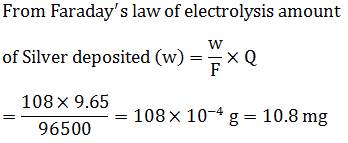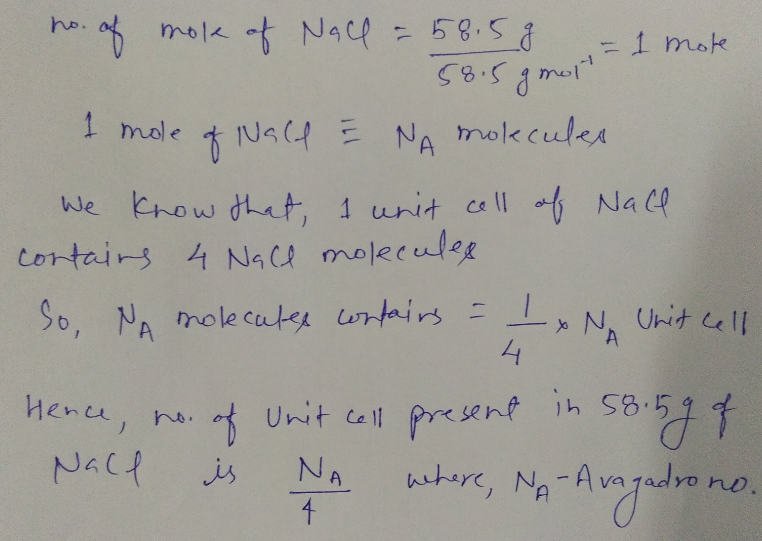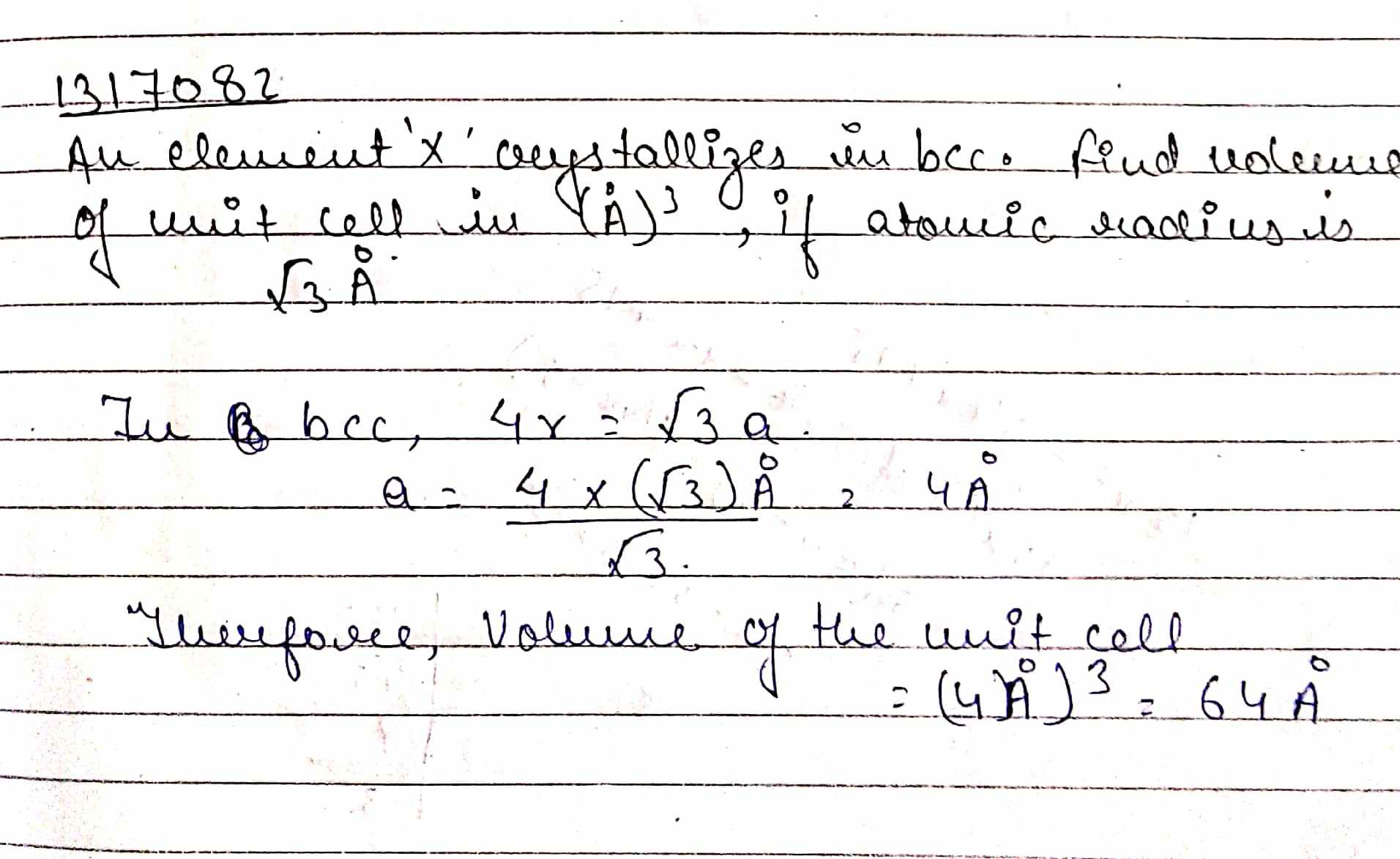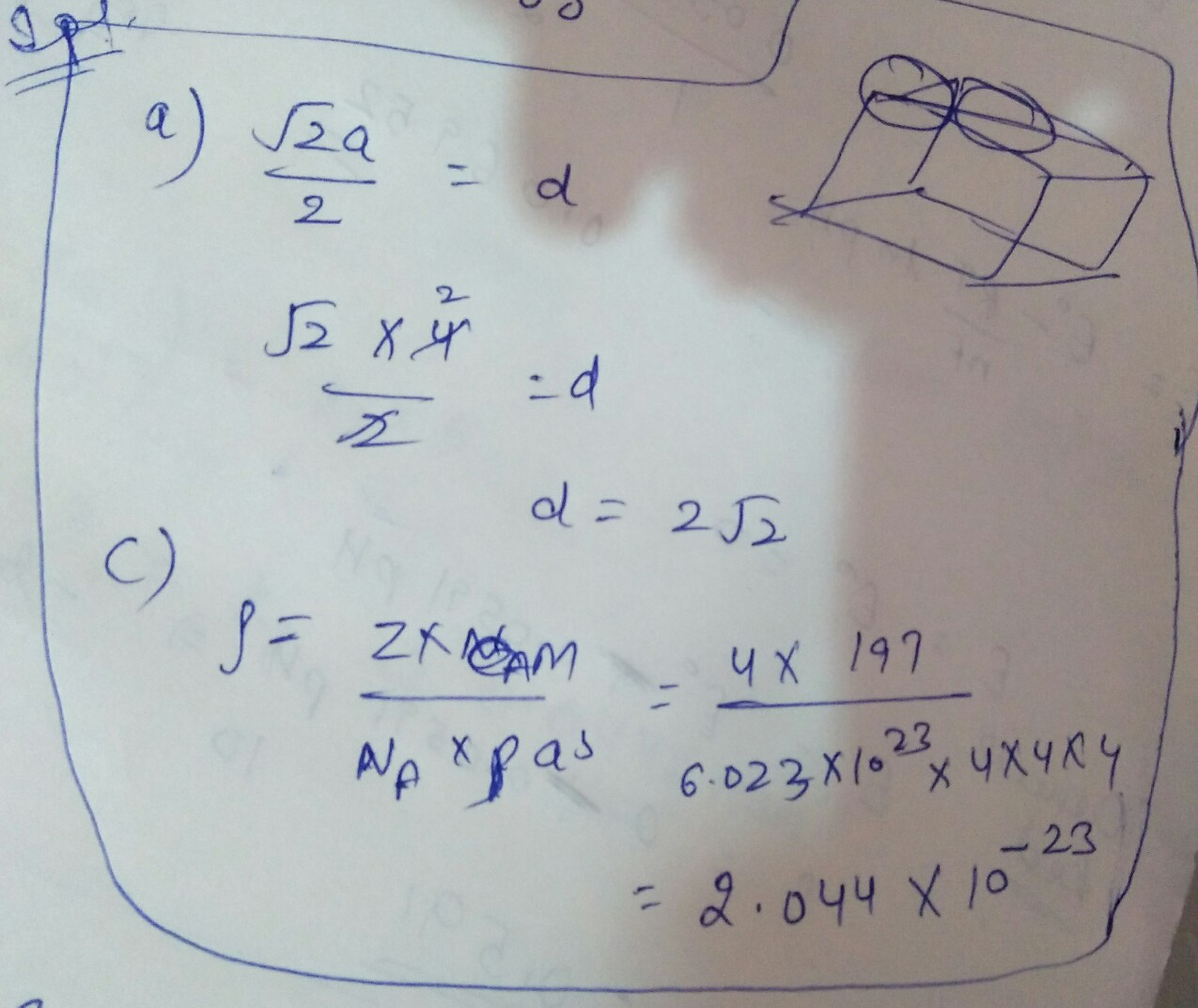The Solid State - Class 12 Engineering Chemistry - Extra Questions
(i) Write the type of magnetism observed when the magnetic moment are oppositely aligned and cancel out each other?
