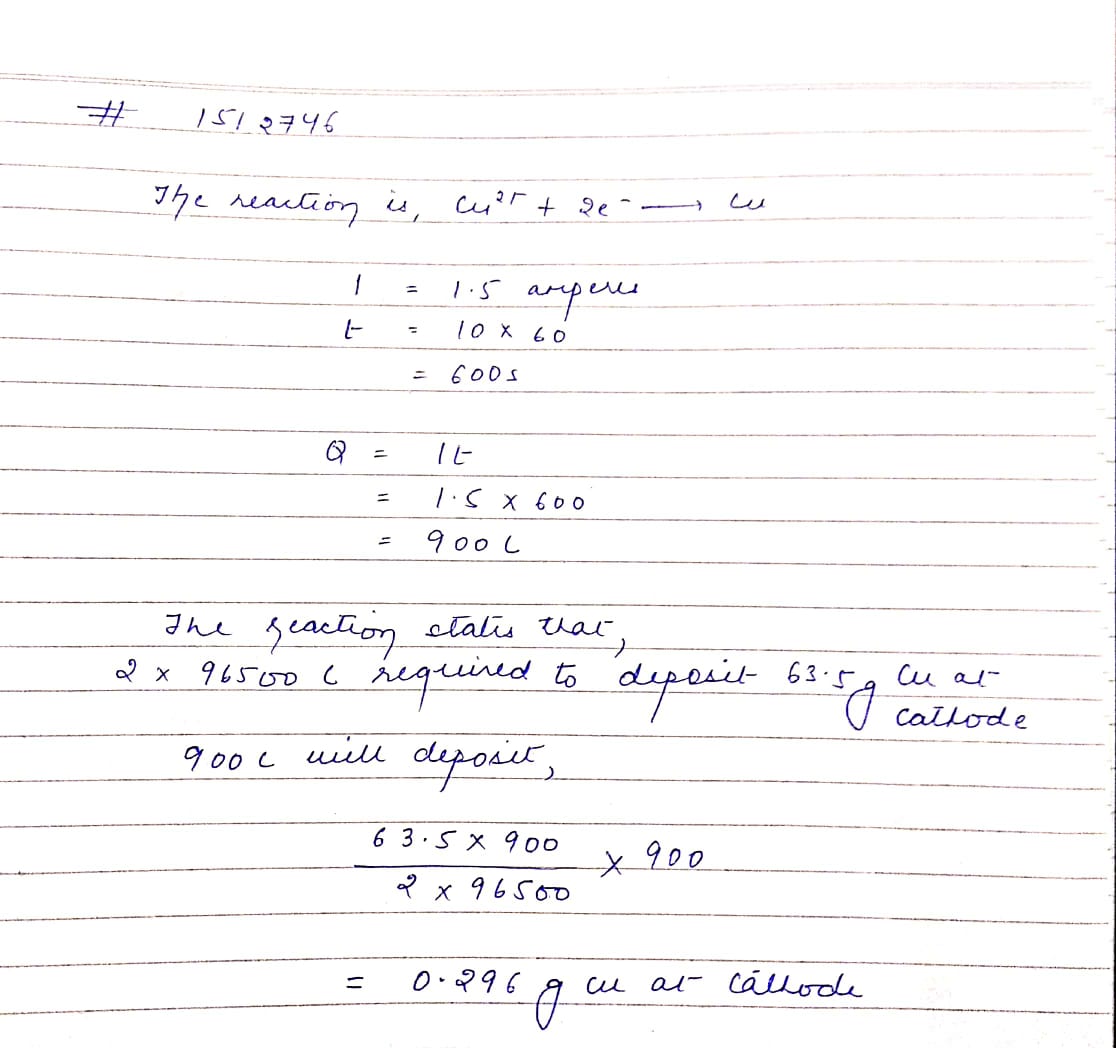Electrochemistry - Class 12 Engineering Chemistry - Extra Questions
Copy and complete the following sentences ?
With platinum electrodes hydrogen is liberated at the ........... and oxygen at the .......... during the electrolysis of acidified water.
During the electrolysis of acidified water, what is the ratio of the volumes of hydrogen produced to the volume of oxygen ?
Give the equation for the discharge of ion at the cathode during the electrolysis of acidified water ?
To carry out the so-called electrolysis of water, sulphuric acid is added to water. How does the addition of sulphuric acid produce a conducting solution ?
Pure water consists entirely of _____________ (ions / molecules).
Name a solid which undergoes electrolysis when molten.
The whole apparatus used for electrolysis is termed as :
Name the substance dissolved in pure water to make it a conductor of electricity.
Solutions which are decomposed due to the current passed through them are called .......... .
Hydrogen gas is liberated at the .......... (negative / positive) electrode called ..........
Acidified water is electrolysed by using carbon electrodes. What is produced at negative carbon electrode?
Acidified water is electrolysed by using carbon electrodes. What is produced at positive carbon electrode?
Oxygen gas is liberated at the .......... (negative / positive) electrode called the .......... .
The chemical reaction is $$2H_2O\, \rightarrow\, .......... \,+\,O_2$$
.......... (chemical / physical) reaction takes place.
Write the equation of the reactions which take place at the cathode and anode when acidified water is electrolysed.
During electrolysis the cations move to the electrode at a ___________ potential.
_________ is the chemical change that takes place by the passage of current through an electrolyte.
By process of electrolysis chemical energy gets converted into electrical energy.
Rusting of iron is an example of ________ reaction.
Can we make use of a.c. in electrolysis? Explain briefly.
$$19\ g$$ of molten $$SnCl_{2}$$ is electrolyzed for some time using inert electrodes until $$0.119\ g$$ of $$Sn$$ is deposited at the cathode. No substance is lost during electrolysis. Find the ratio of masses of $$SnCl_{2} : SnCl_{4}$$ after electrolysis.
How much electricity in terms of faraday is required to produce 20 grams of calcium from molten calcium chloride?
Write the chemistry of recharging lead storage battery highlighting all the materials that are evolved during recharging.
Sea water promotes corrosion. Why?
An old cycle frame was left in open for a few days. A brown layer got slowly deposited on its surface and could not be removed when rubbed with sand paper. What happened actually?
Explain the term with example:Oxidant
How many coulomb are required for the oxidation of one mole of $$ H_{2}O $$ to $$ O_{2} $$?
State given reason, in what state or medium does
i. $$NaCL$$
II. $$HCL$$ gas
iii. $$NH_3$$ gas conduct electricity.
What do you mean by Corrosion ?
Column II gives name of material use for device given in column I :
Statements (A, B, C, D) in list I have to be matched with statements (1,2,3,4) list II.
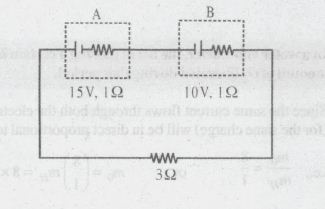
For the circuit shown in the adjoining figure, match the entries of column I with the entries of column II.
Electrolysis of water is carried out in hoffman voltameter. Litmus is added to both cathodic and anodic compartments. What changes do you observe in the above process at the end of electrolysis? Justify.
List 1 and List 2 contains four entries each. Entries of List 1 are to be matched with some entries of ListOne or more than one entries of List 1 may have the matching with the same entries of List 2.
The charge (in F) required to deposites all Al from the electrolysis of 1 mol molten Al$$_2$$O$$_3$$ is :
The quantity of charge (in Faraday) required to reduce 96 g Mg from molten solution of MgCl$$_2$$ is :
In rusting of iron, iron is oxidised and O$$_2$$ is reduced. The no. of electrons used during reduction O$$_2$$ are :
In a galvanic cell electrical energy is generated at the expense of chemical energy.
If true enter 1, else enter 0.
The electric charge for electro deposition of 1 g equivalent of substance is $$x$$ faraday. What is the value of $$x$$?
Presence of CO$$_2$$ in natural water facilitate rusting of iron.
If true enter 1, else enter 0.
If true enter 1, else enter 0.
Explain how electrolysis is an example of redox reaction?
_________ is defined as a process where materials, usually metals, deteriorate as a result of a chemical reaction with air, moisture, chemical, etc. For example, iron, in the presence of moisture, reacts with oxygen to form hydrated iron oxide.
