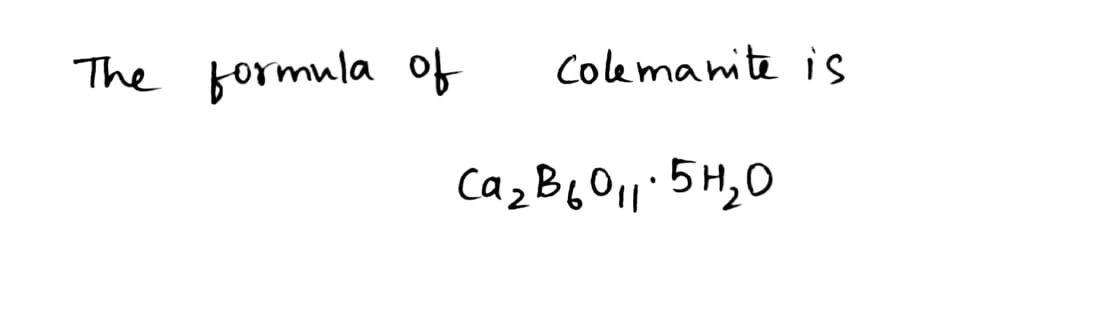General Principles And Processes Of Isolation Of Elements - Class 12 Engineering Chemistry - Extra Questions
Which type of ore is concentrated by froth floatation process?
Why is pine oil used in froth floatation method?
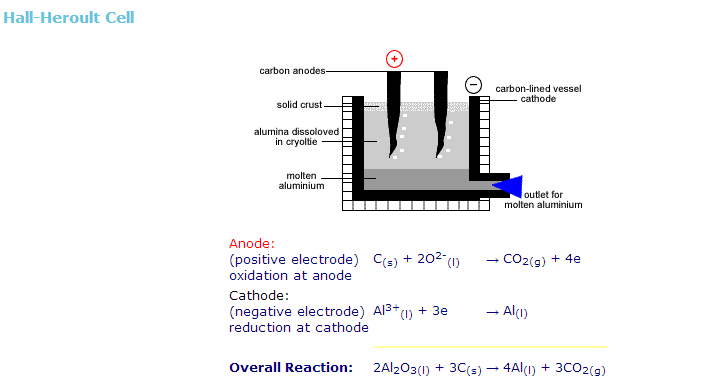
In Hall-Heroult process $$CO_2$$ is released at ?
Why are copper and aluminium are used to make electric wires?
Name the compound of nitrogen occur in earth crust ?
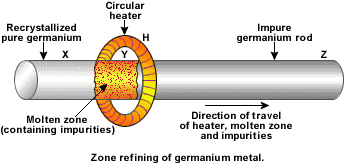
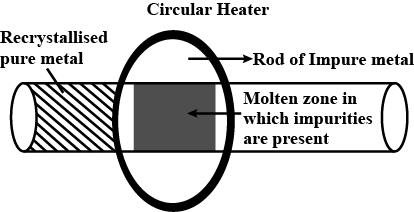
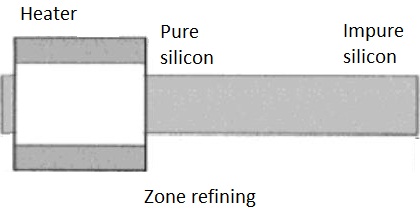
Draw labelled diagram of Zone refining process. In which this process is useful?
How are lanthanides extracted from monazite sand?
Give the importance uses of copper.
Identify the pairs of metals and their ores from the folllowing
What is amalgam ?
What are the uses of copper?
Name two metals which are purified by distillation method.
Match Column-I with Column-II.
A mineral is rich in ZnS and PbS. If it can be concentrate by froth flotation process enter 1 else 0.
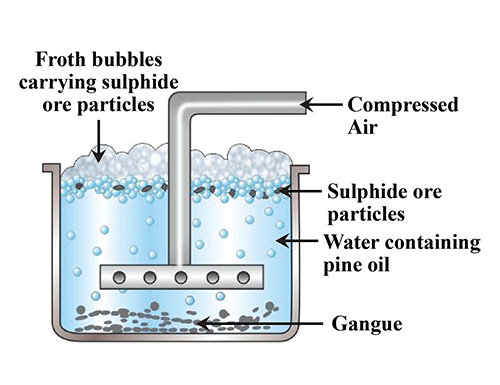
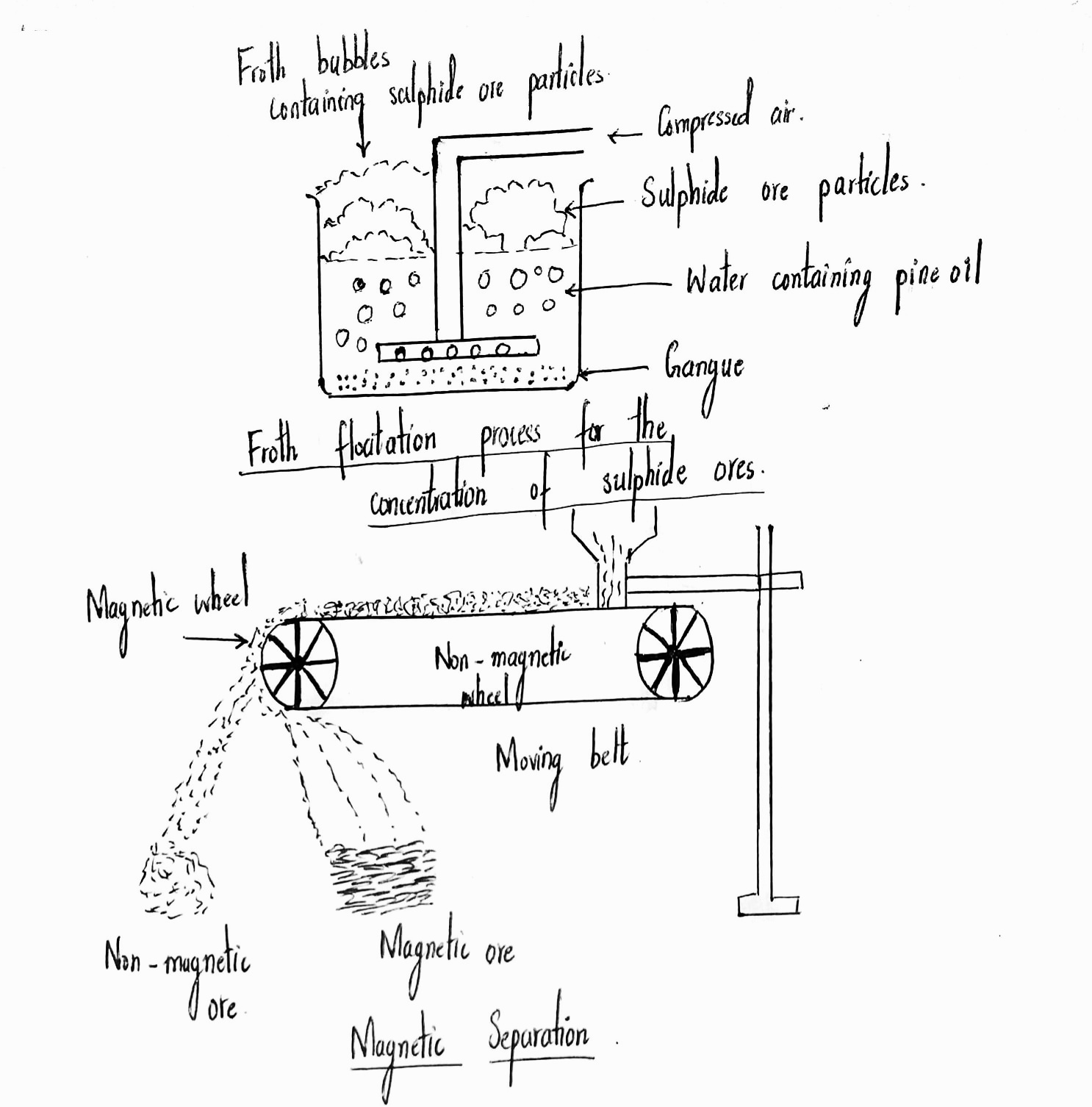
Explain froth flotation process of copper pyrites.
Sulphide ore is concentrated by the method:
Froth flotation process
Magnetic separation
Gravity method
Calcination method
Sulphide ore is common for _______ metal. (Cu, Mg, Na, K)
Choose the correct one.
Based on the above Ellingham diagram, the formation of carbon monoxide from carbon can reduce the metal oxide to metal at a temperature _______ the point of intersection of the two lines.
1. Equal to
Higher than
Lower than
None
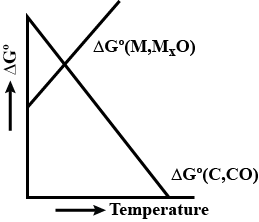