(ii) Which stoichiometric defect does not change the density of the crystal?
(i) Write the type of magnetism observed when the magnetic moment are aligned in parallel and anti-parallel directions in unequal numbers?
(ii) Which stoichiometric defect decreases the density of the crystal?
When 9.65 C of electricity is passed through a solution of silver nitrate (atomic mass of Ag =108 g $$mol^{-1}$$) , the amount of silver deposited is
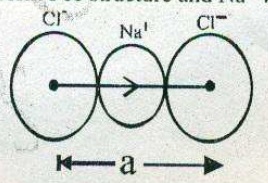
A unit cell of iron crystal has edge length $$288$$ pm and density$$7.86 g cm^{-3}$$. Find the number of atoms per unit cell and type of the crystal lattice.
Given: Molar mass of iron = $$56 g mol^{-1}$$, Avogadro's number $$N_A= 6.022\times 10^{23}mol^{-1}$$
What is the crystallograph dimension of monoclinic unit cell?
Lattice paths are paths consisting of one unit steps in the positive horizontal or positive vertical directions. Let distinct lattice paths from the point $$(-1,0)$$ to the point $$(3, 5)$$, if number of shortest path are $$\lambda$$. Let $$\mu$$ be the sum of all digits of $$\lambda$$. Then find the value of $$\mu$$.
Zinc sulphide crystallises with zinc ions occupying half of the tetrahedral holes in a closed packed array of sulphide ions. What is the formula of zinc sulphide?
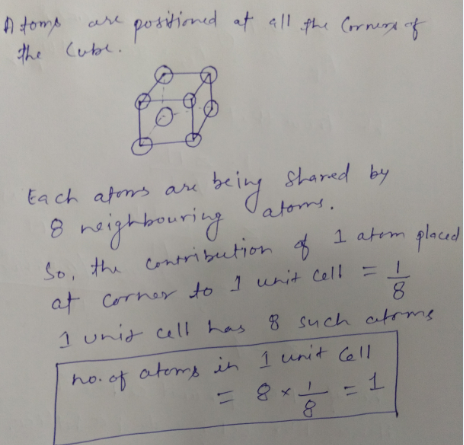
When atoms are placed at all the 8 corners of the cube, how many atoms are present per unit cell?
In $$CaF_2$$ unit cell the co ordination number of $${ F }^{ - }$$ ion is?
The density of iron crystal is 8.54 g $$cm^{-3}$$. If the edge length of unit cell is 2.8 Å and atomic mass is 56 g $$mol^{-1}$$. Find the no. of atoms in the unit cell. (given: Avagadro's number = $$6.022\times 10^{23}, 1 A=1\times 10^{-8}cm)$$
The density of $$KBr$$ is $$2.75g\ cm^{-3}$$. The length of edge of unit cell is $$6.54\ $$Å$$ $$. Predict the type of cubic lattice to which unit cell of $$KBr$$ belongs. (Atomic mass $$K=39, Br=80$$)
Calculate no. of unit cell present $$58.5\ g$$ of $$NaCl$$.
Define the term (a) unit cell (b) space lattice?
Match the Bravais lattices with their crystal systems.
Out of seven possible crystal systems, the number of crystal systems having more than one Bravais lattice is ______.
In cubic system, how many arrangement of atoms exist in nature?
The type of lattice represented by this compound is simple cubic.
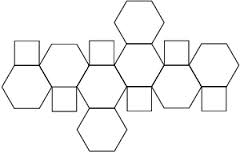
Find the number of hexagonal faces that are present in a truncated octahedral.
A cubic structure of uniform spheres has the unit cell edge length of 0.8 mm. If the radius of the molecule in a simple cubic lattice is $$40\times10^{-x}$$, then what is the value of x?
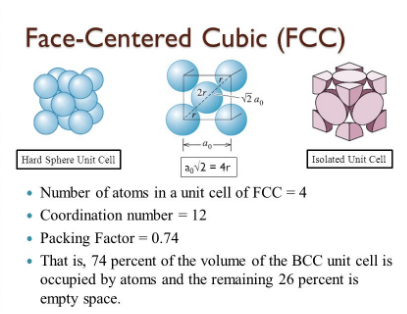
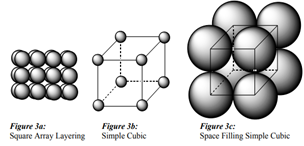
Calculate the efficiency of packing in case of a metal crystal for the following crystal structure (with the assumptions that atoms are touching each other):
(i) simple cubic
(ii) body-centered cubic
(iii) face-centered cubic
(i) simple cubic
(ii) body-centered cubic
(iii) face-centered cubic
Copper crystallises into a fcc lattice with edge length $$3.61 \times 10^{-8} cm$$. Show that the calculated density is in agreement with its measured value of $$8.92\ g\ cm^{3}$$.
Explain the following terms with suitable examples:
(i) Schottky defect (ii) Frenkel defect (iii) Interstitials and (iv) F-centres
Define the term 'amorphous'. Give a few examples of amorphous solids.
What makes a glass different from a solid such as quartz? Under what conditions could quartz be converted into glass?
(i) What type of non-stoichiometric point defect is responsible for the pink colour of $$LiCl$$?
(ii) What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by $$NaCl$$ ?
(i) What type of non - stoichiometric point defect is responsible for the pink color of $$LiCl$$?
(ii) What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by $$NaCl$$?
OR
How will you distinguish between the following pairs of terms:
(i) Tetrahedral and octahedral voids
(ii) Crystal lattice and unit cell
What type of point defect is produced when $$AgCl$$ is doped with $$CdCl_{2}$$?
