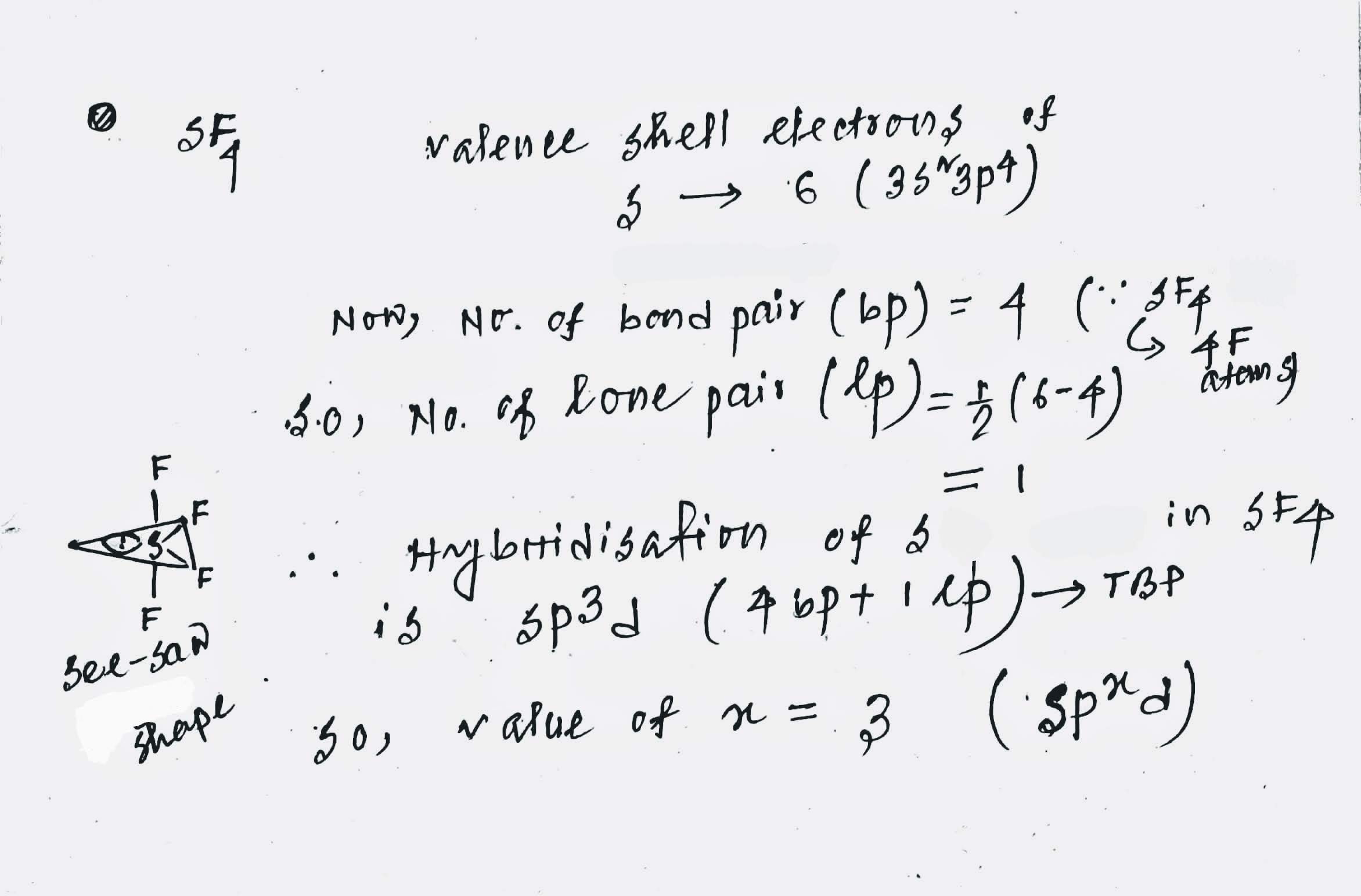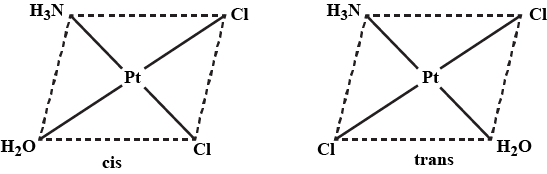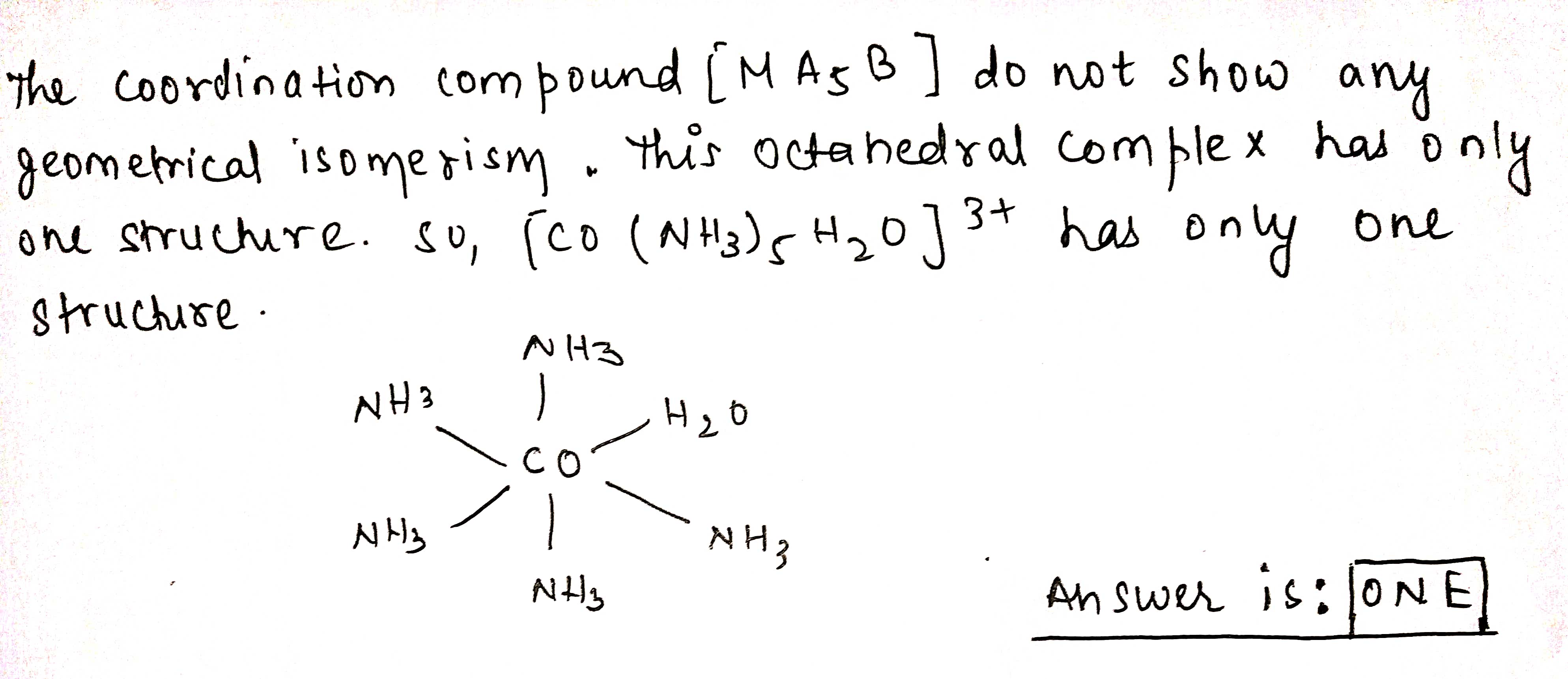Coordination Compounds - Class 12 Engineering Chemistry - Extra Questions
Match each coordination compound in List-I with an appropriate pair of characteristics from List-II. ($$en = H_2HCH_2CH_2NH_2$$; Atomic numbers: $$Ti =22, Cr=24; Co=27; Pt = 78$$)
Blue-green is the complimentary color of red spectral color.If true enter 1, else enter 0.
Orange is the complimentary colour of blue spectral colour.
If true 1 else 0.
Name the series of lines in the hydrogen spectrum which lies in the ultra-violet region :
Haemoglobin is a complex of $$Fe(II)$$ bound to porphyrin rings.
If true enter 1, else enter 0.
Discuss briefly giving an example in each case the role of coordination compound in biological system.
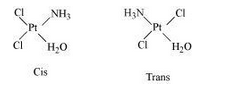
What type of isomerism is exhibited the complex $$[Co(NH_3)_5Cl]SO_4$$?
Identify the type of Isomerism existing in between the following compounds.
$$\left[ {Co\left( {N{H_3}} \right)s\,N{O_2}} \right]$$ and $$\left[ {Co\left( {N{H_3}} \right)s\,ON{O_2}} \right]C{l_2}$$
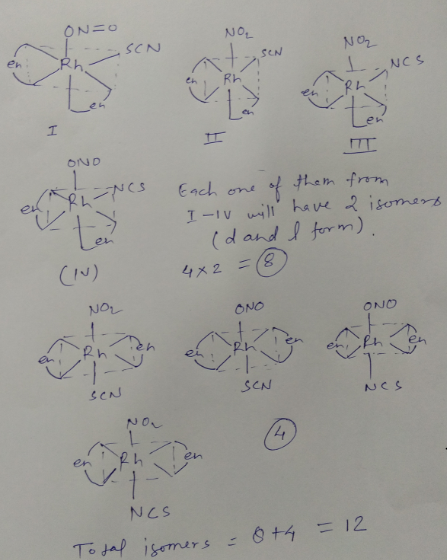
How many isomeric forms are possible for the octahedral complex, $$[Rh(en)_{2}(NO_{2})(SCN)]^{+}$$?
What is the use of coordination compounds for purification of water Medical and catalyst
Indicate the types of isomerism exhibited by the following complex and draw the structure of this isomer.
$$[Co(NH_3)_5(NO_2)](NO_3)_2$$
How are the hybrid orbitals arranged in the molecules?
Match the given pairs.
The primary valency of a central metal ion in a complex is satisfied with _______ .
According to Werner's coordination theory, there are _______ kinds of valency - _____ and ______.
Match column-I with column-II
In $$[Fe(H_2O)_6]Cl_3$$, six $$H_2O$$ are joined by primary valency (PV) and three $$Cl$$ are joined by secondary valency (SV).
If true enter 1, else enter 0.
Match column-I with column
Vitamin $$B_{12}$$ is a complex of cobalt. If true enter 1, else enter 0.
Match the following.
What is hybridisation?
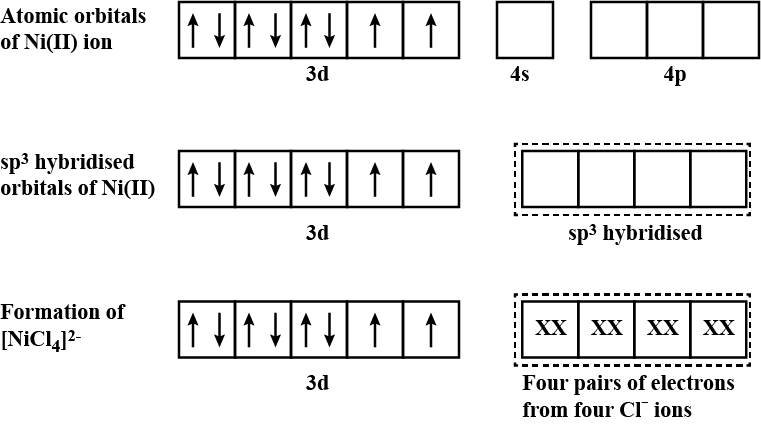
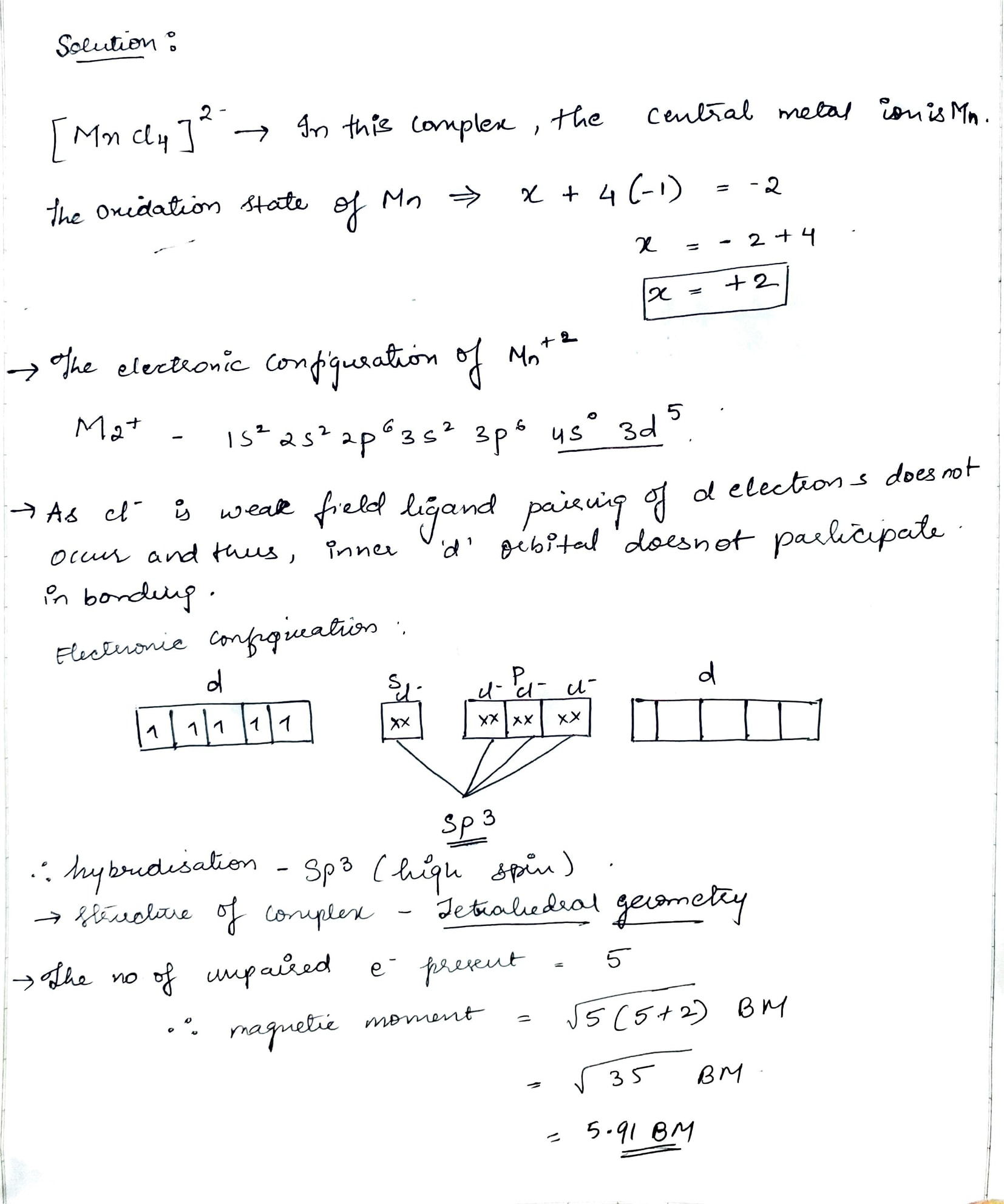
For the complex $$[NiCl_{4}]^{2-}$$, write
(i) the IUPAC name (ii) the hybridization type (iii) the shape of the complex.