Among the methods for extracting metals from their ores, i.e.,roasting a metal sulphide,chemical reduction of a metal oxide, andelectrolysis, the preferred method depends on $$E^{\circ}$$ value for the reducing half-reaction:
$$M^{n+}{(aq)}\, +\, ne^{-}\, \rightarrow\, M(s)$$
Which method is preferred for the metals with the most negative $$E^{\circ}$$ values?
The methods for extracting metals from their ores are: roasting a metal sulphidechemical reduction of a metal oxideelectrolysis, The preferred method depends on $$E^{\circ}$$ value for the reducing half-reaction:$$M^{n+}{(aq)}\, +\, ne^{-}\, \rightarrow\, M(s)$$
Which method is preferred for the metals with the most positive $$E^{\circ}$$ values?
$$M^{n+}{(aq)}\, +\, ne^{-}\, \rightarrow\, M(s)$$
What is the formula of calamine?
Which one is the following ores is best concentrated by froth floatation method?
1.Galina2.Malachite
Early transition metals occur in nature as oxides but the late transition metals occur as sulphides.If it is true enter 1, else enter 0.
ZnS is always contaminated with PbS. We add $$NaCN + ZnS$$ to enrich PbS by froth flotation process. If true enter 1 else 0.
Although iron is only about two-third as abundant as aluminium in Earth's crust but it costs only about one-quarter as much as required to produce aluminium.If true enter 1, else 0.
When an inert atmosphere is needed for a metallurgical process, nitrogen is frequently used. However, in the reduction of $$TiCl_4$$ by magnesium, helium is used. This is because $$N_2$$ can combine with _____.
Metals of high purity (to be used in semiconductors) are obtained by zone-refining.
If true enter 1, else enter 0.
______ is the most abundant element in the earth's crust.
Sulphur is extracted by Frasch process. If true enter 1 else 0.