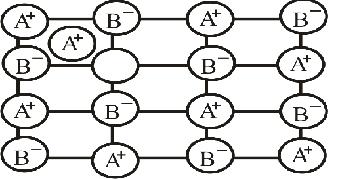
Examine the given defective crystal.
$$\begin{matrix} { A }^{ + } & { B }^{ - } & { A }^{ + } & { B }^{ - } & { A }^{ + } \\ { B }^{ - } & O & { B }^{ - } & { A }^{ + } & { B }^{ - } \\ { A }^{ + } & { B }^{ - } & { A }^{ + } & O & { A }^{ + } \\ { B }^{ - } & { A }^{ + } & { B }^{ - } & { A }^{ + } & { B }^{ - } \end{matrix}$$
Answer the following questions:
(i) What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by crystal?
(ii) How is the density of the crystal affected by this defect?
(iii) What type of ionic substances show such defect?
Examine the given defective crystal.
$$\displaystyle \begin{matrix}X^{+} & Y^{-} & X^{+} & Y^{-} &X^{+} \\ Y^{-} & O &Y^{-} & X^{+} & Y^{-}\\ X^{+}& Y^{-} & X^{+} & O & X^{+} \\ Y^{-}& X^{+} & Y^{-} & X^{+} & Y^{-}\end{matrix}$$
Answer the following questions :
(i) Is the above defect stoichiometric or non-stoichiometric?
(ii) Write the term used for this type of defect. Give an example of the compound which shows this type of defect?
(iii) How does this defect affect the density of the crystal?
$$\displaystyle \begin{matrix}X^{+} & Y^{-} & X^{+} & Y^{-} &X^{+} \\ Y^{-} & O &Y^{-} & X^{+} & Y^{-}\\ X^{+}& Y^{-} & X^{+} & O & X^{+} \\ Y^{-}& X^{+} & Y^{-} & X^{+} & Y^{-}\end{matrix}$$
Answer the following questions :
(i) Is the above defect stoichiometric or non-stoichiometric?
(ii) Write the term used for this type of defect. Give an example of the compound which shows this type of defect?
(iii) How does this defect affect the density of the crystal?
An element crystallizes in a f.c.c. lattice with a cell edge of 250 pm. Calculate the density, if 300 g of this element contain $$2 \times {10}^{24}$$ atoms.
For a crystal of diamond, state the hybridization of the carbon atom.
Distinguish between crystalline solid and amorphous solid?
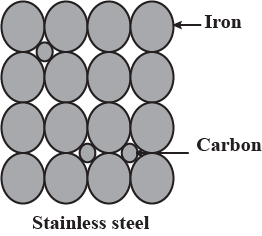
Explain impurity defect in stainless steel with diagram.
For a crystal of diamond, state the type of lattice in which it crystallizes.
On the basis of nature of ionic solids compare Frenkel defect with Schottky defect :
Name the crystal structure of the copper metal.
Calculate the packing efficiency in a Body Centered Cubic (BCC) lattice?
(a) Explain Schottky defect and Frenkel defect.
(b) Write briefly the adsorption theory of catalysis.
Sliver forms a ccp lattice. The edge length of its unit cell is 408.6 pm. Calculate the density of sliver?$$(N_A=6.022\times 10^{23}$$, Atomic mass of $$Ag=108 \,gmol^{-1})$$
a) Calculate the packing efficiency in a unit cell of Cubic Close Packing (CCP) structure?
b) Name the crystal defect which lowers the density in an ionic crystal?
(a) Write about the most common point defects.
Explain Schottky and Frenkel defects in solids.
Explain Schottky and Frenkel defects.
The figures given below show the location of atoms in three crystallographic planes in a fcc lattice. Draw the unit cell for the corresponding structure and identify these planes in your diagram.
A unit cell of sodium chloride has four formula units. The edge length of unit cell is $$0.564\ nm$$. What is the density of sodium chloride?
Match the List-I with List-II and List-III:
| List-I (Solids) | List-II (Unit cell) | List-III (Coordination number) |
| (a) Rock salt | (p) Face-centred cubic, anion in tetrahedral void | (w) 6 |
| (b) Fluorite | (q) Face-centred cubic, cation in octahedral void | (x) Cation (8), anion (4) |
| (c) Agl, ZnS | (r) Face-centred cubic, cation in alternate tetrahedral void | (y) Cation (4), anion (8) |
| (d) $$Na_2O$$ | (s) Face-centred cubic, cation in tetrahedral void | (z) Cation (4), anion (4) |
Lead sulphide has face centered cubic crystal structure. If the edge length of the unit cell of lead sulphide is $$495 pm$$, calculate the density of the crystal. (atomic weight $$Pb=207, S=32$$)
A crystal of lead(II) sulphide has $$NaCl$$ structure. In this crystal the shortest distance between $$ Pb^{+2}$$ ion and $$ S^{2-} $$ ion is 297 pm. What is the length of the edge of the unit cell in lead sulphide? Also calculate the unit cell volume.
Distinguish between crystaline solids and amorphous solid.
A cubic unit cell contains manganese ions at the corners and fluorides ions at the center of each edge. Calculate the density of the compound. (Given that atomic mass $$Mn=55$$amu and F is $$19$$amu).
Determine the density of cesium chloride which cystallises in a bcc type structure with the edge length $$412.1 pm. $$ The atomic masses of $$Cs$$ and $$Cl$$ are 133 and $$35.5$$ respectively.
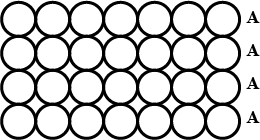
Explain with the help of neat diagram $$AAAA$$ type of three.
Write the value of axial distance and axial angles of triclinic crystal.
Give any one difference between anisotropy and isotropy nature of solid.
Silver crystallizes in face-centered cubic structure. The edge length of the unit cell is found to be 408.7 pm. Calculate the density of silver. ($$Ag= 108g\ { mol }^{ -1 }$$)
What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by:
(i) $$ZnS$$ (ii) $$AgBr$$
If the edge length of a $$NaH$$ unit cell is $$488\ pm$$, what is the length of $$Na-H$$ bond if it crystallizes in the fcc structure?
Calculate the number of unit cells in $$8.1$$g of aluminium if it crystallizes in a face-centred cubic (f.c.c.) structure. (Atomic mass of Al$$=27$$g $$mol^{-1}$$).
A piece of chalk can be broken into small particles by hammering but a piece of iron cannot be broken into small particles. Which characteristic of the particles of matter is illustrated by these observations?
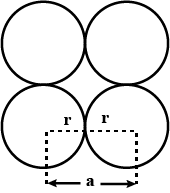
Calculate packing efficiency in simple cubic lattice.
Give the differences between crystalline and amorphous solids with respect to shape and melting point.
What is lattice enthalpy of an ionic crystals? Give the relation.
On heating crystals of $$KCl$$ in potassium vapours, the crystals start exhibiting violet colour. Why?
Preparation of models of crystal (cube).
In a face-centered unit cell with all the positions occupied by A atoms, the body-centered octahedral holes in it are occupied by an atom B of an appropriate size.
Calculate the void fraction per unit volume of a unit cell for such crystal.
Which type of stoichiometric defect is shown by AgCl?
A metal has bcc structure and the edge length of its unit cell is $$3.04\overset{o}{A}$$. Find the volume of the unit cell in $$cm^3$$.