Number of Faradays (F) required to reduce 3 mol of $$MnO_{4}^{\ominus}$$ to $$Mn^{2+}$$ is:
How many Faradays are required to reduce 1 mol of $$BrO_3^{\ominus}$$ to $$Br^{\ominus}$$ in basic medium ?
Electric Unit and Single Unit
Classify the following substances under three headings.Strong electrolytes ,Weak electrolytes
Fill in the blanks :Electrolysis is the passage of_______ (electricity / electrons) through a liquid or a solution accompanied by a _______ (physical/ chemical) change.
Water is broken down into its constituent elements .......... and .......... .
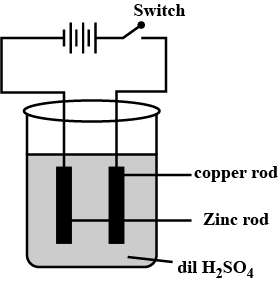
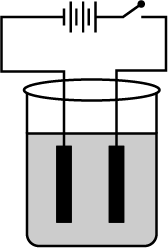
The bulb does not glow in the set up shown in the figure. List the possible reasons. Explain your answer.
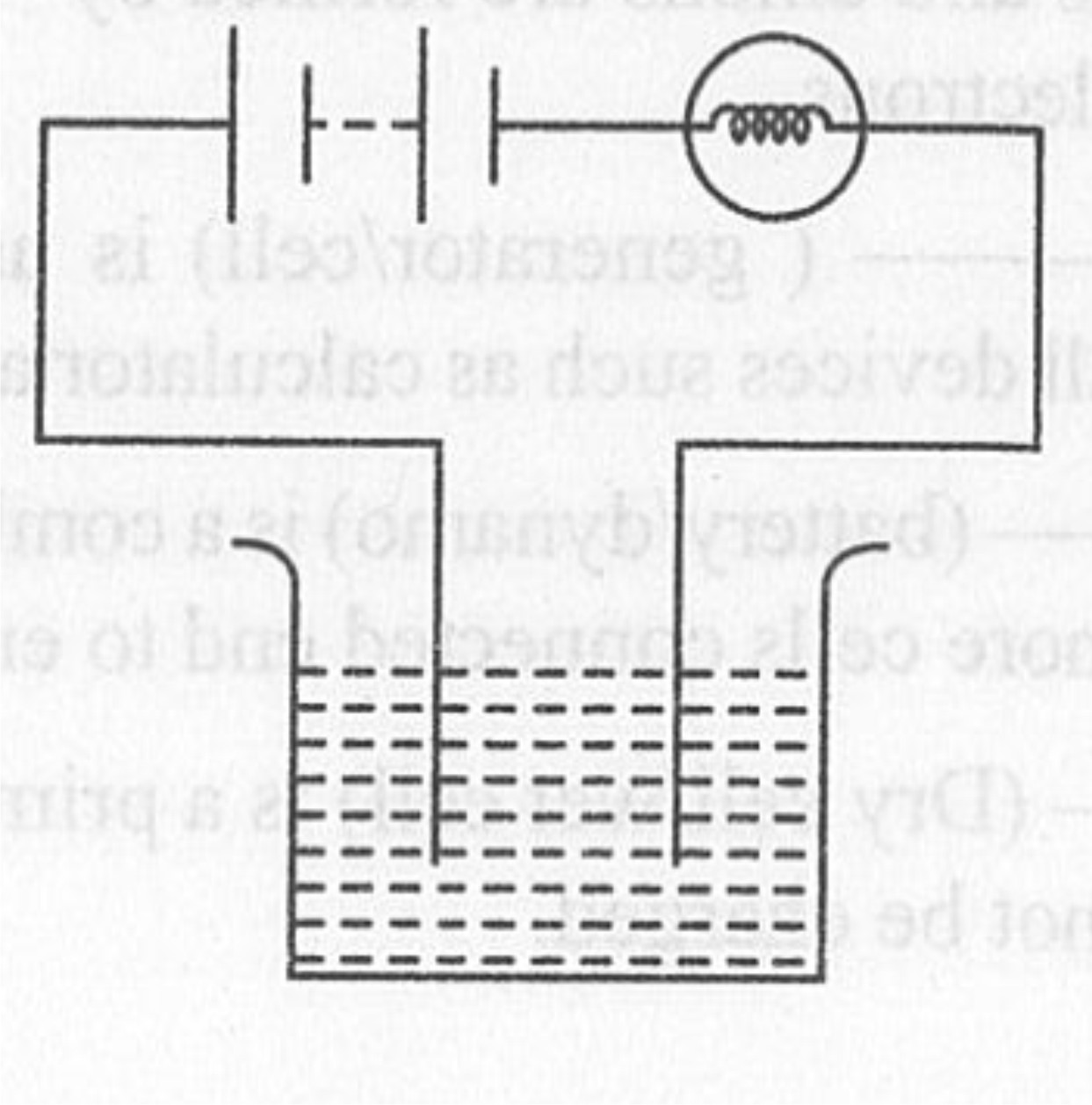
Paheli had heard that rainwater is as good as distilled water. So she collected some rain water in a clean glass tumbler and tested it using a tester. To her surprise she found that the compass needle showed deflection. What could be the reasons?
What happens when
An iron rod is placed in $$CuSO_{4}$$ solution?
Why do caesium ($$Cs$$) and potassium ($$K$$) find applications in photoelectric cells?
What happens when a copper rod is placed in $$FeSO_{4}$$ solution?
Differentiate between the terms strong electrolyte and weak electrolyte.
(sating any two differences)
Corrosion can be prevented by using _________ .
Edible oil is not allowed to stand for a long time in an iron or tin container. Give reasons.
What do you mean by corrosion? How can you prevent it?
Write the SI unit of Resistivity.
Write the complete chemical reaction of rusting of iron.
What is metallic corrosion? Give one example
Write three methods of preventing rusting of iron.
State the first and second law of electrolysis.
What is corrosion? Do gold ornaments corrode? Justify.
What is the chemical formula of rust?
What is electrolysis? A solution of $$CuSO_{4}$$ is electrolysed for $$10$$ minutes with a current of $$1.5$$ amperes. What is the mass of copper deposited at the cathode?
State Faraday's law's of electrolysis. A solution of $$Cu{SO}_{4}$$ is electrolysed for $$10$$ minutes with a current of $$1.5$$ amperes. What is the mass of copper deposited at the cathode?
What is a secondary cell?
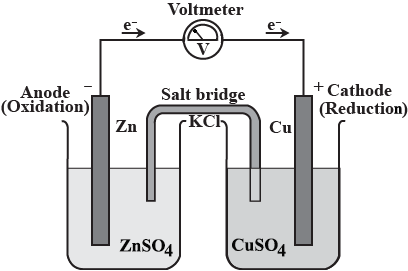
Some equipments and materials are given.