(Atomic no. of $$Ni = 28$$)
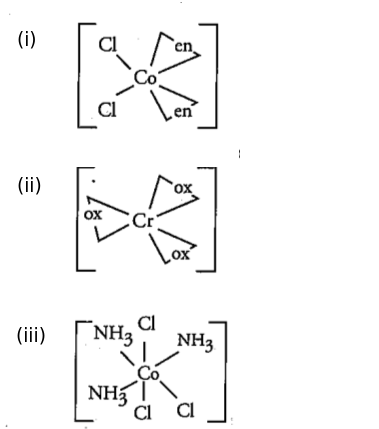
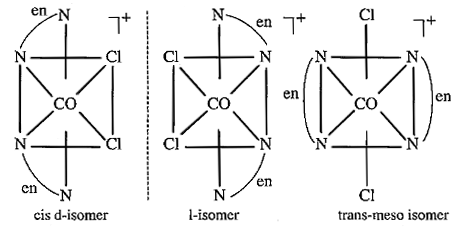
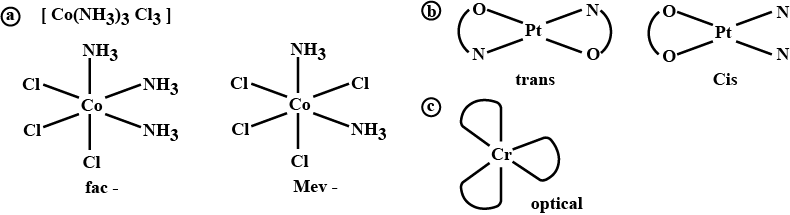
Name the following coordination entities and draw the structures of their steroisomers:
(i) $$[Co(en)_2Cl_2]^+ (en=ethane - 1, 2-diamine)$$
(ii) $$[Cr(C_2O_4)_3]^{3-}$$
(iii) $$[Co(NH_3)_3Cl_3]$$
(Atomic number $$Cr=24, Co=27$$)
Write the IUPAC names of the following coordination compounds:
(i)$$[Cr(NH_3)_3Cl_3]$$
(ii)$$K_3[Fe(CN)_6]$$
(iii)$$[CoBr_2(en)_2]^{+}$$, (en = ethylenediamine)
Write the name, the structure and the magnetic behavior of each one of the following complexes:
(i) $$[Pt (NH_3) Cl (NO_2)]$$
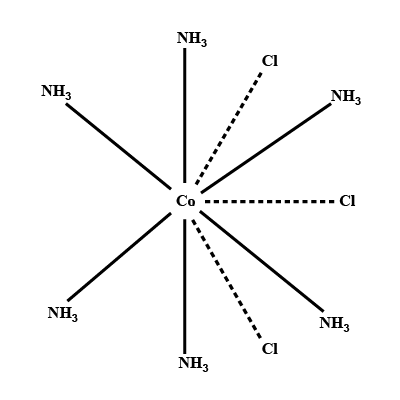
(ii) $$[Co(NH_3)_4Cl_2] Cl$$
(iii) $$Ni (CO)_4$$
(At. Nos. $$Co = 27, Ni = 28, Pt = 78$$)
(i) Write the IUPAC name of the complex $$\left[ Cr{ \left( N{ H }_{ 3 } \right) }_{ 4 }{ Cl }_{ 2 } \right] Cl$$.
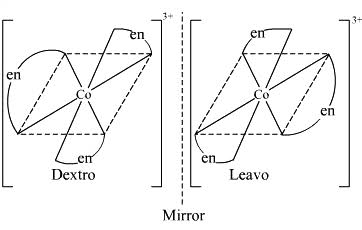
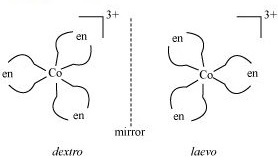
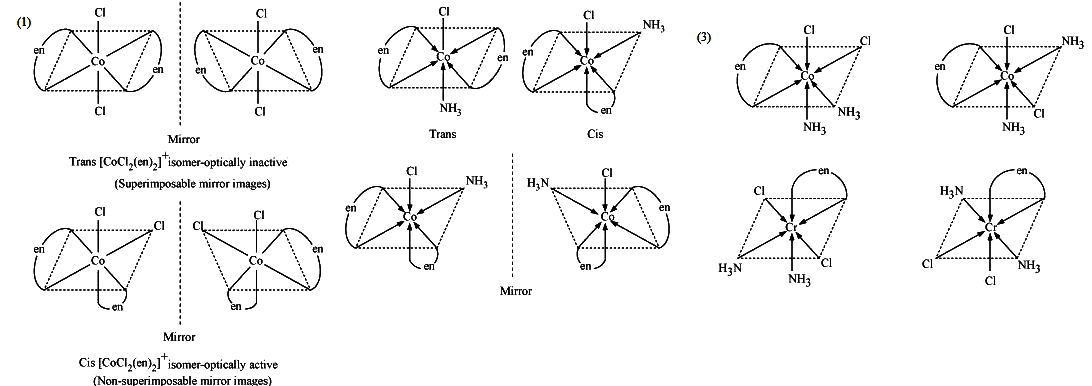
(ii) What type of isomerism is exhibited by the complex $${ \left[ Co{ \left( en \right) }_{ 3 } \right] }^{ 3+ }$$?
($$en=$$ ethane-1, 2-diamine)
(iii) Why is $${ \left[ Ni{ Cl }_{ 4 } \right] }^{ 2- }$$ paramagnetic but $$\left[ Ni{ \left( CO \right) }_{ 4 } \right] $$ is diamagnetic?
($$Cr=24, Co=27, Ni=28$$)
Write the types of isomerism exhibited by the following complexes.
(i) $$[Co(NH_{3})_{5}Cl]SO_{4}$$
(ii) $$[Co(en)_{3}]^{3+}$$
(iii) $$[Co(NH_{3})_{6}] [Cr(CN)_{6}]$$
The electron pairs involved in hybridisation and not involved in bonding are called ___________.
Name the types of isomerism shown by the following pairs of compounds:
(i) $$[CoCl(H_2O)(NH_3)_4Cl_2]$$ and $$[CoCl_2(NH_3)_4]Cl\cdot H_2O$$
(ii) $$[Pt(NH_3)_4][PtCl_6]$$ and $$[Pt(NH_3)_4Cl_2][PtCl_4]$$
How does $${ K }_{ 2 }\left[ Pt{ Cl }_{ 4 } \right]$$ get ionized when dissolved in water? Will it form precipitate when $$ AgN{ O }_{ 3 }$$ solution is added to it? Give a reason for your answer.
What are the dark lines seen in the solar spectrum called?
Illustrate with example, the difference between a double salt and coordination compound.
(i) What type of isomers are $$\left[ Co{ \left( { NH }_{ 3 } \right) }_{ 5 }Br \right] { SO }_{ 4 }$$ and $$\left[ Co{ \left( { NH }_{ 3 } \right) }_{ 5 }{ SO }_{ 4 } \right] Br$$? Give a chemical test to distinguish between them.
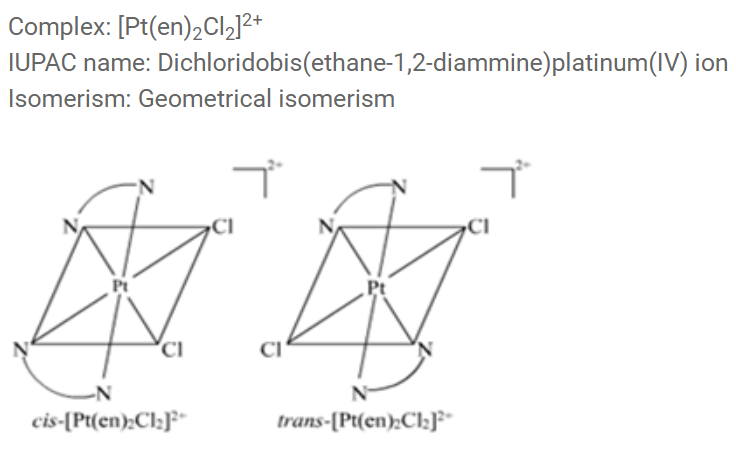
(ii) Write the structures of optical isomers of the complex ion $${ \left[ Co{ (en) }_{ 2 }{ Cl }_{ 2 } \right] }^{ + }$$
Explain co-ordination and ionisation isomeristmes with a suitable example for each.
Explain the difference between a double-salt and a complex, giving an example in each case.
Explain the applications of coordination compounds in the field of metal purification giving an example :
Explain coordination and ionisation isomerism with example.
Write a note on Haemoglobin.
Classify the following into homoleptic & heteroleptic complexes?
i) $$K_4[Fe(CN)_6]$$
ii) $$[Co(NH_3)_5(CO_3)]Cl$$
iii) $$K_2[Zn(OH)_4]$$
iv) $$[Pt(NH_3)_2Cl(NO_2)]$$
Explain the violet colour of $$[Ti(H_2O)_6]^{3+}$$ complex on basis of the crystal field theory?
Explain Werner's theory of coordinate compounds with suitable examples?
(a) Give the postulates of Werner's theory of co-ordination compounds.
(b) Differentiate between chemical reactions and nuclear reactions.
Explain Werner's theory of co-ordination compounds?
Write the IUPAC name of following compounds :
(A) $$K_3[Fe(CN)_6$$
(B) $$[Co(NH_3)_6]Cl_3$$
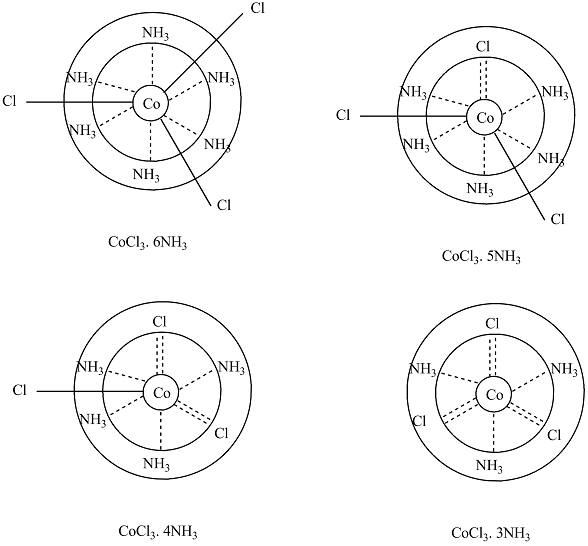
Draw Werner's structure of the following:
(a) $$CoCl_{3} . 6NH_{3}$$
(b) $$CoCl_{3} . 5NH_{3}$$
(c) $$CoCl_{3} . 4NH_{3}$$
(d) $$CoCl_{3} . 3NH_{3}$$
Write any two postulates of Werner's theory of coordination compounds.
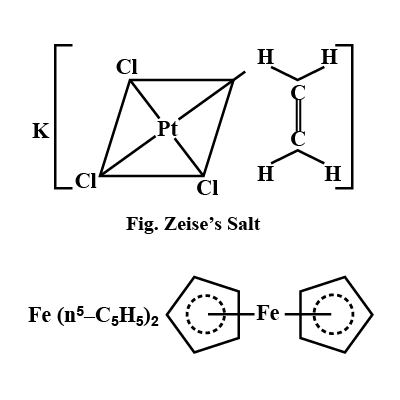
What is Zeise's Salt and Ferrocene? Explain with structure?
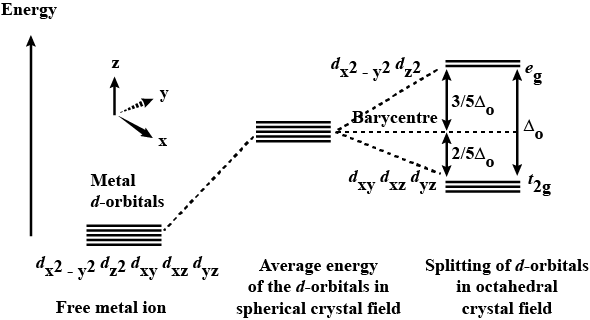
How do 'd' orbitals split in an octahedral crystal field?
What types of isomer are $$[Co(NH_3)_5 Br] SO_4$$ and $$[Co(NH_3)_5 SO_4] Br$$?
Number of $$Cl^{-}$$ ions satisifying both primary and secondary valency are in $$CoCl_{3}5NH_{3}$$.
Define primary and secondary valency of metal ions proposed by werner theory?
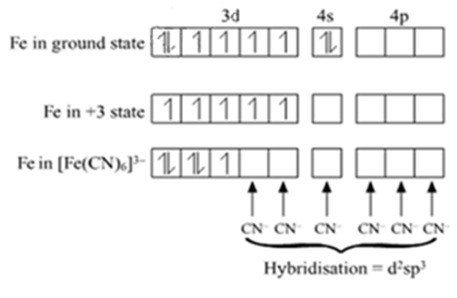
For the complex ion $$[Fe(CN)_6]^{3-}$$, state:
(i) the type of hybridisation.
(ii) the magnetic behaviour.
(iii) the oxidation number of the central metal atom.
Write primary and secondary valency of $$Co$$ in $$[Co(Nn_{3})_{6}]Cl_{3}$$?
Write the name and draw the structures of each of the following complex compounds.
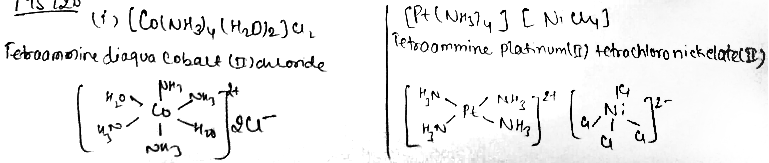
(i) $$\left[ Co{ \left( N{ H }_{ 3 } \right) }_{ 4 }{ \left( { H }_{ 2 }O \right) }_{ 2 } \right] { Cl }_{ 2 }$$
(ii) $$\left[ Pt{ \left( N{ H }_{ 3 } \right) }_{ 4 } \right] \left[ \left( NiC{ l }_{ 4 } \right) \right]$$
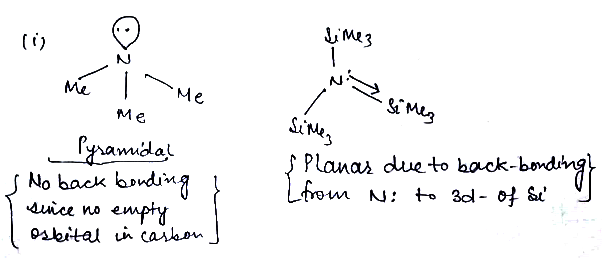
Predict whether the following molecules are isostructural or not. Justify your answer
(i) $$N{Me}_{3}$$ (ii) $$N{(Si{Me}_{3})}_{3}$$
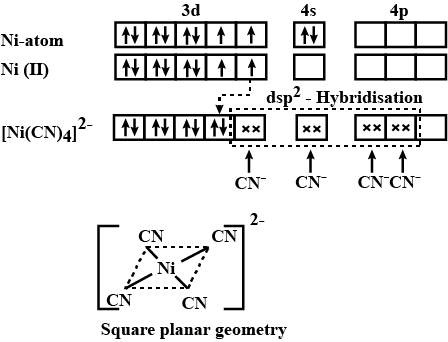
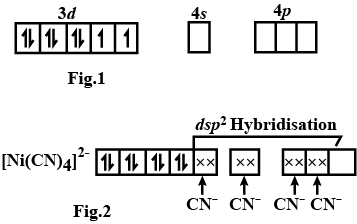
Explain hybridisation, geometry and magnetic property of $$[Ni(CN)_4]^{2-}$$ ion using Valence Bond Theory(VBT). [Atomic number of Ni is $$28$$].
Chlorophyll contains 2.68% of $$Mg$$ by weight. Then the number of $$Mg$$ atom in 2.00 g of chlorophyll is:(Atomic mass of $$Mg = 24$$)
Give two examples of Complex compound.
Define Hybridization.