The density of a metal is $$10.8$$ x $$10^3$$ kg/$$m^3$$. Find the relative density of the metal. (Density of water is $$10^3\ Kg/m^3$$)
Calculate the packing efficiency in primitive unit cell.
Calculate packaging efficiency in simple cubic lattice.
An element crystallizes in fcc structure with a unit cell edge length of 200 pm. Calculate its density if 200g of this element contain $$24\times10^{23}$$ atoms.
Refractive index of a solid is observed to have the same value along all direction. comment on the nature of this solid. would it show cleavage property?
What is the distance between $${ Na }^{ + }$$ and $${ Cl }^{ - }$$ ions in $$NaCl$$ crystal if its density is $$2.165 g { cm }^{ -3 }$$ .[Atomic mass of $$Na-23 u, Cl = 35.5 u$$, Avogadro,s Number=$$6.023 \times 10^{23}$$]
Iron has a body-centered cubic unit cell with a cell edge of $$286.65 pm.$$. The density of iron is $$7.874 g { cm }^{ -3 }$$. Use this information to calculate Avogadro's number. $$(At.mass\ of\ iron=55.845 u)$$
$$\circleddash \oplus \circleddash O\circleddash \oplus \circleddash \oplus $$
$$\oplus \circleddash \oplus \circleddash \oplus \circleddash \oplus \circleddash $$$$\circleddash \oplus O\oplus \circleddash \oplus \circleddash \oplus $$
$$\oplus \circleddash \oplus O\oplus \circleddash \oplus \circleddash $$
$$\circleddash \oplus \circleddash \oplus \circleddash O\circleddash \oplus $$
(a) What are these types of vacancy defects called?(b) How is the density of a crystal affected by these defects?(c) Name one ionic compound which can show this type of defect in the crystalline state.(d) How is the stoichiometry of the compound affected?
What type of change will occur when AgCl is dropped with $$CdCl_2$$.
Ammonium chloride cystallise in a body-centred cubic lattice with a unit distance of $$387pm$$. Calculate
(a) the distance between oppositely charged ion in the lattice and
(b) the radius of the $${NH}_{4}^{+}$$ ion if the radius of $${Cl}^{-}$$ ion is $$181pm$$
Ice crystallizes in a hexagonal lattice. At the low temperature at which the structure was determined, the lattice constants were $$a=34\mathring{A}$$ and $$c=7.41\mathring{A}$$. How many $${H}_{2}O$$ molecules are contained in a unit cell? (The density of ice is $$0.92g/cc$$ at $${0}^{o}C$$ A unit cell of $${H}_{2}O$$ is shown.)
Caesium bromide has $$CsCl$$ structure $$(BCC$$ type of lattice$$)$$. Its density is $$4.49gm.cc$$. Calculate the side of the unit cell. $$[$$Molar mass of $$Cs=132.09 g/mol]$$
The void fraction of ..... and HCP is same.
Calculate the efficiency of packing in case of a metal crystal for face-centered cubic.
How many $$Na^+$$ ions in each unit cell is in a cubic ideal crystal of $$NaCl$$?
Name the types of point defects in solids.
Give one example of amorphous substance.
Iron has an edge length $$288$$pm. Its density is $$7.86 gm cm^{-1}$$. Find the type of cubic lattice to which the crystal belongs. (Atomic mass of iron = $$56$$).
An elements crystallizers in a cubic closed packed structure having FCC unit of an edge length $$200$$ pm. calculate the density if $$200$$g this elements contains $$24 \times 10^{23}$$ atoms.
In the solid, oxide ions are arranged in hcp. one third of $$ O_{v} $$ are occupied by A and one sixth $$ T_{v} $$ are occupied by B. Find the formula ?
Molybdenum has a atomic mass $$96 gmol^{-1}$$ with density $$10.3gcm^{-3}$$.The edge length of unit cell is $$314$$pm.Determine its lattice structure.
An element of atomic mass $$98.5gmol^{-1}$$ occurs in FCC structure. If its density is $$5.22gcm^{-3}$$, determine the edge length of unit cell.
Thallium (I) chloride crystallises in either a SCC or FCC of $$Cl^-$$ ion. The density of the solid is $$8.9gcm^{-3}$$ and edge of the unit cell is $$3.95 \times 10^{-8}cm^{-3}$$. Predict the type of unit cell.[Molar mass of thallium chloride $$=239.8gmol^{-1}]$$
Write an example of elements in which atoms occupy the position of lattice points.
Lowest Lattice energy will be possessed by which molecule?
What is meant by voids in crystal structure?
Write two examples of molecular solids.
Calculate number of unit cells in $$58.5$$ of a compound which forms $$BCC$$. [Molar mass of a compound $$=58.5$$]
Define line defect.
Write an example of soild in which the force between the particles having electro-staic force.
Define crystal lattice.
The radius of cation and anion is $$0.95\ A^{0}$$ and $$1.81\ A^{0}$$. Name of structure of ionic crystal.
What is the packing efficiency of $$BCC$$ unit cell?
A metal crystallizes with a face-centered cubic lattice. The edge length of the unit cell is 408 pm. The diameter of the metal atom is:
Which crystal lattice has most efficient packing efficiency?
The density of $$CaF_2$$ (fluorite structure) is 3.18 $$g/cm^3$$. The length of the side of the unit cell is:
Calculate the packing efficiency of particles in a simple cube.
Lithium metal has a body centred cubic structure. Its density is $$0.53 g \, cm^{-3}$$ and its molar mass is $$6.94g \, mol^{-1}$$. Calculate the volume of a unit cell of lithium metal.
Aluminium forms face centered cubic crystals .The density of $$AI$$ is $$2.7 g/cm^3$$ .Calculate the length of the side of the unit cell $$AI$$. (At.wt. of $$AI=27$$)
The unit cell cube length for $$LiCl$$ is $$5.14 \overset{o}A $$. Assuming anion-cation contact, calculate the ionic radius for chloride ion.
An element having atomic mass $$65.1 g/mol$$ has face centred cubic unit cell with edge length $$3.608 \times 10^{-8} cm$$. Calculate the density of the element. [Given $$N_A$$=$$6.022 \times 10^{23}atoms/mol$$]
A compound $$AB$$ has (rock salt type structure) molecular weight of $$AB$$ is $$6.023 Y \, amu$$ and closest $$A-B$$ distance is $$Y^{1/3}$$ nm, where $$Y$$ is an arbitrary number (in amu). Find the density of lattice, if the density of lattice is found to be $$20 \, kg \, m^{-3}$$.
The density of gold is $$419.3 g per cm^3$$.Calculate the diameter of solid gold sphere having a mass of 4239
Ions replace Na+ ions at the edge centers of NaCI lattice then the number of vacancies in $$1$$ mole of NaCl be:
A Metallic element crystallises into a lattice containing a sequence of layers of $$ABABAB....$$. Any packing of spheres leaves out voids in the lattice. What percentage by volume of this lattice is empty space?
