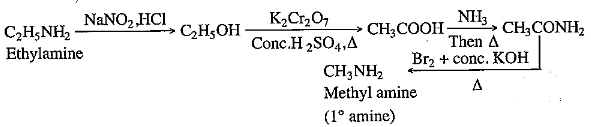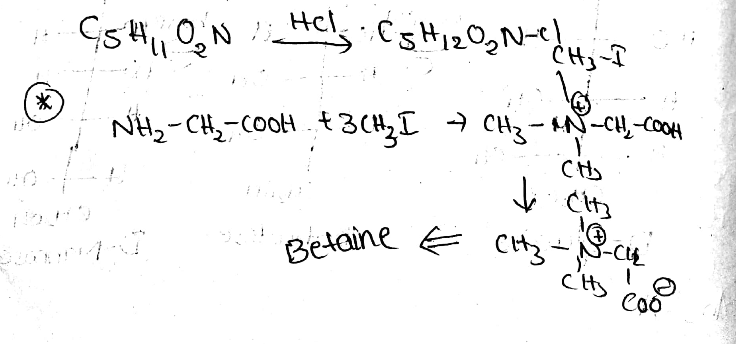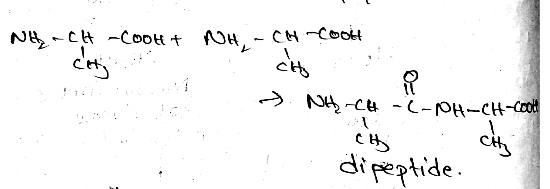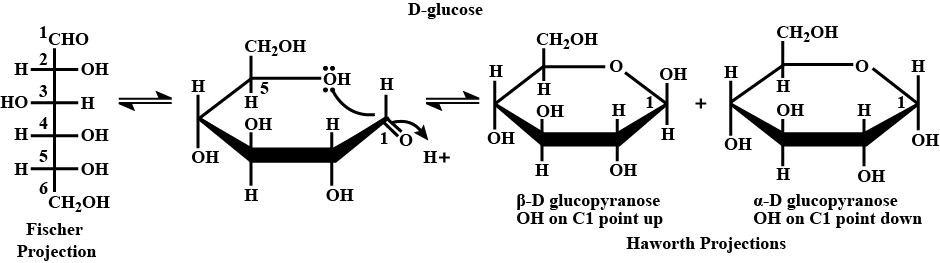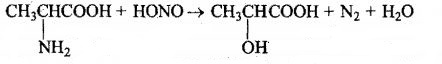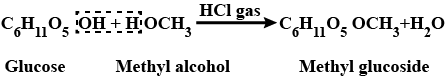Biomolecules - Class 12 Engineering Chemistry - Extra Questions
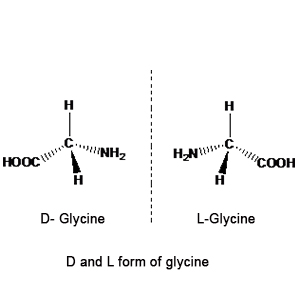
Give the D form of glycine.
Name the nitrogenous base present in sphingolipids.
What are the functions of carbohydrates?
Write the name of deficiency diseases of Vitamin A, Vitamin $$B_1$$ , Vitamin C and Vitamin D.
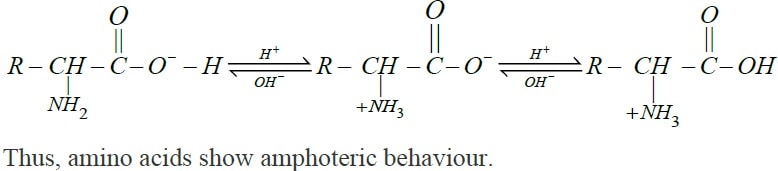
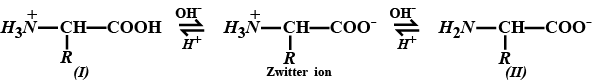
Explain the amphoteric behaviour of amino acids.
Give example for four functional proteins
How will you prepare glucose from cane sugar.
Name the enzymes involved in the breakdown of nucleotides into sugars and bases?