Write formula of the following compound:
(i) dichloridobis (ethylene diamine) cobalt (III) ion.
(ii) sodiumethylenediaminetetraacetatonickelate (II)
(iii) hexaammineplatinum (IV) chloride
The complex studied by Werner had a composition corresponding to the formula $$Pt{Cl}_{4}.2KCl$$. From electrical conductance measurements, he determined that each formula unit contained three ions. He also found that silver nitrate did not give a precipitate of $$AgCl$$ with this complex. Write a formula for this complex that agrees with this information.
What is coordination compound ?
Which of the following can show coordination isomerism?
(i) $$\left[ Cu{ \left( { NH }_{ 3 } \right) }_{ 4 } \right] \left[ Pt{ Cl }_{ 4 } \right] $$ (ii) $${ \left[ Fe{ \left( { NH }_{ 3 } \right) }_{ 6 } \right] }_{ 2 }{ \left[ Pt{ (CN) }_{ 6 } \right] }_{ 3 }\quad$$ (iii) $$\left[ Co{ \left( { NH }_{ 3 } \right) }_{ 6 } \right] \left[ Cr{ \left( { C }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 4 } \right) }_{ 3 } \right] $$ (iv) $$\left[ Pt{ (en) }_{ 3 } \right] { \left( { SO }_{ 4 } \right) }_{ 2 }$$
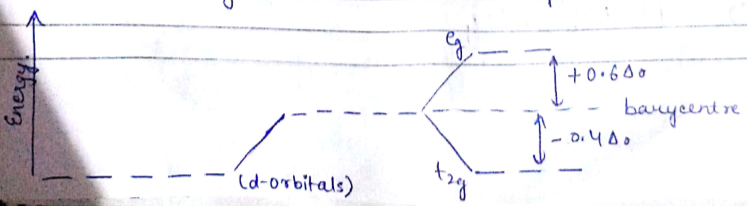
What is crystal field splitting energy? Draw a figure to show spitting of degenerate orbitals in an octahedral crystal field?
What is the Primary and Secondary Valence of $$PtCl_{2}.2NH_{3}$$?
Indicate the types of isomerism exhibited by the following complex and draw the structure of this isomer.
$$[Pt(NH_3)(H_2O)Cl_2]$$
What is the major product in this reaction.

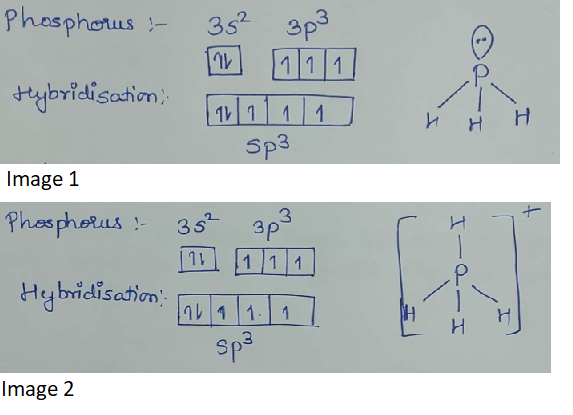
What is the hybridization of central atom in following? $$PH_3, PH_{4}^+, $$
On the basis of Werner's theory explain, why cobalt amine complex, $$CoCl_{ 3 }{ 4NH }_{ 3 }$$ when treated with $${ Ag }{ NO }_{ 3 }$$ solution precipitates only one $${ Cl }^{ - }$$ ion even though there are three $${ Cl }^{ - }$$ ions?
What is EAN? Write it's formula.
Explain the bonding on $$CoCl_{ 2 }.3N{ H }_{ 3 }$$ and $$CoCl_{ 2 }.5N{ H }_{ 3 }$$ structure on the basis at Werner's theory.
If the value of C.F.S.E. for ''Ni" is $$\triangle _{ o }$$ then what is the CFSE value Pd?
What is IUPAC name of $$K_{3}\left [ Fe\left ( CN \right )_{5}NO \right ]$$?
Write the formula of the following complexes.
Bis (ethnylene diammine) dichloro iridium (III) ion
Write the formula of the following complexes.
Tris (ethylene diammine) cobalt (II) sulphate
What is coordinate bond?
Discuss briefly giving an example in each case the role of coordination compound medicinal chemistry.
Write the possible stereo isomers of the following complexes and identify the type :-
a) $$[co(NH_3)_3Cl_3]$$
b) $$[pt(gly)_2]$$
c) $$[cr (en)_3]$$
Draw the isomer of $$[Pt({ { NH }_{ 3 } })_{ 3 }{ Cl }_{ 3 }]$$, $$[Co({ { NH }_{ 3 } })_{ 5 }{ Cl }{ SO }_{ 4 }]$$ .
What is the nomenclature of $$\left[ { CoCl }_{ 2 }({ NH }_{ 3 })_{ 4 } \right] ^{ + }$$ ?
What is the primary valency of $$[Co (NH_3)_4 Cl_2] Cl_2$$ ?
what is the formula of potassium amminetrichlorido platinate(ii)
Differentiate between primary and secondary valencies?
write down the formulae of given compoundtetra amine zinc(II) nitrate
Draw the structure of $$ClO_3^-$$.
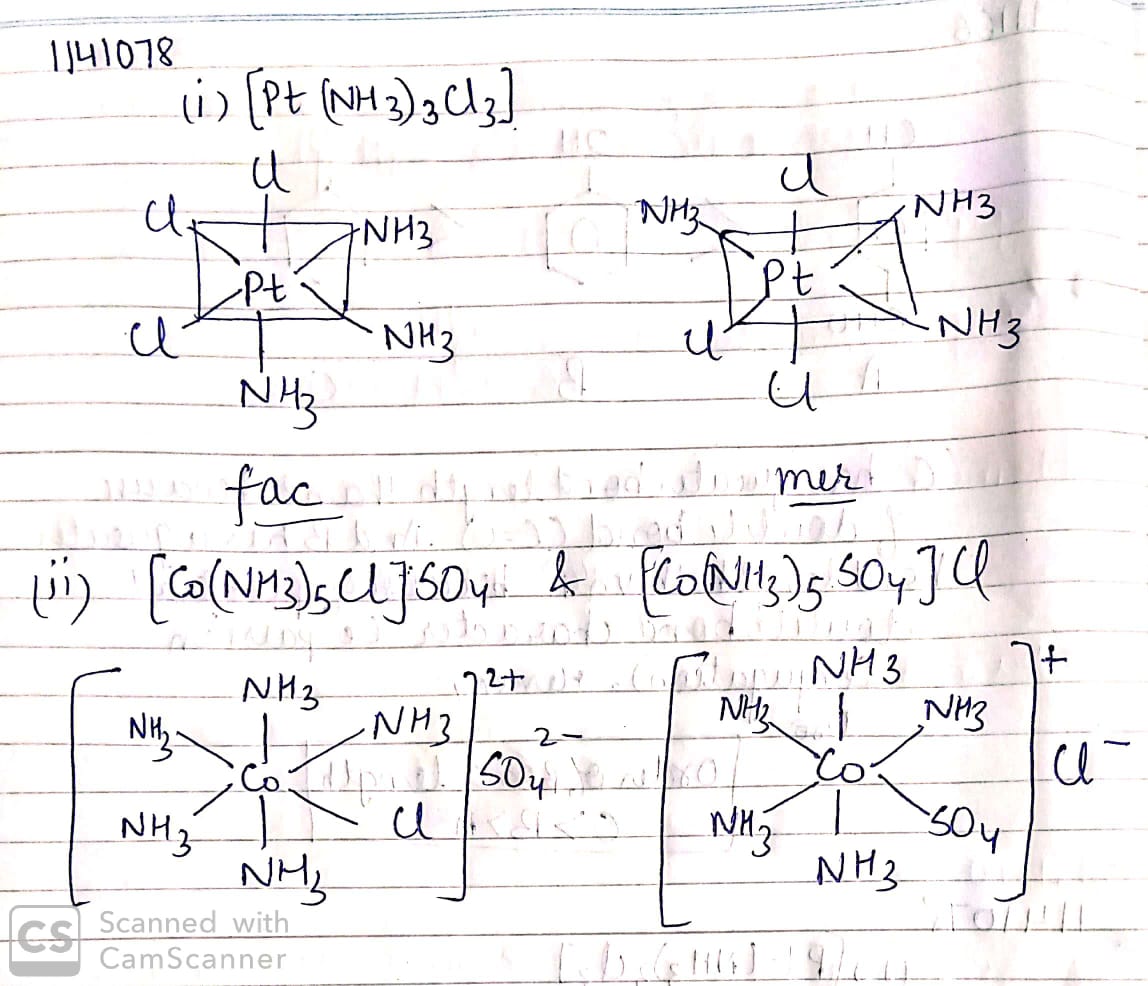
Write down the $$IUPAC$$ name of the complex $$[Pt (en)_2CI_2]^{2+}$$. What type of isomerism is shown by this complex.
write the formulae for Trioxalato cobaltate(III)ion
what is the formula of tetrakis(pyridine) platinum(ii) tetraphenyl borate(iii)
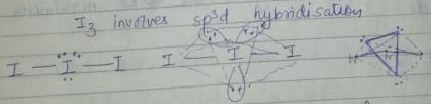
$$Cl_3^{^ - },Br_3^{^ - },ICl_2^{^ - },IBr_2^{^ - }\,including\,I_3^{^ - }$$ . In these ions, one of the halogen atom (in case of similar atom) or halogen atom large in size undergoes $$s{p^3}d$$-hybridization giving a liner shape with three lone pairs at equation positions.
What is Hybridization ?
On the basis of the following observations made with aqueous solutions. assign secondary valences to metals in the following compounds :
Formula Moles of AgCl precipitated per mole of the compounds with excess AgNO,
$$\left( i \right)\,PdC{l_2}.4N{H_3}$$ 2
$$\left( {ii} \right)\,NiC{l_2}.6{H_2}O$$ 2
$$\left( {iii} \right)\,PtC{l_4}.2HCl$$ 0
$$\left( {iv} \right)\,CoC{l_3}.4N{H_3}$$ 1
$$\left( v \right)\,PtC{l_2}.2N{H_3}$$ 0
Name the type of isomerism exhibited by the following isomers : $$[Cr(NH_3)_6][Co(CN_6)]$$ and $$[Co(NH_3)_6][Cr(CN)_6]$$
Find sum of possible value of 'n' for which complex having formula:$$[Pt(NH_{3})_{2}Cl_{2}]_{n}$$ can exit.
What is the hybridization of each in $$CH_{2}=c=CH_{2}$$?
select the correct state of hybridization at $$X_1, X_2, X_3 and X_4$$
$$X_1$$ $$X_2$$ $$X_3$$ $$X_4$$
(a) $$sp^2$$ $$sp$$ $$sp^2$$ $$sp^3$$
(b) $$sp^3$$ $$sp^2$$ $$sp$$ $$sp$$
(c) $$sp^2$$ $$sp^2$$ $$sp$$ $$sp^3$$
(d) $$sp^3$$ $$sp^2$$ $$sp^2$$ $$sp$$
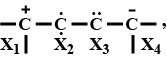
What is denticity?
Draw all of the isomers of boht tetrahedral and square planar complexes which have unidentate ligands of type A and two unidentate ligands of type B.
Draw all of the isomers of an octahedral complex which has three identical bidentate ligands.
Describe the methods by which the presence of complex ions may be detected in solution.
What methods could be used to distinguish between cis and trans isomer of a complex?
Draw energy level diagrams and indicate the occupancy of the orbitals in the following complexes :
(a) $$ d^6 $$ octahedral, low-spin
(b) $$ d^9 $$ octahedral with tetragonal elongation
(c) $$ d^8 $$ square planar
(d) $$ d^6 $$ tetrahedral.
Calculate in units $$ \triangle_0 $$ the difference in crystal field stabilization energy between complexes (a) and (b) assuming that the ligands are strong field ligands.
What are the geometric arrangements of $$sp^3d^2, sp^3d$$ and $$dsp^2$$ hybrid orbitals?
Match the metals of List $$I$$ with the biological organic of List $$II$$
Name the metal present in haemoglobin.
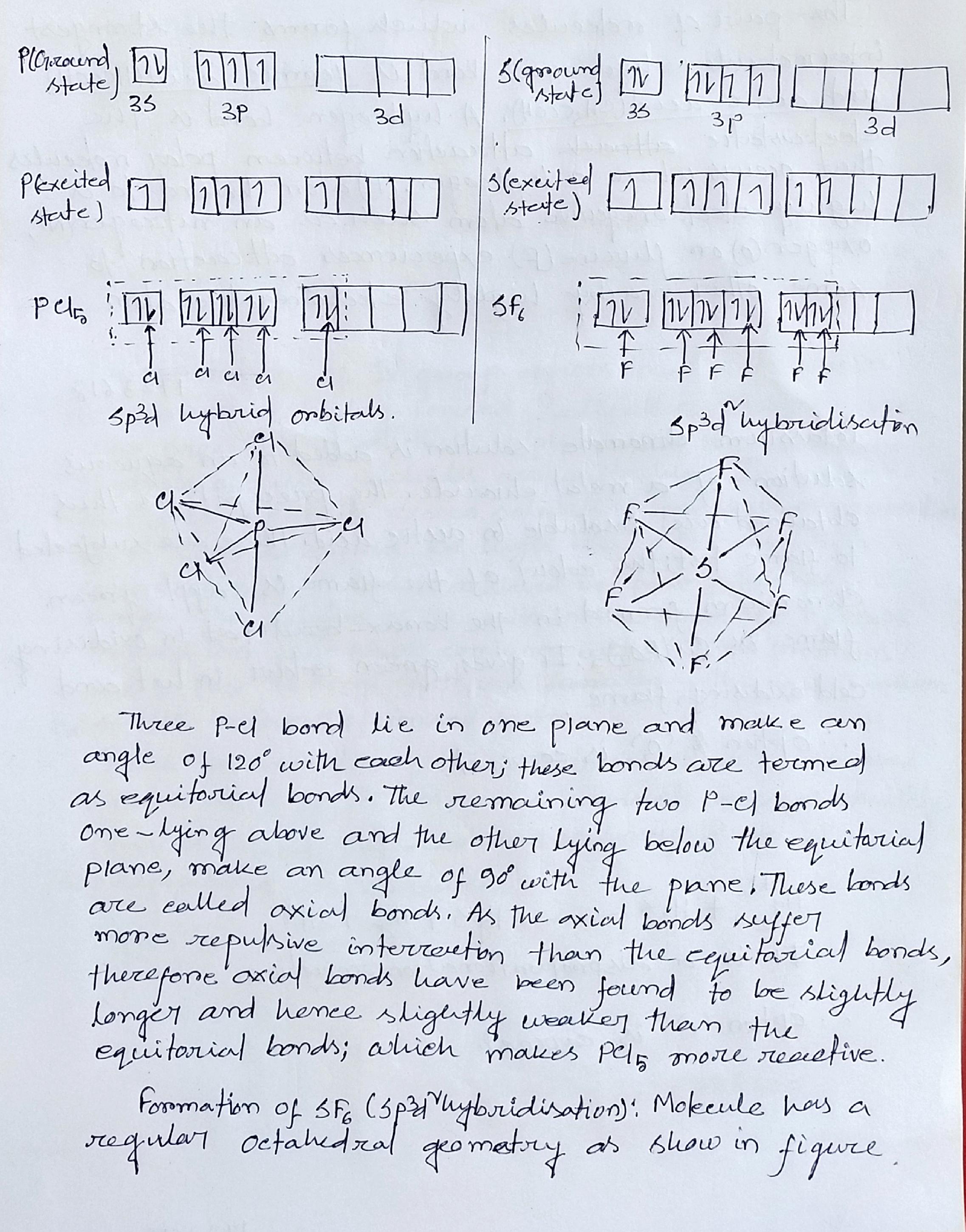
Describe hybridization in the case of $$ PCl_5 $$ and $$ SF_6$$. The axial bonds are longer as compared to equatorial bonds in $$ PCl_5 $$ whereas in $$ SF_6 $$ both axial bonds and equatorial bonds have the same bond length. Explain .