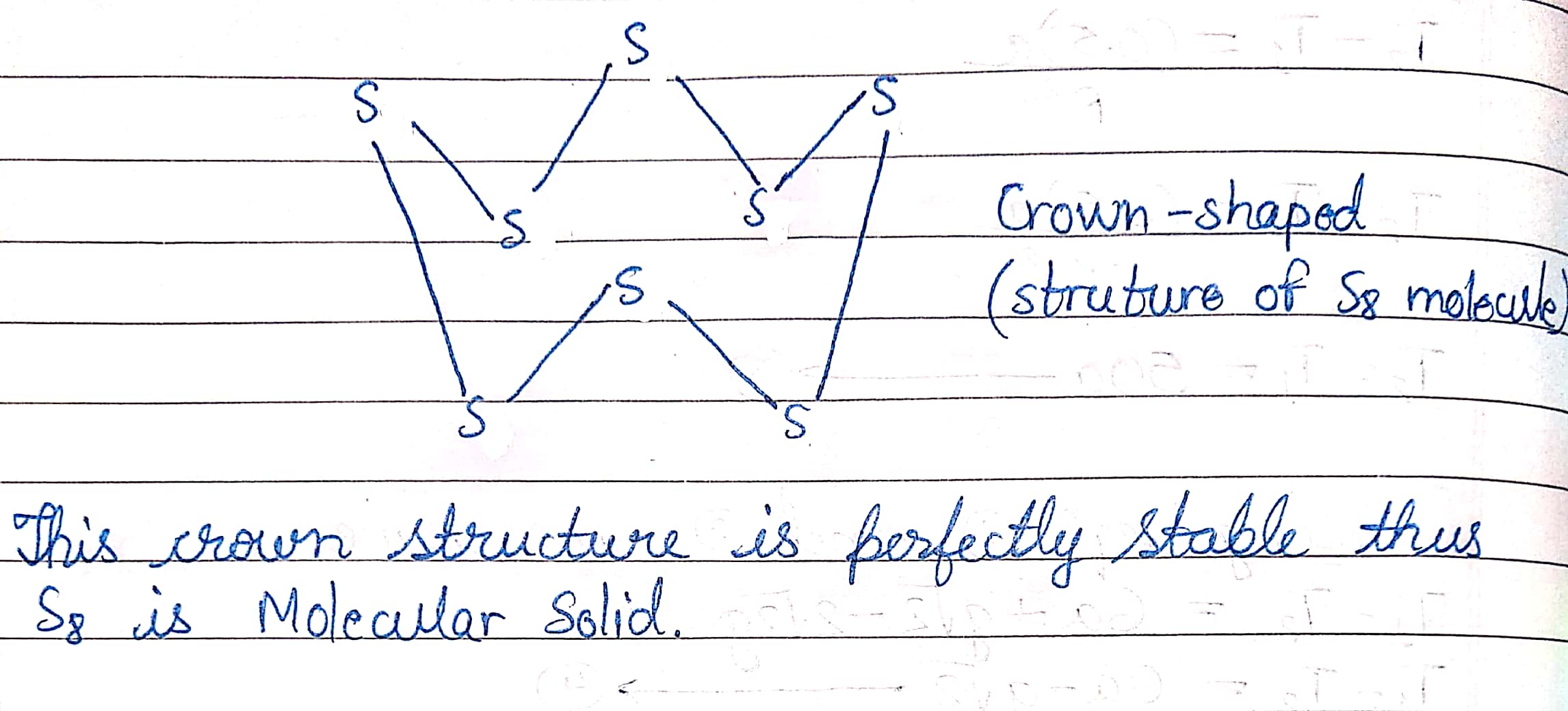
Name the type of solid in $$S_8$$ molecule.
What are mass defect and binding energy?
Mention one consequence of metal excess defect.
The density of copper metal is $$8.95$$ gm $$cm^{ -3 }$$. If the radius of copper atom is $$127.8$$ pm, Will the copper unit cell be a simple cubic, a body-centred cubic or a face centred cubic? (At mass of Cu=$$63.54$$g $$mol^{ -1 }$$ and N$$_A$$ =$$6.02\times 10^{ 23 }\quad mol^{ -1 }$$)
It represents the interatomic distance in a unit cell. It is calculated by using following formula
$$a = \root 3 \of {{{Z \times M} \over {\rho \times {N_A}}}} $$
For simple cubic, body-centred cubic and face-centred cubic structures value of Z is 1, 2 and 4 respectively.
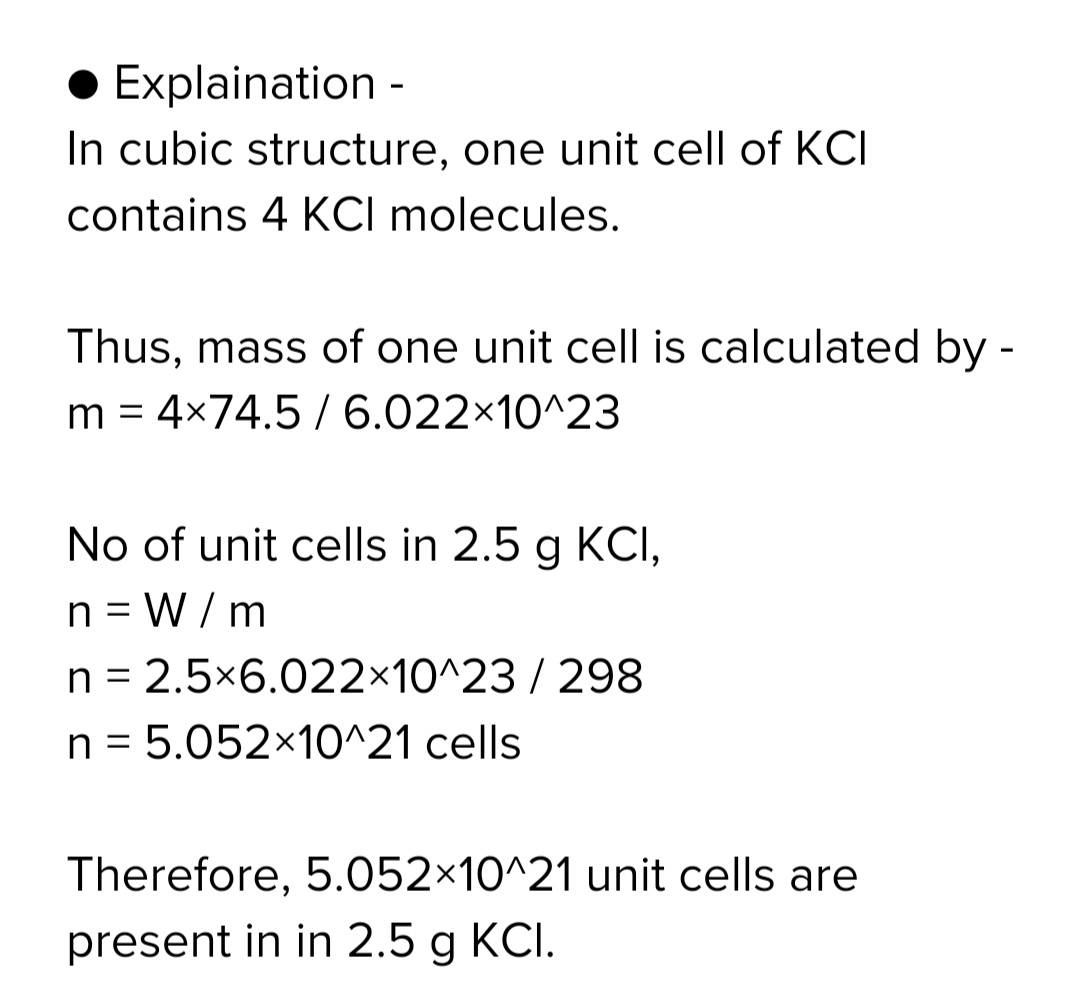
How many unit cells are present in
a] $$2.5$$ cubic crystal of KCl &
b] With each edge of crystal. [ given KCl=$$ 74.5$$, Cell const=4]
Name the parameters which are characteristics of unit cell.