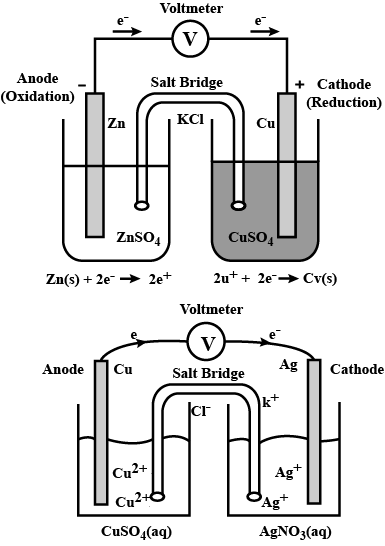
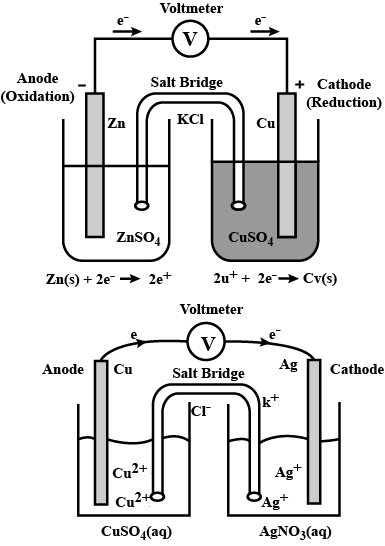
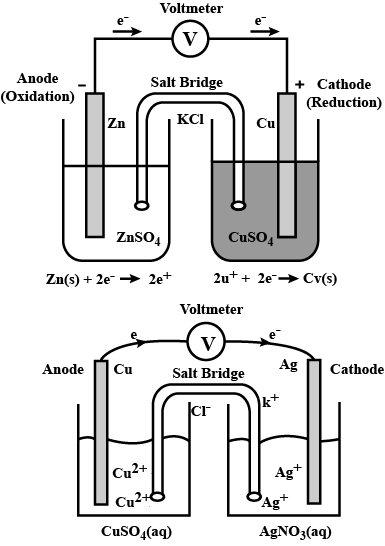
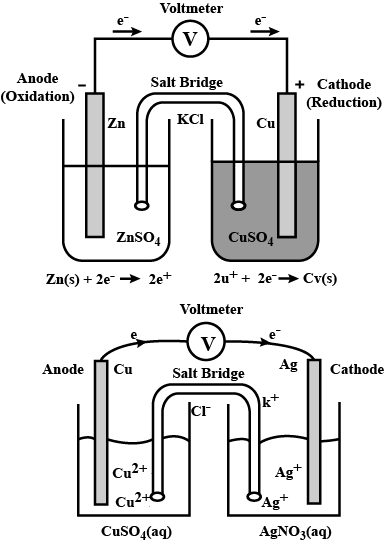
$$Zn{SO}_{4}$$ solution, $$Cu{SO}_{4}$$ solution, $$Zn$$ rod, $$Cu$$ rod, Voltmeter, $$KCl$$ solution, filter paper.
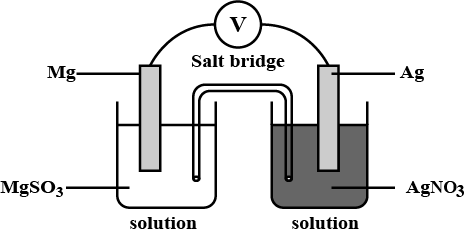
(a) Draw the diagram of the electrochemical cell which can be constructed using these equipments and materials and label the pans.
(b) Write equations of chemical reactions taking place in the two electrodes of this cell.
(Hint: reactivity $$Zn> Cu$$)
$$Mg,\ Al,\ Zn,\ Fe$$ and $$Ag$$ are metals of reactivity series:
(a) Which of this metal shows the highest reactivity?
(b) If an electrochemical cell is devised by dipping Fe in $$FeSO_4$$ solution and Ag in $$AgNO_3$$ solution, which electrode is acting as cathode? Give reason.
What do you mean by metal corrosion? Explain three methods for prevention of corrosion.
The values of $$E^{\circ}$$ of some of the reactions are given below:
$$I_{2} + 2e^{-}\rightarrow 2I^{-}; E^{\circ} = + 0.54\ volt$$
$$Cl_{2} + 2e^{-}\rightarrow 2Cl^{-}; E^{\circ} = + 1.36\ volt$$
$$Fe^{2+} + e^{-}\rightarrow Fe^{2+}; E^{\circ} = + 0.76\ volt$$
$$Ce^{4+} + e^{-}\rightarrow Ce^{3+}; E^{\circ} = + 1.60\ volt$$
$$Sn^{4+} + 2e^{-}\rightarrow Sn^{2+}; E^{\circ} = +0.15\ volt$$
On the basis of the above data, answer the following questions:
(a) Whether $$Fe^{3+}$$ oxidises $$Ce^{3+}$$ or not?
(b) Whether $$I_{2}$$ displaces chlorine from $$KCl$$?
(c) Whether the reaction between $$FeCl_{3}$$ and $$SnCl_{2}$$ occurs or not?
Resistance of a solution (A) is $$50\ ohm$$ and that of solution (B) is $$100\ ohm$$, both solutions being taken in the same conductivity cell. If equal volumes of solutions (A) and (B) are mixed, what will be the resistance of the mixture, using the same cell? Assume that there is no increase in the degree of dissociation of (A) and (B) on mixing.
Write short notes on :
(i)Nernst equation
(ii)Corrosion.
(a) What do you understand by corrosion?
(b) Write electro-chemical theory of corrosion (Rust).
(c) Write prevention (two) of corrosion.
Explain corrosion on the basis of following points :
(i) Definition
(ii) Factors affecting any two
(iii) Prevention of corrosion any two.
The emf of a cell corresponding to the reaction,
$$Zn + 2H^{+}(aq.) \rightarrow Zn^{2+} (0.1\ M) + H_{2}(g) 1\ atm$$
is $$0.28$$ volt at $$25^{\circ}C$$. Write the half-cell reactions and calculate the $$pH$$ of the solution at the hydrogen electrode.
$$E^{\circ}_{Zn^{2+}/Zn} = -0.76\ volt$$ and $$E^{\circ}_{H^{+}/H_{2}} = 0$$.
What ratio of $$Pb^{2+}$$ to $$Sn^{2+}$$ concentration is needed to reverse the following cell reaction?
$$Sn(s) + Pb^{2}(aq.) \rightarrow Sn^{2+}(aq.) + Pb(s)$$
$$E^{\circ}_{Sn^{2+}/ Sn} = -0.136\ volt$$ and $$E_{Pb^{2+}/ Pb}^{\circ} = -0.126\ volt$$.
Calculate the charge of $$6.24\times 10^{18}$$ electrons (in coulomb).
How many moles of electrons will together contribute to the charge of 289500 coulomb?
State Faraday's first law of electrolysis.
At what $$[OH^{-}]$$ does the following half-reaction have a potential of $$0 V$$ when other species are at $$1\ M$$?
$$NO_{3}^{-} + H_{2}O + 2e^{-}\rightarrow NO_{2}^{-} + 2OH^{-}, E_{cell}^{\circ} = 0.01\ V$$.
If one Faraday was to be $$48250$$ coulomb instead of $$96500$$ coulomb, what will be charge of an electron?
If $$0.5\ L$$ of a $$0.6\ M\ SnSO_{4}$$ solution is electrolysed for a period of $$30$$ min, using a current of $$4.6\ A$$. If insert electrodes areas. What is the final concentration of $$Sn^{2+}$$ remaining in the solution?
What is an electrochemical series? How is it useful in predicting whether a metal can liberate hydrogen from acid or not?
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word/words from those given in the brackets:
(square pyramidal, electrical, 74, 26, $$sp^3d^2$$, $$sp^3d$$, chemical, 68, 32, tetrahedral, yellow, white, iodoform, Lucas).
A Galvanic cell converts __________ energy into ___________ energy.
The resistance of a conductivity cell containing $$0.001\ M\ KCl$$ solution at $$298\ K$$ is $$1500\Omega$$. What is the cell constant if conductivity of $$0.001\ M\ KCl$$ solution at $$298\ K$$ is $$0.146\times 10^{-3} S\ cm^{-1}$$.
Find the distance between $$(345)$$ plane is a cubic batteries of length $$7-7\overset{o}{A}$$.
Write the equations for the reactions taking place at anode and cathode in lead storage cell.
Can you store copper sulphate solution in a zinc pot?
A metal carbonate X on reacting with an acid gives a gas which when passed through a solution gives the carbonate black. On the other hand, A gas G that is obtained at anode during electrolysis of brine is passed on dry Y, it gives compound Z, used for disinfecting water. Identify X, Y, G and Z.
Calculate volume of the gases liberated at STP if L of $$0.2$$ molar solution of $$CuSO_4$$ is electrolysed by $$5.79 A $$ Current for $$10000 seconds.$$
$$5.79\times 10000$$
In electrolysis of water:
(a) Name the gas collected at cathode and anode.
(b) Why is volume of one gas collected at one electrode is double of anode?
(c) Why are few drops of dilute $$H_2SO_4$$ added to water?
(a) Name the gas collected at cathode and anode.
(b) Why is volume of one gas collected at one electrode is double of anode?
(c) Why are few drops of dilute $$H_2SO_4$$ added to water?