Find the number of total possible coordination isomers in $$[Pt(NH_3)_4][Cu(Cl)_4]$$.
Give the electronic configuration of the following complexes on the basis of crystal field splitting theory.
$$[CoF_6]^{3-}, [Fe(CN)_6]^{4-}$$ and $$[Cu(NH_3)_6]^{2+}$$.
In $$ SF_4 $$ atom has $$ sp^x d$$ hybridisation.What is the value of x?
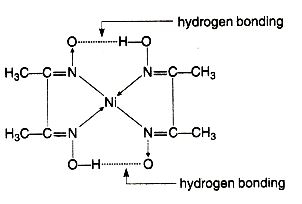
$$NiCl_2$$ in the presence of dimethyl glycoxime (DMG) gives a complex which precipitates in the presence of $$NH_4OH$$, giving a bright red color.
Draw its structure and show H bonding.
Write the formulae of the following complex.
Pentamminechlorocobalt(III) ion.
The number of orbitals involved in the hybridization of $$ XeF_2 $$ is:
A complex of the type $$[M(AA)_2X_2]^{n+}$$ is known to be optically active. What does this indicate about the structure of the complex? Give one example of such complex.
Match the complexes in List-I with their stereoproperties in List-II:
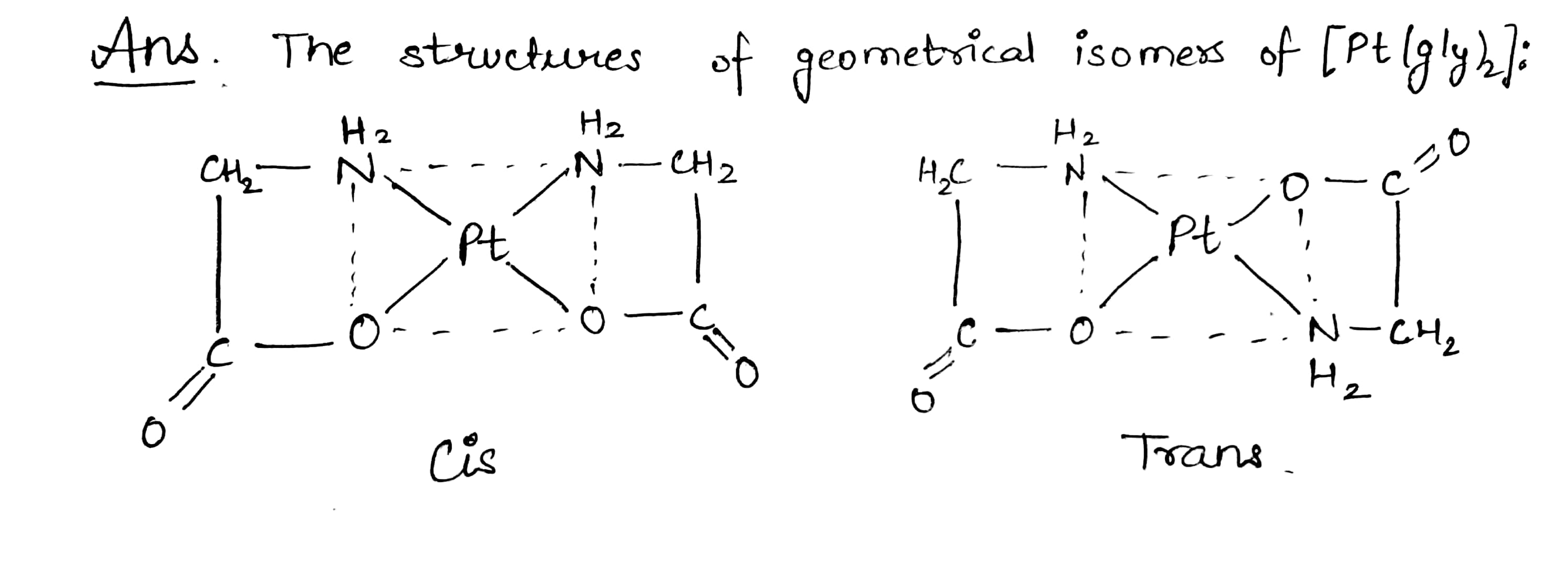
Draw the structure of geometrical isomers of $$[Pt(gly)_2]$$ where $$gly \to NH_2CH_2COO^-$$.
Match the hybridization in List-I with its reference in complex compounds List-II:
What type of isomers are the following ?
$$[Co(py)_2(H_2O)_2Cl_2]Cl$$ and $$[Co(py)_2(H_2O)Cl_3]H_2O$$
Write the formulae of the following complexes:
Potassium ethylenediamine tetraacetate ferrate (II)
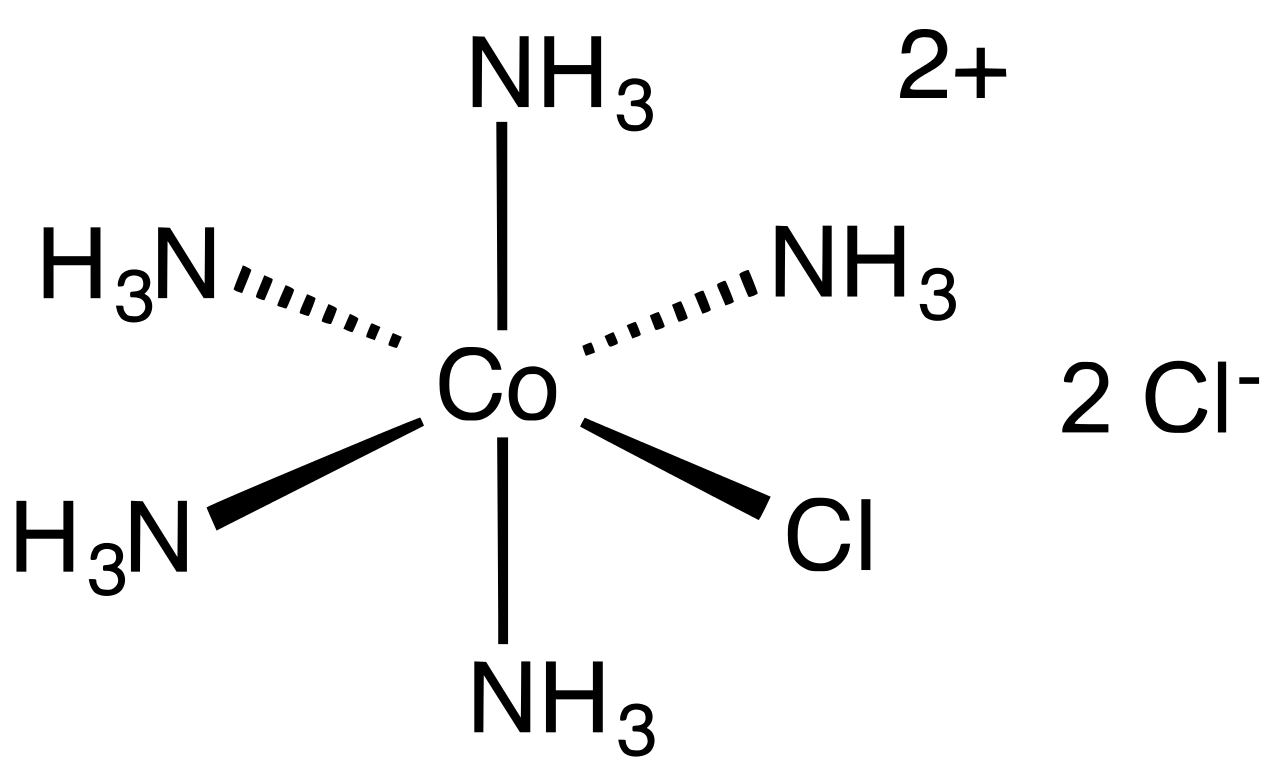
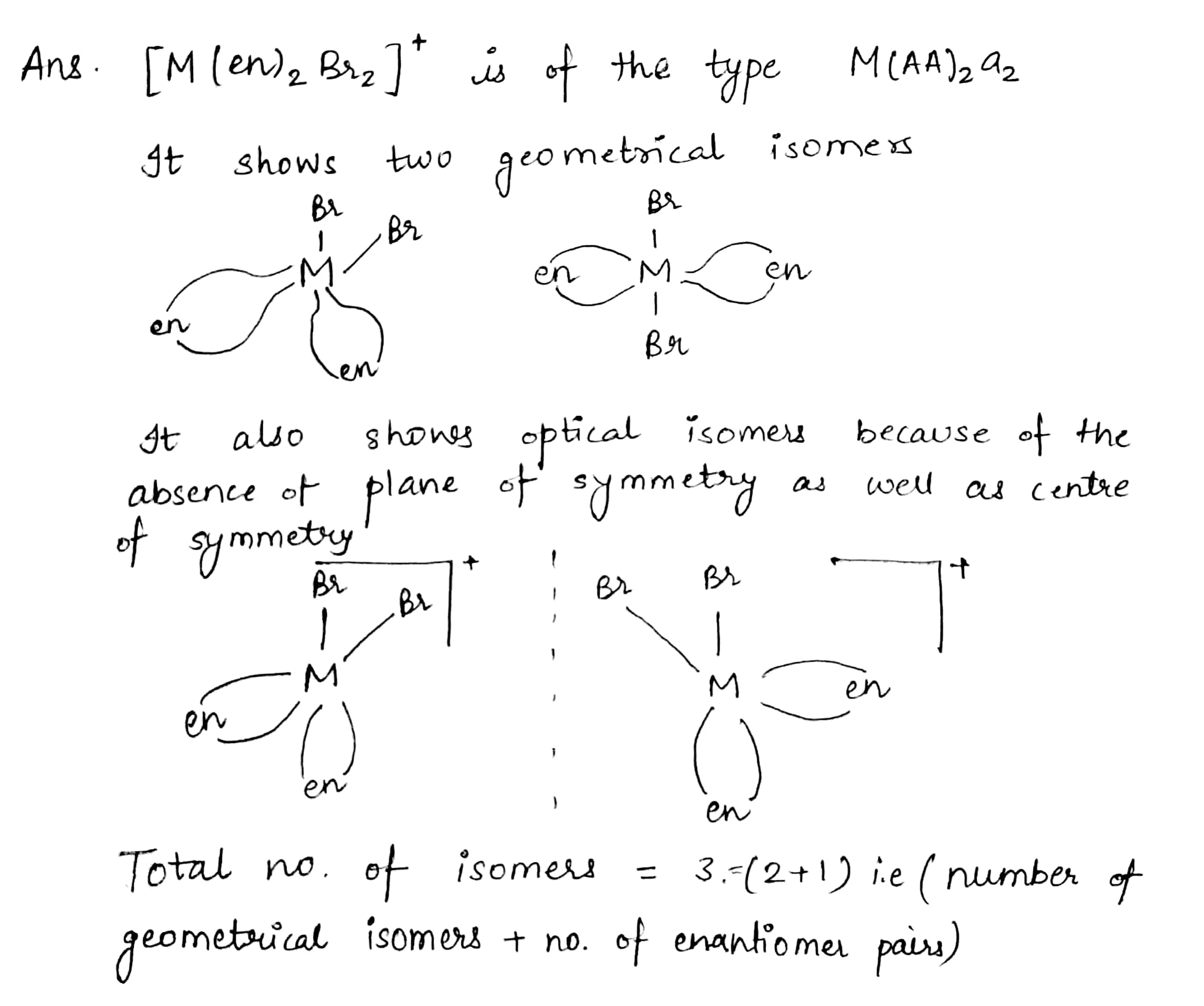
A certain complex ion has the formula $$[M(en)_2Br_2]^+$$ where $$M$$ is the metal ion and en = ethylene diamine. How many isomers are possible for this?
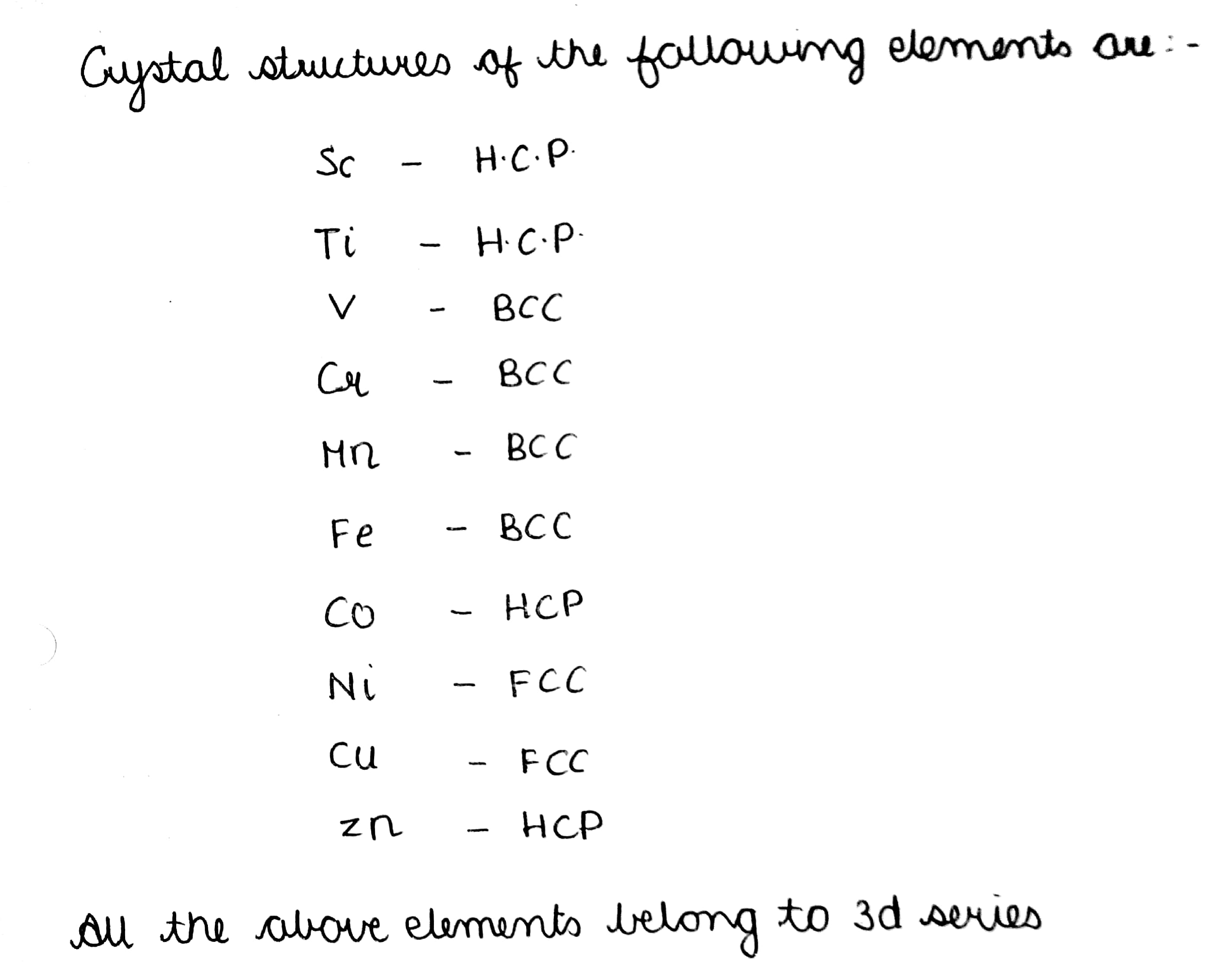
Write down the names of crystal structures in which the following elements are present.