What is two-dimensional coordination number in square close packing layer of a molecule?
Perovskite a mineral containing calcium, oxygen and titanium. crystallises in the unit cell as shown below.
On the basis of above information write the formula of perocskite?
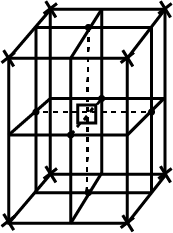
How many unit cells are there in $$1.00\ cm^{3}$$ of aluminium?
An element $$'X'$$ crystallizes in $$bcc$$. Find volume of unit cell in $$(\mathring {A})^{3}$$, if atomic radius is $$\sqrt {3}\mathring {A}$$.
Find the distance between $$K^+$$ and $$F^-$$ ion in potassium fluoride, which has sodium chloride type of crystal lattice. The density of KF is $$2.4\,g\, cm^{-3}$$. ($$M=58, N_A=6.022 \times 10^{23}$$)
Classify the following solids into different types
Graphite
In the cubic crystal of $$CsCl(d=3.97 g\quad cm^{-3})$$ the eight corners are occupied by $$Cl^{-}$$ with a $$Cs^{+}$$ at the centre and vice-versa. Calculate the distance between the neighbouring $$Cs^{+}$$ and $$Cl^{-}$$ ions. What is the radius ratio of the two ions? (At. wt. of Cs$$=132.91$$ and Cl=$$35.45$$)
Classify the following solids into different types
Plastic
Classify the following solids into different types
Ammonium Phosphate
Give the significance of a lattice point
Which of the following lattices has the highest packing efficiency?
(i) simple cubic
(ii) body-centred cubic
(iii) hexagonal close-packed lattice.
Potassium crystallizes in a body centred cubic lattice. How many unit cells are present in $$2g$$ potassium? (At. mass of $$K=39$$)
What makes the crystal of $$KCl$$ appear sometimes violet?
The density of $$KBr$$ is $$2.38\ g\ cm^{-3}$$. The length of the edge of the unit cell is $$700\ pm$$. Find the number of formula unit of $$KBr$$ present in the single unit cell.
$$(N_{A} = 6\times 10^{23} mol^{-1}$$, At. mass : $$K = 39, Br = 80)$$.
Unit cell or iron crystal has edge length of 288 pm and density of 7.86 g $$cm^{-3}$$. Determine the type of crystal lattice [Fe = 56]
Name the parameters that characterize a unit cell
Explain how much portion of an atom located at (i) corner and (ii) body-centre of a cubic unit cell is part of its neighbouring unit cell.
$$AgCl$$ has the same structure as the $$NaCl$$. The edge length of unit cell of $$AgCl$$ is found to be $$555$$ pm and the density of $$AgCl$$ is $$5.561$$ g $$cm^{-3}$$. Find the percentage of sites that are unoccupied.
A compound is formed by two elements M and N. The element N forms ccp and atoms of M occupy 1/3rd of tetrahedral voids. What is the formula of the compound?
Analysis shows nickel oxide has the formula $$Ni_{0.98} O_{1.00}$$. What fraction of $$Ni$$ exists as $$Ni^{2+}$$ and $$Ni^{3+}$$ ions in given oxide?
Assertion (A): The packing efficiency is maximum for the fee structure. Reason (R): The coordination number is 12 in fee structures
Under which situations can an amorphous substance change to crystalline form?
In spite of long range order in the arrangement of particles why are the crystals usually not perfect?
Define Anisotropy. Distingusih between crystalline solids and amorphous solids.
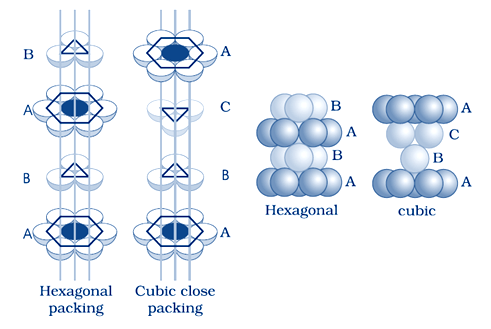
Name and draw the three common crystal structures adopted by metals.
The following are some statements related with solid state of matter:
(i) All crystalline solids are isotropic.
(ii) Amorphous solids are super cooled liquids with high viscosity
(iii) In crystals, short range order exists.
(iv) A unit cell is the smallest building unit in the crystals
(v) Every object possesses an identity element
(vi) Each lattice point in a crystal has the same environment
(vii) The basic unit must have the same stoichiometric composition as the entire crystal
(viii) A crystal space lattice cannot have a positive ion at one lattice point and a negative ion at another lattice point
The number of true statements is
A metal (atomic mass $$=307.2$$) exist in BCC structure. If the uncovered distance between the atoms along the edge is equal to $$120pm$$, the density of crystal (in $$g/{cm}^{3}$$) is $$\left( { N }_{ A }=6\times { 10 }^{ 23 },\sqrt { 3 } =1.732 \right) $$
List the type of defect that occur in the solid state and given an example of each. Explain in each case if any electrical conduction is possible and by what mechanism.
What is the approximate percentage of vacant space in a Silicon cubic cell having crystal structure similar to diamond?
What is peculiarity in electrical property of quartz?
Find type of defect.
Calculate the Avogadro constant from the following data:
Density of solid $$NaCl = 2.165\ g/cc$$.
Distance between centres of adjacent $$Na^{+}$$ and $$Cl^{-} = 0.2819\ nm$$.
Also, calculate the edge length of a cube containing $$1\ mole$$ of $$NaCl$$ and the number of ions $$(Na^{+} + Cl^{-})$$ along one edge of the cube.
Total number of faces in a truncated octahedron $$= x$$
Total number of faces in a truncated tetrahedron $$= y$$
Then $$x + y$$ is :
Calculate the number (n) of atoms contained with:
(a)cubic cell,
(b)a body-centred cubic cell,
(c)a face-cenred cubic cell.
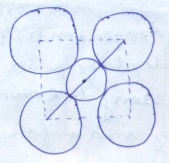
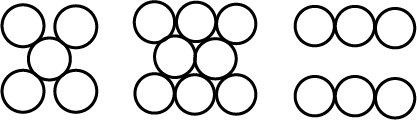
Consider the arrangement of circles of equal radii with their centres arranged as per the 2-dimensional lattice defined by $$a = b,\ \theta =60^{\circ }$$ such that each circle is touching all its nearest neighbour. If all the void areas present are additionally occupied by smaller circles of relevant size so that the void circles are just contacting their neighbours find the packing efficiency of the configuration in percent.
Why does the window glass of the old buildings look milky ?
Which point defect in its crystal units increases the density of a solid ?
How can a material be made amorphous ?
What is the meaning of the term imperfection in solids ?
Why is the window glass of old building thick at the bottom ?
Complete the statement given below by selecting the correct word/s.
___________ is an example of a crystalline substance .
[wax, sugar, tea]
___________ is an example of a crystalline substance .
[wax, sugar, tea]
Answer the following questions .
Why does presence of excess of lithium makes LiCl crystals pink ?
Tearing of paper is said to be a change that cannot be reversed. What about paper recycling?
What is the difference between sugar and sand ?
Examine the given crystal :
$$ X^+ $$ $$ Y^- $$ $$ X^+$$ $$ Y^-$$ $$X^+$$
$$ Y^- $$ $$ X^+$$ $$Y^- $$ $$X^+ $$ $$Y^- $$
$$ X^+ $$ $$ Y^- $$ $$ X^+$$ $$ e^-$$ $$X^+$$
$$ Y^- $$ $$ X^+$$ $$Y^- $$ $$X^+ $$ $$Y^- $$
Answer the following questions :
Is the above defect stoichiometric or non-stoichiometric ?