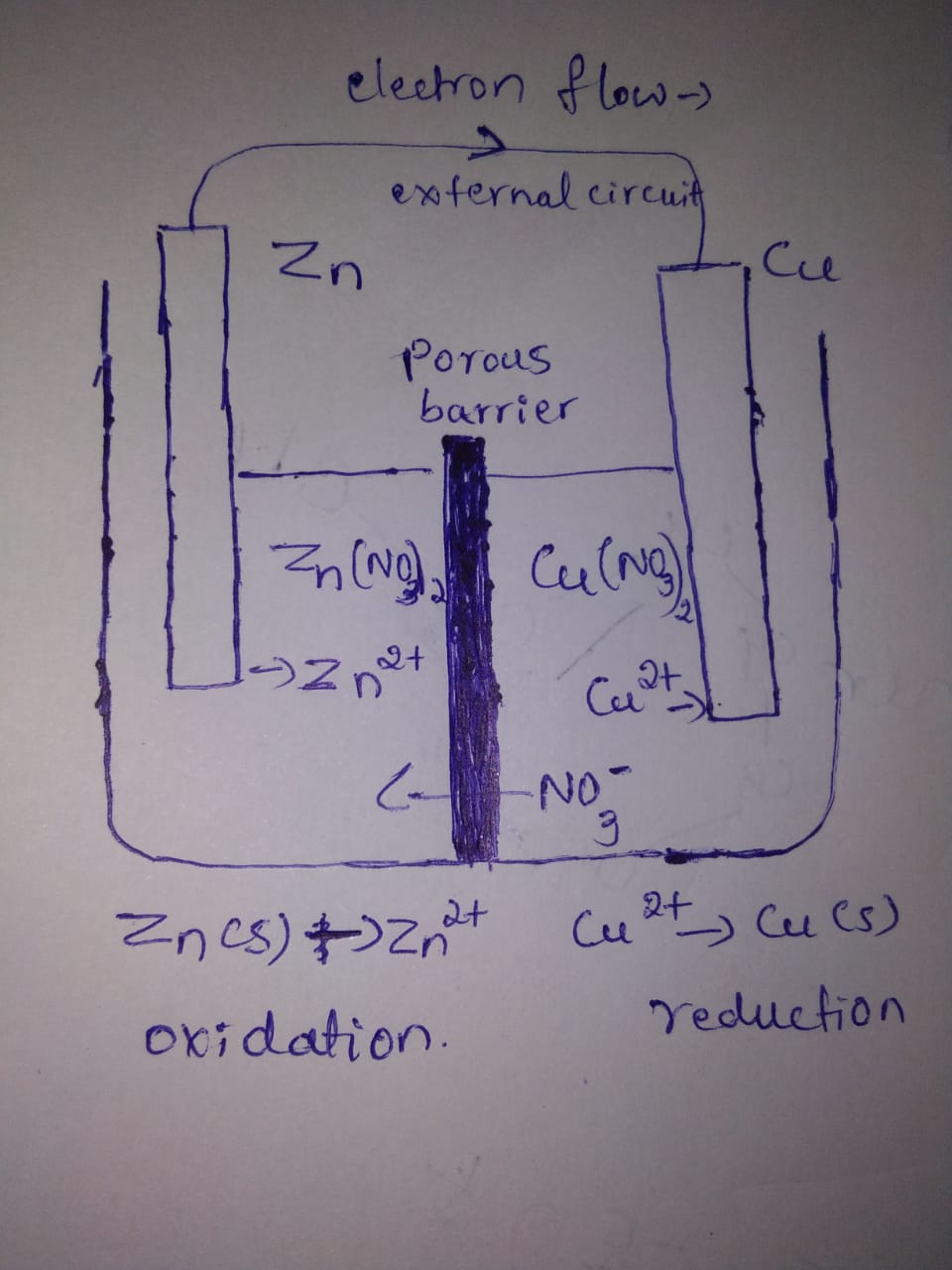
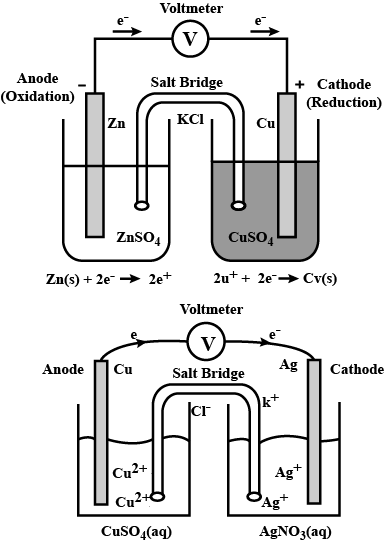
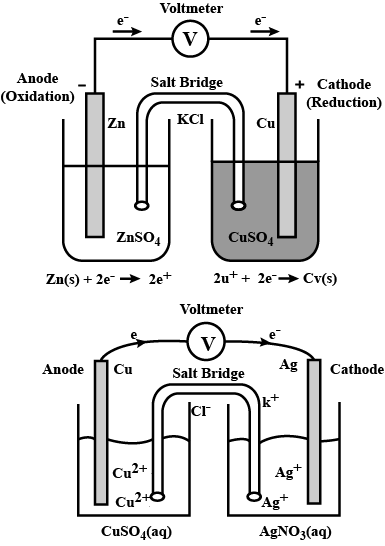
Represent the galvanic cell in which the reaction takes place.
$$Zn(s)+{Cu}^{2+}(aq)\rightarrow {Zn}^{2+}(aq)+Cu(s)$$
Calculate the no.of colombs of electricity, required to deposit
A) $$2.7\times 10^{-4}kg$$ of aluminium
B) $$6.5\times 10^{-5}kg$$ of Zn
Specific charges pf two particles $$A$$ and $$B$$ are in ratio $$2 : 3$$, If their mass ratio $$m_{A};m_{B}$$ is $$2:3
$$, then find ratio of their charges $$\left(\dfrac{q_{A}}{q_{B}}\right)$$ ?
Calculate the number of coulombs required to deposit $$5.4g$$ of $$Al$$, when the electrode reaction is $${Al}^{3+}+3{e}^{-}\rightarrow Al$$
(At.mass of $$Al=27,F=96500$$ coulomb per mole)
Calculate the number of faradays required to electrolyze $$6.35 \,g$$ of $$Cu^{+}(aq)$$ ions from an aqueous solution.
On passing 4 amperes of current for 10min, during electrolysis of acidulated water at STP, what quantity of oxygen in $$dm^3$$ will be liberated?
How many faradays of electricity will be required by $$3\times 10^{12}$$ electrons?
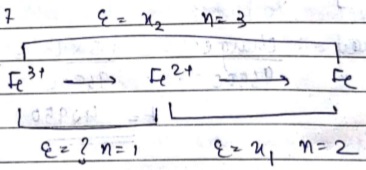
If $$E^{+}_{Fe^{2+}/Fe}$$ is $$x_1$$, $$E^{+}_{Fe^{3+} / Fe}$$ is $$x_2$$ then what will be $$E^+_{Fe^+/Fe^{2+}}$$?
How many minutes are required to deliver $$3.21 \times 10^{6} coulombs$$ using a current of $$500$$ A?. That is used in the commercial production of chlorine.
What weight of Ni is plated out in an electrolysis of aqueous $${ NiSO }_{ 4 }$$ solution that it takes place to deposit 2g of Ag in a silver coulometer that is arranged in series with $${ NiSO }_{ 4 }$$ electrolytic cell.[atomic weight of Ag=107.8 amu,atomic weight of Ni=58.7 amu]
How many coulombs of electricity is required to oxidize one mole of $$Al$$ to $$Al^{3+}$$?
Answer the following.
a. What is done to prevent corrosion of metals?
b. What are the metals that make the alloys brass and bronze?
0.2864g of $$Cu$$ was deposited on passage of a current of 0.5 ampere for 30 minutes through a solution of copper sulphate. What is the electrochemical equivalent of copper?
What is corrosion?
Write the reaction occurring at the cathode and anode in $$ H_2$$ AND $$ O_2$$ fuel cell.
Answer the following :
What are the constituents of Nichrome wire?
Define Corrosion
In the adjacent diagram the electrolytic cell contains $$1L$$ of an aqueous $$1M$$ Copper (II) sulphate solution. If $$0.4$$ mole of electrons are passed through the cell, the molar concentration of copper ion after passing of the charge will be :
Name the process of depositing a layer of zinc on iron. Give two examples of objects on which zinc coating is done.
What special name is given to the corrosion of iron?
How much charge is required for the following reductions?
