Surface Chemistry - Class 12 Engineering Chemistry - Extra Questions
What is adsorption?
Name the two groups into which phenomenon of catalysis can be divided. Given an example of each group with the chemical equation involved.
The catalyst used for hydrogenation of oils is __________.
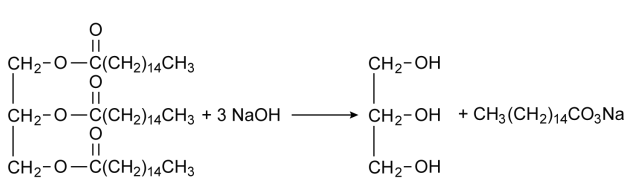
How is Soap industrially manufactured?
Write briefly about the preparation of colloids by chemical methods.
What is catalysis? Give an example.
Name the adsorbent used to removal of colouring matter from solution.
The conductance of an emulsion increases on adding common salt. What type of emulsion is this?
The emulsifying agent forms an interfacial film between suspended particles and the medium. The principal emulsifying agents for O/W emulsions are?
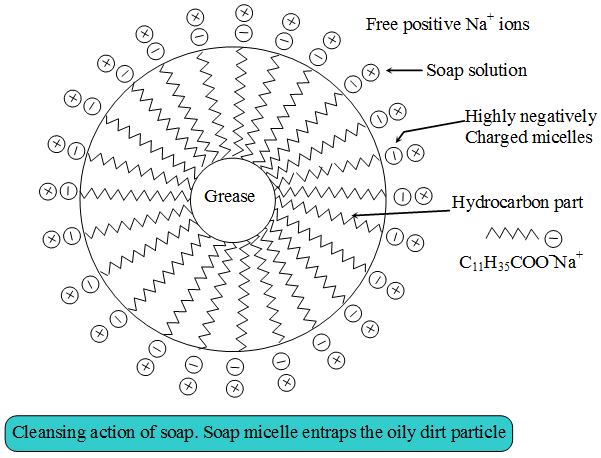
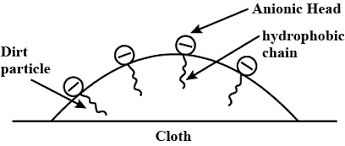
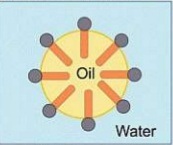
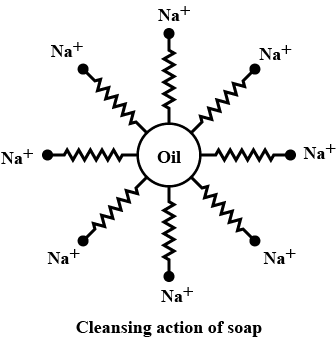
Explain cleaning action?
Describe the cleansing action of soap?
Name the temperature above which the formation of micelles takes place.
What type of semiconductor is obtained when silicon is doped with arsenic ?
During the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide glycerine acts as positive catalyst. If this is true enter 1 and if false enter 0.
Explain the mechanism of cleaning action of soap.
Match the List I with the List II.
_________ (Adsorption/Chemisorption) process is involved in the decolourisation of sugar cane juice.
Match list I with list II.
The reaction having catalyst and reactants phase ≥ ____________ is heterogeneous catalysis.1
2
3
0
2
3
0
The reaction in which reactants and the catalyst have one phase is _________ .
heterogeneous catalysis
homogeneous catalysis
solid state catalysis
solution catalysis
The phenomenon when a reaction influences the rate of other reaction is ___.
homogenous catalysis
heterogeneous catalysis
induced catalysis
competitive catalysis
homogenous catalysis
heterogeneous catalysis
induced catalysis
competitive catalysis
The substance that __________ the activity of catalysts is poisoner.
increases
decreases
maintains
none
The substance that _________ the activity of catalysts is called promoter.
Increases
Decreases
Maintains
None of the above
Match the following.
| List-A | List-B | List-C |
| (A) Lyophilics | Froth floatation | a. Charge depends on pH |
| (B) Lyophobics | Organic substances | b. Charge is independent of pH |
| (C) Protection | Artificial rain | c. Digestion of food |
| (D) Smoke | Inorganic substances | d. Spray of Agl |
| (E) Coagulation | Blue tinge | e. Gelatin |
| (F) Emulsification | Gold number | f. Tyndall effect |
If A matches with a and with number 2. What number does F match with?
Rivers on meeting with oceans form ____________ .
estuaries
swamps
deltas
none of the above
Choose the correct option.
Electrostatic precipitation of carbon from smoke is used to control what type of pollution?