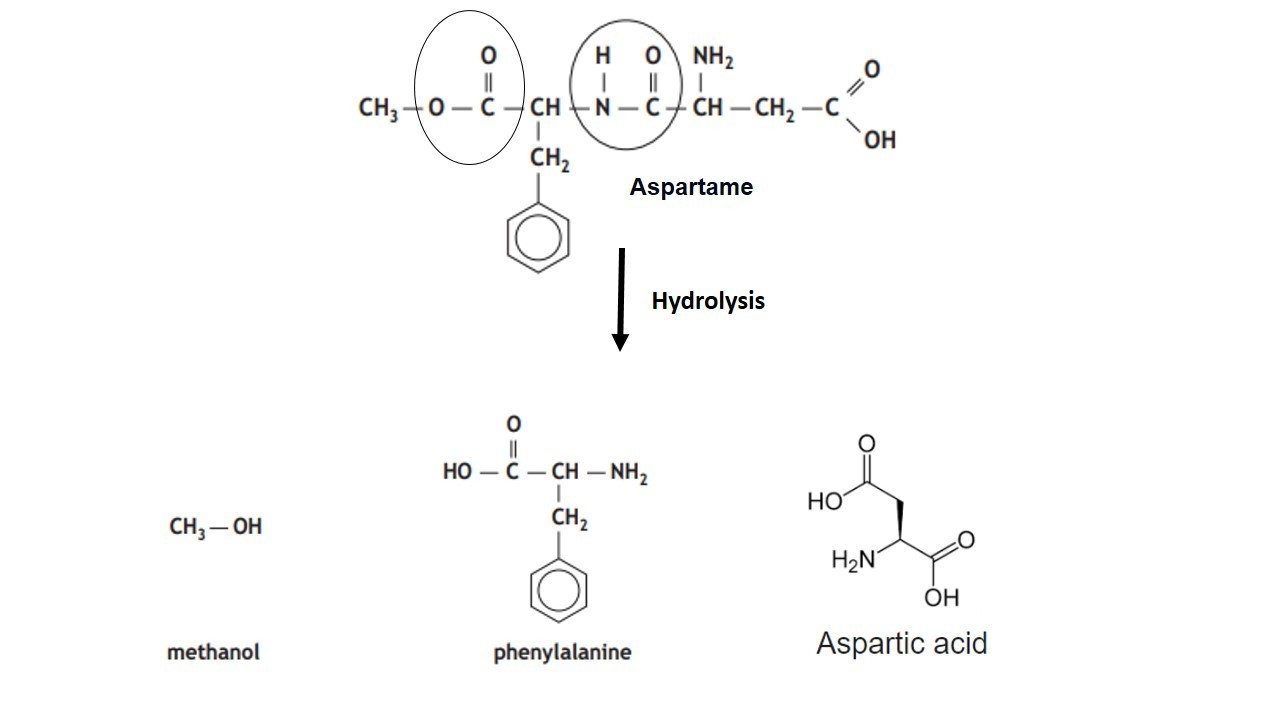
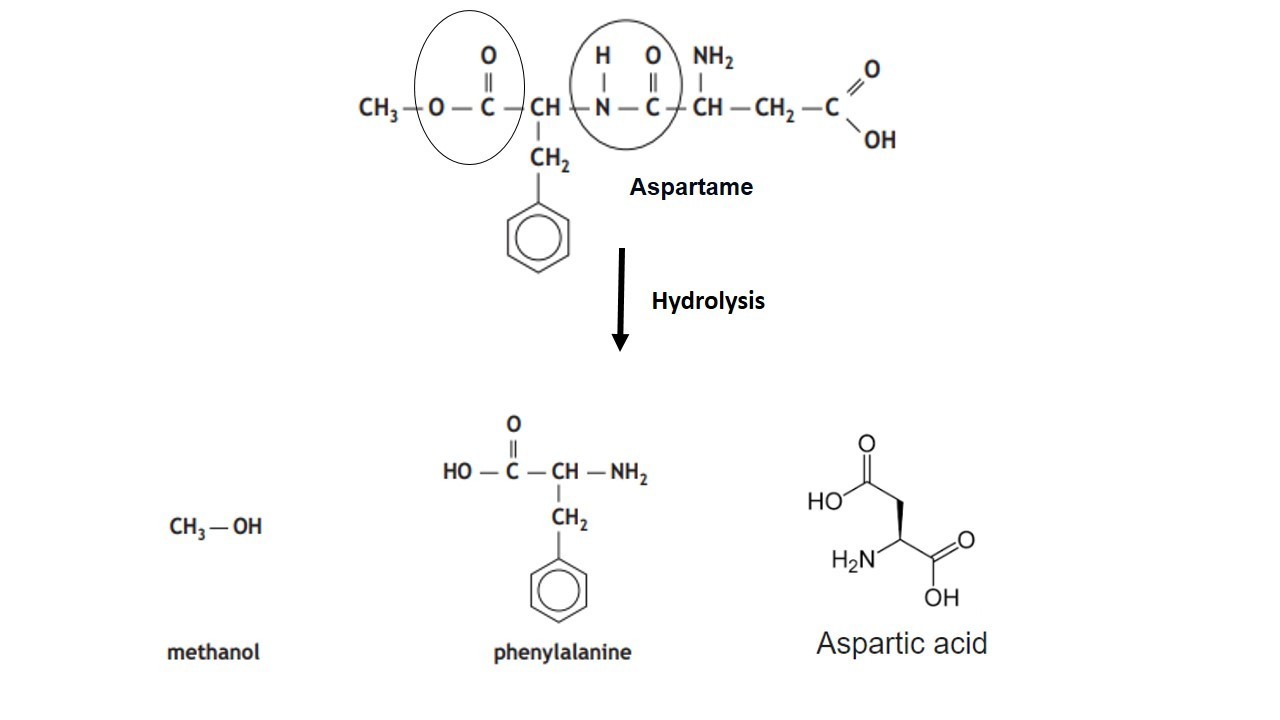
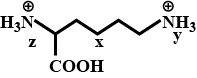
Give the Free amino acids obtained on the hydrolysis of 'Aspartame'.
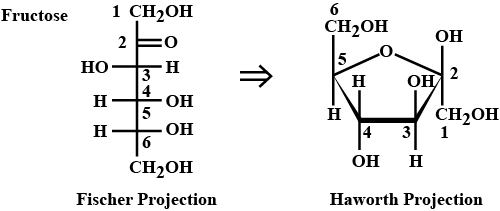
Draw the structure of fructose for haworth projection formulae.
Fructose $$\xrightarrow{Br_2/H_2O}$$ ?
Match List-I with List-II.
What are the different ways in which glucose is oxidised to provide energy in various organism ?
Photosynthesis of a carbohydrate in plants is given by chemical equation:
$$6C{ O }_{ 2 }+6{ H }_{ 2 }O\longrightarrow { C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 12 }{ O }_{ 6 }+6{ O }_{ 2 }$$
If you have net result as:
$$6C{ O }_{ 2 }+6{ H }_{ 2 }O\longrightarrow { C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 12 }{ O }_{ 6 }+6{ O }_{ 2 }$$
Check whether this reaction is correct or not.
Match the compounds in column I with their characteristic(s)/test(s)/reaction(s)/reagent(s)/stereochemistry/isomer(s) given in column II. Matching can be one or more than one.