(i) $$1\ mol$$ of $$Al^{3+}$$ to $$Al$$
(ii) $$1\ mol$$ or $$Cu^{2+}$$ to $$Cu$$
(iii) $$1\ mol$$ of $$MnO^{-}_4$$ to $$Mn^{2+}$$.
Why is ethanol is used as a fuel?
The $$E^{e}$$ $$(M^{2+}/M)$$ value for copperis positive (+0.34V). What is possibly the reason for this ?
What is Primary Battery? Give one example.
Calculate the force of attraction between an electron ans a body having two proton charge when they are $$0.529\times 10^{-8}\ cm$$ apart. Assume charge of one electron and one proton equal to $$-1.6\times 10^{-19}C$$ and $$+1.6\times 10^{-19}C$$ respectively.
Write the cell reaction and calculate the emf of the cell
$$Pt |H_2 (g, 1 atm) | H^+ (0.5 M) || KCl (1 M) |Hg_2Cl_2 (s) | Hg (l) | Pt$$ at $$25^o C, \, E_{} = 0.28 V$$
What are Galvanic cells? Explain the working of Galvanic cells with one example.
Observe the following picture and answer the following question:
What is corrosion ?
A solution of $${ CuSo }_{ 4 }$$ is electrolysed for 10 minutes with a current of 1.5 amperes. What is the mass of copper deposited at the cathode?
How much amount of substance is deposited by passing one Faraday of electricity?
Given the standard electrode potentials :
$$ K^+/K = -2.93 \,V $$, $$ Ag^+ /Ag = 0.80\,V $$ , $$ Hg^{2+} / Hg= 0.79\,V$$ ,
$$ Mg^{2+}/Mg = -2.37\,V $$ , $$ Cr^{3+}/Cr = -0.74\,V $$
Arrange these metals in their increasing order of reducing power.
$$ K^+/K = -2.93 \,V $$, $$ Ag^+ /Ag = 0.80\,V $$ , $$ Hg^{2+} / Hg= 0.79\,V$$ ,
$$ Mg^{2+}/Mg = -2.37\,V $$ , $$ Cr^{3+}/Cr = -0.74\,V $$
Arrange these metals in their increasing order of reducing power.
How many hour are required for a current of $$ 3.0 $$ amperes to decompose $$ 18\,g $$ water.
What would be the effect on the potential of this cell if $$Na_2S$$ were added to the $$Cd^{2+}$$ half cell and CdS were precipitated? Why?
Explain the term "corrosion" with an example.Write a chemical equation to show the process of corrosion of iron.
What does the negative value of $$ E^{\circ}_{cell} $$ indicate ?
What is meant by corrosion ? How corrosion is caused ? How it can be prevented ? What is the effect of corrosion on : (a) copper (b) Silver ?
(a) What is meant by corrosion? Name any two methods used for the prevention of corrosion.
(b) Suppose you have to extract metal M from its enriched sulphide ore. If M is in the middle of the reactivity series, write various steps used extracting this metal.
(b) Suppose you have to extract metal M from its enriched sulphide ore. If M is in the middle of the reactivity series, write various steps used extracting this metal.
Define the following terms
Secondary batteries .
Why is alternating current used for measuring resistance of an electrolytic solution ?
What is the effect of catalyst on:(a) Activation energy (Ea), and(b) Gibbs energy $$ ( \Delta G ) $$
Fill in the blanks:Iron benches kept in lawns and gardens get ___(a)___. It is a ___(b)___ change because a new ___(c)___ is formed.
A bucket made of plastic does not rust like a bucket made of iron. Why?
Write overall cell reaction for lead storage battery when the battery is being charged .
Give reactions taking place at the two electrodes if these are made up of Ag .
Why do copper objects develop a green coating in air?
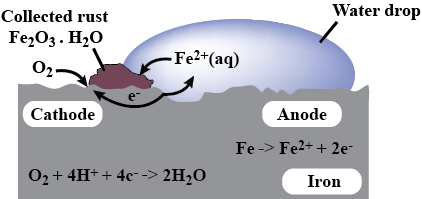
The chemistry of corrosion of iron is essentially an electrochemical phenomenon . Explain the reactions occurring during the corrosion of iron in the atmosphere .
An electric current is passed through a conducting solution. List any three possible observations.
Name the constituents of a cell.
Corrosion can be advantageous in some cases. Explain.
Which metals do not corrode easily?
Explain how the activity series accounts for the following:
Tendency to corrode
State under what conditions corrosion is faster.
What do you observe, when Lead nitrate is heated?
Cell 'A' has $$E_{Cell} = 2V$$ and cell 'B' has $$E_{Cell} = 1.1V$$. Which of the two cells 'A' or 'B' will act as an electrolytic cell. Which electrode reactions will occur in this cell?
Represent an electrochemical cell showing indirect redox reaction between $$Zn$$ and $$ZnSO_{4}+Cu$$ solution
Draw maximum number of Galvanic cell using substances given in the table.
Salt bridge, Zinc rod, Copper rod, Voltmeter, Aluminium chloride, Copper sulphate, Zinc sulphate, Silver nitrate, Silver rod, Calcium chloride
Metals in that electrode in the reactivity series is (in the Top,Bottom)
What is the reason for this?
What is the reason for the change in intensity of the colour of $$CuSO_{4}$$ solution?
Sketch the cell constructed.
Is this reaction oxidation or reduction? Why?
What is the name of this reaction? Why?
$$Zn (s)+2AgNO_3(aq)\to Zn(NO_3)_2 (aq)+2Ag(s)$$
Write the chemical equation for oxidation and reduction.
Complete the equation given below.
Analyse the reactions and answer the following questions:
Explain the oxidation and reductions taking place here including the chemical equation?
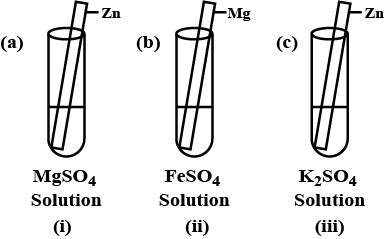
What happened to the $$Zn$$ rod?
Draw maximum number of Galvanic cell using substances given in the table.
Salt bridge, Zinc rod, Copper rod, Voltmeter, Aluminium chloride, Copper sulphate, Zinc sulphate, Silver nitrate, Silver rod, Calcium chloride
Direction of the flow of electron
Draw maximum number of Galvanic cell using substances given in the table.
Salt bridge, Zinc rod, Copper rod, Voltmeter, Aluminium chloride, Copper sulphate, Zinc sulphate, Silver nitrate, Silver rod, Calcium chloride
Write the down the balanced equation taking place in both electrodes.
| Galvanic Cell | Electrode which Gives Electron | Electrode which accept Electron |
Name of some scientists and their contribution are given in the following table. Match them suitably in the chronological order.
Draw maximum number of Galvanic cell using substances given in the table.
Salt bridge, Zinc rod, Copper rod, Voltmeter, Aluminium chloride, Copper sulphate, Zinc sulphate, Silver nitrate, Silver rod, Calcium chloride
(a) Process of accepting electrons is called
How electrical energy is produced by batteries?
Iron is a metal which corrodes fast.
a. What are the factors that favour the corrosion of iron?
b. In coastal regions, copper nails are preferred to iron nails. What could be the reason?
c. Can you suggest some measure to prevent the corrosion of iron?
Complete the figure given below:
What are the components affecting rusting of iron?