$$Sc,\ Ti,\ V,\ Cr,\ Mn,\ Fe,\ Co,\ Ni,\ Cu,\ Zn.$$
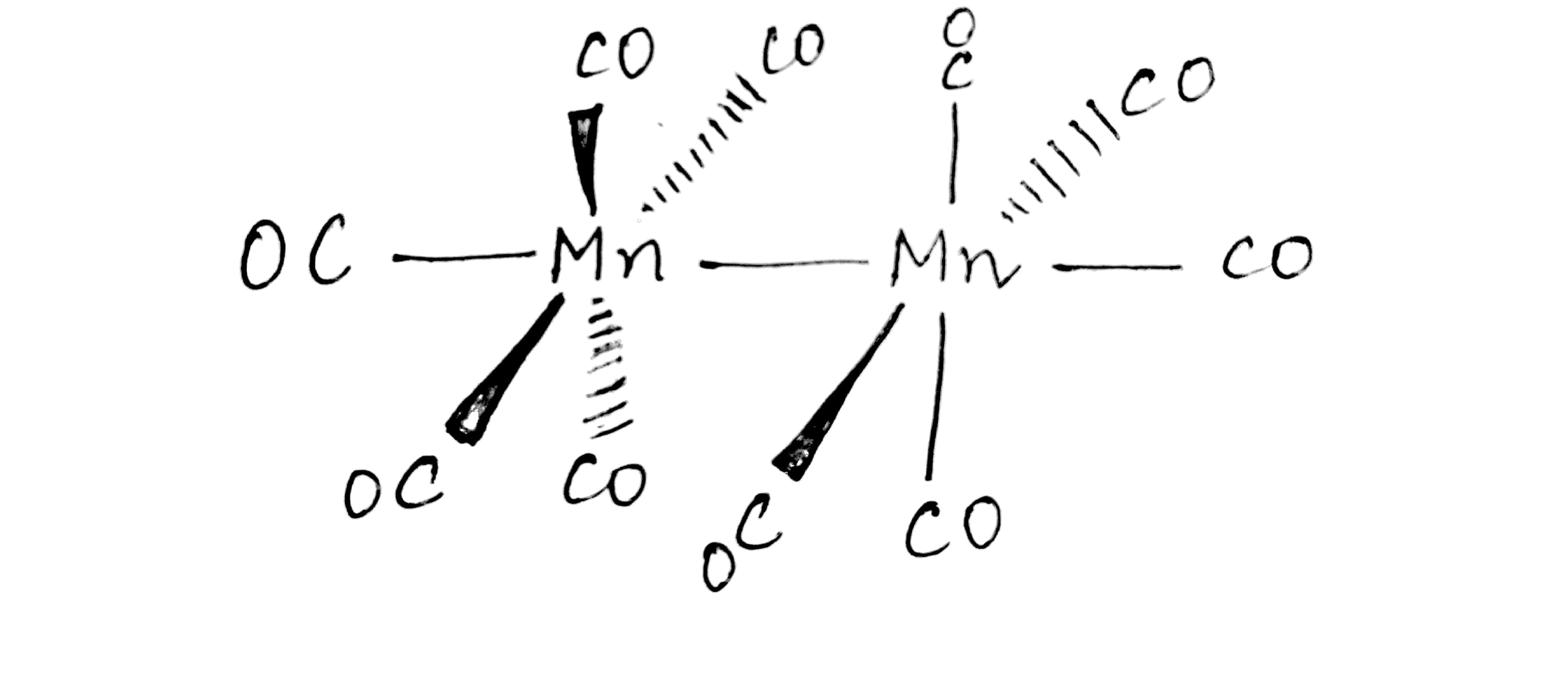
The EAN of each $$Mn(Z=25)$$ in $$Mn_2(CO)_{10}$$ is $$36$$. What is the structure of this complex?
The decahydrate form of sodium carbonate i.e. washing soda on standing in air effloresces and crumbles to powder. The number of water molecule (s) present in the compound formed is
Account for the following:
Give the formula and describe the structure of a noble species which is isostructural with $$IBr_{2}^{-}$$.
$$CO^{3-}$$ ion is bound to one $$Cl$$, one $$NH_3$$ molecule and two bidentate ethylene molecule.
Write the formula, name and magnetic behaviour of the above coordination entity.
Name a complex used in treatment of cancer.
$$Ni^{2+}$$ ion is bound to two water molecules and two oxalate ions.
Write the formula, name and magnetic behaviour of the above coordination entity.
What are crystal fields?
Write the formula of the following :
Tetraammineaquachloridocobalt (III) nitrate
What type of isomerism is shown by the following complex:
$$[Co(NH_{3})_{6}][Cr(CN)_{6}]$$
Giving a suitable example for each, explain the following:
Crystal field splitting
What type of isomerism is exhibited by the following complex:
$$[Co(NH_{3})_{5}SO_{4}]Cl$$
A coordination compound with the molecular formula $$CrCl_{3}.4H_{2}O$$ precipitates $$AgCl$$ with $$AgNO_{3}$$ solution. Its molar conductivity is found to be equivalent to two ions. What is the structural formula and name of the compound?
What type of isomerism is shown by the complex $$[Cr(H_2 O)_6]Cl_3$$?
Name the following coordinates entity and describe its structure
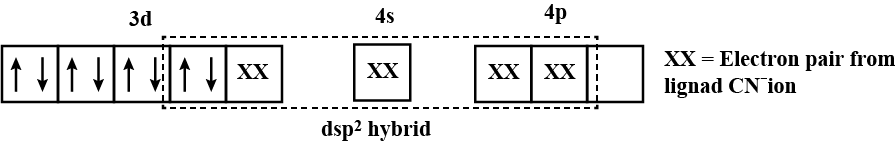
$$[Fe(CN)_6]^{4-}$$
(Atomic Number: $$Fe=26$$)
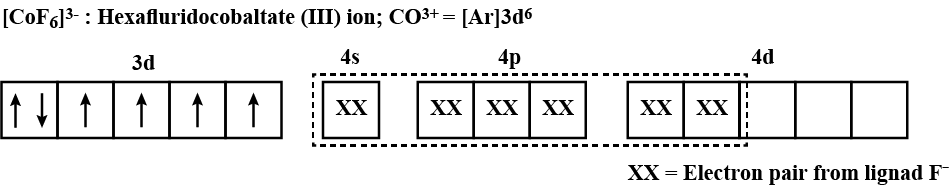
Write the state of hybridisation, shape and IUPAC name of the complex $$[CoF_6]^{3-}$$.
What is meant by crystal field splitting energy? On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration of $$d^4$$ in terms of $$t_{2g}$$ and $$e_g$$ in an octahedral field when
$$\Delta_0 < P$$
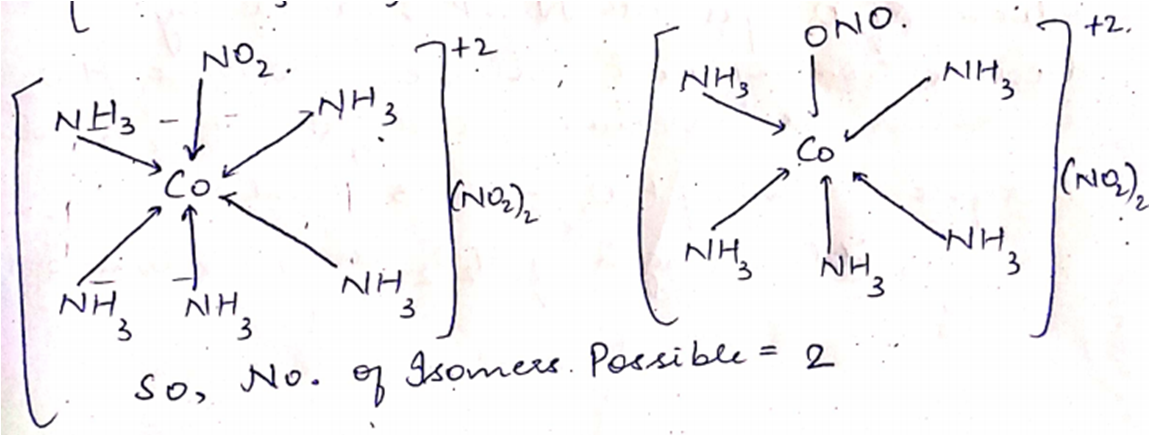
What type of isomerism is shown by $$[Co(NH_3)_5 ONO]Cl_2$$?
What type of isomerism is shown by the complex $$[Co(NH_3)_5 (SCN)]^{2+}$$?
What is meant by crystal field splitting energy? On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration of $$d^4$$ in terms of $$t_{2g}$$ and $$e_g$$ in an octahedral field when
$$\Delta_0 > P$$
What type of isomerism is shown by the complex $$[Co(NH_3)_6] [Cr(CN)_6]$$?
Name the following coordinates entities and describe their structures
$$[Ni(CN)_4]^{2-}$$
(Atomic Numbers: $$Ni=28$$)
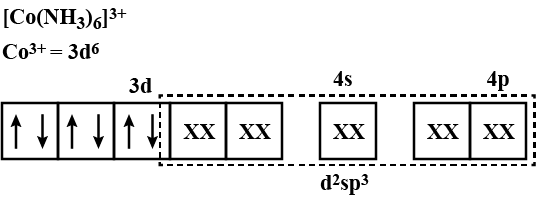
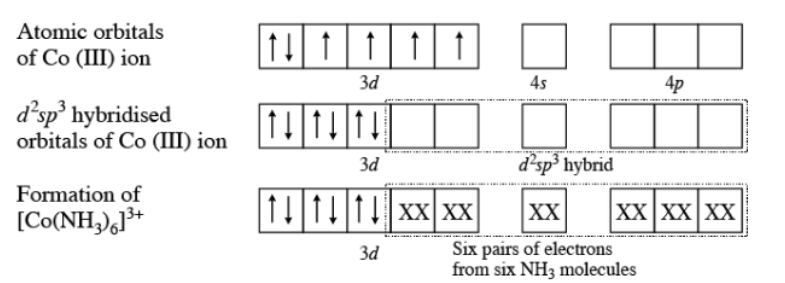
Using valence bond theory explain the $$[Co(NH_3)_6]^{3+}$$ in relation to the term given below:
Type of hybridisation
Answer the following question:
On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration for $$d^4$$ ion, if $$\Delta_0 < P$$.
Described for the following complex ion, the type of hybridisation, shape and magnetic property:
$$[NiCl_4]^{2-}$$
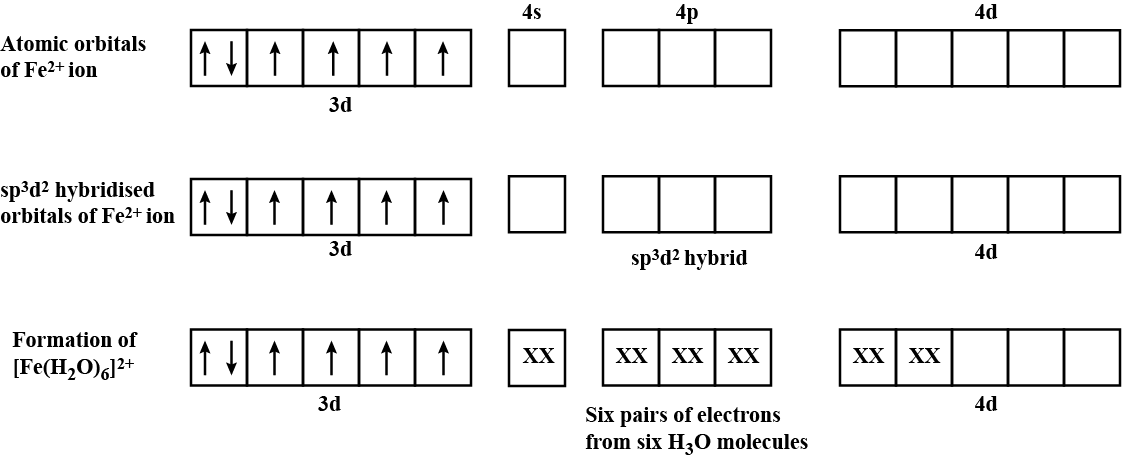
Described for the following complex ion, the type of hybridisation, shape and magnetic property:
$$[Fe(H_2 O)_6]^{2+}$$
Explain the following with two examples:Coordination entity
Described for the following complex ion, the type of hybridisation, shape and magnetic property:
$$[Co(NH_2)_6]^{3+}$$
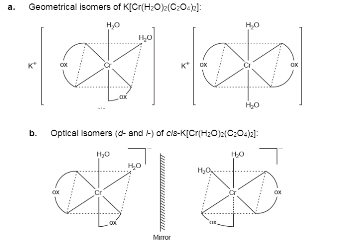
Indicate the types of isomerism exhibited by the following complex and draw the structures of the isomers:
$$K[Cr(H_2O)_2(C_2O_4)_2]$$
Answer the following question:
On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration for $$d^4$$ ion if $$\Delta_0 < P$$.
Answer the following question:
Define crystal field splitting. On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration for $$d^{4}$$ ion if $$\Delta_0 < P$$.
Answer the following question:
Name two complexes which are used in medicines.
Write all the possible isomers of $$[Co(NH_3)_5(SCN)]Cl$$
Indicate the types of isomerism exhibited by the following complex and draw the structures of the isomers:
$$[Pt(NH_3)(H_2O)Cl_2]$$
A metal ion $$M^{n+}$$ having $$d^4$$ valence electronic configuration combines with three bidentate ligands to form a compound. Assuming $$\Delta_0 > P$$:
Name the type of isomerism exhibited by this complex.
$$CoSO_4Cl.5NH_3$$ exists in two isomeric forms $$'A'$$ and $$'B'$$. Isomer $$'A'$$ reacts with $$AgNO_3$$ to give white precipitate, but does not react with $$BaCl_2$$. Isomer $$'B'$$ gives white precipitate with $$BaCl_2$$ but does not react with $$AgNO_3$$. Answer the following question:
Name the type of isomerism involved.
What is the hybridization of each carbon in $$H_2C=C=CH_2$$?
A metal ion $$M^{n+}$$ having $$d^4$$ valence electronic configuration combines with three bidentate ligands to form a compound. Assuming $$\Delta_0 > P$$:
What type of hybridisation will $$M^{n+}$$ ion have?
$$CoSO_4Cl.5NH_3$$ exists in two isomeric forms $$'A'$$ and $$'B'$$. Isomers $$'A'$$ reacts with $$AgNO_3$$ to give white precipitate, but does not react with $$BaCl_2$$. Isomer $$'B'$$ gives white precipitate with $$BaCl_2$$ but does not react with $$AgNO_3$$. Answer the following questions:
Identify $$'A'$$ and $$'B'$$ and write their structural formulae.
Answer the following question:
Give the electronic configuration of the $$d-$$orbitals of $$Ti$$ in $$[Ti(H_2O)_6]^{3+} $$ ion in an octahedral crystal field.
Explain, how is the electronegativity of carbon atoms related to their state of hybridization in an organic compound?
Explain the following:
Low spin octahedral complex of nickel are not known.
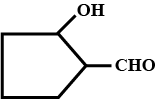
Give the structure of the following compounds.
2-Hydroxycyclopentanecarbaldehyde
Explain the following term with example.