Classify the following solid as ionic, metallic, molecular, network (covalent) or amorphous.
$$I_2$$
Answer the following questions .
Write any two differences between amorphous solids and crystalline solids .
Calculate the efficiency of packing in case of metal crystal for body-centred cubic.
What do you understand by 'lattice point' ?
Why solids are hard ?
What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by ZnS
How does amorphous silica differ from quartz ?
Calculate the efficiency of packing in case of metal crystal for simple cubic.
What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by AgBr ?
Classify the following solid as ionic, metallic, molecular, network (covalent) or amorphous.
Brass.
Calculate the efficiency of packing in case of metal crystal for face-centred cubic.
Ionic solids which have anionic vacancies due to metal excess defect , develop colour. Explain with the help of a suitable example.
How will you distinguish between the following pairs of terms
Hexagonal and monoclinic unit cell
Explain the following term with suitable examples:
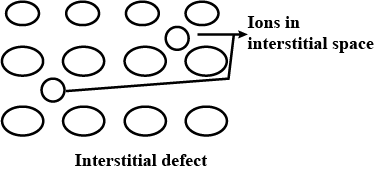
Interstitial defect
What are crystals; How can we make growing crystals?
The crystalline parts of the amorphous solids are called ....... .
An element X (atomic weight $$= 24$$ g/mol) forms a face centered cubic lattice. If the edge length of the lattice is $$4\times10^{-8}$$ cm and the observed density is $$2.40 \times10^{3}$$ g cm$$^{-3}$$, then the percentage occupancy of lattice points by element X is : (Use $$N_A=6\times10^{23}$$)
In face centred cubic (fcc) crystal lattice, edge length is $$400$$ pm. Find the diameter (in pm) of a greatest sphere which can be fit into the interstitial void without distortion of a lattice.(Give your answer to the nearest integer)
Match the crystal system/unit cells mentioned in Column I with their characteristic features mentioned in Column II.
Indicate your answer by darkening the appropriate bubbles of the 4 X 4 matrix given in the ORS.
This section contains questions each with two columns-I and II. Match the items given in column I with that in column II (unoccupied volume).
Give the total score of the correct statements of the following.
| Statements | Score | |
| a. | In an antifluorite structure, cations are present in all tetrahedral voids. | $$1$$ |
| b. | If the radius of cation is $$0.35$$ pm and that of anion is $$0.95$$ pm, then the co-ordination number of the crystal is $$4$$. | $$2$$ |
| c. | An atom or ion is transfered from a lattice site to an interstitial position in Frenkel defect. | $$3$$ |
| d. | The density of a crystal always decreases in point defects. | $$4$$ |
Which stoichiometrie defect increases the density of a solid?
If $$NaCl$$ is doped with $$10^{-3}$$ $$mol$$ percent of $$SrCl_{2}$$, what is the concentration of cation vacancies?
When heated above $$916^{\circ}C$$, iron changes its crystal structure from body-centered cubic to cubic closed packed structure. Assuming that the metallic radius of the atom does not change, calculate the ratio of the density of the bcc crystal to that of the ccp crystal.
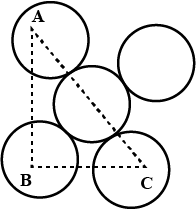
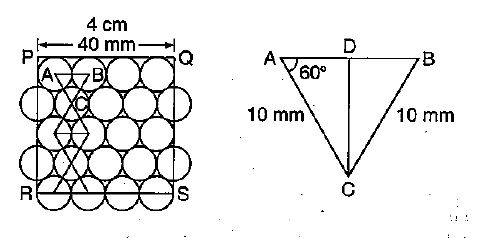
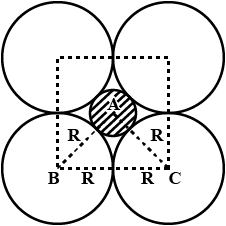
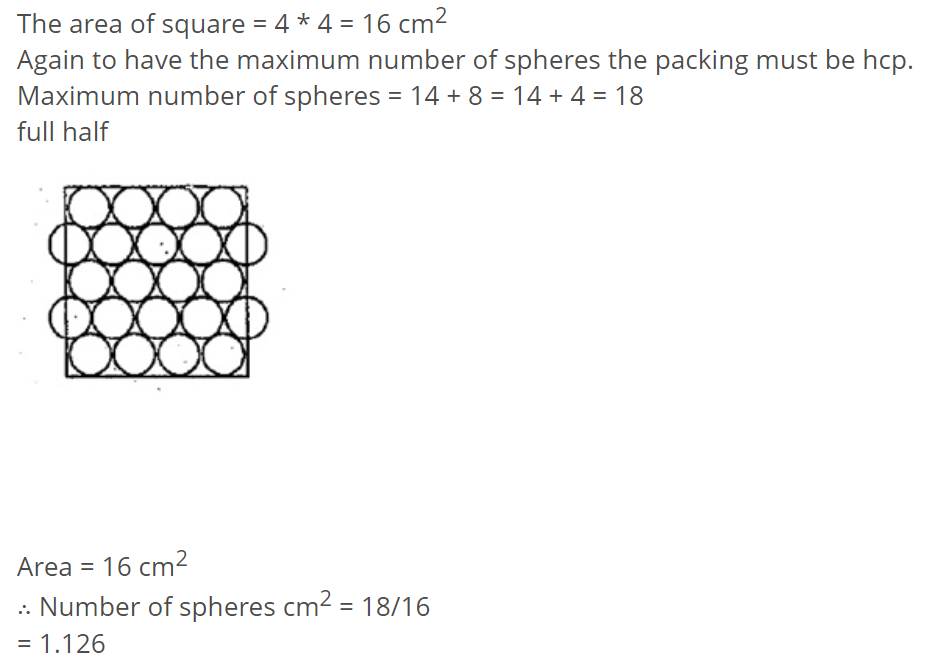
You are given marbles of diameter $$10\ mm$$. They are to be placed such that their centers are lying in a square bond by four lines each of length $$40\ mm$$. What will be the arrangement of marbles in a plane, so that, the maximum number of marbles can be placed inside the area? Sketch the diagram and derive the expression for the number of marbles per unit area.
Distinguish between crystalline solid and amorphous solid.
$$BaTiO_3$$ crystallizes in the perovskite structure. This structure may be described as a cubic lattice, with barium ions occupying the corners of the unit cell, oxide ions occupying the face centers and titanium ions occupying the centers of the unit cells.
(a) If titanium is described as occupying holes in the $$BaO$$ lattice, what type of hole does it occupy?
(b) What fraction of the holes of this type does it occupy?
(c) Can you suggest a reason why it has certain holes of this type but not the other of the same type?
An element 'X' (At. mass $$=40$$g $$mol^{-1}$$) having f.c.c structure, has unit cell edge length of $$400$$ pm. Calculate the density of 'X' and the number of unit cells in $$4$$g of 'X'. $$(N_A=6.022\times 10^{23}mol^{-1})$$.
Using the data given below, find the type of cubic lattice to which the crystal belongs.
| $$Fe$$ | $$V$$ | $$Pd$$ | |
| $$a$$ in pm | $$286$$ | $$301$$ | $$388$$ |
| $$\rho$$ in gm $$cm^{-3}$$ | $$7.86$$ | $$5.96$$ | $$12.16$$ |
Aluminium crystallises in a cubic close-packed structure. Its metallic radius is $$125\ pm$$. (i) What is the length of the side of the unit cell? (ii) How many unit cells are there in $$1.00\ cm^{3}$$ of aluminium?