The standard reduction potential data at $$25^{\mathrm{o}}\mathrm{C}$$ is given below:
$$\mathrm{E}^{\mathrm{o}} (\mathrm{F}\mathrm{e}^{3+}, \mathrm{F}\mathrm{e}^{2+})=+0.77\mathrm{V}$$;
$$\mathrm{E}^{\mathrm{o}} (\mathrm{F}\mathrm{e}^{2+}, \mathrm{F}\mathrm{e})=-0.44\mathrm{V}$$
$$\mathrm{E}^{\mathrm{o}} (\mathrm{C}\mathrm{u}^{2+}, \mathrm{C}\mathrm{u})=+0.34\mathrm{V}$$
$$\mathrm{E}^{\mathrm{o}} (\mathrm{C}\mathrm{u}^{+}, \mathrm{C}\mathrm{u})=+0.52\mathrm{V}$$
$$\mathrm{E}^{\mathrm{o}}[\mathrm{O}_{2}(\mathrm{g})+4\mathrm{H}^{+}+4\mathrm{e}^{-}\rightarrow 2\mathrm{H}_{2}\mathrm{0}]=+1.23\mathrm{V}$$;
$$\mathrm{E}^{\mathrm{o}}[\mathrm{O}_{2}(\mathrm{g})+2\mathrm{H}_{2}\mathrm{O}+4\mathrm{e}^{-}\rightarrow 4\mathrm{0}\mathrm{H}^{-}]=+0.40\mathrm{V}$$
$$\mathrm{E}^{\mathrm{o}} (\mathrm{C}\mathrm{r}^{3+}, \mathrm{C}\mathrm{r})=-0.74\mathrm{V}$$;
$$\mathrm{E}^{\mathrm{o}} (\mathrm{C}\mathrm{r}^{2+}, \mathrm{C}\mathrm{r})=-0.91\mathrm{V}$$Match $$\mathrm{E}^{0}$$ of the redox pair in List 1 with the values given in List 2 and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists.
$$\mathrm{E}^{\mathrm{o}} (\mathrm{F}\mathrm{e}^{3+}, \mathrm{F}\mathrm{e}^{2+})=+0.77\mathrm{V}$$;
$$\mathrm{E}^{\mathrm{o}} (\mathrm{F}\mathrm{e}^{2+}, \mathrm{F}\mathrm{e})=-0.44\mathrm{V}$$
$$\mathrm{E}^{\mathrm{o}} (\mathrm{C}\mathrm{u}^{2+}, \mathrm{C}\mathrm{u})=+0.34\mathrm{V}$$
$$\mathrm{E}^{\mathrm{o}} (\mathrm{C}\mathrm{u}^{+}, \mathrm{C}\mathrm{u})=+0.52\mathrm{V}$$
$$\mathrm{E}^{\mathrm{o}}[\mathrm{O}_{2}(\mathrm{g})+4\mathrm{H}^{+}+4\mathrm{e}^{-}\rightarrow 2\mathrm{H}_{2}\mathrm{0}]=+1.23\mathrm{V}$$;
$$\mathrm{E}^{\mathrm{o}}[\mathrm{O}_{2}(\mathrm{g})+2\mathrm{H}_{2}\mathrm{O}+4\mathrm{e}^{-}\rightarrow 4\mathrm{0}\mathrm{H}^{-}]=+0.40\mathrm{V}$$
$$\mathrm{E}^{\mathrm{o}} (\mathrm{C}\mathrm{r}^{3+}, \mathrm{C}\mathrm{r})=-0.74\mathrm{V}$$;
$$\mathrm{E}^{\mathrm{o}} (\mathrm{C}\mathrm{r}^{2+}, \mathrm{C}\mathrm{r})=-0.91\mathrm{V}$$
Match $$\mathrm{E}^{0}$$ of the redox pair in List 1 with the values given in List 2 and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists.
An aqueous solution of X is added slowly to an aqueous solution of Y as shown in List The variation in conductivity of these reactions is given in List Match List 1 with List 2 and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
Match the columns.
Calculate the value of $$E^o$$ (in V, upto two decimal points) from the given figure and report your answer as $$100\times E^o$$.
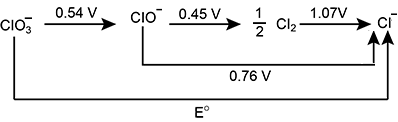
The redox reaction involving the reducing power of hydrogen sulphide is:
$$\quad S + 2H^+ + 2e^- \rightarrow H_2S, \quad E^{\small\circ}_{S/H_2S} = + 0.14V$$
Two other half equations are:
$$\quad Fe^{3+} + e^- \rightarrow Fe^{2+} \quad E^{\small\circ}_{Fe^{3+}/Fe^{2+}} = +0.77 V$$
$$\quad Br_2 + 2e^- \rightarrow 2Br^- \quad E^{\small\circ}_{Br_2/Br^-} = 1.07 V$$
Under standard conditions, hydrogen sulphide reacts with iron $$(III)$$ ions. If this statement is true enter 1, else enter 0.
How many faraday's are required for the reduction of $$1\space mol\space C_6H_5NO_2$$ into $$C_6H_5NH_2$$?
E.M.F. diagram for some ions is given as:
$$\displaystyle FeO_4^{2-} \xrightarrow{E^o = +2.20 V} Fe^{3+} \xrightarrow{E^o= 0.77 V} Fe^{2+} Fe^{2+} \xrightarrow{E^o= 0.445 V} Fe^0$$
The value of $$\displaystyle E^o_{FeO_4^{2-}/ Fe^{2+}}$$ is _________(as nearest integer).
$$\displaystyle FeO_4^{2-} \xrightarrow{E^o = +2.20 V} Fe^{3+} \xrightarrow{E^o= 0.77 V} Fe^{2+} Fe^{2+} \xrightarrow{E^o= 0.445 V} Fe^0$$
The value of $$\displaystyle E^o_{FeO_4^{2-}/ Fe^{2+}}$$ is _________(as nearest integer).
In the manufacture of $$Al,\ Al$$$$_2$$O$$_3$$ is dissolved in $$Na$$$$_3$$$$AlF$$$$_6$$ at $$300 K$$ and electrolysed between $$Al$$ and carbon electrodes following the net reaction,
$$2 Al_2O_3 (solution) + 3C \rightarrow 4 Al(l) + 3 CO_2 (g)$$
The minimum voltage required between the electrodes if the Gibbs energy change for the above reaction is $$-1370$$ $$kJ mol$$$$^{-1}$$ is________. (write nearest integer)
The standard electrode potential in V for the electrode $$MnO^-_4 / MnO_2$$ in solution is: (round off the answer to the nearest integer)
Given: $$E^o_{MnO^-_4 / Mn^{2+}} = 1.51 V$$ and $$E^o_{MnO_2 / Mn^{2+}} = 1.23 V$$
How much current is required to produce $$Cl_{2}(g)$$ at the rate of $$10^{-3}\, L\, s^{-1}$$ electrolysis of molten KCl? (in A)
All the energy released from the reaction $$\displaystyle X\rightarrow Y,\ \Delta_{r} G^{\circ}=-193\ kJ . mol^{-1}$$ is used for oxidizing $$\displaystyle M^{+}$$ as $$\displaystyle M^{+}\rightarrow M^{3+}+2e^{-}, E^{\circ}=-0.25V.$$
Under standard conditions, the number of moles of $$\displaystyle M^{+}$$ oxidized when one mole of X is converted to Y is:
$$\displaystyle \left [ F=96500\ C mol^{-1} \right ]$$
The resistance of a conductivity cell containing $$0.001M\ KCl$$ solution at $$298\ K$$ is $$1500 \Omega$$. What is the cell constant if conductivity of $$0.001M\ KCl$$ solution at $$298\ K$$ is $$0.146 \times 10^{-3} S\ cm^{-1}$$?
Depict the galvanic cell in which the reaction $$Zn(s) + 2Ag^{+} (aq) \rightarrow Zn^{2+}(aq) + 2Ag(s)$$ takes place. Further show:
(i) Which of the electrode is negatively charged?
(ii) The carriers of the current in the cell.
(iii) Individual reaction at each electrode.
Using the standard electrode potentials given in Table $$3.1$$, predict if the reaction between the following is feasible:
(i) $$Fe^{3+}(aq)$$ and $$I^{-}(aq)$$
(ii) $$Ag^{+} (aq)$$ and $$Cu(s)$$
(iii) $$Fe^{3+} (aq)$$ and $$Br^{-} (aq)$$
(iv) $$Ag(s)$$ and $$Fe^{3+} (aq)$$
(v) $$Br_{2} (aq)$$ and $$Fe^{2+} (aq)$$
Predict the products of electrolysis in each of the following:
(i) An aqueous solution of $$AgNO_{3}$$ with silver electrodes.
(ii) An aqueous solution of $$AgNO_{3}$$ with platinum electrodes.
(iii) A dilute solution of $$H_{2}SO_{4}$$ with platinum electrodes.