Most abundant metal in the earth's crust is _________.
The reducing agent used in thermite process is ___________.
Carbon
Aluminium
Iron
Sodium
$$Mg$$ can be used to reduce $$TiCl_4$$ into $$Ti$$ in __________.
Monds
van Arkel
Hall
Kroll
Differentiate between roasting and calcination.
Find the number of metals from the given metals which can be commercially purified by zone refining methods:
( Si, Ge, Ga, AI, Ti, Zr )
In froth floatation process in the concentration of sulphide ore froth adsorbs ore particles.
If true enter 1 else enter 0
Among the following processes, how many are employed for the extraction of lead from ore galena?
(i) Self reduction , (ii) Carbon reduction , (iii) Metal displacement method , (iv) electrolytic reduction ,(v) Carbon monoxide reduction, (vi) Hydrogen reduction
(i) Self reduction , (ii) Carbon reduction , (iii) Metal displacement method , (iv) electrolytic reduction ,(v) Carbon monoxide reduction, (vi) Hydrogen reduction
Gallium arsenide is purified by __________ .Froth floating process.Zone-refining method.
MATCH THE COLUMN
Predict whether the following statement is true or false.The most abundant metal in the earth's crust is Al.
If true enter 1,else enter 0.
If true enter 1,else enter 0.
Match the following and select the correct answer from codes given below
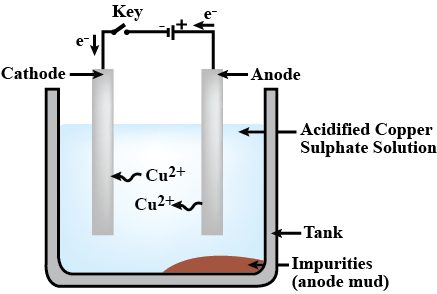
In the electrolytic refining of a metal $$M$$, what would you take as the anode, the cathode, and the electrolyte?
What is the role of depressant in froth floatation process?
The choice of a reducing agent in a particular case depends on thermodynamic factor. How far do you agree with this statement? Support your opinion with two examples.
State the role of silica in the metallurgy of copper.
Write down the reactions taking place in different zones in the blast furnace during the extraction of iron.
Out of $$C$$ and $$CO$$, which is a better reducing agent for $$ZnO$$?
Why copper matte is put in silica lined converter?
The value of $$\Delta_{f} G^{0}$$ for formation of $$Cr_{2} O_{3}$$ is $$-540\ kJmol^{-1}$$ and that of $$Al_{2} O_{3}$$ is $$-827 kJmol^{-1}$$. Is the reduction of $$Cr_{2} O_{3}$$ possible with $$Al$$?
How can you separate alumina from silica in a bauxite ore associated with silica? Give equations, if any.
How is leaching carried out in case of low grade copper ores?
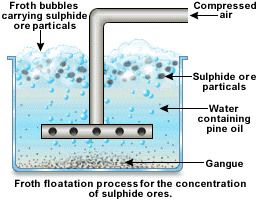
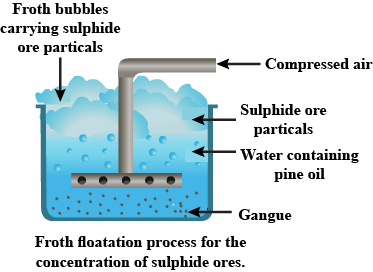
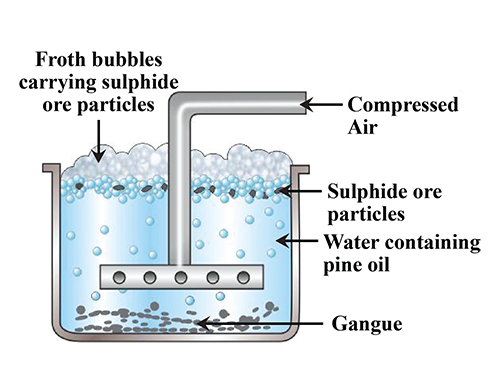
Write the principle behind the froth floatation process. What is the role of collectors in this process?
What chemical process is used for obtaining a metal from its oxide?
Write the principles of the following methods.
(i) Froth floatation method (ii) Electrolytic refining
(i) Name the method of refining to obtain silicon of high purity.
(ii) What is the role of $$SiO_{2}$$ in the extraction of copper?
(iii) What is the role of depressants in froth floatation process?
What is the role of collectors in froth flotation process?
Give an example of zone refining of metals.
Outline the principles of refining of metals by the following methods:
(i) Zone refining (ii) Vapour phase refining
Iron is not found naturally in the form of the free metal. Gold can be found naturally as the free metal. Explain.
The principle of difference in boiling points of liquid is used in the _______.
Why gangue is removed from an ore?
Which of the following ores can be concentrated by froth floatation method and why?
$$Fe_{2}O_{3}, ZnS, AI_{2}O_{3}$$
A mixture of barium sulphate and H$$_2$$O can be separated by the method of ...................
What are ellingham diagrams ? Write any two features of it.
Write short notes on froth floatation process?
The ___________ minerals are the compounds of metal with sulphur.
Explain why: In the electrolysis of alumina using Hall Heroult's Process the electrolyte is covered with powdered coke.
Identify the term/substance in each of the following :
(i) The tendency of an atom to attract electrons to itself when combined in a compound.
(ii) The method used to separate ore from gangue by preferential wetting.