Air
Soil
Both 1 and 2
None of the above
In oil solution of soap, the head is towards the surface of the oil and the tail is pointing away from the oil.If the given statement is true, enter 1, else enter 0.
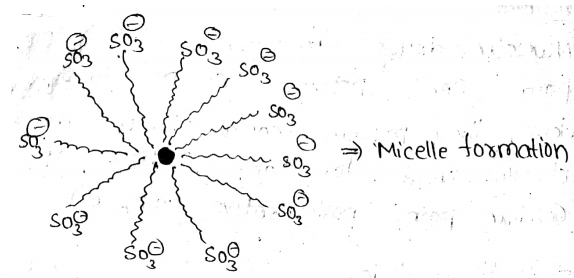
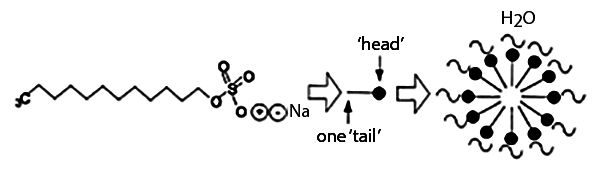
Draw the diagram showing micelle formation by the following detergent.CH3(CH2)10CH2OS¯O3+Na
Explain the mechanism of the cleansing action of soaps?
In aqueous solution of soap, head is towards the surface of water and tail is pointing away from the water.
if true, enter 1, else enter 0.
Why does micelle formation take place when soap is added to water? Will a micelle be formed in other solvents like ethanol also?
Adsorption is a phenomenon of accumulation of higher concentration of one substance on the surface of another.State whether True or False.
Peptization is a process of converting a freshly prepared precipitate into a colloidal form by the addition of a suitable electrolyte.
State whether the statement is True or False.
Water which gives good lather readily with soap is known as hard water.
If this is true enter 1, if false enter 0.
Adsorption is surface phenomenon and absorption is bulk phenomenon
If this is true enter 1, if false enter 0.
If both absorption and adsorption occur simultaneously it is called sorption
If this is true enter 1, if false enter 0.
Match various processes in surface chemistry from List 1 with their definition from List 2.
The liquid or solid on the surface of which the molecule of the substance are adsorbed is called adsorbate.
If this is true enter 1, if false enter 0.
The substance whose molecules are adsorbed is called adsorbent.
If this is true enter 1, if false enter 0.
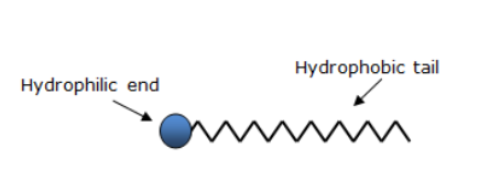
Label the hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts in the following compounds.
(i) CH3(CH2)10CH2OS¯O3+Na
(ii) CH3(CH2)15+N(CH3)3¯Br
(iii) CH3(CH2)16COO(CH2CH2O)nCH2CH2OH
Explain the cleansing action of soaps.
(i) Differentiate between adsorption and absorption.
(ii) Out of MgCl2 and AlCl3, which one is more effective in causing coagulation of negatively charged sol and why?
(iii) Out of sulphur sol and proteins, which one forms multimolecular colloids?
Give one example each of lyophobic sol and lyophillic sol.
Explain the following terms giving one example for each:
(i) Micelles
(ii) Aerosol
What are the dispersed phase and dispersion medium in milk?
Give one example each of 'oil in water' and 'water in oil' emulsion.
A delta is formed at the meeting point of sea water and river water. Why?
What are emulsions? What are their different types? Give one example of each type.
Define peptization.
What are emulsions? What are their different types? Give one example of each type.
What is meant by 'shape selective catalysis'?
Define the following terms with an example in each case:
(i) Macromolecular sol (ii) Peptization (iii) Emuslion
What is the difference between oil/water (O/W) type and water/oil (W/O) type emulsions? Give an example of each type.
What are the characteristics of the following colloids? Give one example of each
(i) Multimolecular colloids (ii) Lyophobic sols (iii) Emulsions
Explain the cleansing action of soap.
Give one example (equation) of a homogeneously catalysed reaction and name the catalyst.
(a) What is enzyme catalysis? Write an example.
(b) Which type of emulsion is milk? Explain.
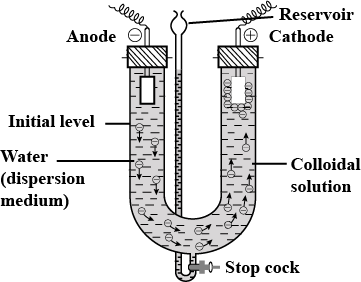
(c) Explain Electrophoresis with labelled diagram.