(iv) An aqueous solution of $$CuCl_{2}$$ with platinum electrodes
Arrange the following metals in the order in which they displace each other from the solution of their salts.
$$Al, Cu, Fe, Mg$$ and $$Zn$$
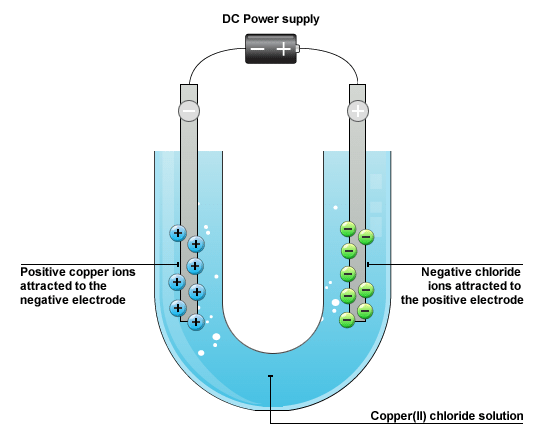
Draw the diagram of an electrolytic cell of copper chloride solution.
Iron rod is immersed in $$KClKCl$$ solution such that half its length is exposed to air and the other half immersed in $$KClKCl$$ solution. The part corroded faster is
Give reasons:
On the basis of $$E^o$$ values, $$O_2$$ gas should be liberated at anode but it is $$Cl_2$$ gas which is liberated in the electrolysis of aqueous NaCl.
$$V_1$$ L of solution A (resistance 500ohm) is mixed with $$V_2$$ L of solution B (Resistance 100ohm) resistance of final solution is 80 then $$V_2$$/$$V_1$$ :
How much $$O_2$$ gas will be collected at the anode at $$300$$K temperature and $$1$$ bas pressure if $$2.5$$ ampere electric current is passed for one hour in electrolysis of aqueous solution of $$Na_2SO_4$$. (F$$=96500$$ Coulomb) [$$1$$ mole gas volume is $$22.4$$ litre at STP].
How will you show that air and moisture both are required for rusting of iron?
If for the half-cell reactions
$${ Cu }^{ 2+ }+{ e }^{ - }\longrightarrow Cu^{ + }\quad { E }^{ o }=0.15\ V$$
$${ Cu }^{ 2+ }+2{ e }^{ - }\longrightarrow Cu\quad \quad { E }^{ o }=0.34\ V$$
Calculate $${ E }^{ o }$$ of the half cell reaction $${ Cu }^{ + }+{ e }^{ - }\longrightarrow Cu$$
Also predict whether $${ Cu }^{ + }$$ undergoes disproportionation or not.
Why do silver articles become black after sometime when exposed to air?
The voltage of a cell whose half cell reactions are given below is:
$${Mg}^{2+}+2{e}^{-}\rightarrow Mg(s);E=-2.37V$$
$${Cu}^{2+}+2{e}^{-}\rightarrow Cu(s); E=+0.34V$$
Can absolute electrode potential of an electrode is measured ?
Ammonium perchlorate $${NH}_{4}{ClO}_{4}$$, used in the solid fuel in the booster rockets on the space shuttle , is prepared of sodium perchlorate, $${NaClO}_{4}$$ which is produced commerically by the electrolysis of a hot, stirred solution of sodium chloride. How many Faradays are required to produce. $$1.0kg$$ of sodium perchlorate ?
$$NaCl+4{H}_{2}O\longrightarrow {NaClO}_{4}+{4H}_{2}$$
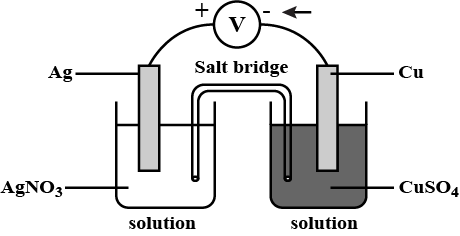
Consider a cell given below:
$$Cu| Cu^{2+} || Cl^- | Cl_2, Pt$$
Write the reactions that occur at anode and cathode.
Give reasons for the following :
In the preparation of hydrogen by electrolysis of water - the distilled water used is acidified.
* Reaction in Fuel cell
(a) At cathode :
$$O_{2(g)}+2H_2O(I)+4e^- \rightarrow 4OH^-_{(aq)} $$
(b) Reaction at anode :
$$ 2H_{2(g)}+4OH^-_{(aq)} \rightarrow 4H_2O_{(I)}+4e^- $$
What is the relationship between Gibbs free energy of the cell reaction in a galvanic cell and the emf of the cell? When will the maximum work be obtained from a galvanic cell?
Why does the conductivity of a solution decreases with dilution?
Find the charge required to flow through an electrolyte to liberate one atom of (a) a monovalent material and (b) a divalent material.
The electrode reaction for charging of a lead storage battery are:
$$ PbSO_{4}+2e\rightarrow Pb+SO_{4}^{2-}$$
$$ PbSO_{4}+2H_{2}O\rightarrow PbO_{2}+SO_{4}^{2-}+4H^{+}+2e $$
The electrolyte in the battery is an aqueous solution of sulphuric acid. Before charging, the specific gravity of the liquid was found to be 1.10 (16% $$H_{2}SO_{4}$$ by wt.) After charging for $$ \dfrac{965}{9}$$ h, the specific gravity of the liquid was found to be 1.42 (40% $$ H_{2}SO_{4}$$ by weight). If the battery contained 2 L of the liquid and the volume remains constant during charge, the average current (in A) used charging the battery is
Calculate the reduction potentials for the following half cells:
(i) $$Ag|{ Ag }^{ + }\left( { 10 }^{ -5 }M \right) ;{ E }_{ { Ag }^{ + },Ag }^{ o }=0.80V$$
(ii) $$Cu|{ Cu }^{ 2+ }(0.2M);{ E }_{ { Cu }^{ 2+ },Cu }^{ o }=0.34V$$
The water is electrolysed in a cell , hydrogen is liberated at one electrode and oxygen is simultaneously liberated at the other . in a particular experiment hydrogen and oxygen so produced were collected together and the total volume measured 16.8 mL at NTP . How many coulombs were passed through the cell in the experiment ?
From the electrochemical series given in the text, determine the approximate value of $${E}^{o}$$ for $${ X }^{ 2+ }(aq)+2e\longrightarrow X(s)$$
(a) The metal $$X$$ dissolves in nitric acid but not in hydrochloric acid. It can displace $${Ag}^{+}$$ but not $${Cu}^{2+}$$
(b) The metal $$X$$ dissolves in hydrochloric acid producing $${H}_{2}$$ but does not displace either $${Zn}^{2+}$$ or $${Fe}^{2+}$$
Find the amount of silver liberated at cathode if $$0.500 A $$ of current is passed through $$AgNO_3$$ electrolyte for $$1$$ hour. Atomic weight of silver is $$107.9\,g\,mol^{-1}$$
Calculate the potential of a silver electrode in a saturated solution of $$AgBr\left( { K }_{ sp }=6\times { 10 }^{ -13 } \right) $$ containing, in addition, $$0.1$$ mole per $$KBr$$.
$${ E }_{ { Ag }^{ + },Ag }^{ o }=0.80volt$$
A $$Cu$$ rod is dipped in a $$0.1M$$ $$Cu{SO}_{4}$$ solution. Calculate the potential of this half cell if $$Cu{SO}_{4}$$ undergoes 90% dissociation at this dilution at $${25}^{o}C$$.
$${ E }_{ Cu|{ Cu }^{ 2+ } }^{ o }=-0.34V$$
What happens when?
Concentrated solution of $$NH_4HSO_4$$ in $$H_2SO_4$$ is electrolysed using current of high density.
Calculate the electrode potential for $$\underset{(1 atm)}{(Pt)|H_2}|H^+(c=0.1 M)$$.
Define and give an example of Half-Cell.
Consider the electrochemical cell represented by
$$Mg|{ Mg }^{ 2+ }\parallel { Fe }^{ 3+ }|{ Fe }^{ 2+ }$$
If $$150mA$$ is to be drawn from this cell for a period of $$20$$ minutes, what is the minimum mass for the magnesium electrode?
During an electrochemical experiment, $$0.2773$$ g of Ag was transferred from one electrode to the other electrode in a coulometer. What electric charge did pass through the circuit?