Drop a crystal of copper sulphate or potassium permanganate into a glass of hot water and another containing cold water. Do not stir the solution. Allow the crystals to settle at the bottom.
What do you observe just above the solid crystal in the glass?
What happens as time passes?
What does this suggest about the particles of solid and liquid?
Does the rate of mixing change with temperature? Why and how?
An element has a body centered cubic (bcc) structure with a cell edge of 288 pm. The density of the element is 7.2g/c$$m^3$$. How many atoms present in 208g of the element.
Why is glass considered a super cooled liquid?
Find the void space in fluorite structure per unit volume of unit cell.
Why do hexagonal and trigonal lattice do not have bcc and fcc variations?
What is the packing efficiency for end centred unit cell?
In terms of bond theory, explain the difference between a conductor (metal) , semiconductor and insulator. Give examples.
Examine the defective crystal lattice given below and answer the following questions:
(a) Name of defect present in ionic solid.
(b) Out of AgCl and NaCl, which is most likely to show this type of defect and why?
(c) Why the defect is also as dislocation defect?
Metallic gold crystallises in a face-centredcubic lattice. The length of the cubicunit cell is a = 4.0 mass of gold = 197 u)
(a) What is the closest distance between gold atoms?
(b) How many "nearest neighbours" does each gold atom have at a distance calculated in (a)?
(c) What is the density of gold?
If the radius of the octahedral void is $$r$$ and the radius of the atoms in the close packing is $$R,$$ derive relationship between $$r$$ and $$R$$.
Ag forms $$CCP$$ lattice with edge length $$408.6$$pm calculate density of silver. $$(Atomic mass =107.9\mu)$$
What type of stichiometric defect is shown by $$KCl$$ and Why?
What is the relation between edge length and angles between the edges in triclinic crystal system.
Give reasons:
In stoichiometric defects, $$NaCl$$ exhibits Schottky defect and not Frenkel defect.
There are three solids made up of aluminium, steel and wood, of the same shape and same volume. Which of them would have highest inertia? Give reason for your answer.
How you distinguish between the following pairs of terms: (i) Hexagonal close-packing and cubic close-packing? (ii) Crystal lattice and unit cell? (iii) Tetrahedral void and octahedral void?
Why are solids incompressible?
Which of the following is true about the value of refractive index of quartz glass? (a) Same in all directions (b) Different in different directions (c) Cannot be measured (d) Always zero
Draw a diagram of 'two dimension square closed packing'.
Out of NaCl and AgCl, which one shows Frenkel defect and why?
Calculate the packing fraction for the $$K$$ unit cell. $$K$$ crystallizes in a body-centred cubic unit cell.
The density of solid argon is $$1.65g/{ cm }^{ 3 }$$ at $$-{ 233 }^{ o }C$$. if the argon atoms are assumed to be spheres of radius $$1.54\times { 10 }^{ -8 }cm$$, the approximate percentage of empty space in solid argon is $$(Ar=40)$$
Calculate the percentage of vacant space in a Si unit cubic cell. The unit-cell content for Si is $$8$$ and $$r = \dfrac {\sqrt {3}a}{8}$$.
Match Column I with Column II and Column III
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| (A) $$NaCl$$ | (P) FCC, anion in all tetrahedral voids | (W) Cation (6), anion (6) |
| (B) $$Ca{F}_{2}$$ | (Q) FCC, cation in all octahedral voids | (X) Cation (8), anion (4) |
| (C) $$ZnS$$ (Zinc blende) | (R) FCC, cation in alternate tetrahedral voids | (Y) Cation (6), anion (6) |
| (D) $${Na}_{2}O$$ | (S)FCC, cation in all tetrahedral voids | (Z) Cation (6), anion (6) |
You are given marble of diameter $$10mm$$. They are to be placed such that their centres are lying in a square bond by four lines each of length $$40mm$$. The maximum number of marbles which may be placed inside this area is
A simple cubic lattice consists of eight identical spheres of radius $$R$$ in contact, placed at the corners of a cube. What is the volume of the cubical box that will just enclose these eight spheres and what fraction of this volume is actually occupied by the spheres?
Rutile, a mineral that contains only titanium and oxygen atoms, has a structure that can be described as a closest packed array of oxide ions with titanium ions in one-half of the octahedral voids.
$$(Ti=48)$$
$$ab=$$ the mass percentage of titanium in rutile
$$c=$$ magnitude of oxidation state of titanium in rutile
$$d=1$$ if the oxidation state of $$Ti$$ is positive and $$2$$ if the oxidation state of $$Ti$$ is negative
The value $$abcd$$ is
Define void .
What are types of lattice imperfections found in crystals ?
Calculate the packing factor for spheres occupying (a) a body-centred cubic structure, and (b) a simple cubic structure, where closest neighbours in both cases are in contact.
What are primitive unit cells and what are non- primitive unit cells ?
Explain the following term with suitable examples:
Interstitials.
How will you distinguish between the following pairs of terms :
Crystal lattice and unit cell
What type of stoichiometric defects is shown by KCl and why?
What are stoichiometric defects or intrin sic defects in ionic crystals ?
Answer the following questions .
What happens when $$ CdCl_2 $$ vis doped with $$ AgCl $$ ?
Calculate the efficiency of packing in the case of a metal crystal for body-centred cubic.(with the assumption that atoms are touching each other).
What are interstitials in a crystal ?
Examine the given defective crystals :
| $$ X^+ $$ | $$ Y^- $$ | $$ X^+ $$ | $$ Y^- $$ | $$ X^+ $$ |
| $$ Y^- $$ | $$ Z^{2+} $$ | $$ Y ^- $$ | $$ X^+ $$ | $$ Y^- $$ |
| $$ X^+ $$ | $$ Y^- $$ | $$ Y^- $$ | $$ X^+ $$ | |
| $$ Y^- $$ | $$ X^+ $$ | $$ Y- $$ | $$ X^+ $$ | $$ Y^- $$ |
Write the term used for this type of defect .
Examine the given crystal :
$$ X^+ $$ $$ Y^- $$ $$ X^+$$ $$ Y^-$$ $$X^+$$
$$ Y^- $$ $$ X^+$$ $$Y^- $$ $$X^+ $$ $$Y^- $$
$$ X^+ $$ $$ Y^- $$ $$ X^+$$ $$ e^-$$ $$X^+$$
$$ Y^- $$ $$ X^+$$ $$Y^- $$ $$X^+ $$ $$Y^- $$
Answer the following questions :
Give an example of the compound which shows this type of defect .
In seven possible crystal system how many crystal system have more than one Bravais lattice ?
Class 12 Engineering Chemistry Extra Questions
- Alcohols,Phenols And Ethers Extra Questions
- Aldehydes,Ketones And Carboxylic Acids Extra Questions
- Amines Extra Questions
- Biomolecules Extra Questions
- Chemical Kinetics Extra Questions
- Chemistry In Everyday Life Extra Questions
- Coordination Compounds Extra Questions
- Electrochemistry Extra Questions
- General Principles And Processes Of Isolation Of Elements Extra Questions
- Haloalkanes And Haloarenes Extra Questions
- Polymers Extra Questions
- Solutions Extra Questions
- Surface Chemistry Extra Questions
- The D-And F-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The P-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The Solid State Extra Questions