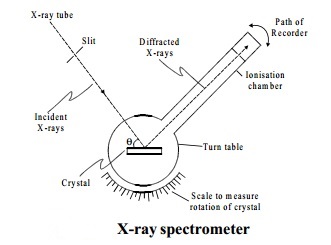
a) Explain bragg's spectrometer method.
b) Write about the preparation of colloids by chemical methods.
What is peptization? Explain.
Explain the mechanism of cleansing action of soaps.
What is emulsifying agent? Give one example?
What is emulsion? How are emulsions classified? Give example?
What are emulsions? How they are classified? Give one example of each.
What is Emulsion?
Write the chemical method by which Fe(OH)3 sol is prepared from FeCl3.
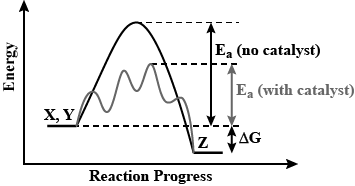
Draw a graph of potential energy v/s reaction coordinate showing the effect of a catalyst on activation energy.
What is Heterogeneous catalysis? Give an example.
Conversion of precipitate into colloidal solution is known as______.
Catalysts which increase rate of a reaction are called ___________ catalyst.
Peptisation is a method of preparation of sols. Write a general procedure for peptization.
What is peptization?
Who used the word 'catalyst' for the first time?
For the coagulation of 100mL of arsenious sulphide solution, 5mL of 1M NaCl is required. What is the coagulating power of NaCl?
Match the terms in List 1 with those of List 2.
Match the phenomena in Column-I with example in Column-II:
| Column-I | Column-II |
| (a) Persorption | (p) H2 on Ni surface |
| (b) Sorption | (q) CH3OH in chabazite |
| (c) Negative adsorption | (r) NH3inH2O |
| (d) Occlusion | (s) Dil. NaCl on blood charcoal |
Define Semipermeable membrane.
What is a catalyst? give one example.
What is scum and how is it formed?
What are the causes of Peptization?
526.3 mL of 0.5 M HCI is shaken with 0.5 g of activated charcoal and filtered. The concentration of the filtrate is reduced to 0.4M. What is the amount of adsorption (x/M)?
What are emulsions ? Give examples
Choose the correct set of identifications for the reaction
Substrate(S)⟶Product(P)
Whose mechanism is
E+S⇌ES
ES⇌EP
EP⇌E+P
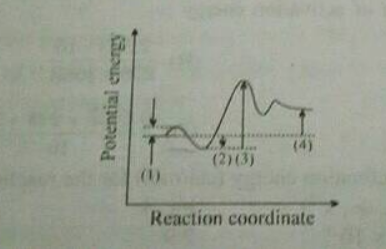
Name the catalyst used in contact process.
Name the catalyst generally used in the hydrogenation of oils.
Based on the type of dispersed phase,what type of colloids are micelles?
Why does physisorption decrease with the increase of temperature?
Give an example of a liquid in liquid type solution.
50 ml of 1 M oxalic acid (mol. wt. =126) is shaken with 0.5 g of wood charcoal. The final concentration of solution after adsoption is 0.5 M. Calculate the amount of oxalic acid adsorbed per gram of charcoal.
Explain the preparation of Gold Sol by Bredig's arc method ?
On increasing the temperature, the solubility of the solute in the solvent________.
Explain Adsorption theory of Heterogeneous Catalysis.
Define Adsorption theory of Heterogeneous Catalysis.
What is the role of promoters and poisons in catalysis?
What is observed when an emulsion is centrifuged?
In the reaction below the substance acting as a catalyst : -
2KCIO3→2KCI+3O2
Classify into alkanes, alkenes and alkynes : Ethane, ethene, methane, ethyne, propene, propyne
Name the structure shown in the figure. Also label 1 and 2
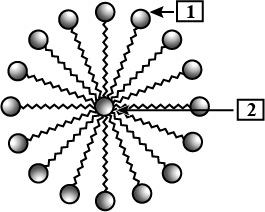
What are Emulsions? How are they classified?
(a) Explain the process of preparation of soap in laboratory.
(b) Why is common salt (sodium chloride) added during the preparation of soap?
(c) Why is soap not suitable for washing clothes when the water is hard?
Define the following term:
Emulsifying agents
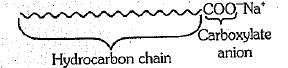
(a) What is a soap? Name one soap.
(b) Describe the structure of a soap molecule with the help of a diagram.