(iii) The catalyst used in the conversion of ethyne to ethane.
(iv) The type of reactions alkenes undergo.
(v) The electrons present in the outermost shell of an atom.
Write a short note on gangue and anode mud.
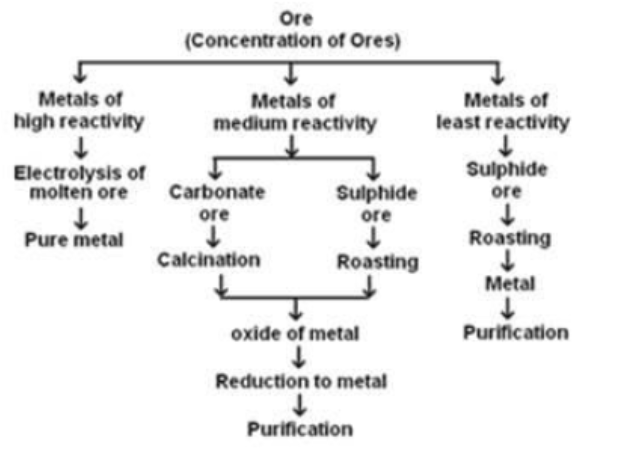
Which method do you suggest for extraction of high reactivity metals? Why?
Explain the purification of sulphide ores by froth floatation method?
Name the refining method used to produce semiconductors.
Explain calcination and roasting with example.
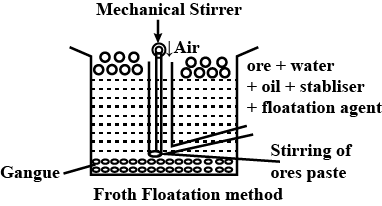
Draw the diagram showing froth floatation method and label its parts.
(a) Explain the following. (i) Roasting
(ii) Calcination.
(b) What are amphoteric oxides? Write the name of such one oxide.
(c) By which two metals is brass alloy formed?
(ii) Calcination.
(b) What are amphoteric oxides? Write the name of such one oxide.
(c) By which two metals is brass alloy formed?
What is a concentration of ores? Explain the process with diagram by which metallic ore with sulphide as an impurity is purified.
What is the role of depressants in the forth floatation process?
The impurities which are not removed during ore concentration are called .........
(Gangue, flux, slag)
Write the name of the metal whose ore is siderite.
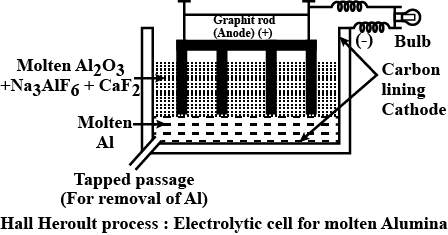
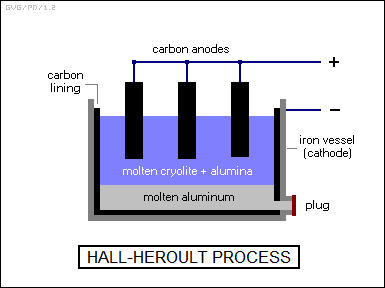
Draw labelled diagram of Hall-Heroult Electrolytic cell for the extraction of aluminium. Write anode and cathode reactions.
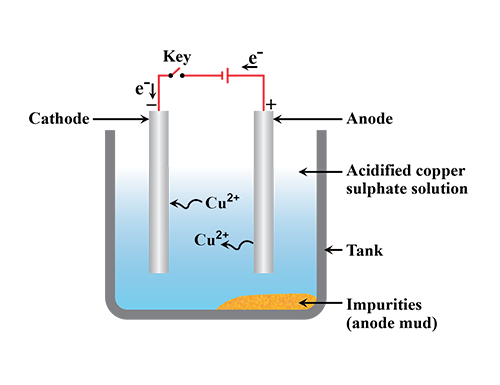
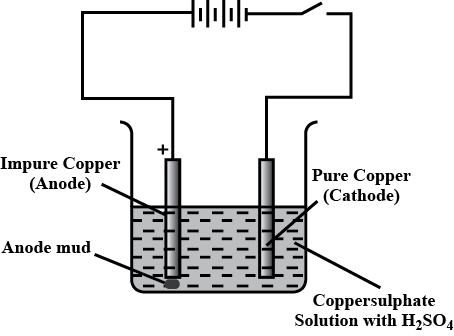
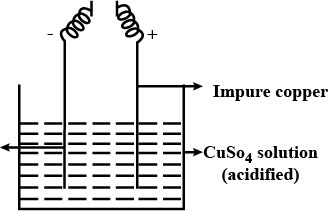
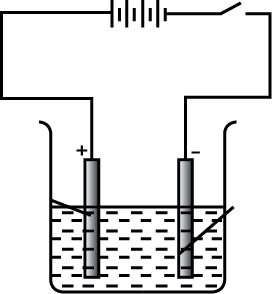
What is refining of metals? Explain with diagram the method of electrolysis by which copper is purified.
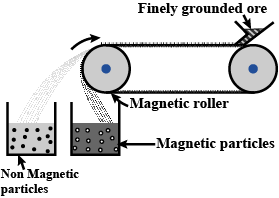
Explain magnetic separation process of ores with the help of a neat, labelled diagram.
The metal whose oxide, which is amphoteric, is reduced to metal by carbon reduction ___________. $$(Fe/ Mg/ Pb/ Al)$$.