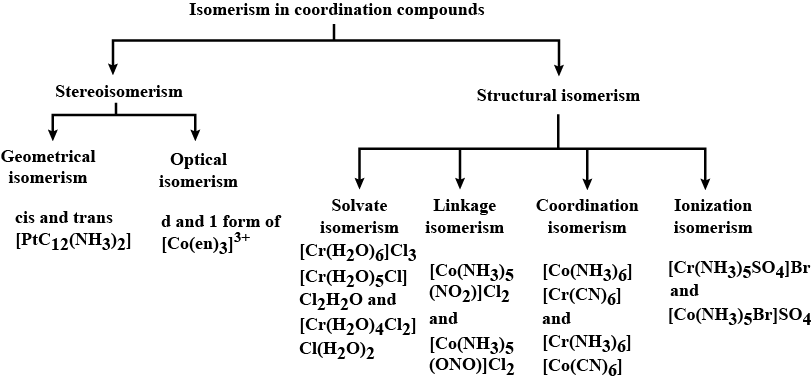
Structural isomerism
Column-I and Column-II contains four entries each. Entries of Column-I are to be matched with one or more than one entries of Column-II. Each entry of Column-I may have the matching with one or more than one entries of Column-II.
Brown colour of the complex $$[Fe(H_{2}O)_{5}(NO)]SO_{4}$$ is due to C.T. spectrum which causes momentary change in oxidation state. Find out oxidation state of $$Fe$$ in this complex.
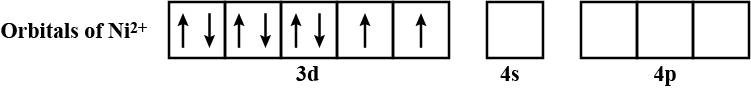
Calculate the magnetic moment of $$ Ni^{2+} $$ ion.
Explain the hybridization of the central metal atom in the complex $$ [Ni(CN)_4]^{2-} $$ with the help of diagram.
What is hybridization ?
What is meant by hybridisation of atomic orbitals? Describe $$sp, sp^2$$ and $$sp^3$$ hybridixation with examples.
What will be geometry of complexes having hybridization $$sp^3$$ and $$dsp^2$$. Give an example of each.
How many structural isomers can you draw for pentane?
Define Hybridization.
The valence atomic orbital on carbon in silver acetylide is .................hybridized.
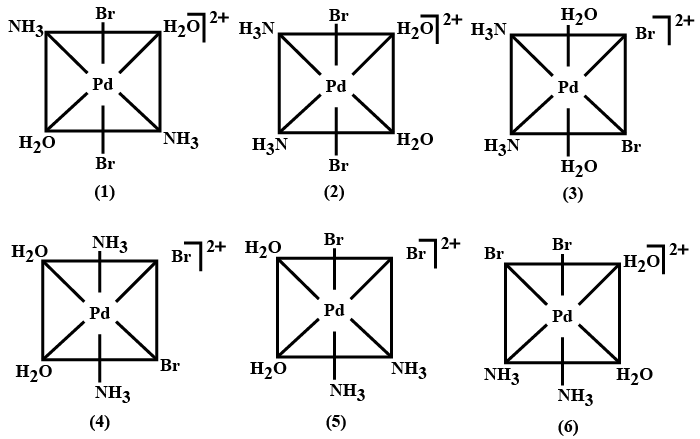
The maximum number of stereoisomers possible for the ion $$[\overset {IV}{Pd}(NH_{3})_{2}(H_{2}O)_{2}Br_{2}]^{2+}$$ is :
Match the complex in List-I with the type of isomerism given in List-II.
Match the complex in List-I with its corresponding property(ies) given in List-II.
| Column $$\displaystyle -$$ I | Column $$\displaystyle -$$ II |
| Column I | Column II |
Match the complexes in List 1 with their properties in List 2.
There are ............... electron in $$t_{2g}$$ orbitals in $$[CoF_6]^{3-}$$.
Match the column.
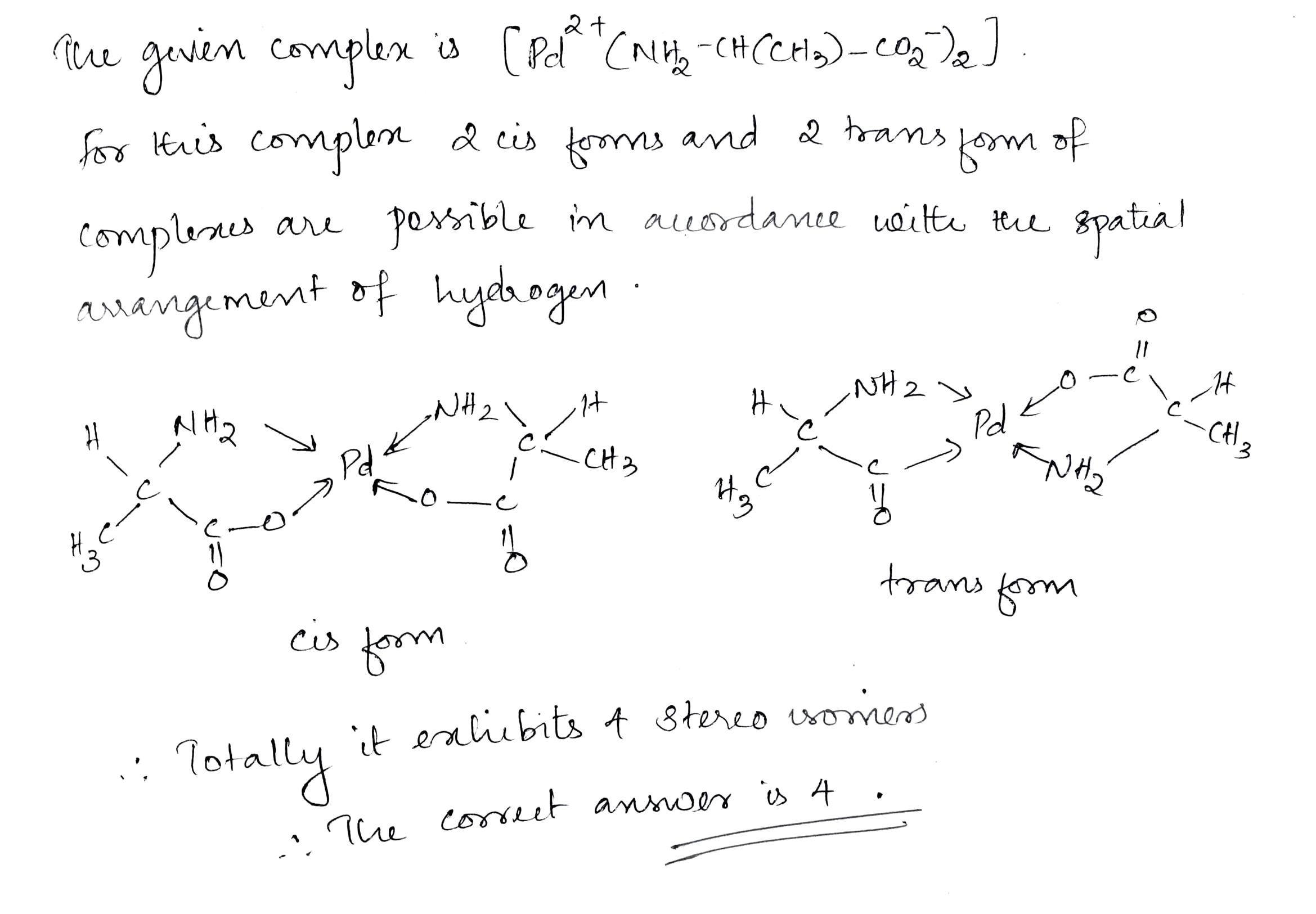
Write the sum of geometrical isomers in [Pt(H$$_2$$N - CH(CH$$_3$$) - COO$$^-$$)$$_2$$] complex and stereoisomers of [Pt(gly)$$_3$$]$$^+$$ complex.
Match the complex (in Column I) with the type of isomerism (in Column II) (unitary match).
Find the total number of possible structural isomers of the compound $$[\overset{II}{Cu}(NH_3)_4]\overset{II}{[Pt}Cl_4].$$
Explain the bonding in coordination compounds in terms of Werners postulates.
$$S^{2-}+Na_2[Fe(CN)_5NO]\longrightarrow$$ Complex is having violet/purple coloration(X)
The total number of possible isomers for complex X is ......... provided the ambident behavior of $$CN^-$$ is not considered.
Specify the oxidation numbers of the metals in the following coordination entities:
(i) $$[Co(H_{2}O)(CN)(en)_{2}]^{2+}$$ (ii) $$[CoBr_{2} (en)_{2}]^{+}$$ (iii) $$[PtCl_{4}]^{2-}$$ (iv) $$K_{3} [Fe(CN)_{6}]$$ (v) $$[Cr(NH_{3})_{3}Cl_{3}]$$
What is the oxidation state of Co in the complex $$[CoCl_2(en)_2]^+$$?
[Note: Ethylenediamine (en) $$=H_2N-CH_2-CH_2-NH_2$$]
List various types of isomerism possible for coordination compounds, giving an example of each.
Aqueous copper sulphate solution (blue in colour) gives:
(i) a green precipitate with aqueous potassium fluoride and
(ii) a bright green solution with aqueous potassium chloride. Explain these experimental results.
What is the coordination entity formed when excess of aqueous $$KCN$$ is added to an aqueous solution of copper sulphate? Why is it that no precipitate of copper sulphide is obtained when $$H_{2}S(g)$$ is passed through this solution?
Amongst the following, the most stable complex is:
(i) $$[Fe(H_{2}O)_{6}]^{3+}$$ (ii) $$[Fe(NH_{3})_{6}]^{3+}$$ (iii) $$[Fe(C_{2}O_{4})_{3}]^{3-}$$ (iv) $$[FeCl_{6}]^{3-}$$
Draw all the isomers (geometrical and optical) of:
(i) $$[CoCl_{2} (en)_{2}]^{+}$$ (ii) $$[Co(NH_{3})Cl(en)_{2}]^{2+}$$ (iii) $$[Co(NH_{3})_{2}Cl_{2} (en)]^{+}$$
Discuss briefly giving an example in each case the role of coordination compounds in:
(i) biological systems (ii) medicinal chemistry and (iii) analytical chemistry (iv) extraction/metallurgy of metals.
Draw figure to show the splitting of d orbitals in an octahedral crystal field.
Amongst the following ions which one has the highest magnetic moment value?
(i) $$[Cr(H_{2}O)_{6}]^{3+}$$ (ii) $$[Fe(H_{2}O)_{6}]^{2+}$$ (iii) $$[Zn(H_{2}O)_{6}]^{2+}$$
(i) What are the postulates of Werner's theory?
(ii) Write the IUPAC names fo $${K}_{3}\left[Fe{\left(CN\right)}_{6}\right]$$, $$\left[Co{\left(N{H}_{3}\right)}_{6}\right]{Cl}_{3}$$.
Rules of hybridization say that hybrid orbitals form only sigma bonds. However, unsaturated hydrocarbons like (ethylene and acetylene) possess multiple bonds between carbons.
Write the formula of the following coordination compound.
Iron(III) hexacyanoferrate(II).
Define linkage and ionisation isomerism?
$$Co.{ Cl }_{ 3 }.5{ NH }_{ 3 }{ H }_{ 2 }O$$ is a pink solid, the solution of this salt is also pink and formed $$3$$ mol of $$AgCl$$ with silver nitrate solution. On heating pink solid, it loses one water molecule and forms purple solid having same ratio of $$Co:{ NH }_{ 3 }:Cl$$ as that of pink solid. The purple solid when dissolved in water and treated with silver nitrate forms $$1$$ mol of $$AgCl$$. Draw the structures and name of the pink and purple solids.
Match each coordination compound in List-I with an appropriate of characteristics from List-II. ($$en={ H }_{ 2 }HC{ H }_{ 2 }C{ H }_{ 2 }N{ H }_{ 2 }$$; Atomic numbers: Ti = 22, Cr = 24; Co = 27; Pt = 78)
| List I | List II | ||
| A | $$\left[ Cr{ \left( { NH }_{ 3 } \right) }_{ 4 }{ Cl }_{ 2 } \right] Cl$$ | 1 | Paramagnetic and exhibits ionization isomerism |
| B | $$\left[ Ti{ \left( { H }_{ 2 }O \right) }_{ 3 }Cl \right] { \left( { NO }_{ 3 } \right) }_{ 2 }$$ | 2 | Diamagnetic and exhibits cis-trans isomerism |
| C | $$\left[ Pt\left( en \right) { \left( N{ H }_{ 3 } \right) }Cl \right] { NO }_{ 3 }$$ | 3 | Paramagnetic and exhibits cis-trans isomerism |
| D | $$\left[ Co{ \left( { NH }_{ 3 } \right) }_{ 4 }{ \left( { NO }_{ 3 } \right) }_{ 2 } \right] { NO }_{ 3 }$$ | 4 | Diamagnetic and exhibits ionization isomerism |
What is meant by complex compound? Describe the main points of Werner's theory.
On the basis of the following observations made with aqueous solutions, assign secondary valences to metals in the following compounds:
| Formula | Moles of $$AgCl$$ precipitated per mole of the compounds with excess $$AgNO_3$$ |
| (i) $$PdCl_2.4NH_3$$ | $$2$$ |
| (ii) $$NiCl_2.6H_2O$$ | $$2$$ |
| (iii) $$PtCl_4.2HCl$$ | $$0$$ |
| (iv) $$CoCl_3.4NH_3$$ | $$1$$ |
| (v) $$PtCl_2.2NH_3$$ | $$0$$ |
Which of the following is ore stable and why? $${ \left[ Co{ \left( { NH }_{ 3 } \right) }_{ 3 } \right] }^{ 3+ }$$ and $${ \left[ Co{ \left( en \right) }_{ 3 } \right] }^{ 3+ }$$. Name the following coordination compound and draw its possible structures $$\left[ { Co }Cl_{ 2 }{ \left( en \right) }_{ 2 } \right] Cl$$
What is Werner's Theory
What is the change in colour of potassium dichromate when aq. KOH is added in it .
Explain, on the basis of crystal filed splitting in case of $$[Ni(H_{2}O)_{6}]^{2+}, [Ni(H_{2}O)_{4}en]^{2+}$$ and $$[Ni(H_{2}O)_{2}(en)_{2}]^{2+}$$ ions.
Co-ordinates complexes involving $$F^-$$ ions are more stable than those having $$CI^-$$ & $Br^-$ ions?
What is the hydrate isomerism? Explain with in example?