Describe in words the atomic composition denoted by chemical formula $$C_{12}\, H_{22}\, O_{11}$$.
After watching a programme on TV about the adverse effects of junk food and soft drinks on the health of school children, Sonali, a student of Class XII, discussed the issue with the school principal. The principal immediately instructed the canteen contractor to replace the fast food with the fiber and vitamins rich food like sprouts, salad, fruits etc. This decision was welcomed by the parents and the students. After reading the above passage, answer the following questions:
(a) What values are expressed by Sonali and the Principal of the school?
(b) Give two examples of water-soluble vitamins.
What is pro-enzyme?
What are the products of hydrolysis of sugar?
Give two example of water-soluble vitamins.
Shanti, a domestic helper of Mrs. Anuradha, fainted while mopping the floor. Mrs. Anuradha immediately took her to the nearby hospital where she was diagnosed to be severely 'anaemic'. The doctor prescribed an iron rich diet and multivitamins supplement to her. Mr.s Anuradha supported her financially to get the medicines. After a month, Shanti was diagnosed to be normal.
(i) What values are displayed by Mrs. Anuradha?
(ii) Name the vitamin whose deficiency causes 'pernicious anaemia'.
(iii) Give an example of a water soluble vitamin
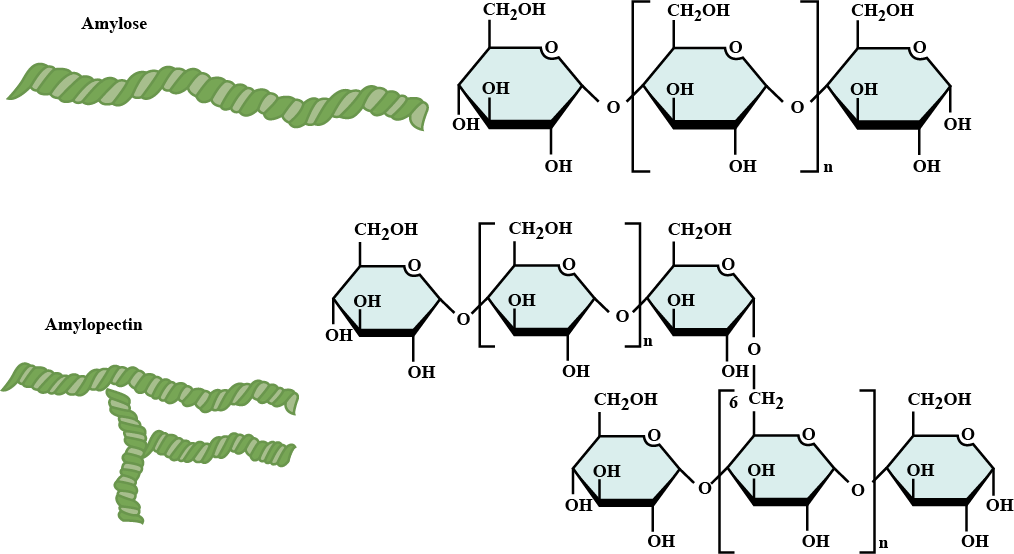
Which component of starch is a branched polymer of $$\alpha$$-glucose and insoluble in water?
Which of the two components of starch is water soluble?
Define the following terms:
(i) Glycosidic linkage
(ii) Invert sugar
(iii) Oligo saccharides
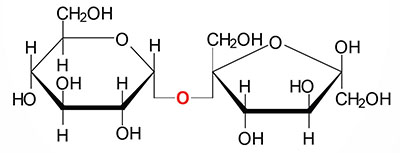
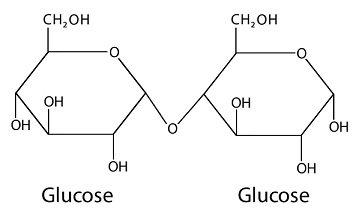
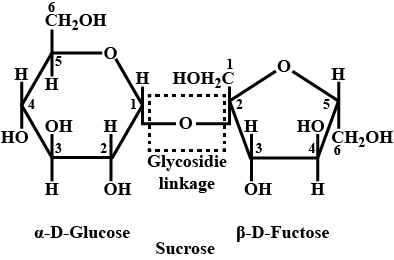
What is a glycosidic linkage?
Carbohydrates such as glucose, fructose and sucrose are sweet in taste. But, starch has bland taste though it is a carbohydrate. How do you account for this?
Does our blood have proteases and nucleases?
Give balanced equations for the following reactions:
(i) How will you convert ethyl amine to methyl amine?
(ii) What is the effect of denaturation on the structure of proteins?
(iii) Name the nitrogen base residues present in DNA.
(a) Write the Haworth structure of sucrose.
(b) Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar. Why?
Explain the preparation of glucose from cane sugar.
a) i) Name the water insoluble component of starch.
ii) Mention one water soluble vitamin.
iii) Is Lysine an essential or non-essential amino acid?
b) Write the structure of Maltose.
Name the steps in the manufacture of common sugar from sugarcane and explain the first step.
Write the functional groups present in a molecule of Glycine.
Classify Vitamins $$A, B, C$$ and $$D$$ depending upon their solubility in water and fat and compare them.
Define carbohydrates. What are reducing and non-reducing sugars?
(a) What is fermentation? Give one example.
(b) Write the balanced chemical equations of the reactions taking place in the manufacture of ethyl alcohol from sugar.
What are 'nucleic acids'?
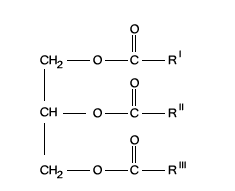
Define complex lipids. Mention any 'two' functions of lipids.