Explain zone refining.
Explain zone - refining (figure not necessary).
Write reactions involved in extraction of silver from it's ore by leaching process. O-nitrophenol is more acidic than O-cresol; Explain.
A trivalent Metal "M" occurs in nature in the form of its oxide $$M_{2}0_{3}$$. The metals is widely used in making household utensils and bodies of aircraft.(i) Identify the metal (ii) Name the chief ore of metal(iii) Write down the reaction involved during the extraction of metal with figure.
During the extraction of aluminium by Hall-He'roult process,
i) Write a neat labeled diagram of the electrolytic cell.
ii) Write over all cell reaction.
iii) At which electrode oxygen gas is liberated?
How many of the given metals can be obtained by carbon reduction in their extractive metallurgy.
Cu, Zn, Pb, Na, Sn, Ag, Au, Mg, Al, Fe
Lemon or tamarind is used for cleaning copper vessel turned greenish.Comment on the above statement.
ZnS and PbS are separated by using?
Which of the metal ores can be obtained in hydrometallurgical reduction?
Explain briefly the extraction of aluminium from bauxite.
Which elements occurs in its native or elemental stage?
In Bayer's process leaching is carried out using:
What is the function of collectors in the froth floatation process for the concentration of ores?
Why is it that only sulphide ores are concentrated by froth floatation process?
What is metallurgy ?
Explain the purification of sulphide ore by Froth floatation method.
Although carbon and hydrogen better reducing agents but they are not used to reduced metallic oxides at high temperatures. Why?
Name the anode and the cathode used in the electrolytic refining of impure copper metal.
Write an example for a metal which can be refined by liquation?
Describe the extraction of two metals and two non-metals by electrolysis.
What happens when $$NaCN$$ is added in ore containing $$PbS$$ and $$ZnS$$ during concentration by froth floatation method?
How are metals used as semiconductors refined? What is the principle of the method used?
How many ores are sulphide ores from the given ores?
Azurite, Chalcocite, Iron pyrites, Limonite
Azurite, Chalcocite, Iron pyrites, Limonite
Wrought iron is the purest form of iron. Write a reaction used for the preparation of wrought iron from cast iron. How can the impurities of sulphur, silicon and phosphorus be removed from cast iron?
What is the role of flux in metallurgical processes?
Why are sulphide ores converted to oxide before reduction?
In the thermite process, __________ is used as a reducing agent.
Each of the following statements is true only under some specific conditions. Write the condition for each sub-question in not more than two sentences.
(i) Metals can be recovered from their ores by chemical methods.
(ii) High purity metals can be obtained by zone refining method.
Write down the reactions involved in the extraction of Pb. What is the oxidation number of lead in litharge?
Explain the following:
Carbon and hydrogen are not used as reducing agents at high temperatures.
Carbon and hydrogen are not used as reducing agents at high temperatures.
Name the following:
Two metals which always occur both in native and in combined states.
Name the following:
Two metals which always occur naturally in an uncombined states.
Which one out the two many be found in native state?
Iron and silver
Name the diagram which can be used to compare the reducing nature of the different elements.
Name the following:
Two metals which never occur in native state.
Write short note on:
Autoreduction
Write short notes on:
Reverberatory
Which ores generally concentrated by forth floatation process?
Answer the following
Name the metal which is commonly used as a reducing agent in metallurgical operations.
Name two principal ores of each of the following metals:
Iron
Answer the following:
Write the two important minerals of fluorine.
What happens when : manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder ?
What is liquation?
Make a flowchart to explain the various steps involved in extraction of metals from ores .
What happens when iron(III) oxide is heated with aluminium powder ?
Define the term Mineral .
Define the term Ore .
An ore sample of galena $$(PbS)$$ is contaminated with zinc blende $$(ZnS)$$. Name one chemical which can be used to concentrate galena selectively by froth floatation method.
What name is given to carbon reduction process for extracting the metal?
What is gangue?
Why is it advantageous to roast a sulphide ore to the oxide before reduction?
State briefly the principles involved in the following operations in metallurgy. Give an example.
Zone refining.
Two ores A and B were taken. On heating ore A gives $$CO_2$$ whereas, ore B gives $$SO_2$$.
What steps will you take to convert them into metals?
Why should the metal sulphides and carbonates be converted to metal oxides in the process of extraction of metal from them?
What is the principle of the method used for refining metals used as semiconductors?
Answer the following questions:
What is the role of collectors in the froth floatation process? Give an example of a collector.
Mention two uses of the following metals and non-metals:
Aluminium
Give an example of a sulphide ore which reduced to metal by heating alone, i.e., by roasting.
Account for the following facts:
Pine oil is used in the froth floatation process used to concentrate sulphide.
Give the steps involved in the extraction of metals of low and medium reactivity from their respective sulphide ores.
Answer the following questions:
Out of $$PbS$$ and $$PbCO_{3}$$ (ores of lead), which one is concentrated by froth floatation process preferably?
State two important uses of following metals:
Uses of copper.
What is the role of cryolite $$(Na_{3}AlF_{6})$$ in the electrolytic reduction of alumina in Hall's process?
Give reason :
Copper is used in making electric cables.
Give reason:
Aluminium is used in making aircrafts.
Why does iron or zinc not occur free in nature?
Give the principles of hydraulic washing.
Name an ore which is concentrated by:
(a) forth floatation process
(b) magnetic separation
Answer the following:(a) Name the process by which the refining of aluminium is done.