Total number of cis $$N-Mn-Cl$$ bond angles (that is, $$Mn-N$$ and $$Mn-Cl$$ bonds in cis position) present in a molecule of cis $$[Mn(en)_2Cl_2]$$ complex is ______. $$(en=NH_2CH_2CH_2NH_2)$$
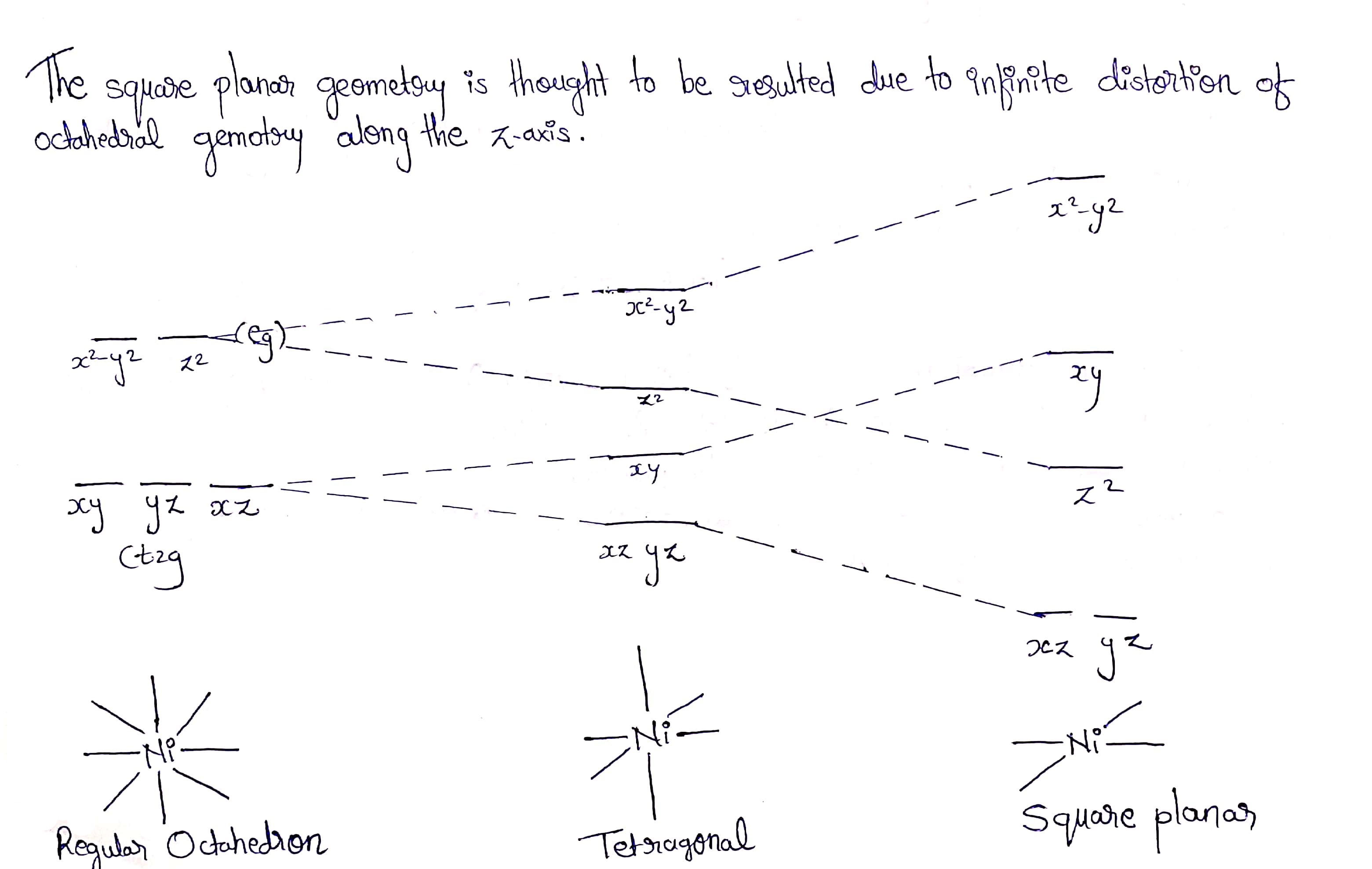
Show by means of a diagram how the pattern of d orbital splitting changes as an octahedral complex undergoes tetragonal distortion and eventually becomes a square planar complex.
Given that the maximum absorption in the d-d peak for $$ [ Ti(H_2O)_6]^{3+}$$ occurs at $$ 20300cm^{-1} $$predict where the peaks will occurs for $$ [Ti(CN)_6]^{3-} $$ and $$ [Ti(Cl)_6]^{3-} $$
Write the formula for each of the following complexes :
(a) tetraamminecopper (II) sulphate
(b) potassium tetracyanonickelate (0)
(c) bis (cyclopentadiehyl)iron(II)
(d) tetrathicyanato -N-zinc (II)
(e) diamminebis (ethylenediamine) cobalt (III) chloride
(f) tetraammineddithiocyanatochromium (III)
(g) potassium tetraoxomanganate (VII)
(h) potassium terioxalatoalumminate (III)
(i) tetrapyridineplatinum (II) tetrachloroplatinate (II)
The sum of primary and secondary valencies of chromium in the complex $$CrCl_3\cdot 6NH_3$$ is?
Find the total number of possible isomers of $$[CrCl_3(NH_3)_3]$$.
Find the number of isomeric forms in which $$[Co(NH_3)_4Cl_2]^+$$ ion can occur.
Find the total number of possible isomers of $$[CrCl_2(CN)(NH_3)en]$$.
The number of total possible stereoisomers for $$[Pd(NH_2-CH(CH_3)-CO^-_2)_2]$$ is?
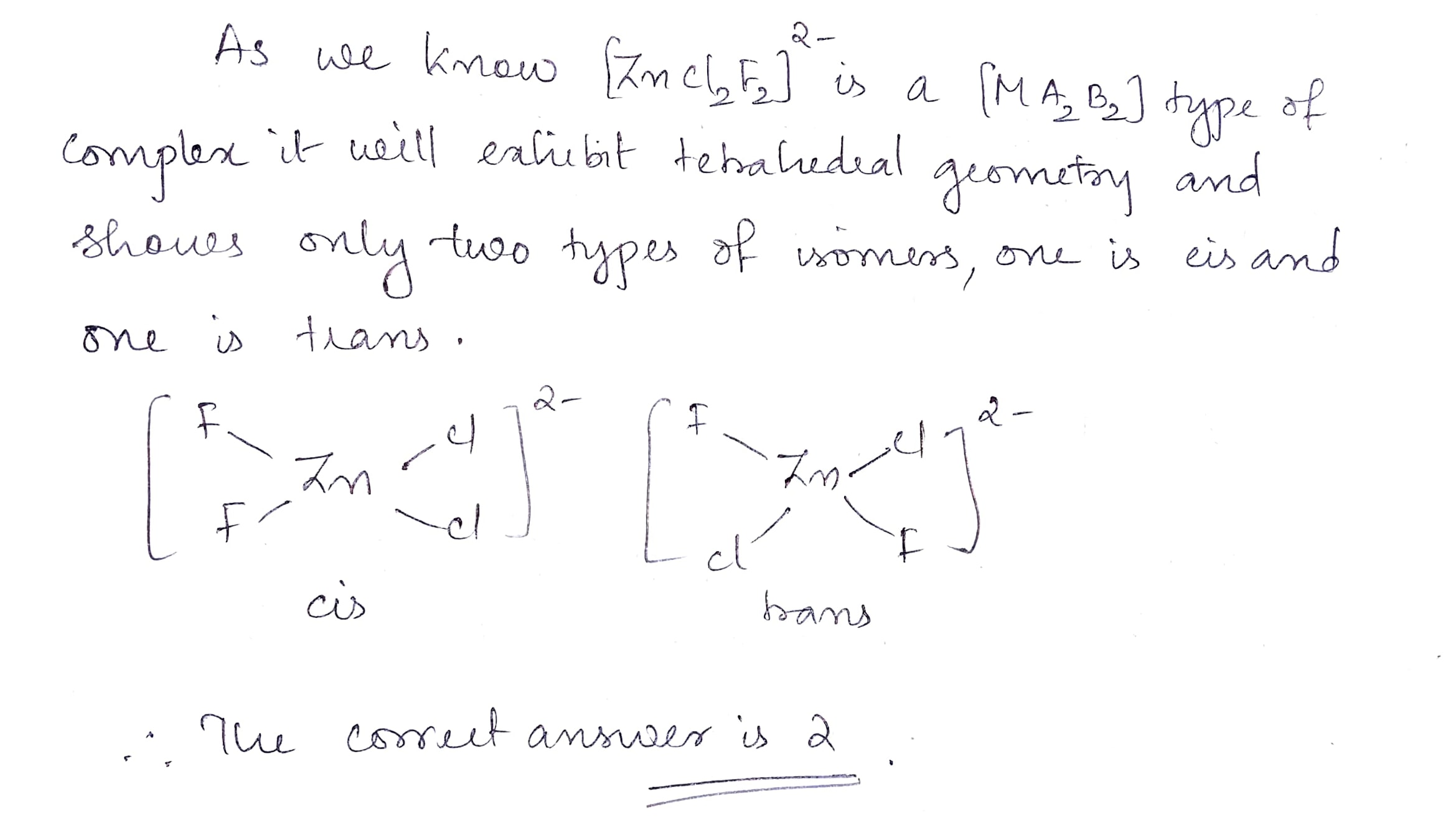
Find the total number of possible isomers of $$[ZnCl_2F_2]^{2-}$$.
Write the sum of geometrical isomer in $$[Ma_2b_2c_2]$$ complex and stereoisomers in $$[M(AB)_3]$$ complex.
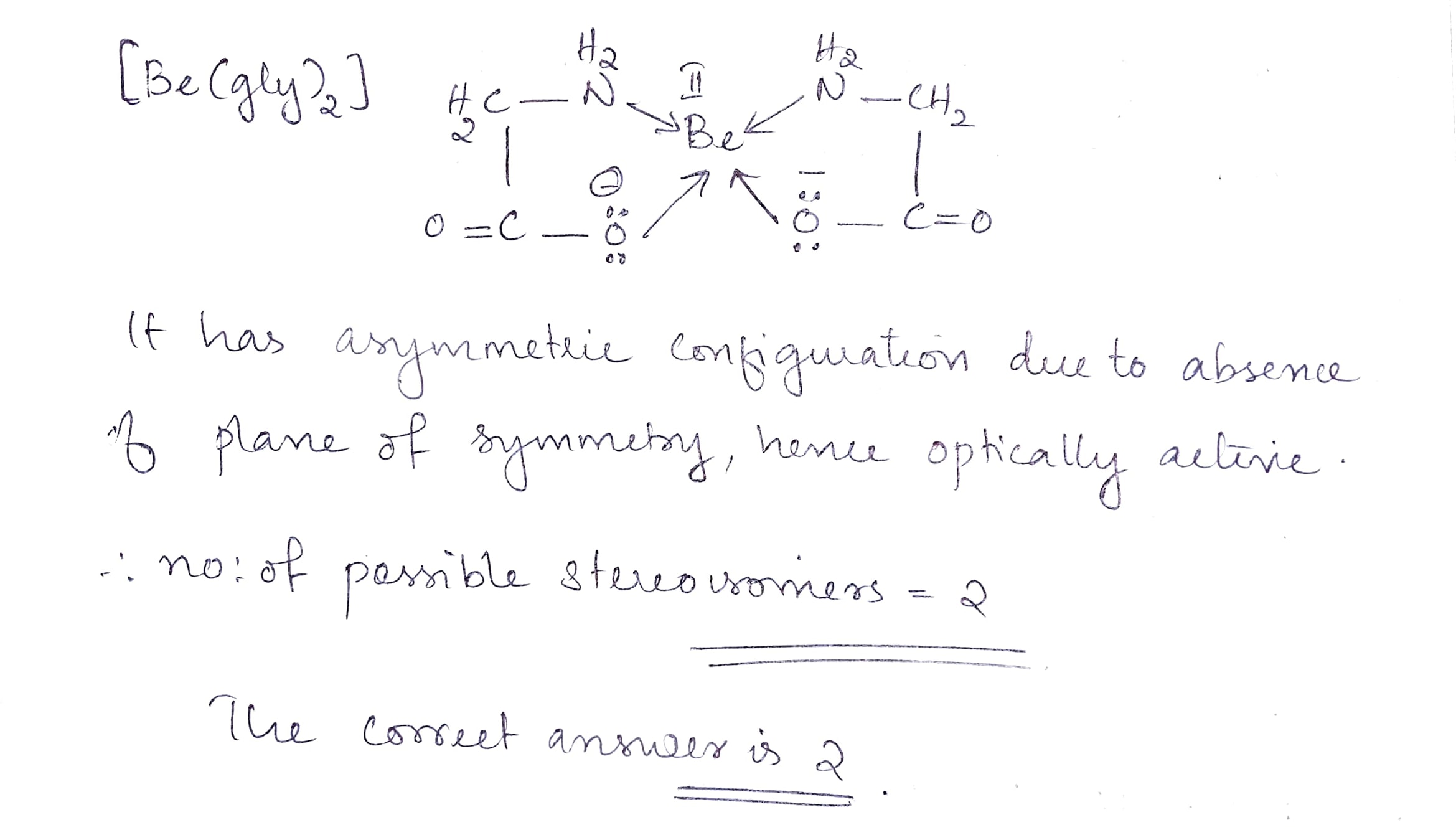
Find the total number of isomer of $$[Be(gly)_2]$$.
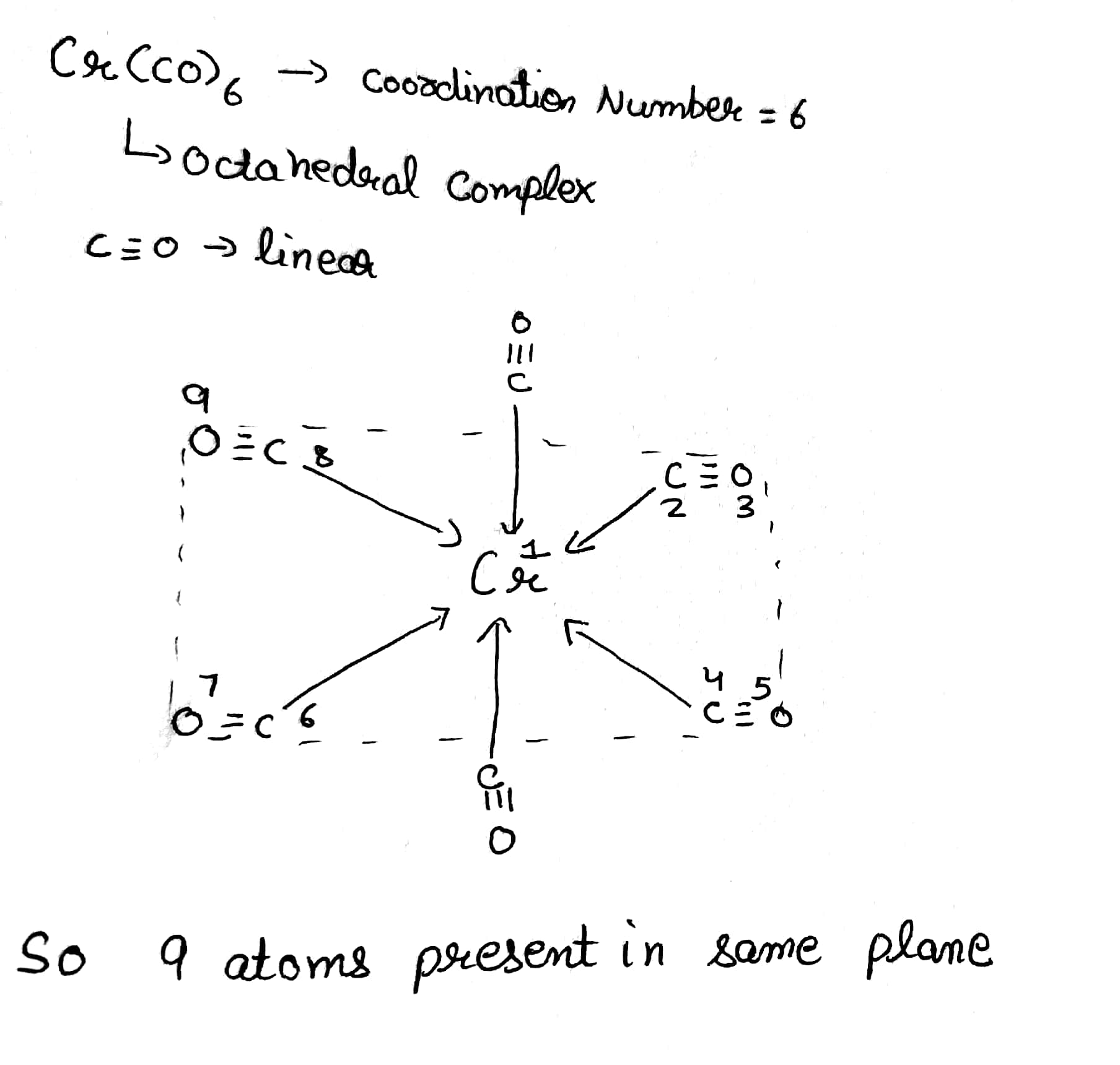
How many maximum atom(s) is/are present in same of plane of $$Cr(CO)_6?$$
Match the column:
A coordination compound $$CrCl_3\cdot 4H_2O$$ precipitates silver chloride when treated with silver nitrate. The molar conductance of its solution corresponds to a total of two ions. Write structural formula of the compound and name it.