Mention any one hydrolytic product of lecithin.
Explain the functions of polysaccharides.
Give the classification of carbohydrates with examples.
State whether the following statements are true or false :
(i) The general formula of alkanes is $${C}_{n}{H}_{2n+2}$$.
(ii) Carbohydrates are body building nutrients.
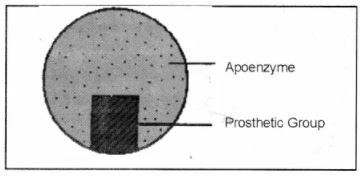
What is a coenzyme?
Equations of preparation of alcohol from sugar are given:
$${C}_{12}{H}_{22}{O}_{11}+{H}_{2}O\xrightarrow [ ]{ Invertase } \underset { A }{ { C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 12 }{ O }_{ 6 } } +\underset { B }{ { C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 12 }{ O }_{ 6 } } $$
$${C}_{6}{H}_{12}{O}_{6}\xrightarrow [ ]{ zymase } 2{C}_{2}{H}_{5}OH+2{CO}_{2}$$
(a) Write the names of the Compounds $$A$$ and $$B$$.
(b) The alcohol obtained here is known as .............
(c) How can this alcohol be converted into reflected spirit?
(d) How can power alcohol be prepared?
Match the pairs correctly.
Write the properties of hormone.
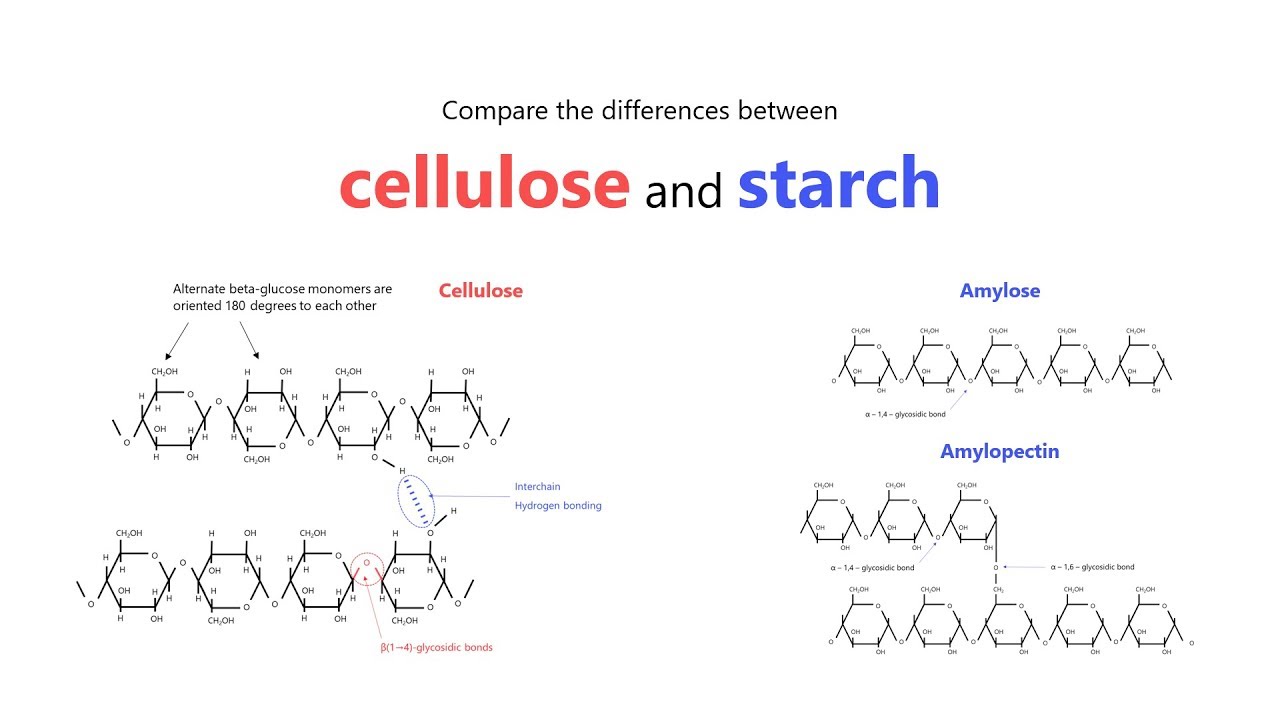
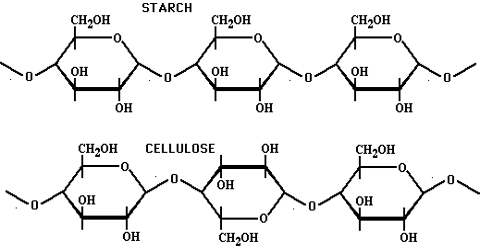
Mention the difference between amylose and amylopectin.
Write the functions of the following vitamins:
(i) Vitamin A (ii) Vitamin D
(iii) Vitamin E (iv) Vitamin K
Cane Sugar, Glucose and Starch are Carbohydrates.
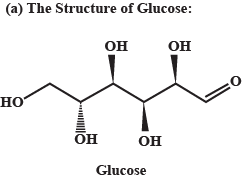
(a) Represent the structure of Glucose.
(b) Write a method to prepare Glucose from Starch. Write the chemical equation of the reaction.
(c) Suggest any two uses of Carbohydrates.
Name two energy-providing nutrients.
What are vitamins? Write various kinds of vitamins?
Starch is __________ saccharide.
What are carbohydrates?
What is turn over number?