(b) Where are the cathode and anode in the electrolytic cell? Name the material used for these.
(c) State the reactions at the electrodes.
Give the principle of froth floatation.
State two important uses of following metals:
Uses of aluminium.
In order to obtain 1 tonne of aluminium, 4 tonnes of bauxite, 150 kg of sodium hydroxide and 600 kg of graphite is required. The aluminium compound in bauxite is aluminium oxide and the main impurity is iron (III) oxide, Aluminium is obtained by the electrolysis of aluminium oxide dissolved in cryolite.
When bauxite is treated with sodium hydroxide solution, what happens to
(i) the aluminium oxide
(ii) the iron (III) oxide
Aluminium is extracted from its chief ore, bauxite. The ore is first purified and then the metal is extracted from it by electrolytic reduction.
Write equations for the reactions which takes place at the anode during the extraction of aluminium by the electrolytic process.
Aluminium is extracted from its chief ore, bauxite. The ore is first purified and then the metal is extracted from it by electrolytic reduction.
Mention one reason for the use of aluminium in thermite welding.
In order to obtain 1 tonne of aluminium, 4 tonnes of bauxite, 150 kg of sodium hydroxide and 600 kg of graphite is required. The aluminium compound in bauxite is aluminium oxide and the main impurity is iron (III) oxide, Aluminium is obtained by the electrolysis of aluminium oxide dissolved in cryolite.
In construction work, why is the alloy of aluminium(duralumin) used rather than pure aluminium?
Give reasons why aluminium is used in:
(a) making alloys
(b) wrapping chocolates
(c) painting electric and telegraphic poles
(d) aluminothermy
(e) making ships
Explain the significance of graphite in the extraction of aluminium.
In order to obtain 1 tonne of aluminium, 4 tonnes of bauxite, 150 kg of sodium hydroxide and 600 kg of graphite is required. The aluminium compound in bauxite is aluminium oxide and the main impurity is iron (III) oxide, Aluminium is obtained by the electrolysis of aluminium oxide dissolved in cryolite.
(i) Write the formulae of cryolite.
(ii) Write down the word which correctly completes the following sentence.
By dissolving aluminium oxide in cryolite a ____ (conducting/ non conducting) solution is produced.
(iii) Why is so much graphic required for the electrolytic process?
(iv) Write the equation for the reaction which takes place at cathode.
Explain the term Gangue.
Aluminium is used in thermite welding.
(a) What is thermit?
(b) What is ignition mixture?
(c) Write the reaction for the process.
Aluminium is extracted from its chief ore, bauxite. The ore is first purified and then the metal is extracted from it by electrolytic reduction.
Name a chemical used for dissolving aluminium oxide. In which state of subdivision is the chemical used?
Write chemical equation for the event.
Zinc oxide is dissolved in dilute hydrochloric acid.
Write scientific reason.
Pine oil is used in froth flotation.
Column - I and Column II contain four entries. Entries of column I- are to be matched with some entries of column-II. Each entry of column-I may have the matching one or more than one entries of Column- II
State briefly the principles which serve as basis for the following operation in metallurgist.
Refining by liquation
State briefly the principles which serve as basis for the following operation in metallurgist.
Froth floatation process.
State briefly the principles which serve as basis for the following operation in metallurgist.
Zone refining.
There are several methods for refining of crude metals:
Explain liquation.
Why copper wire is use for wiring at our houses? Explain.
From the figure, give the electrode reaction. What is this process called ?
Outline the principles of refining of metals by the following method:
Zone refining.
The reaction, $$Cr_2O_3 + 2Al \rightarrow Al_2O_3 + 2Cr (\Delta \epsilon P = -421 \,KJ)$$ is thermo dynamically feasible as is apparent from the Gibbs energy value. Why does it not take place at room temperature ?
Explain the terms gauge, Flux and slag in metallurgy.
List out some metals which occur free in nature.
Write two uses of borane and aluminium.
There are several methods for refining of crude metals:
What is the principle of zone refining ?
Write chemical reaction of reduction of metal chromium oxide in alumino thermite process.
Draw labelled figure of zone refining process. Where this process is widely used?
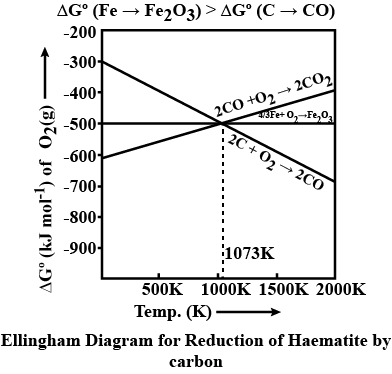
Explain thermodynamic principle in : reduction of haematite ore from Elligham diagram.
Give example of following steps used in froth floatation method:
(i) Frothing agent
(ii) Collector/ Floating agent
(iii) Forth stabilizers
(iv) Activator
(v) Depressant or depresser.
What is difference between mineral and ore. Explain it.
Write name of any two metals which are found in native state.
Write name and role of collectors and froth stabilizers in froth floatation method.
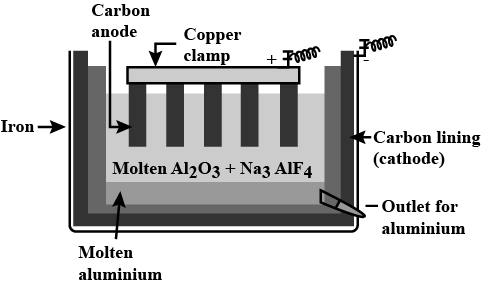
Write chemical reaction of Hall-Heroult process of bauxite ore and draw labelled diagram of electrolytic cell.