(c) Explain the cleansing action of soap. Draw diagrams to illustrate your answer.
(a) How is ethanoic acid obtained from ethanol? Write down the chemical equation of the reaction involved.
(b) How would you distinguish between ethanol and ethanoic acid by chemical test?
(c) Explain the formation of scum when hard water is treated with soap.
Give only the machanism of cleansing action of soaps.
Complete the following with appropriate reagent :

Answer the following question.
Out of silica gel and anhydrous CaCl2, which will adsorb the water vapours?
Match the columns
How are emulsions different from Gels ? Give one example of each.
How are the following collodial solutions prepared?
i. Sulphur in water
ii. Gold in water.
Answer the following questions.
What happens when a freshly precipitated Fe(OH)3 is shaken with water containing a small quantity of FeCl3?
What is the role of diffusion in heterogeneous catalysis?
Mention the use of colloids?
Explain what is observed when.
Silver nitrate solution is added to potassium iodide solution.
Explain the following observation:
Sun looks red at the time of setting.
Complete the missing components/variables given as x in the following reaction:
CaCO3x⟶CaO(s)+CO2(g)
CaCO3x⟶CaO(s)+CO2(g)
Define Adsorption
Motor cars are coated with ......
How will you distinguish between dispersed phase and dispersion medium in an emulsion?
Select the correct statements which are related to the influence of catalyst in a reversible reaction.
a. Forward reaction takes place when a catalyst is used in a reversible reaction, h. Attains equilibrium faster,
c. Catalyst does not help to form more pro-duct
d. The catalyst increase the rates of both the forward and the backward reactions to the same extent.
e. Increase the speed of backward reaction.
f. Does not helps to produce more product.
Explain why finely divide substance is more effective adsorbent.
Why alum is used to prevent bleeding from wound of body?
Which type of colloid is cheese?
Which catalyst and promoter are used in Haber's process ?
Write the name of catalysis which convert methanol into gasoline.
What is purple of cassius ?
Define absorption.
Write an example of each type of emulsion.
Write one example of homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis.
Give the reasons:
Alum purifies drinking water.
Alum purifies drinking water.
The volume of nitrogen gas Vm (measured at S.T.P.) required to cover a sample of silica gel with a mono- molecular layer is 129cm3g−1 of gel. Calculate the surface area per gram of the gel if each nitrogen molecule occupies 16.2×10−20m2.
SnO2 forms a positively charged colloidal sol in acidic medium and a negatively charged sol in the basic medium. Why? Explain.
Match the following.
Distinguish between the meaning of the terms adsorption and absorption. Give one example of each.
What are emulsions? What are their different types? Give examples of each type.
Action of soap is due to emulsification and micelle formation. Comment.
What role does adsorption play in heterogeneous catalysis?
How do emulsifying agents stabilise the emulsion?
Explain the cleaning action of soap. Why do soap not work in hard water?
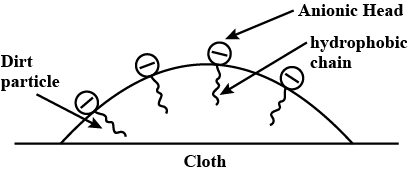
Name the two groups into which phenomenon of catalysis can be divided. Give an example of each group with the chemical equation involved.
Give four examples of heterogeneous catalysis.
Give four uses of emulsions.
Explain the following giving a suitable example for each. (i) Aerosol (ii) Emulsion (iii) Micelle
Draw the simple figure of a soap molecule.
Match the pairs (choose the correct answer from section 'B' for section 'A'):
Write one difference in each of the following:
(a) Multimolecular colloid and Associated colloid
(b) Coagulation and Peptization
(c) Homogeneous catalysis and Heterogeneous catalysis
a) Which types of an emulsion is 'vanishing cream'. Write its appropriate name.
b) Draw neat and labelled diagram of above emulsion.
What happens when an emulsion is centrifuged?
What is peptisation? Give an example
Write the difference between absorption and adsorption.
Write short notes on Peptization.
Write down the cleansing action of soap?
What is a protective colloid ?
Write any two characteristics of Chemisorption.
Define adsorption with an example. Why is adsorption exothermic in nature? Write the types of adsorption based on the nature of forces between adsorbate and adsorbent.
Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis with one example of each.
What is the role of desorption in the process of catalysts?
What is an emulsion?
Match list I (Colloidal system) with List II (Example)
Define the following term:
Protective colloid
Define desorption.
What is physical adsorption?
Match the columns
What is sorption?
Match the compounds in Column I with their characteristics/ tests/ reaction(s) / stereochemistry given in Column II. Matching can be more than one.