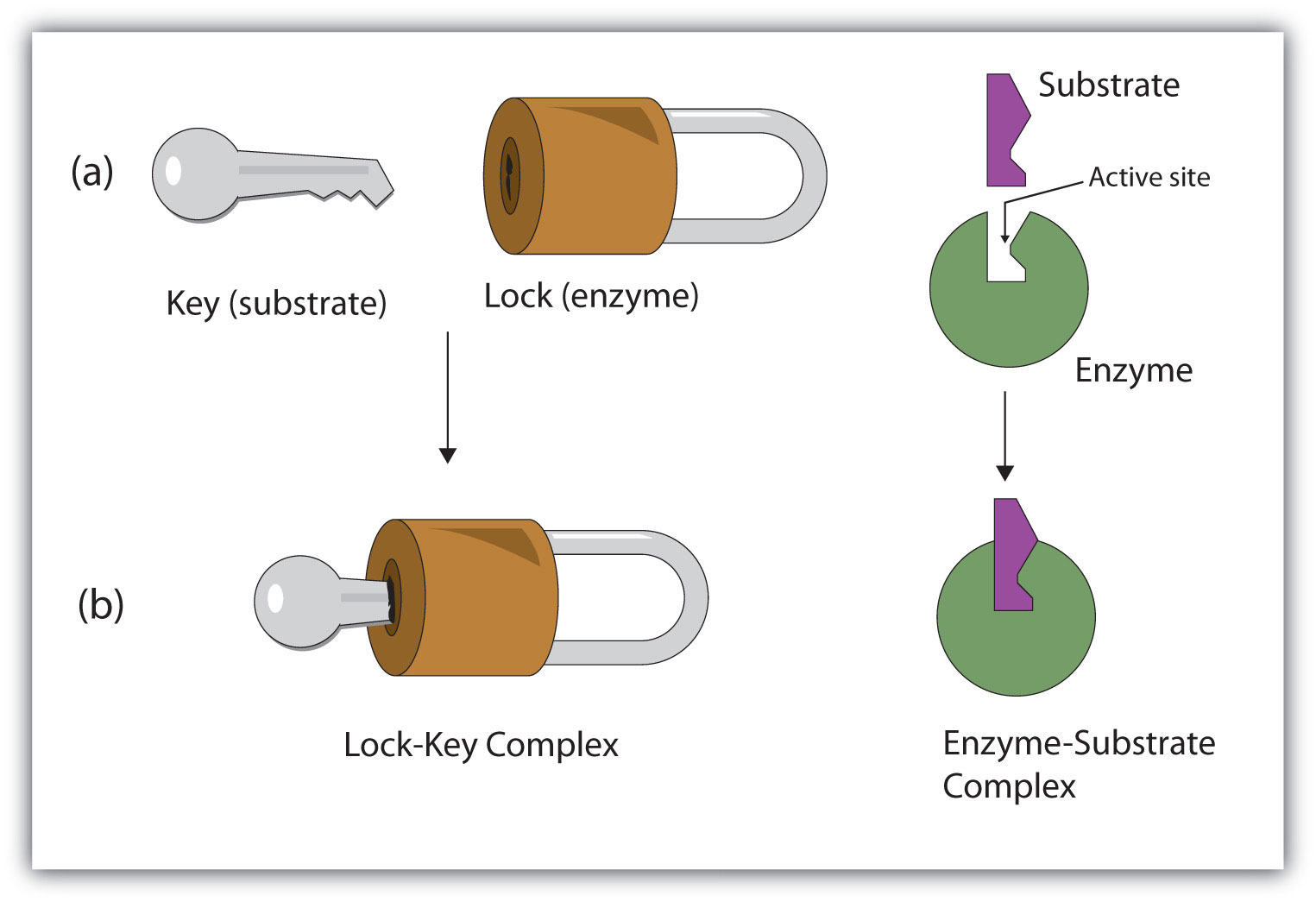
(a) What are enzymes ?
(b)Discuss the mechanism of enzyme action.
Arrange the following carbohydrates in the order of increasing complexity of chemical structures: fructose, starch, oligosaccharide, maltose, triose.
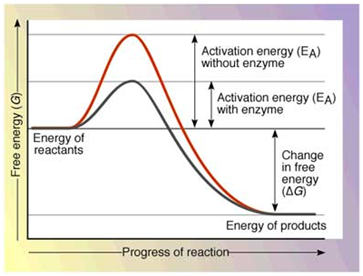
How are enzymes able to enhance the rate of reaction ?
Betaine $$C_{5}H_{11}O_{2}N$$, occurs in beet sugar molasses. It is water soluble solid that melts with decomposition at $$300^{\circ}C$$. It is unaffected by a base but reacts with hydrochloric acid to form a crystalline product $$C_{5}H_{12}O_{2}NCl$$. It can be made from glycine with methyl iodide or treatment of chloroacetic acid with trimethyl amine. Draw structure for betaine which will account for all properties given above.
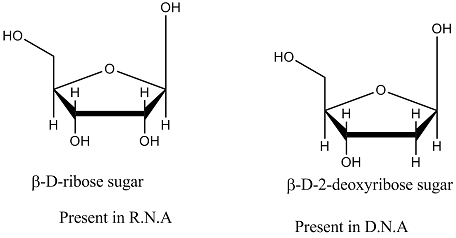
On the basis of 'sugar' differentiate D.N.A. and R.N.A:
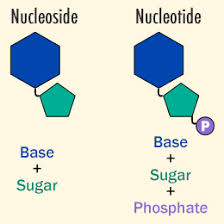
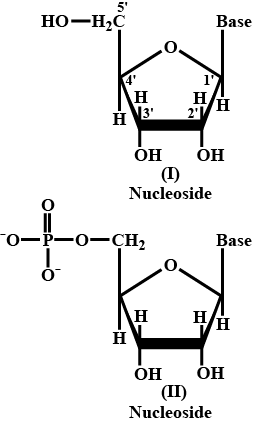
Write down any two difference between nucleoside and nucleotide.