Nature of some ores are given. Pick ore concentration from the bracket.
(Magnetic Separation , Froth Floatation , Levigation , Leaching)
Ores are lighter and impurities are heavier.
Which reducing agent is good among $$C$$ and $$CO$$ at low temperature range in blast furnance to obtain iron form iron oxide and why?
Write short notes on following:
(i) Gangue/ Matrix
(ii) Slag
(iii) Flux.
To which electrodes does $$ Al^{3+} $$ move ?
Purification of copper is depicted here.
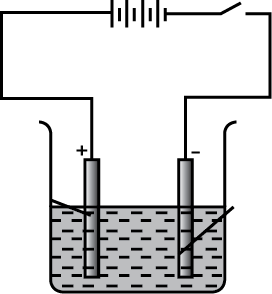
Identify the anode , cathode and electrolyte.
What are gangue, flux, and slag?
Copper is used for making wires. Which property of copper is used in making wires?
Which ores are concentrated by froth flotation process. Write in brief description and draw labelled diagram.
Why is froth-floatation used as the method of concentration for copper-pyrites ore?
What is the refining method used for the refining of copper?
What is the refining method used for the refining of Mercury?
What is meant by stabilizer? Give example.
Element with strongest reducing nature is:
How does $$NaCN$$ act as a depresent in preventing $$ZnS$$ forming the froth?
In general which metals do you expect to occur in the native state in nature? Give examples.
Which method would you suggest for the separation of the metals is in the following mixture?
$$Zn$$ from iron
Give a reason for your choice.
Copper and silver lie below in the electrochemical series and yet they are found in the combined state as sulphide in nature. Comment.
Why do some metals occur in the native state?
What is a depressant. Give one example.
What is the role of a stabilizer in froth-floatation process?
Give the chemical formula of Bauxite
Give the appropriate term defined by the statements given below:
The process by which certain ores, specially carbonates, are converted to oxides in the absence of air.
Match the conversions in List 1 with the type(s) of reaction(s) given in ListIndicate your answer by darkening the appropriate bubbles of the $$4 \times 4$$ matrix given in the ORS.
How much approx aluminium in g can be produced by a current of 94 A flowing through a Hall-Heroult cell for 1.00h?(If the answer is $$X$$, then write $$\dfrac X8$$)
State whether the given statement is True or False.
$$CuO$$ can't be reduced by carbon but it can be reduced by $$H_2$$.
given : $$\Delta G^{\circ}_{f}$$ for $$CuO =$$ -129.7 kJ $$mol^{-1}$$, $$CO =$$ - 137.2 kJ $$mol^{-1}$$ $$H_2O$$ = - 237.2 kJ $$mol^{1}$$
Out of $$C$$ and $$CO$$, which is a better reducing agent at $$673 K$$?
Name the common elements present in the anode mud in electrolytic refining of copper. Why are they present?
Predict conditions under which $$Al$$ might be expected to reduce $$MgO$$.
Write chemical reactions taking place in the extraction of zinc from zinc blende.
What is the role of cryolite in the metallurgy of aluminium?
Why is zinc not extracted from zinc oxide through reduction using $$CO?$$
Outline the principles of refining of metals by the following methods:
(i) Zone refining
(ii) Electrolytic refining
(iii) Vapour phase refining
Relate all the four columns of the table with u
| Metal | Ore | Chemical formula | Reduction process |
| Al | haemetite | $$PbS$$ | blast furnace |
| Cu | bauxite | $$Fe_2O_3$$ | bessemerisation |
| Fe | copper pyrite | $$Al_2O_2H_2O$$ | froth floatation |
| Pb | galena | $$CuFeS_2$$ | Hall's process |
In the extraction of aluminium ;
(i) name the process of concentration of bauxite.
(ii) write the cathode reaction in electrolytic reduction of alumina.
(iii) write the function and chemical formula of cryolite.
(iv) write a chemical equation for the action of heat on aluminium hydroxide.
(v) why is it necessary to replace anodes time to time?
Explain Hall-Heroult method of obtained pure aluminium from alumina with figure.
In which furnace the smelting is done?
Answer the following questions with respect to the electrolytic process in the extraction of aluminium:
Explain why powdered coke is sprinkled over the elecrolytic mixture.
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of zone refining process.
Generally which ores are concentrated by froth floatation method? Describe this method.
Describe the extraction of Mercury metal from its ore Cinnabar $$(HgS)$$.
The oil used as frothing agent in froth floatation process is ?
A tetravalent element forms monoxide and dioxide with oxygen. When air is passed over heated element $$\left(1273\ K\right)$$, producer gas is obtained. Monoxide of the element is a powerful reducing agent and reduces ferric oxide to iron. Identify the element and write formulas of its monoxide and dioxide. Write chemical equation for the formation of producer gas and reduction of ferric oxide with the monoxide.
Draw the diagram showing i) Froth floatation ii) Magnetic separation. $$\left( { AS }_{ 5 } \right) $$
Define the term 'metallurgy'. State the processes involved in metallurgy.