Arrange the following complexes in the increasing order of conductivity of their solution:
$$[Co(NH_3)_3Cl_3],\ [Co(NH_3)_4Cl_2]Cl, \ [Co(NH_3)_6]Cl_3,\ [Cr(NH_3)_5Cl]Cl_2$$.
$$CoSO_4Cl_5NH_3$$ exists in two isomeric forms 'A' and 'B'. Isomer 'A' reacts with $$AgNO_3$$ to give white precipitate, but does not react with $$BaCl_2$$. Isomer 'B' gives white precipitate with $$BaCl_2$$ but does not react with $$AgNO_3$$. Answer the following question.
Identify 'A' and 'B' and write their structural formulas.
$$AgCl$$ dissolves in excess of $$KCN$$ solution to give the ________ complex compound.
$$S^{2-}+Na_2[Fe(CN)_5NO]\rightarrow $$ Complex is having violet/purple coloration (X).
The total number of possible isomers for complex X is.....provided the ambient behaviour of $$CN^{-}$$ is not considered.
What type of isomers are the following ?
$$[(CO)_5MnSCN]$$ and $$[(CO)_5MnNCS]$$
What type of isomers are the following ?
$$[Co(en)_3][Cr(CN)_6]$$ and $$[Cr(en)_3][Co(CN)_6]$$
Describe a simple chemical test that would allow you to distinguish between the compounds, $$[Co(NH_3)_5Br]SO_4$$ and $$[Co(NH_3)_5SO_4]Br$$.
What type of isomers are the following ?
$$[Co(NH_3)_5NO_3]SO_4$$ and $$[Co(NH_3)_5SO_4]NO_3$$
Explain the geometry and magnetic nature of the following complex ion on the basis of valence band theory: $$[MnCl_4]^{2-}$$
What are the main features of the ligand field theory?
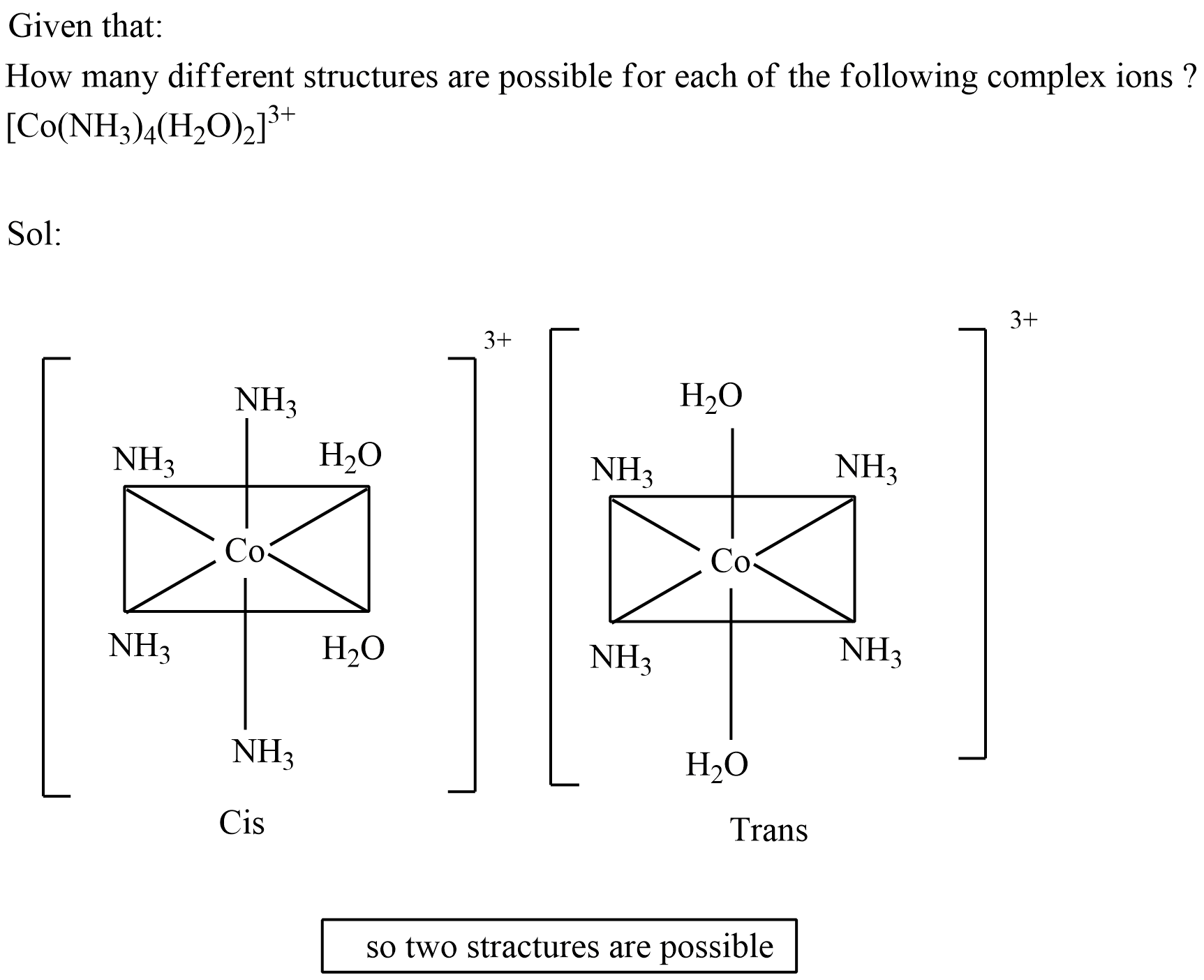
How many different structures are possible for each of the following complex ions ?
$$[Co (NH_3)_4(H_2O)_2]^{3+}$$
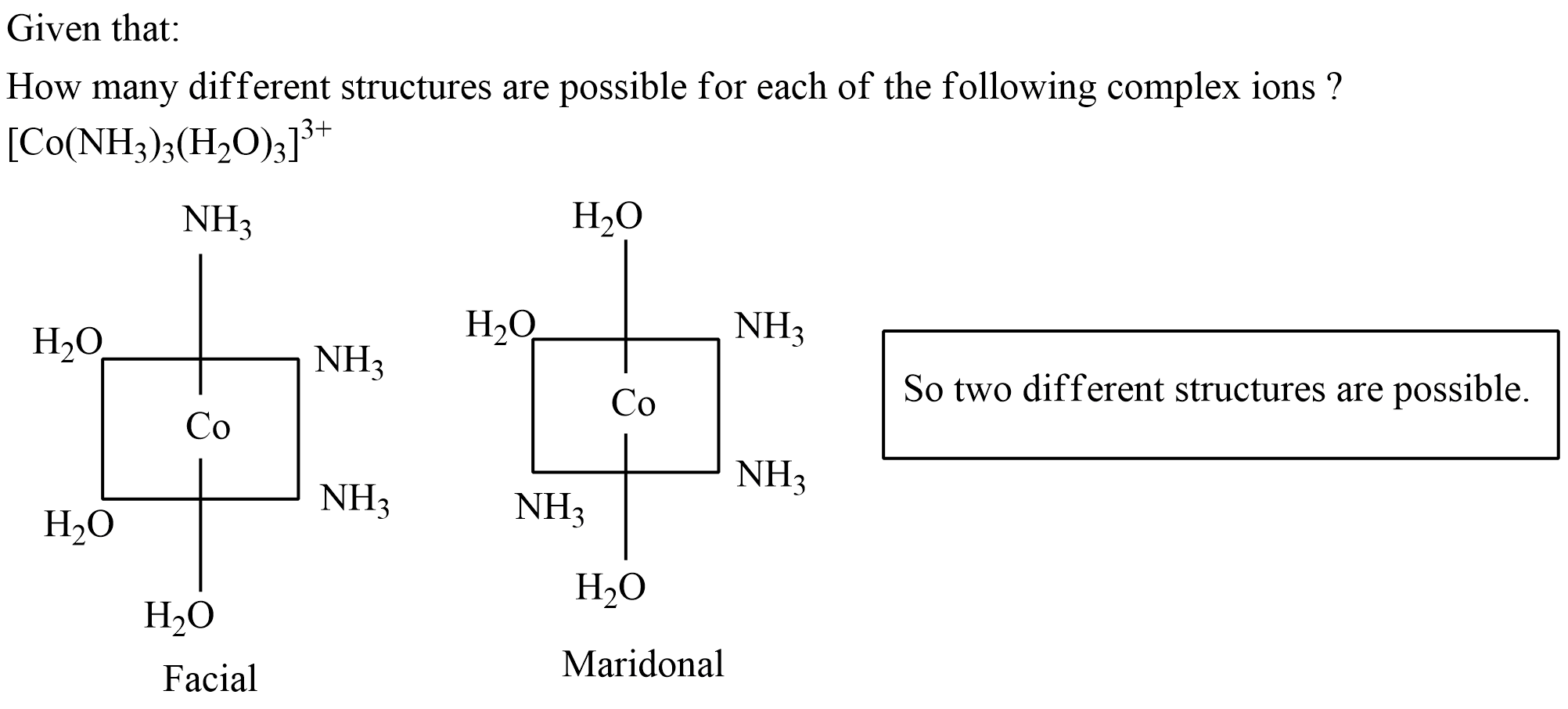
How many different structures are possible for each of the following complex ions ?
$$[Co (NH_3)_3(H_2O)_3]^{3+}$$
How many different structures are possible for each of the following complex ions ?
$$[Co(NH_3)_5H_2O]^{3+}$$
Describe at least three applications of coordination compounds.
How many different structures are possible for each of the following complex ions ?
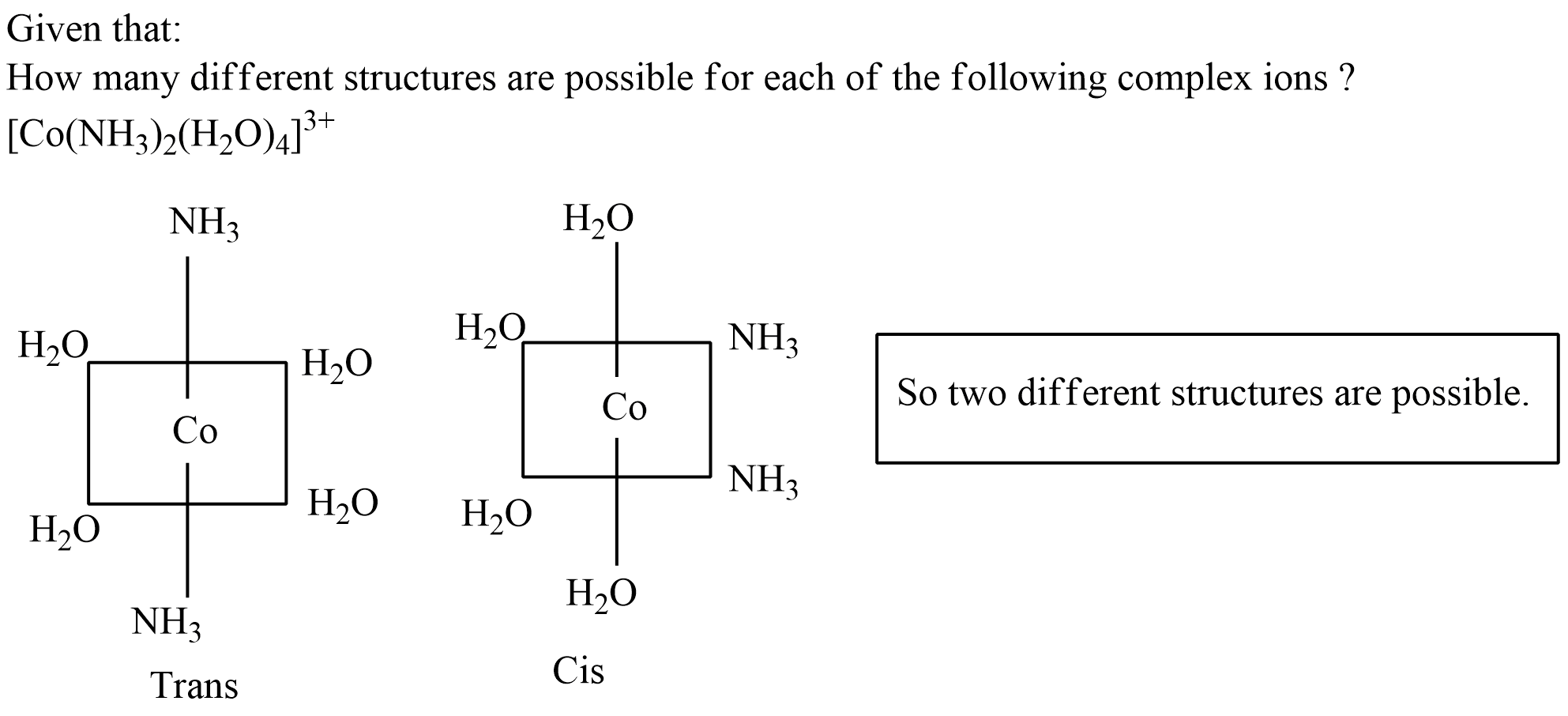
$$[Co(NH_3)_2(H_2O)_4]^{3+}$$
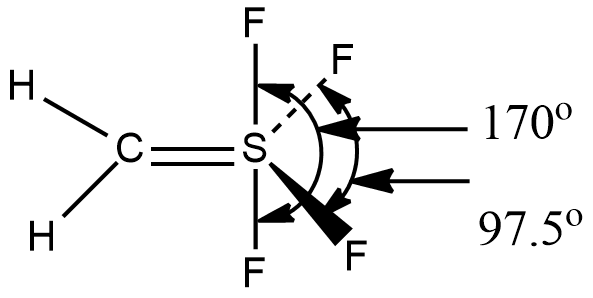
How many maximum atoms lie in the same plane in the structure of methylenesuphurtetrafluoride $$(CH_{2}SF_{4})$$?
How many isomers of the complex, $$[Pt \left ( NH_{3} \right )_{2}\left ( SCN \right )_{2}]$$ are possible ?
What are the products and type of isomers when $$Br_2$$ adds to:
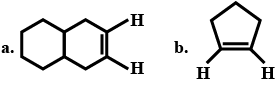
Define hybridisation.
What are the postulates of Werner's theory of coordination compounds?
Give two examples of complex compounds.
Name the main metal present in the following:
(a) Haemoglobin
(b) Chalk
(c) Chlorophyll
(d) Chocolate wrappers
Draw the mirror image of $$ [CO(en)_2Cl_2]^+ $$
What is $$CFSE$$ of complex ion $$[FeF_{6}]^{4-}$$ in terms of $$\Delta _O$$?
Explain the importance of coordination compounds in extraction of metals.
Class 12 Engineering Chemistry Extra Questions
- Alcohols,Phenols And Ethers Extra Questions
- Aldehydes,Ketones And Carboxylic Acids Extra Questions
- Amines Extra Questions
- Biomolecules Extra Questions
- Chemical Kinetics Extra Questions
- Chemistry In Everyday Life Extra Questions
- Coordination Compounds Extra Questions
- Electrochemistry Extra Questions
- General Principles And Processes Of Isolation Of Elements Extra Questions
- Haloalkanes And Haloarenes Extra Questions
- Polymers Extra Questions
- Solutions Extra Questions
- Surface Chemistry Extra Questions
- The D-And F-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The P-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The Solid State Extra Questions