For a polymerization reaction: $$6HCHO\rightleftharpoons C_{6}H_{12}O_{6}$$ degree of association was found to be $$0.96$$. Calculate mean mass of mixture at equilibrium. Report value of mean molar mass of mixture dividing by $$50$$.
What are the main characteristics of an enzyme?
Define and give example of Essential amino acids :
Name the enzyme which catalyses the conversion of soluble fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin.
Short / Long answer type questions.
What happens to the starchy part of a meal from the time it is eaten till it is made available to body tissues?
What was the discovery for which Sumner Was awarded Nobel Prize?
Name one element invariably found in proteins but not in all carbohydrates and lipids.
Differentiate between.
Enzymes and inorganic catalysts
A substance that accelerates a chemical reaction, but itself is unchanged when the reaction is over, is a.......... In living systems, most of these substances are proteins known as..........
Write the general (empirical) formula for a carbohydrate.
Write only equation for the reactions for preparation of glucose from sugar and starch.
Write a short note on heterocyclic base present in nucleic acids. (structure is not required).
Write a note on significance of carbohydrates.
Which enzymes are called molecular scissors?
Preparation of soyabean milk and its comparison with the natural milk.
Write a short note on glycogen.
Explain the importance of carbohydrates.
Write a short note on starch:
Classify Amino acids on basis of function and on basis of Nature of amino acids.
Why Vitamin C can't be stored in our body?
How do you explain the amphotoric behaviour of aminoacids.
Why carbohydrates are important in our diet?
Enzyme catalyzed reaction proceed at rates vastly higher than that of uncatalysed reactions. prove this statement by taking a proper example.
What are amino acids?
Prepare Dipeptide from Alanine.
Classify the following into monosaccharides,oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
(1) starch, (2) glucose, (3) stachyose, (4) maltose, (5) raffinose,
(6) cellulose, (7)sucrose, (8) lactose.
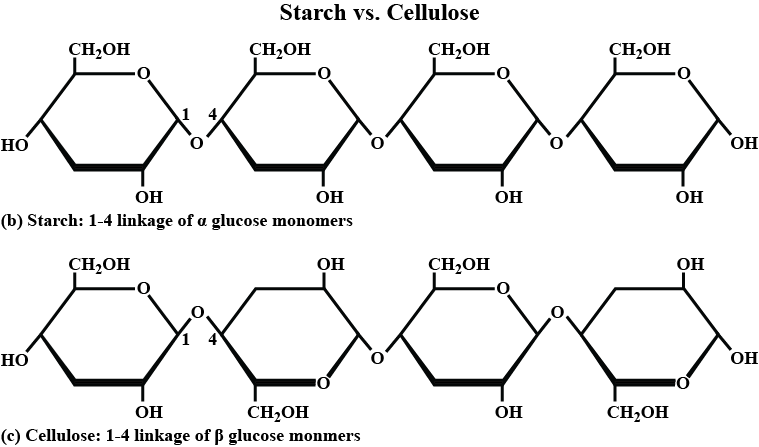
What is the basic structural difference between starch and cellulose ?
What are enzymes? Name any one enzyme of our digestive system and write its function.
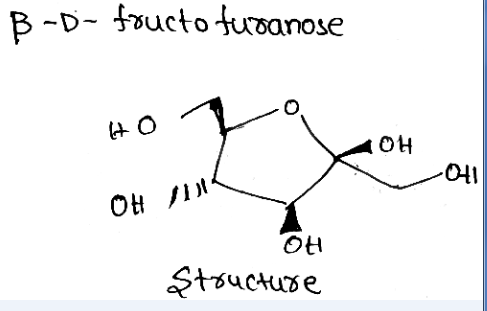
Write the structure of $$\beta-D-$$ fructo furanose.
Name the compound that does nit fit into the formula $$C_x (H_2O)_y$$, but is a carbohydrate.
What are reducing sugars?
What is the general formula of carbohydrates?why this formula is no applicable to all the carbohydrates?
name two water soluble vitamins, their sources and the diseases caused due to their deficiency in diet.
What are enzymes? Name an enzyme which is present in saliva and state its function.
The binding of the substrate induces the enzyme to alter its shape fitting more tightly around the substrate.
Can enzymes start a particular reaction? Explain your answer.
How are vitamins classified? Name the vitamin responsible for the coagulation of blood.
What are nucleic acids?
Classify the following into monosaccharides and disaccharides. Ribose, 2-deoxyribose, maltose, galactose, fructose and lactose.
Write two main functions of carbohydrates in plants.
Fill in the blanks:
Polymer of nucleotides are called ......
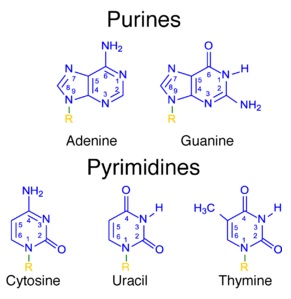
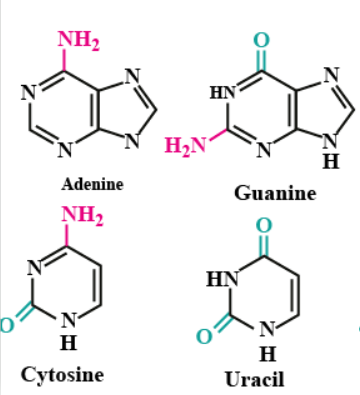
What is the Difference Between Purines and Pyrimidines?