Draw an Ellingham diagram for metal oxides and explain what information can be obtaines from it.In addition explain why why most of the lines slope upwards from left 10 right,why the lines change in slope, and what happens when a line crosses the $$ \Delta G = 0 $$ axis
Describe the extraction of magnesium and bromine from sea water.
Use the Ellingham diagram for oxides to find:1. If Al will reduce chromium oxide2. At what temperature C will reduce magnesium oxide, and3. At what temperature mercuric oxide will decompose into its elements.
Find the number of metals from the given metals which can be commercially purified by zone refining methods.
Si, Ge, Ga, Al, Ti, Zr
Match the items of column I with items of column II and assign the correct code
At temperatures above 1073 K coke can be used to reduce FeO to Fe. How can you justify this reduction with Ellingham diagram?
Explain the following:$$CO_2$$ is a better reducing agent below 710 K whereas $$CO$$ is a better reducing agent above 710 K.
Name the following:
Two metals which are used for the reduction in metallurgical process.
Write short note on:
Forth floatation process
Match List-I with List-II:
Answer the following:What is the silver paint?
Described the thermodynamic principle of metallurgy. How the Ellingham diagram useful in predicting the feasibility of thermal reduction of a metal oxide.
Write down the formula of the following:
Leuna saltpetre
Give formula of the following:
Colemanite
Colemanite
Explain how the properties of an alloy are different from those of constituent metals.
How will you obtain mercury from cinnabar ?
Free energies of formation $$(\triangle_{f}G)$$ of $$MgO(s)$$ and $$CO(g)$$ at $$1273\ K$$ and $$2273\ K$$ are given below.
$$\triangle_{f}G[MgO(s)] = -941\ kJ/mol$$ at $$1273\ K\ \triangle_{f}G[MgO(s)] = -314\ kJ/mol$$ at $$2273\ K$$
$$\triangle_{f}G[CO(g)] = -439\ kJ/mol$$ at $$1273\ K\ \triangle_{f}G[CO(g)] = -628\ kJ/mol$$ at $$2273\ K$$
On the basis of above data, predict the temperature at which carbon can be used as a reducing agent for $$MgO(s)$$.
Draw the diagram of an electrolytic cell used in the purification of Copper and label the electrode having impure copper.
How zinc is extracted from its ore?
Molten cryolite is mixed Alumina in the extraction of aluminium by electrolysis. Why? Name the substances that are used as anode and cathode in this method.
Some metals and their methods of concentration are given . Match them suitably.
Mercury , Zinc , Tin , Copper , Lead
Liquification , Electrolytic refining , Distillation
(a) Illustrate the arrangement of refining copper and label the anode, cathode and electrolyte.
(b) Write the chemical equation at the anode and cathode and sustain it as redox reaction.
Purification of copper is depicted here.
Write the chemical equation during electrolysis.
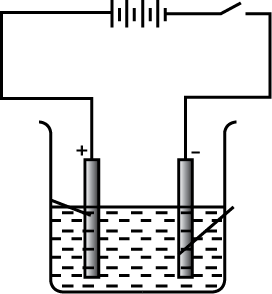
Purification of copper is depicted here.
What is seen below the positive electrode ?
Features of ore and impurity are given in the table. Write down the method used for the separation of the ore.
| Ore | Impurity | Method |
| High density | Low density | (i) |
| Magnetic | Non magnetic | (ii) |
| Low density | High density | (iii) |
| Dissolved in the solvent | didn't dissolve | (iv) |
What is the refining method used for the refining of Calcium?
Aluminium is prepared industrially by Hall-Heroult process. Various steps in the concentration of ore are given below . Write them in the correct order.
i. The precipitate formed is separated , washed and strongly heated to get alumina.
ii. Crushed bauxite is leached with hot sodium hydroxide solution.
iii. Impurities are removed from the sodium aluminate solution for filtration.
iv. Solution is diluted after adding a little aluminium hydroxide , to precipitate aluminium hydroxide.
Which method can be used for separating aluminium from alumina ?
(i) Write down the names of Anode , Cathode , Electrolyte used in the Electrolyte cell for the manufacturing of copper.
(Ii) Write down the equations for the reaction in anode and cathode.
The materials like stone, rock and earthy impurities present in naturally occurring ores are known as...
Describe the principal of forth flotation process, What is the role of a stabilizer and of a depressant?
Give one example each.
Differentiate between the following:
Gangue and flux.
Is carbon a satisfactory reducing agent for all metal oxides? Give reasons.
Low melting metals like lead are refined by _________.
Answer the following questions based on the extraction of aluminium from alumina by Hall Heroults Process:
(i) What is the function of cryolite used along with alumina as the electrolyte?
(ii) Why is powdered coke sprinkled on top of the electrolyte?
(iii) Name the electrode, from which aluminium is collected.
Class 12 Engineering Chemistry Extra Questions
- Alcohols,Phenols And Ethers Extra Questions
- Aldehydes,Ketones And Carboxylic Acids Extra Questions
- Amines Extra Questions
- Biomolecules Extra Questions
- Chemical Kinetics Extra Questions
- Chemistry In Everyday Life Extra Questions
- Coordination Compounds Extra Questions
- Electrochemistry Extra Questions
- General Principles And Processes Of Isolation Of Elements Extra Questions
- Haloalkanes And Haloarenes Extra Questions
- Polymers Extra Questions
- Solutions Extra Questions
- Surface Chemistry Extra Questions
- The D-And F-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The P-Block Elements Extra Questions
- The Solid State Extra Questions