Consider an electrochemical cell, $$A(s)|{ A }^{ n+ }(aq,2M)\parallel { B }^{ 2n+ }(aq,1M)|B(s).$$ The value of $$\Delta {H}^{o}$$ for the cell reaction is twice that of $$\Delta {G}^{o}$$ at $$300K$$. If the emf of the cell is zero, the $$\Delta {S}^{o}$$ (in $$J{ K }^{ -1 }\ { mol }^{ -1 }$$) of the cell reaction per mole of $$B$$ formed at $$300K$$ is ________.
(Given: $$\ln { (2) } =0.7,R=8.3J{ K }^{ -1 }\ { mol }^{ -1 }.\ H,\ S,\ G$$ are enthalpy, entropy and Gibbs energy, resepctively)
Does the physical size of a galvanic cell govern the potential that it will deliver? What does the size affect?
If in a galvanic cell, say, Daniell cell, inert platinum is used instead of a salt bridge, will the cell still produce a potential.
What is the meaning of a positive sign for a half-cell potential?
Write the half reactions and number of moles of electrons involved in the oveall cell reaction for the electrochemical cell designated by
$$Pt|Ag(s)|AgCl(s)|Cl^-(c=1)|Cl_2(c=1)|C$$ (graphite)$$|Pt$$.
Write electrode reactions taking place in Lead Acid Accumulator .
What does the negative sign in the expression $$ E^{\circ}_{Zn^{2+} / Zn} = -0.76 \, V $$ mean ?
Two half-reaction of an electrochemical cell are given below :
$$ MnO_{4}^{-} (aq) + 8H^+ + 5e^- \rightarrow Mn^{2+} (aq) + 4H_2O (l) ; E^{\circ} = +1.51\,V $$
$$ Sn^{2+} (aq) \rightarrow Sn^{4+}(aq) + 2e^- , E^{\circ} = +0.15\,V $$
Construct the redox equation from the standard potential of the cell and predict if the reaction is reactant favoured or product favoured .
What is primary cell ? Give an example .
Answer the following questions
Calculate the standard free energy change for the following reaction at $$ 25^{\circ}\,C $$.
$$ Au(s) + Ca^{2+} (1 \, M) \rightarrow Au^{3+}(1\,M) + Ca(s) $$
$$ E^{o}_{Au^{3+} / Au} = + 1.50 \,V , E^{o}_{Ca^{2+} / Ca} = - 2.87\,V $$
Predict whether the reaction will be spontaneous or not at $$ 25^{\circ}\,C $$ . Which of the above two half cells will act as an oxidizing agent and which one will be a reducing agent ?
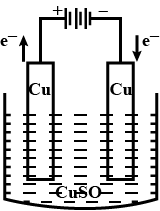
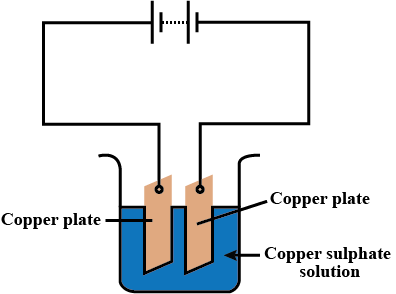
In the circuit given in the above figure, Boojho observed that copper is deposited on the electrode connected to the negative terminal of the battery. Paheli tried to repeat the same experiment. But she could find only one copper plate. Therefore she took a carbon rod as negative electrode. Will copper be still deposited on the carbon rod? Explain.
What advantage do the fuel cells have over primary and secondary batteries?
Answer the following questions:
Define the electro chemical cell. What happens if external potential applied becomes greater than $$ E^{0}_{cell} $$ of electrochemical cell?
Define the electro chemical cell. What happens if external potential applied becomes greater than $$ E^{0}_{cell} $$ of electrochemical cell?
Tarnished silver contains $$ Ag_2S $$ . can this tarnish be removed by placing tarnished silver were in an aluminium pan containing an inert electrolytic solution such as $$ NaCl $$? The standard electrode potential for half reaction :
$$ Ag_2S (s) + 2e^- \rightarrow 2Ag(s) + S^{2-} $$ is $$ -0.71\, V $$
and for $$ Al^{3+} + 3e^- \rightarrow aAl (s) $$ is $$ -1.66\,V $$
Redraw the diagram to show the direction of electron flow.
Answer the following questions
A current of $$ 1.50 \,A $$ was passed through an electrolytic cell containing $$ AgNO_3 $$ solution with inert electrodes . The weight of $$ Ag $$ deposited was $$ 1.50\,g $$ . How long did the current flow ?
Give reasons:
Silver articles when exposed to air gradually turn blackish.
What are the adverse effects of corrosion?
Draw the diagram of the Apparatus used in electroplating and label the following parts:
The substance to be electroplated.
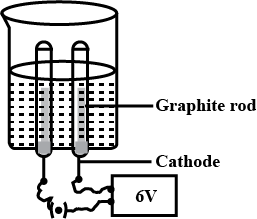
Draw the diagram of the apparatus used in the electrolysis of water. Label the following parts:
(i) Graphite rod
(ii) Cathode
What is electrolysis ?
When will the cell stop functioning?
The flow of electrons in certain galvanic cells are given below:
i) $$Cu \to Ag$$
ii) $$Ag\to Zn$$
iii) $$Na\to Mg$$
iv) $$Fe\to K$$
Choose the incorrect ones.
Write the equations of the oxidation and reduction reactions.
What are the changes that can be observed with the iron rod and the colour of copper sulphate solution ?
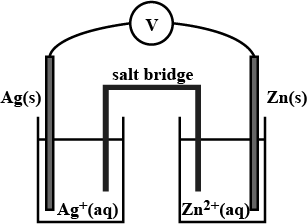
You are given a solution of $$AgNO_3$$, a solution of $$MgSO_4$$, a $$Ag$$ and a $$Mg$$ ribbon. How can you arrange a Galvanic cell using these? Write down the reactions taking place at the cathode and the anode.
Draw maximum number of Galvanic cell using substances given in the table.
Salt bridge, Zinc rod, Copper rod, Voltmeter, Aluminium chloride, Copper sulphate, Zinc sulphate, Silver nitrate, Silver rod, Calcium chloride
Write down the general names used for an electrode which gives electrons.
Draw maximum number of Galvanic cell using substances given in the table.
Salt bridge, Zinc rod, Copper rod, Voltmeter, Aluminium chloride, Copper sulphate, Zinc sulphate, Silver nitrate, Silver rod, Calcium chloride
Complete the table based on the figure drawn.
| Galvanic Cell | Electrode which Gives Electron | Electrode which Gain Electron |
Certain metals are given below:
$$Ag, Zn, Pb, Sn, Fe$$
When a galvanic cell is constructed using these metals, which one acts only as anode? Give the reason.
Explain how rusting of iron is considered as setting up of an electrochemical cell.
Take Cupric Chloride $$(CuCl_2)$$ solution in a beaker. Dip two graphite rod in it. Pass $$5V$$ electricity through it.
Why does electricity pass through a Cupric Chloride solution?
Why does electricity pass through a Cupric Chloride solution?
Take Cupric Chloride $$(CuCl_2)$$ solution in a beaker. Dip two graphite rod in it. Pass $$5V$$ electricity through it.
Write one word for the process of chemical change happening in a Electrolyte while passing Electricity?
Write one word for the process of chemical change happening in a Electrolyte while passing Electricity?
Take Cupric Chloride $$(CuCl_2)$$ solution in a beaker. Dip two graphite rod in it. Pass $$5V$$ electricity through it.
Which gas evolved out through a positive electrode? How did you identify that gas?
Take Cupric Chloride $$(CuCl_2)$$ solution in a beaker. Dip two graphite rod in it. Pass $$5V$$ electricity through it.
At which electrode oxidation and reduction take place?
Class 12 Engineering Chemistry Extra Questions
- Alcohols,Phenols And Ethers Extra Questions
- Aldehydes,Ketones And Carboxylic Acids Extra Questions
- Amines Extra Questions
- Biomolecules Extra Questions
- Chemical Kinetics Extra Questions
- Chemistry In Everyday Life Extra Questions
- Coordination Compounds Extra Questions
- Electrochemistry Extra Questions
- General Principles And Processes Of Isolation Of Elements Extra Questions
- Haloalkanes And Haloarenes Extra Questions
- Polymers Extra Questions
- Solutions Extra Questions
- Surface Chemistry Extra Questions
- The D-And F-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The P-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The Solid State Extra Questions