Fill in the blanks:
The formula $$C_{x}(H_{2}O)_{y}$$ can be assigned to $$...........$$
Give one example of each of the following
Reducing sugar, Non-reducing sugar
Name the sources of following vitamins: Vitamin D
Classifying the following into monosaccharides, disacharides and polysaccharides
Ribose,glycogen,maltose,deoxyribose,lactose,fructose,glucose,cane-sugar ,starch cellulose
Starch is a polymer of ...while cellulose that of ...
Explain the observed $${K}_{b}$$ order:
$$E{t}_{2}NH> E{t}_{3}N> Et{NH}_{2}$$ in aqueous solution
Which monosaccharide units are present in starch, cellulose, and glucose, and which linkage link these units?
What are polysaccharides ? Give on example?
Unscramble the following word related to components of food.
BOCATRADHYER
What is the basic structural difference between starch and cellulose?
Name two biologically important compounds that contain both oxygen and nitrogen.
Arrange the order of increasing acidic strength.
Name the link connecting monosaccharide unit in polysaccharides.
Carbohydrates and ___-provide_____ to our body.
Write any two methods for the preparation of glucose.
Enzymes are proteins. Proteins are long chains of amino acids linked to each other by peptide bonds. Amino acids have many functional groups in their structure. These functional groups are, many of them at least, ionisable. As they are weak acids and bases in chemical nature, this ionization is influenced by pH of the solution. For many enzymes, activity is influenced by surrounding pH. This is depicted in the curve given, explain briefly.
Write the name of the disease caused by the deficiency of vitamin $$ B_{12} $$ and vitamin A. Also, write the source of these vitamins.
Write the name of nitrogenous bases found in DNA.
What are the constituent elements of sugar?
Why are hormones known as 'glandular juice' ?
Which vitamin is soluble in water ?
The compound in food materials are given, Filling the missing ones
a)Carbohydrates - Carbon, Hydrogen
b)Protein - Carbon, Hydrogen, oxygen
c)Fats - Carbon, Hydrogen
Biochemical reactions are regulated by catalysts called ...........
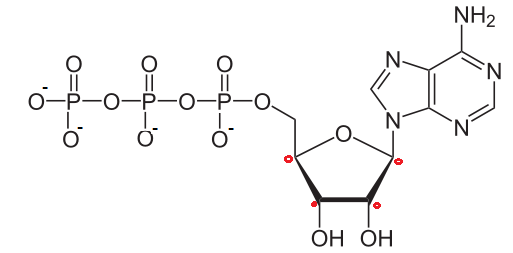
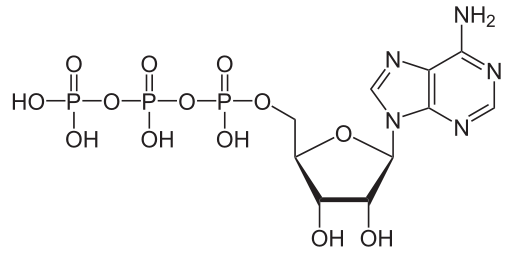
The structure of Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecule is given above. The value of $$n_{1}+n_{2}$$ is (where $$n_{1}$$ is the net negative charge in neutral medium and $$n_{2}$$ is number of chiral carbon atoms)
Match the one-letter code for each amino acids:
Give two examples of water soluble vitamins.
Which polysaccharide component of carbohydrates is commonly present in bread?
What are hormones? Write the structure of simple triglycerides.
Match the following and choose the correct option.
Explain the classification of hormones in detail.
Amino acids show amphoteric behaviour. Why?
Give the main sources of Vitamins $$A,C$$ and $$D$$. Write down the names of diseases caused by their deficiency.
Name an enzyme where RNA acts as a biological catalyst.
What are carbohydrates? Classify them and also write their characteristics.
What kind of reaction do Dehydrogenases enzymes catalyse?
Differentiate between Starch and Glucose.
Are enzymes specific for only specific compounds? Explain.
Why are enzymes specific, and why can not each one speed up many different reactions?
Write short notes on the following:
(a) Enzyme specificity (b) Enzyme inhibition
Aspartame, an artificial sweetener, is a peptide and has the following structure
(I) Identify the four functional groups
(II) Write the zwitter ionic structure
(III) Write the structures of the amino acids obtained from the hydrolysis of aspartame
(IV) Which of the two amino acids is more hydrophobic?$$H_2N-\underset{\underset{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,CH_2-COOH}{|}}{C}H-CONH-\overset{\overset{\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,CH_2-C_6H_5}{|}}CH-COOCH_3$$
ATP ase enzyme consists of two parts. what are those parts ? How are they arranged in the thylakoid membrane ? Conformational change occurs in which part of the enzyme ?
Give scientific reason: Microbial enzymes are said to be eco-friendly
Answer the following questions:
Write Haworth projection formula of $$\alpha -D-(+)-$$glycopyranose.
Define hormones.
Write Haworth projection formula of $$\alpha -D-(+)-$$glycopyranose.
Define hormones.
Define the following terms with a suitable example:
Polysaccharides
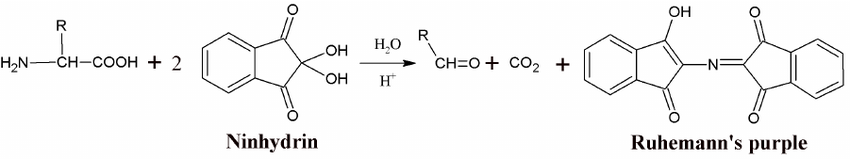
Write the reaction of an amino acid with ninhydrin reagent?
Fill in the blanks:
A disaccharide consists of two ..... joined by ..... bonds.
Fill in the blanks:
A polysaccharide is a polymer of ..........
Fill in the blanks:
Protein is a polymer of......
Fill in the blanks:
A compound that contains both.....and......is called amino acid.
Fill in the blanks.Amino acids are the end products of the digestion of .......
