in one or two sentences.
'Acid-catalysed dehydration of t-butanol is faster than that of n-butanol'.
Give reasons for the following:
Alcohols are more soluble in water than the hydrocarbons of comparable molecular masses.
Complete the following reaction.
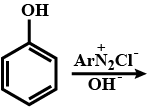
Complete each synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or products:

What is the order of dehydration of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols?
How will you convert:
Propene to Propan-1-ol?
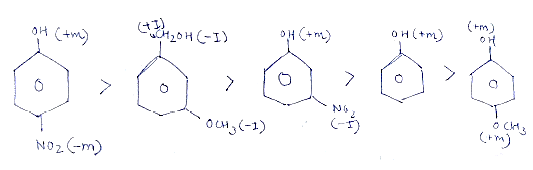
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of acidity and give a suitable explanation. Phenol, o-nitrophenol,o-cresol.
Preperation of alcohols from alkenes involves the electrophilic attack on alkene carbon atom. Explain its mechanism.
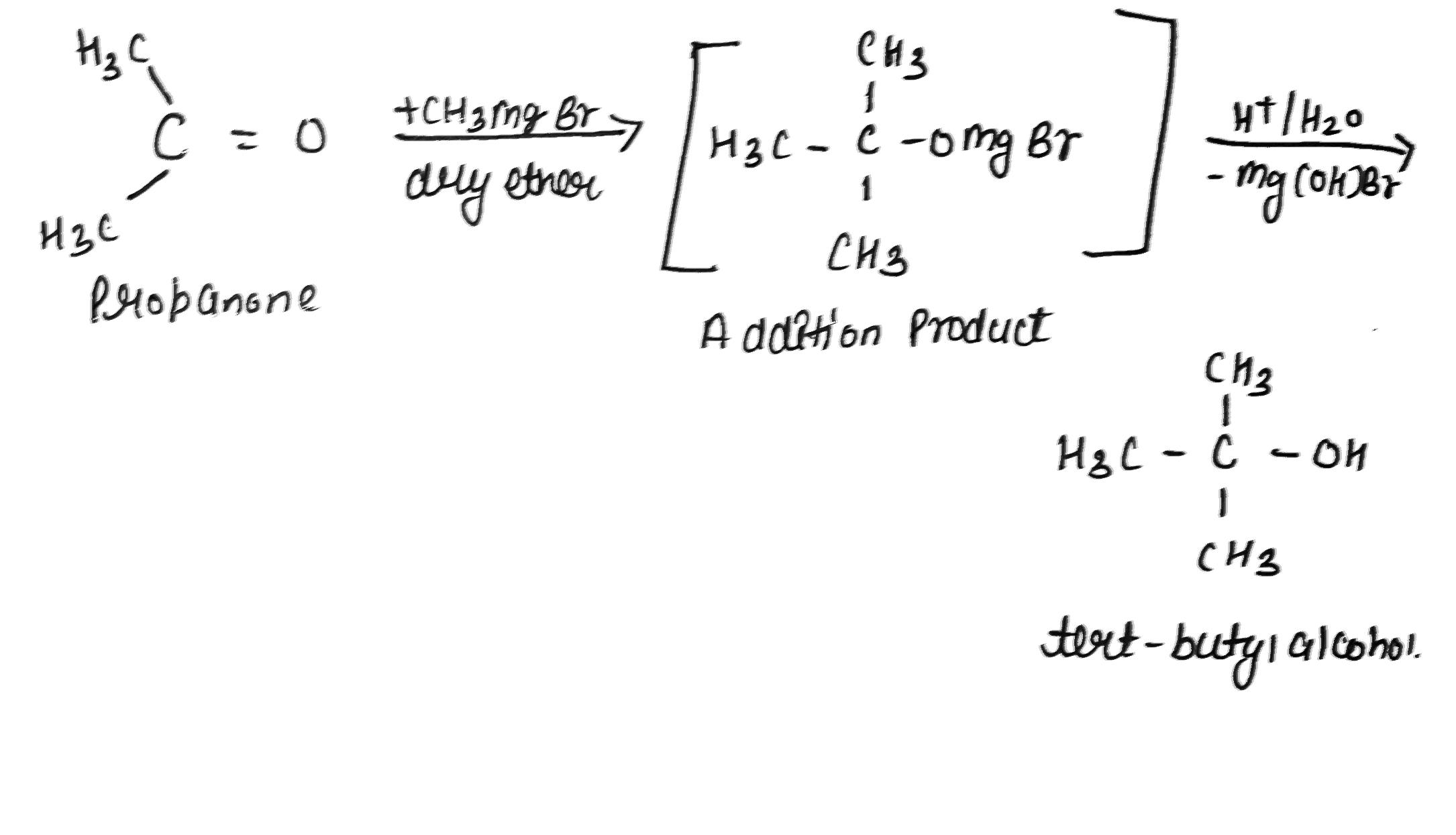
How can propan-2-one be converted into tert-butyl alcohol?
Explain why is $$ O=C=O $$ nonpolar while $$ R-O-R $$ is polar.
Ethers can be prepared by Williamson's synthesis in which an alkyl halide is reacted with sodium alkoxide. Di-tert-butyl ether can't be prepared by this method. Explain.
Explain why alcohols and ethers of comparable molecular mass have different boiling points
Alcohols react with active metals e.g. Na, K etc. to give corresponding alkoxides. Write down the decreasing order of reactivity of sodium metal towards primary. secondary and tertiary alcohols.
Explain why nucleophilic reactions are not very common in phenols.
Give three methods of preparation of anisole.
Identify if phenol is insoluble, partially soluble or highly soluble in water?
Write the equation of the reaction of hydrogen iodide with:
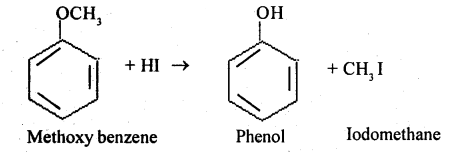
Methoxy benzene
Alcohols are soluble in water whereas diethyl ether is not, explain with reason.
Show how you will synthesise:
$$1$$-phenylethanol from a suitable alkene.
How would you distinguish experimentally between primary alcohol and a carboxylic acid?
The carbon-oxygen bond in phenol is slightly stronger than that in methanol. Why?
Write the equation of the reaction of hydrogen iodide with:
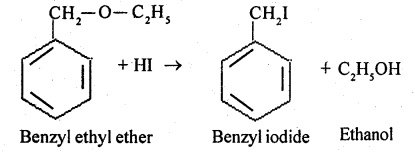
Benzyl ethyl ether.
How will you prepare the following from chloroform?
$$HC(OC_2H_5)_3 $$
Give the mechanism of dehydration of alcohols.
Class 12 Engineering Chemistry Extra Questions
- Alcohols,Phenols And Ethers Extra Questions
- Aldehydes,Ketones And Carboxylic Acids Extra Questions
- Amines Extra Questions
- Biomolecules Extra Questions
- Chemical Kinetics Extra Questions
- Chemistry In Everyday Life Extra Questions
- Coordination Compounds Extra Questions
- Electrochemistry Extra Questions
- General Principles And Processes Of Isolation Of Elements Extra Questions
- Haloalkanes And Haloarenes Extra Questions
- Polymers Extra Questions
- Solutions Extra Questions
- Surface Chemistry Extra Questions
- The D-And F-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The P-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The Solid State Extra Questions