Why is desorption important for a substance to act as good catalyst?
How does a catalyst work?
Answer the following questions.
How does BF3 act as a catalyst in industrial process?
Answer the following questions.
Why is a finely divided substance more effective as an adsorbent?
Give reasons:
Gelatin which is a peptide is added in ice-creams.
Indicate a chemical reaction involving a homogeneous catalyst.
How will you distinguish between dispersed phase and dispersion medium in an emulsion?
A colloidal solution of ferric oxide is prepared by two different methods as shown below. [HOTS]
i. What is the charge on colloidal particles in two test tubes (A) and (B)?
ii. Give reasons for the origin of charge.
Write two difference between sols and emulsions.
A colloidal solution of AgI is prepared by two different methods as shown in figure below.
i. What is the charge of AgI colloidal particles in the two test tubes (A) and (B)?
ii. Give reasons for the origin of charge.
Answer the following questions.
Differentiate between adsorption and absorption.
Give reasons for the following:
Rough surface of catalyst is more effective than smooth surface.
Answer the following questions.
Heterogeneous catalysis.
Define the following terms:
Homogeneous catalysis.
How does a solid catalyst enhance the rate of combination of gaseous molecules?
What type of collodial sols are formed in the following:
i. Sulphur vapours are passed through cold water.
ii. White of an egg is mixed with water.
iii. Soap solution.
Give reasons for the following:
Smoke passed through charged plates before allowing it to come out of chimneys in factories.
What happens when a freshly precipitated Fe(OH)3 is shaken with a little amount of dilute solution of FeCl3?
SnO2 forms a positively charged colloidal sol in acidic medium and a negatively charged sol in the basic medium. Why? Explain.
Write one difference in each of the following:
Homogeneous catalysis and Heterogeneous catalysis.
Match the items of Column I and Column II.
Give two examples of emulsifying agents for O/W and W/O type of emulsions.
Both soap and detergent are some type of salts. what is the difference between them Describe in brief the cleansing action of soap. why do soaps not form lather in hard water List two problems that arise due to the use of detergents instead of soaps.
What is the function of catalyst in a chemical reaction?
Name the catalyst which facilitates change of vegetable oil to vegetable ghee.
Differentiate between following :
Catalyst promoter and catalyst poison.
Explain different types of catalyst.
What do you know about types of catalyst and about characteristics of catalyst?
Mention the dispersed phase and dispersion medium present in the following colloids
(A) Paint (B) Froths of air
Write short notes of Catalytic poison. Give example.
What are Catalyst?
What is the purpose of catalyst promoter and catalyst poison?
Name different types of catalyst.
It is found that when litmus is shaken with animal charcoal adsorption takes place.
Find out the adsorbent and adsorbate in this process.
Find out the adsorbent and adsorbate in this process.
Classify the following into homogenous and heterogenous catalysis
Hydrolysis of an organic ester
It is found that when Litmus is shaken with animal charcoal adsorption takes place
explain the terms adsorbent and adsorbate.
Classify the following into homogenous and heterogenous catalysis
Catalytic decomposition of ozone by chlorine
What are emulsions? What are their different types? Give example of each type.
Give reason why a finely divided substance is more effective as an adsorbent.
Differentiate between following :
Homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts.
What is Colloid?
Explain the cleansing action of soaps and detergents with the help of micelle formation.
Why does physisorption decrease with the increase of temperature ?
Action of soap is due to emulsification and micelle formation. Comment .
Give four uses of emulsions.
What is demulsification ? Name two demulsifiers.
It is found that when Litmus is shaken with animal charcoal adsorption takes place
Explain the term "sorption"
Why are powdered substance more effective adsorbent than their crystalline forms?
Write two difference in adsorption and absorption.
Describe the following methods for the formation of colloidal solutions:
Bredig - Arc method
Bredig - Arc method
Which adsorbent is used to remove hardness of water ?
Class 12 Engineering Chemistry Extra Questions
- Alcohols,Phenols And Ethers Extra Questions
- Aldehydes,Ketones And Carboxylic Acids Extra Questions
- Amines Extra Questions
- Biomolecules Extra Questions
- Chemical Kinetics Extra Questions
- Chemistry In Everyday Life Extra Questions
- Coordination Compounds Extra Questions
- Electrochemistry Extra Questions
- General Principles And Processes Of Isolation Of Elements Extra Questions
- Haloalkanes And Haloarenes Extra Questions
- Polymers Extra Questions
- Solutions Extra Questions
- Surface Chemistry Extra Questions
- The D-And F-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The P-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The Solid State Extra Questions