Fill in the blank
Exposure of body to sunrays produces...
Name the sources of following vitamins: Vitamin A
What happens when
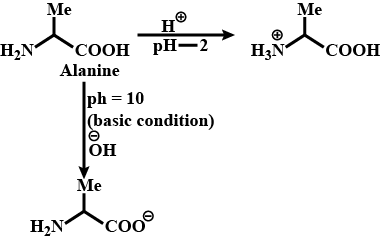
Alanine is treated with nitrous acid
Name the sugars present in nucleic acid
What is nucleoside ? when does it become nucleotide ?
Find the average molecular mass of starch given that an aqueous solution of 10.0 g/L of starch has an osmotic pressure $$5.0\times 10^{-3}$$ atm at $$25^{\circ}C$$. What is the approximate number of glucose units in this sample of starch?
Name the base present in RNA
Name the sources of following vitamins: Vitamin C
Name the monosaccharides which the following give on hydrolysis?
(a) sucrose (b) lactose (c) maltose (d) Raffinose
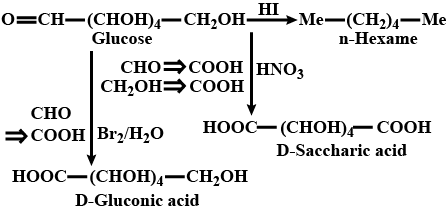
What happens when $$S-$$ glucose is treated with the following reagents?
$$HNO_{3}$$
Which of the two components of starch is water soluble ?
Seema likes sugar apple which is a multiple purpose , an all-rounder fruit . It can be used by athletes as high calorie fruit for high energy. The powder of its seeds is an effective pesticide in agriculture and horticulture and also used to remove head lice. Its leaves have anti-diabetic properties . The alcoholic extract of its leaves and stems can treat tumours . This extract is an antidepressant . Fruits are sweet and increase the haemoglobin , cooling and act as sedative. Seeds are insecticides . Its roots are powerful purgatives and used in dysentery.
Why should we use it as a pesticides and insecticides instead of chemicals ? Which value is associated with its use ?
Why are carbohydrates generally optically active ?
What is the major structural polysaccharide in higher plants ?
Seema likes sugar apple which is a multiple purpose , an all-rounder fruit . It can be used by athletes as high calorie fruit for high energy. The powder of its seeds is an effective pesticide in agriculture and horticulture and also used to remove head lice. Its leaves have anti-diabetic properties . The alcoholic extract of its leaves and stems can treat tumours . This extract is an antidepressant . Fruits are sweet and increase the haemoglobin , cooling and act as sedative. Seeds are insecticides . Its roots are powerful purgatives and used in dysentery.
Why is sugar apple used by athletes ?
What are nucleic acids? Mention their two important functions.
Write the structure of alanine at $$pH=2$$ and $$pH=10$$.
Name the two components which constitutes starch.
Give two examples of water-soluble vitamins.
What type of linkage is present in nucleic acids ?
Define Glycosidic linkage
State two main functions of carbohydrates.
Among B group vitamins $$ B_1, B_2, $$ and $$ B_{12} $$ which vitamin can be stored in our body ?
Name the enyme that is used to dissolve blood clots.
Name the enzymes that breaks large protein into small peptides.
Out of aspartic acid and ascorbic acid which one in a vitamin?
Name two water-soluble vitamins. State their sources and the diseases caused due to their deficiency in the diet.
Give the chemical name of vitamin $$ B_{12} $$
Define Enzymes.
Define Amino acids
Give one example each for water-soluble vitamins and fat-soluble vitamins
Amino acids show amphoteric behaviour. Why ?
Define Polysaccharides
Name the three major classes of carbohydrates and give an example of each of these classes.
Which one of the following is a polysaccharide?
Starch, Maltose, Fructose, Glucose
Which of the following biomolecules is insoluble in water? justify.
Insulin, Haemoglobin, Keratin
Give one structural difference between amylose and amylopectin.
What are glycosidic linkages? In which type of biomolecules are they present?
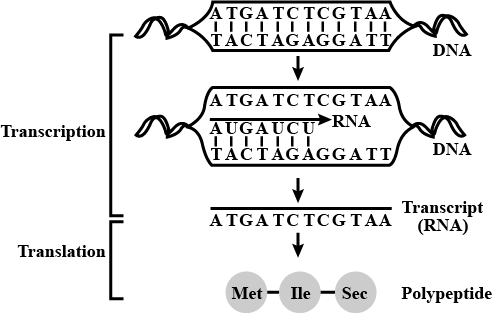
How protein is synthesized by nucleic acid ? Explain.
Write the general chemical reactions of glucose.
Write notes on Polysaccharides.
Write the names and biological functions of hormones secreted by the pituitary gland and thyroid gland.
What are the main sources of cellulose and starch? Explain their structure in brief.
What is the final product obtained by the hydrolysis of Starch?
Describe the term $$D-$$ and $$L-$$ configuration used for an amino acid with examples.
Describe the structure of the enzyme and explain their specific characteristics.
Class 12 Engineering Chemistry Extra Questions
- Alcohols,Phenols And Ethers Extra Questions
- Aldehydes,Ketones And Carboxylic Acids Extra Questions
- Amines Extra Questions
- Biomolecules Extra Questions
- Chemical Kinetics Extra Questions
- Chemistry In Everyday Life Extra Questions
- Coordination Compounds Extra Questions
- Electrochemistry Extra Questions
- General Principles And Processes Of Isolation Of Elements Extra Questions
- Haloalkanes And Haloarenes Extra Questions
- Polymers Extra Questions
- Solutions Extra Questions
- Surface Chemistry Extra Questions
- The D-And F-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The P-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The Solid State Extra Questions